Physical and Chemical Processes Final
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
55 Terms
electroneutrality
principle that in any given system the total positive charge must always equal the total negative charge
Alkalinity
a measure of the acid-neutralizing capacity of water. Volume of acid consumed (mL) × Molarity of acid (M) × 50 × 1000 / Volume of water sample (mL)
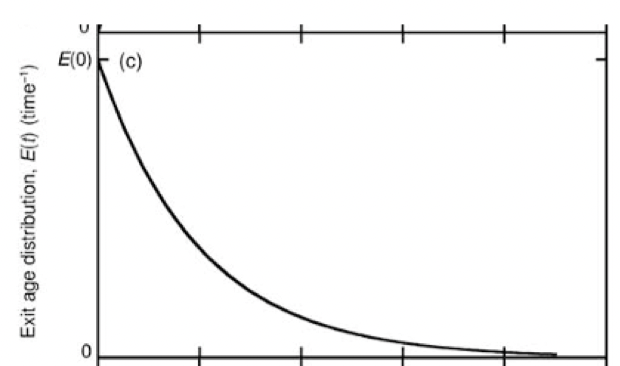
E(t)
exit age distribution. rate at which molecules are exiting a system
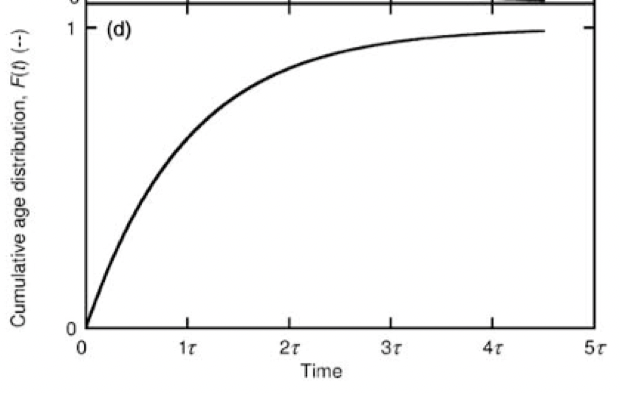
F(t)
cumulative age distribution. fraction of fluid with residence time less than or equal to a given value
Mean hydraulic detention time
tau = V/Q
Alkalinity: for pH between 6 and 9
CO3
Alkalinity: for pH less than 9
CO3 and OH can be ignored **don't ignore if given though
E(t) of a CFSTR for pulse input tracer
F(t) of CFSTR for pulse input tracer
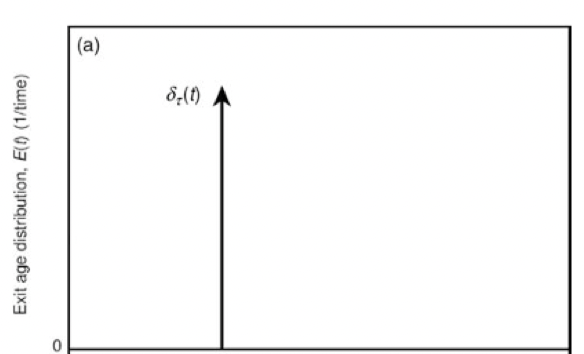
E(t) in a PFR for pulse input
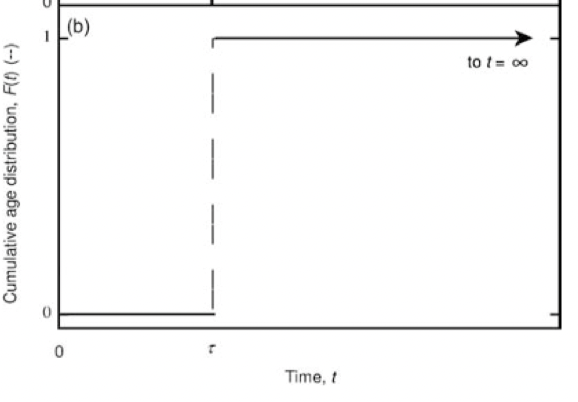
F(t) of a PFR for pulse input
relationship between F(t) and E(t)
E(t) = dF(t)/dt
F(t) =∫E(t)dt (from 0 to t)
PFR Mass Balance, no diffusion/dispersion and no reaction
Rate of change of mass stored in control volume = Rate of input of mass to cv − Rate of output of mass from cv
∂c/∂t = -vx∂c/∂x
CFSTR Mass Balance for pulse input, no diffusion/dispersion and no reaction
Rate of change of mass stored in control volume = Rate of input of mass to cv − Rate of output of mass from cv
𝑐p(t) = 𝑐0𝑒−𝑡/𝜏
CFSTR Mass Balance for step input, no diffusion/dispersion and no reaction
Rate of change of mass stored in control volume = Rate of input of mass to cv − Rate of output of mass from cv
𝑐s(t) = 𝑐in(1 - e(-t/τ))
F(t) equation for a CFSTR with step input tracer
F(t) = 1 − 𝑒−𝑡/𝜏
E(t) for a CFSTR with step input tracer
E(t) = 1/𝜏 (e−𝑡/𝜏)
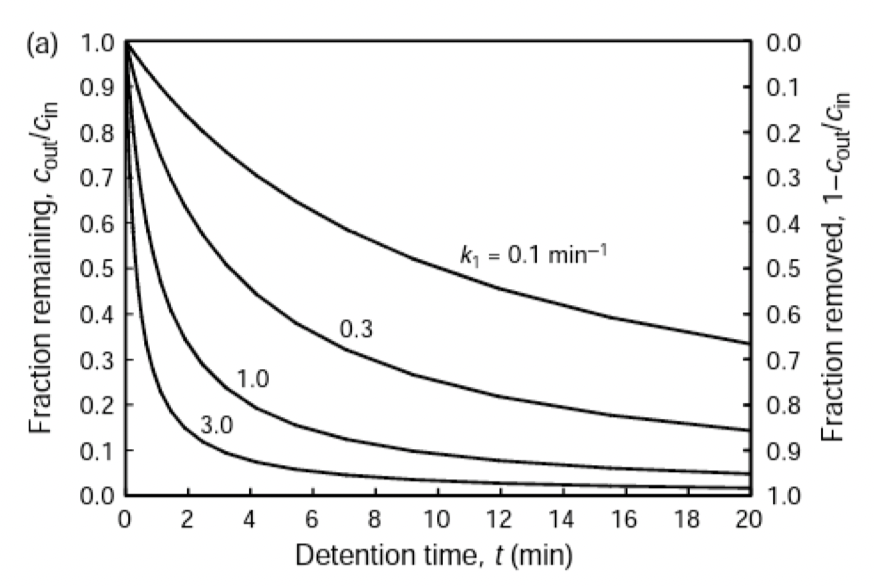
Relationship between effluent concentration and detention time for CFSTR with irreversible first order reaction
Freundlich isotherm
q = kFcn
log transformed freundlich isotherm
logq = logkF + nlogc
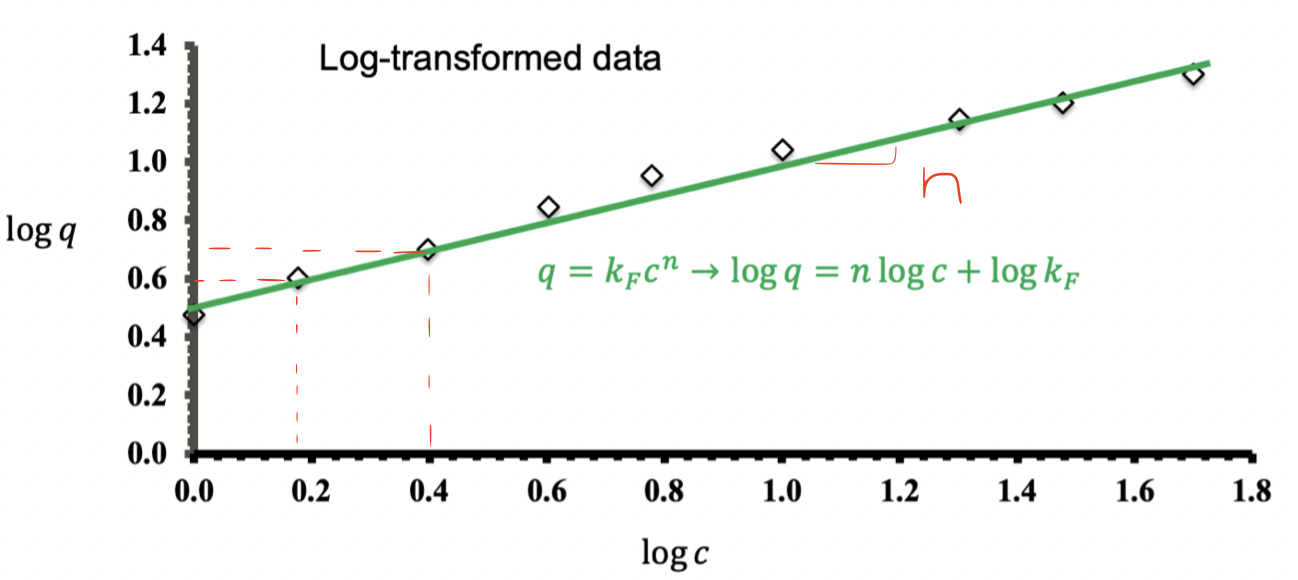
Logarithmic plot of equilibrium concentration data that can be used to obtain the Freundlich parameters
equation for time to ½ concentration in a batch reactor for a first order reaction
t1/2 = ln2/k1
fraction of liquid-phase resistance (percent of the gas transfer resistance that’s in the liquid phase) equation
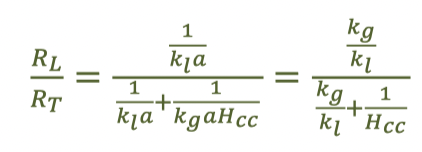
equation for finding the effluent concentration after a first-order reaction in a series of 30 CFSTRs
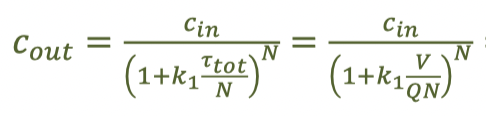
1 cubic meter equals
1000 liters
concentration of adsorbate (i.e. PAC) equation
cPAC = (c0 — ceq)/(qeq — q0)
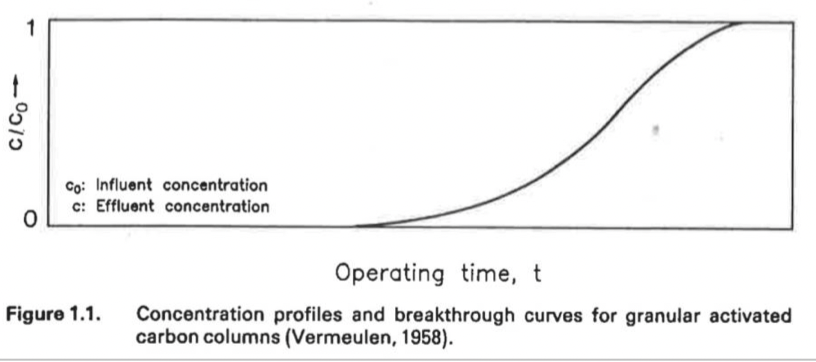
Formula for time to breakthrough
tbt = NBV, bt x EBCT
Number of bed volumes at breakthrough equals
NBV, bt = (pb x qin)/cin
EBCT equals
EBCT = Vr/Q
Mass of adsorbent (usually carbon) at breakthrough equals
Madsorbent = pb x Vr
adsorption
molecules adhere to the surface of the phase
adsorbate or sorbate
molecule (liquid or gas) that adsorbs
adsorbent or sorbent
solid on which adsorption occurs is called
adsorption density
Amount of material (adsorbate) adsorbed per unit of adsorbent
mass sorbate/mass sorbent
concentration adsorbed
ci, adsorbed = qicsolid, sorbent
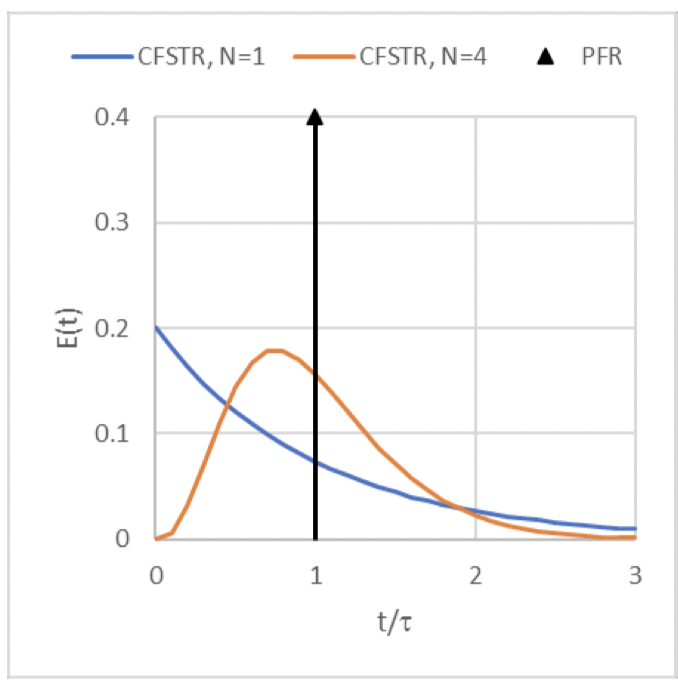
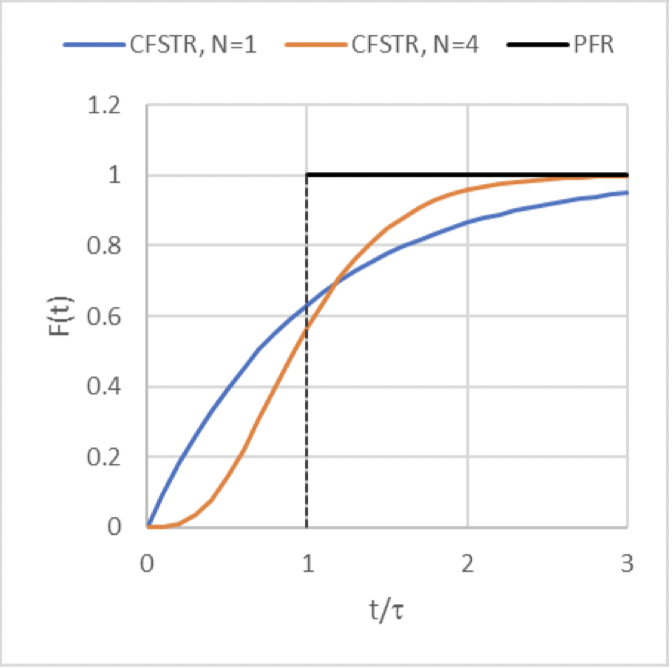
E(t) curve for pulse input of a non-reactive tracer to the series of 𝑁 CFSTRs
(the orange curve)
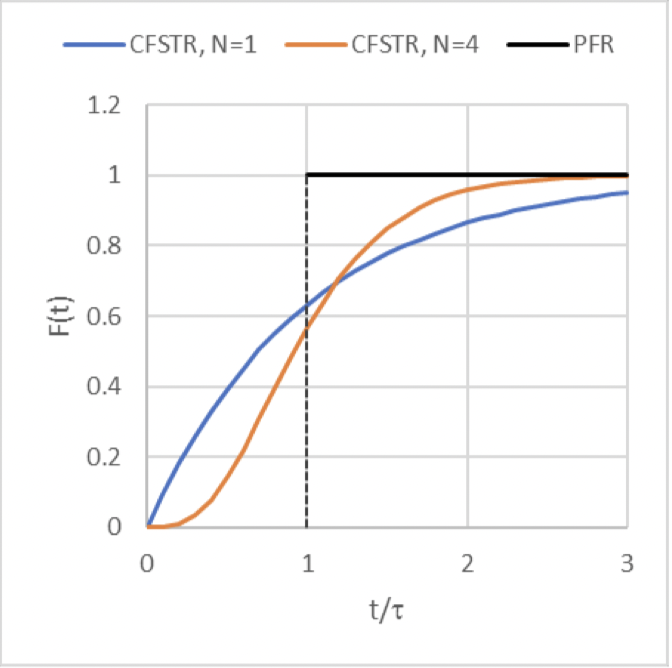
F(t) curve for a pulse input of a non-reactive tracer to the series of 𝑁 CFSTRs
(the orange curve)
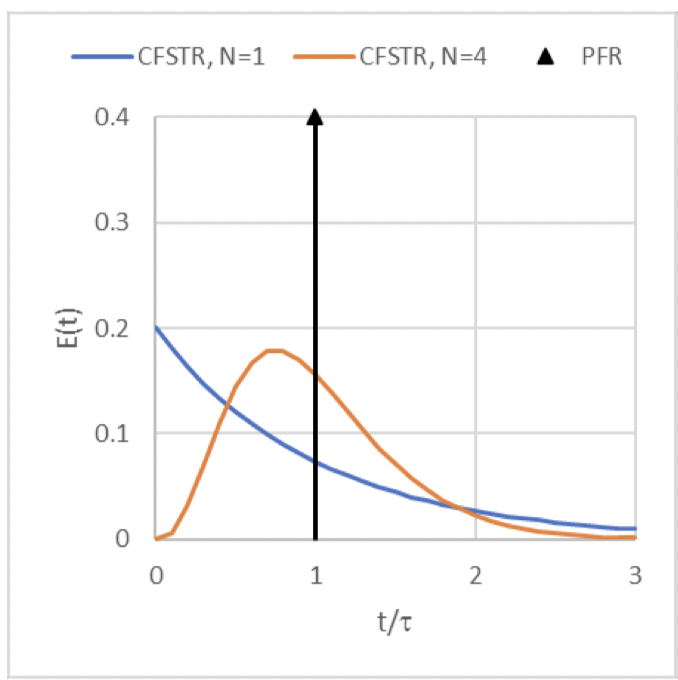
E(t) curve for a pulse input of a non-reactive tracer if you were modeling the reactor system as a PFR
(the black curve)
F(t) curve for a pulse input of a non-reactive tracer if you were modeling the reactor system as a PFR
(the black curve)
mass balance for oxygen transfer for a single droplet from a surface aerator, assume no diffusion/dispersion
(have to integrate and solve in some cases)
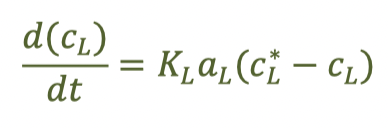
area of sphere
4πr2
aL equals
aL = A/VL
Volume of a sphere
4/3πr3
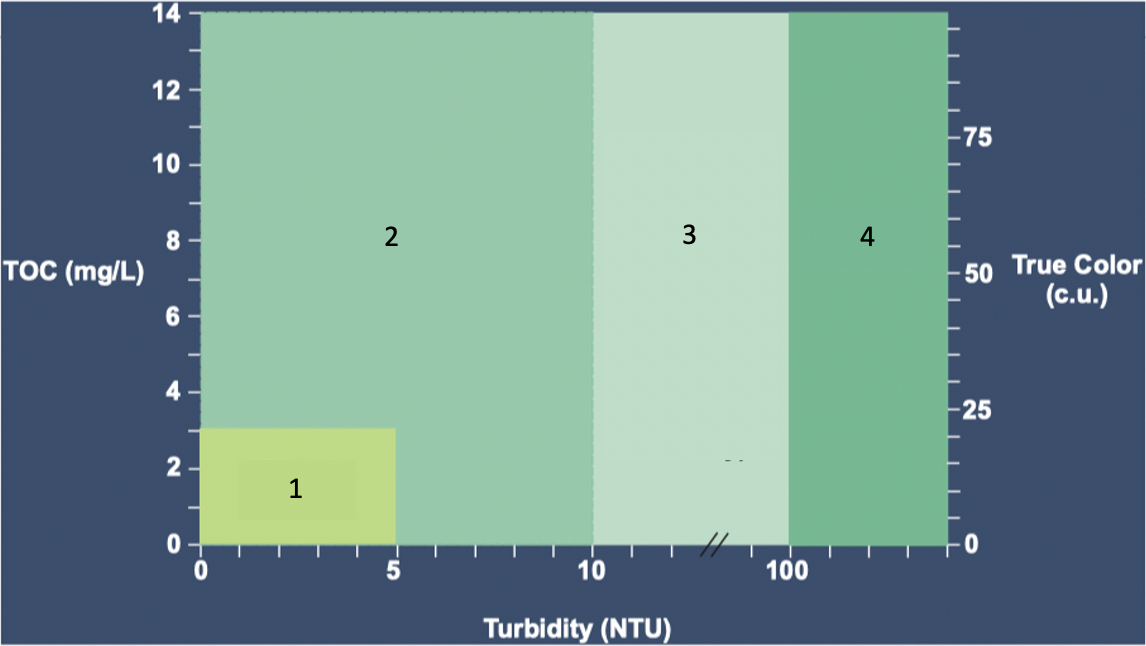
Based on the Average WQ graph, where do the different types of WTP design occur.
Direct Filtration
DAF
DAF or Settling
Settling
What conditions (TOC, Turbidity, and True Color) are Direct Filtration best suited for under average water quality?
TOC: 0-3 mg/L
Turbidity: 0-5 NTU
True Color: 0-20 c.u.
What conditions (TOC, Turbidity, and True Color) are DAF best suited for under average water quality?
TOC: 0-14 mg/L
Turbidity: 0-10 NTU
True Color: 0-100 c.u.
What conditions (TOC, Turbidity, and True Color) are DAF or Settling best suited for under average water quality?
TOC: 0-14 mg/L
Turbidity: 10-100 NTU
True Color: 0-100 c.u.
What conditions (TOC, Turbidity, and True Color) are Settling only best suited for under average water quality?
TOC: 0-14 mg/L
Turbidity: 100+ NTU
True Color: 0-100 c.u.
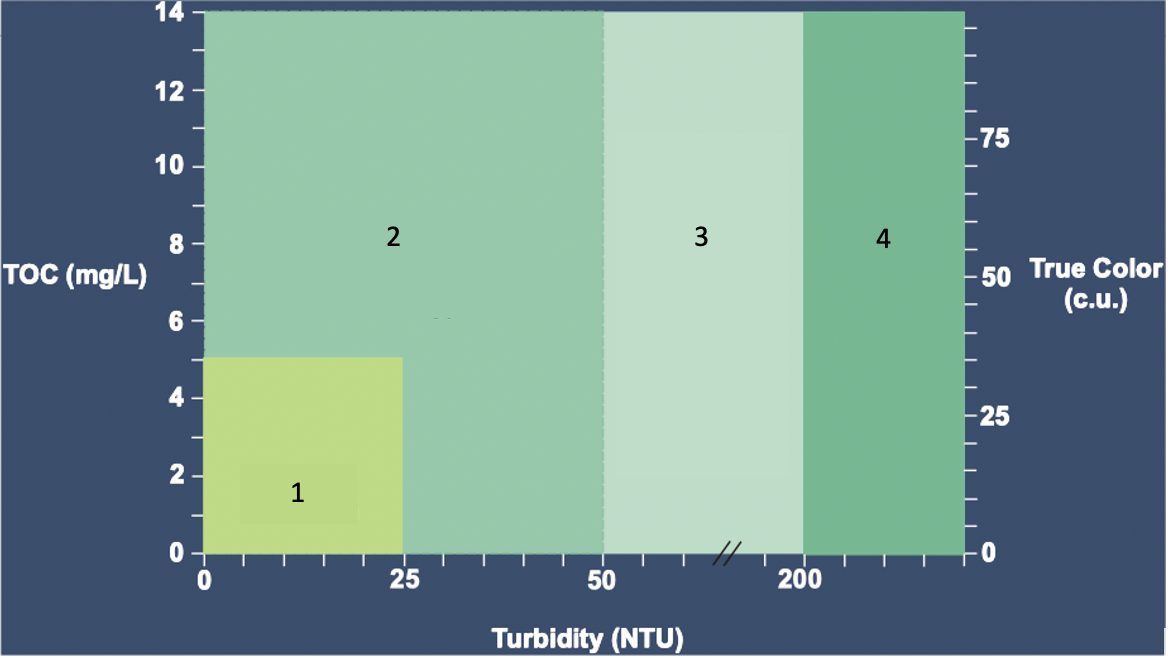
Based on the Max WQ graph, where do the different types of WTP design occur.
Direct Filtration
DAF
DAF or Settling
Settling
What conditions (TOC, Turbidity, and True Color) are Direct Filtration best suited for under max water quality?
TOC: 0-5 mg/L
Turbidity: 0-25 NTU
True color: 0-35 c.u.
What conditions (TOC, Turbidity, and True Color) are DAF only best suited for under max water quality?
TOC: 0-14 mg/L
Turbidity: 0-50 NTU
True Color: 0-100 c.u.
What conditions (TOC, Turbidity, and True Color) are DAF or settling best suited for under max water quality?
TOC: 0-14 mg/L
Turbidity: 50-200 NTU
True Color: 0-100 c.u.
What conditions (TOC, Turbidity, and True Color) are Settling only best suited for under max water quality?
TOC: 0-14 mg/L
Turbidity: 200+ NTU
True Color: 0-100 c.u.

What graph is this?
Rapid Equilibrium Breakthrough Graph
Breakthrough curve for GAC columns