Coordination compounds
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
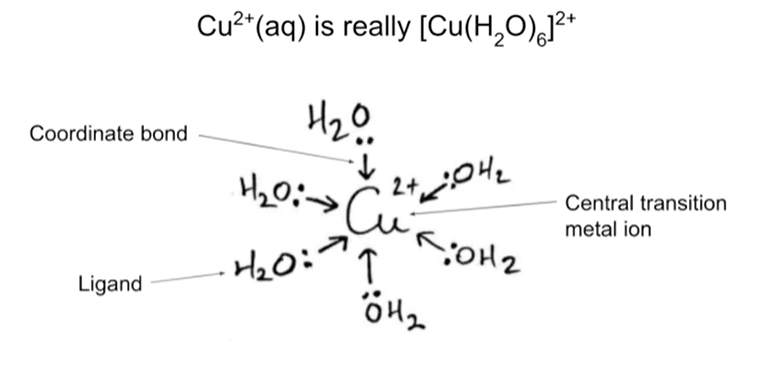
What is a coordination compound?
Coordination compounds have stable complex ions in their lattice and their solutions. These ions are formed from metal ion surrounded by anions or neutral molecules held together with coordinate covalent bond.
What is a complex ion?
A central metal ion surrounded by ligands
What is a ligand?
An atom, ion, or molecule which can donate a lone electron pair
Coordinate bond
Shared pair of electrons between 2 atoms where both electrons came from the SAME atom
Coordination number
Total number of coordinate bonds formed between the ligands and central metal ion
What are the types of ligands?
Monodentate - Form one coordinate bond, donate one lone pair of electrons e.g water, ammonia, chloride
Bidentate - Form 2 coordinate bonds, donate two lone pairs e.g ethanedioate (C2O42-)
Multidentate
What are the types of coordination compounds? (3)
Depending on the nature of ligands
Depending on electrical charge of the complex
Depending on the types of the ligands
Nature of ligands
CC can have inorganic ligands - K[Ag(CN)2] [Co(NH3)6]Cl3
CC can have organic molecules as ligands (chelates) - haemoglobin, chlorophyll etc.
Electrical charge of complex
Can be cations (+ve) [Ag(NH3)2]+Cl-, anions (-ve) K3+[Fe(CN)6]3-, neutral [Co(NO3)3(NH3)3]
Type of ligands
Complexes having amines (R-NH2) as ligands
Complexes of the NH3
Complexes with H2O
How are CC named depending on electrical charge
Anions - add the ending ‘-o’ (Cl- - chloro, CN- cyano, OH⁻ → Hydroxo)
Neutral - names of neutral molecules, no change
Name begins with the cation
NB! Special names - H2O aqua, NH3 ammine, NО nitrozyl, CO → Carbonyl
Naming rules
Begin with +ve ion, could be the complex OR counter ion
Identify the ligands and name them alphabetically. (numerical prefixes do not affect)
Use prefixes (di-, tri-, etc.) for multiple ligands.
Name the metal, using "-ate" if the complex is an anion.
Specify the oxidation state of the metal in Roman numerals.
Include counterions if present.
Names of metals in anions for : copper, gold, iron, lead, silver, tin
cuprate, aurate, ferrate, plumbate, argentate, stannate
Shapes & coordination number
4 - square planar, cisplatin Pt(NH3)Cl2
4 - tetrahedral
6 - octahedral
[Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl - list 6 things from this compound
Name - dichlorotetraaquacromium (III) chloride
Central metal - Cr3+
Ligands - Н2О, Cl2
Counterions - Cl-
Complex ion - [Cr(H₂O)₄Cl₂]⁺
H₂O (water): Neutral charge = 0.
Cl⁻ (chloride ligands inside the complex): Each has a charge of -1, and there are 2 Cl⁻, so total = -2.
x+(−2)=+1 so Cr is +3
Coordination number - 6
Common metal forming complexes - Fe, Cu, Cr, Ag, Zn, Al, Ca, Ba
Fe2+, Fe3+, Cu2+, Cr3+, Ag+ , Zn2+, Al3+, Ca2+, Ba2+
Determine whether these complexes are neutral or ions :
Fe(CO)5
K3[Fe(CN)6]
K2[PtCl6]
[Cr(H2O)4Cl2]Cl
Neutral
(-1×6) + 3 = -3 → [Fe(CN)6]3-
(-1×6) + 4 = -2 → [PtCl6]2-
(-1×2) + 3 + 4 = +1 → [Cr(H2O)4Cl2]1+
Complex ions exist as stable units in the lattice of coordination compounds and in their solutions
Counterbalancing ions
these are the ions with opposite electrical charge of the complex ion → form external coordination sphere
What are the counterbalancing ions :
K3[Fe(CN)6]3-
K2[PtCl6]2-
[Cr(H2O)4Cl2]1+Cl
[Cu(NH3)4](OH)2
K+
K+
Cl-
OH-
Stability complex (Kf or Kst)
Mn+ + xLm- ⇌ [MLx] p+
Kst = [ [MLx]p+]
[Mn+].[Lm-]x
What does the stability complex tell you about the ion?
Quantifies how strongly the ligand(s) bind to the central metal ion in solution. A higher stability constant indicates a more stable complex, meaning the equilibrium favours complex formation.
Factors affecting Kf (3)
charge and size of metal ion - smaller, highly charged metal ions form more stable complexes
nature of ligands - strong > weak ligands, higher Kf
chelation effect - multidentate ligands form more stable complexes
What is the Kst of : K4[Fe(CN)6]
4K+ + [Fe(CN)6]4-
Fe2+ + 6CN- ⇌ [Fe(CN)6]4-
Кst = [[Fe(CN)6]4-]
[Fe2+].[CN-]6
What is the structure of this compound : K4[Fe(CN)6]
Central ion - Fe+2
Ligands - CN-
Complex ion - [Fe(CN)6]4-
Counter ions - K+
Coordination number - 6
Charge of central ion - +2
Bonding in coordination compounds
In complex : the central metal ion and ligands are held together by coordinate bond.
The complex ion and counter ions are linked via IONIC INTERACTIONS
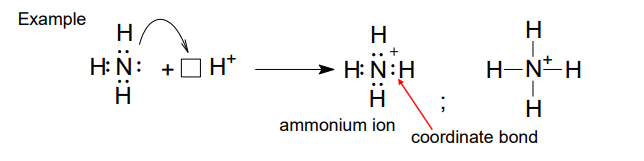
What is a chelate?
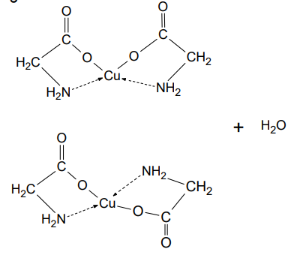
Coordination compounds with organic molecules as ligands - usually polydentate
Depending on the type of organic molecule chelates are formed with (7)
amino acids, peptides & proteins
polyols
salt of tartaric acid
phenol & salicylic acid
EDTA
protoporphyrin
polypeptide chain of the enzymes
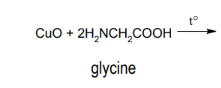
Reaction - chelate with amino acids as ligands
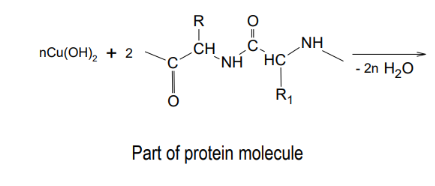
Reaction - chelate with peptides/proteins
biuret test - detects peptide bond, blue →purple

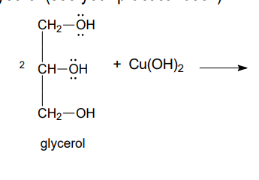
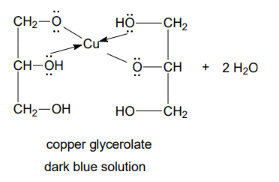
Reaction - chelate with polyols
The reaction is used to prove the presence of -OH groups attached to adjacent carbon atoms
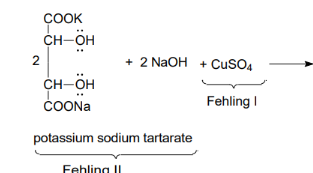
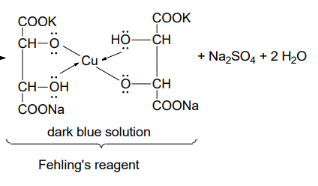
Reaction - chelate with salt and tartaric acid
EDTA forms chelates with…
Ca2+, Mg2+,Pb2+, Cu2+,Cd2+
Tests hardness of water, treatment of heavy metal poisoning, enlarges root canals
What part of haemoglobin is a chelate?
Haem group (non-protein part). Central metal ion - Fe2+, ligand - protoporphyrin
Methaemoglobin contains Fe3+ a stable oxidized form of haemoglobin that is unable to release oxygen to the tissues.
What is vitamin B12?
collection of cobalt & corrin ring
vitamin B12 is important for the normal functioning of the brain and nervous system
What are cytochromes?
Generally membrane bound haemoproteins that contain haem groups, and carry out electron transport
Metal ion is iron, interconverts between Fe2+ (reduced) and Fe3+ (oxidized) states