Dev Psych Exam #2
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/312
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
313 Terms
1
New cards
Cephalocaudal Principle
the principle that growth follows a pattern that begins with the head and upper body parts and then proceeds down to the rest of the body
2
New cards
Proximodistal Principle
states that development proceeds from the center of the body outward
3
New cards
Principle of Hierarchical Integration
the principle that simple skills typically develop separately and independently but are later integrated into more complex skills
4
New cards
Principle of the Independence of Systems
suggests that different body systems grow at different rates
5
New cards
Neurons can communicate with other cells, using a cluster of fibers called _______ and carries out messages through the _______ with neurons called ________________
dendrites, axon, neurotransmitters
6
New cards
Neurons
the basic nerve cell of the nervous system
7
New cards
Cerebral Cortex-
the upper layer of the brain; these cells are responsible for higher-order processes such as thinking and reasoning
8
New cards
Over time, the cells in the ______________ become more developed and interconnected
cerebral cortex
9
New cards
Shaken Baby Syndrome
an infant is shaken by a caretaker, leading the brain to rotate within the skill, causing blood vessels to tear and destroying intricate connections between neurons
10
New cards
Shaken Baby Syndrome can lead to:
-severe medical problems
-long-term physical disabilities such as blindness, hearing impairment and speech disabilities
-in the worse cases death
-long-term physical disabilities such as blindness, hearing impairment and speech disabilities
-in the worse cases death
11
New cards
Plasticity
the degree to which a developing structure or behavior is modifiable due to experience
12
New cards
Sensitive Period
a specific, but limited, time usually early in an organism's life, during which the organism is particularly susceptible to environmental influences relating to some particular facet of development
13
New cards
Rhythms
repetitive, cyclical patterns of behavior
14
New cards
State
the degree of awareness an infant displays to both internal and external stimulation
15
New cards
Rapid Eye Movement (REM) Sleep
the period of sleep that is found in older children and adults which is associated with dreaming
16
New cards
Sudden Infant Death Syndrome (SIDS)
the unexplained death of a seemingly healthy baby
17
New cards
There is no known reason or cure for SIDS, but it is suggested to:
have the baby lie on their back with a pacifier during sleep
18
New cards
Reflexes
unlearned, organized, involuntary responses that occur automatically in the presence of certain stimuli

19
New cards
rooting reflex
reflex consisting of head-turning and sucking movements elicited in a normal infant by gently stroking the side of the mouth or cheek; disappears after 3 weeks
20
New cards
stepping reflex
movement of legs when held upright with feet touching the floor; disappears after 2 months
21
New cards
swimming reflex
infant's tendency to paddle and kick in a sort of swimming motion when lying face down in a body of water; disappears after 4-6 months
22
New cards
moro reflex
activated when support for the neck and head is suddenly removed. The arms of the infant are thrust outward and then appear to grasp onto something; disappears after 6 months
23
New cards
babinski reflex
an infant fans out its toes in response to a stroke on the outside of its foot; disappears after 8-12 months
24
New cards
startle reflex
an infant flings out its arms arches its back and spreads its fingers in response to a sudden noise; reflex remains in different form throughout lifespan
25
New cards
eye-blink reflex
rapid shutting and opening of the eye on exposure to direct light; never disappears
26
New cards
sucking reflex
infant's tendency to suck at things that touch its lips; never disappears
27
New cards
gag reflex
an infant's reflex to clear its throat; never disappears
28
New cards
Dynamic Systems Theory
a theory of how motor skills develop and are coordinated
29
New cards
Norms
the average performance of a large sample of children of a given age
30
New cards
It isn't always reliable to base a child's health on norms, because it lacks representation of the ____________________ between each child, and most research is done only on middle/upper-class Caucasian babies.
individual differences
31
New cards
Brazelton Neonatal Behavioral Assessment Scale (NBAS)
a measure used to determine infants' neurological and behavioral responses to their environment
32
New cards
Nutrition of infants
-Studies have found breast milk to be more advantageous than formula
-Babies are suggested to start taking 1-2 tablespoons of solids around 6 months and 2-3 snacks per day after 9 months
-Children are more at risk of malnourishment in developing countries
-There is no clear evidence if overfeeding actually causes for adult/child obesity or not, but regardless it is good to not overfeed an infant
-Babies are suggested to start taking 1-2 tablespoons of solids around 6 months and 2-3 snacks per day after 9 months
-Children are more at risk of malnourishment in developing countries
-There is no clear evidence if overfeeding actually causes for adult/child obesity or not, but regardless it is good to not overfeed an infant
33
New cards
Nonorganic Failure to Thrive
a disorder in which infants stop growing due to a lack of stimulation and attention as the result of inadequate parenting
34
New cards
Sensation
the physical stimulation of the sense organs
35
New cards
Visual Perception of infants
-Infants are able to see about 20 feet in front of them with visual accuracy
-Babies also quickly develop depth perception, which has been tested through the use of "visual cliffs"
-They also prefer to look at more complex patterns, as well as learn how to distinguish faces
-Babies also quickly develop depth perception, which has been tested through the use of "visual cliffs"
-They also prefer to look at more complex patterns, as well as learn how to distinguish faces
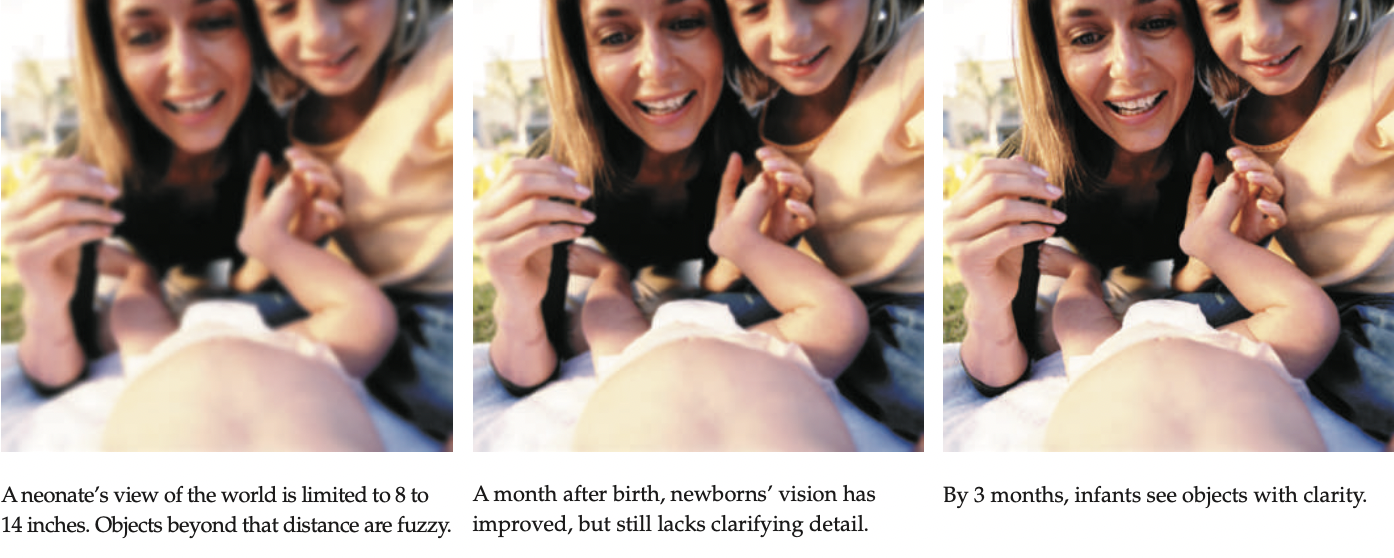
36
New cards
Auditory Perception of infants
-infants are able to hear before the time of birth, and even in the womb the fetus responds to sounds outside of its mother
-Infants are born with preferences for particular sound combinations
-Infants are born with reasonably good auditory perception, and are more sensitive to high and low frequencies than adults, while less sensitive to middle-range frequencies
-Sound localization is pretty good and improves within the first two years of life
-Babies are able to distinguish the sounds of different languages, and similar sounds
-Infants are born with preferences for particular sound combinations
-Infants are born with reasonably good auditory perception, and are more sensitive to high and low frequencies than adults, while less sensitive to middle-range frequencies
-Sound localization is pretty good and improves within the first two years of life
-Babies are able to distinguish the sounds of different languages, and similar sounds
37
New cards
Infants senses of smell, taste and feel:
-infant's sense of smell is so well developed that some newborns (12-18 days) can distinguish their mother on the basis of smell alone
-Babies are born with an innate sweet tooth, with a distaste for bitter things
-Infants are born with the capacity to experience pain, and pain produces distress in infants
-Touch is one of the most highly developed sensory systems in a newborn, and is one of the first to develop
-There is evidence that by 32 weeks after conception the entire body is sensitive to touch
-Many reflexes are revolved around an infant's touch perception
-Babies are born with an innate sweet tooth, with a distaste for bitter things
-Infants are born with the capacity to experience pain, and pain produces distress in infants
-Touch is one of the most highly developed sensory systems in a newborn, and is one of the first to develop
-There is evidence that by 32 weeks after conception the entire body is sensitive to touch
-Many reflexes are revolved around an infant's touch perception
38
New cards
Multimodal Approach to Perception
the approach that considers how information that is collected by various individual sensory systems is integrated and coordinated
39
New cards
Affordances
the action possibilities that a given situation or stimulus provides
40
New cards
Gross motor skills
• Grasp reflex---->ulnar grasp------->neat pincer grasp
• Catching/throwing
• Head control (at 6 weeks)
• Rolling
• Sitting
• Crawling
• Creeping
• hitching
• Standing
• Walking
• Running
• Climbing
-Jumping
41
New cards
Visual Cliff Experiment
children will not cross a visual cliff, showing depth perception in young infants and toddlers
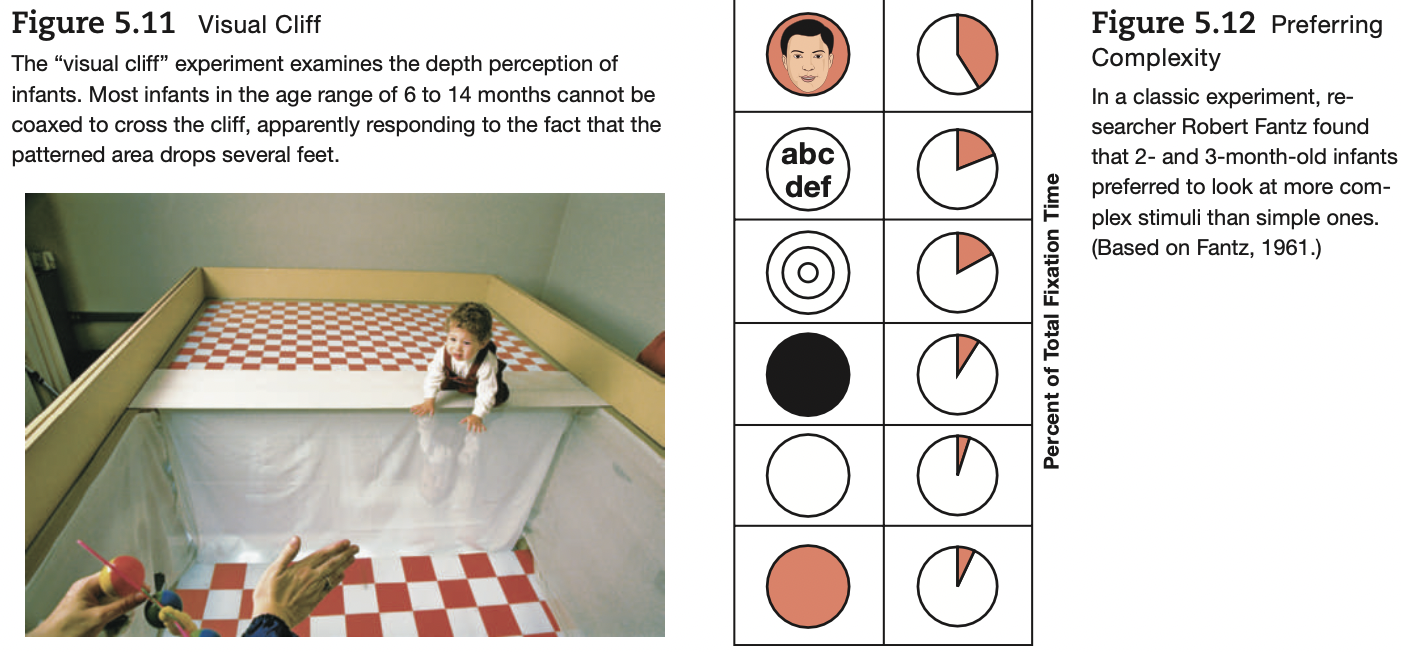
42
New cards
Myelin
the fatty substance that coats the neurons, and is responsible for the increased efficiency in communication for neurons across the brain
43
New cards
Synapses
the spaces between neurons where information is processed
44
New cards
Infants are more likely to recover from _________ during the first two years of life
brain damage
45
New cards
Jean Piaget
a Swiss psychologist that suggested that knowledge is the product of direct motor behavior, and created many essential theories on cognitive development
46
New cards
Schemes
organized mental structures and patterns
47
New cards
Assimilation
the process in which people understand an experience in terms of their current stage of cognitive thinking
48
New cards
Accommodation
changes in existing ways of thinking that occur in response to encounters with new stimuli or events
49
New cards
Sensorimotor Stage
piaget's initial major stage of cognitive development, which can be broken down into six substages
50
New cards
The 6 substages of the sensorimotor stage are:
Simple reflexes, First habits and primary circular reactions, secondary circular reactions, Coordination of secondary circular reactions, Tertiary Circular Reactions, and Beginnings of thought
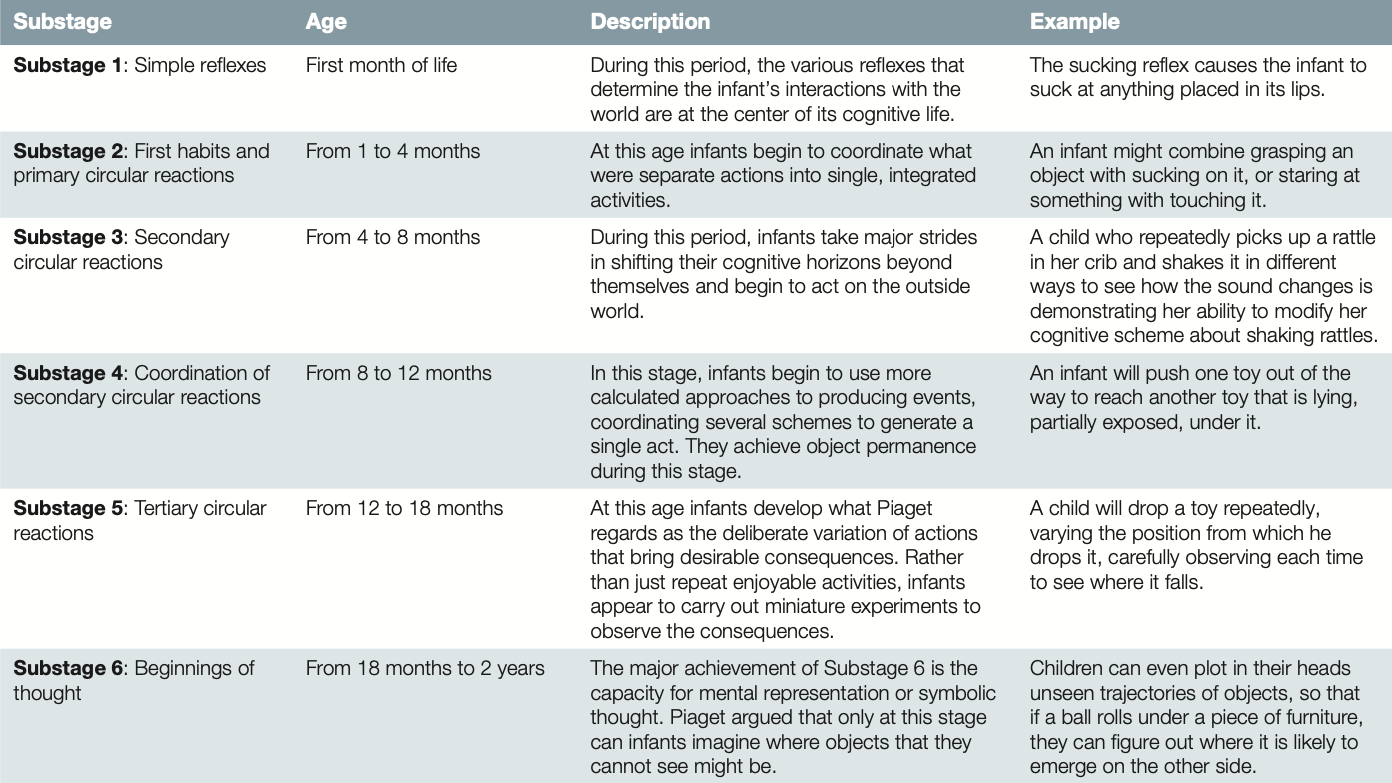
51
New cards
Substage 1: Simple reflexes
The various inborn reflexes are at the center of a baby's physical and cognitive life, and some reflexes begin to accommodate the infant's experience with the nature of the world; encompasses the first month of life
52
New cards
Substage 2: First habits and primary circular reactions
Occurs from 1 to 4 months; infants begin to coordinate separate actions into integrated activities
53
New cards
Substage 3: secondary circular reactions
Occurs from 4 to 8 months; infants begin to act upon the outside world, seeking to repeat enjoyable events in their environments
54
New cards
Substage 4: Coordination of secondary circular reactions
Occurs from 8 to 12 months; infants begin goal-oriented behaviors and gain object permanence
55
New cards
Substage 5: Tertiary Circular Reactions
Occurs from 12 to 18 months; develops schemes regarding the deliberate variation of actions that bring desirable consequences
56
New cards
Substage 6: Beginnings of thought
From 18 months to 2 years; develops the capacity for mental representation, or symbolic thought, and deferred imitation
57
New cards
Goal-Oriented Behavior
behavior in which several schemes are combined and coordinated to generate a single act to solve a problem
58
New cards
Object Permanence
the realization that people and objects exist even when they cannot be seen
59
New cards
Mental Representation
an internal image of a past event or object
60
New cards
Deferred Imitation
an act in which a person who is no longer present is imitated by children who have witnessed a similar act
61
New cards
Doubts/skepticism on Piaget's Theory:
-Development proceeds in more continuous fashion
-Robert Seigler suggests that development happens in waves rather than stages
-The connection made between cognitive and motor development is exaggerated
-Baillargeon conducted studies that demonstrate earlier capabilities of infants in understanding object permanence
-Other behaviors also seen to emerge earlier than piaget suggested
-Describes western countries better than children from non-western countries
-Robert Seigler suggests that development happens in waves rather than stages
-The connection made between cognitive and motor development is exaggerated
-Baillargeon conducted studies that demonstrate earlier capabilities of infants in understanding object permanence
-Other behaviors also seen to emerge earlier than piaget suggested
-Describes western countries better than children from non-western countries
62
New cards
Information-Processing Approaches
the model that seeks to identify the way that individuals take in, use and store information
63
New cards
Encoding
the process by which information is initially recorded in a form usable to memory
64
New cards
Storage
the placement of material into memory
65
New cards
Retrieval
the process by which material in memory storage is located, brought into awareness, and used
66
New cards
Automatization
the degree to which an activity requires attention
67
New cards
_________ can be thought of as a computer’s keyboard, through which one inputs information; _______ is the computer’s hard drive, where information is stored; and ________is analogous to soft- ware that accesses the information for display on the screen.
encoding, storage, retreival

68
New cards
Motor development of infants:
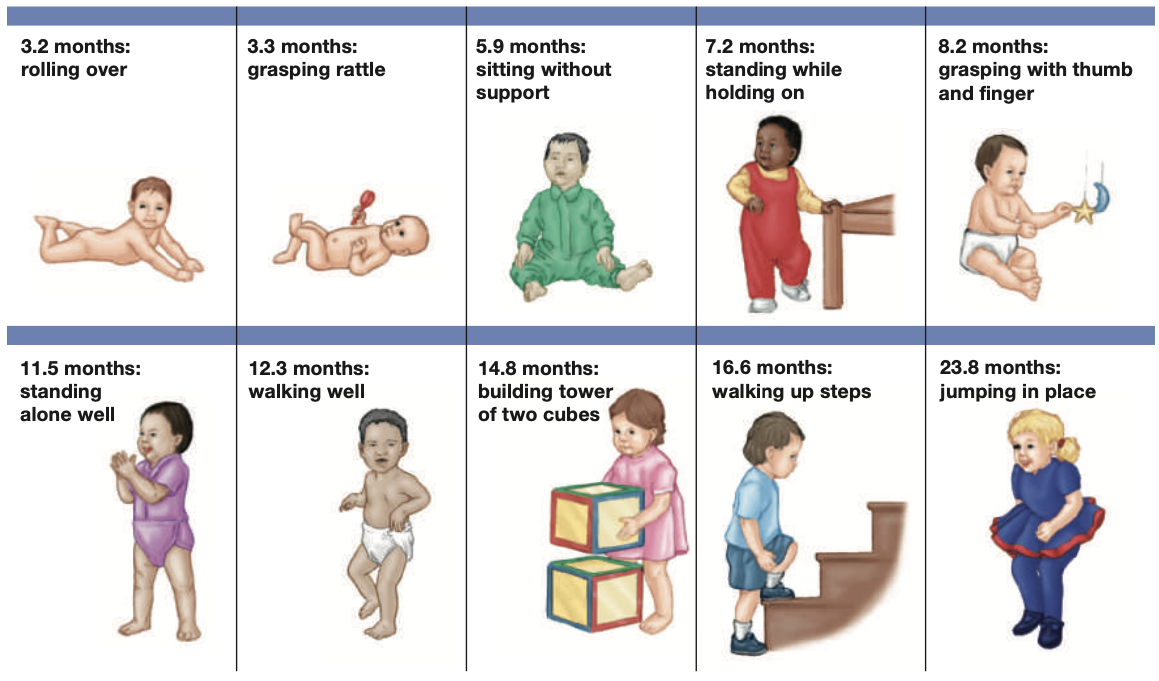
69
New cards
Memory
the process by which information is initially recorded, stored and retrieved
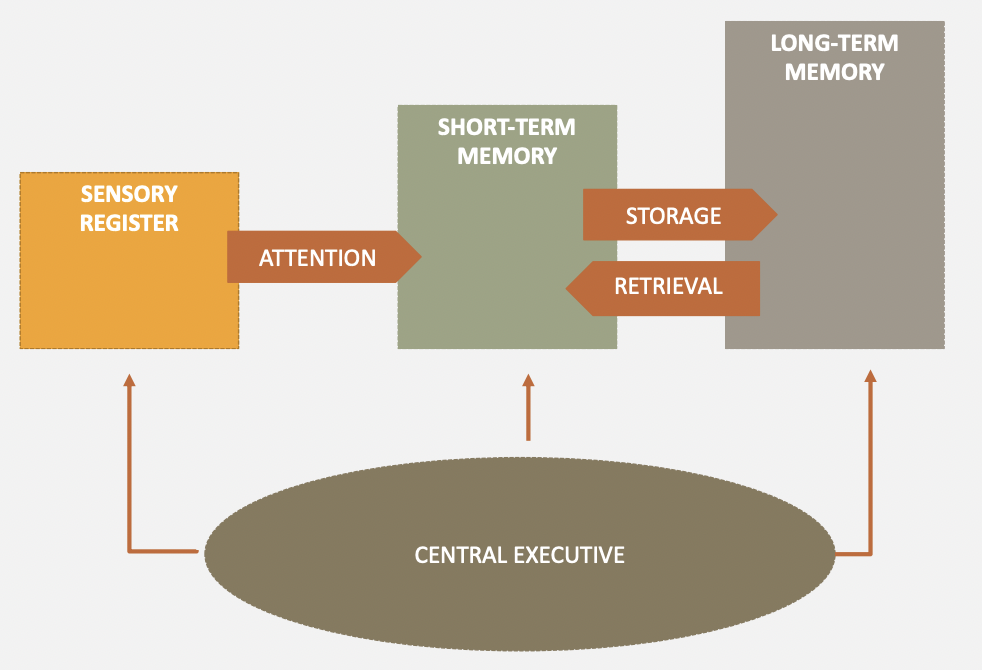
70
New cards
Infantile Amnesia
the lack of memory for experiences that occurred prior to 3 years of age
71
New cards
Explicit Memory
the memory that is conscious and which can be recalled intentionally
72
New cards
Implicit Memory
consists of memories of which we are not consciously aware but that affect performance and behavior
73
New cards
Developmental Quotient
an overall developmental score that relates to performance in four domains: motor skills, language use, adaptive behavior, and personal-social
74
New cards
Bayley Scales of Infant Development
a measure that evaluates an infant's development from 2 to 42 months
75
New cards
the relatively recent finding that an association exists between efficiency of information processing and later IQ scores does suggest some consistency of ___________________ across the life span.
cognitive development
76
New cards
Language
the systematic, meaningful arrangement of symbols, which provides the basis for communication
77
New cards
Phonology
the basic sounds or a language that can be used to produce words and sentences
78
New cards
Morphemes
the smallest language unit that has meaning
79
New cards
Semantics
the rules that govern the meaning of words and sentences
80
New cards
Babbling
making speech-like but meaningless sounds
81
New cards
Holophrases
one-word utterances that stand for a whole phrase, whose meaning depends on the particular context in which they are used
82
New cards
Telegraphic speech
speech in which words not critical to the message are left out
83
New cards
Underextension
the overly restrictive use of words, common among children just mastering spoken language
84
New cards
Overextension
the overly broad use of words, overgeneralizing their meaning
85
New cards
Referential Style
a style of language use in which language is used primarily to label objects
86
New cards
Expressive Style
a style of language use in which language is used primarily to express feelings and needs about oneself and others
87
New cards
Learning Theory Approach
the theory that language acquisition follows the basic laws of reinforcement and conditioning
88
New cards
Nativist Approach
by Noam Chomsky; the theory that a genetically determined, innate mechanism directs language development
89
New cards
Universal Grammar
Noam Chomsky's theory that all the world's languages share a similar underlying structure
90
New cards
Language-Acquisition Device (LAD)
a neural system of the brain hypothesized to permit understanding of language
91
New cards
Interactionist perspective
by Jerry Bruner; the theory that language development is produced through a combination of genetically determined predispositions and environmental circumstances that help to teach language
92
New cards
Infant-Directed Speech
a type of speech directed toward infants, characterized by short, simple sentences
93
New cards
Cognitive Development
processes and outcomes of thought
94
New cards
Examples of cognitive skills:
-Attention
-Perception
-Memory
-Higher-order thinking (concept development, learning, and problem solving)
-Language
-Perception
-Memory
-Higher-order thinking (concept development, learning, and problem solving)
-Language
95
New cards
Piaget vs Vygotsky
Piaget focuses on "higher order" cognitive building, while Vygotstky focused on the process rather than the product of cognitive development and felt that learning is shaped through social interaction
-both felt that children learn through interactions in the environment and construct their opinions based on the world around them; are constructivist
-both felt that children learn through interactions in the environment and construct their opinions based on the world around them; are constructivist
96
New cards
equilibration
Children go between a state of equilibrium and dis-equilibrium while learning new information and their understanding of the world
97
New cards
piaget felt that the stages of development are _____________
culturally universal
98
New cards
Storing Strategies
rehearsal, organization, and elaboration
99
New cards
Retrieval strategies
recognition and recall
100
New cards
Rehearsal
repeating information to oneself