Light and Properties of Waves
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Science GACE
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
Law of Reflection
Reflected light rays travel away from a surface at the same angle as the incoming ray with the surface.
Convex Mirror
A mirror that curves outward (the center is closer to the observer than the edges)
Concave Lens / Diverging Lens
A lens that is thinner in the middle than at the edges. Causes light rays to diverge, or spread apart.
Dual Nature
light has both a wave nature and a particle nature
In Phase
Waves of the same frequency and direction that have crests and troughs in the same positions at the same times.
Visible Light
light with frequencies that humans can see
Electromagnetic Spectrum
the entire range of frequencies of electromagnetic waves from very long radio waves to very short gamma rays
Threshold Frequency
Term definition.
The minimum frequency for which electrons are ejected from a metal during the photoelectric effect
Term,Plane Mirror
Term definition.
A flat mirror.
Term,Concave Mirror
Term definition.
A mirror that curves inward (the center is further from the observer than the edges)
Example.
Makeup mirror
Term,Destructive Interference
Term definition.
The interference pattern produced when a crest and a trough overlap and the new amplitude equals the difference of the individual amplitudes.
Term,Planck's Constant
Term definition.
A constant relating the frequency of a light particle to its energy
Term,Diffuse Reflection
Term definition.
a reflection in which no image is seen
Example.
reflection from a wall
Term,Emission Spectrum
Term definition.
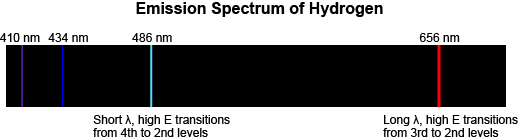
A series of colored lines of different wavelengths (or frequencies) produced when electrons in atoms fall from higher to lower energy levels
Term,Fiber Optics
Term definition.
A cable with a glass core that transmits light over long distances by the process of total internal reflection.
Example.
Communications
Term,Coherent Light
Term definition.
A light beam in which every light ray has the same frequency and phase.
Term,Stimulated Emission
Term definition.
The process occuring in a laser in which existing light rays cause identical light rays to form and travel coherently with the first rays.
Term,Virtual Image
Term definition.
An image that only appears to exist. In a mirror, it forms from diverging light rays that appear to have originated behind the mirror.
Example.
Image in a plane mirror
Term,Normal Line / Normal
Term definition.
A line perpendicular to a surface or boundary between materials.
Term,Excited Electrons
Term definition.
electrons in orbitals higher than the ground state
Term,Quantized
Term definition.
Is present only in discrete amounts rather than in a continuous distribution
Term,Diverge
Term definition.
Spread apart or fan out.
Term,Resultant Wave
Term definition.
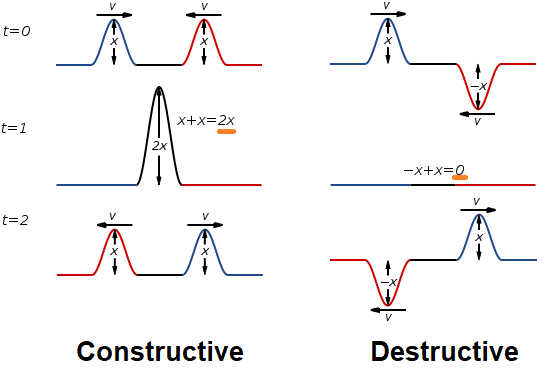
The wave produced when two or more waves interfere with each other.
Term,Entanglement
Term definition.
Entangled particles instantly share information with each other even when separated by a great distance
Term,Refraction (of Light)
Term definition.
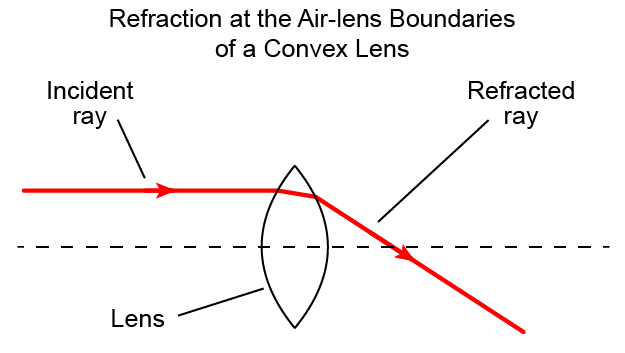
the bending of a light ray's direction of travel as it passes from one material to another
Example.
A pencil looks bent when placed in water.
Term,Oscillating
Term definition.
vibrating
Term,Electron Transitions
Term definition.
the movement of electrons from the ground state in atoms to higher orbitals and back due to the absorption and emission of energy
Example.
neon lights
Term,Scattering
Term definition.
Light from a single direction is absorbed by a particle and reemitted in random directions.
Example.
Blue sky
Term,Real Image
Term definition.
An image for which the light rays come to a focus. A real image can be projected on a screen.
Example.
Slide projector
Term,Phase
Term definition.
The difference between the position of the crests in waves that have the same frequency and direction of travel.
Term,Specular Reflection
Term definition.
a reflection that looks like the image
Example.
mirrors
Term,Interference
Term definition.

The amplitudes of waves that overlap in space and time combine to make a wave with a new amplitude.
Term,Photoelectric Effect
Term definition.
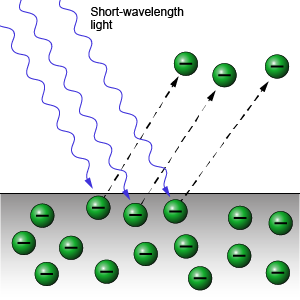
Electrons are ejected from a metal when illuminated with light at a high enough frequency
Term,Total Internal Reflection
Term definition.
A perfect reflection that occurs when a light beam strikes the boundary from glass to air at an angle greater than the critical angle.
Example.
Mirrors used in magic shows
Term,Laser
Term definition.
A device that uses stimulated emission, reflection, and interference to produce a very intense, coherent beam of light.
Term,Transverse Wave
Term definition.
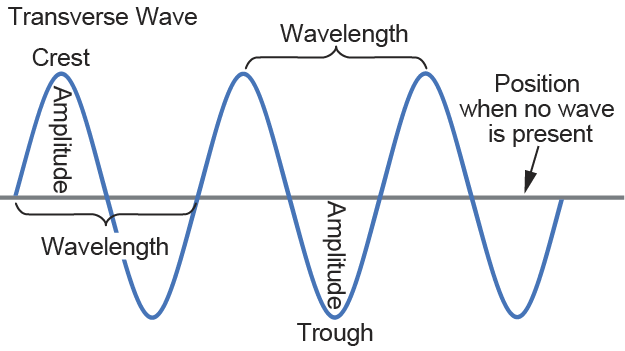
a wave in which the direction of the vibration is perpendicular to the direction the energy travels
Example.
light, vibrating guitar string
Term,Polarization
Term definition.
A process in which a light beam is filtered so the electric fields of all rays oscillate in the same direction.
Example.
Polaroid sunglasses
Term,Wave Model of Light
Term definition.
The description of light as a wave with a frequency and wavelength
Term,Constructive Interference
Term definition.
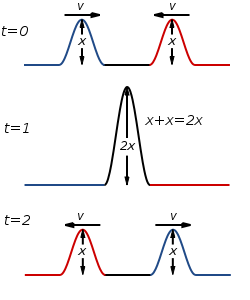
The interference pattern produced when two crests or two troughs overlap and the new amplitude equals the sum of the individual amplitudes.
Term,Photon
Term definition.
a particle of light energy
Example.
particle nature of light
Term,Particle Model of Light
Term definition.
The description of light as a particle with a definite location
Term,Reflection (of Light)
Term definition.
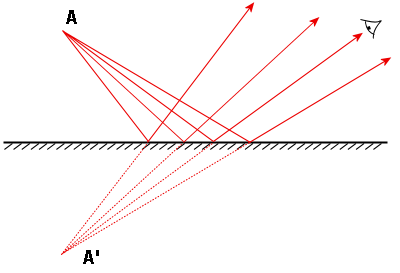
The bouncing of light off of a surface
Example.
Light reflects off of a mirror
Term,Convex Lens / Converging Lens
Term definition.
A lens that is thicker in the middle than at the edges. If the object is far enough away, the lens causes light rays to converge, or bend toward one another.
Example.
Magnifying glass
Term,Diffraction
Term definition.
The bending and spreading of a wave after it passes through a narrow slit or a sharp corner.
Example.
Hear sound around a corner
Term,Dispersion (of Light)
Term definition.
The spreading of white light into its constituent colors
Example.
Prism
Term,Quantum Physics
Term definition.
The study that includes the effects of light as both a wave and a particle
Term,Prism (for light)
Term definition.
A transparent object, usually a triangular solid with two parallel end faces, that separates white light into the colors (frequencies) of the visible spectrum.
Example.
Prism
The teacher of an eighth-grade science class asks a student to stand in front of a full-length, flat mirror and wiggle the fingers on their right hand. She then leads the class in a discussion of whether the mirror reverses the image horizontally, vertically, both, or neither. Which of the following properties of light is the teacher most likely exploring with the class?
reflection
Light spreads into the colors of the rainbow when passing through a prism. What name is given to this spreading effect?
dispersion
When a voltage is applied to a laser, electrons in the gas inside the laser are excited to higher energy levels. When an electron falls back to a lower energy level it emits a photon which stimulates other excited electrons to fall to the same energy level and emit more photons with exactly the same frequency and phase. Which of the following explains why a laser is considered a quantum application?
The individual photons all have the same frequency.
Which of the following is the reason lenses can focus light?
refraction
Why does a red dress appear red when white light shines on it?
The pigments in the red dress reflect red light and absorb most other colors.
Which of the following colors of light in the visible spectrum would have the lowest frequency and longest wavelength?
red
When we say light has a wave/particle duality, we mean:
light is always both a wave and a particle, never one or the other.
Laser light can be so concentrated that it can cut through steel. Which of the following gives the reason laser light is so concentrated?
The light waves in a laser are all in phase.
During the photoelectric effect, shining a specific wavelength of light on a metal ejects electrons from the metal. Increasing the brightness of the light has which of the following effects?
It increases the number of ejected electrons.
Why is the sky blue?
Blue light is scattered from sunlight by small molecules in the atmosphere.
Which color light experiences the greatest amount of refraction by a prism?
violet