BIO252-Anatomy and Physiology 2-Exam 2 Review-Chamberlain
1/127
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Layers or meninges, anatomy of the spinal cord, hard columns, neuroglial cells action, cranial nerves, 3 questions, trace out the patient, sensory deficit, which part of the precentral gyrus, ride side, functions of the hypothalamus, where Wernickes (temporal) is located and what Brocas does., division of dorsal horn-grey matter and sensory neurons, autonomic system -enteric, sympathetic, parasympathetic, 2 neurons in autonomic nervous system, the cell body is in the lateral grey horn in autonomic nervous system in the synapses in the ganglion, parasympathetic-lateral grey horn it bypasses system and goes to the terminal ganglion. Sympathetic synapses and sympathetic chamber. ACH is secreted in the sympathetic, and nurepidemical is in the parasympathetic. Know your reflex type, know where visual cortex is located, and know how many components the reflex arc is. cross sections of brain Ascending arc, 2 cranial nerve naming, cross sections, explain the stretch relflex. anterior lobe.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
128 Terms
Olfactory
Number: 1
Type: Sensory
Function: Sense of Smell
Optic
Number: 2
Type: Sensory
Function: Vision
Oculomotor
Number: 3
Type: Motor
Function: Raise eyelids, move eyes, regulate the size of pupils, focus of lenses.
Troclear
Number: 4
Type: Motor
Function: Eye movements, proprioception
Trigeminal
Number: 5
Type: Mixed
Function: Sensations of the head and face, chewing movements, and muscle sense.
Abducens
Number: 6
Type: Motor
Function: Produce movements of the eyes
Facial
Number: 7
Type: Mixed
Function: Facial expressions, secretion of saliva, taste.
Vestiulocochlear
Number: 8
Type: Sensory
Function: Balance or equilibrium sense. Hearing.
Glossopharyngeal
Number: 9
Type: Mixed
Function: Taste and other sensations of tongue, swallowing, secretion of saliva, aid in reflex control of blood pressure and respiration.
Vagus
Number: 10
Type: Mixed
Function: Transmit impulses to muscles associated with speech, swallowing, the heart, smooth muscles of visceral organs in the thorax, and abdomen.
Accessory
Number: 11
Type: Motor
Function: Turning movements of the head, movements of the shoulder and viscera, voice production.
Hypoglossal
Number:12
Type: Motor
Function: Tongue movements
Contractability
ability of muscle tissue to shorten and contract forcefully
Excitability
ability to generate an action potential in response to a stimulus
Extensibility
ability of muscle to stretch or get longer
Eslasticity
ability to return to its original shape
4 properties of muscle tissue
contactility, excitability, extensibility, and elasticity
Schwann cells
make myelin in PNS
Satelite cells
surround and provide nutrients for neurons in PNS
Astrocytes
Provide structural and metabolic support for neuron in CNS
Oligodendrocytes
create and wrap axons in a myelin sheath in CNS
Microglia
act as the brains immune system in CNS
Ependymal
lines the central cavities of the brain and spinal cord in CNS
types of glial cells in PNS
schwann and satellite
types of cells in CNS
astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and ependymal
exocrine glands
secrete chemical substances into ducts that lead either to other organs or out of the body
endocrine cells
hormones pass directly into the bloodstream or tissues of the body for distrubution
Receptor
site of stimulus action
sensory neurons
neurons that carry incoming information from the sensory receptors to the brain and spinal cord
Integration Center
either monosynaptic or polysynaptic region within the CNS
Motor Neuron
a neuron that sends an impulse to a muscle or gland, causing a reaction
Effector
Muscle fiber or gland cell that responds to efferent impulses by contracting or secreting
somatic reflexes
activate skeletal muscle
Autonomic (visceral) reflexes
Reflexes that activate smooth or cardiac muscle and/or glands.
Stretch Reflex
the contraction of a muscle in response to stretch of that muscle
All stretch reflexes are:
monosynaptic and ipsilateral (motor activity in on same side of body).
frontal lobe function
important for cognitive functions and control of voluntary movement or activity
parietal lobe function
processes information about temperature, taste, touch and movement
temporal lobe function
processes memories, integrating them with sensations of taste, sound, sight and touch.
occipital lobe function
visual processing
Medulla
the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing
Cerebellum function
Balance and coordination
cerebrum function
thinking, personality, sensations, movements, memory
brain stem function
Connects the brain and spinal cord
Synergists
(helper)- Small muscle that aids prime mover
Antagonists
(against) Muscle that is opposing an action
Agonist
(leader) Primer mover. Muscle that is causing an action
dura mater
-outermost layer
-made of tough, white, fiborous connective tissue
-contains many blood vessels
-attaches to inside of cranial cavity
arachnoid mater
-middle layer
-thin, web-like membrane
-lacks blood vessels
-between dura and pia
*subarachnoid space: between arachnoid and pia, contains cerebrospinal fluid
pia mater
-innermost layer
-thin, contains blood vessels
-attached to surface of brain and spinal cord
-nourishes brain cells & protects
Broca's area
Controls language expression - an area of the frontal lobe, usually in the left hemisphere, that directs the muscle movements involved in speech.
Wernickes area
it is involved in the understanding of written and spoken language
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
plasma-like clear fluid circulating in and around the brain and spinal cord
subarachnoid space
the space between the arachnoid mater and pia mater.
CSF production
Produced by choroid plexus lining the ventricles
Diencephalon
Contains thalamus and hypothalamus
What act as levers in the body?
bones
What act as pivots in the body?
joints
What provides the effort to move loads?
muscles
Give an example of a class 1 lever
Nodding your head
The pivot lies between the effort and the load (see-saw)
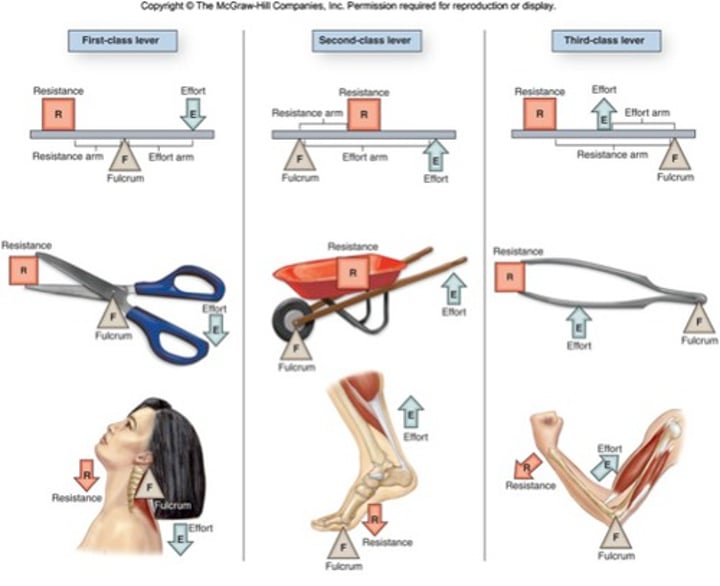
Give an example of a class 2 lever
Stand on the tip of your toes
Load is between the pivot and the effort
(wheel barrow)
Mechanical advantage because the effort is less than the load.
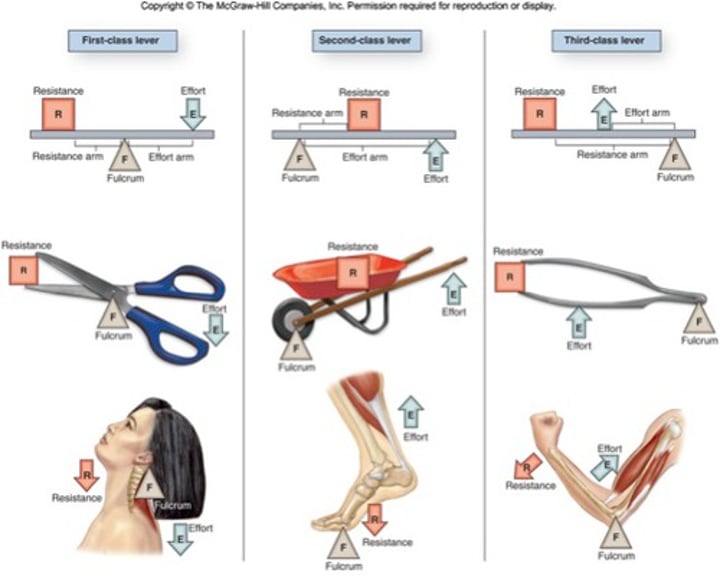
Give an example of a class 3 lever
Bend your arm
Load is further away from the pivot than the effort
Hypothalamus
found inferior to the thalamus, has 4 major regions, controls many body activities and is one of
the major regulators of homeostasis.
Thalamus
located superior to the midbrain & contains nuclei that serves as relay station for all sensory
impulses (EXCEPT SMELL) to the cerebral cortex. Plays role in maintenance of consciousness
Epithalamus
lies superior and posterior to the thalamus and contains the pineal gland. The pineal gland
secretes melatonin (what helps us sleep) and habenular nuclei which are involved in olfaction
How do the hypothalamus and pituitary gland work together?
the hormones of the pituitary help regulate functions of other endocrine glands. the hypothalamus sends signals to the pituitary to release or inhibit pituitary hormones.
Skeletal Muscle Cells
-Longest type of muscle cell
-Length is greater than width
-Look like "fibers" in a microscope (muscle cells/muscle fibers)
-Multinucleated (more than one nucleus)
What is the Fascia?
the membrane around entire muscle tissue
What is a Fascicle?
a bundle of muscle fibers
What is the Sarcolemma?
the membrane around one muscle fiber
What is a Myofibril?
Many of these units make up a single muscle fiber. These are made up of sarcomeres.
Skeletal Muscle Cells consist of two muscle proteins
Myosin (A bands): Thick and dark protein
Actin (I bands): Thin and light (color) protein
electrical excitability
the ability to respond to a stimulus and convert it into an action potential
Fixator
stabilizes the origin of a prime mover
Action Potential (AP)
allow communication over short and long distances
graded potential GP
allow communication over short distances only
blood flow to the brain
via the vertebral and carotid arteries and flows back to the heart via the jugular veins
pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
adrenal glands
a pair of endocrine glands that sit just above the kidneys and secrete hormones (epinephrine and norepinephrine) that help arouse the body in times of stress.
lacrimal gland
produces tears
Pancreas
insulin and glucagon
posterior pituitary
ADH and oxytocin
pineal gland
secretes melatonin
sweat glands
The glands that secrete sweat, located in the dermal layer of the skin.
Sensation
the conscious or subconscious awareness of changes in the external or internal environment
Perception
the conscious interpretation of sensations performed by the cerebral cortex
sensations are called
sensory modality (touch, pain, vision & hearing)
somatic senses
touch, pressure, temperature, pain
special senses
vision, hearing, taste, smell, equilibrium
Exteroreceptors
hearing, vision, smell, taste, pressure, vibration, & pain
Interoreceptors
monitor the body's INTERNAL environment
Propioreceptors
provide information about body position, muscle length, and tension & position and movements of joints.
Tactile sensations
touch, pressure, vibration, itch and tickle
first order neuron
impulses from somatic receptors to the brain stem or spinal cord
second order neurons
impulses from the brain stem and spinal cord to the thalamus
third order neurons
impulses from the thalamus to the primary somatosensory area of the cortex on the same side
Posterior column-medial lemniscus pathway
impulses from the limbs, trunk, neck, & posterior head
Anterolateral (spinothalamic) pathway
impulses for pain, temperature, itch, tickle, & posterior head
Trigeminothalamic pathway
impulses from MOST somatic sensations- tactile, thermal & pain- from face, nasal cavity, oral cavity & teeth
Anterior & posterior spinocerebellar pathway
convey nerve impulses from proprioceptors in trunk, and lower limb of ONE side of body and to same side of cerebellum