Exam 5: Cytology Image Practice
1/164
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
165 Terms
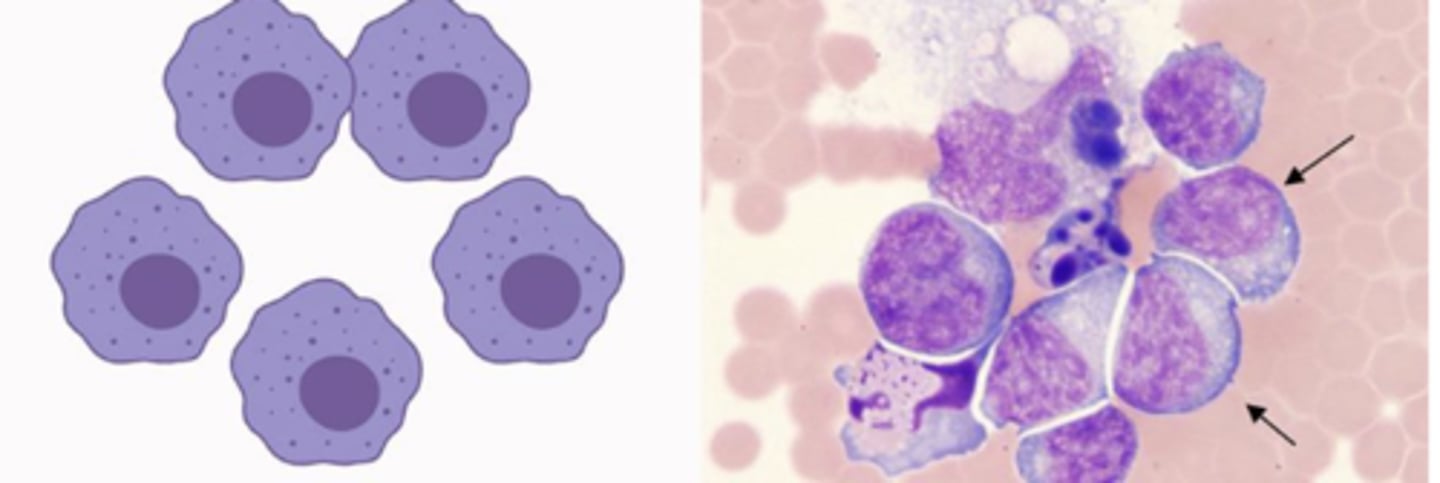
What category of cells are these?
Round cells
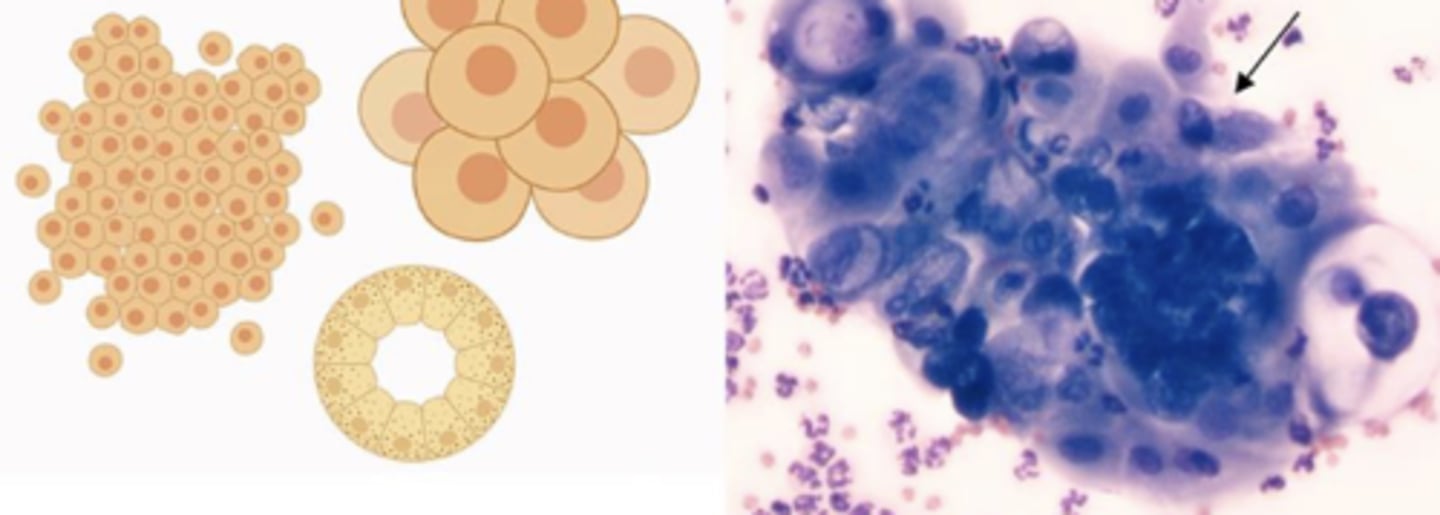
What category of cells are these?
Epithelial cells
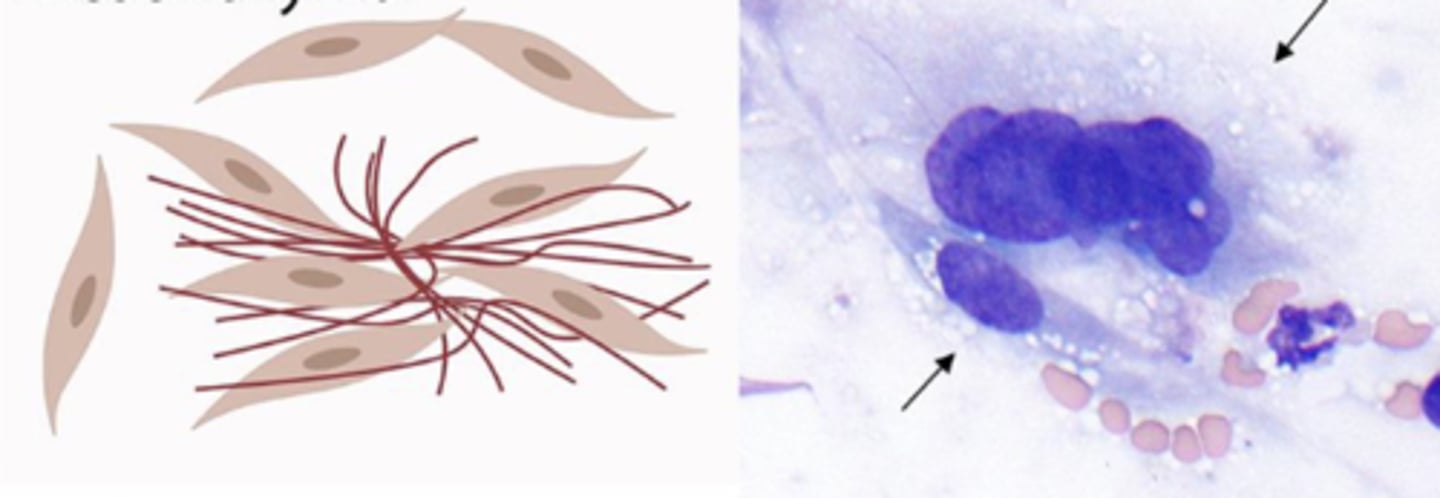
What category of cells are these?
Mesenchymal cells
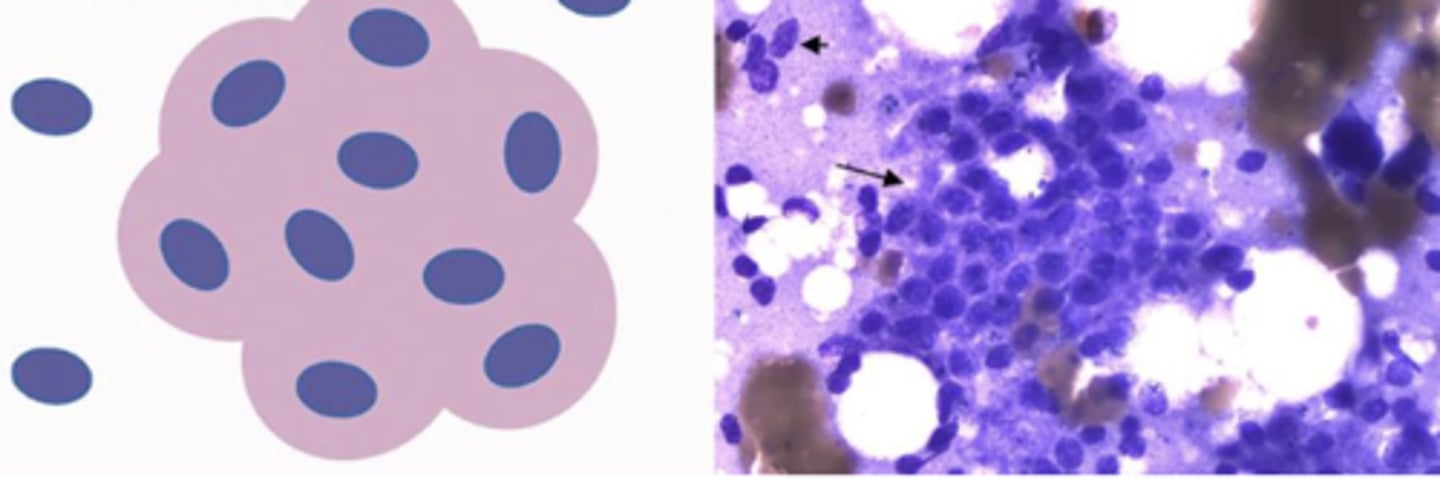
What category of cells are these?
Endocrine cells
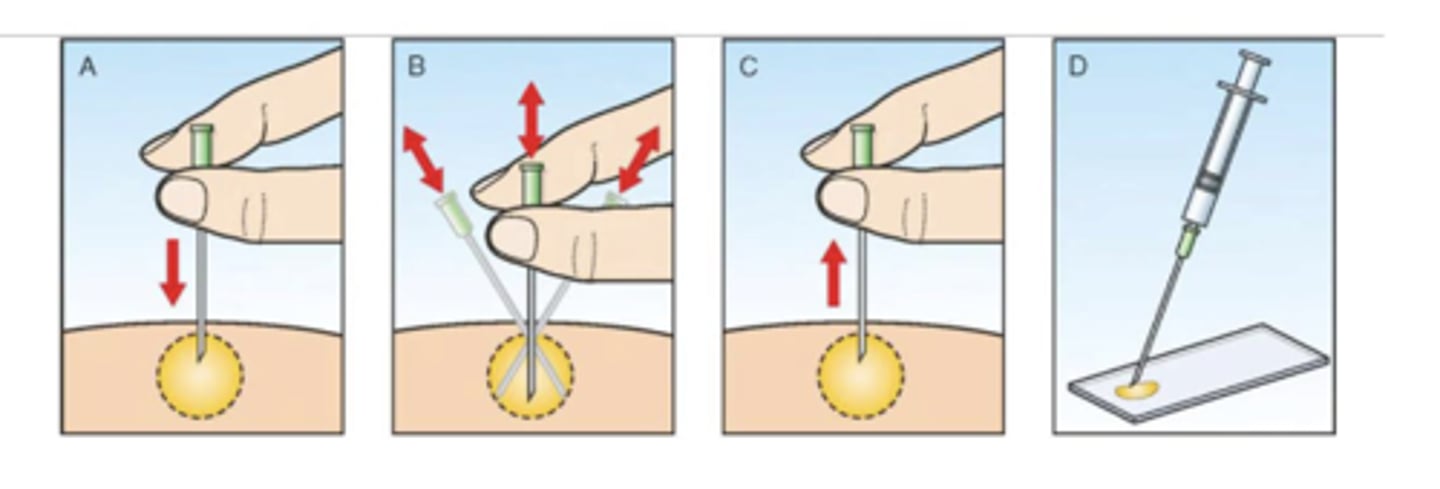
What fine needle aspirate technique is this?
Non-aspiration/capillary/ stab technique
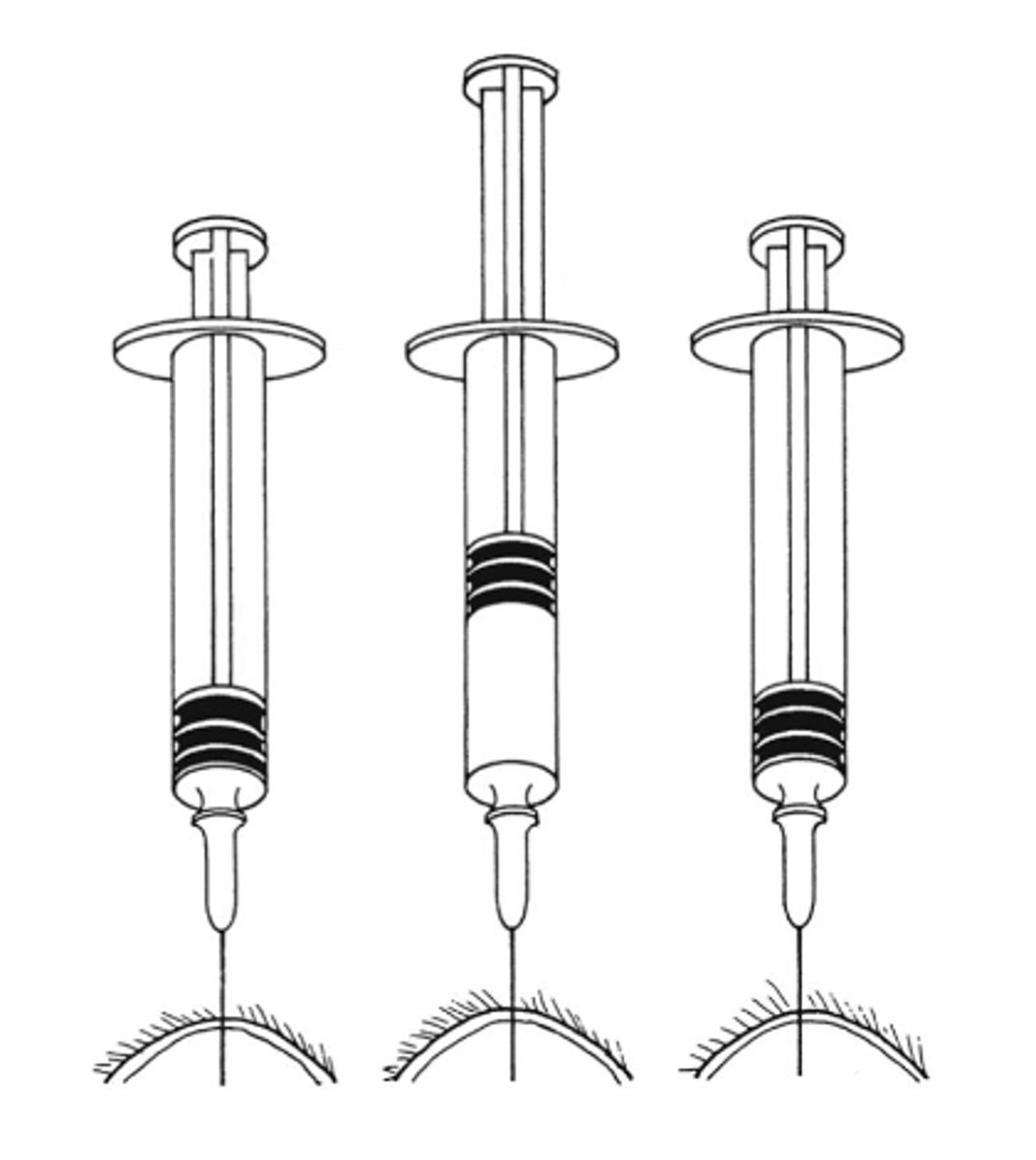
What fine needle aspirate technique is this?
Apiration procedure
-stabilize the mass with the hand
-syringe with needle attached inserted into the center of mass
-strong negative pressure- pull back plunger- and maintain pressure
-The needle is moved back and forth
-Remove the needle and fill the syringe with air
-put the needle back on and express the sample onto a slide
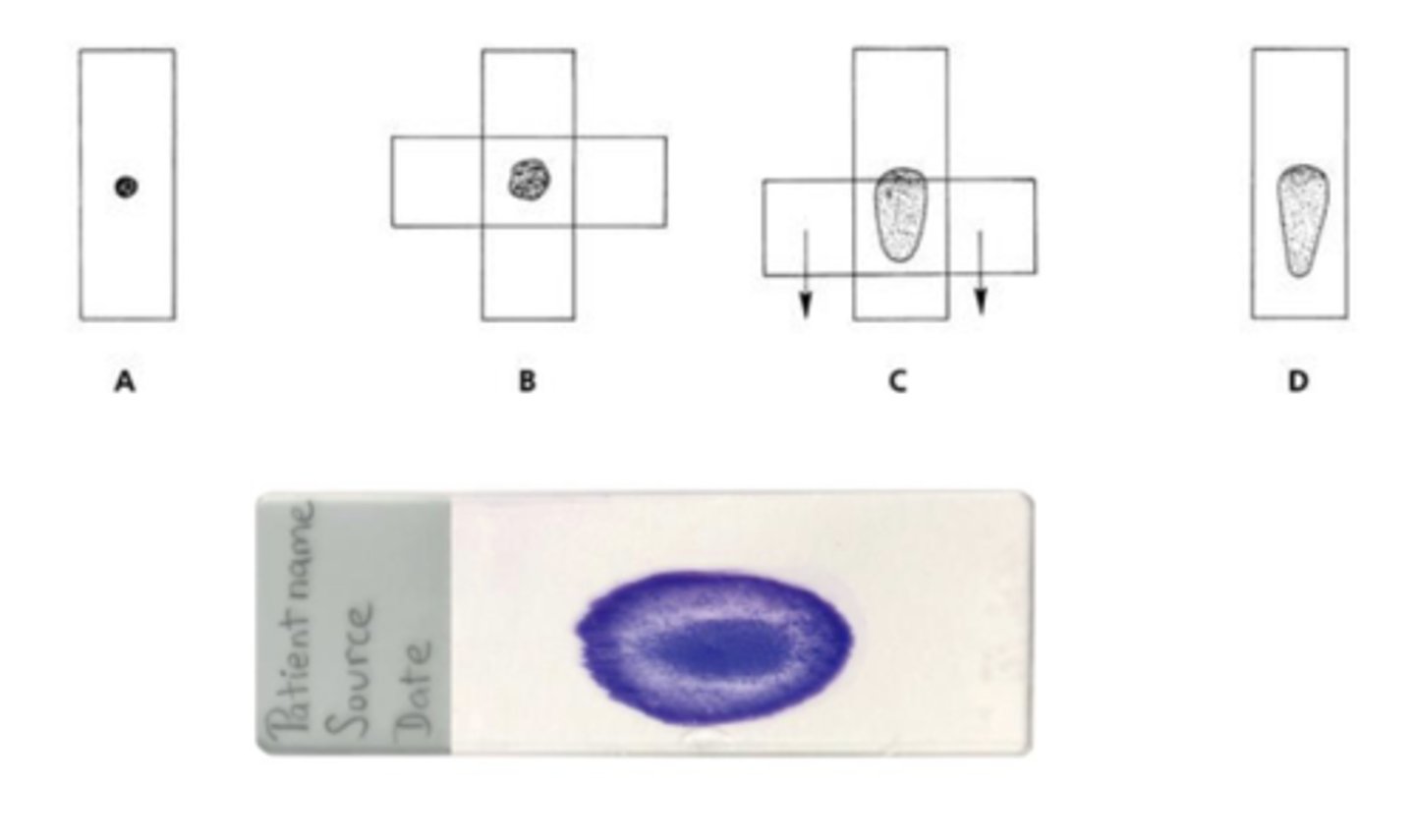
What method is this?
Slide over slide (squash prep)
-Material collected expressed on one side of the slide
• Second slide placed on top perpendicular to the slide
• The sample will spread out between the 2 slides
• Spreader slide is lightly drawn out the bottom of the side
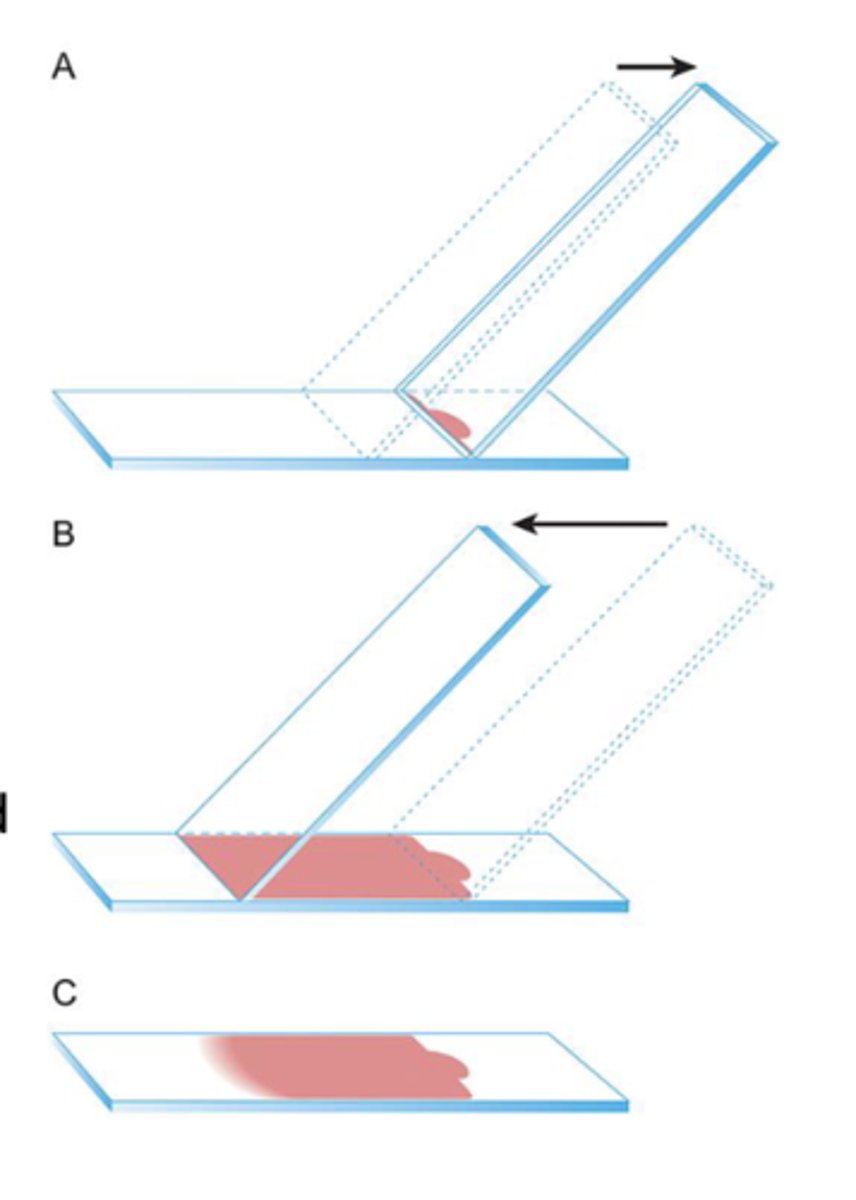
What slide prep method is this?
Blood Smear Technique
-good for fluid samples
-creates a feathered edge
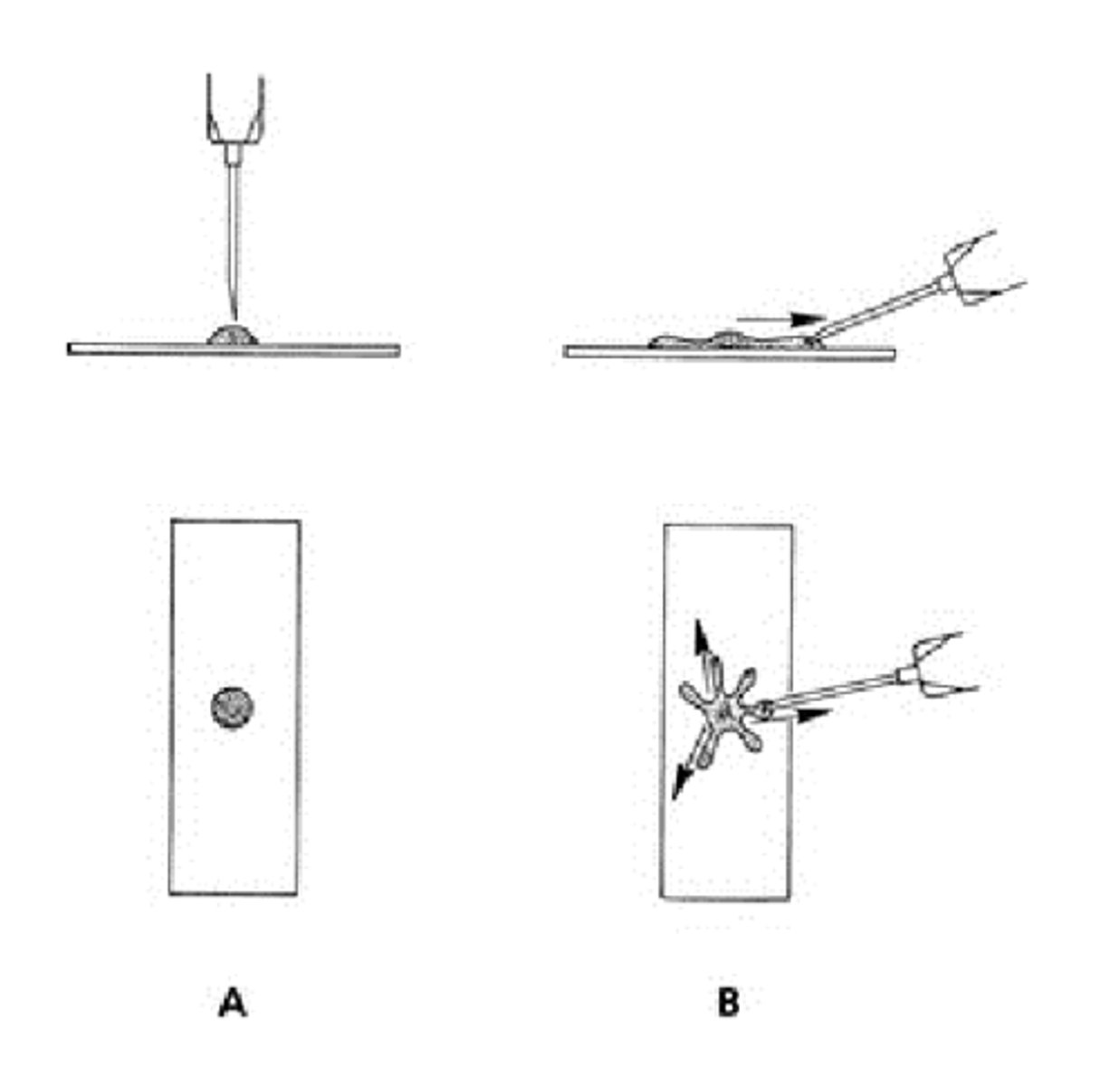
What slide prep method is this?
Starfish slide prep
-not preferred
-will damage cells
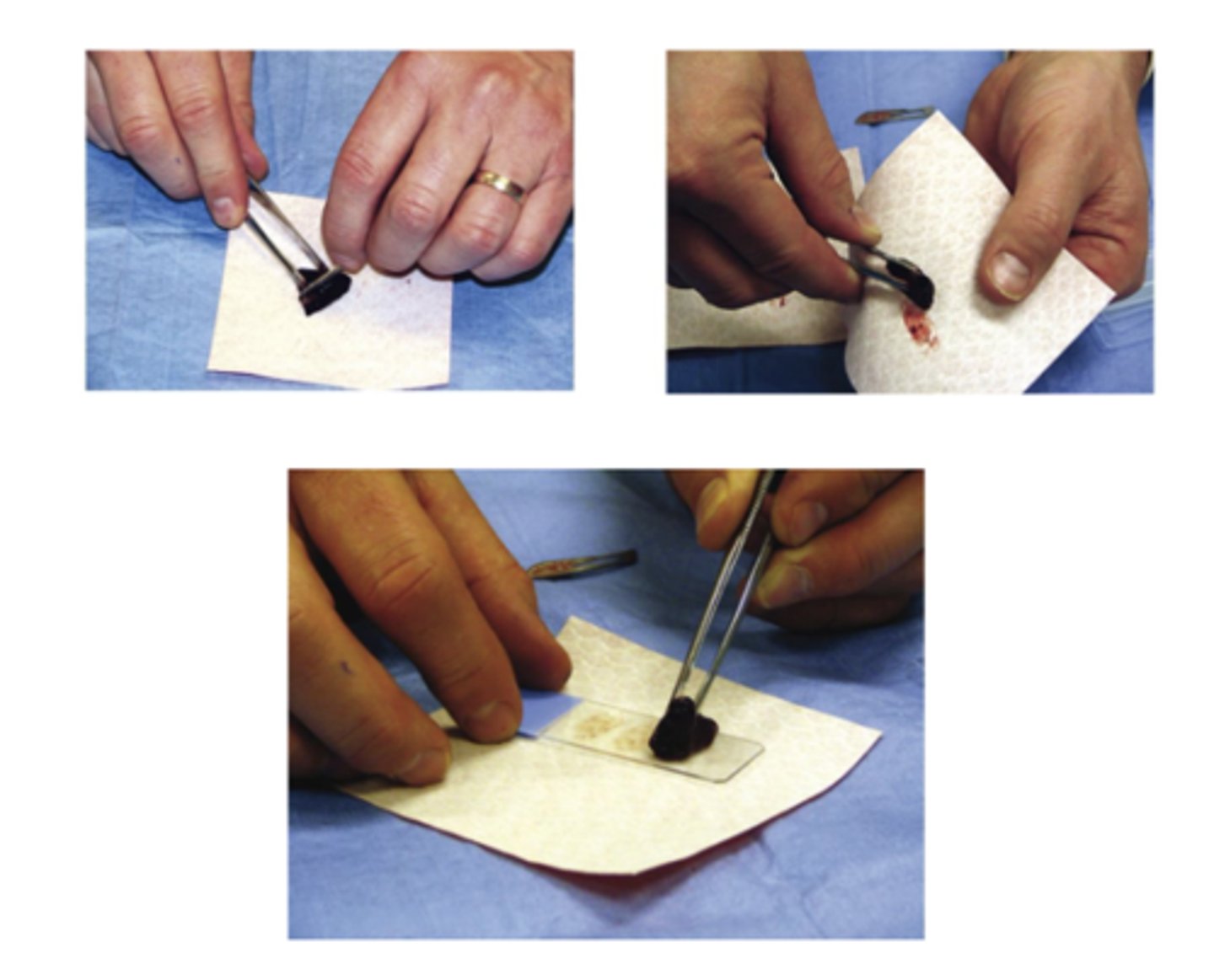
What slide prep method is this?
Impression smear
-used for ulcerative or exudative lesions
-inflammation
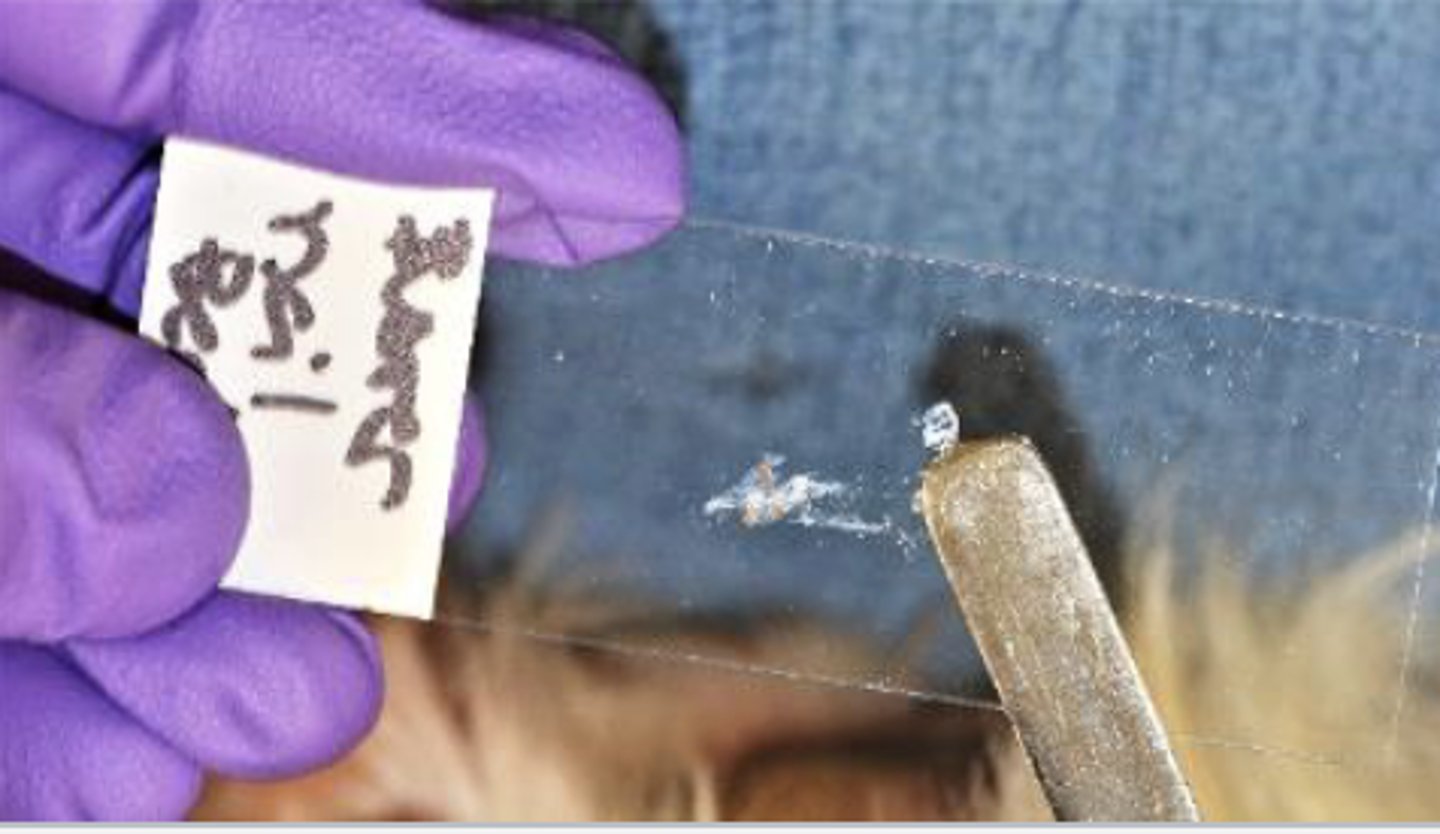

What slide prep method is this?
Scraping
-produces more cellular slide vs impression
-good for cutaneous lesions that are flat and dry
-more surface contamination
-not as valuable for the diagnosis of neoplasia
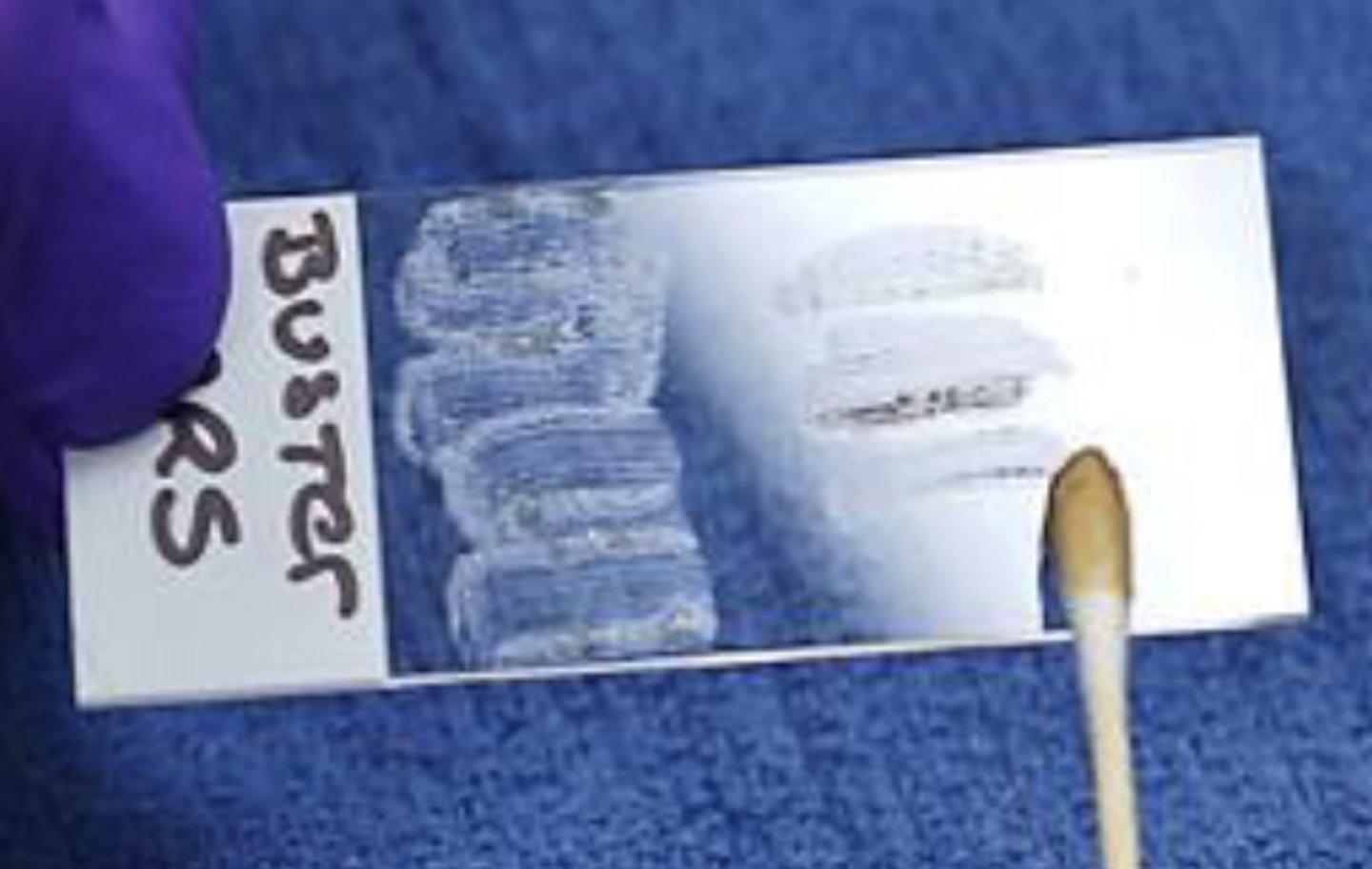

What slide prep method is this?
Swab
-used for the vagina, ear canal, and fistulous tracts
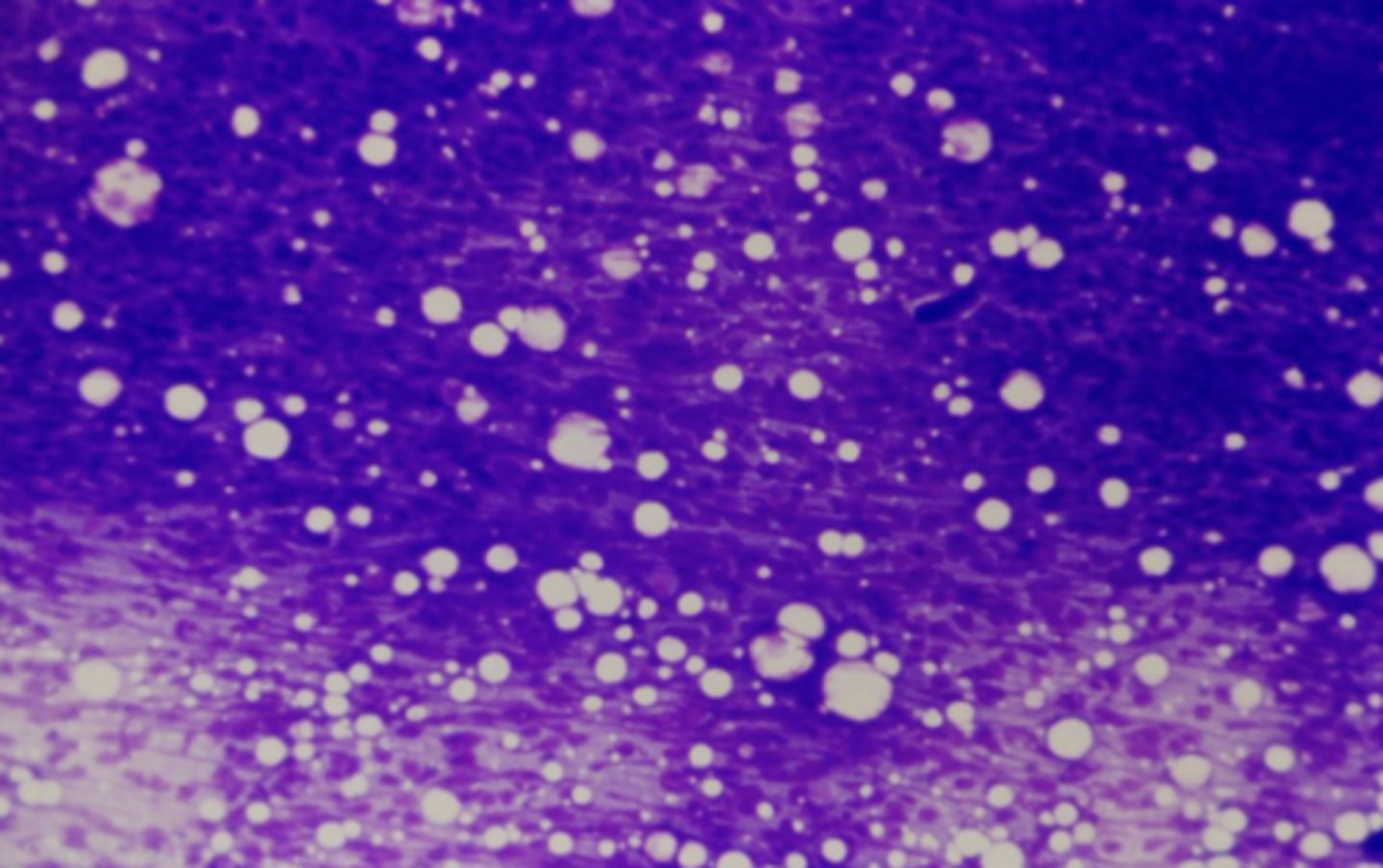
What's wrong with this sample?
The sample is too thick
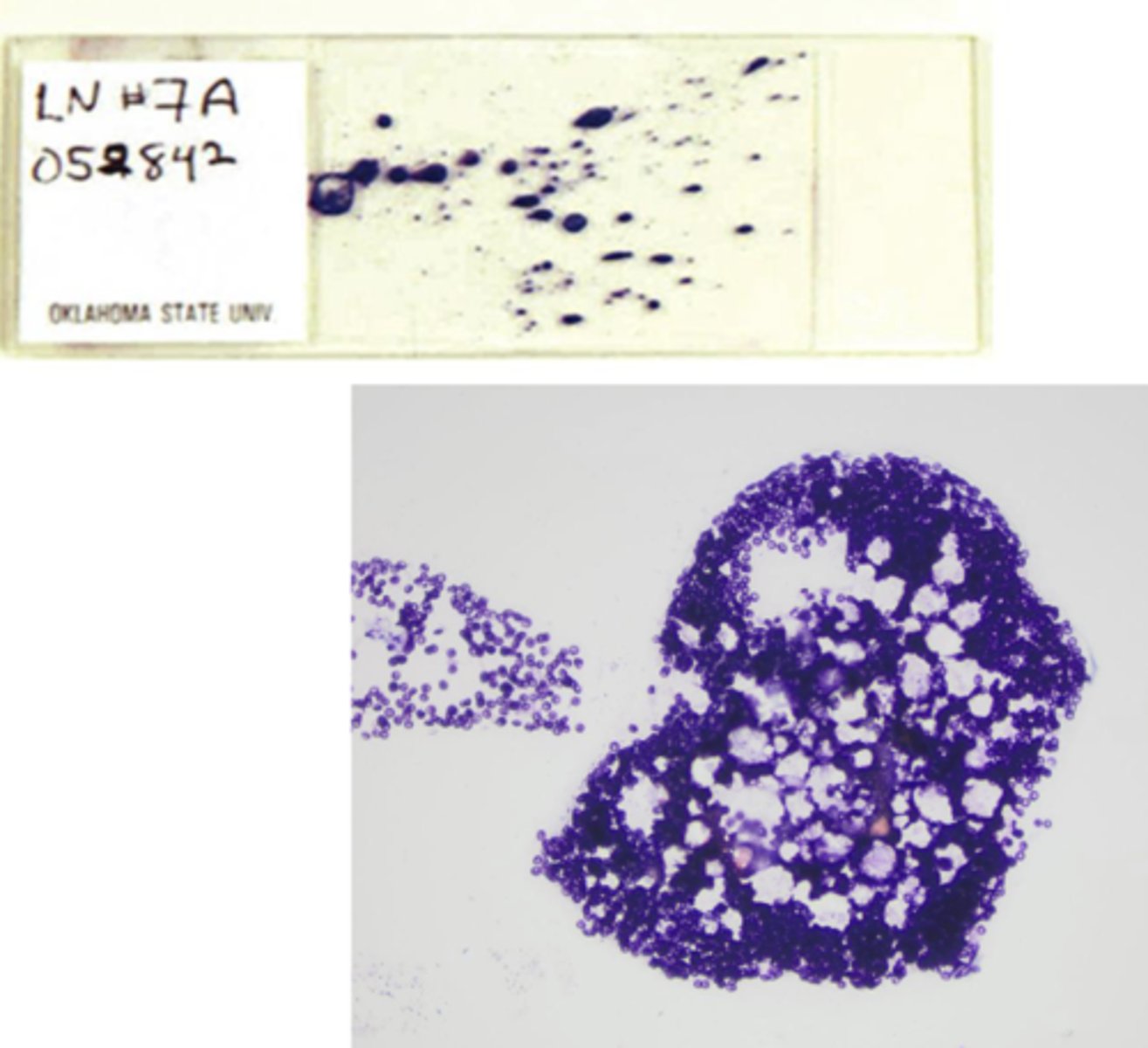
What's wrong with this sample?
Splatter
-The syringe was too far away from slide when expelling the contents
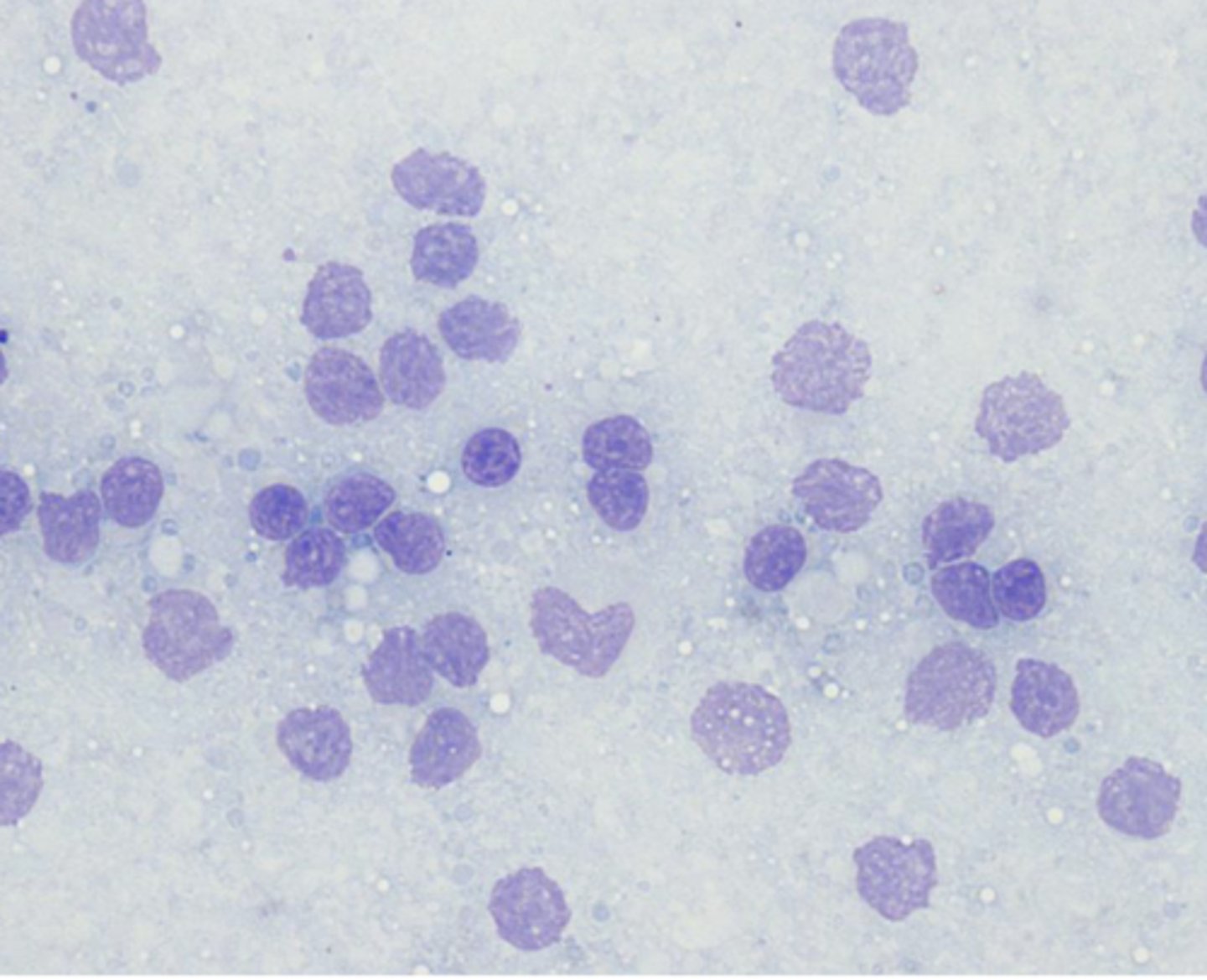
What's wrong with this sample?
Ruptured cells
Causes:
-negative pressure when aspirating
-too much pressure when spreading slide
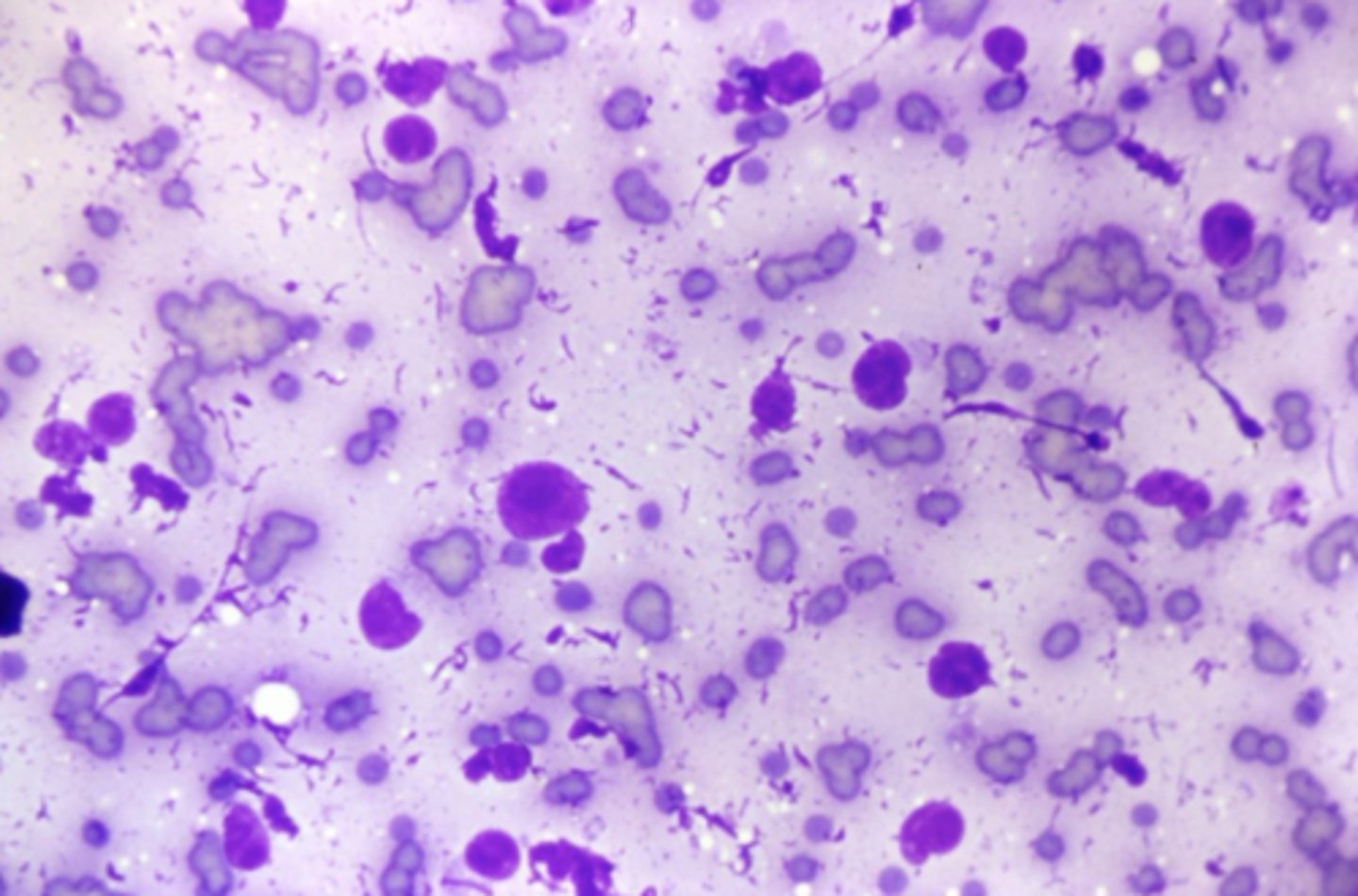
What's wrong with this sample?
Nuclear streaming/stripping
-likely due to excessive pressure during squash prep
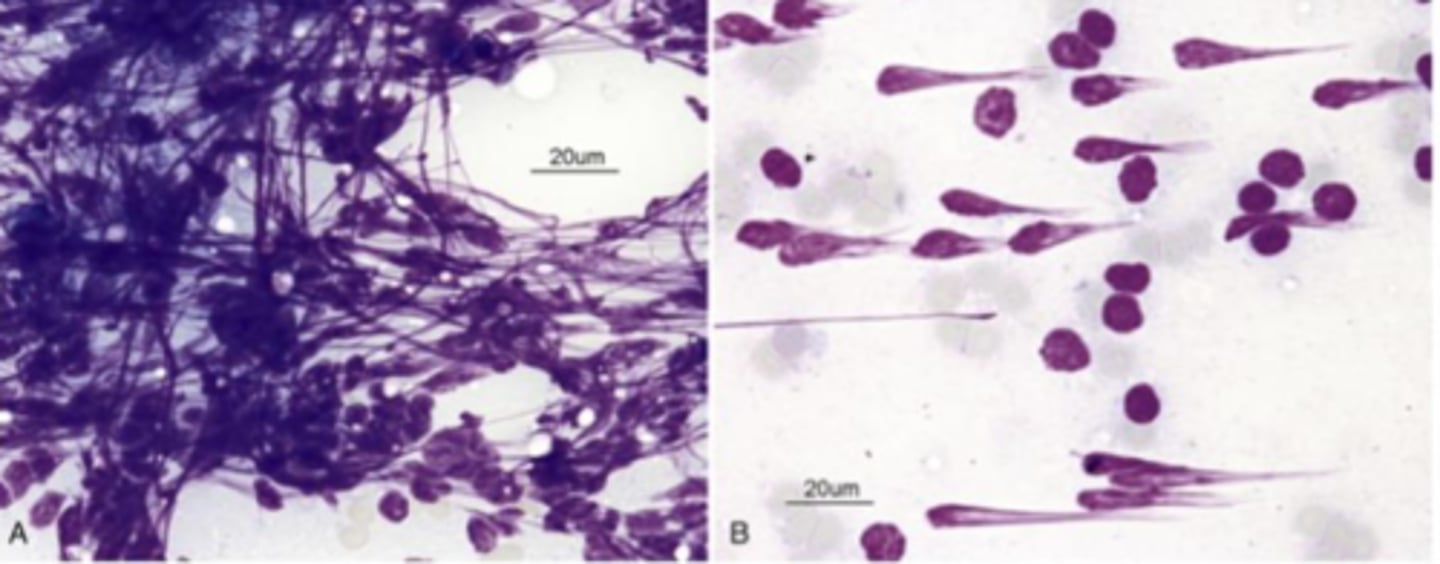
What's wrong with this sample?
Comet tails (more nuclear stripping)
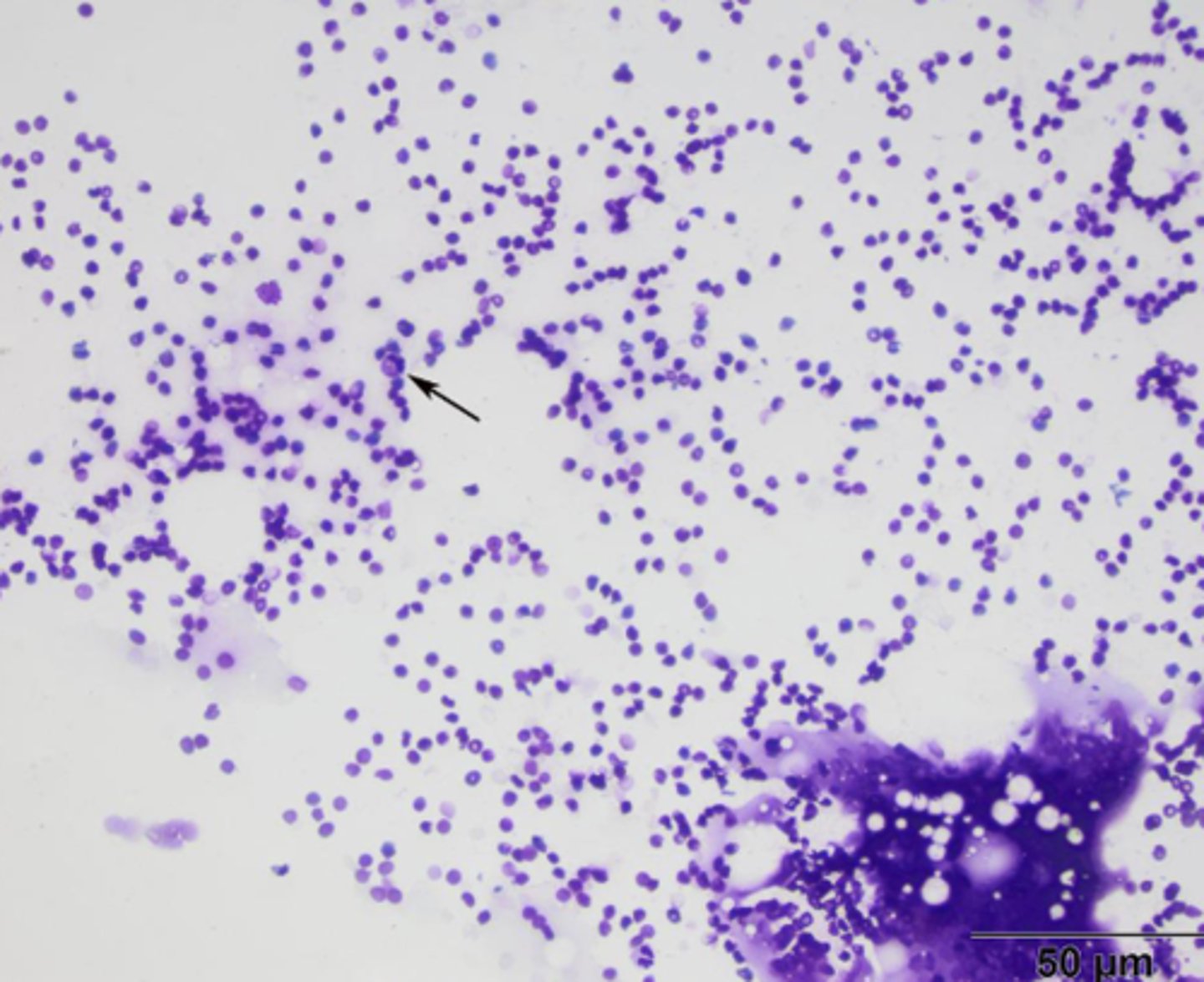
What's wrong with this sample?
Overstaining
-can't see the details of individual cells
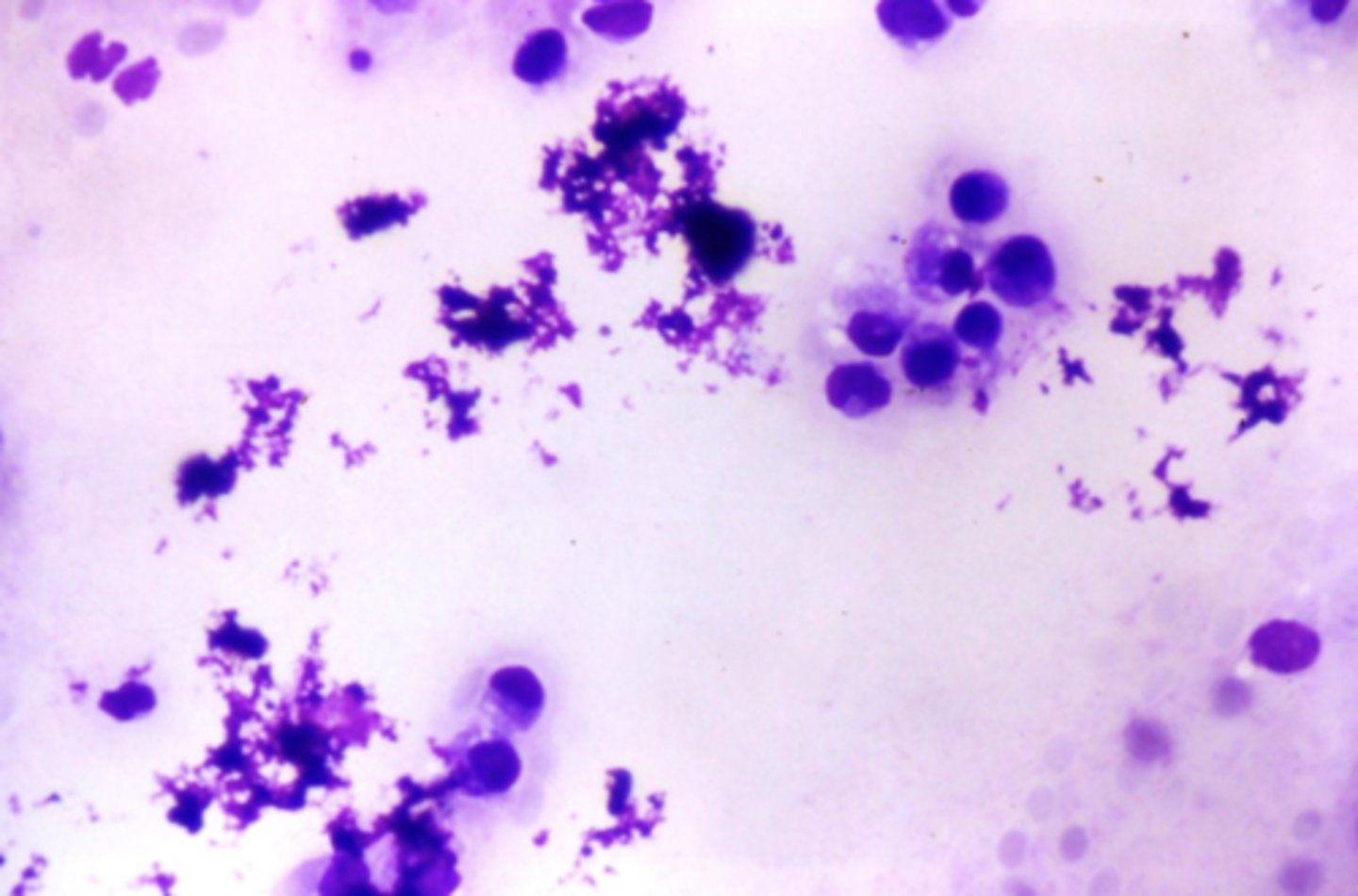
What's wrong with this sample?
Stain precipitant
-The stain needed to be replaced
-stain needs to dry before staining
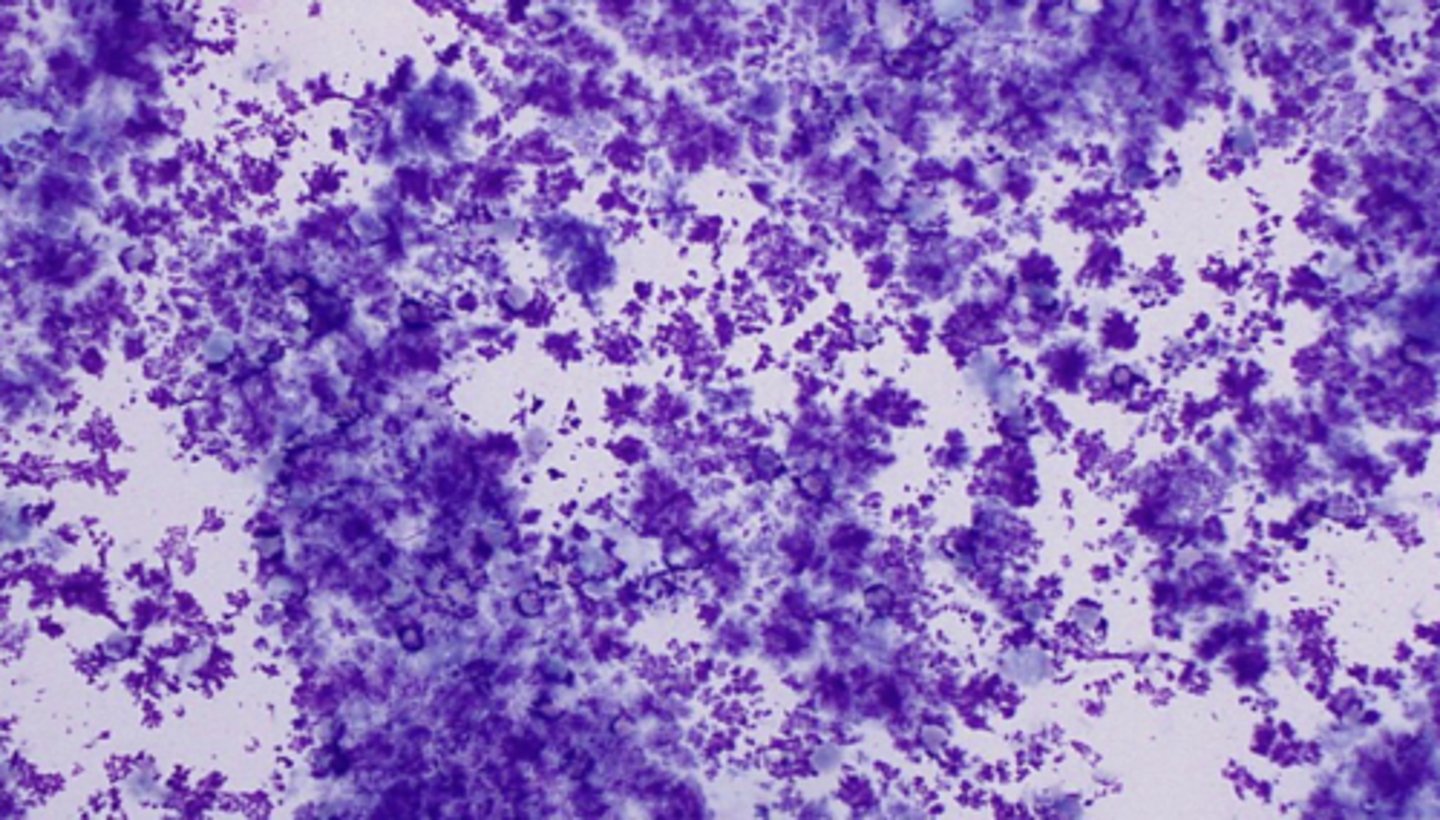
What has caused the appearance of this slide?
Lubricant artifact
-from ultrasound gel
-can also be seen with traumatic urethral catheterization
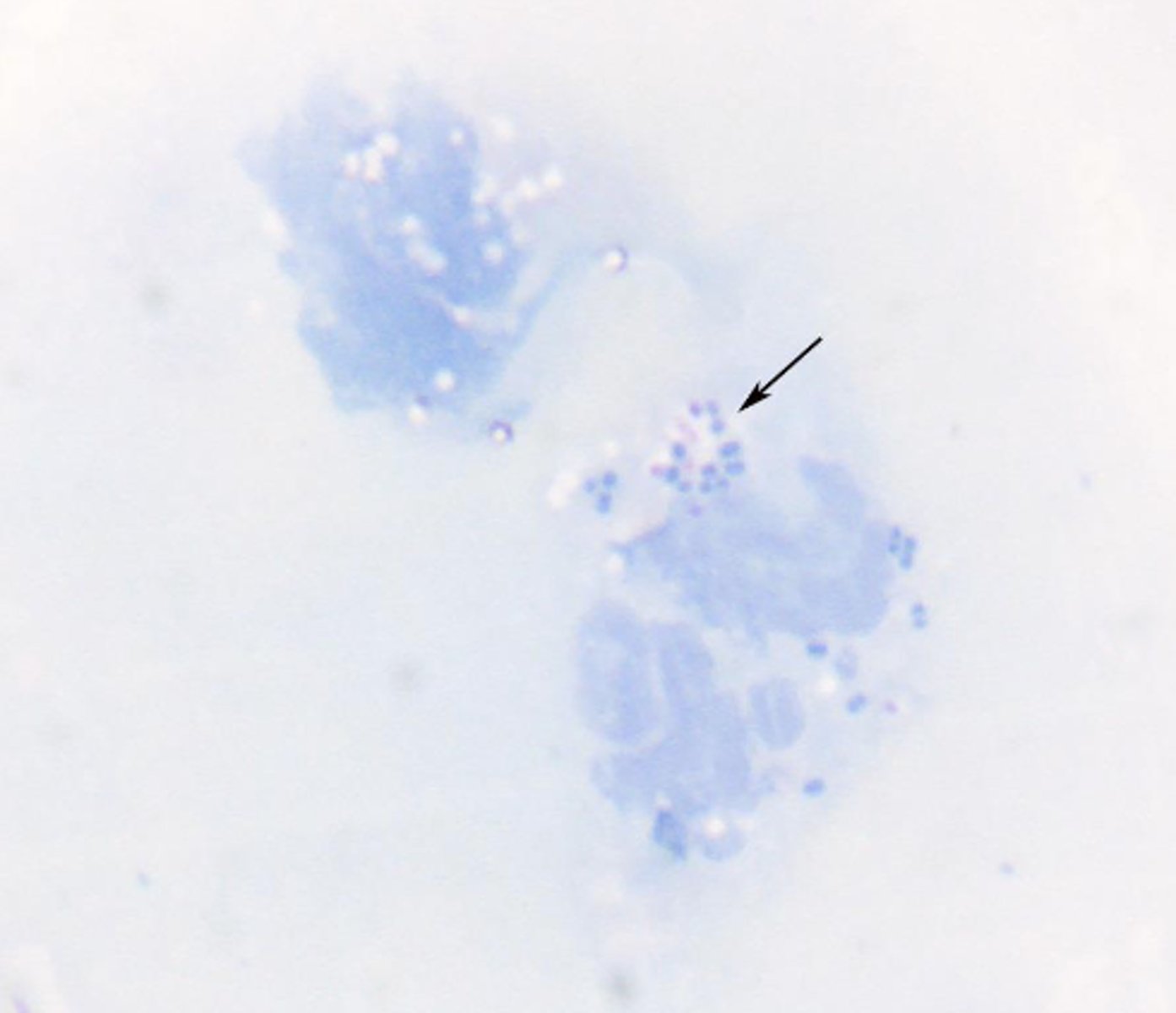
What has caused the appearance of this slide?
Formalin
-Formalin fumes prevent cells from being stained appropriately
-"fixes them" and prevents staining
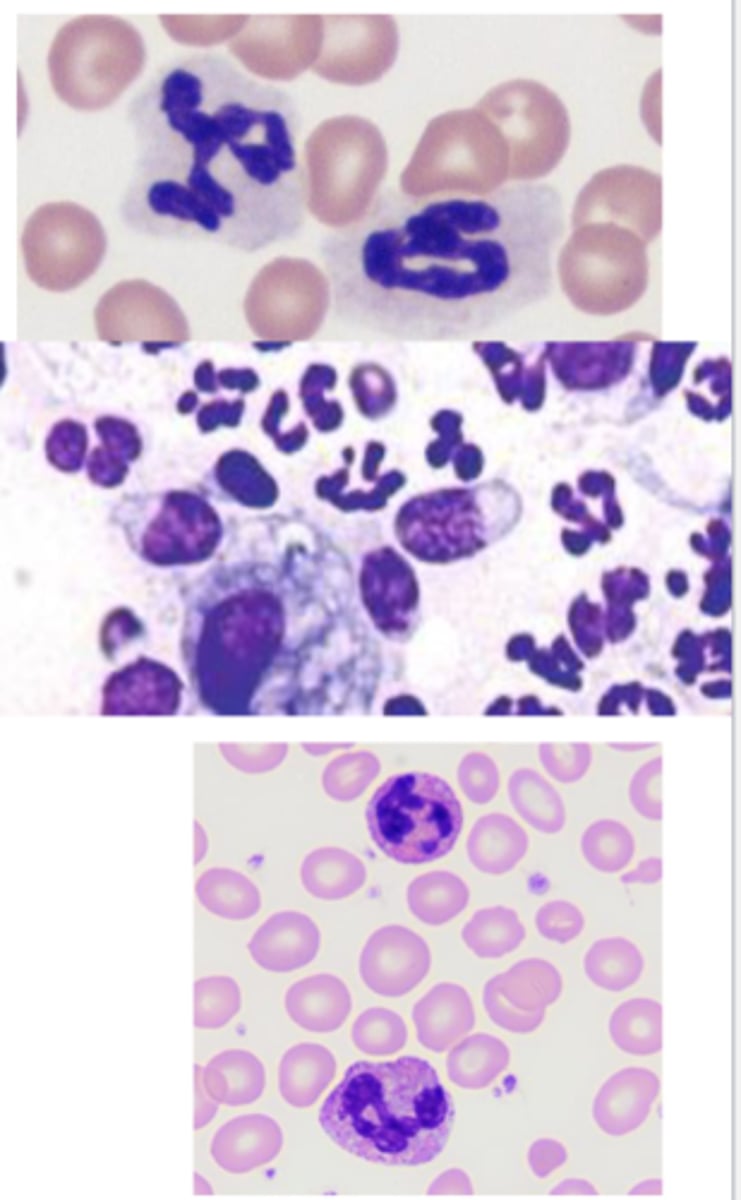
What type of inflammatory cells are these?
Neutrophils
-dark purple segmented nuclei
-reptiles and birds have heterophils
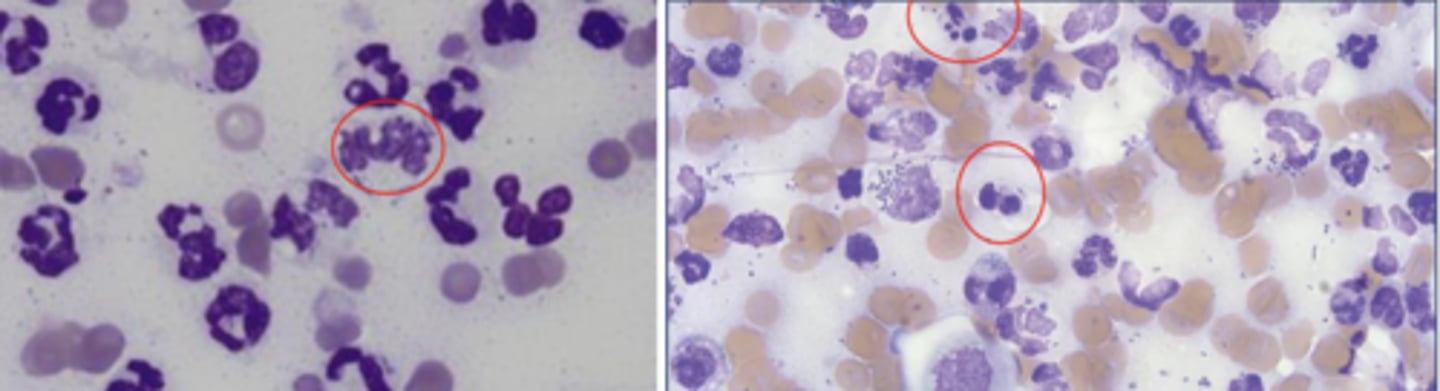
What kind of inflammation is this?
Neutrophilic inflammation
-suppurative, purulent
>85% neutrophils in the lesion
non-degenerative: normal-looking neutrophils
degenerative: oncotic necrosis, pyknosis, karyorrhexis
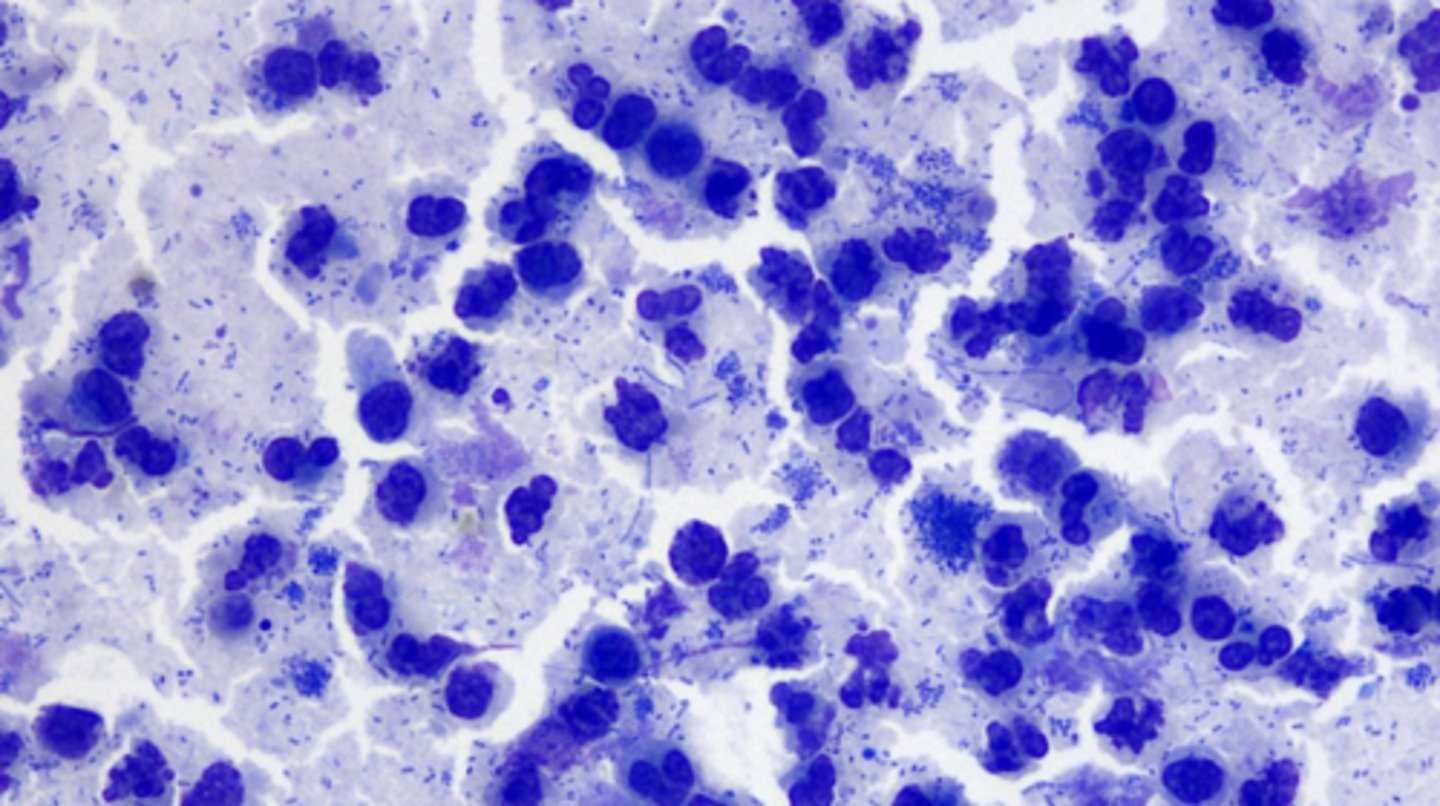
What kind of inflammation is this?
Neutrophilic inflammation
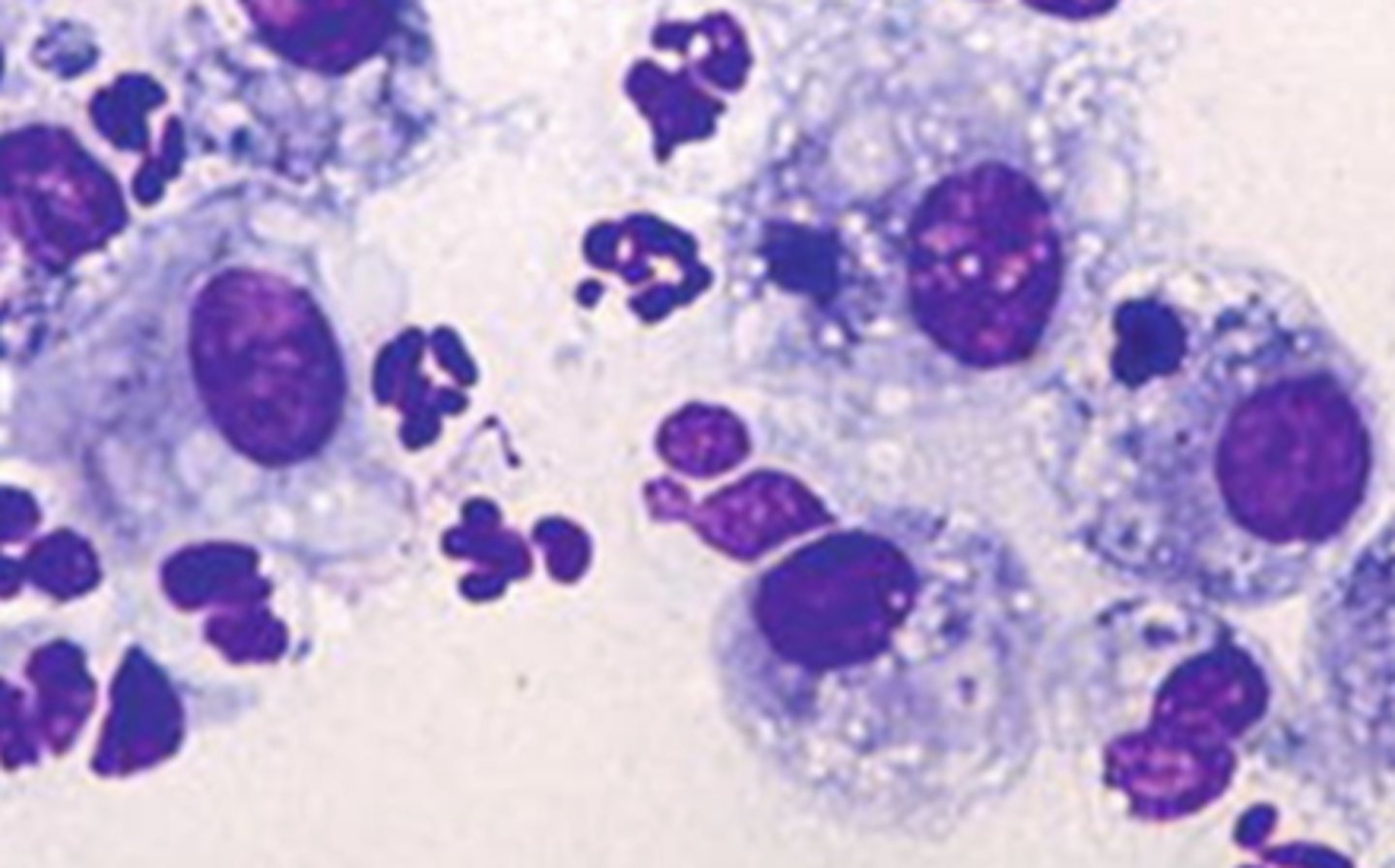
What type of inflammatory cells are these?
Macrophages
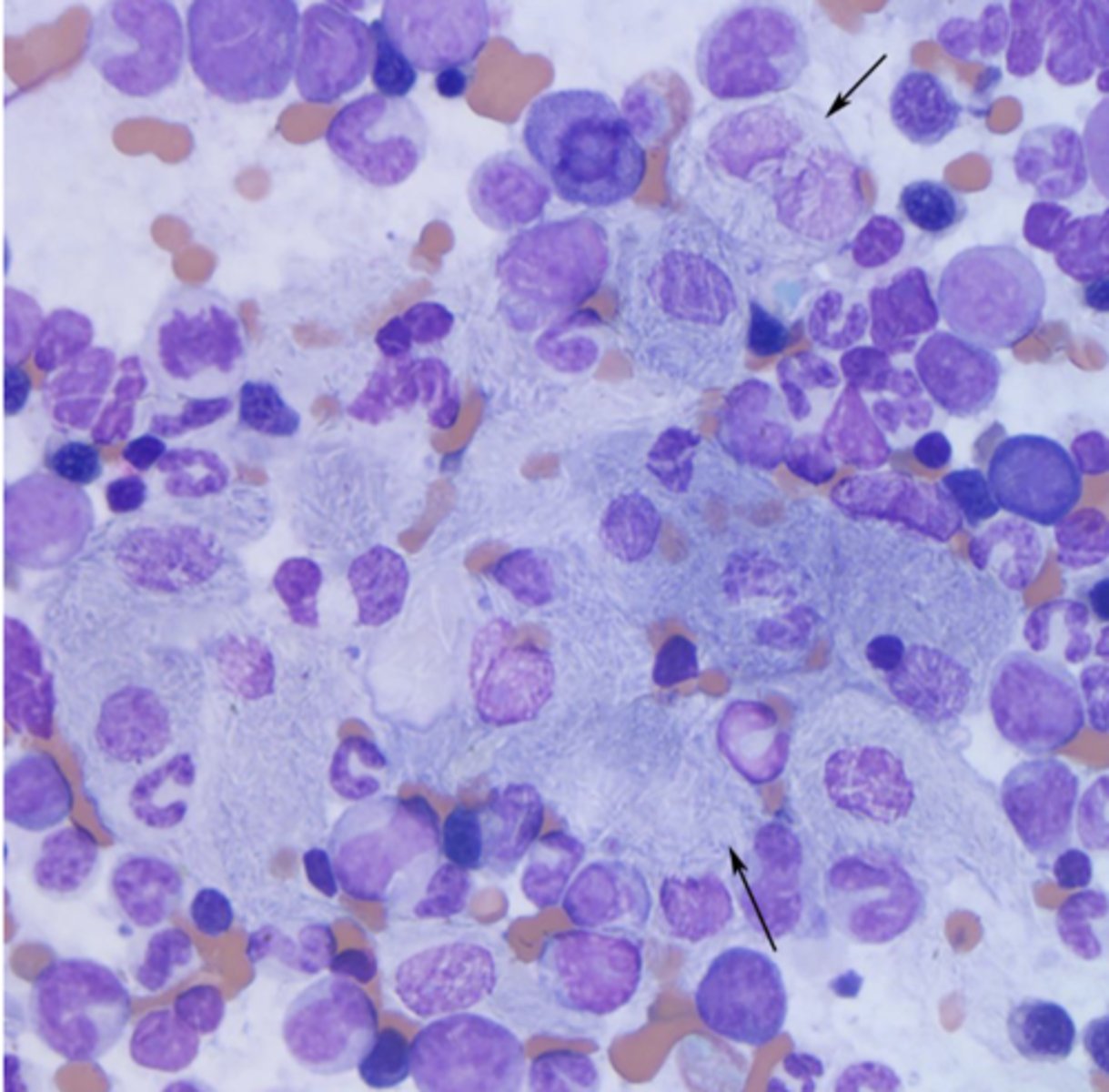
What type of inflammation is this?
Macrophage inflammation
-mostly macrophages
-granulomatous
-pyogranulomatous: neutrophils + macrophages
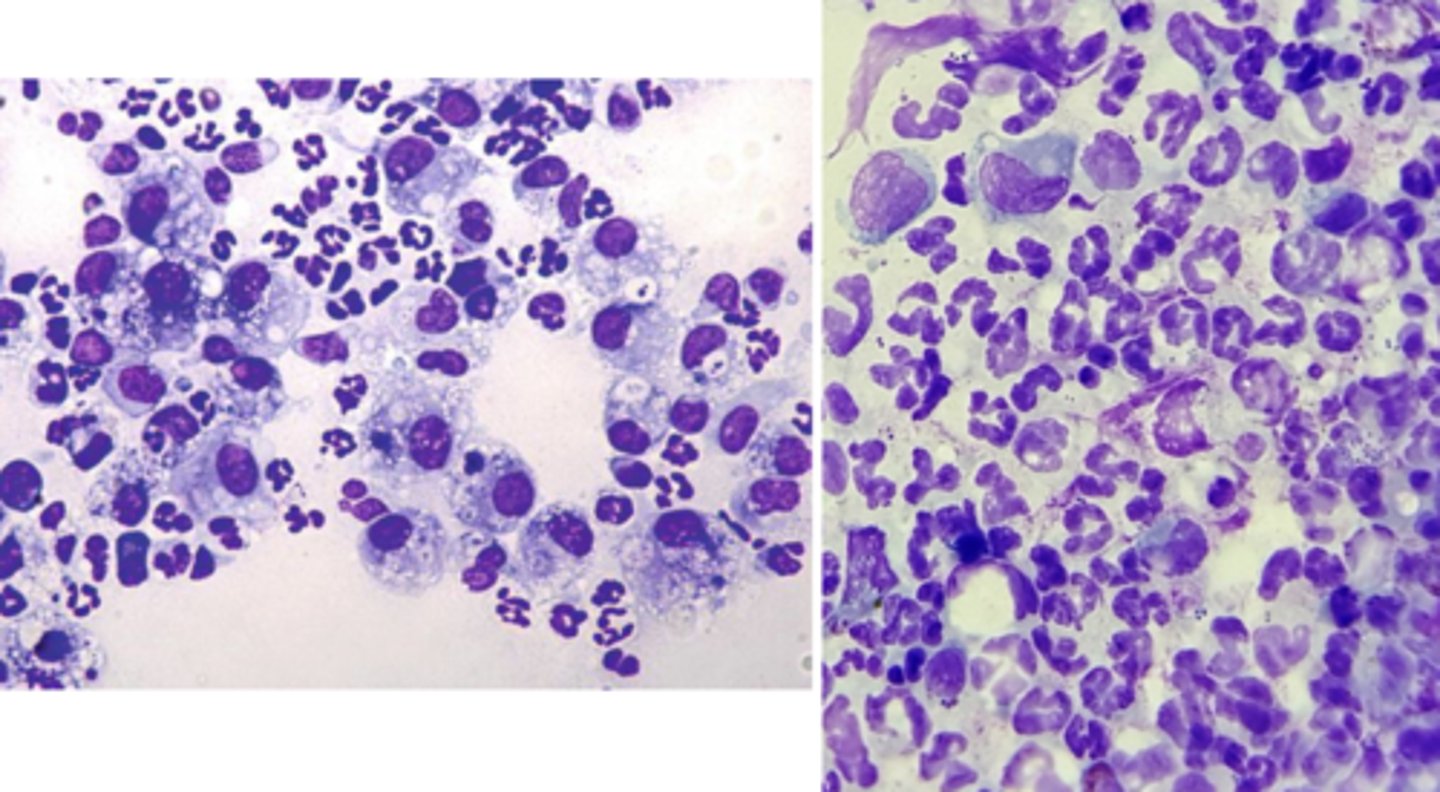
What type of inflammation is this?
Pyogranulomatous inflammation
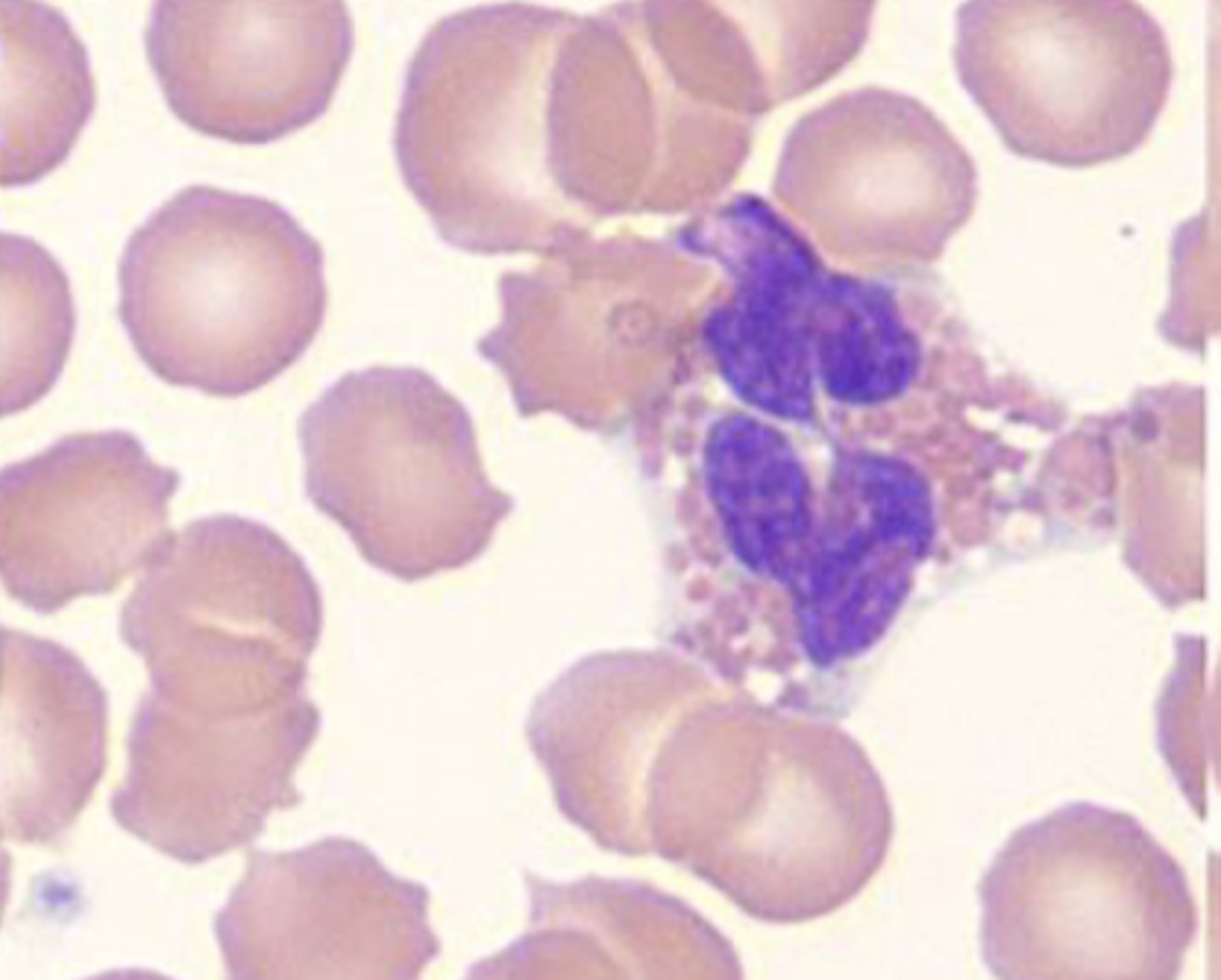
What type of inflammatory cell is this?
Eosinophils
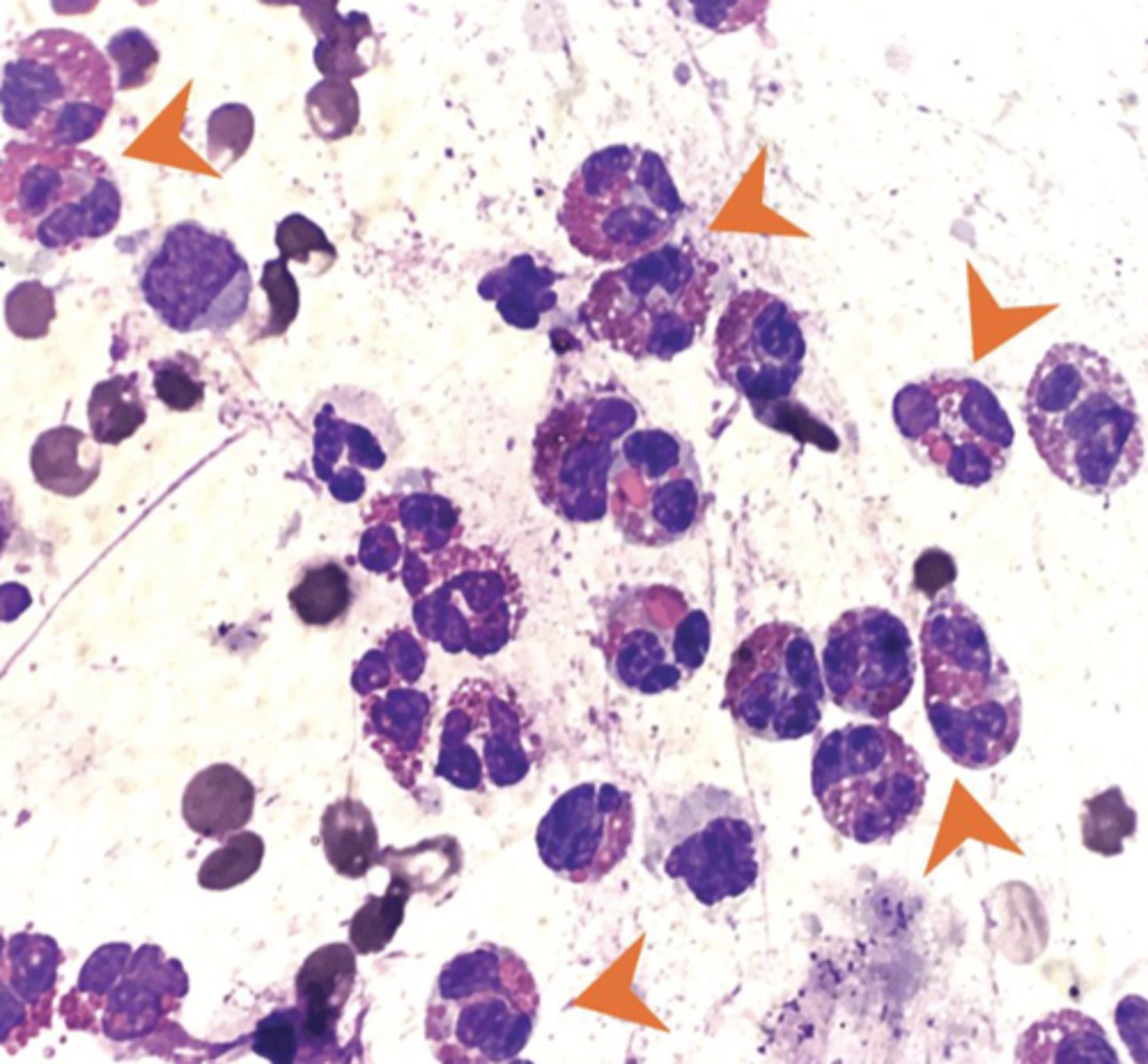
What type of inflammation is this?
Eosinophilic inflammation
>10% eosinophils +/- mast cells
-occurs secondary to acute or chronic inflammation
-hypersensitivity/allergy
-parasitic migrations
-fungal infections
-mast cell tumor
"worms, wheezes, weird diseases"
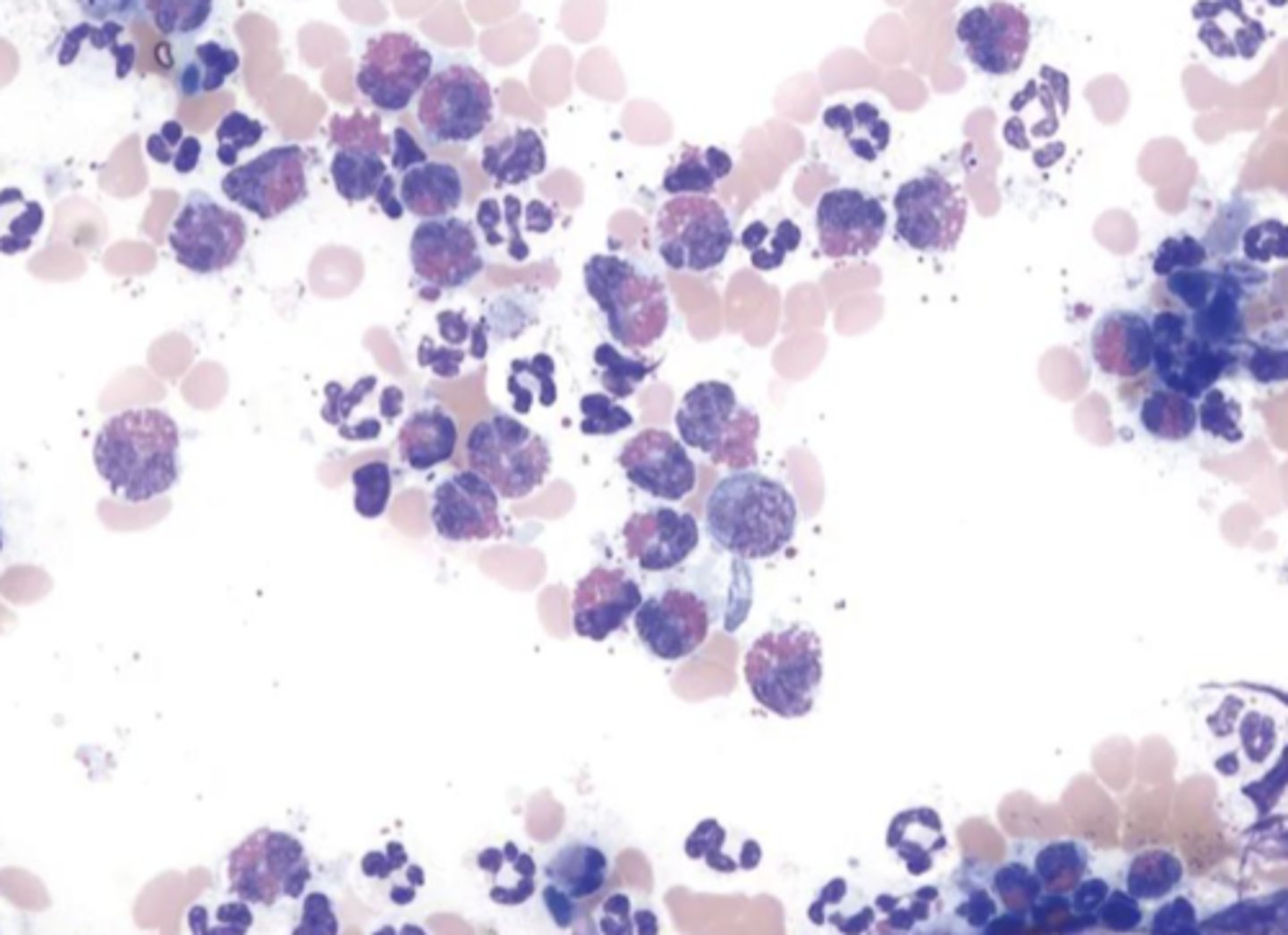
What type of inflammation is this?
Eosinophilic inflammation
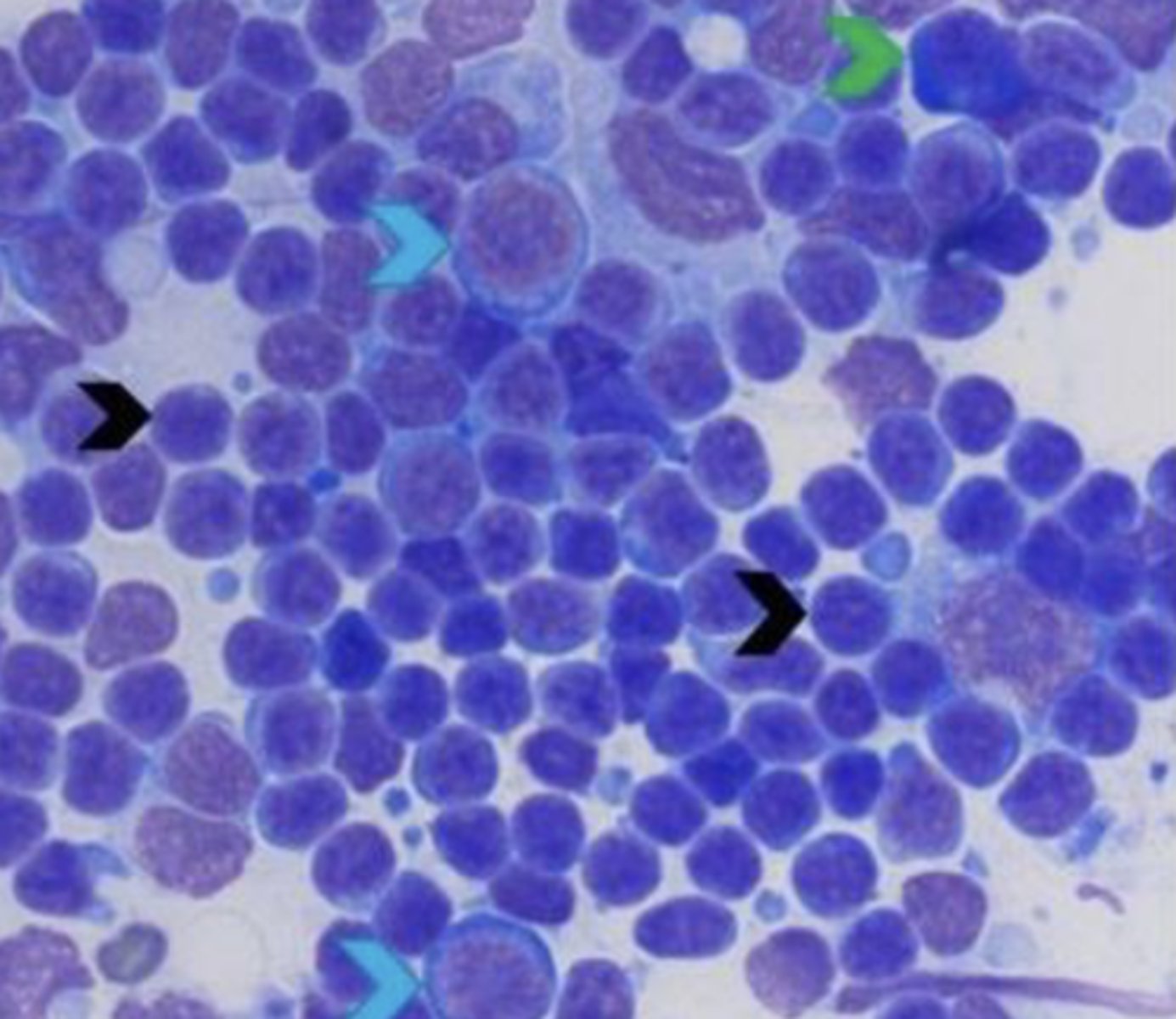
What type of inflammatory cell is this?
Lymphocytes
-round, dark nuclei, scant cytoplasm
Medium: slightly larger, pink-purple nuclei
Large: larger than neutrophils, pinkish nuclei, abundant cytoplasm
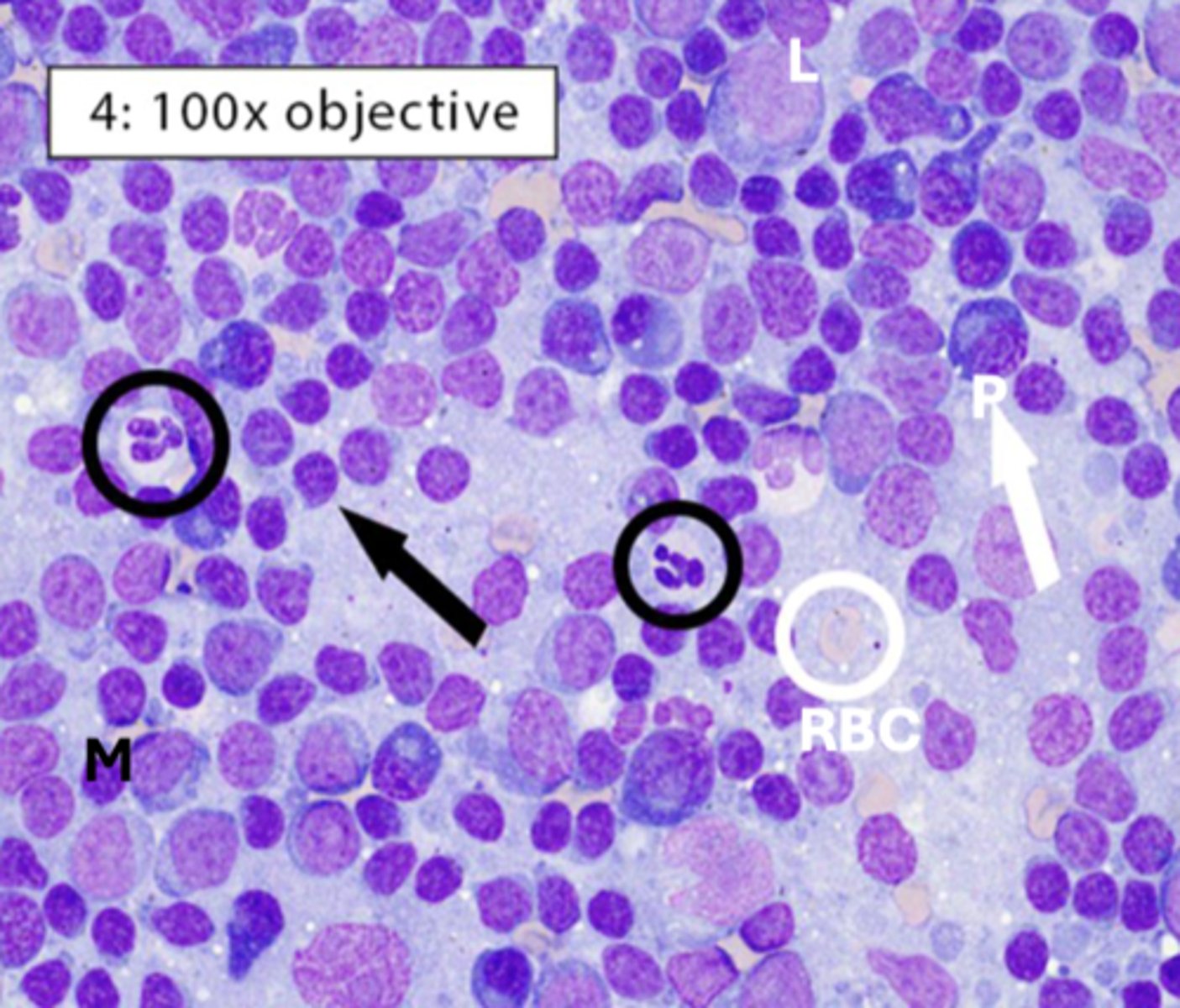
What type of inflammation is this?
Lymphocytic inflammation
-mostly small lymphocytes
-some plasma cells
-indicates chronic inflammation or immune reactivity
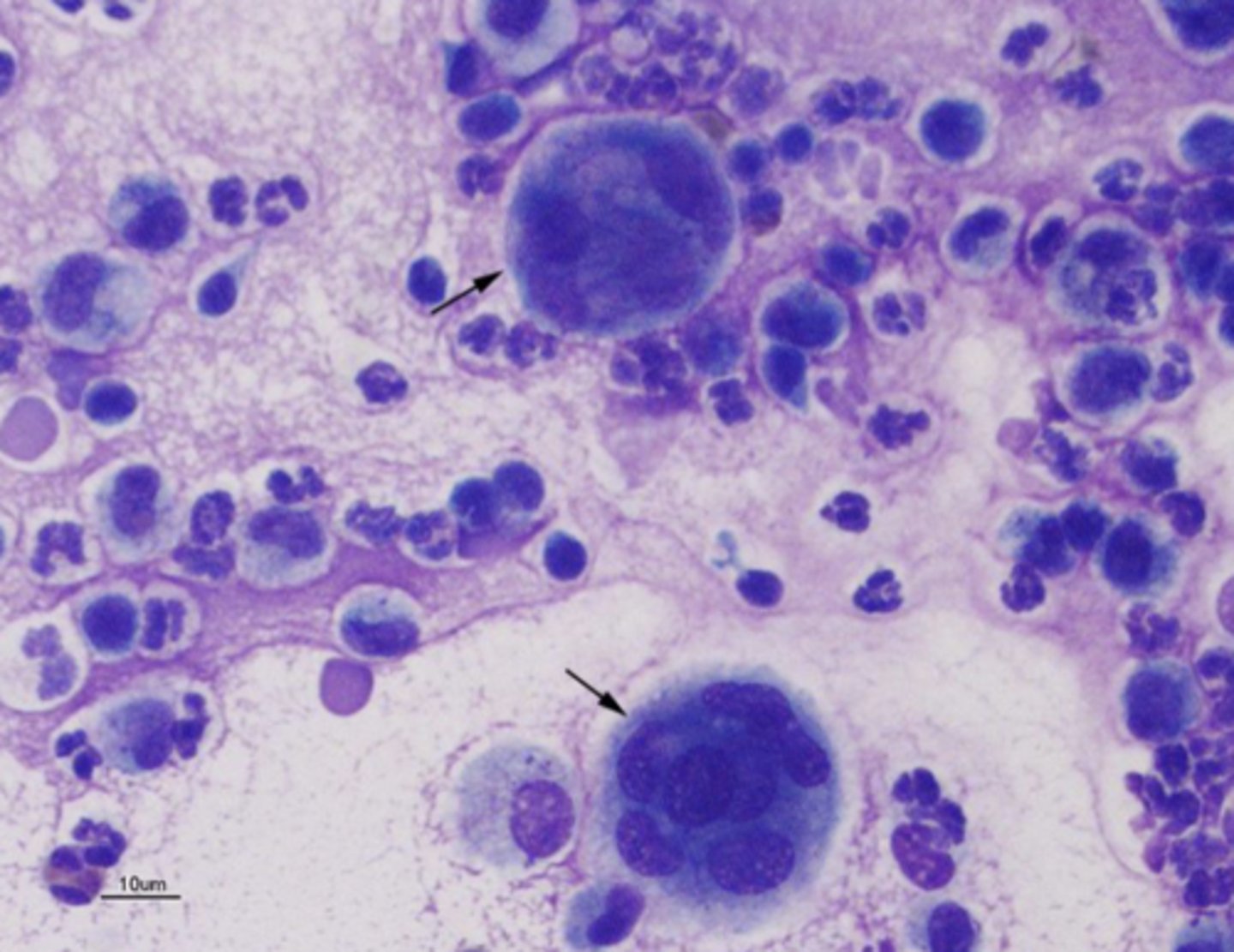
What type of infiltrates is this?
Pyogranulomatous w/lymphoplasmacytic infiltrate
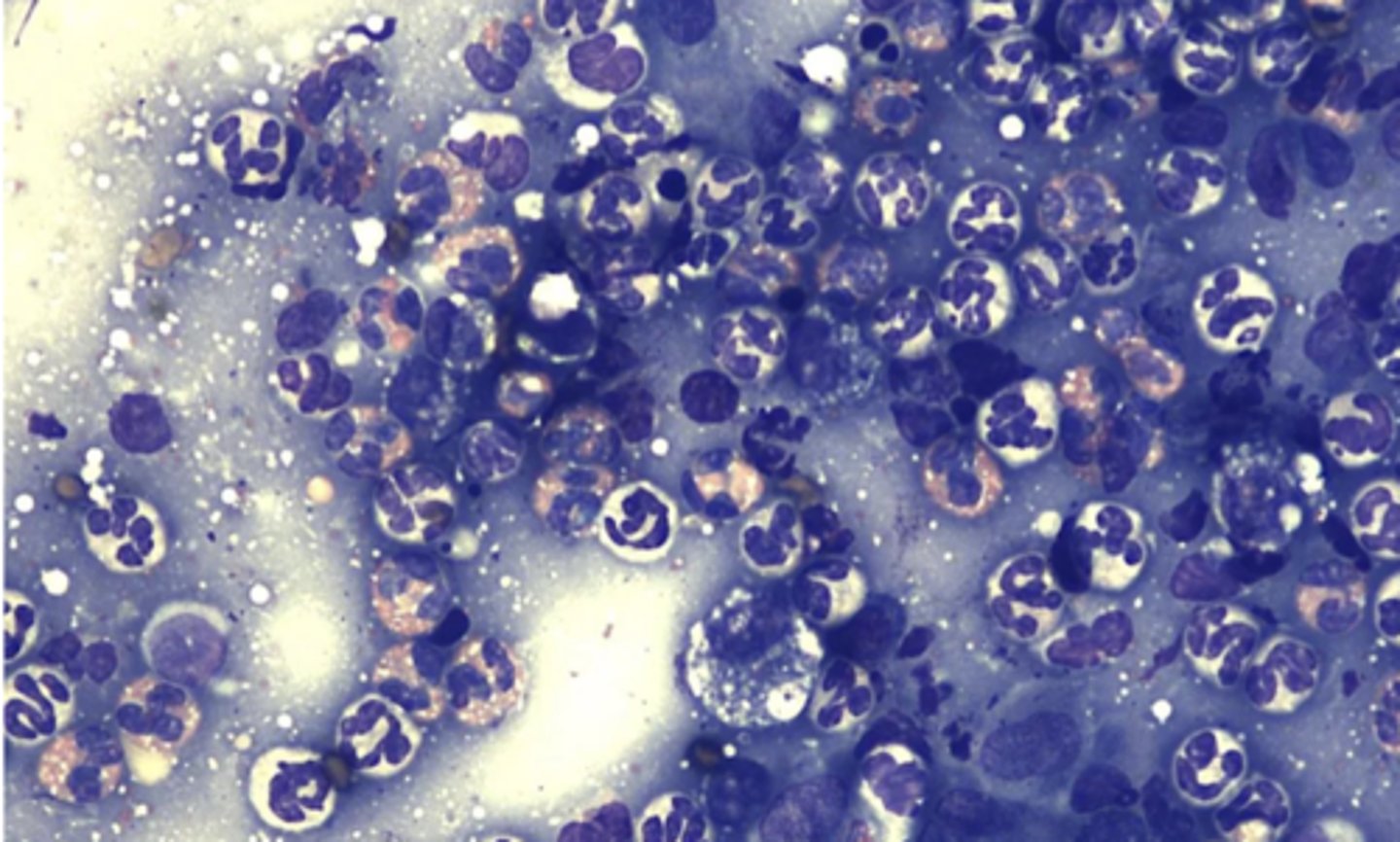
What type of inflammation is this?
Mixed inflammation
-state what cells are present
-etiology depends on what cells are present
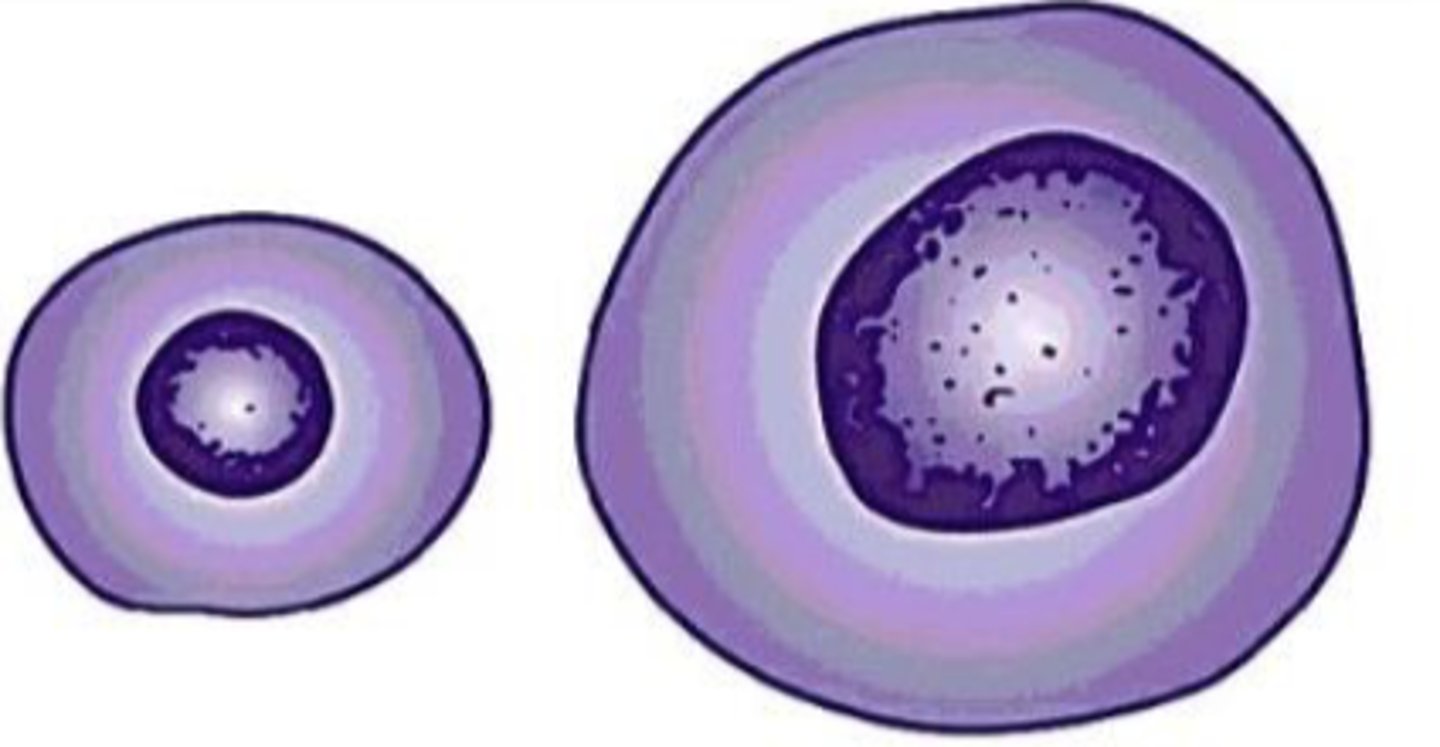
What term is used for cells > 2 times larger than normal?
Anisocytosis and macrocytosis
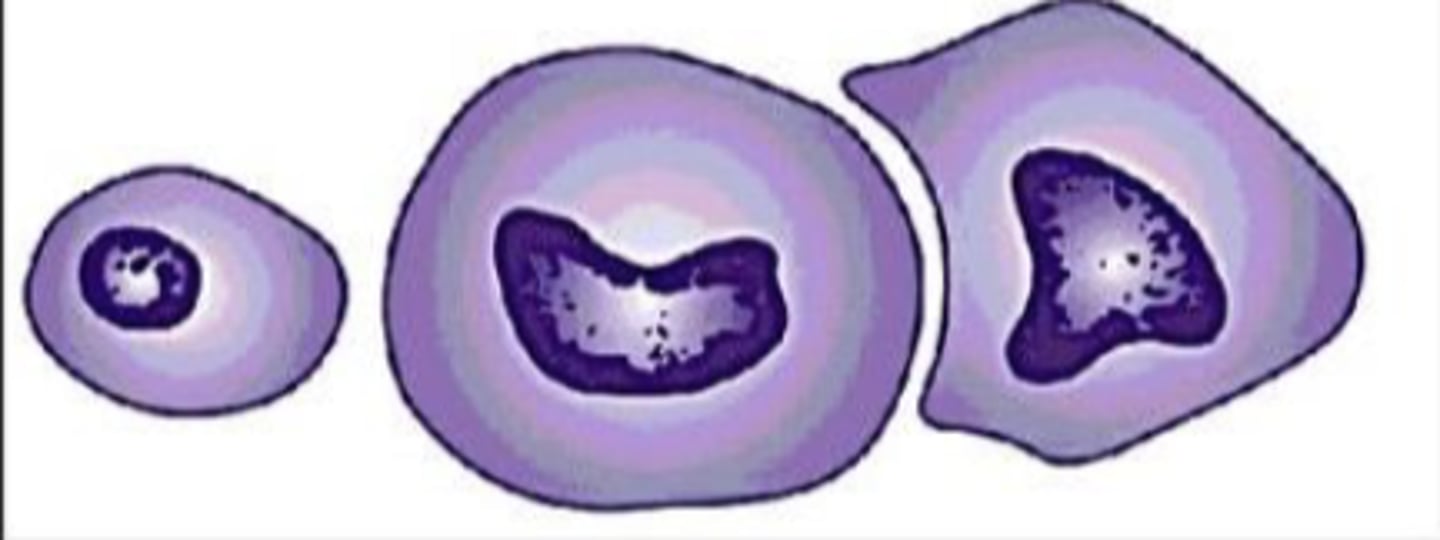
What term is used for variable size and shape in a cell of the same type?
Pleomorphism
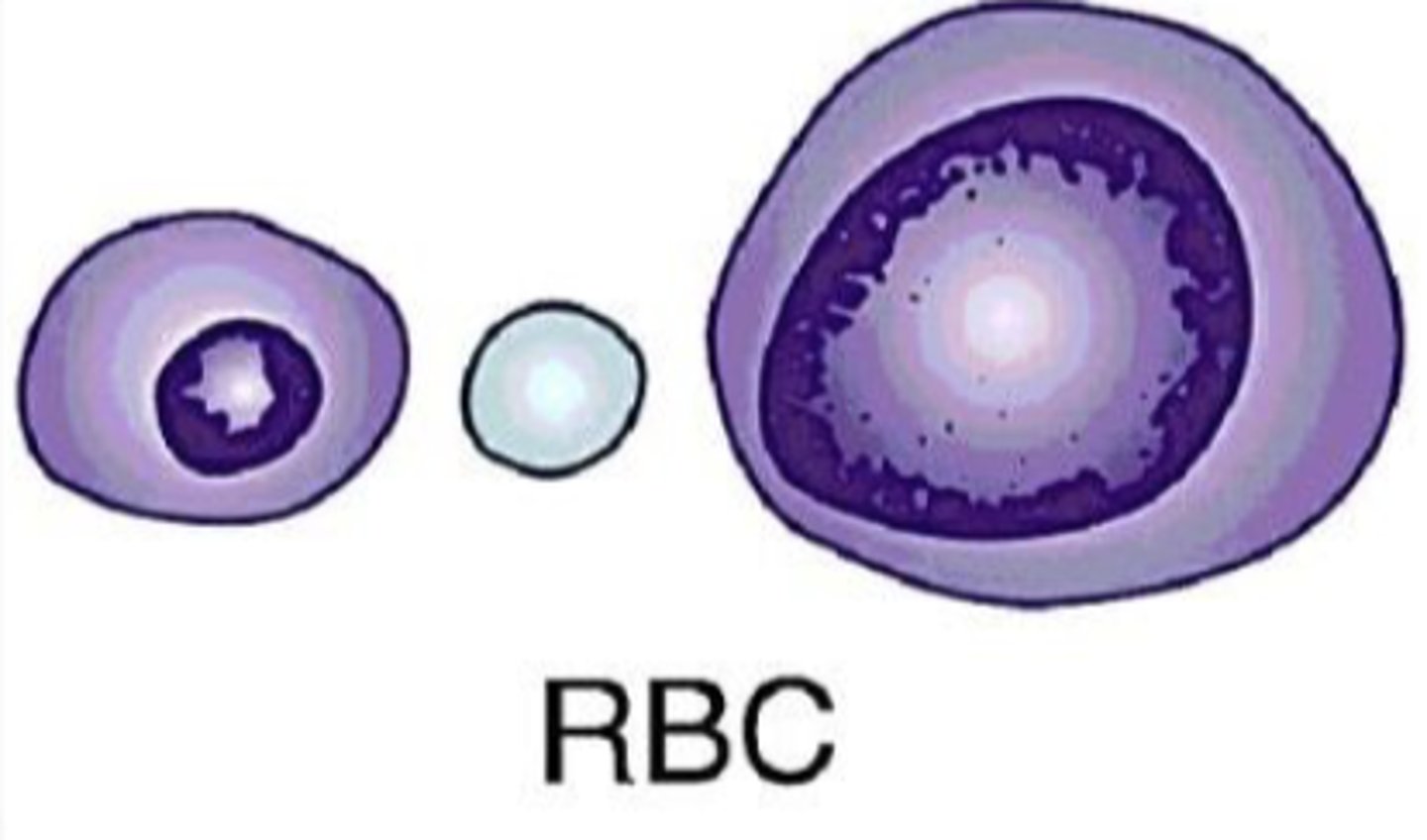
What is the term for increased nuclear size?
Macrokaryosis
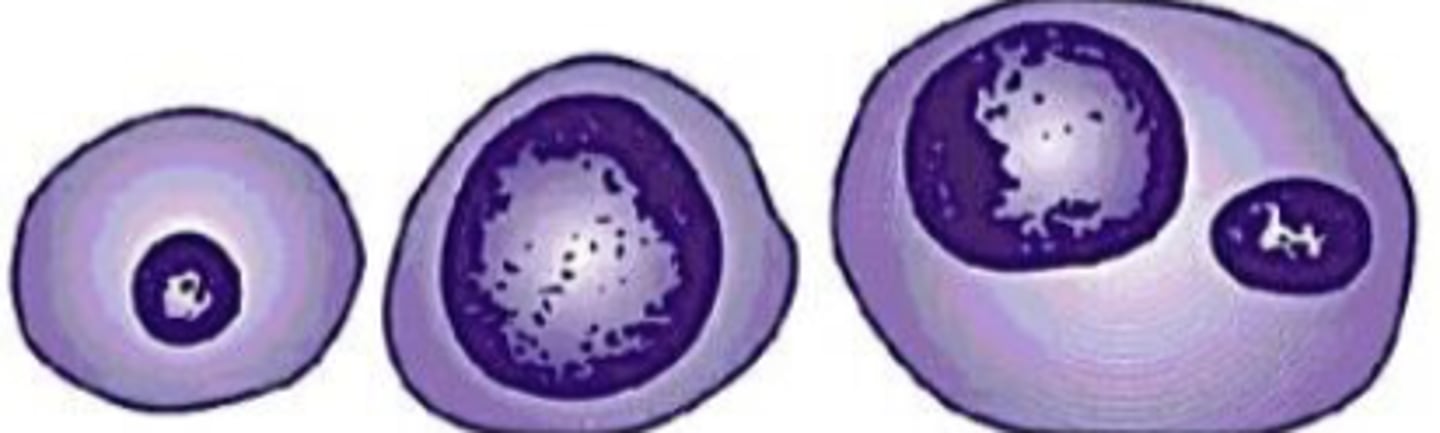
What term is used for variation in nuclear size?
Anisokaryosis
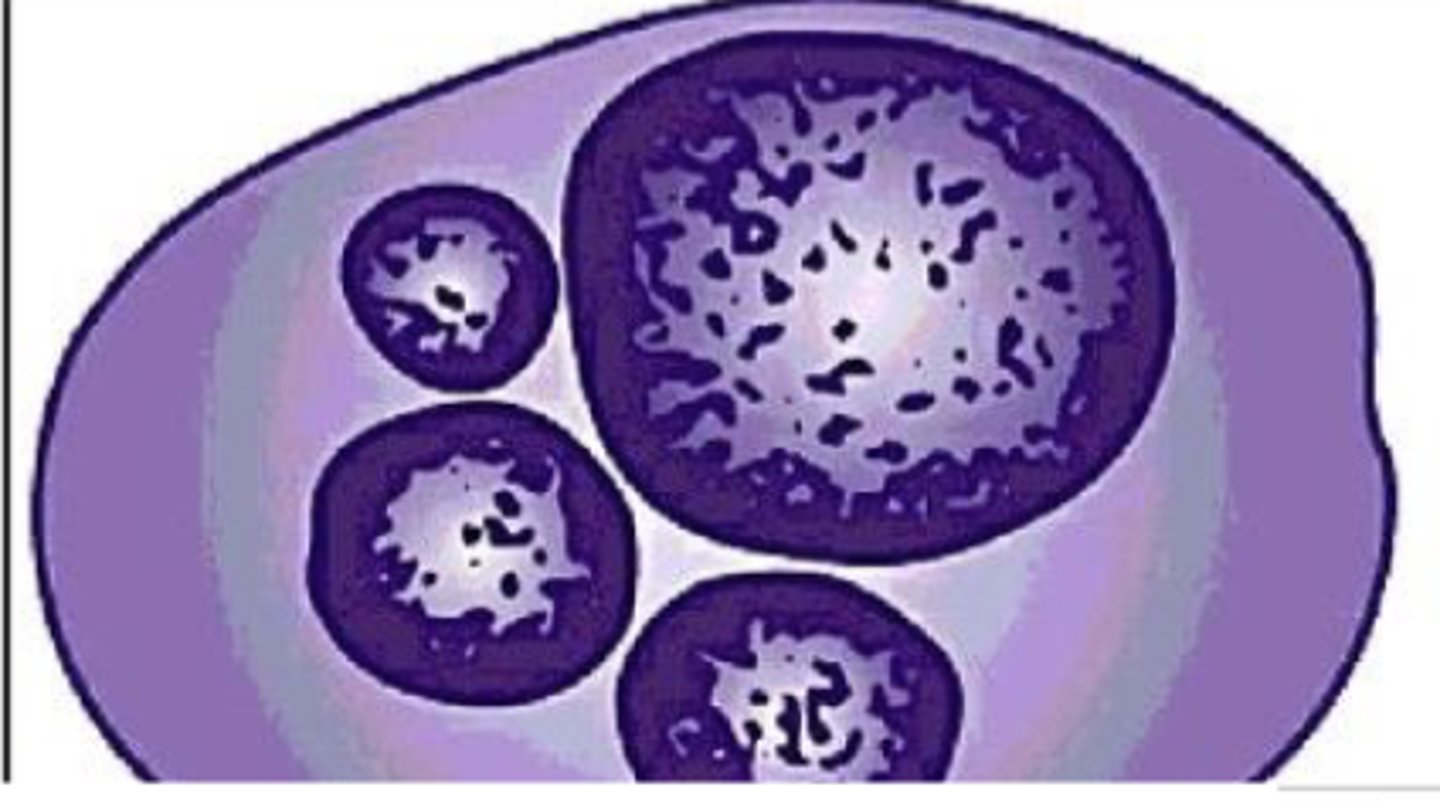
What is the term used for multiple nuclei in a cell; especially important if the nuclei vary in size
Multinucleation
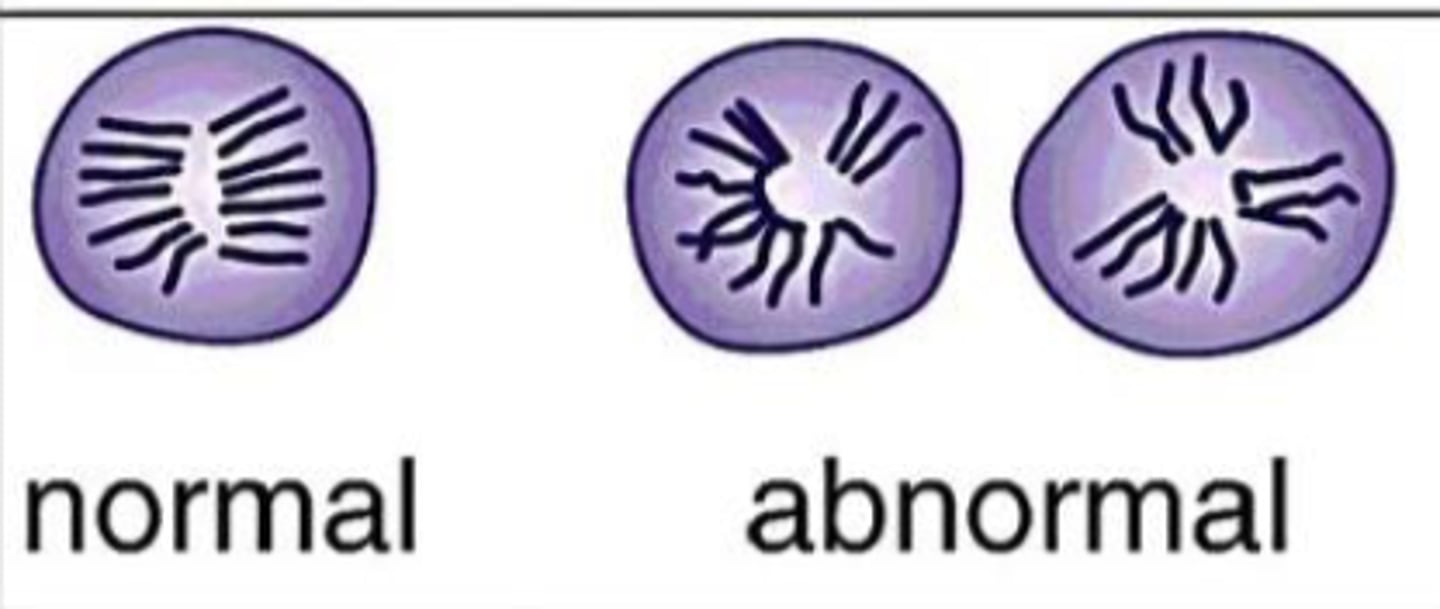
What is seen in these cells?
Increased mitotic figures
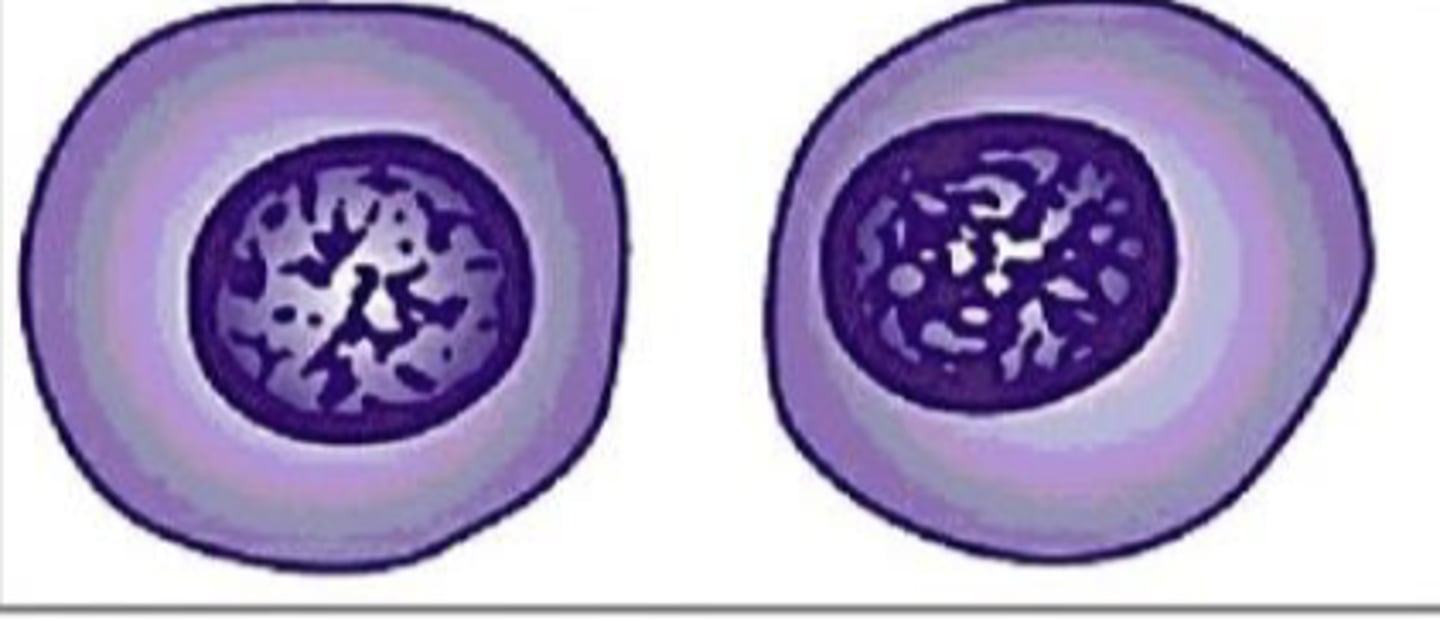
What term is used for the pattern that is coarser than normal, which may appear cordlike?
Coarse chromatin pattern
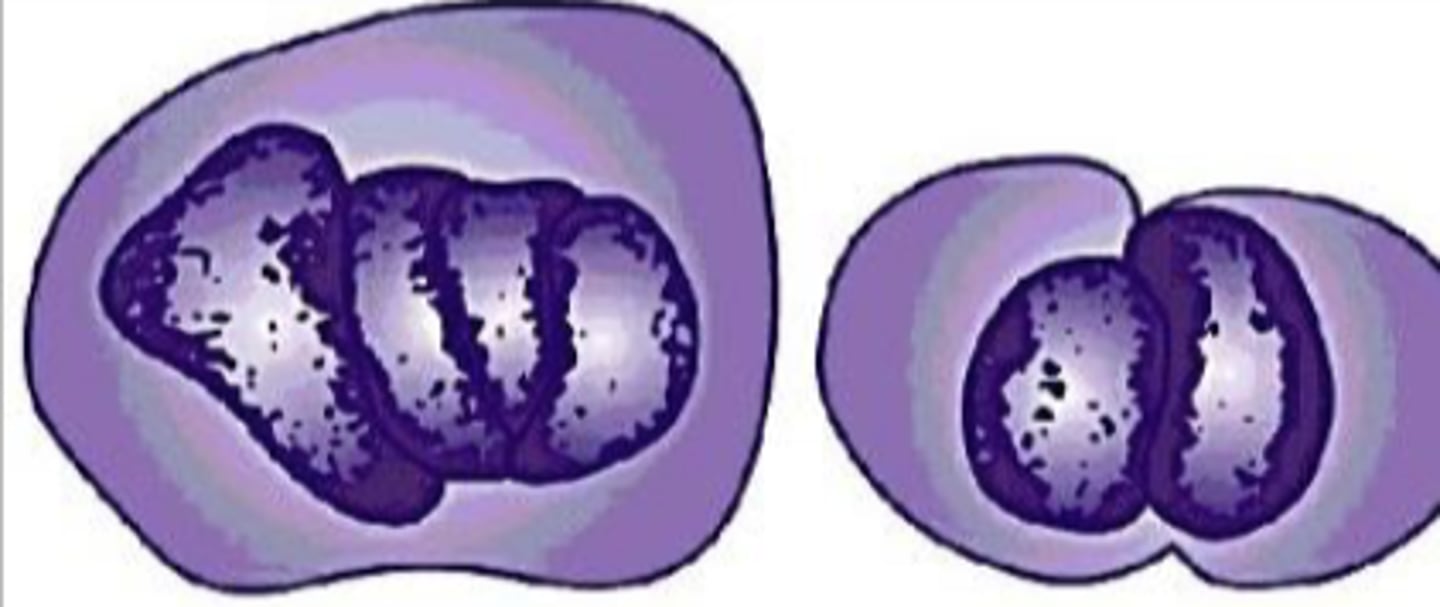
What term is used for the deformation of nuclei by other nuclei within the same or adjacent cells?
Nuclear molding
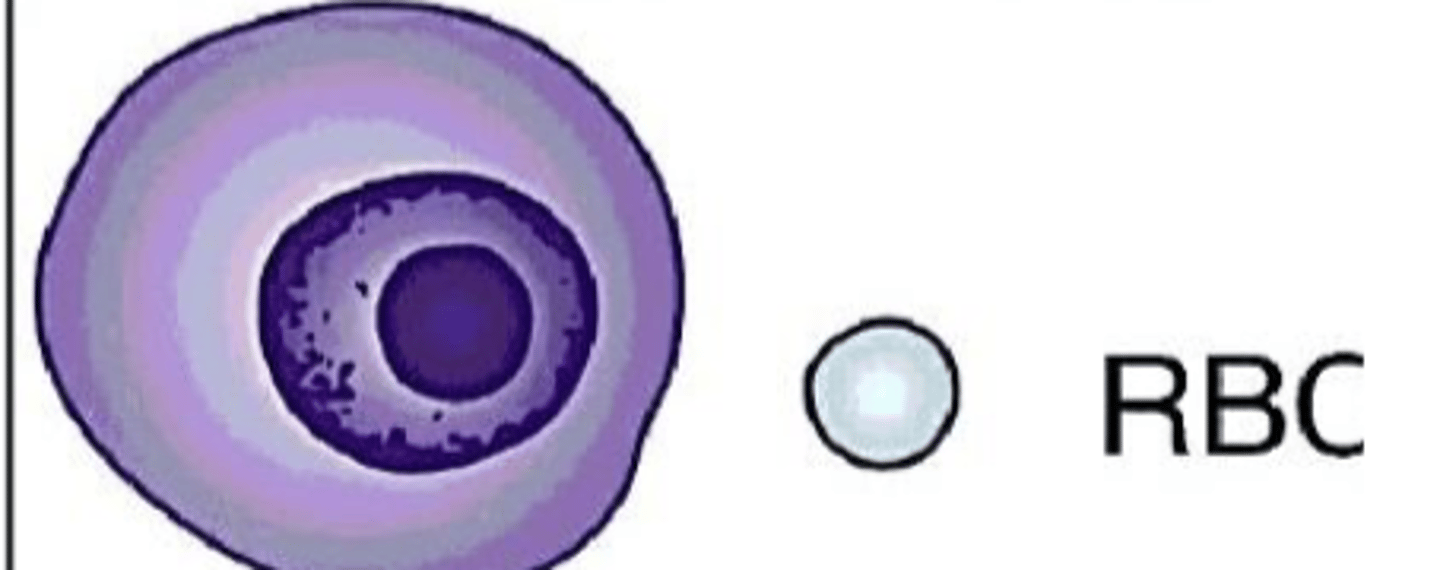
What term is used for nuclei that are increased in size?
Macronucleoli
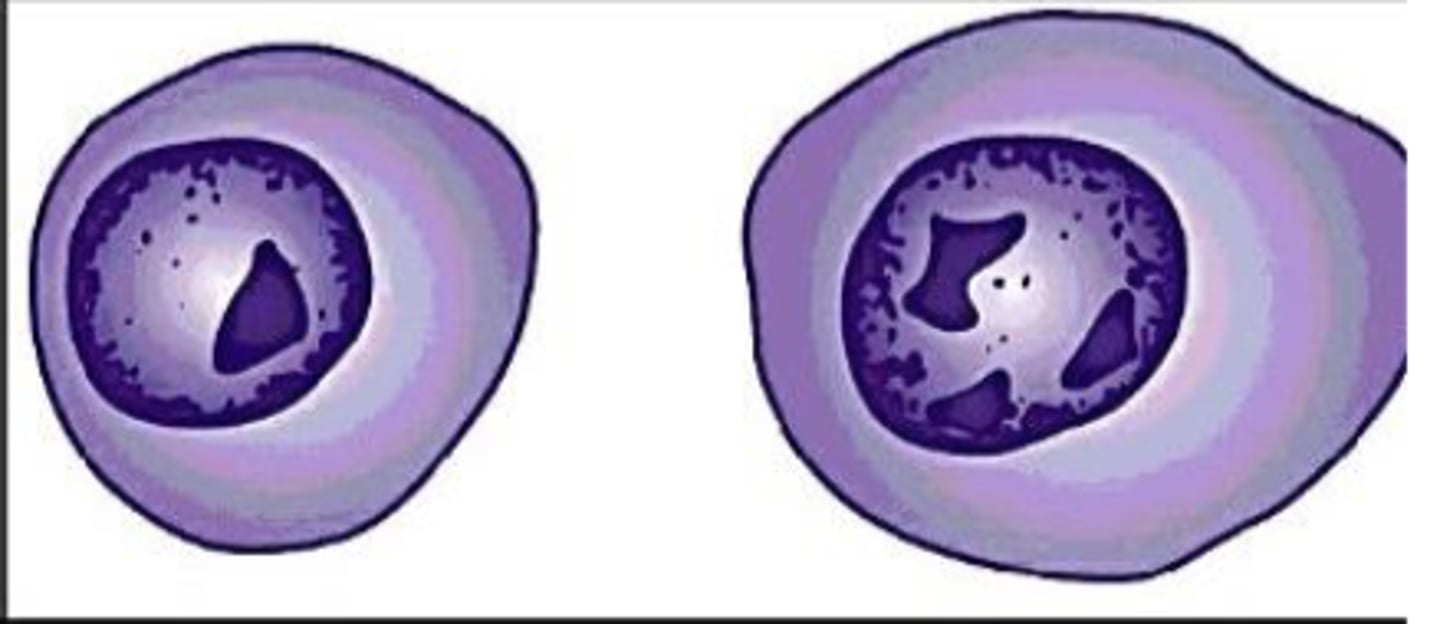
What term is used for nucleoli that have fused?
Angular nucleoli
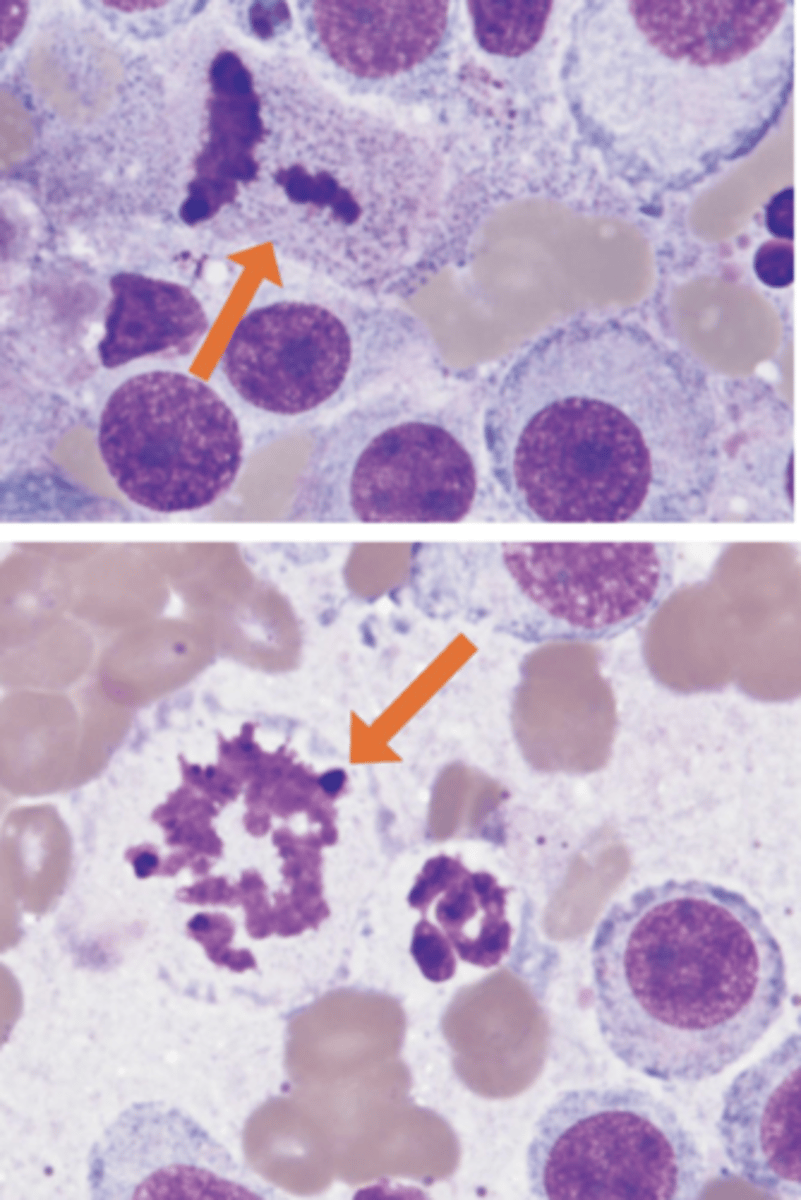
What abnormal features do you note about these cells?
Atypical mitotic figures
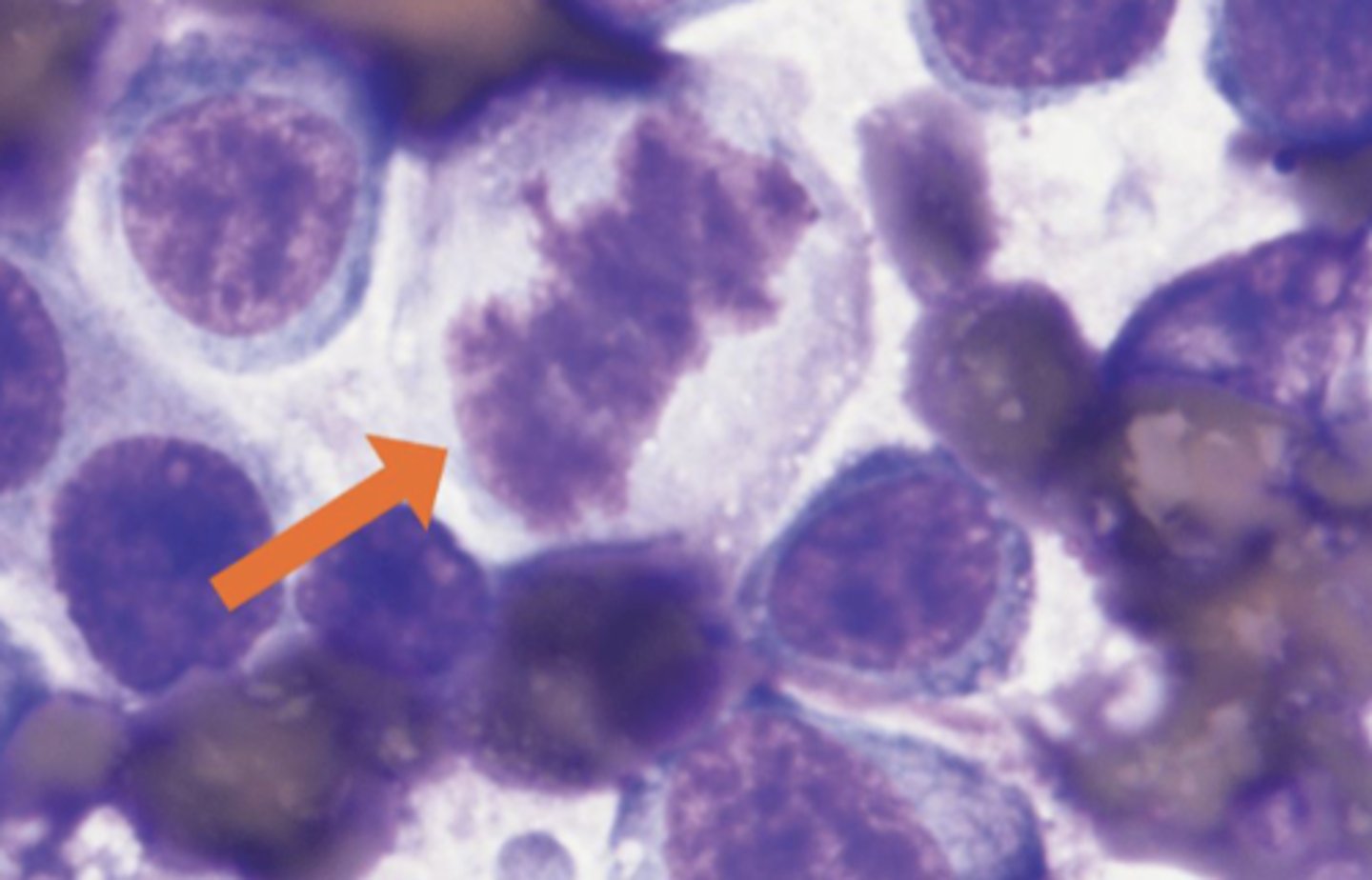
What is this?
Normal mitotic figure
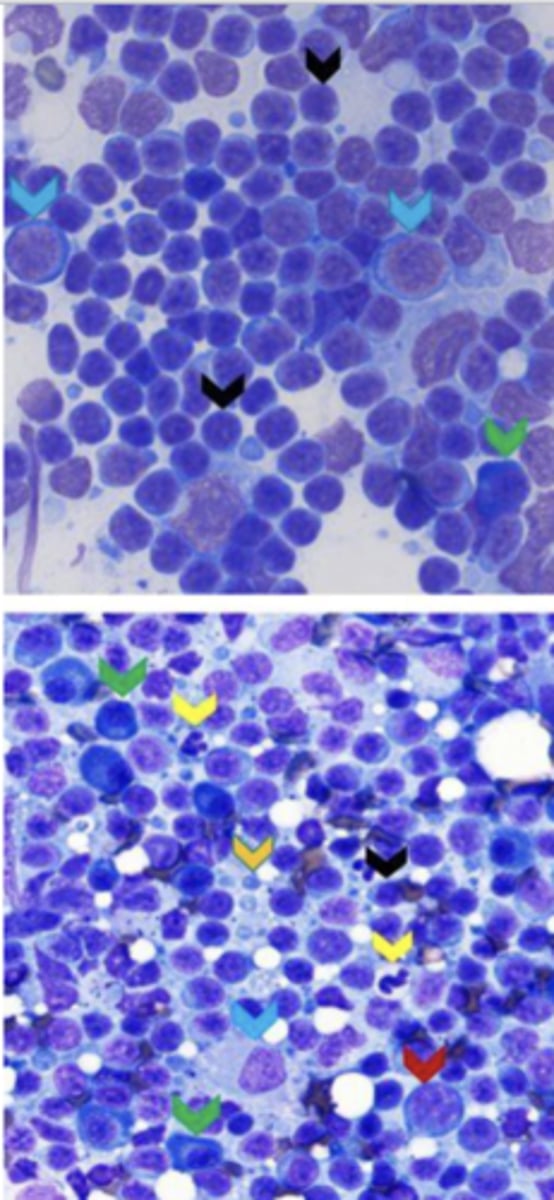
What term is used for this increased number of cells?
Hyperplasia
enlargement of tissue due to:
-hormonal disturbances
-tissue injury
-antigenic stimulation
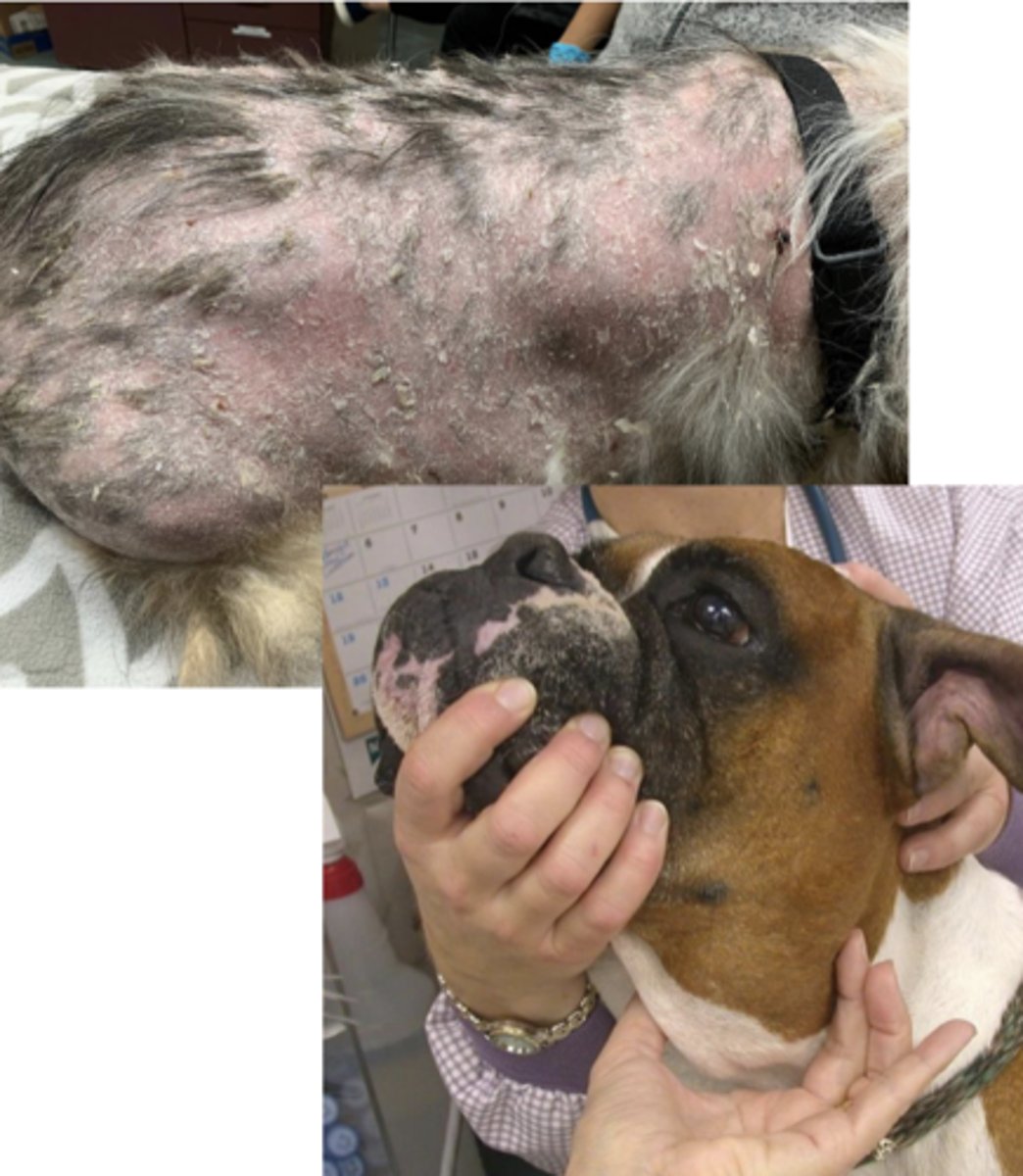
Boxer with generalized lymphadenopathy, what type of round cell tumor do you suspect?
Lymphoma
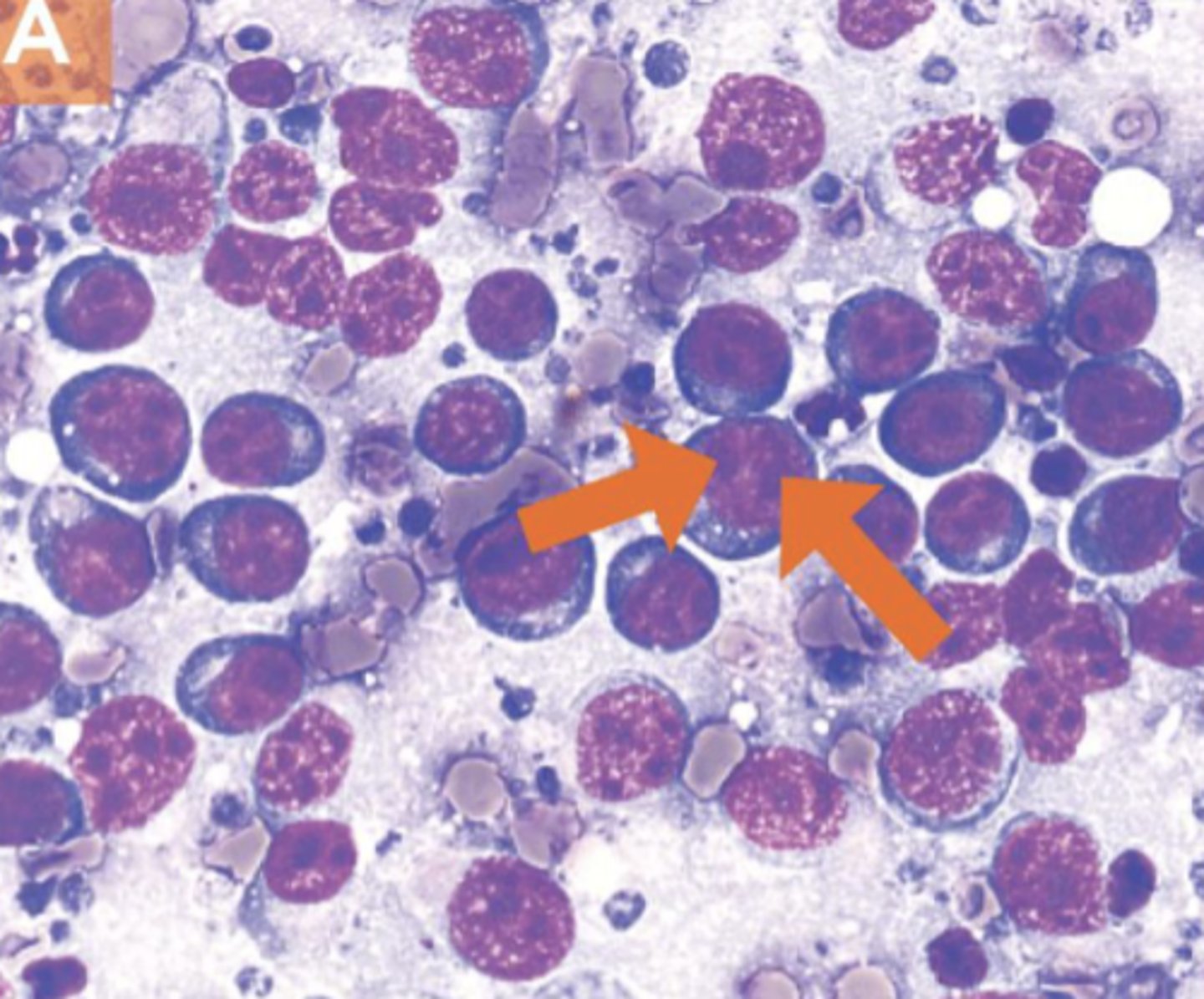
You aspirate a swollen lymph node and examine it under the microscope. What do you see?
Large lymphocytes
-LYMPHOMA
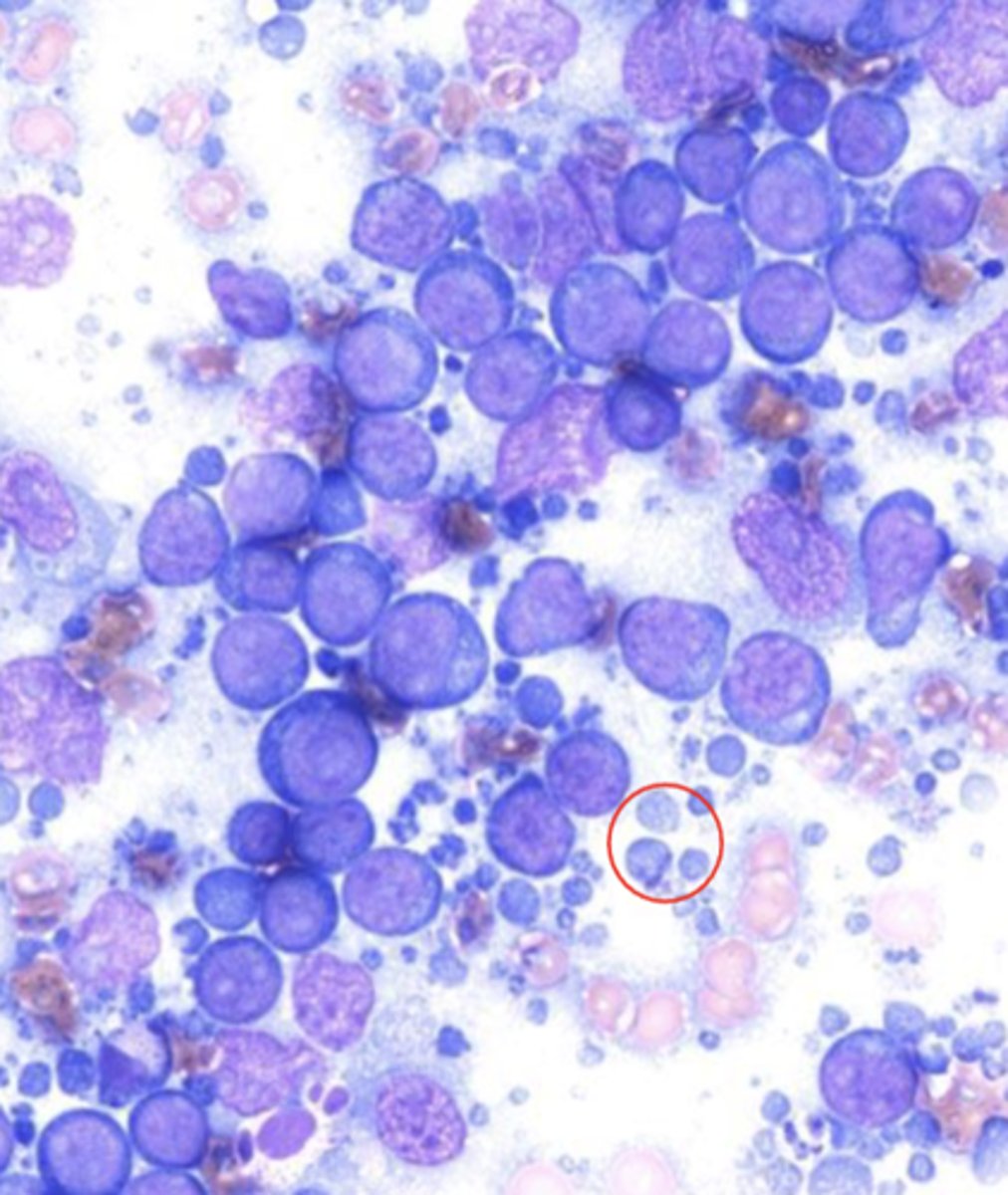
normal or abnormal?
abnormal
Large Cell Lymphoma
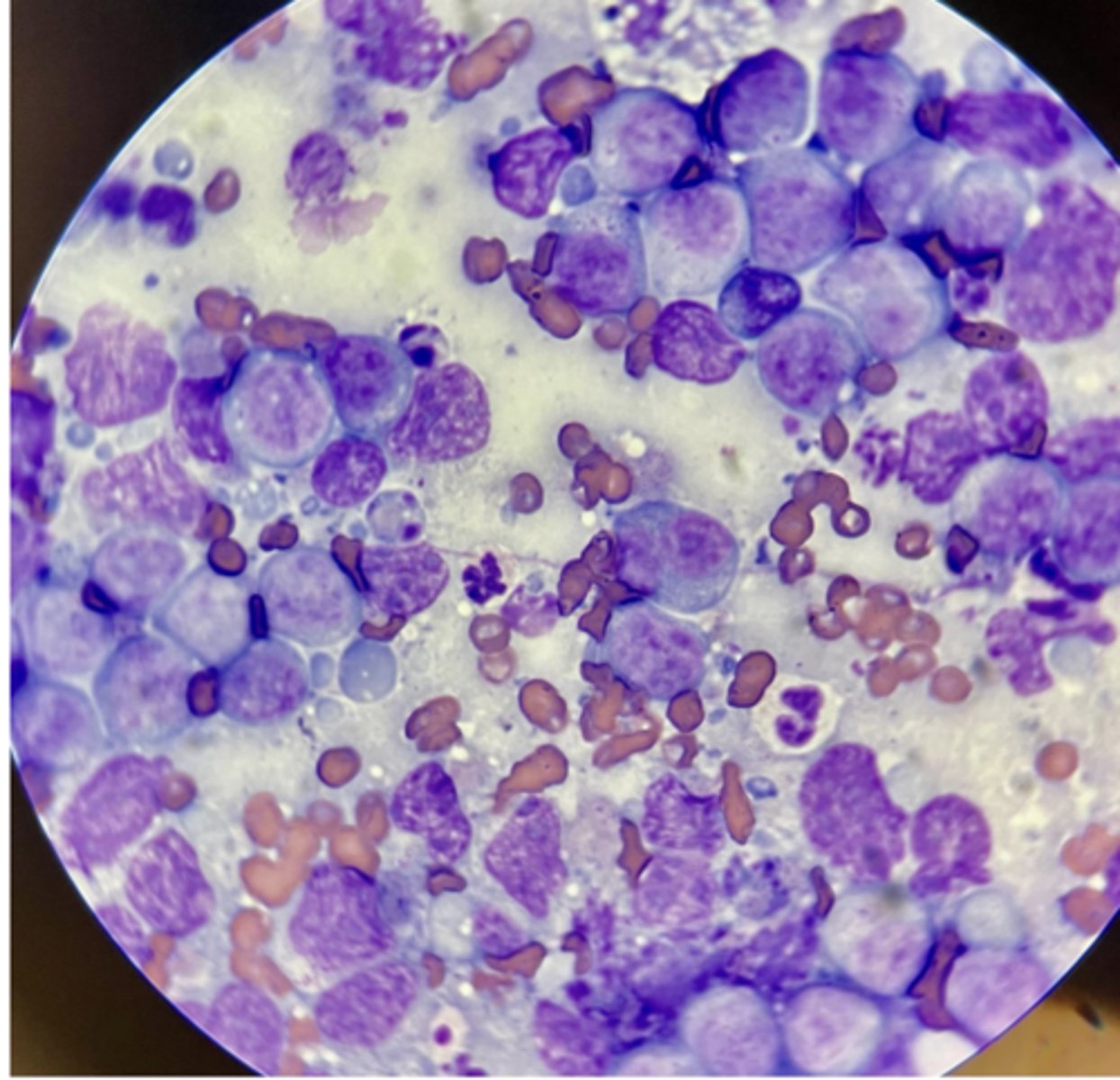
What malignancy characteristics are present?
large lymphocytes
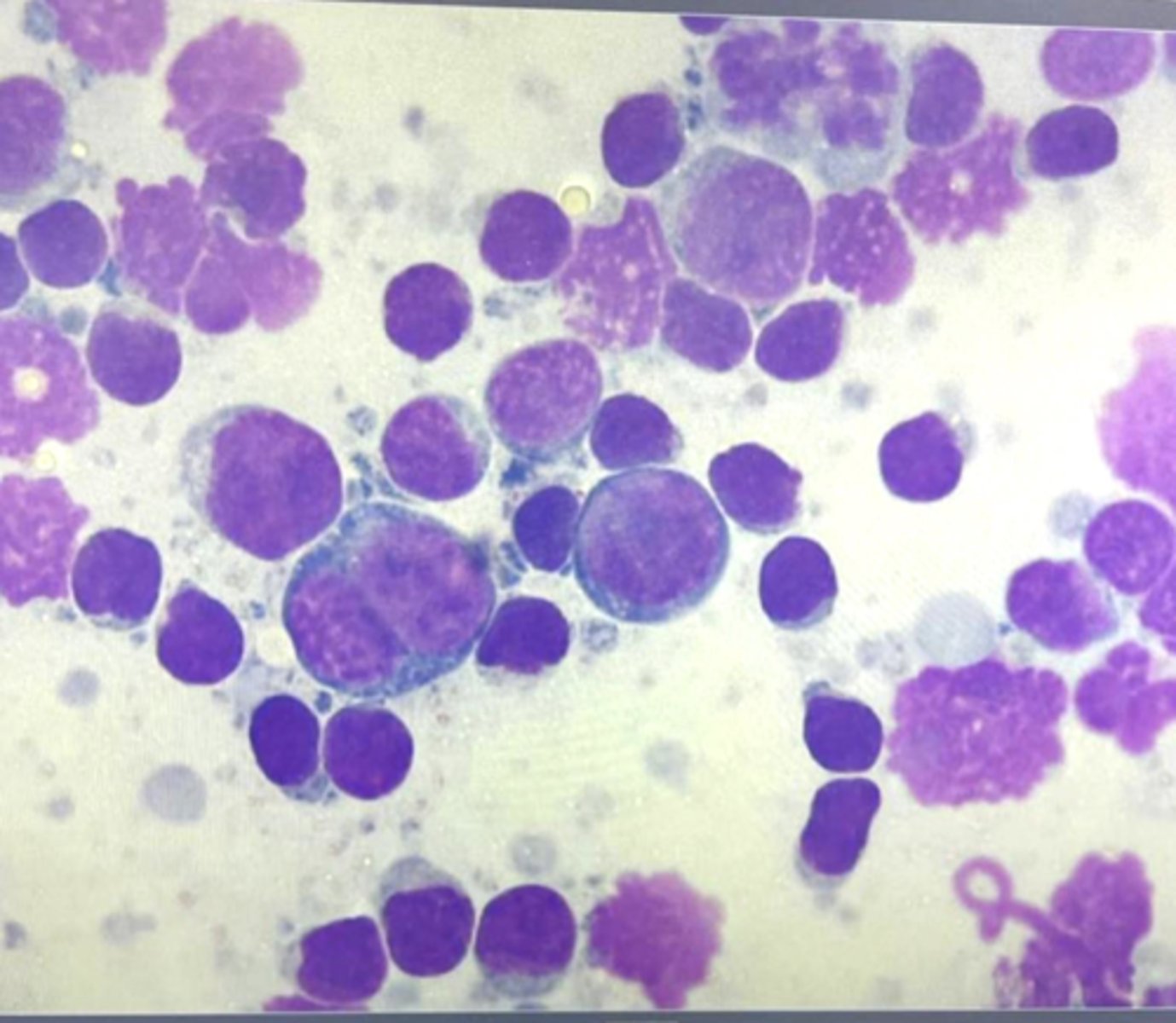
What type of round cell tumor is this?
Lymphoma
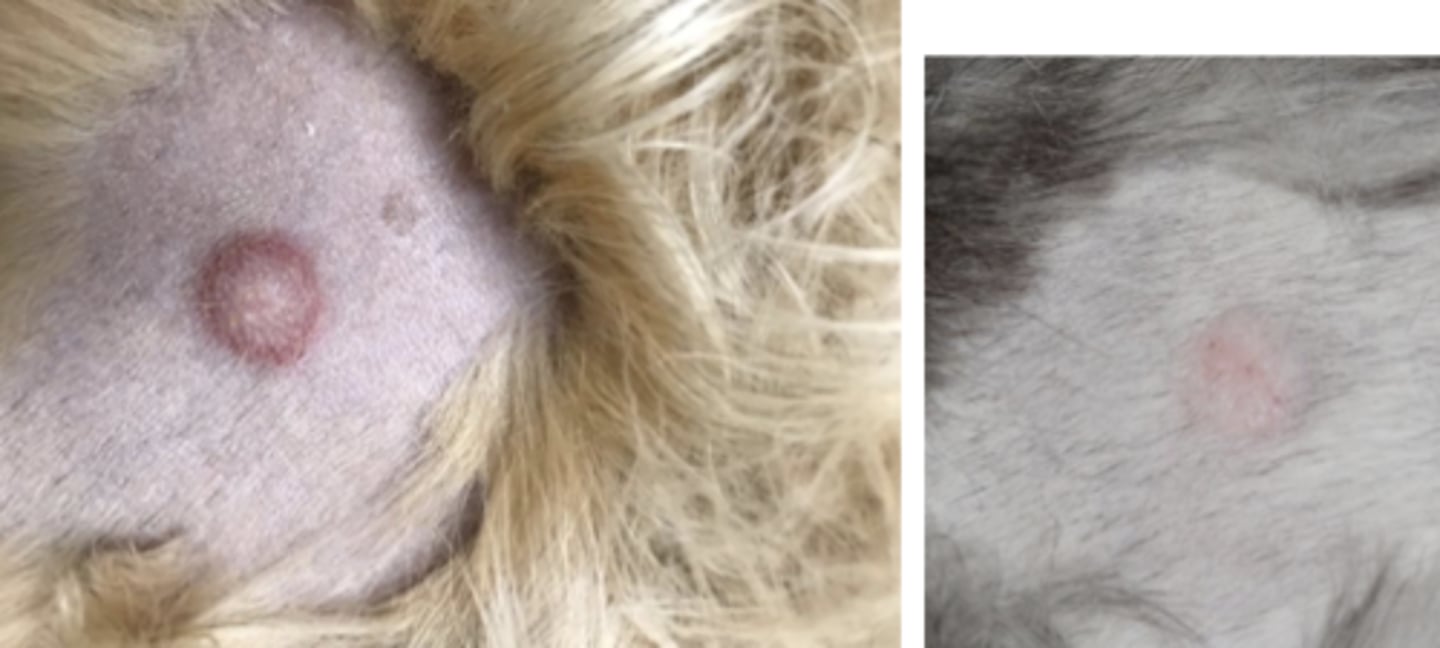

What type of round cell tumor is this?
Mast cell tumors
-hairless, raised, solitary nodule/mass
-diffuse swellings, nodular rashes, or soft mass invading the subcutis
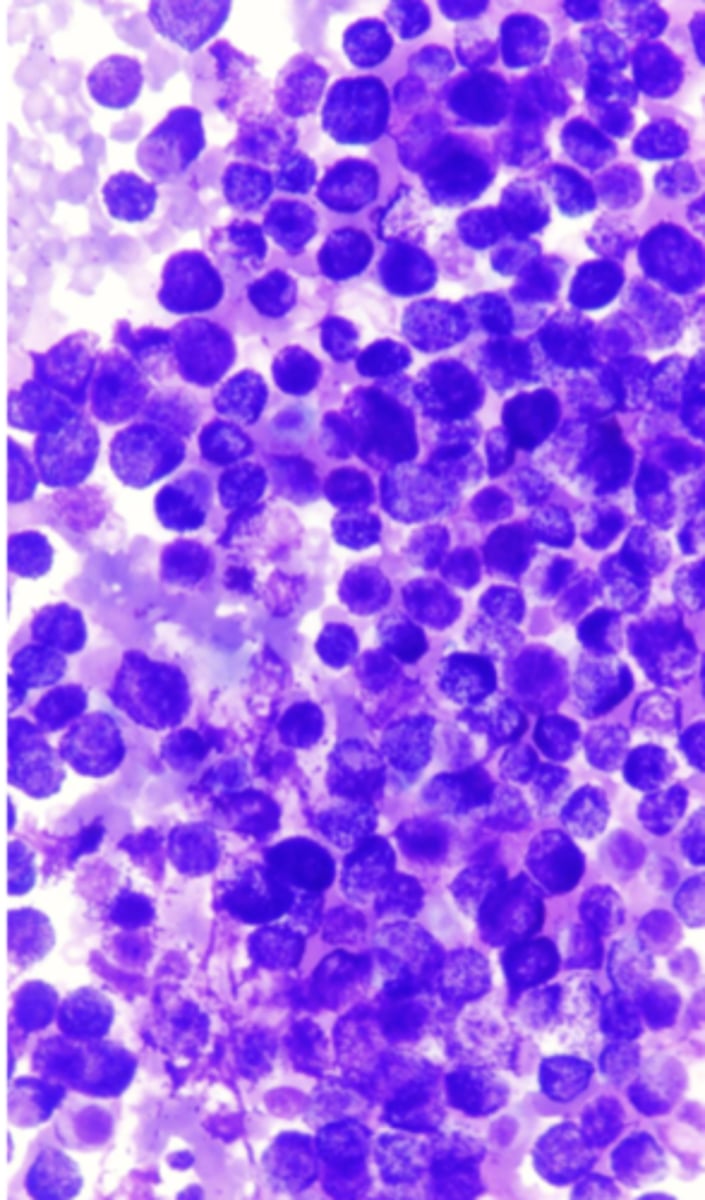
What type of tumor is this?
Mast cell tumor
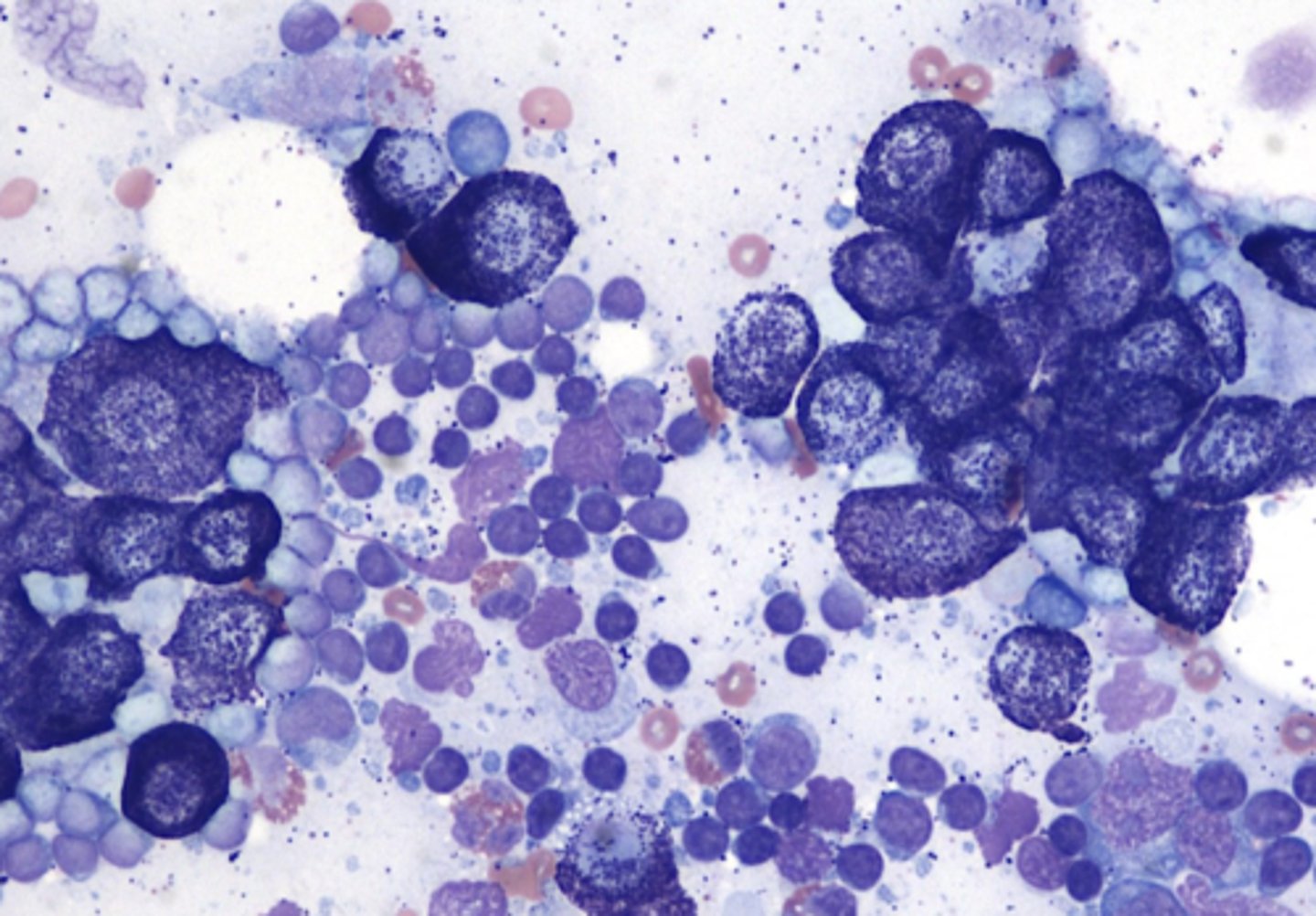
What type of tumor is this?
mast cells in lymph node
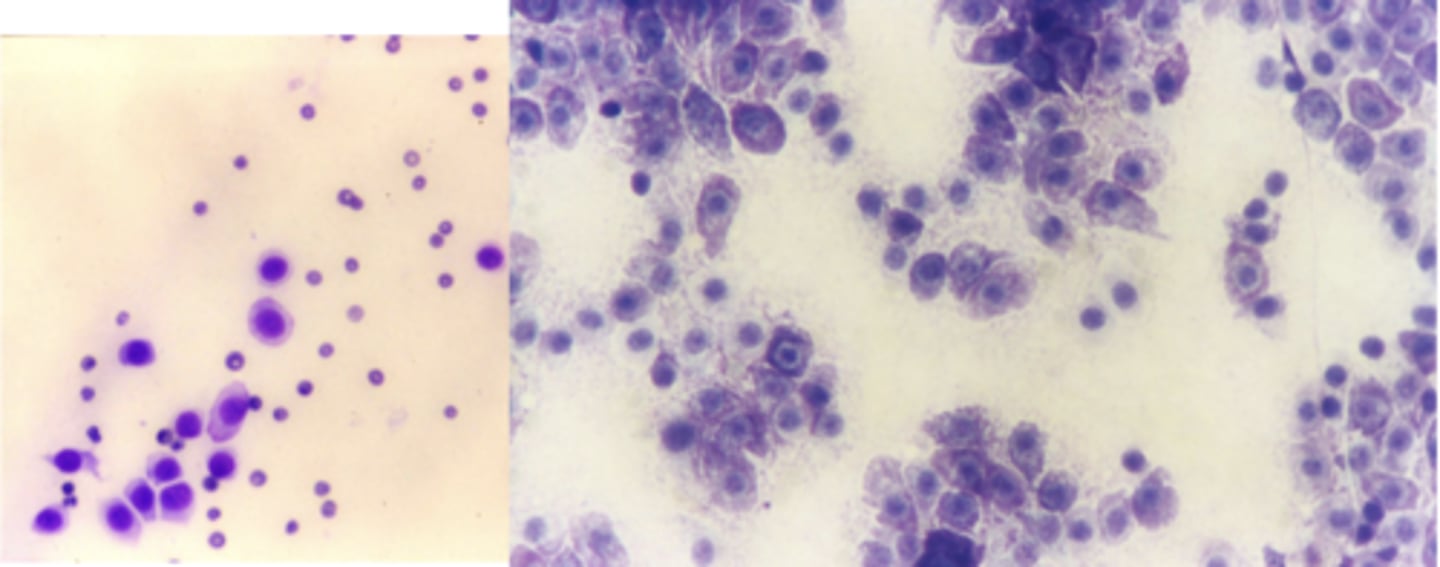
What kind of round cell tumor is this found in a cat?
Feline Mast Cell Tumor
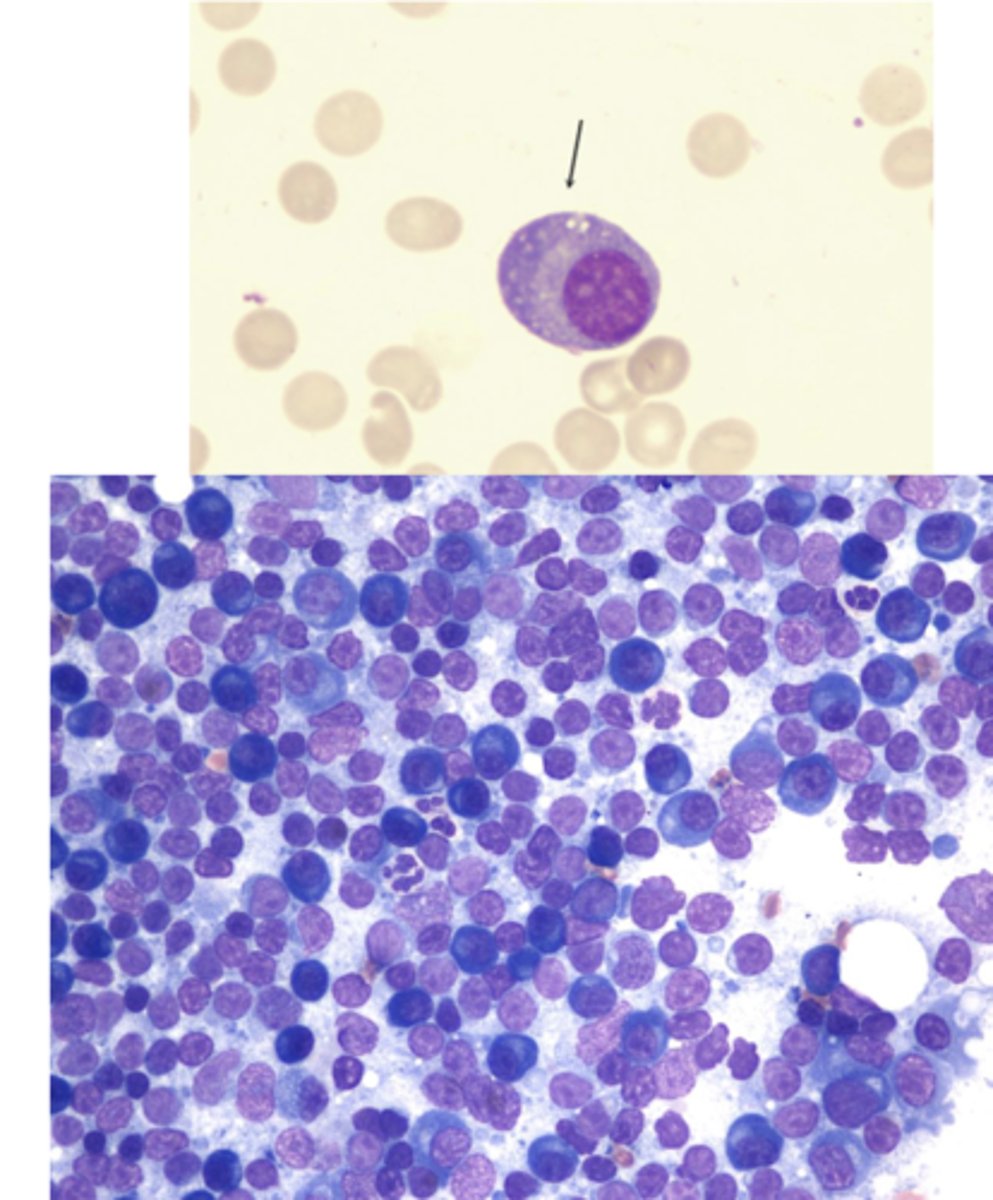
What type of round cell tumor is this?
Plasma cell tumor
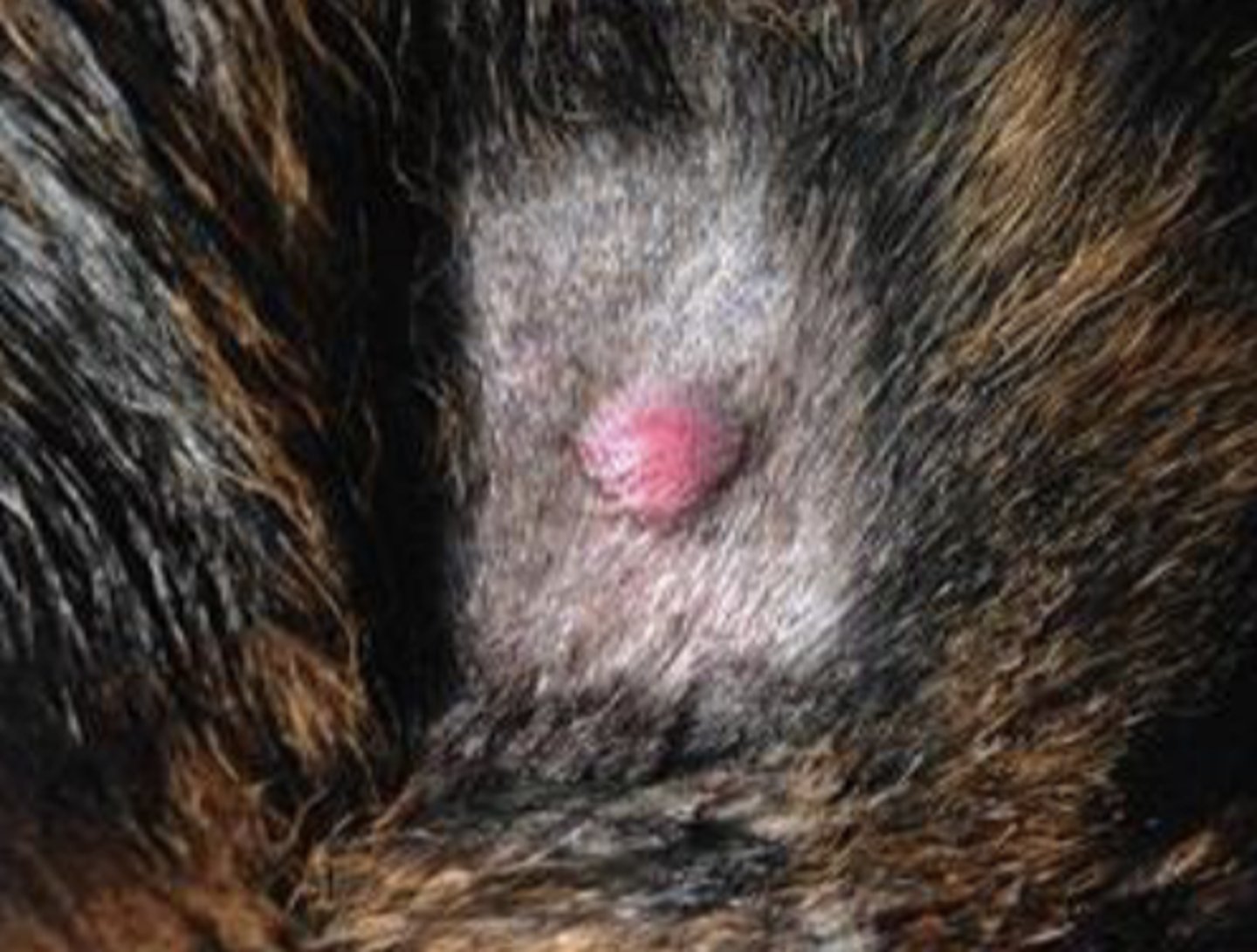
What type of round cell tumor is this?
Extramedullary plasmacytoma
-solitary, pink, alopecic-ulcerated mass/nodule
-seen on the digits, pinna, and mouth
-usually benign
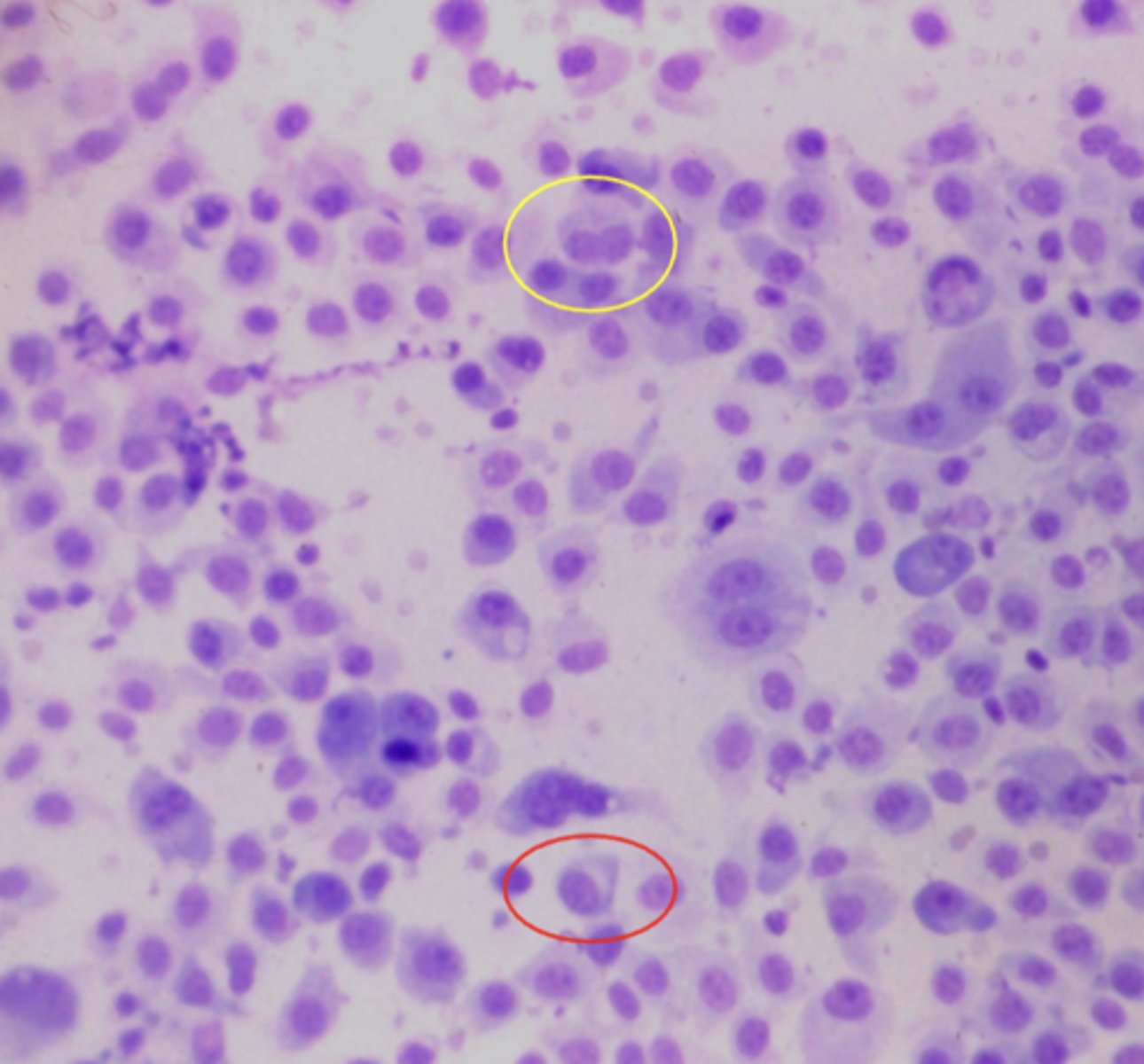
What type of round cell tumor is this cytology sample taken from?
Plasmacytoma
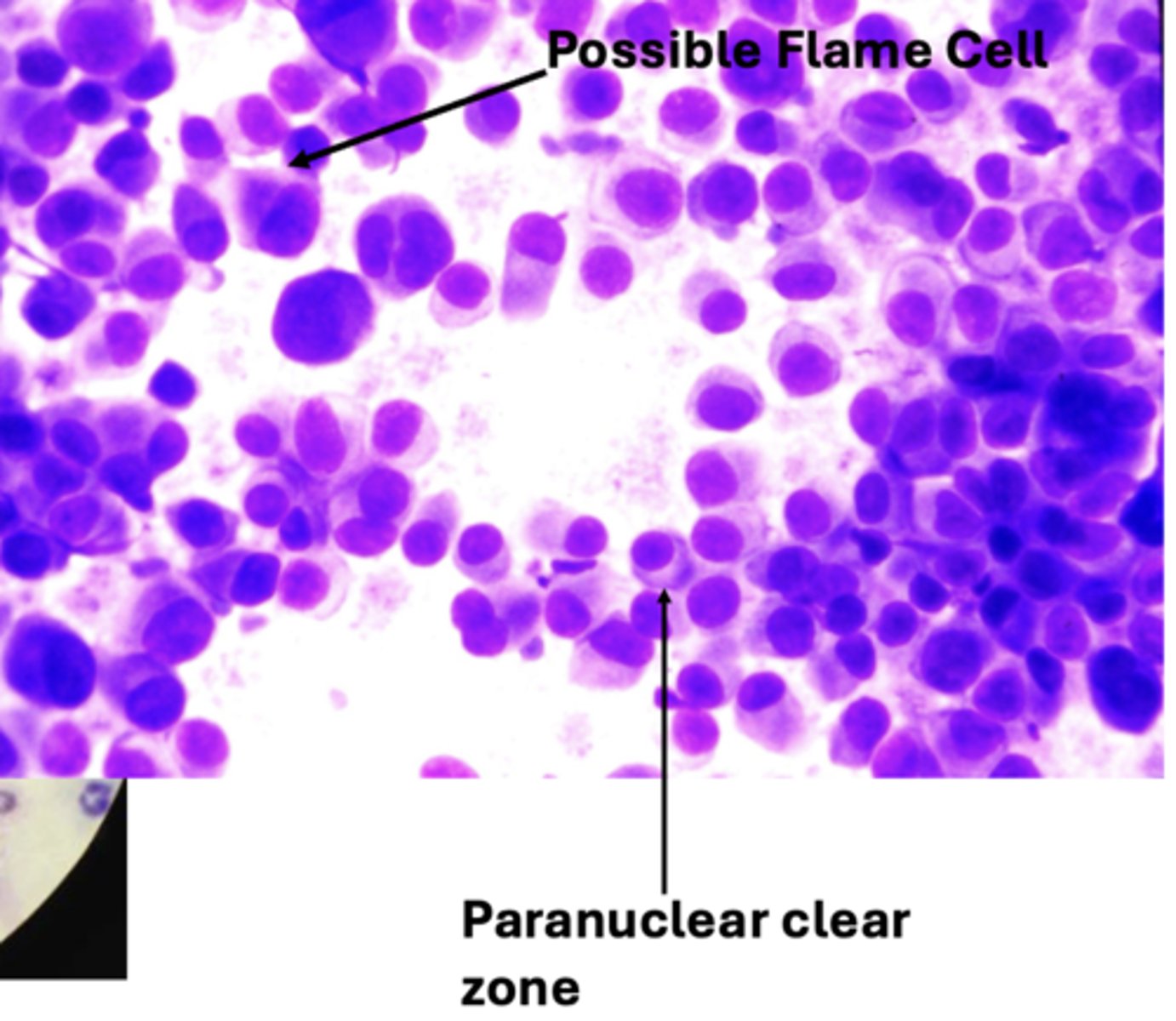
What type of round cell tumor has these features?
Plasmacytoma
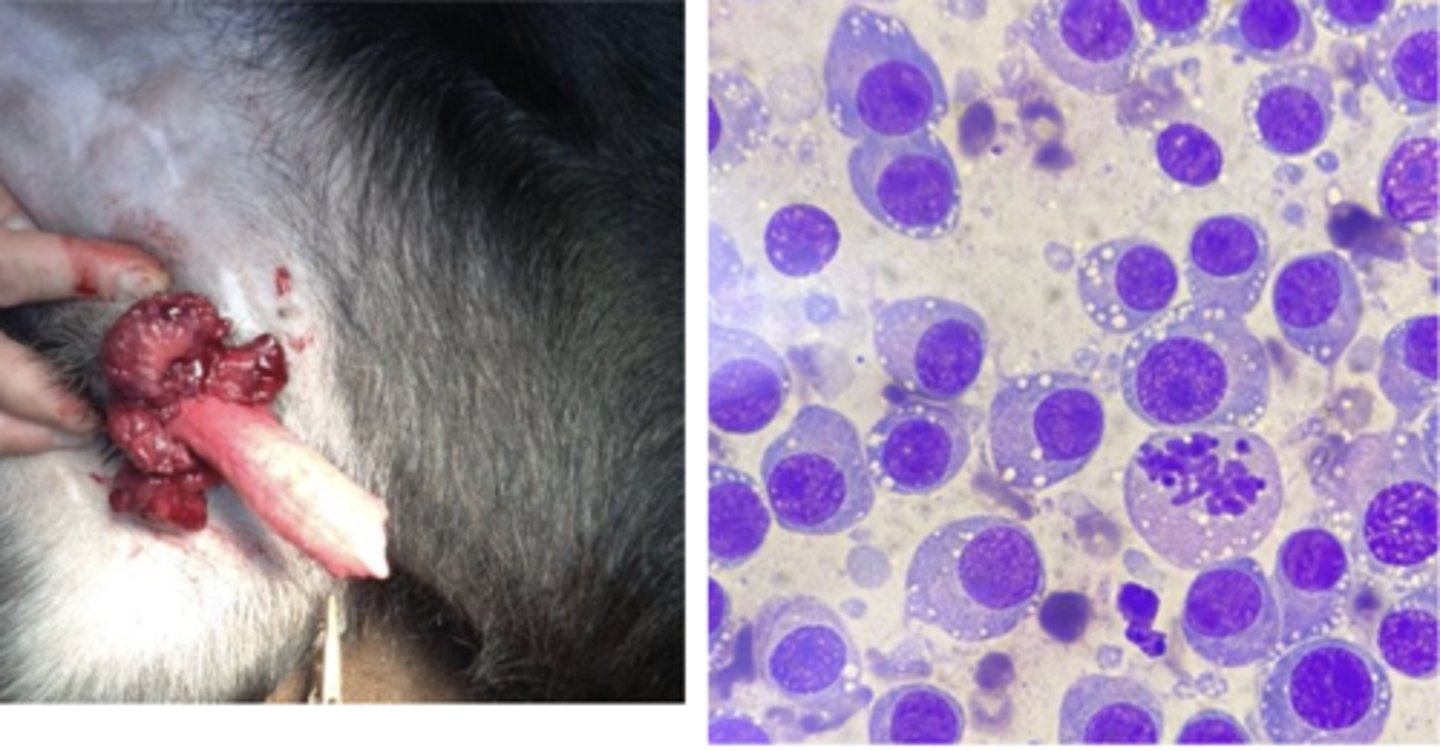
What type of round cell tumor is this?
Transmissible Venereal Tumor (TVT)
-cells have a medium to large round nucleus, possibly eccentric
-clumped chromatin, common to see mitotic figures
-multinucleation
-cytoplasm light blue/gray with discrete vacuoles
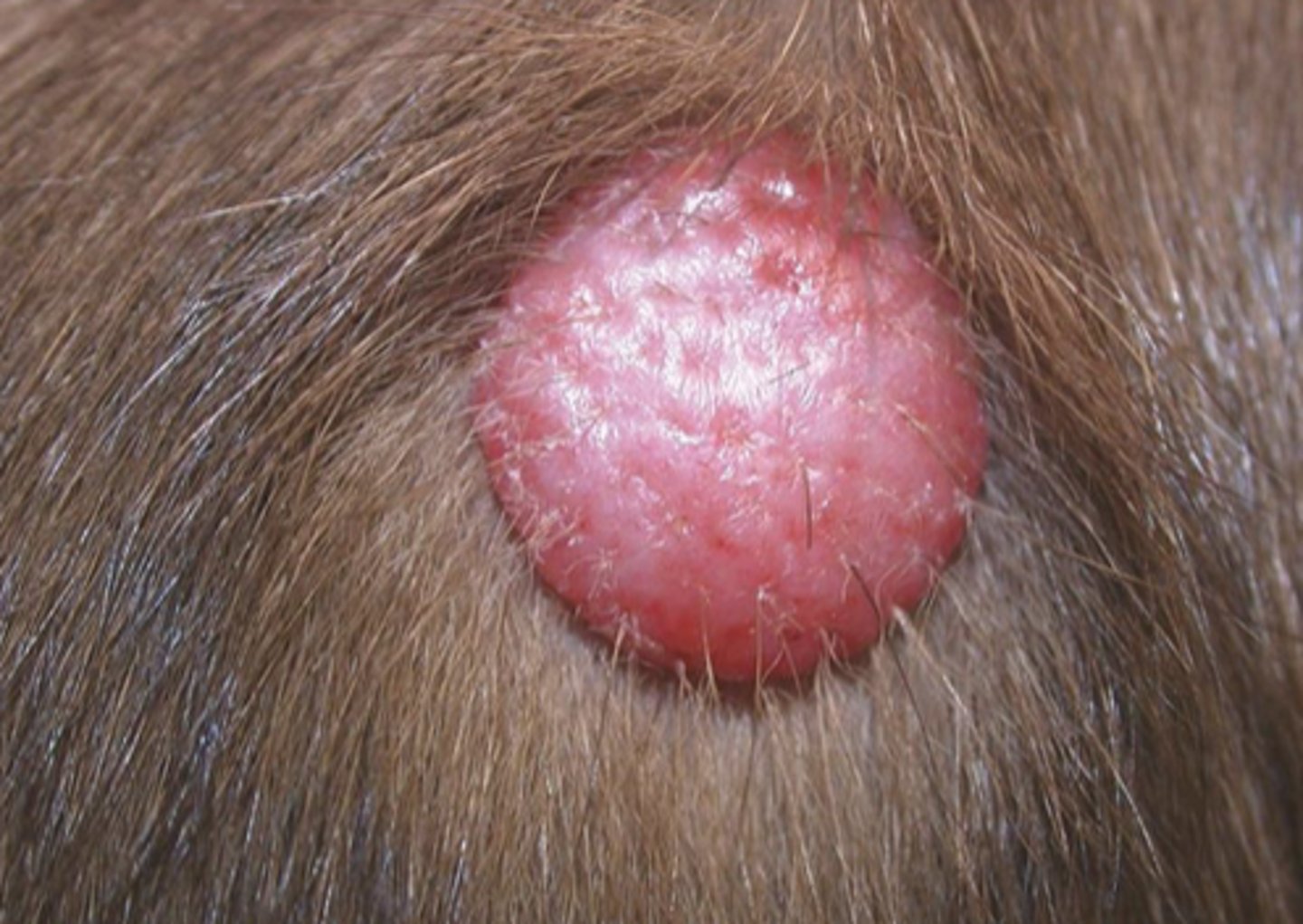
What type of round cell tumor is this?
Cutaneous Histiocytoma
-benign tumor
-more common in young dogs
-common site: head/pinnae
-regress spontaneously within 3 months
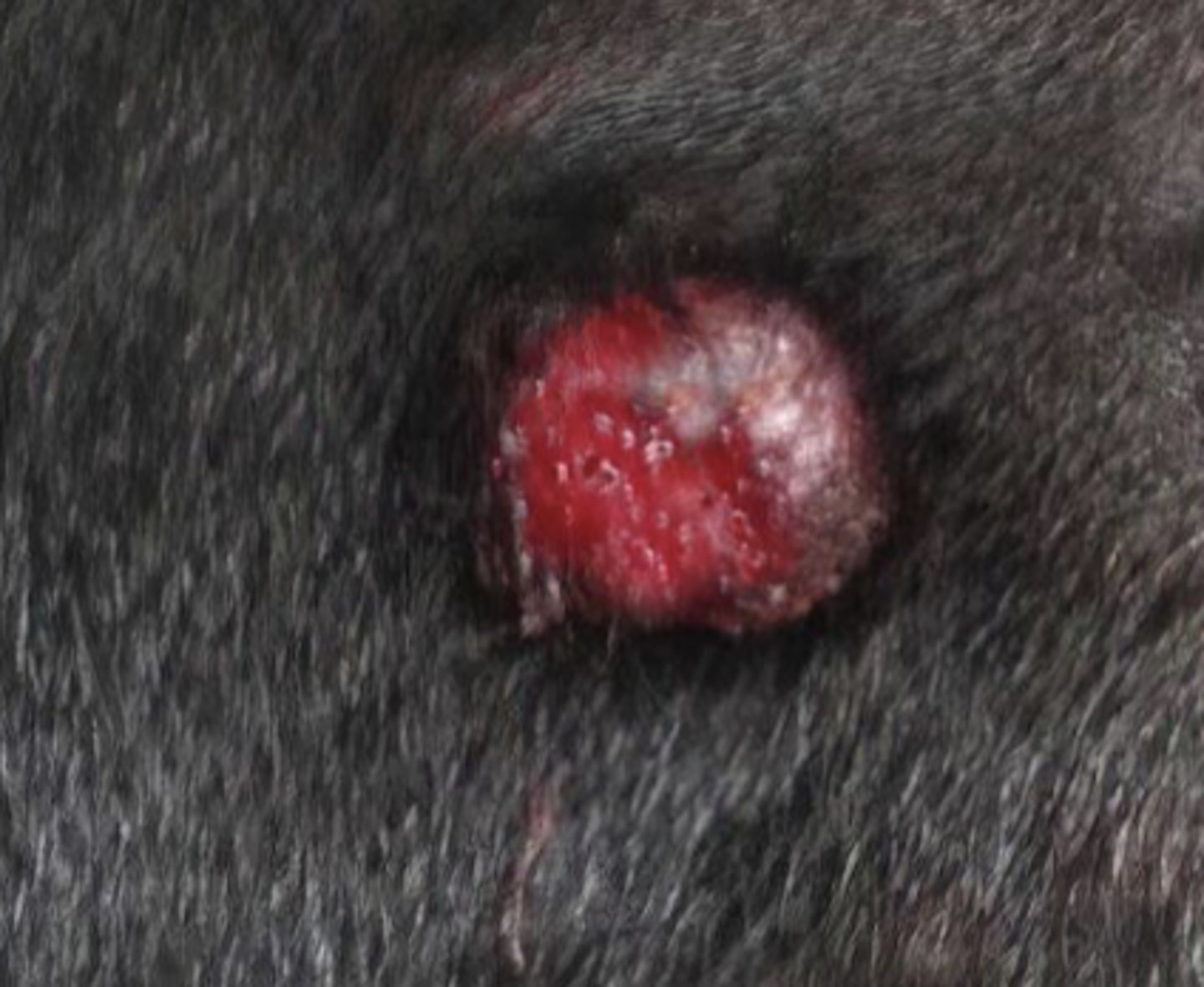
What type of round cell tumor is this?
Cutaneous histiocytoma
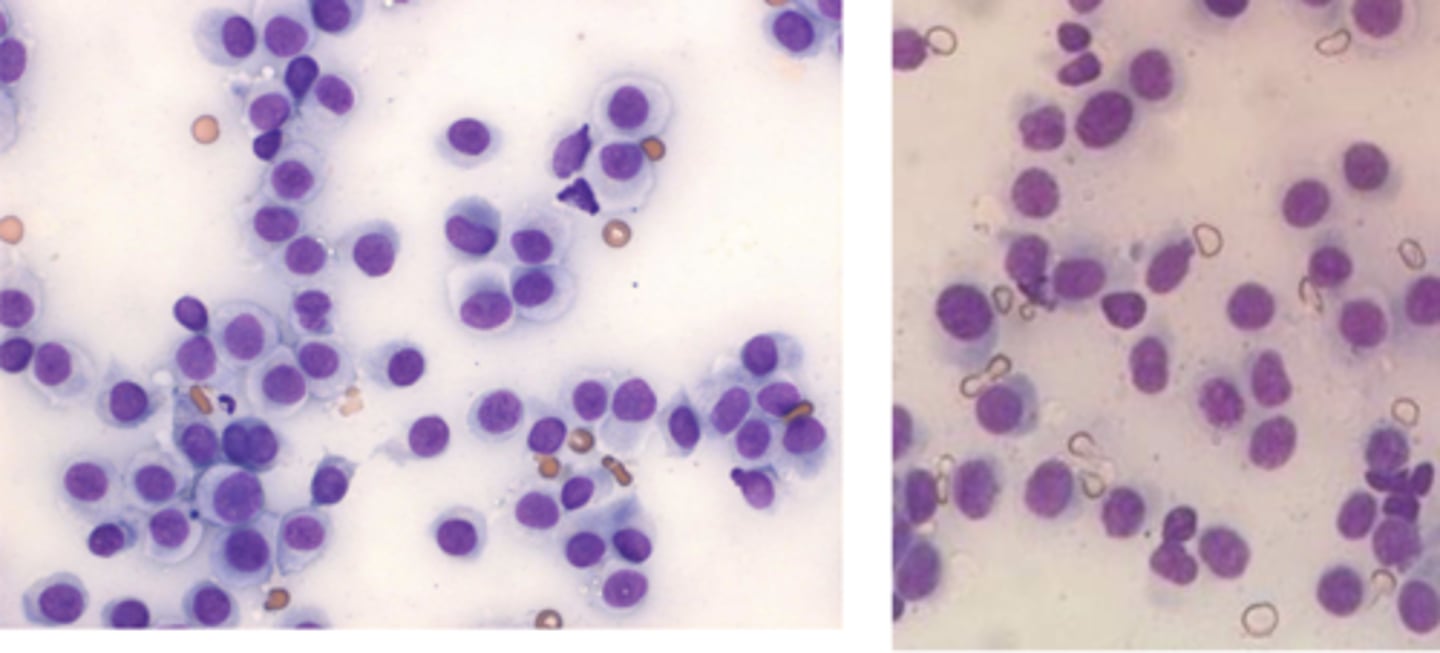
What type of round cell tumor is this cytology from?
Cutaneous Histiocytoma
- Medium-sized cells, slightly larger than neutrophils
• Round to oval nuclei
• May be indented/bean-shaped
• Moderate light blue/gray cytoplasm
• if there's proteinaceous fluid, cell borders may be indistinct
• Small lymphocytes indicate regression
What type of round cell tumor is this?
regressing histiocytoma
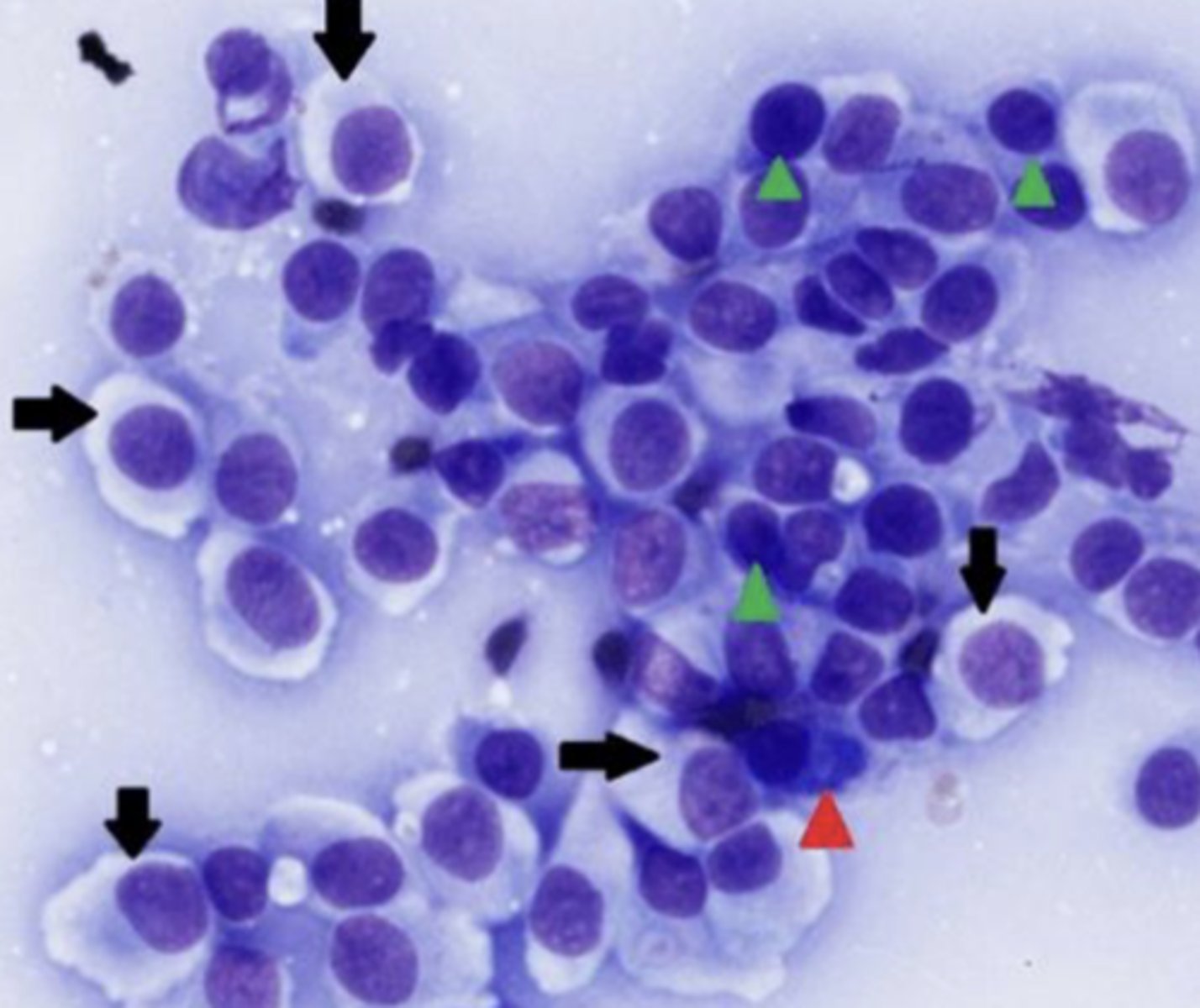
What type of round cell tumor is this?
Histiocytic Sarcoma
What type of round cell tumor is this?
Histiocytic sarcoma
-Sheets of large, pleomorphic, mononuclear and multinucleated giant cells
- Can appear as spindle-shaped cells
- Abundant basophilic cytoplasm with vacuoles, may see phagocytosis of RBCs/WBCs
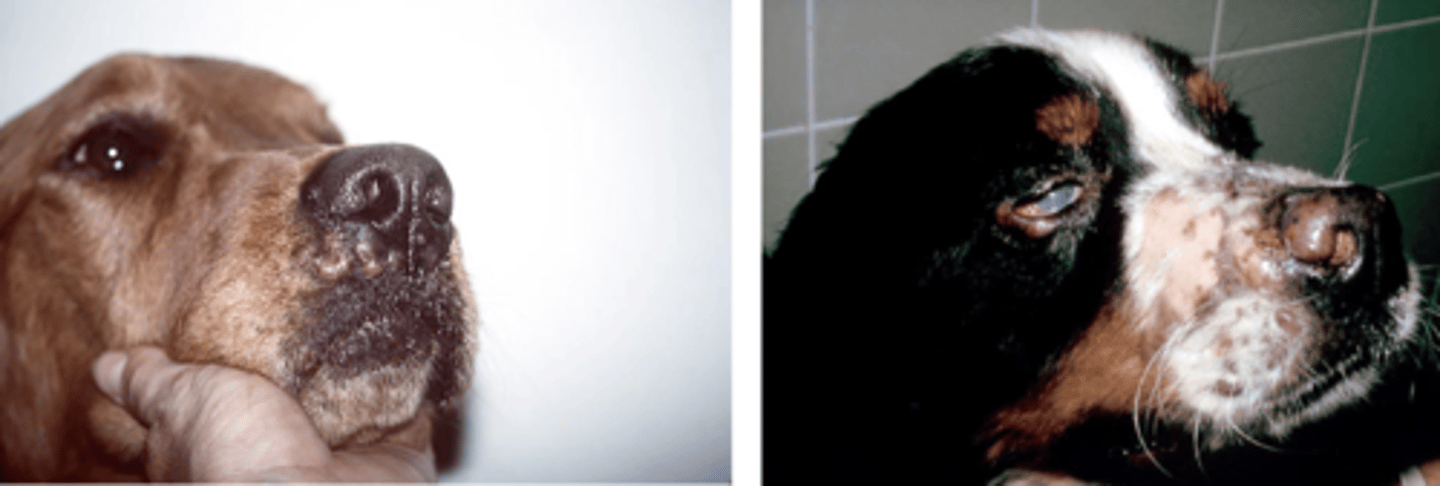

What has caused these lesions?
reactive histiocytosis
-Bernese Mtn dogs !
-Common sites: face, nose, neck, extremities, perineum
- Appear as multiple cutaneous and subcutaneous firm nodules
- Can regress spontaneously and reappear in new sites
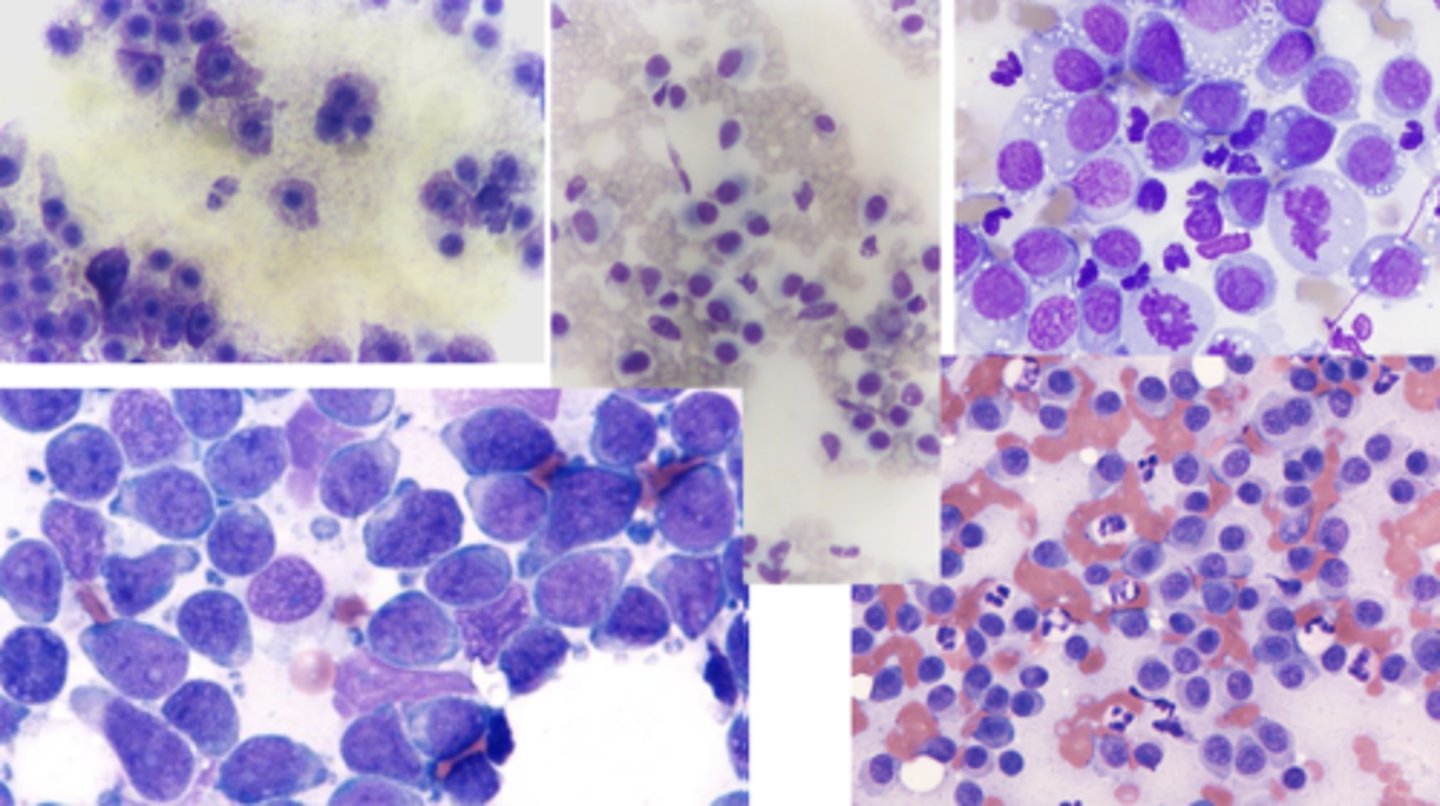
What type of round cell tumor is this?
Reactive histocytosis
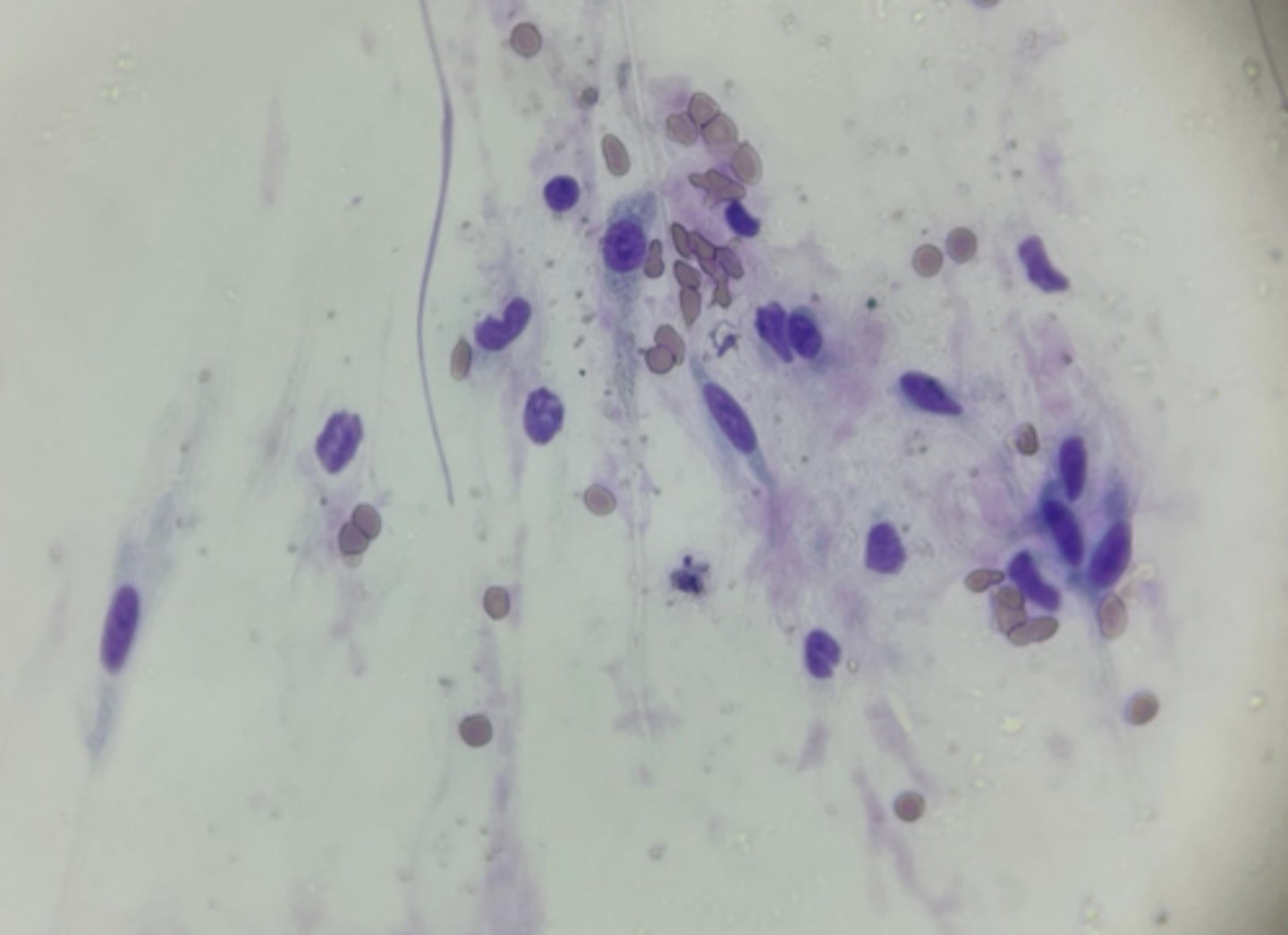
What type of cells are these spindle-shaped, wispy appearing cells?
Mesenchymal neoplastic cells
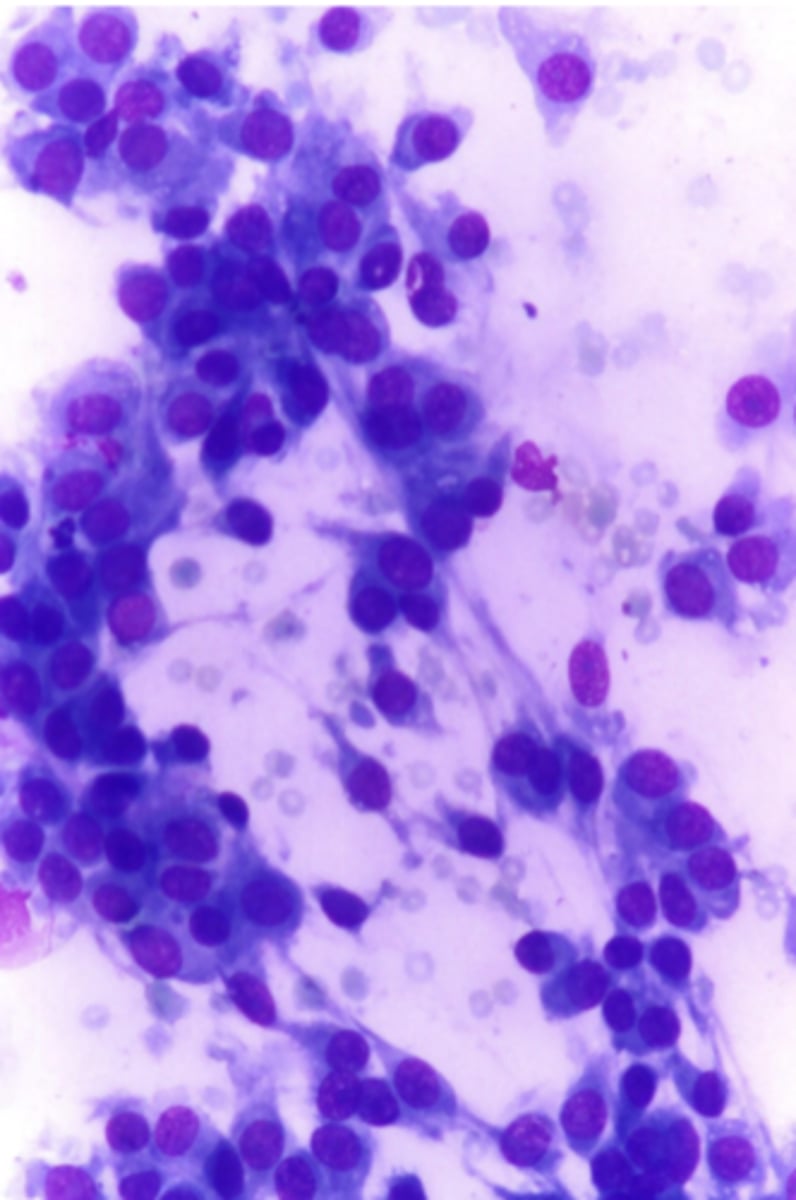
What type of neoplastic tumor is this?
- Very exfoliative, sheets of cells that break away into a single spindle cells
soft tissue sarcoma (STS)
-spindle cell tumors
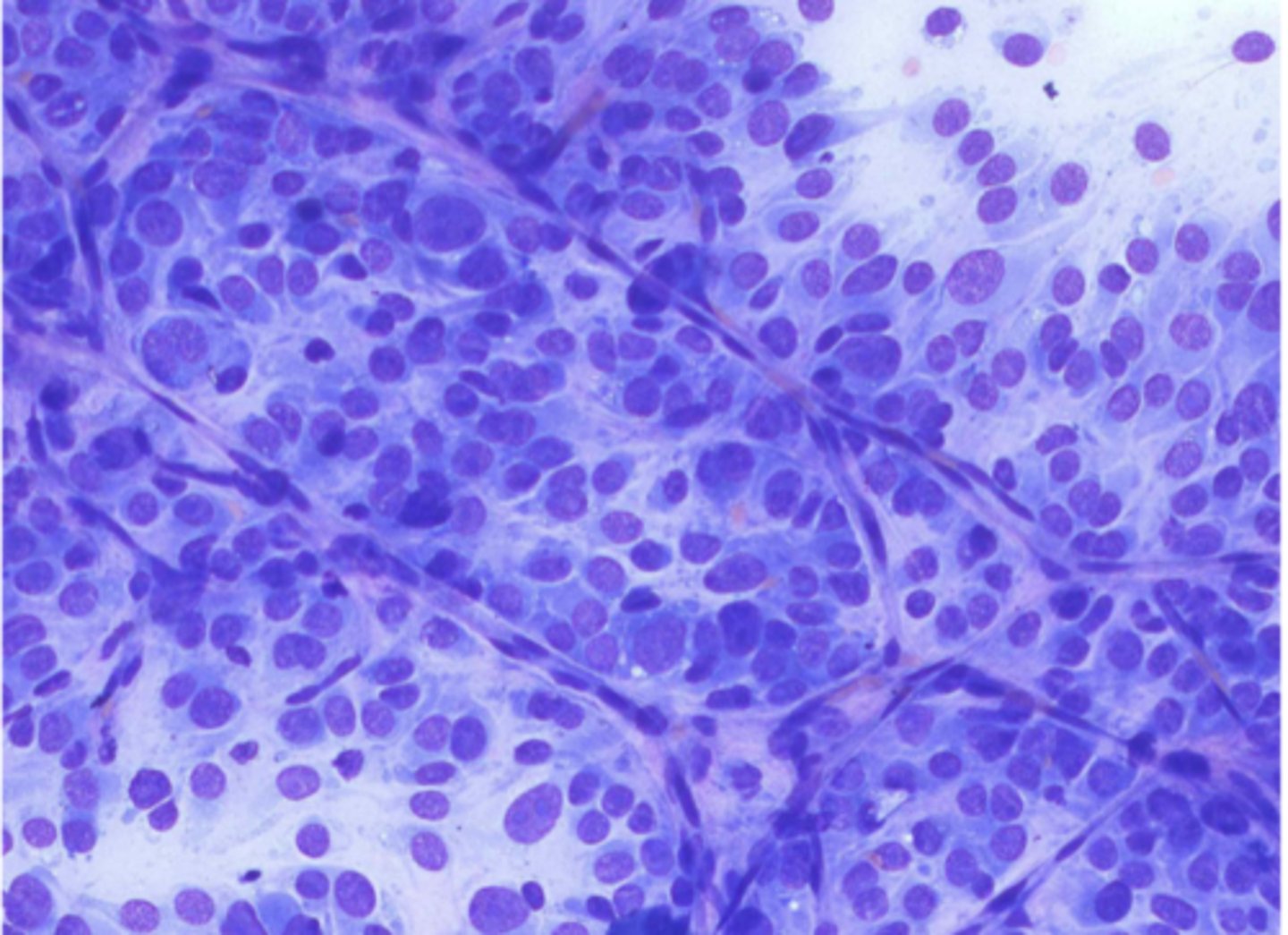
You are examining a slide of a perivascular wall tumor. You note wispy cytoplasm, cells that break away from the sheet, and crown cells.
What is your top differential?
Hemangiopericytoma
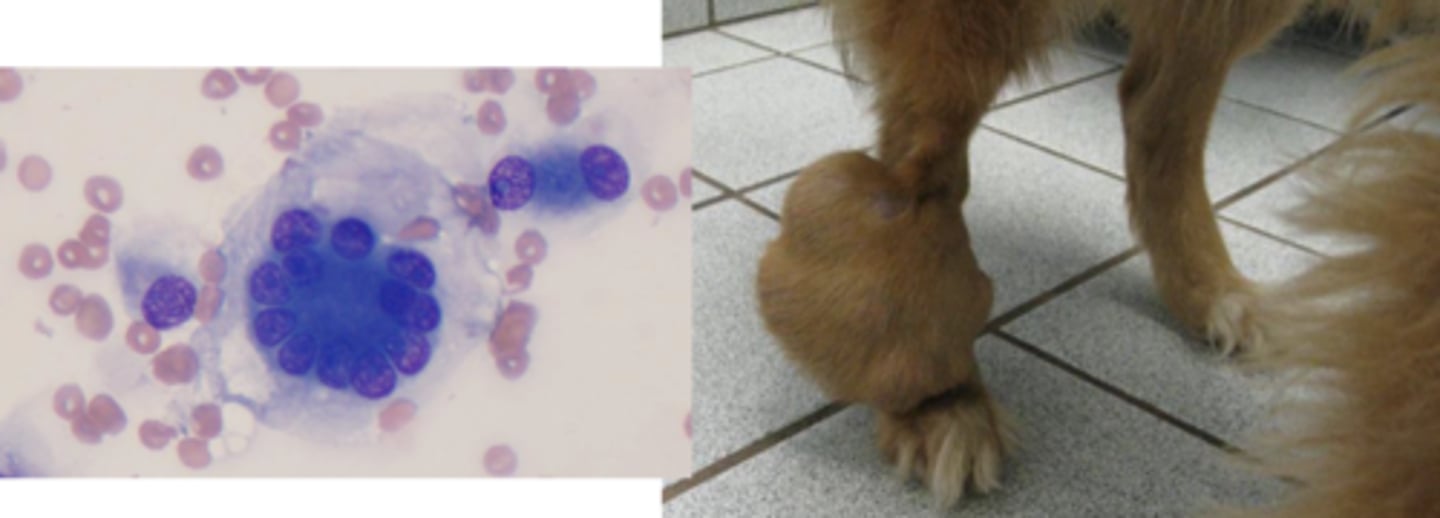
What type of tumor is this?
Hemangiopericytoma
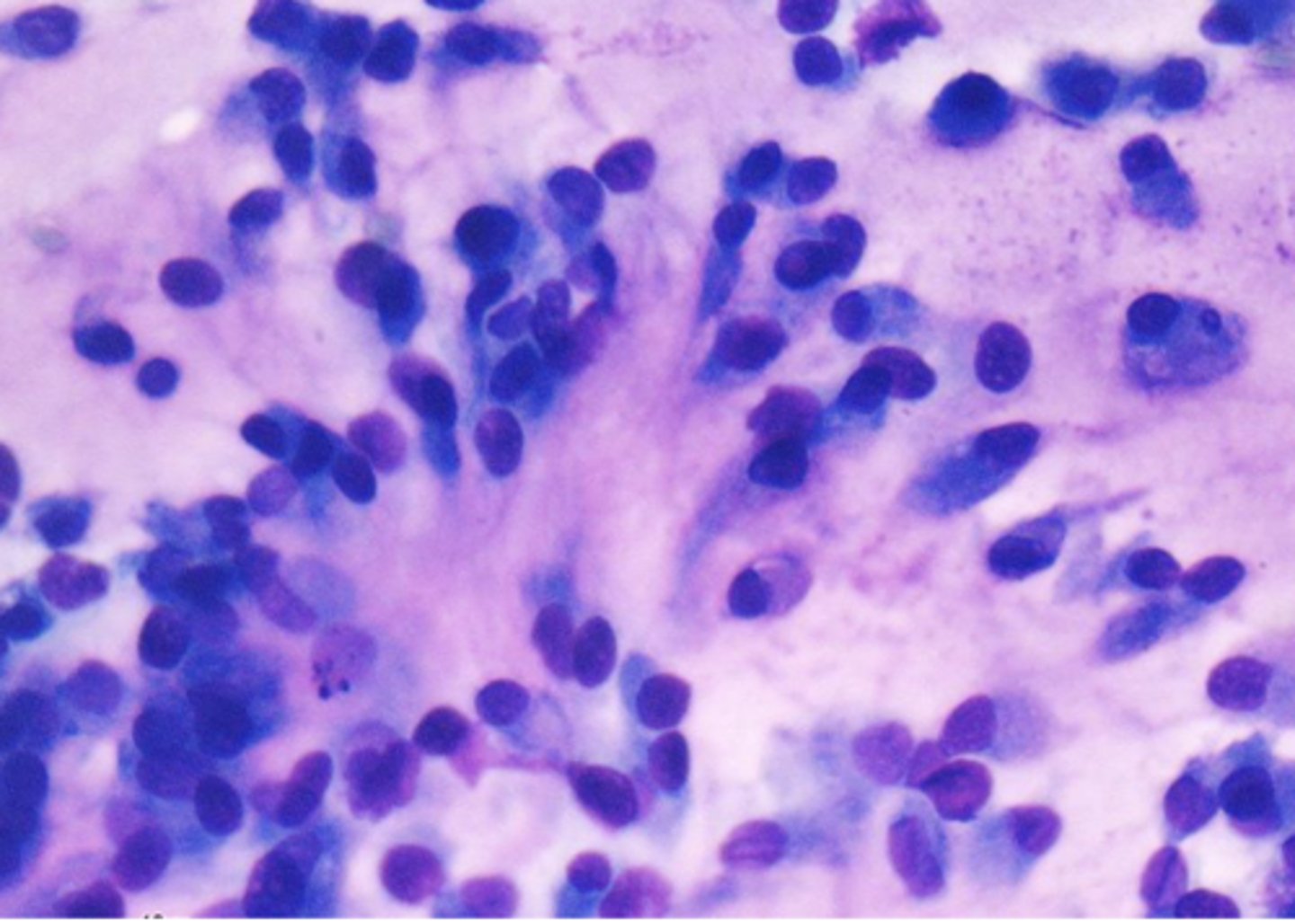
You take a cytology sample from the brachial plexus area from a dog exhibiting signs of pain, lameness to muscle atrophy, and paresis.
The sample appears to have palisading spindle cells
What is your top differential?
Peripheral nerve sheath tumor
-maybe schwannoma
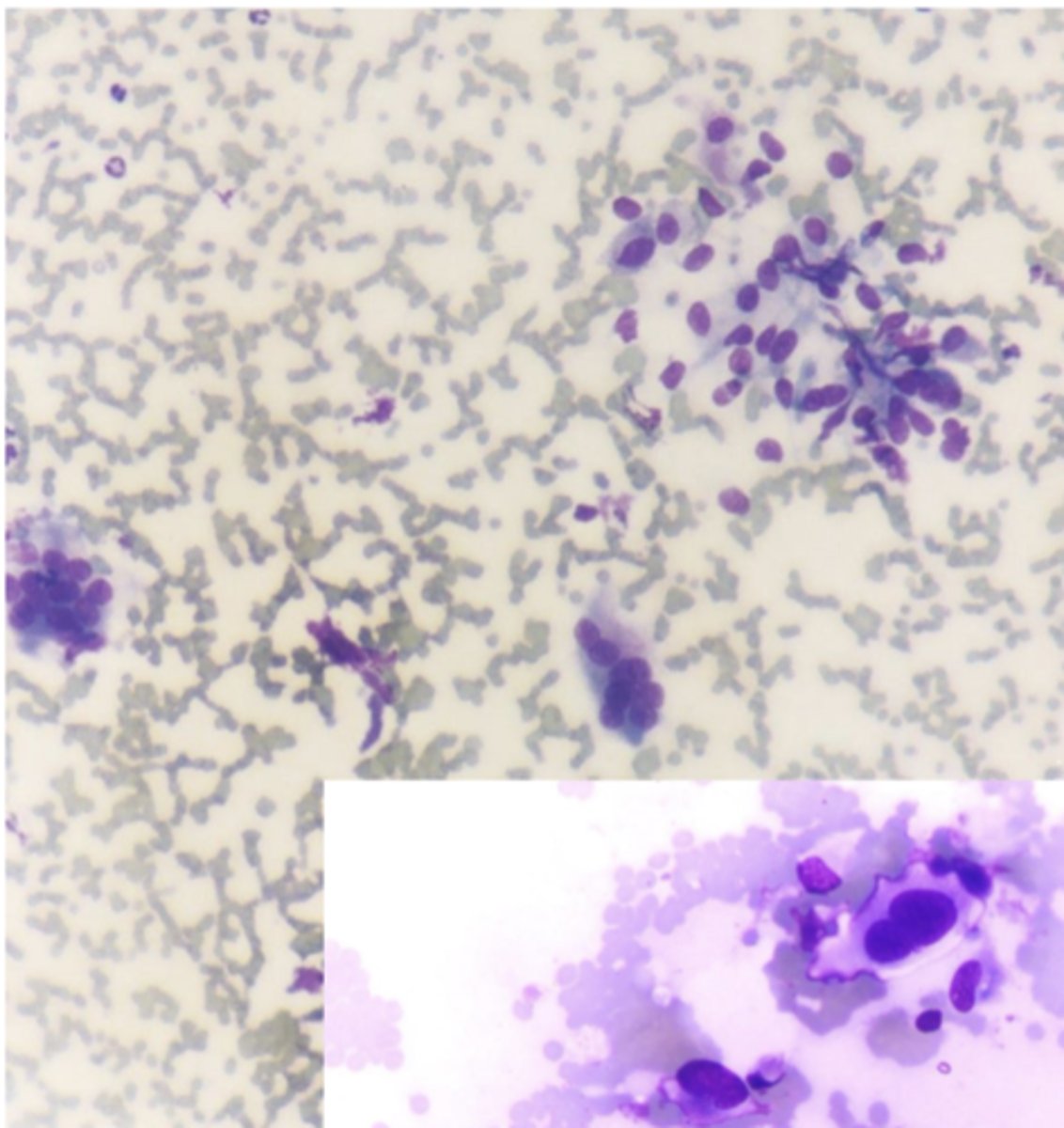
what type of neoplastic tumor is this?
Fibrosarcoma
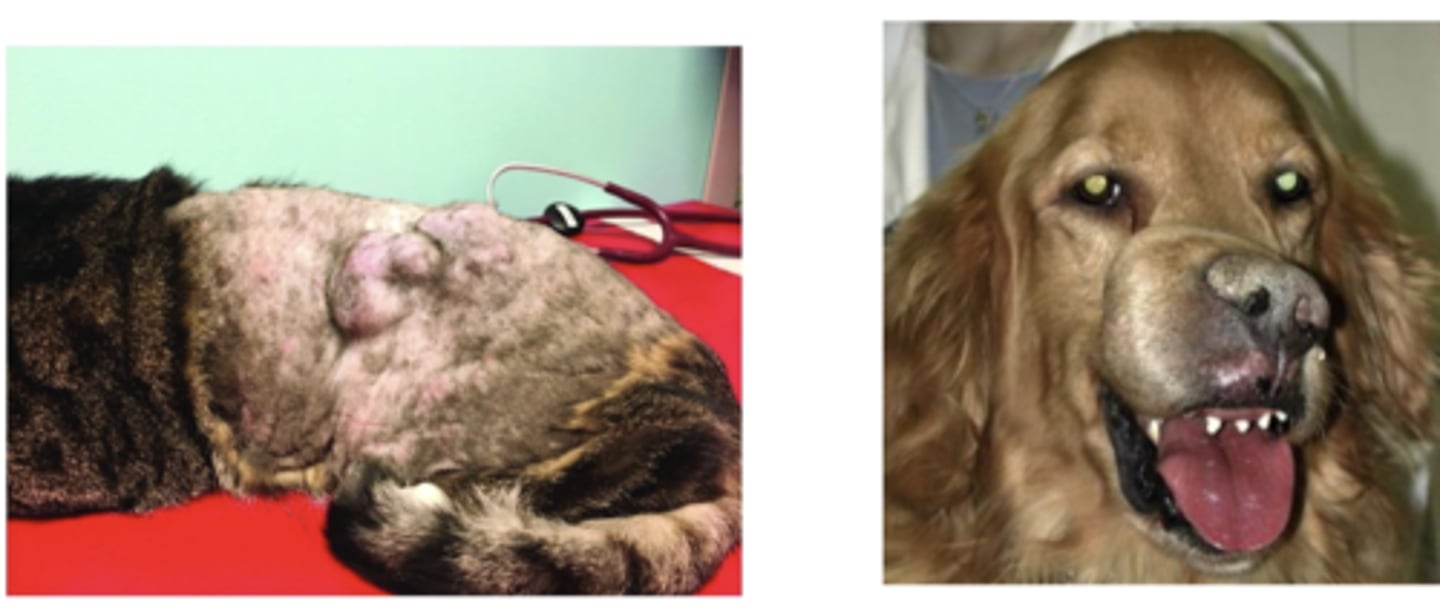

what type of neoplastic tumor is this?
Fibrosarcoma
-Common on trunk, extremities
• Firm, fleshy, involving dermis, SC and possible muscle
• Invasive, rarely metastasizes
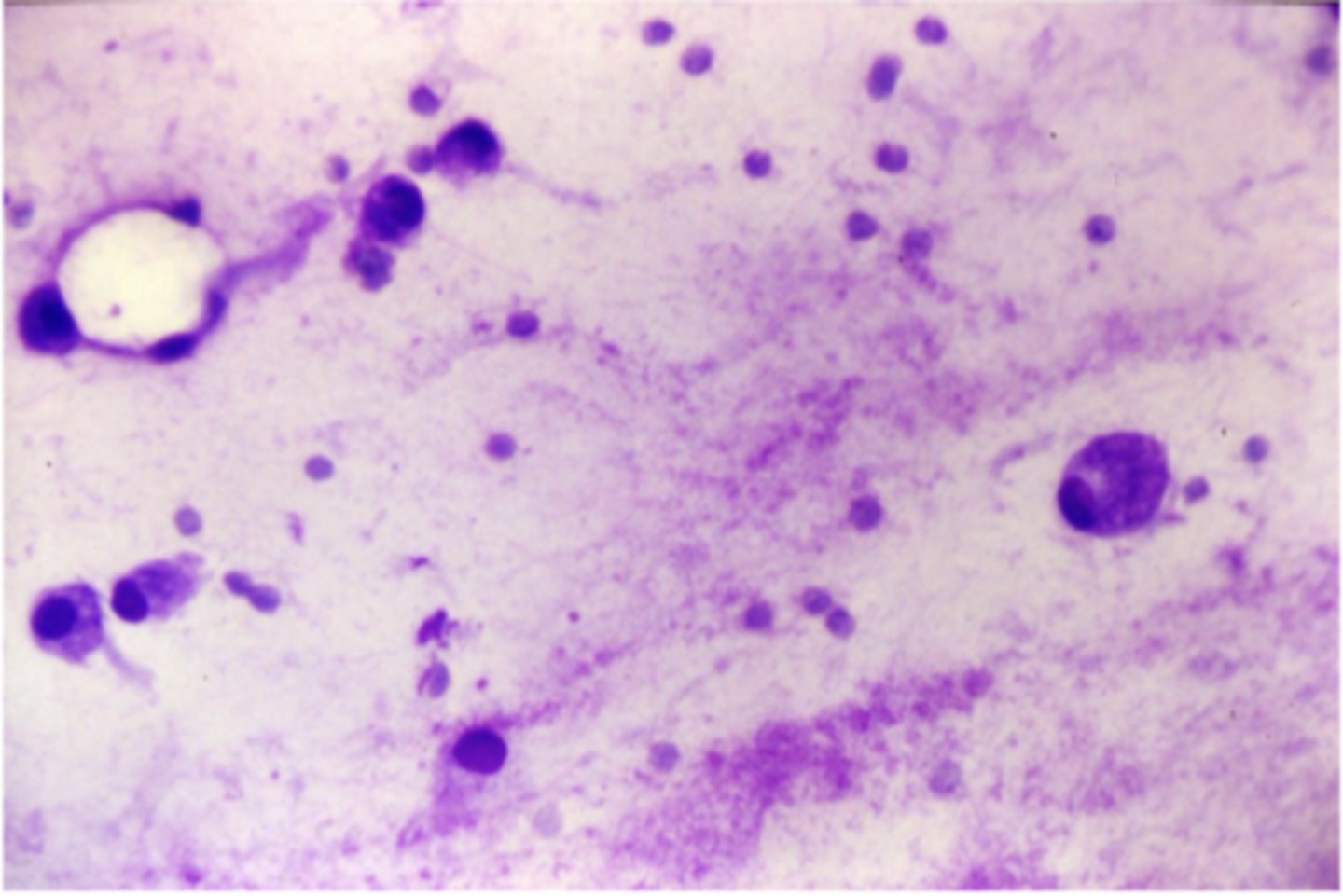
What type of neoplastic tumor is this?
Myxosarcoma/Myxoma
-rare
-fibroblast origin
-soft, fluctuant mass
-spindle-shaped cells
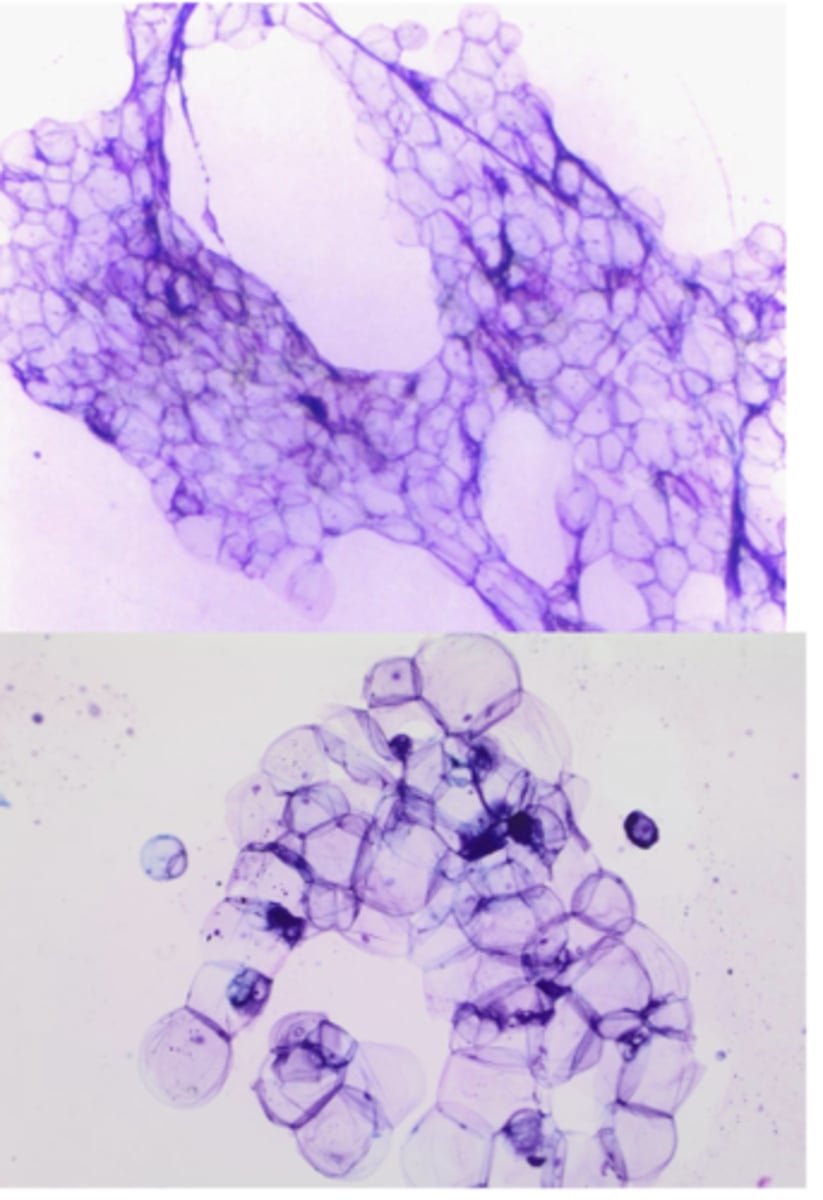
You take a FNA of a soft, movable mass within the subcutis and note this on your sample.
What is youe top differential?
Lipoma
-very common
-hard to stain slide: use new methylene blue or Oil Red O
-Lipocytes have a large, clear cytoplasm
-tiny nucleus pushed to one side
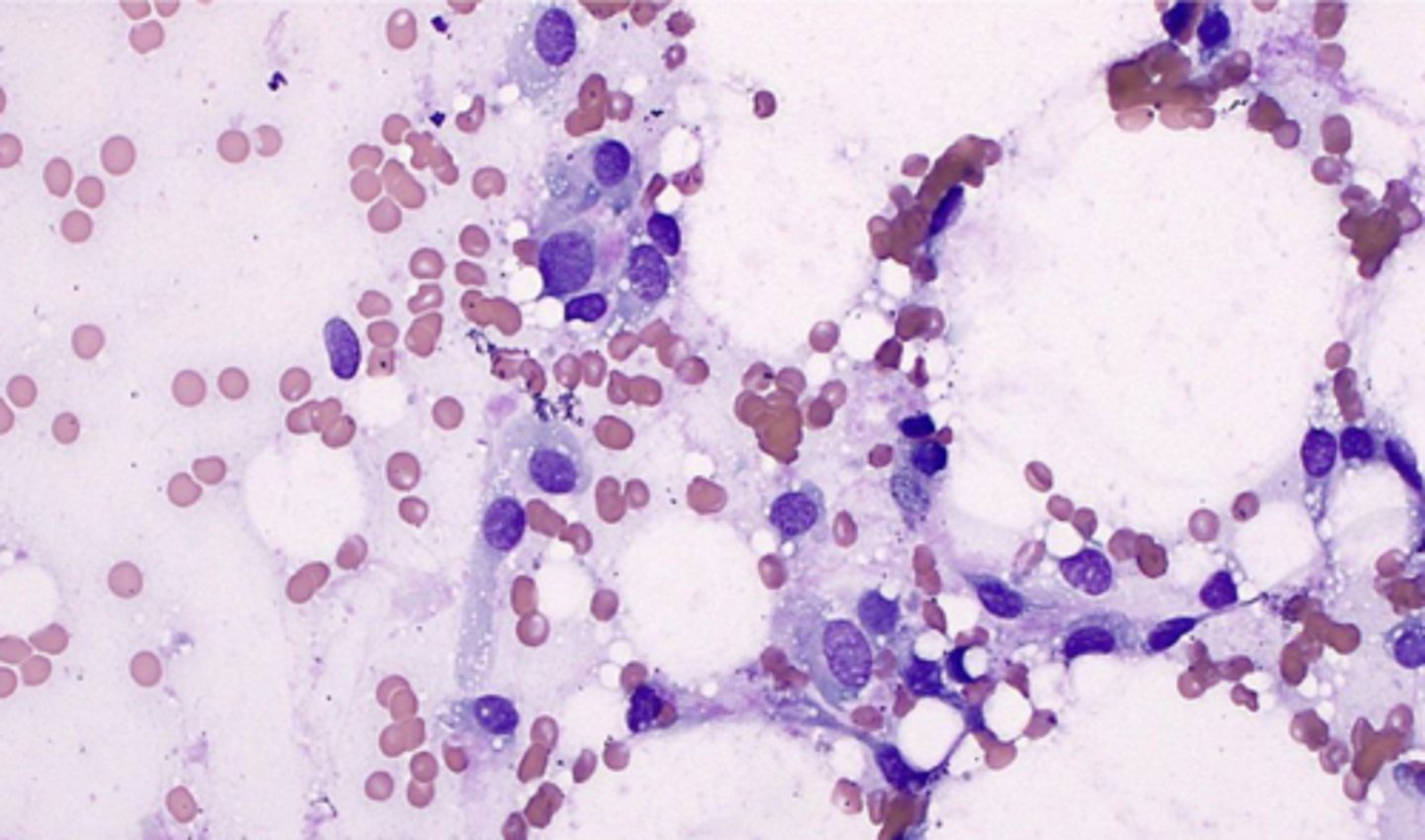
You take an FNA from a dog with a firm, poorly circumscribed, adherent to the underlying tissue mass.
On the slide, you note plump, spindle cells with large nuclei, fat vacuoles in the cytoplasm.
What is your top differential?
Liposarcoma
-possibly metastatic
-can also recur
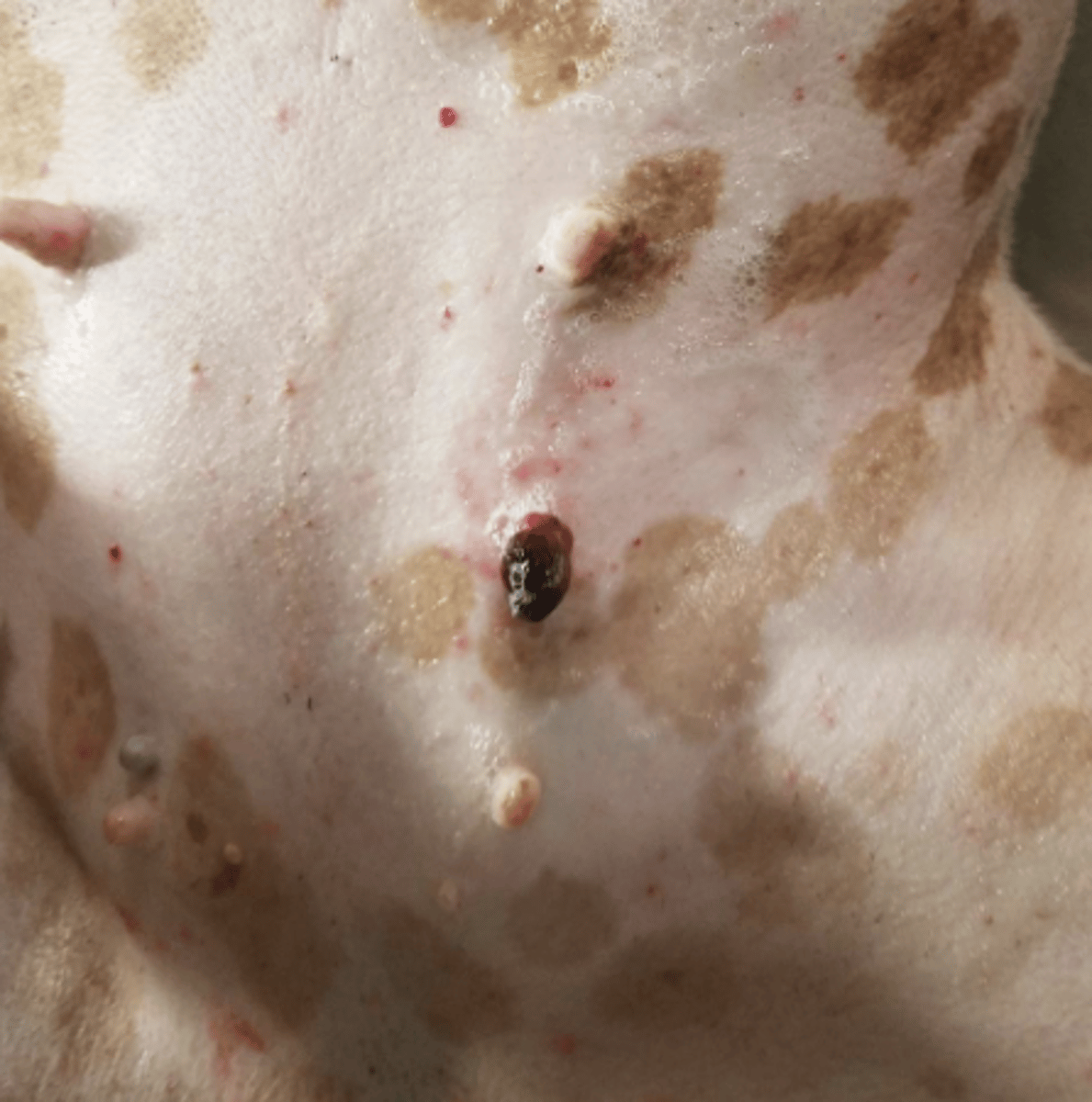
You are examining a dog with a light colored coat that likes to sunbathe. You note this red/purple nodule on the ventral aspect of its trunk.
What is your top differential?
Hemangiosarcoma
-Extends into SC or muscle: locally invasive and morelikely to metastasize
-Typically singular SC mass that bruise or bleedeasily, +/- painful
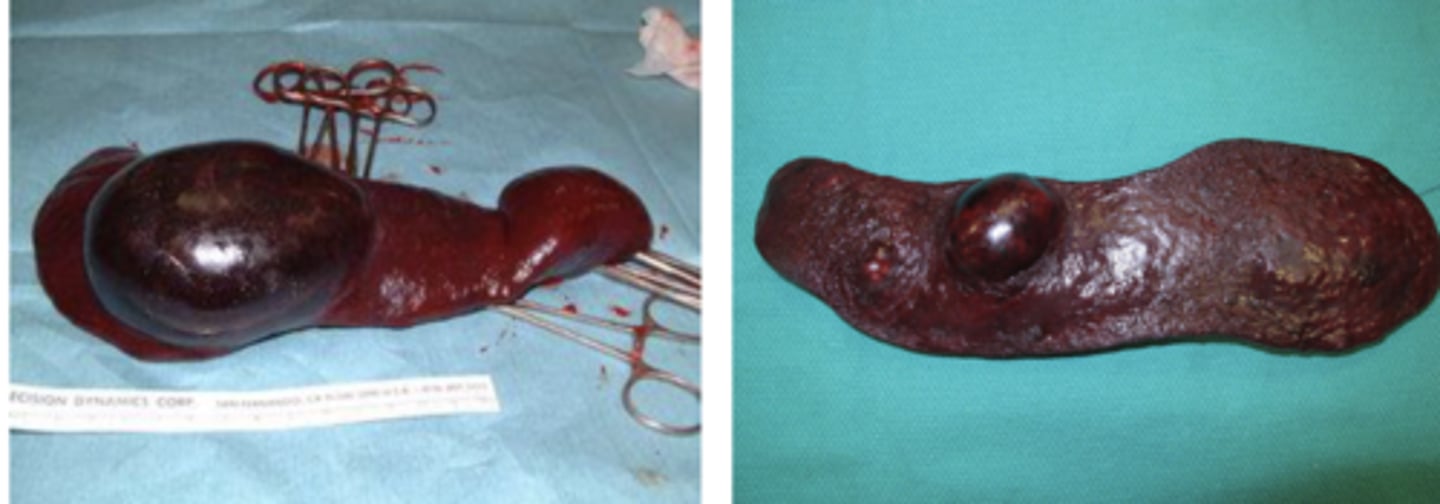
Are these masses a hemangioma or hemangiosarcoma?
can't say !
-biopsy is required to differentiate
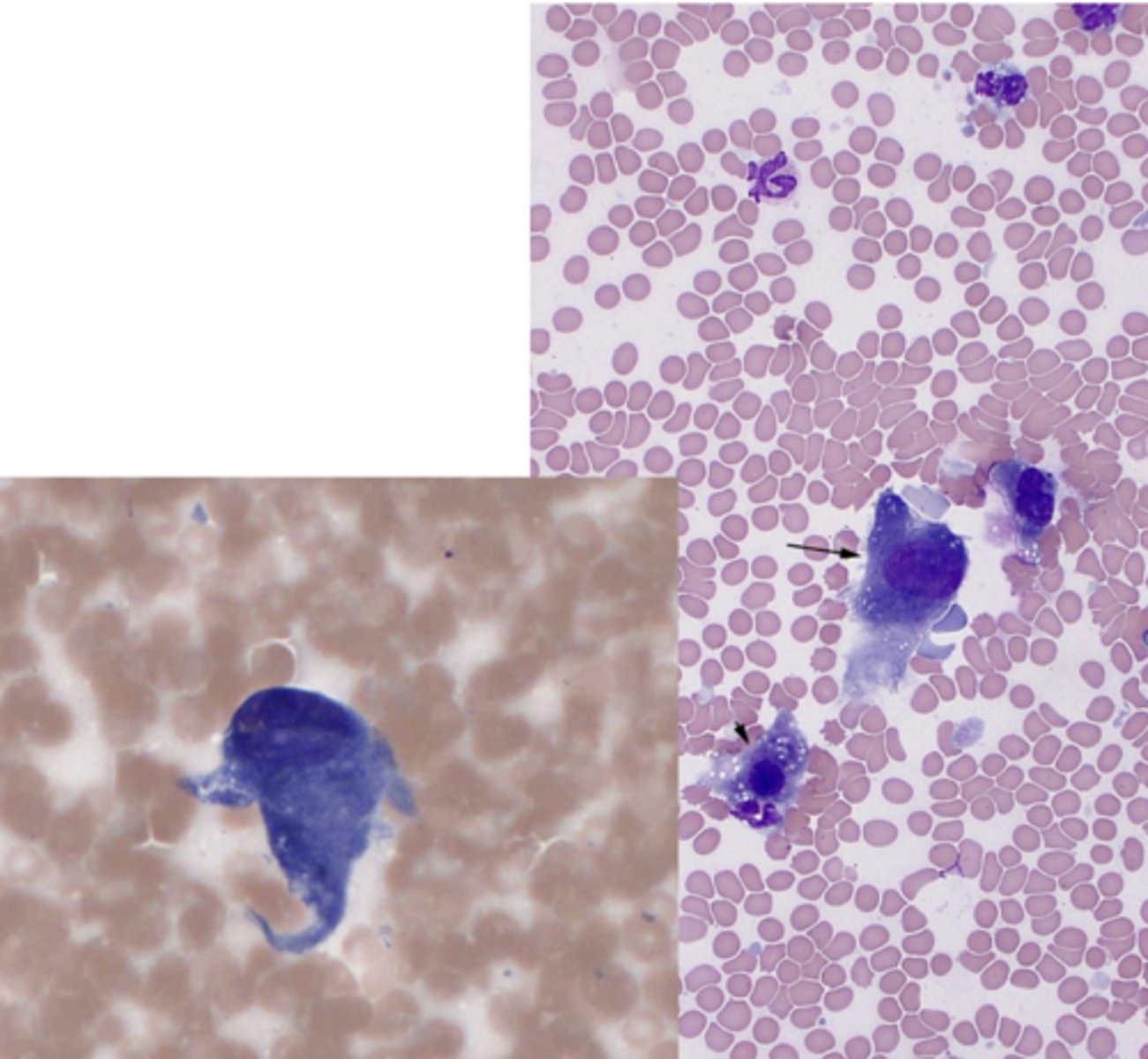
What kind of neoplastic tumor is this?
Hemangiosarcoma
-lots of RBC
-macrophages with hemosiderin
-spindle-shaped, plump cells
-basophilic cytoplasm: clear vacuoles
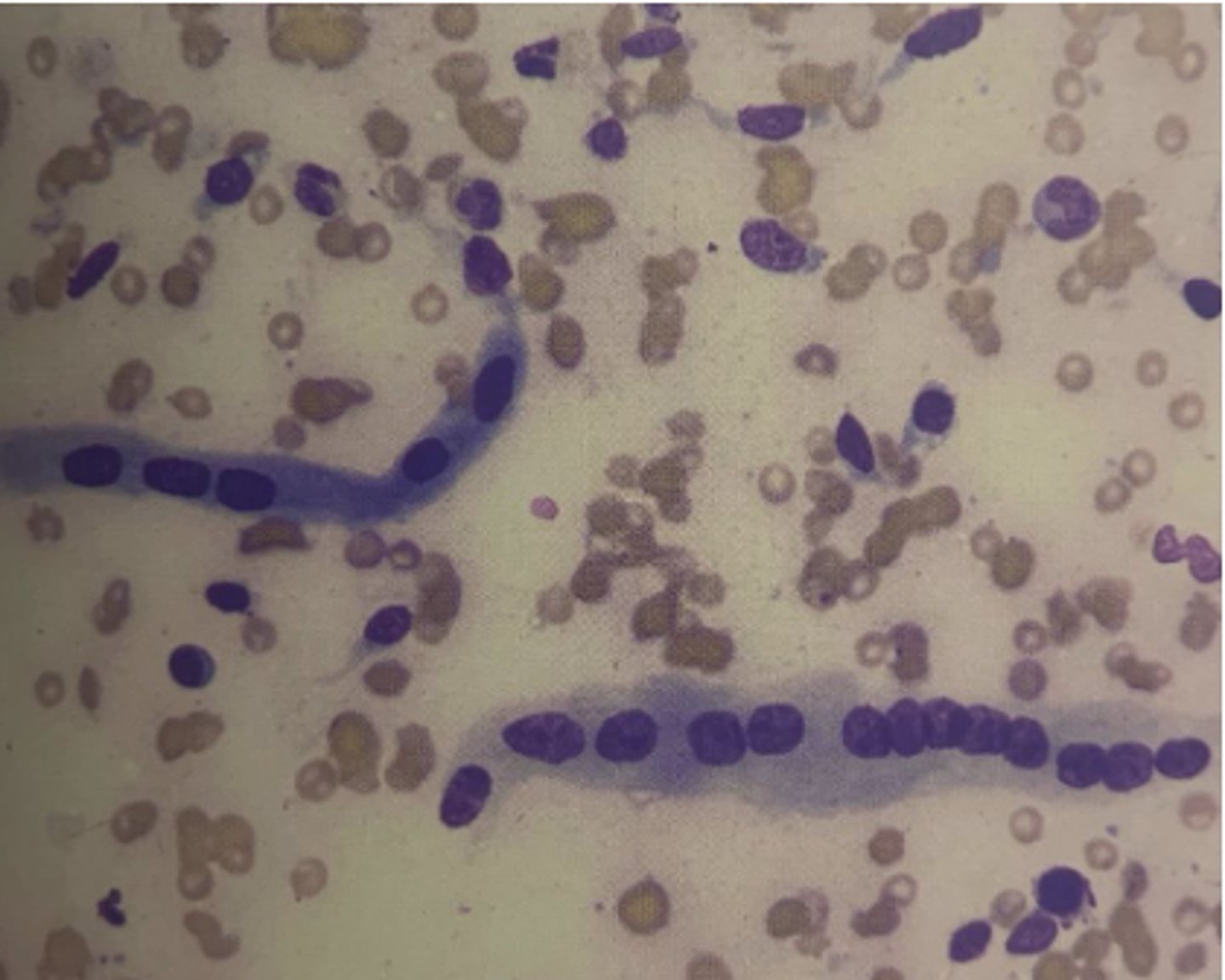
You are examining a cytoplogy slide of multinucleated "strap cells" arranged in a row taken from skeletal muscle myocytes in a dog.
What is your top differential?
Rhabdomyosarcoma
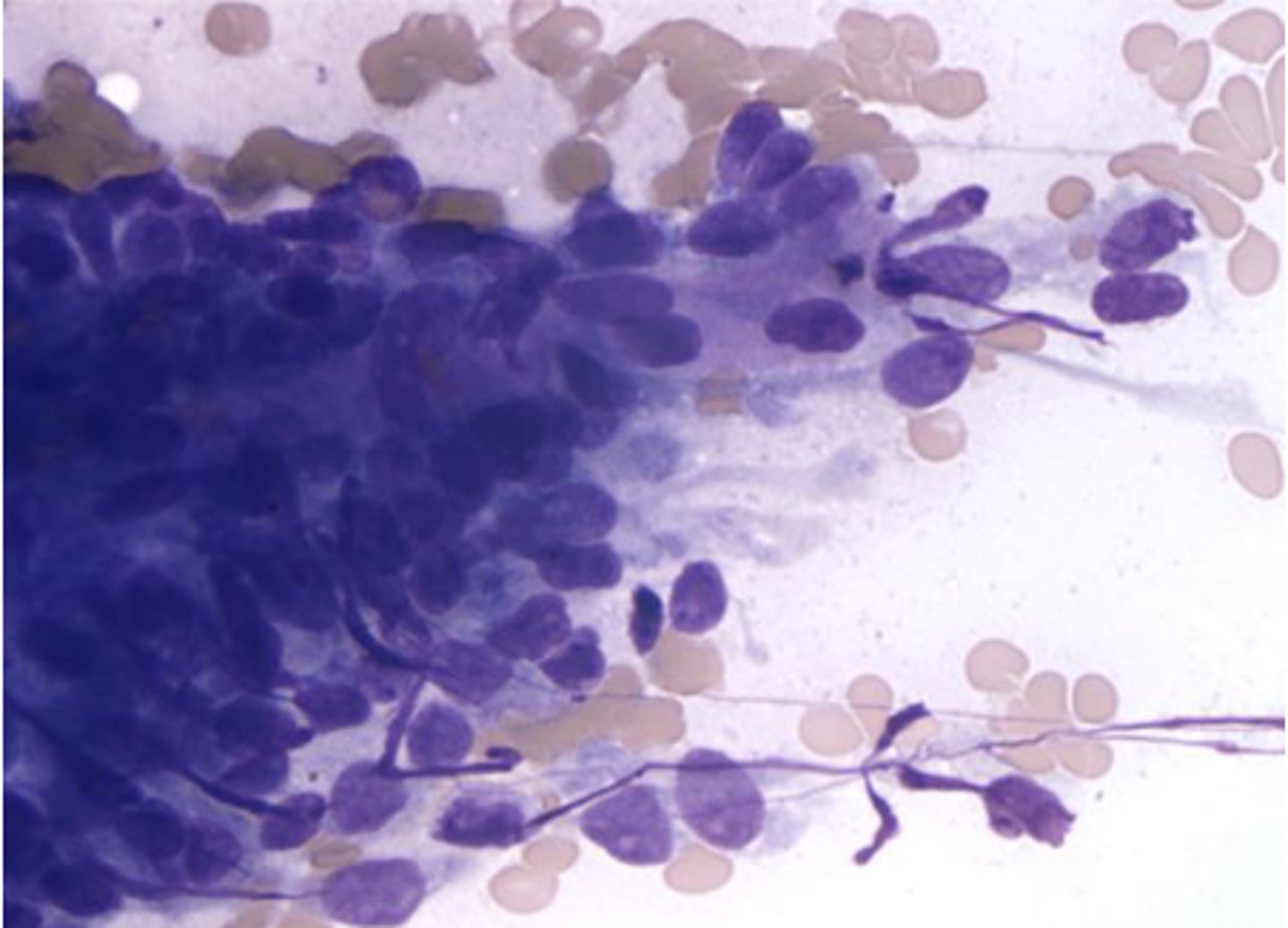
You are examining a cytology slide derived from smooth muscle and note these cigar-shaped nuclei.
What is your top differential?
Leiomyosarcoma/Leiomyoma Gastrointestinal stromal cell tumor
-Need IHC to dx GIST vs LS
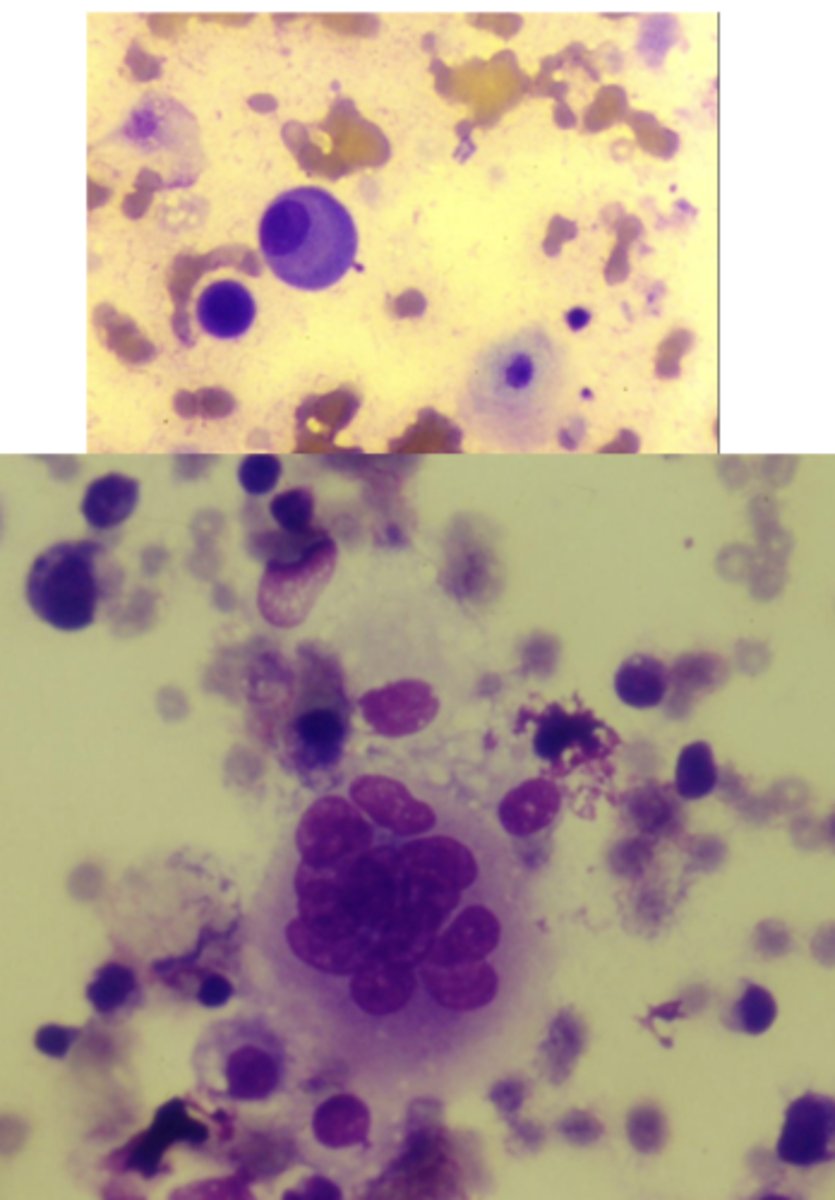
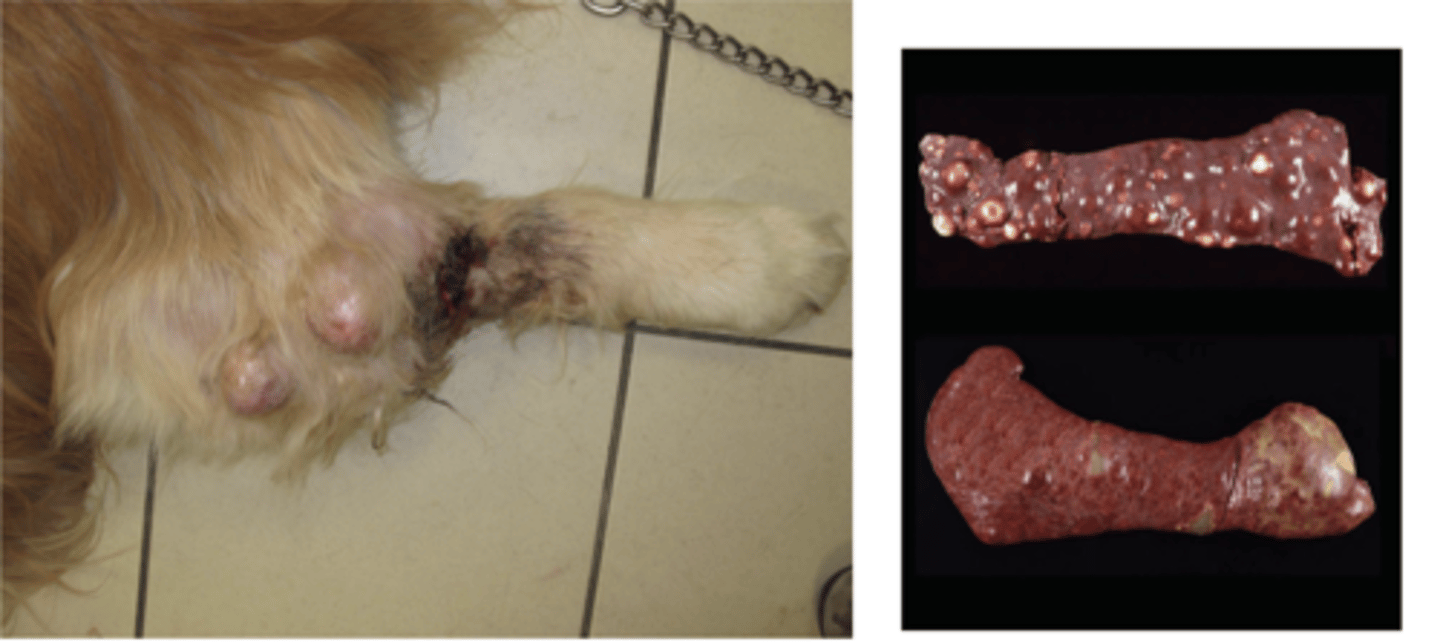
This is a cytology slide taken from a long bone of a large breed dog.
What is your top differential?
osteosarcoma
-very cellular
-Osteoblast with basophilic cytoplasm + pink granules
-osteoclasts
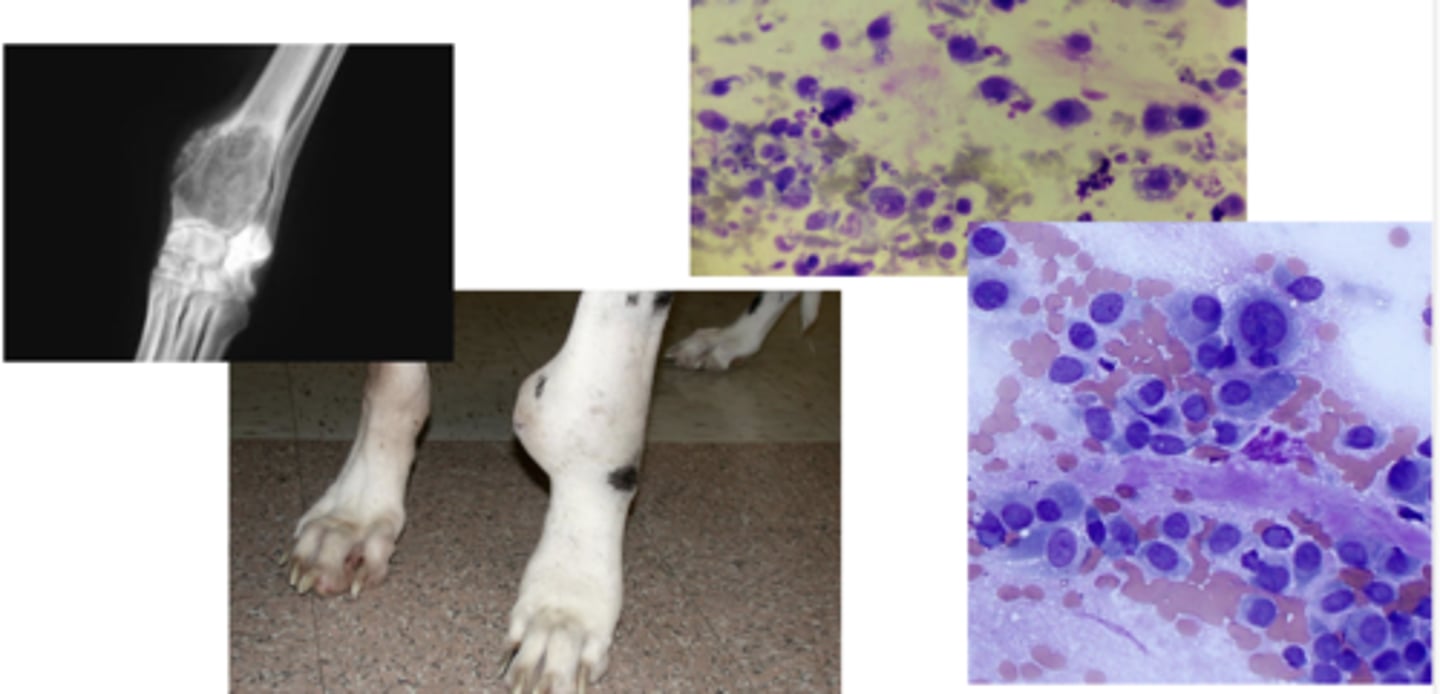
What kind os neoplastic tumor are these characteristic of ?
Osteosarcoma
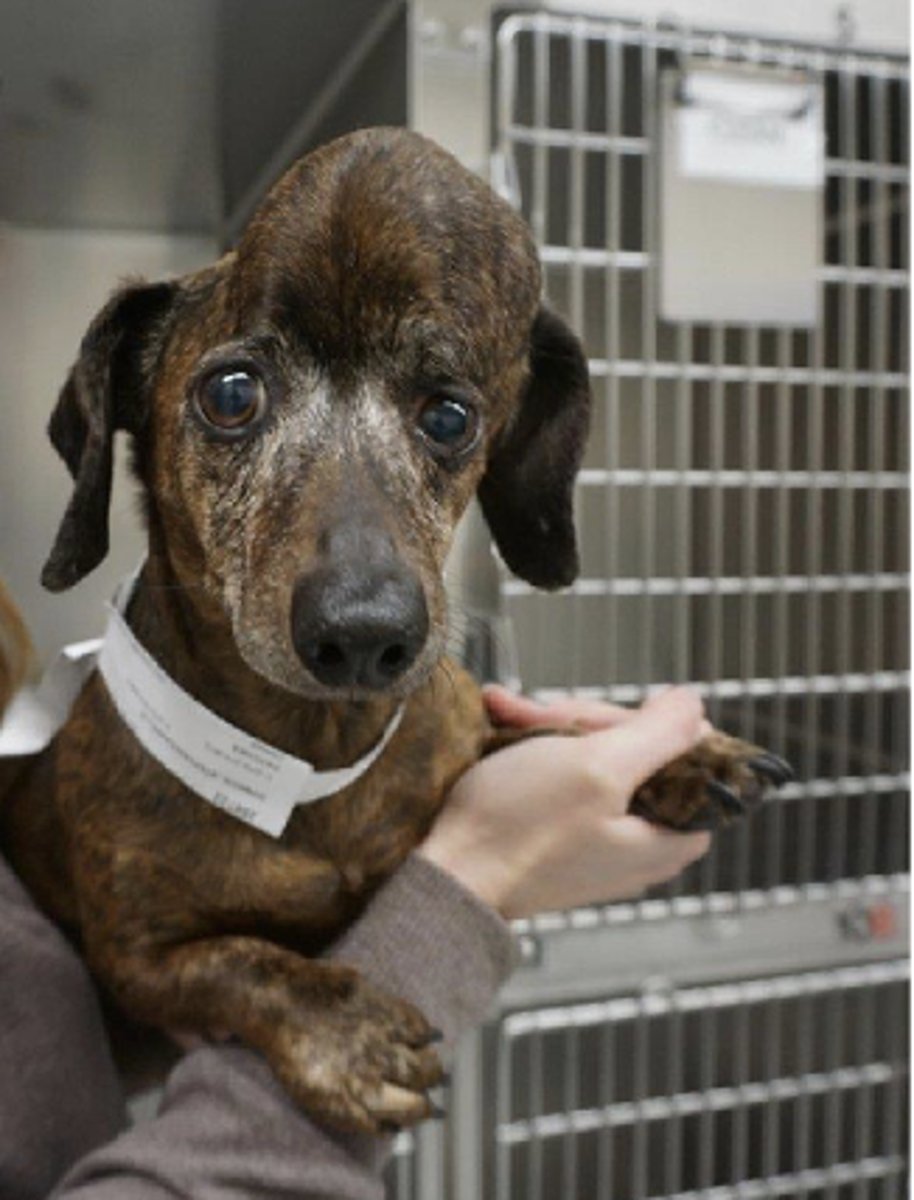
What kind of rare tumor does this dog have that is affecting its skull- and looks like a popcorn call on rads?
Multi-lobular osteochondrosarcoma
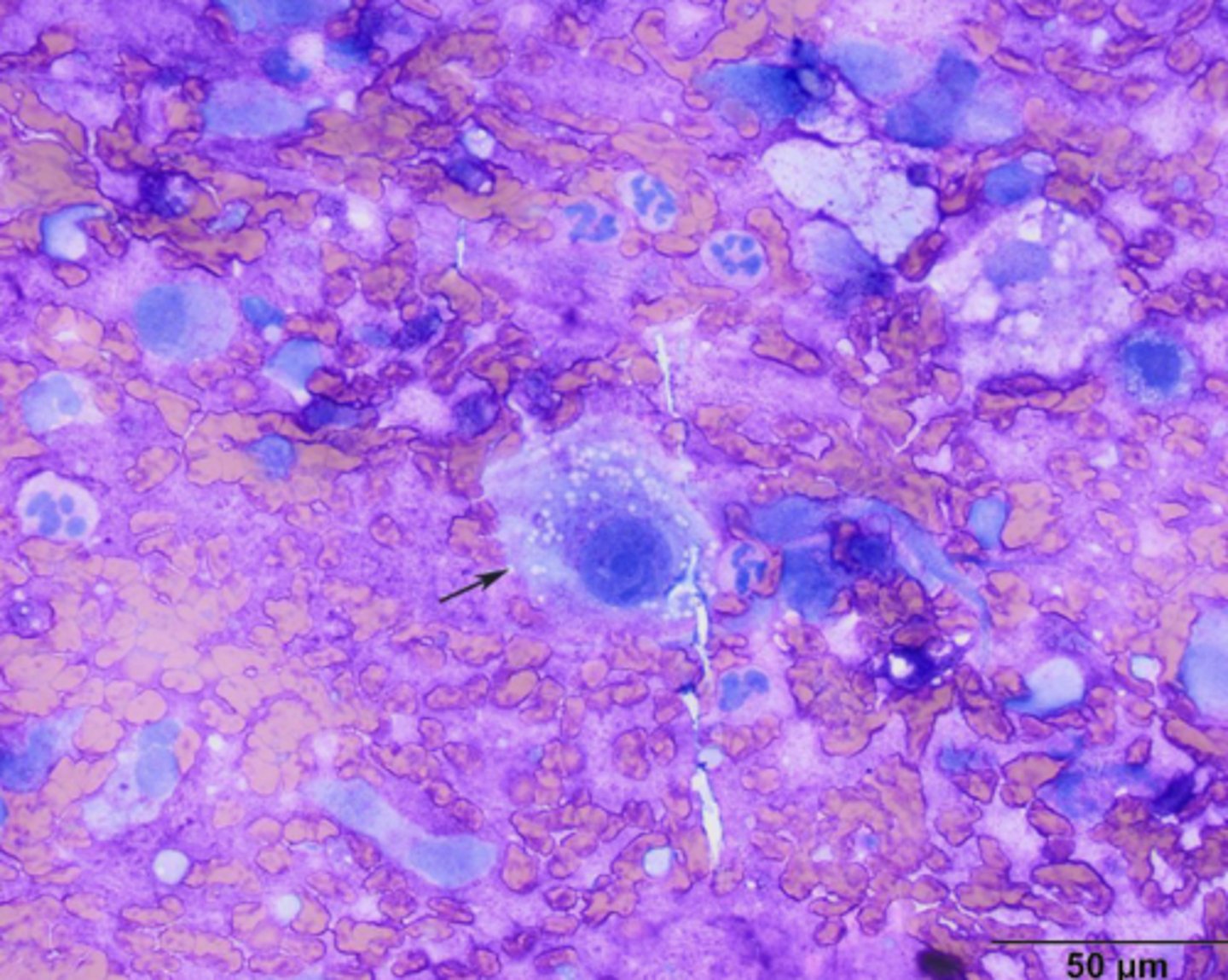
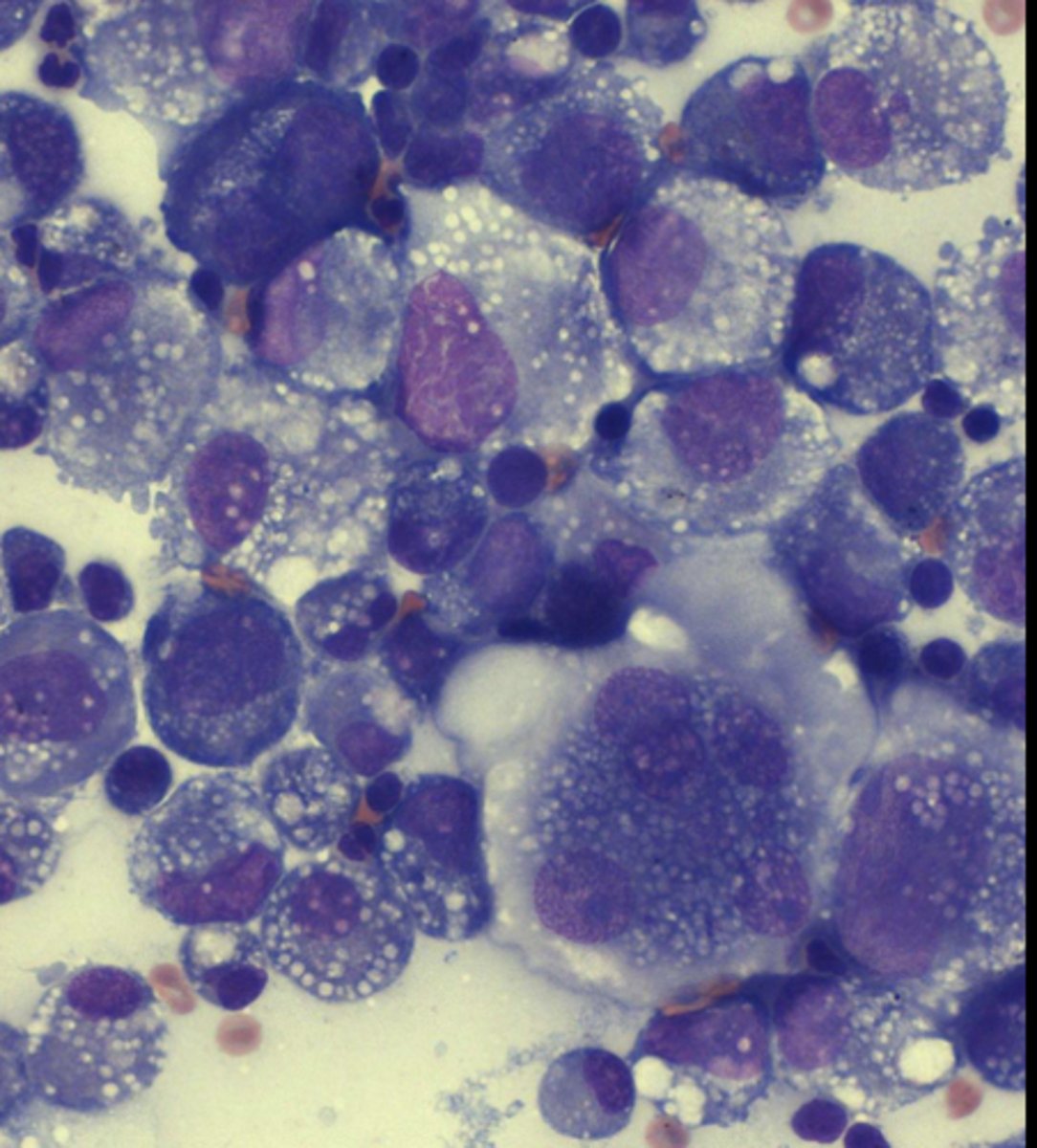
On this cytology sample, you note a bright, pink pool of granular material and round-spindle-shaped, large nuclei, blue cytoplasm with small, clear vacuoles.
What is your top differential?
Chrondrosarcoma
-2nd most common bone tumor
-has chondroids and chrondroblasts
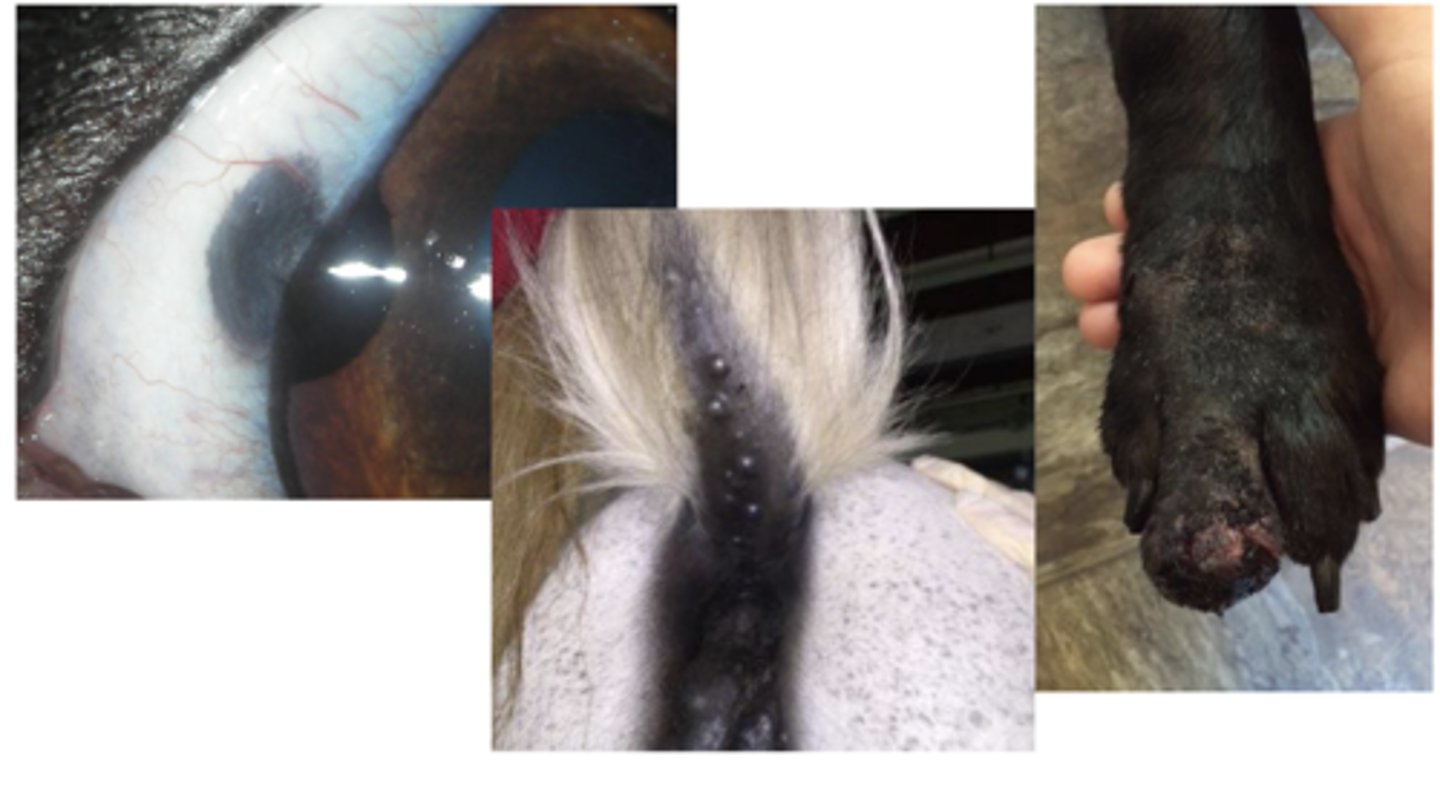

What type of neoplastic tumors are these?
Melanocytic tumors
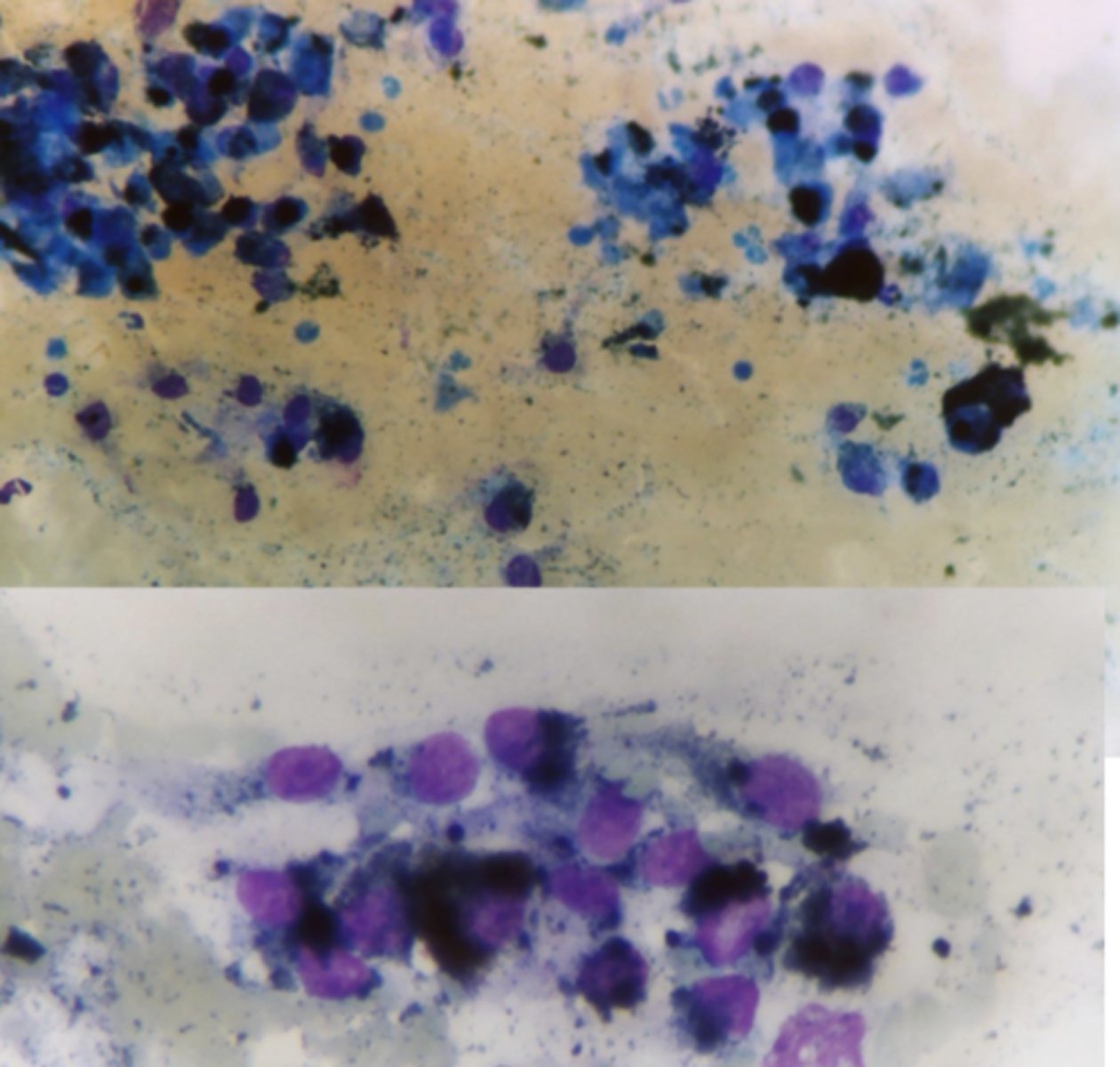
What type of tumor is this cytology sample taken from?
Melanocytoma/Malignant melanoma
-Heavily pigmented: dark black, circular cells, cell detail is obscured, may see free melanin granules in the background
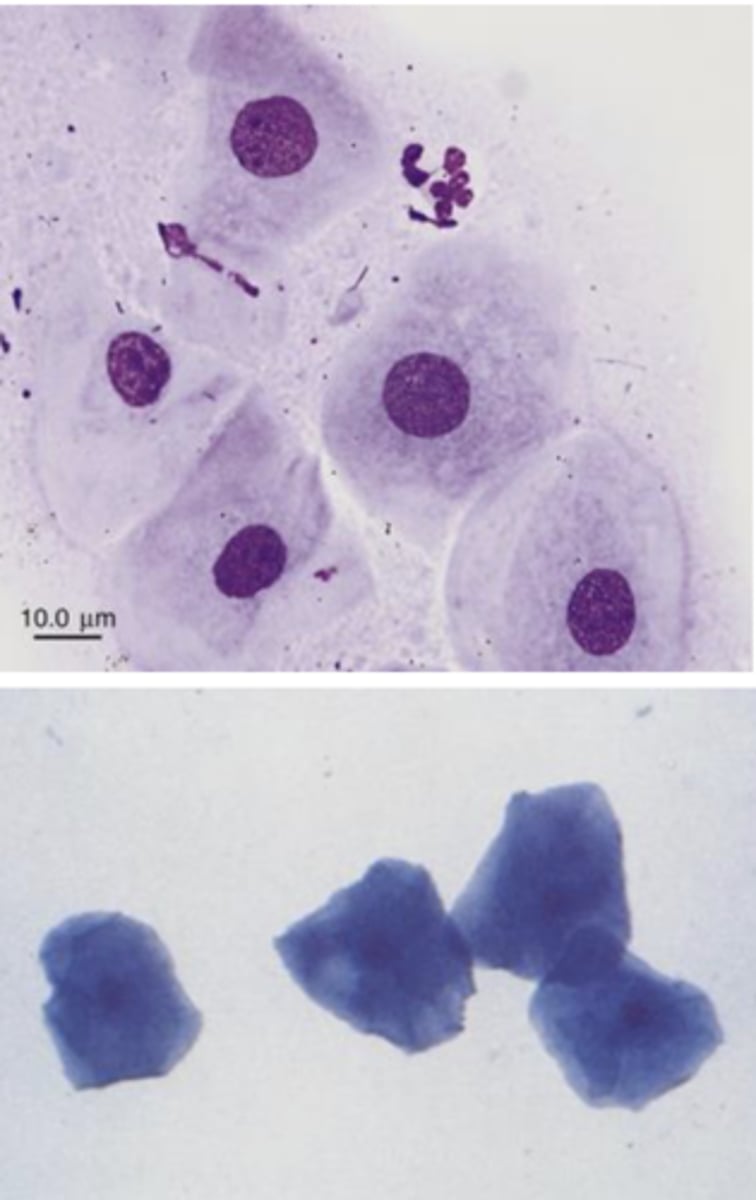
What type of cells are these?
Epithelial cells
-found in scrapes/swabs, washes, normal exfoliation
-can be found in hyperplasia and neoplasia
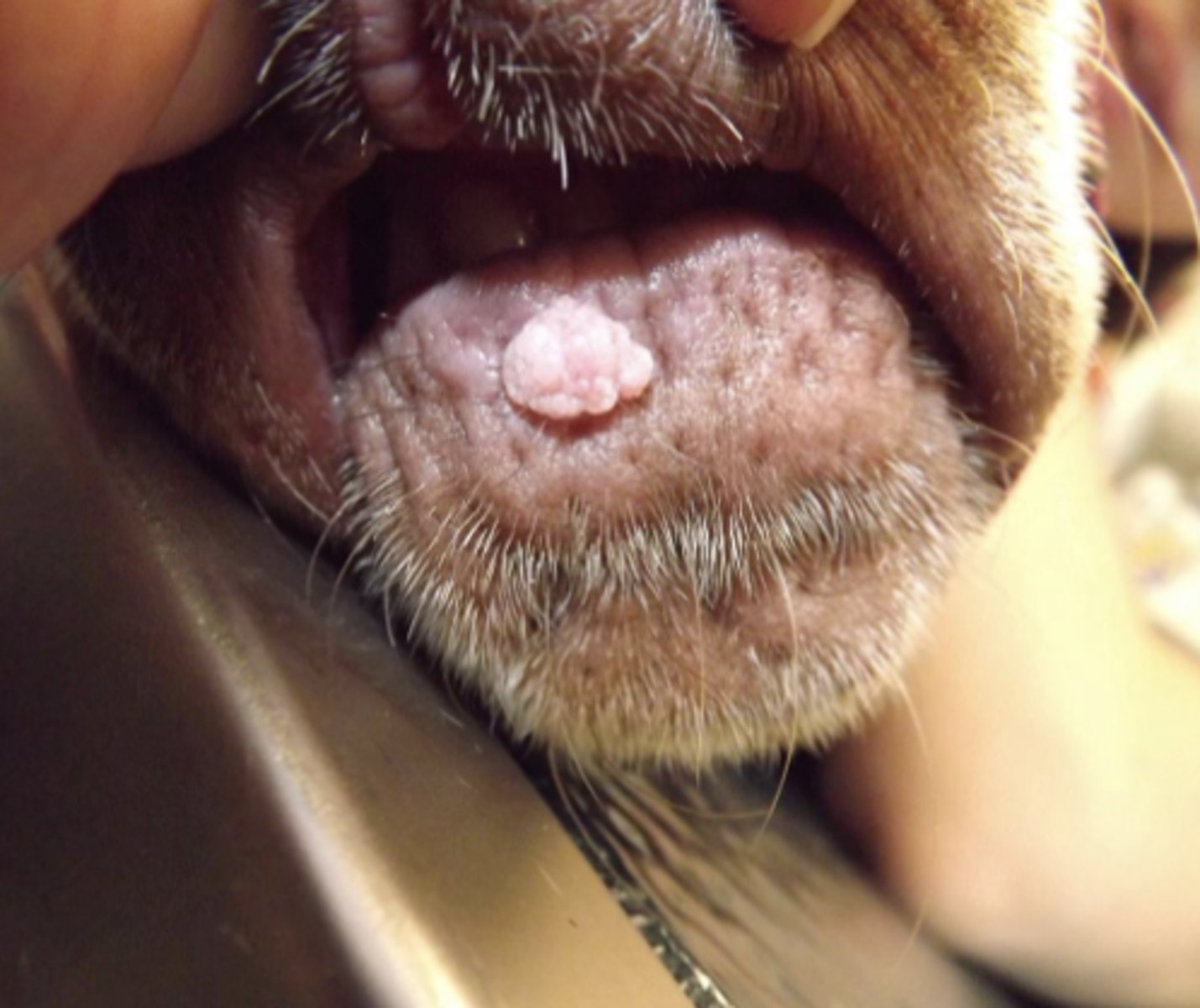
What type of tumor is this- pedunculated, papillated, "cauliflower" like. ?
papilloma
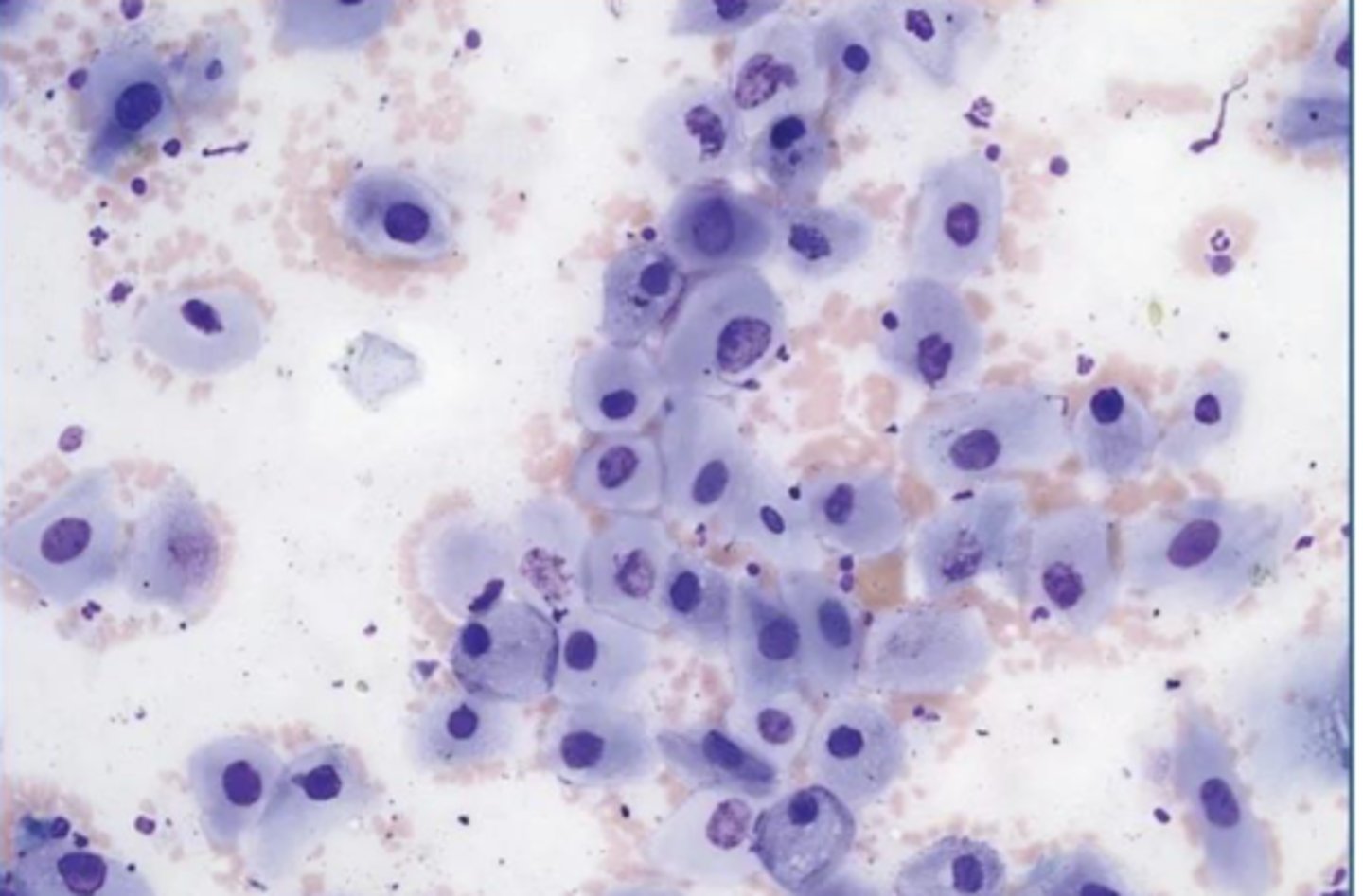
You are examining a slide with large, ovoid to spindle-shaped cells with large, eccentric nuclei.
What is your top differential?
Papilloma
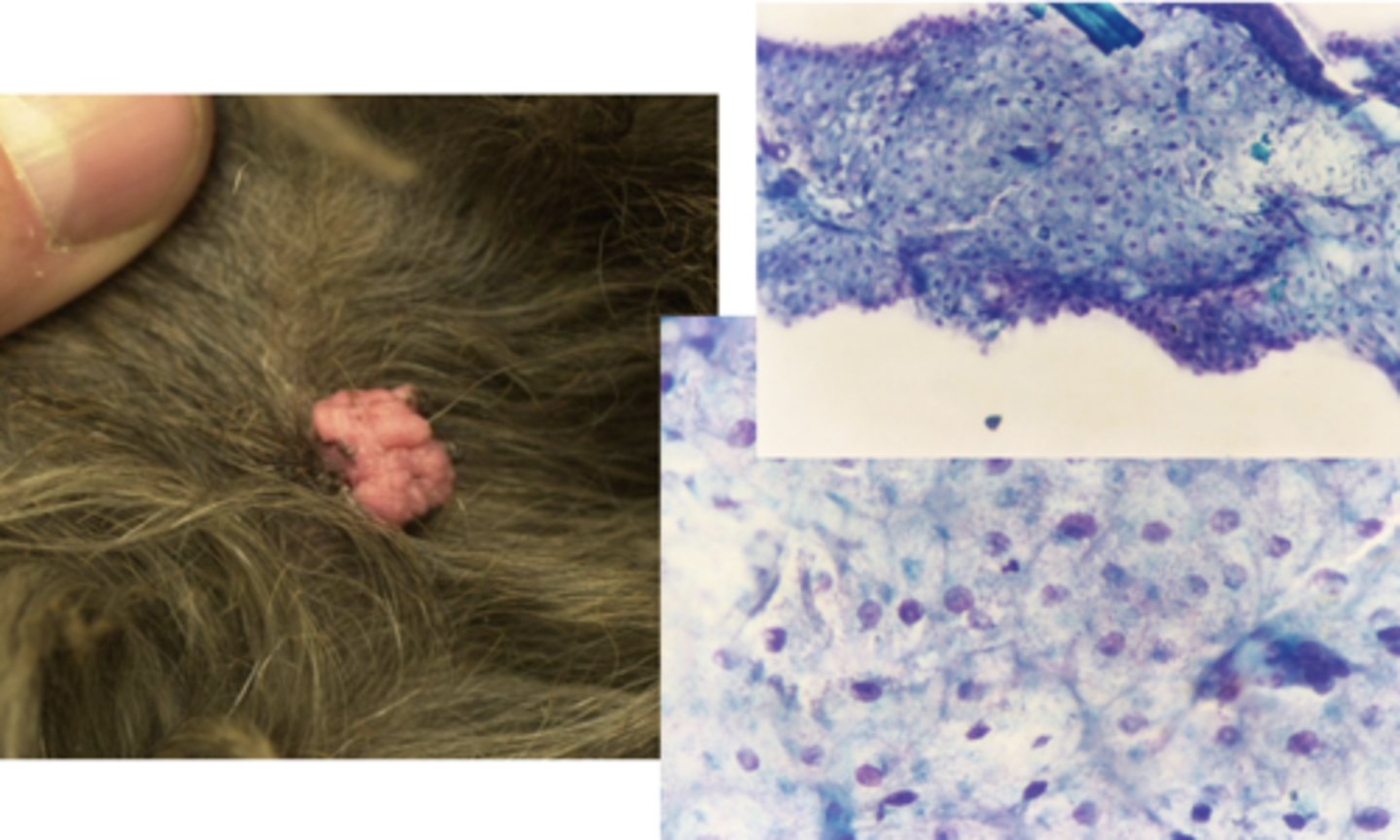
What type of tumor is this?
Sebaceous tumors
-cluster of well-differentiated sebocytes
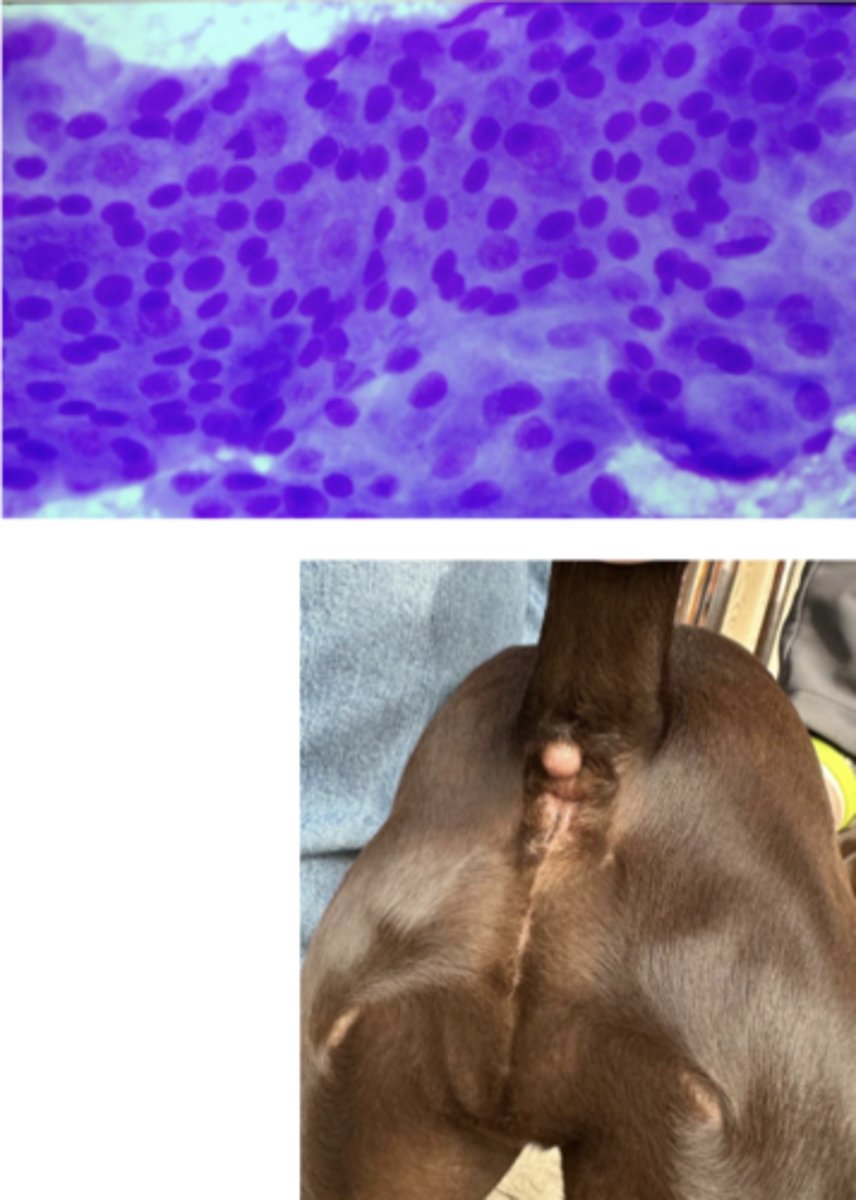
You are examining an older, intact male dog and note this round, pink mass in its perianal region. You make a cytology slide and note these cells that appear similar to hepatocytes that are round, abundant, fine-granular with a pinkish/blue cytoplasm with a very dark nucleus.
What is your top differential?
Perianal gland tumor
What are the 3 types of Apocrine Gland tumors?
-AGASACA
-Cerminous gland (ear)
-Sweat gland adenomas
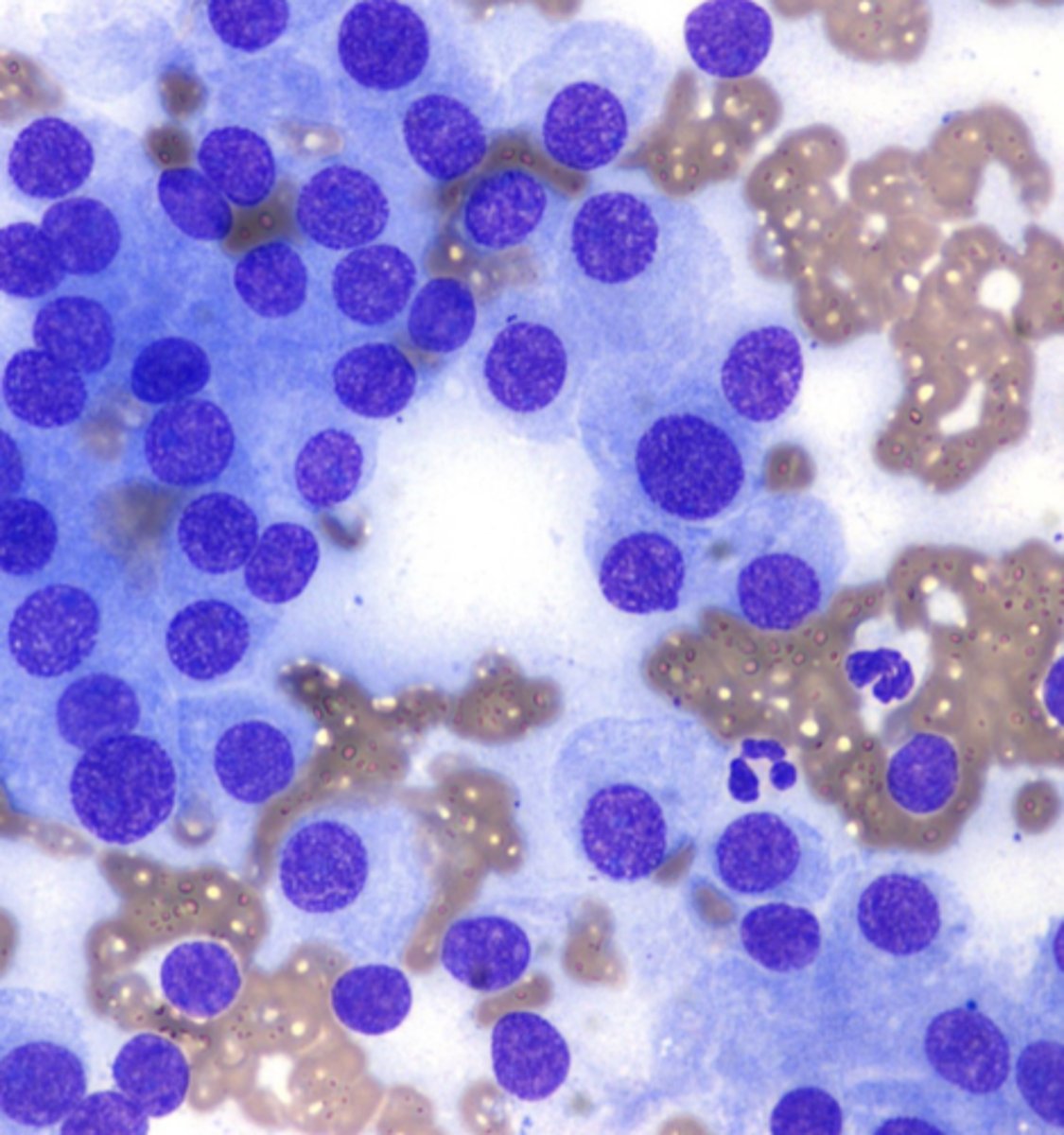
You are examining a cytology slide taken from a mass affixed to the anal sacs and note these clusters of moderately sized cells, round nuclei with stippled chromatin, moderate pale cytoplasm, and indistinct borders.
What is your top differential?
AGASACA - Apocrine gland adenocarcinoma of the anal sac
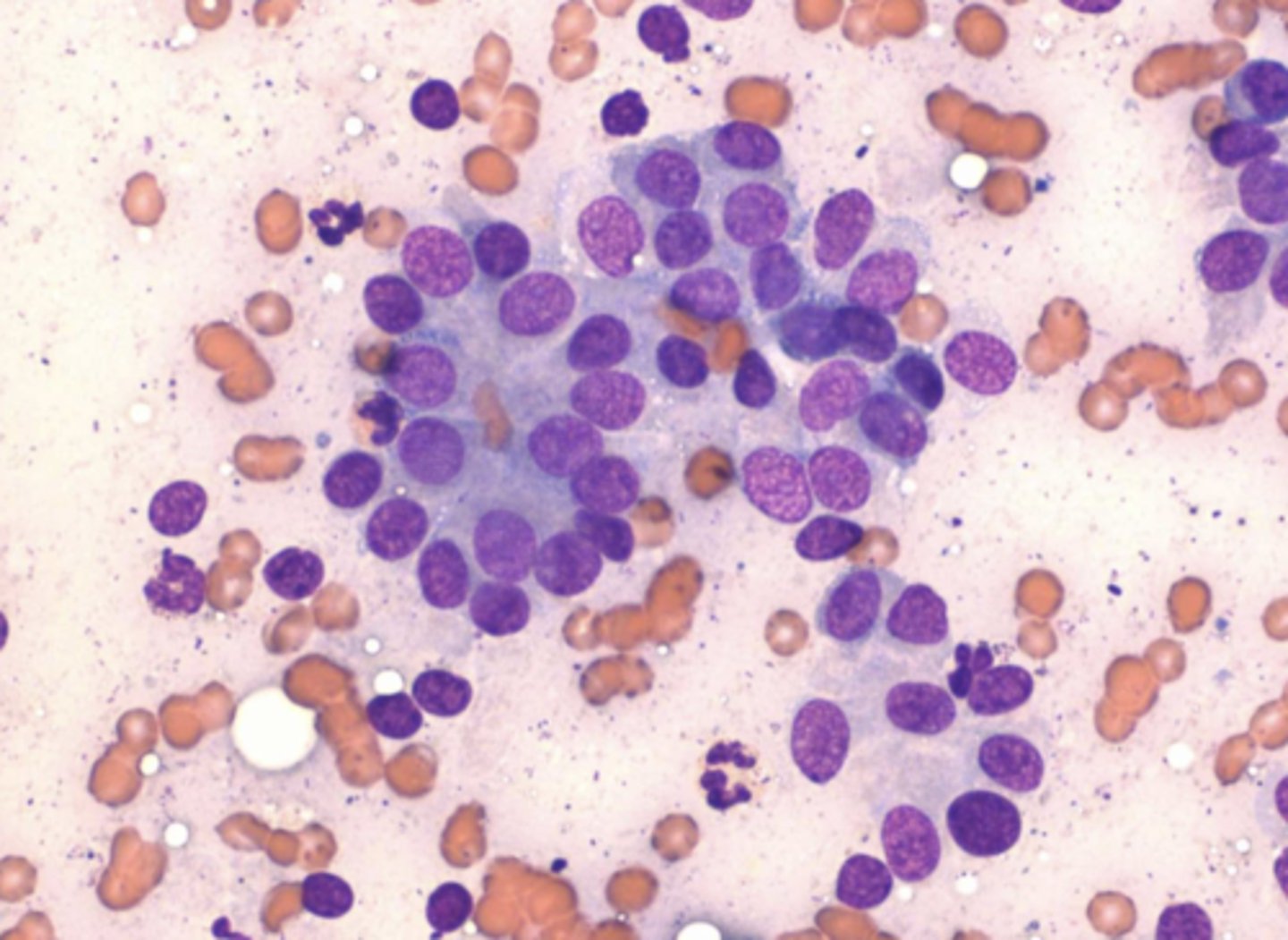
What type of tumor produces this cellular pattern?
AGASACA
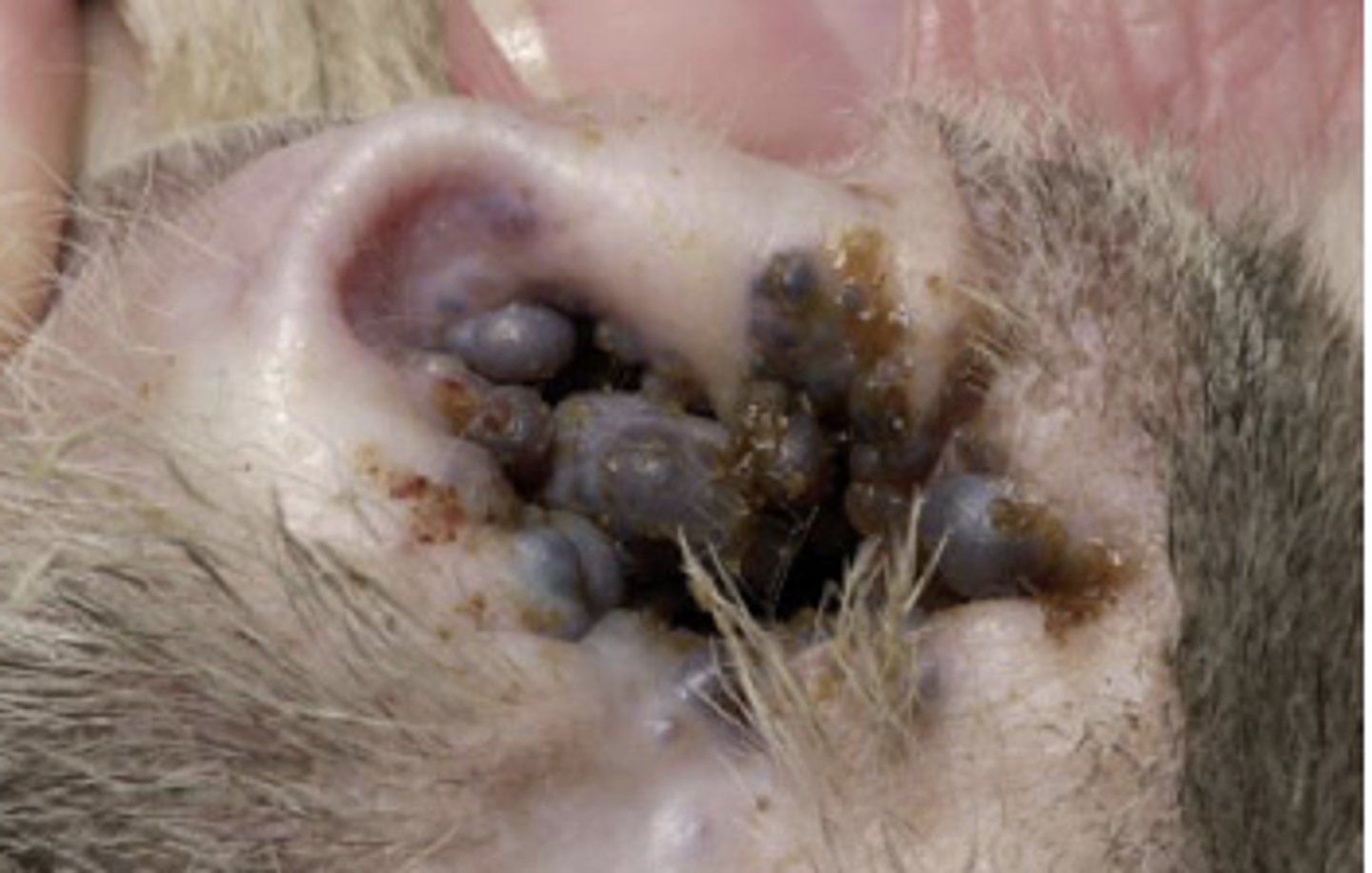
You take a FNA from these blue/black cystic lesions at the external opening of a cat's ear.
Based on the gross appearance, what is your top differential?
Cystomatosis
-ceruminous hyperplasia
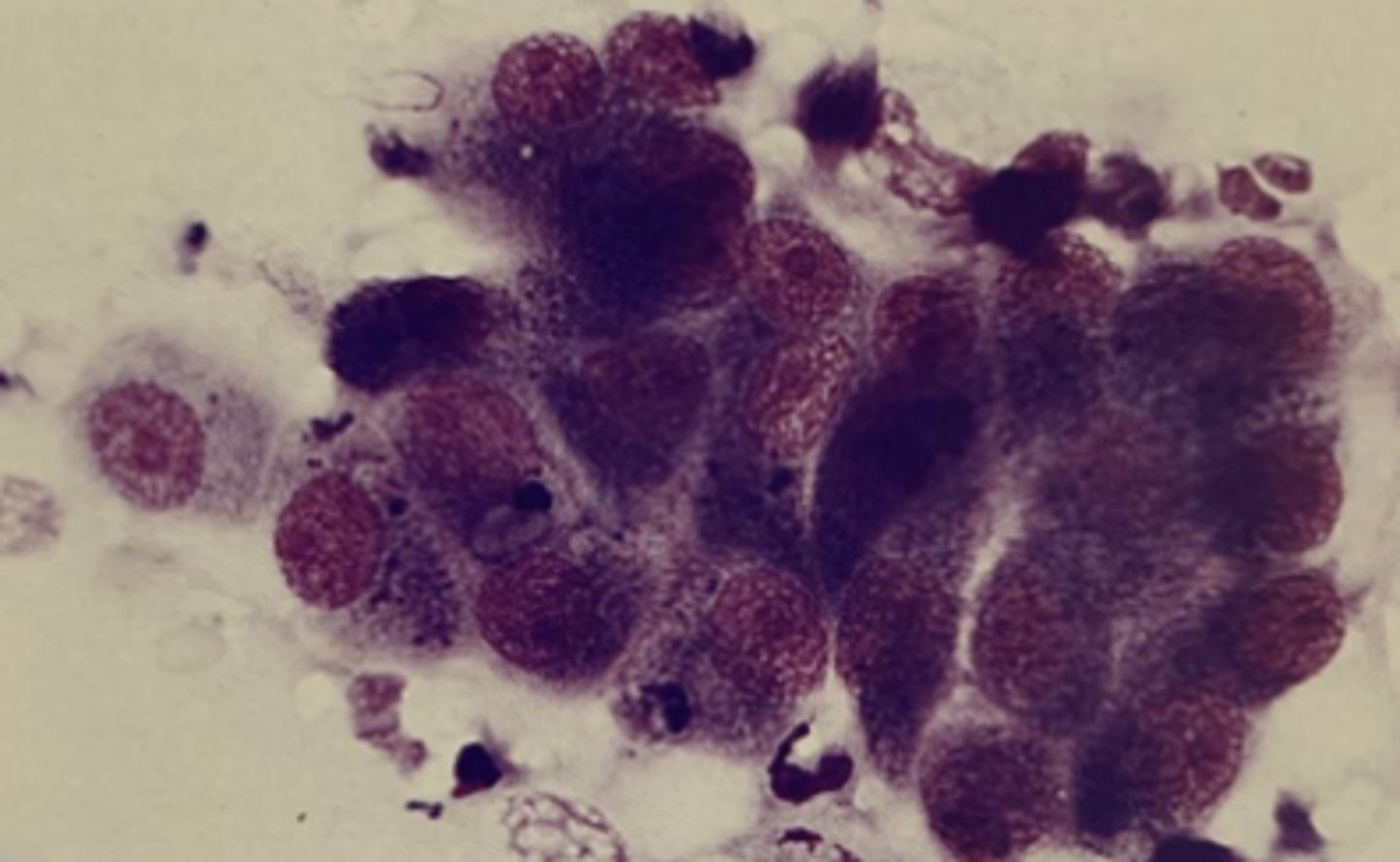
__________________ is the most common type of malignany at the external ear canal.
Ceruminous gland adenoma/adenocarcinoma (CGAC)
-Tight clusters of epithelial cells, high N:C, prominent nucleoli
• Black cytoplasmic granules
• Locally invasive, spread to draining LN