Population and Community Ecology Exam 1
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
True or False: Three types of dispersal are random, clumped, and uniform.
False
What is the most common dispersion pattern in nature?
Clumped/Aggregated
True or False: Emigration is the movement of individuals into an area occupied by the population.
False
True or False: Immigration is the movement of individuals into an area occupied by the population.
True
True or False: The age structure of a population is determined by age-specific rates of natality and mortality.
True
True or False: The per capita natality rate of a population can be expressed properly in terms of the number of individuals born per year.
False
True or False: A life table contains the mean age-specific body weights and annual survival rates of the individuals in the population.
False
Which of the following are among the basic characteristics that ecologists use to describe an animal population? A. Density B. Pattern of dispersion C. Age and sex ratios D. Natality and mortality rates E. All the above
E. All the above
Which of the following is the most common pattern of dispersion of plants and animals found in nature? A. Uniform B. Random C. Lognormal D. Aggregated E. Normal
D. Aggregated
Probable causes of the clumped (or aggregated) patterns of dispersion exhibited by many plants and animals include which of the following? A. Environmental gradients B. Preferred distance to closest individual of the same species C. habitat heterogeneity D. All the above E. None of the above
D. All the above
Important population parameters that affect density include which of the following? A. Natality B. Mortality C. Immigration and emigration D. All the above E. None of the above
D. All the above
Thinking about the three main types of survivorship curves described in your textbook, which of the following statements is correct? A. A Type 1 curve represents age-specific mortality, with relatively low age specific mortality rates until individuals reach a relatively old age B. A Type 2 curve represents age-specific mortality, with relative age-specific mortality decreasing gradually as individuals grow older C. A Type 3 curve represents age-specific mortality, with relatively low age specific mortality until individuals reach a relatively old age D. A and B E. All the above
A. A Type 1 curve represents age-specific mortality, with relatively low age specific mortality rates until individuals reach a relatively old age
which of the following statements is correct? A. The Type 1 curve represents an indefinite lifespan B. The Type 2 curve represents constant per capita mortality across all ages C. The Type 3 curve represents high survival to old age D. All three curves represent the age-specific mean number of offspring produced
B. The Type 2 curve represents constant per capita mortality across all ages
True or False: Static life tables assume constant rates of mortality for each age class.
True
Under what conditions will a static life table and a dynamic life table be identical? A. They never will be identical B. They always will be identical C. When population size is constant and environmental conditions do not change D. When the population is at carrying capacity E. When the population is at the inflection point on the logistic growth curve
C. When population size is constant and environmental conditions do not change
What is the most basic difference between a static life table and a dynamic (or cohort) life table regarding the way the field data are collected? A. The time elapsing between field sampling dates is longer for a dynamic life table B. Field data collected for a static life table must be transformed to a logarithmic scale C. Field data collected for a dynamic life table come from a single cohort of individuals D. The is no difference in the collection of field data, but the data are analyzed differently
C. Field data collected for a dynamic life table come from a single cohort of individuals
What is the difference between a static life table and a dynamic (or cohort) life table regarding the assumptions we must make to generate the lx column? A. For a dynamic life table, we must assume population size has been constant B. For a static life table, we must assume age-specific birth and death rates have been constant C. For a dynamic life table, we must assume age-specific birth and death rates have been constant D. A and C
C. For a dynamic life table, we must assume age-specific birth and death rates have been constant

Based on the following life table, which of the following statements is correct? A. The value of l0 is 1.0 B. The value of l0 is 1000 C. There are insufficient data to calculate l0 D. The value of l0 is ln (1000)
A. The value of l0 is 1.0

Based on the following life table, which of the following statements is correct? A. The value of d0 is 900 B. The value of d0 is 0.9 C. There are insufficient data to calculate d0 D. The value of d0 is 0
A. The value of d0 is 900

Based on the following life table, which of the following statements is correct? A. The value of q0 is 0.9 B. The value of q0 is 0.1 C. There are insufficient data to calculate q0 D. The value of q0 is 1
A. The value of q0 is 0.9

Based on the following life table, which of the following statements is correct? B. The nx column is representative of a species with a Type 2 survivorship curve C. The nx column is representative of a species with a Type 3 survivorship curve D. The nx column does not look like any of the three types (Type 1, Type 2, or Type 3) of survivorships curves
C. The nx column is representative of a species with a Type 3 survivorship curve
The intrinsic capacity for increase of a population commonly is represented by which of the following? A.R0 B. λ C. r D. b E. d
C. r
The net reproductive rate (R0) is defined as which of the following? A. The multiplication rate of the population per generation B. The total number of female offspring produced by all females in the population C. The average number of female offspring produced per female aged x to x+1 D. The mean number of female offspring produced by females in all post reproductive age classes
A. The multiplication rate of the population per generation
The finite per capita rate of increase of a population commonly is represented by which of the following? A. λ B. r C. b D. d
A. λ
A fertility table (or fertility schedule) contains a column of bx values, which are defined as which of the following? A. The time elapsing between birth of a female and the average birth date of her female offspring B. The average number of female offspring produced per female aged x (over the time period that she is aged x) C. The mean number of female offspring produced by a female during her lifetime D. The mean number of female offspring produced by females in all age classes during the time period x
B. The average number of female offspring produced per female aged x (over the time period that she is aged x)
Demographic projections based on life tables: A. Assume that age-specific per capita birth and death rates are constant B. Can project an exponentially increasing population size C. Can project an exponentially decreasing population size D. Can project a stable population size E. All the above
E. All the above
Although the evolution of demographic (life history) traits is a complex topic, there are some general conclusions that ecologists have reached. If you had to identify just one factor or process that could determine whether a species evolved “big bang” or repeated reproduction (semelparity or iteroparity), what would that one factor or process be? A. The number of competing species in the community in which the species has evolved B. The relative variability of the environmental conditions under which the species has evolved C. The average daily energy requirements of individuals of the species D. The average longevity of individuals of the species
B. The relative variability of the environmental conditions under which the species has evolved
True or False: Regarding “big bang” versus repeated reproduction (semelparity versus iteroparity), you would expect a species to evolve repeated reproduction if it evolve under a fluctuating environment in which the probability of surviving to adult stages was low.
False
Which of the following are among the most fundamental limitations, or most basic problems, that ecologists face when studying populations? A. It is difficult to determine what constitutes a population for any given species B. Populations do not exist in isolation, but are embedded in a community with populations of other species C. Some populations are too large to enumerate D. A and B E. All the above
D. A and B
True or False: When the intrinsic rate of population increase is large, the life history parameter that has the most profound effect on population growth is the number of progeny in each reproductive event.
False
True or False: Within the context in which we are using them in class, the terms dispersion and dispersal are synonymous.
False
True or False: All animals are unitary organisms and all plants are modular organisms.
False
Theoretically, a population that is growing in an unlimited environment will exhibit what growth form, that is, what is the shape of the curve that represents population growth? A. Linear B. Exponential (or geometric) C. Logistic D. Sinusoidal E. None of the above
B. Exponential (or geometric)
Theoretically, a population that is growing in a limited environment will exhibit what growth form, that is, what is the shape of the curve that represents population growth? A. Linear B. Exponential (or geometric) C. Logistic D. Sinusoidal E. None of the above
C. Logistic
As we discussed in lecture, the ((K-N)/K) term in the logistic growth equation can be interpreted ecologically as: A. The effect of interspecific competition B. The effect of intra-specific competition C. Exponential growth D. Stochastic growth
B. The effect of intra-specific competition
True or False: According to our class discussion related to the definition of predation in the Key Terms list in the Population Growth chapter, for predation to have an impact on the prey population, a predator must eat its prey.
False
True or False: According to our class discussion related to the definition of disease in the Key Terms list in the Population Growth chapter, a disease is a condition of an organism, which can result from a variety of causative factors. That is, disease per se is not a causative factor.
True
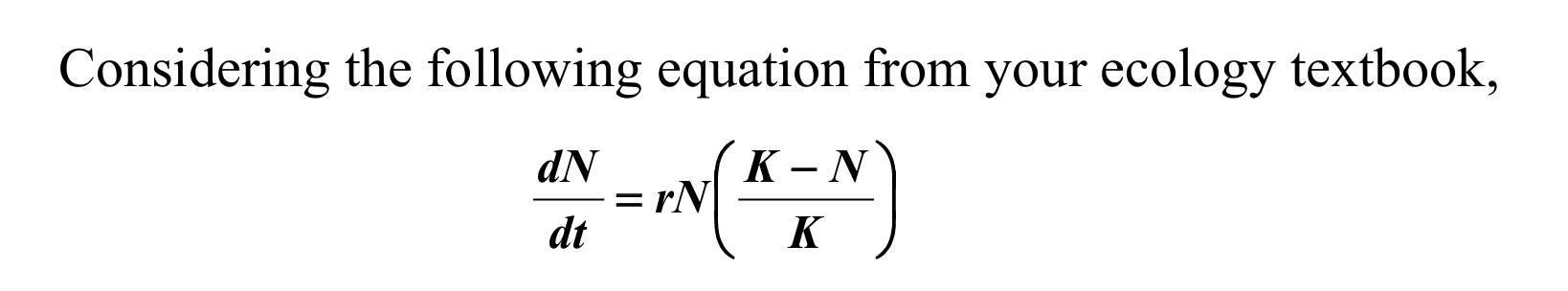
which of the following statements are correct? A. r represents the number of new individuals added to the population each year B. K represents the current population size C. dN/dt represents the instantaneous rate of change in population size D) B and C
C. dN/dt represents the instantaneous rate of change in population size
Under which of the following circumstances would you expect a population to be growing exponentially? A. A relatively hot environment B. A relatively cold environment C. A markedly seasonal environment D. A stable environment E. An unlimited environment
E. An unlimited environment
Under which of the following circumstances would you expect a population to exhibit a logistic growth form? A. A relatively hot environment B. A relatively col C. A markedly seasonal environment D. A stable environment E. A limited environment
E. A limited environment
If a population has an intrinsic rate of increase (or per capita rate of population growth) equal to 0.5, is the population increasing or decreasing?
Increasing
Based on our discussion in lecture and the graph of population growth shown in your textbook, whooping crane population growth from 1918 to 2004 can be described as A. Exponential B. Logistic C. Time lagged D. Intrinsic E. Cyclical
A. Exponential
The theta-logistic model represents one of the attempts that ecologists have made to generalize the basic logistic model of population growth. Which of the following assumptions of the basic logistic growth model is relaxed in the θ logistic model? A. Density-dependent growth above a threshold population size B. A linear decrease in per capita growth rate as population density increases C. Age-specific mortality rates D. Age-specific natality rates E. C and D
B. A linear decrease in per capita growth rate as population density increases
True or False: In time-lagged models of population growth, longer time lags produce population fluctuations of larger amplitudes.
True
Time-lagged models of population growth can produce which of the following forms of population fluctuations? A. Exponential B. Logistic (sigmoidal) C. Convergent (damped) D. Chaotic E. C and D
C. Convergent (damped)
True or False: Stochastic models of population growth are most often used to produce chaotic population growth forms.
False
Stochastic models of population growth always are characterized by which of the following? A. Time lags B. Exponential growth C. Logistic growth D. Random variables E. None of the above
D. Random variables
A Leslie matrix A. Is a computer model B. Is a description of population age structure C. Is constructed based on age-specific birth and survival rates D. Represents a population with discrete generations E. Is appropriately described by all the above
C. Is constructed based on age-specific birth and survival rates
A Leslie matrix can be used to A. Project future population sizes B. Project future population age-class distributions C. Project maximum population size D. Calculate age-specific natality and mortality rates E. A and B
B. Project future population age-class distributions
Which of the following are among the attributes of many vertebrate populations that are explicitly represented by the logistic growth model? A. Age specific rates of mortality B. Age specific rates of natality C. Exponential population growth D. Varying rates of population increase E. None of the above
D. Varying rates of population increase
True or False: Theoretically, a population growing in a limited environment will exhibit logistic (or sigmoid) growth.
True
True or False: If a population has a net reproductive rate equal to 0.05, the population is increasing.
False
For a population with overlapping generations that is growing in an unlimited environment, which of the following statements correctly describes the form of the theoretical population growth trajectory? A. Population size will fluctuate in a chaotic fashion forever B. Population size will increase exponentially forever C. Population size will increase from relatively small to relatively large and then will fluctuate between relatively small and relatively large forever D. Population size will decrease exponentially forever (approach zero asymptotically) E. None of the above
B. Population size will increase exponentially forever
For a population with overlapping generations that is growing in a limited environment, which of the following statements correctly describes the form of the theoretical population growth trajectory? A. Population size will fluctuate in a chaotic fashion forever B. Population size will increase almost exponentially from relatively small to about one-half of carrying capacity and then growth rate will become slower and slower and finally become zero at carrying capacity C. Population size will increase from relatively small to relatively large and then will fluctuate between relatively small and relatively large forever D. None of the above
B. Population size will increase almost exponentially from relatively small to about one-half of carrying capacity and then growth rate will become slower and slower and finally become zero at carrying capacity
True or False: One assumption of the logistic model of population growth that is relaxed in the θ-logistic model is that the relationship between change in population size and change in rate of population growth is linear.
True
True or False: One assumption of the logistic model of population growth that is relaxed in the θ-logistic model is that population growth rate becomes zero at carrying capacity.
False
True or False: Thinking about time-lagged models of population growth, longer time lags result in population oscillations with greater amplitude.
True
True or False: Thinking about time-lagged models of population growth, the time lag refers to the amount of time between birth of a female and the average birth date of her offspring.
False
Based on the essay on “What is a “good” population growth model?” in your textbook, which of the following is the most important characteristic of a “good population growth model?” A. The model must make accurate forecasts B. The model must make precise forecasts C. The model must make useful forecasts D. The model is not too complicated E. A and B are equally important
C. The model must make useful forecasts
True or False: One of the most important criteria upon which to base choice of the type of population growth model to use is the amount of background information available on the species.
True
Which of the following describes the most basic difference between an age-based versus a stage-based population projection matrix model? A. The stage-based model has more classes into which individuals are categorized B. The age-based model has more classes into which individuals are categorized C. The two models are essentially the same with regard to structure D. The stage-based model allows surviving individuals to stay in the same class for more than one time step E. The stage-based model is represented by a bigger matrix
D. The stage-based model allows surviving individuals to stay in the same class for more than one time step
True or False: Inter-specific competition occurs when two species use the same limited resource to the detriment of both.
True
True or False: The type of natural selection experienced by populations living near carrying capacity and hence subject to strong competition is called “K-selection”
True
In the Lotka-Volterra equations, α and β represent: A. The adjusted carrying capacities for species 1 and 2, respectively B. The adjusted intrinsic rates of increase for species 1 and 2, respectively C. Competition coefficients D. A and B
C. Competition coefficients
Which of the following statements about resource and interference competition is correct? A. Resource competition occurs when organisms utilize common resources that are in short supply B. Interference competition can occur among organisms when resources are not in short supply C. Interference competition occurs only when organisms can see and/or hear each other D. A and B
D. A and B
Tilman’s model of competition includes the effects of A. Rate of resource use B. Predation C. Stochastic variables D. Time lags
A. Rate of resource use
K-selection implies A. Resource competition B. Interference competition C. Colonization and growth D. r-selection
A. Resource competition
Which of the following statements is correct? A. Resource competition between species occurs when these species utilize common resources that are in abundant supply B. Animals need to see or hear their competitors for competition to occur C. Competition between species can result from interference in gaining access to needed resources D. Ecologists agree that competition is rare in natural populations of plants and animals
C. Competition between species can result from interference in gaining access to needed resources
True or False: The Lotka-Volterra model of competition emphasizes the mechanisms by which competition occurs.
False
True or False: The main feature of Tilman’s model of competition that distinguishes it from the Lotka-Volterra model of competition is that Tilman’s model emphasizes the mechanisms by which competition occurs.
True
Which statement regarding inter-specific and intra-specific competition is correct? A. Inter-specific competition occurs among members of the same species B. Inter-specific competition occurs among members of different species C. Intra-specific competition occurs among members of different species D. Intra-specific competition also occurs among different predator species E. none of the above
B. Inter-specific competition occurs among members of different species
Under which of the following conditions would you expect that competitive exclusion would not occur? A. In unstable environments that never reach equilibrium and are occupied by colonizing species B. In constant environments in which resources always are in short supply C. In fluctuating environments in which competitive advantage is repeatedly shifted from one species to another D. A and C
D. A and C
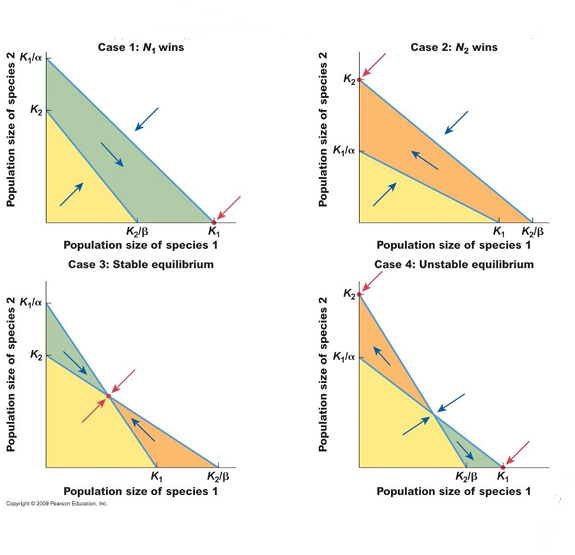
Considering the figures below, which of the following statements is correct? A. The figures represent the outcomes of competition predicted by Tilman’s model of inter-specific competition B. The figures represent the outcomes of competition predicted by the Lotka Volterra model of inter-specific competition C. The blue arrows represent the rates of resource utilization of the two species D. The blue lines (without arrowheads) represent the zero growth isoclines for the two species E. B and D
E. B and D
True or False: According to the author of your textbook (Krebs), descriptive ecology is the foundation of all ecological sciences.
True
What biological discipline(s) are most closely related to ecology? A. Physiology B. Sociology C. Evolution D. A and C E. All the above
D. A and C
The scientific method includes which of the following? A. Creating an image of real world structure B. Formulating hypotheses C. Making predictions D. Collecting data E. All the above F. None of the above
E. All the above
The author of your textbook describes three broad methods of approaching ecology. Which of the following approaches does he mention? A. Theoretical B. Laboratory C. Field D. All the above E. None of the above
D. All the above
True or False: Scientists use the scientific method to prove that their hypotheses are correct.
False
Where does a scientific hypothesis come from? A. Previous research B. Intuition C. Inspiration D. A and B E. All the above
E. All of the above
True or False: A scientific experiment always involves manipulation of the system being studied.
False
Recalling our discussion in class about the film “Powers of Ten,” if we wanted to stop the film when we were looking at the most accurate representation of reality, which of the following images would we be looking at? A. The Planet Earth B. The people on the beach C. It is an impossible choice to make D. It depends on what we are interested in
D. It depends on what we are interested in
True or False: When the intrinsic rate of population increase is large, the life history parameter that has the most profound effect on population growth is the age at first reproduction
True
The scientific method includes which of the following? A. Creating an image of real-world structure B. Formulating hypotheses C. Making predictions D. Collecting data E. All the above
E. All the above
True or False: The scientific method involves both inductive and deductive reasoning.
True
Thinking about the different levels of integration studied in biology, as we move from cells to individuals to populations to communities, scientific understanding A. Increases B. Decreases C. Stays about the same D. No one really knows
B. Decreases
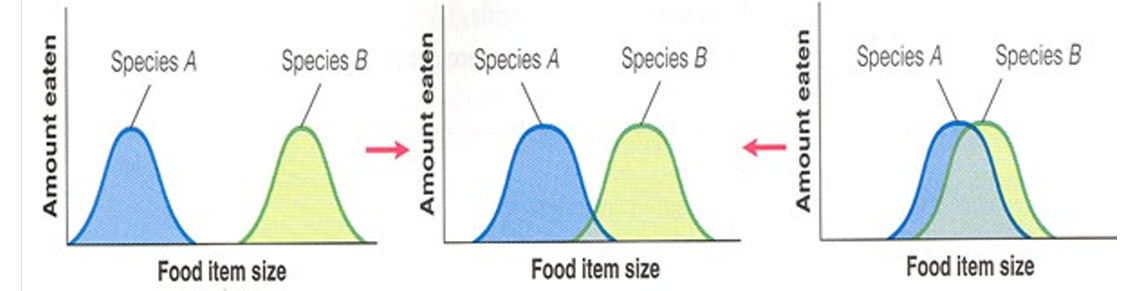
Recalling our class discussion, which of the following can be seen in this set of graphs? A. Niche segregation B. Resource partitioning C. Adaptation D. Niche overlap E. All the above
E. All the above
True or False: Phytoplankton (a large number of autotrophic species using a common pool of nutrients and undergoing photosynthesis) are an exception to the principle of competitive exclusion.
False
Which of the following are among the most important results of the "classical" laboratory experiments dealing with inter-specific competition that help us understand the coexistence of closely related competitors in nature? A. The outcome of competition was robust to changes in temperature B. The outcome of competition was robust to changes in relative humidity C. One of the competing species invariably went extinct D. Both competing species invariably reached a steady state equilibrium E. None of the above
C. One of the competing species invariably went extinct
True or False: The “paradox of the plankton” could be stated correctly as follows: The coexistence of a large number of species of phytoplankton in a relatively unstructured environment, which often is deficient in nutrients, remains an unsolved mystery and is thought to be an exception to the competitive exclusion principle.
False
True or False: The ecological paradox of competition could be stated correctly as follows: How can we reconcile the frequent extinction of closely related species in laboratory experiments with the apparent coexistence of large numbers of closely related species in the field?
True
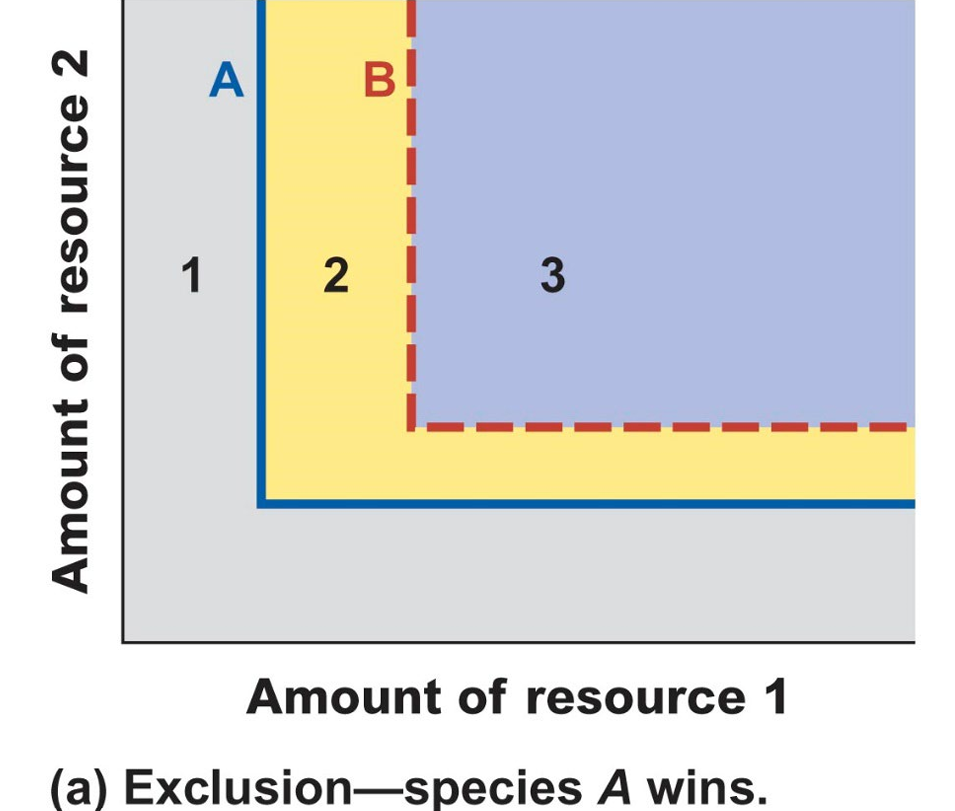
Considering the figure below, which of the following statements is correct?A. The figure represents an outcome of competition predicted by Tilman’s model of inter-specific competition B. The figure represents an outcome of competition predicted by the Lotka Volterra model of inter-specific competition C. Given that Species A wins, the blue line must represent the zero isocline for Species A D. Given that Species A wins, the red dotted line must represent the zero isocline for Species A E. A and C
E. A and C
What assumption of the competitive exclusion principle was relaxed (not met) in the “classical” laboratory experiments to allow coexistence of closely related competing species? A. More than two species were allowed to compete with each other B. A constant food supply was provided C. Environmental conditions were varied D. A parasite was introduced
C. Environmental conditions were varied
The author of your textbook (Krebs) defines ecology as: A. All relations of animals to both their biotic and abiotic environment B. Scientific natural history C. Study of the structure and function of nature D. Study of the interactions that determine the distribution and abundance of organisms
D. Study of the interactions that determine the distribution and abundance of organisms
Which of the following is the definition of a hypothesis used in the textbook? A. A universal proposition that suggests an explanation for some observed ecological situation B. A set of observations that test a question C. A scientific method for answering a question or understanding a phenomenon D. A universal statement that is generally accepted because it is so well corroborated in the scientific community
A. A universal proposition that suggests an explanation for some observed ecological situation
True or False: The author of your textbook defines ecology as “all relations of animals to both their biotic and abiotic environment.”
False
The author of your textbook discusses three approaches to ecology, theoretical, laboratory and descriptive. According to him, which of the three forms the foundation of all ecological sciences?
Descriptive
Recalling that the author of your textbook distinguishes among “descriptive ecology,” “functional ecology,” and “evolutionary ecology,” which of the following statements is correct? A. Descriptive ecology is the foundation of all ecological science B. Functional ecology studies the proximate causes of the dynamic responses of the biota to current environmental factors C. Evolutionary ecology studies the ultimate (historical) causes of the adaptations present in the current biota D. A and B E. All the above
E. All the above
Recalling that the author of your textbook distinguishes among “descriptive ecology,” “functional ecology,” and “evolutionary ecology,” which does he suggest is the most important? A. Descriptive ecology B. Functional ecology C. Evolutionary ecology D. He suggested that they are equally important E. He did not comment on their relative importance
D. He suggested that they are equally important
Thinking about the different levels of integration studied in biology, as we move from cells to individuals to populations to communities, scientific understanding A. Increases B. Decreases C. Stays about the same D. No one really knows
B. Decreases
Thinking about the essay on “Science and Values in Ecology” that we discussed in class, which of the following statements is/are correct? A. Science is value free, that is, it is not influenced by human value judgements. B. Scientists should not be advocates of particular public policies C. Scientific principles provide the basis for public policies D. Scientists carry out objective science that obtains data and tests hypotheses E. All the above
D. Scientists carry out objective science that obtains data and tests hypotheses