BIO 107: Unit 3 - Ch 12 Neural Tissue
1/112
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Be sure to enable 'answer with term' in the Practice Test and Learn feature.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
113 Terms
What is the central nervous system (CNS)?
Which type of nervous system:
Consists of the spinal cord and brain
Processes and coordinates sensory data, motor commands, & higher brain functions
What is the peripheral nervous system (PNS)?
Which type of nervous system:
Consists of all of the nervous tissue outside of the CNS, including the special senses (eyes, ears, etc)
Deliver sensory information to the CNS
Carry motor commands to peripheral tissues and systems
What are peripheral nerves?
Which type of nerve is:
Carry sensory information and motor commands in PNS
What are cranial nerves?
Which type of nerve is:
Connect to brain
What are spinal nerves?
Which type of nerve is:
Attach to spinal cord
What is the afferent division of the PNS?
Which division of the PNS:
Brings sensory information from PNS’s sensory receptors to CNS
Arriving
What are receptors?
What sensory structure is able to detect change or stimuli?
What is the efferent division of the PNS?
Which division of the PNS:
Carries motor commands from CNS to PNS’s muscles and glands
Exiting
What are effectors?
What target cells and organs that respond by doing something?
What is the somatic nervous system (SNS)?
Which type of nervous system controls skeletal muscle contractions & reflexes?
What is the autonomic nervous system (ANS)?
Which type of nervous system controls automatic regulation of cardiac & smooth muscle, and glandular secretions?
What is the sympathetic division of the ANS?
Which division of ANS has a stimulating effect (fight or flight)?
What is the parasympathetic division of the ANS?
Which division of ANS has a relaxing effect?
What are neuron cells?
What kind of cell send and receive signals?
What are neuroglia cells?
What kind of cell support and protect neurons?
What is the cell body of neuron?
Which part of the neuron is:
Centrally located, contains a large nucleus and cytoplasm

What are the dendrites of neuron?
Which part of the neuron is:
Highly branched area that receives information

What are the axons of neuron?
Which part of the neuron is:
Are long cytoplasmic processes that carry an electrical signal (action potential) to target
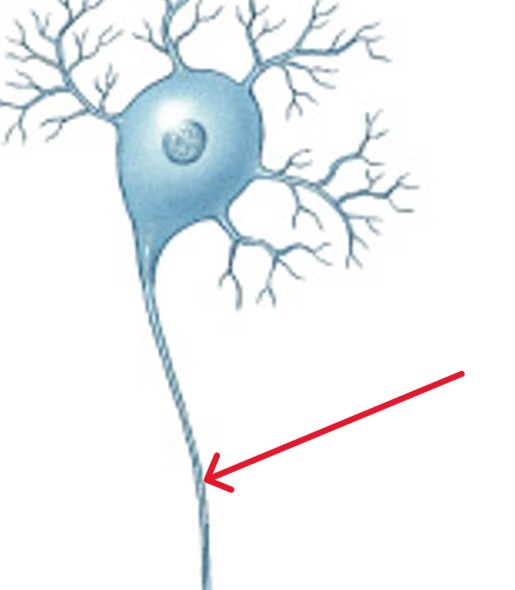
What is the synapse of neuron?
Which part of the neuron is:
Specialized area where a neuron communicates with another cell

What are the functions of neurotransmitters?
What are these functions of:
Are chemical messengers
Are released at presynaptic membrane
Affect receptors of postsynaptic membrane
Are broken down & reassembled by enzymes
What is neuromuscular junction of synapse?
Which type of synapse is:
Synapse between neuron and muscle
What is neuroglandular junction of synapse?
Which type of synapse is:
A synapse between neuron and gland
What is presynaptic cell membrane?
Which cell membrane type sends message (releases neurotransmitter)?
What is postsynaptic cell membrane?
Which cell membrane type receives message (receives neurotransmitter)?
What are anaxonic neurons?
Which neuron type is:
Small & round
Dendrites and axons look alike
Found in brain & sense organs

What are bipolar neurons?
Which neuron type is:
1 dendrite, 1 axon
Found in sense organs
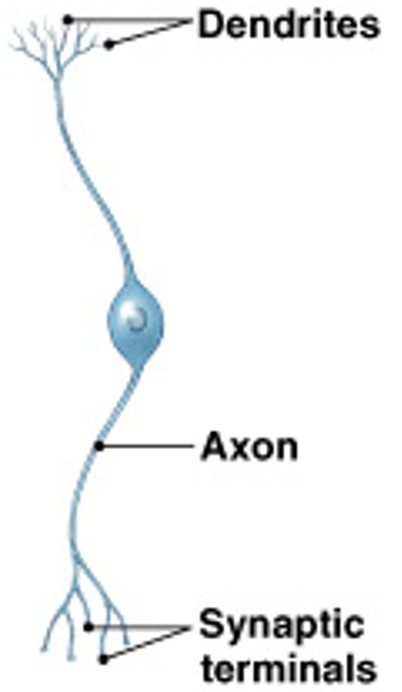
What are unipolar neurons?
Which neuron type is:
Dendrites and axon are continuous, cell body to 1 side
PNS neurons
Axons can be very long - (feet)
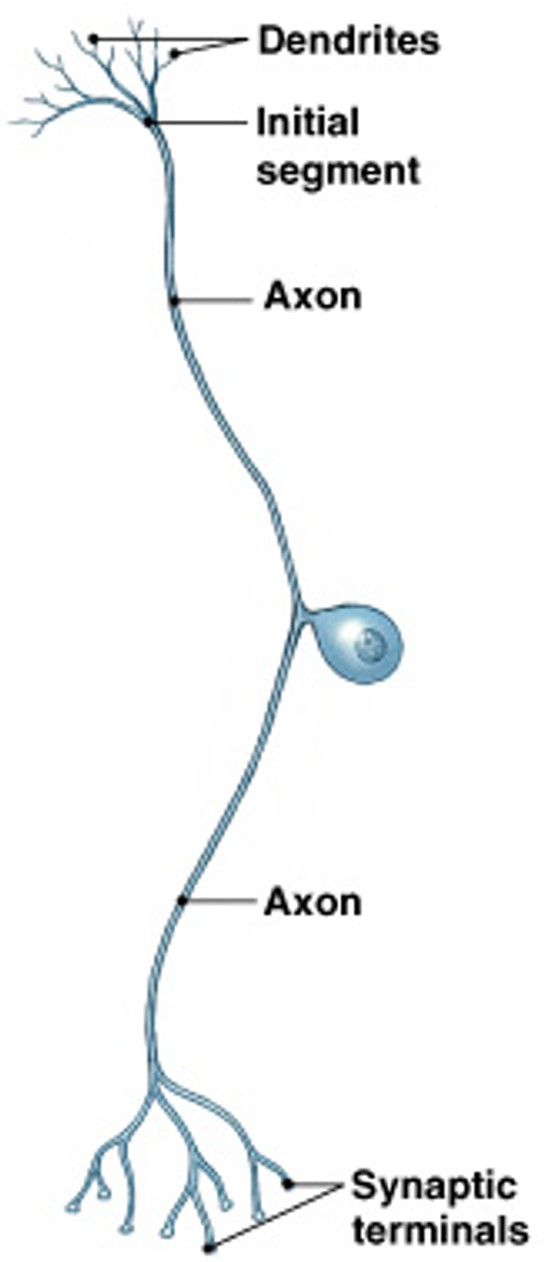
What are multipolar neurons?
Which neuron type is:
Multiple dendrites, 1 axon
CNS neurons & skeletal muscle neurons
Axons can be very long - (feet)

What is the sensory neuron classification?
Which classification of neuron performs the following:
Afferent, (PNS)
Extend from sensory receptors to CNS
Cell bodies grouped in sensory ganglia
What are somatic sensory neurons?
Which type of sensory neuron:
Monitors effects of external environment & body position
What are visceral sensory neurons?
Which type of sensory neuron:
Monitors internal environment, organ systems
What are interoceptors?
Which type of sensory receptor:
Monitors internal systems (digestive, respiratory, cardiovascular, urinary, reproductive)
Internal senses (taste, deep pressure, pain)
What are exteroceptors?
Which type of sensory receptor:
Monitors external environment (sight, smell, hearing)
External senses (touch, temperature, pressure)
What are proprioceptors?
Which type of sensory receptor:
Monitors position and movement (skeletal muscles and joints)
What is the motor neuron classification?
Which classification of neuron performs the following:
Efferent, (PNS)
Carry instructions from CNS to peripheral effectors
Via efferent fibers (axons)
What are somatic motor neurons?
Which type of motor neuron:
Innervates skeletal muscles
What are visceral motor neurons?
Which type of motor neuron:
Innervates smooth & cardiac muscles, adipose tissue, glands (uses pre & post ganglionic fibers)
What is the interneuron classification?
Which classification of neuron performs the following:
(CNS)
Located inside spinal cord and brain
Distributes sensory and motor information
Involved with memory and learning
How much do neuroglia take up?
What take up half the volume of the nervous system?
What are ependymal cells of neuroglia (CNS)?
Which type of neuroglia in the CNS:
Form epithelium called ependyma
Line central canal of spinal cord and ventricles of brain
Secrete & monitor CSF
Have cilia that circulate CSF
What is cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) of ependymal cells?
What surrounds brain & spinal cord, provides protective cushion & material transport?
What are the functions of astrocytes in neuroglia (CNS)?
What are these functions of:
Large and most numerous
Maintain blood - brain barrier - separates blood from CNS interstitial fluid
CNS framework - cytoskeleton framework for brain & spinal cord
Repair damaged neural tissue - can make structural repairs
Guide neuron development - directs growth & neuron connections
Controls interstitial environment of CNS
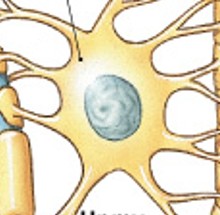
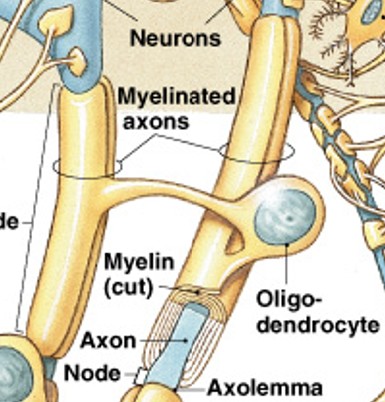
What are oligodendrocytes of neuroglia (CNS)?
Which type of neuroglia in the CNS:
Forms membranous wrapping called myelin
Processes contact other neuron cell bodies
Wrap around axons to form myelin sheaths
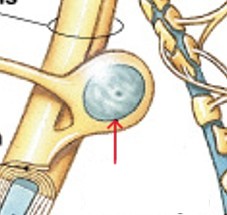
What is the myelination (myelin sheath) of oligodendrocytes?
What part of the oligodendrocytes:
Increases speed of action potentials
Myelin insulates myelinated axons
Makes nerves appear white (white matter)
What is the white matter of myelin?
Which part of myelin:
Appears white due to myelinated axons
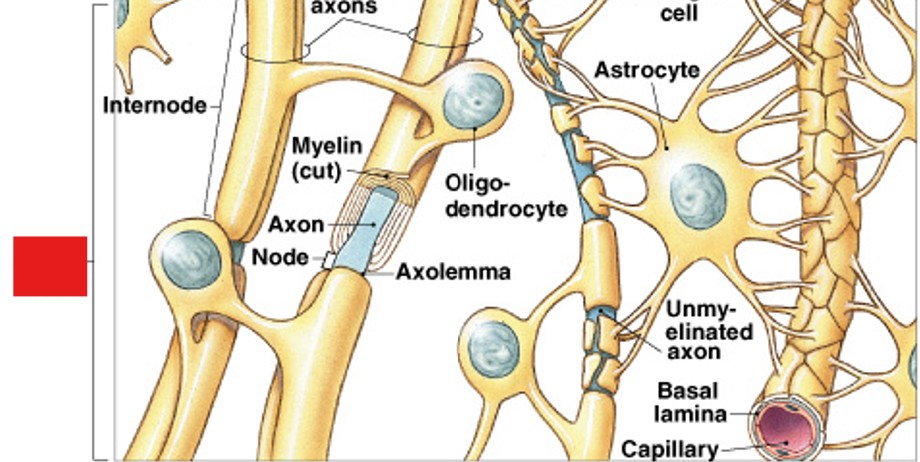
What are the nodes of myelin?
Which part of myelin:
Also called nodes of Ranvier
Area in between internodes (not myelinated)
Where axons may branch
What are the internodes of myelin?
Which part of myelin:
Large myelinated segments of axon
Large area of axon that is covered with myelin
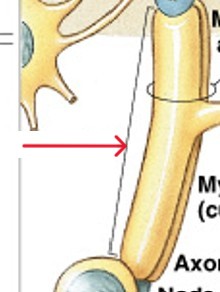
What does unmyelinated means?
What are axons that do not have a myelin sheath?

What are gray matter of unmyelinated?
What part of the unmyelinated:
Appears gray due to cell bodies, dendrites, & unmyelinated axons
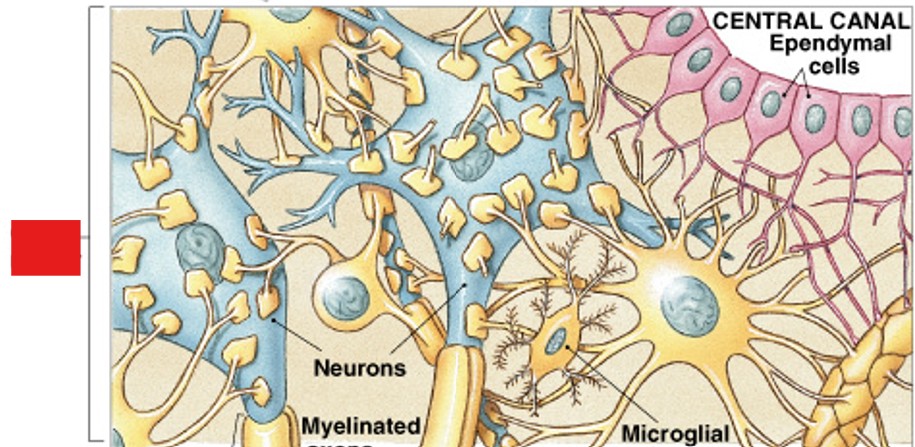
What is microglia of neuroglia (CNS)?
Which type of neuroglia in the CNS:
Migrate through neural tissue
Clean up cellular debris, waste products, and pathogens
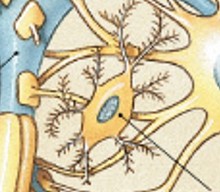
What are satellite cells of PNS?
Which neuroglia of the PNS:
Surround cell bodies in ganglia
Regulate environment around neuron
What are Schwann cells of PNS?
Which neuroglia of the PNS:
Myelinates PNS axons
1 Schwann cell sheaths 1 segment of axon
Many Schwann cells needed to sheath entire axon
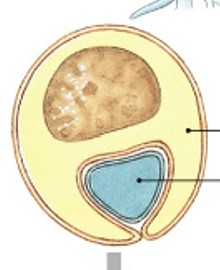
What is the neurilemma of Schwann cell?
What part of Schwann cell is:
The myelin sheath in PNS
What is the ganglia of Schwann cell?
What part of Schwann cell is:
Masses of neuron cell bodies
Surrounded by neuroglia
Found in the PNS
What is the resting potential in neural activities?
Which membrane process type in neural activities is:
The transmembrane potential of resting cell
What is the graded potential in neural activities?
Which membrane process type in neural activities is:
Temporary, localized change in resting potential, caused by stimulus
What is the action potential in neural activities?
Which membrane process type in neural activities is:
An electrical impulse produced by graded potential that propagates along surface of axon to synapse
What is the synaptic activity in neural activities?
Which membrane process type in neural activities is:
Releases neurotransmitters at presynaptic membrane that produces graded potentials in postsynaptic membrane
What is the information processing in neural activities?
Which membrane process type in neural activities is:
Response (integration of stimuli) of postsynaptic cell
What is transmembrane potential?
What is the intracellular fluid & extracellular fluid that differ in ionic composition?
What are passive channels (leak)?
Which type of membrane channel is:
Also called leak channels
Are always open
But permeability changes with conditions
What are active channels (gated)?
Which type of membrane channel is:
Also called gated channels
Open and close in response to stimuli
At resting potential, most gated channels are closed
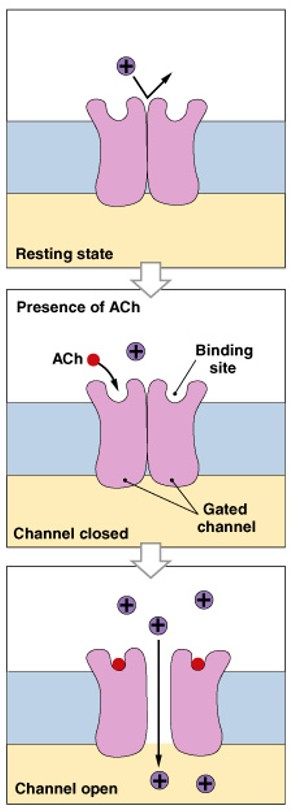
What are chemically regulated gated channels?
Which class of gated channels is:
Bind with specific chemicals to open or close
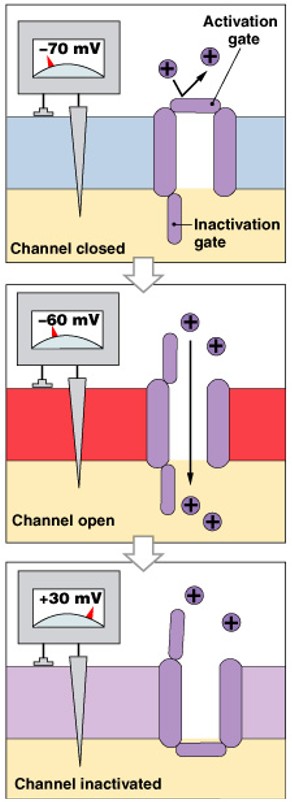
What are voltage-regulated gated channels?
Which class of gated channels is:
Respond to changes in transmembrane potential
Found in neural axons, skeletal muscle sarcolemma cardiac muscle
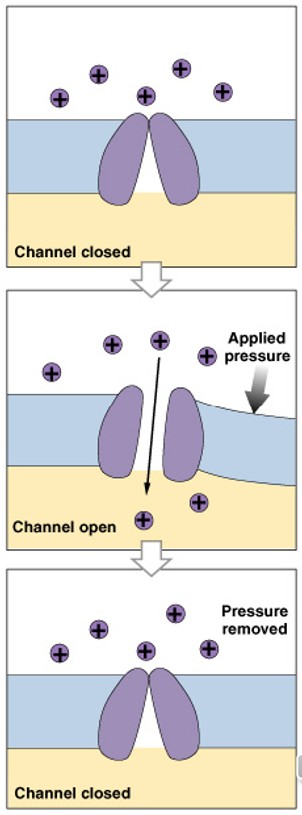
What are mechanically regulated gated channels?
Which class of gated channels is:
Respond to membrane distortion
Found in sensory receptors (touch, pressure, vibration)
What are graded potentials?
What are changes in transmembrane potential that cannot spread far from site of stimulation (local potentials)?
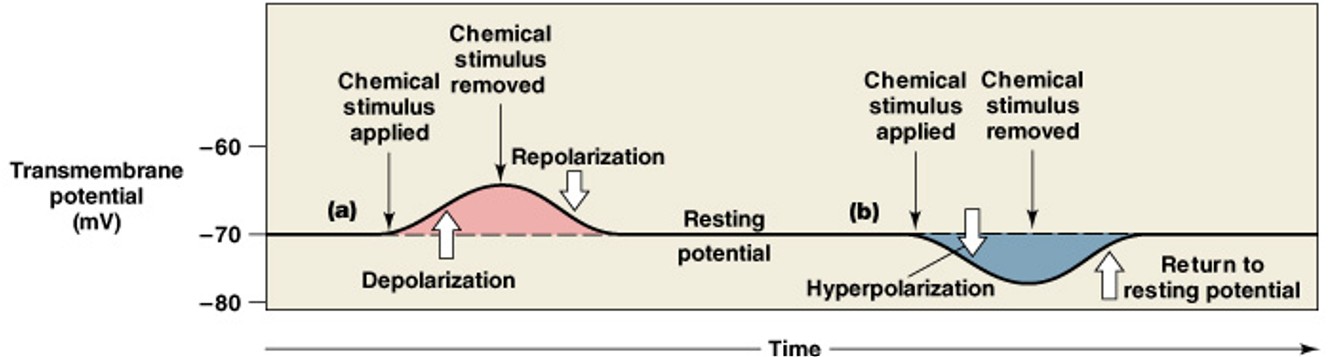
What is the depolarization of graded potentials?
Which graded potential is:
A shift in transmembrane potential toward 0 mV (-70 → 0)
What is the repolarization of graded potentials?
Which graded potential is:
When the stimulus is removed, transmembrane potential returns to normal
What is the hyperpolarization of graded potentials?
Which graded potential is:
Increasing the negativity of the resting potential by opening a potassium channel (-70 to -80)
What are action potentials in the muscle?
How do propagate membrane changes in transmembrane potential (chain reaction across surface of membrane → down axon)?
What is the threshold of action potentials?
-60 to -55 mV is the threshold level of what?
What is the process and steps of generation?
What is this the process of:
Depolarization to threshold
Activation of Na+ channels
Activation of K+ channels, inactivation of Na+ channels
Return to normal permeability
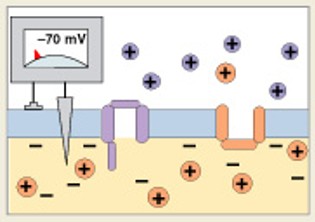
What is the first step of generation?
Which step of generation is:
Depolarization to threshold - membrane reaches threshold
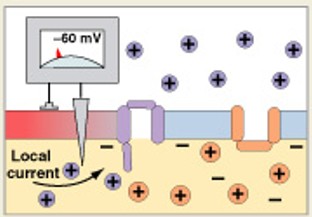
What is the second step of generation, after depolarization to threshold?
Which step of generation is:
Activation of Na+ channels
Rapid depolarization
Na+ ions rush into cytoplasm
Inner membrane changes from negative to positive
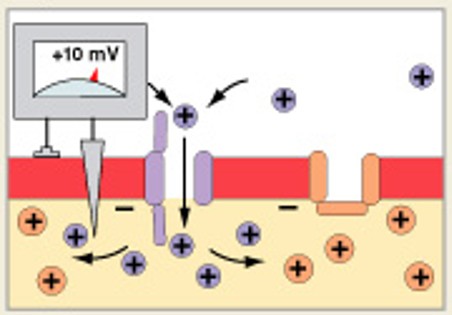
What is the third step of generation, after activation of Na+ channels?
Which step of generation is:
Activation of K+ channels
Inactivation of Na+ channels
Repolarization begins

What is the fourth step of generation, after activation of K+ channels and inactivation of Na+ channels?
Which step of generation is:
Return to normal permeability
Action potential is over
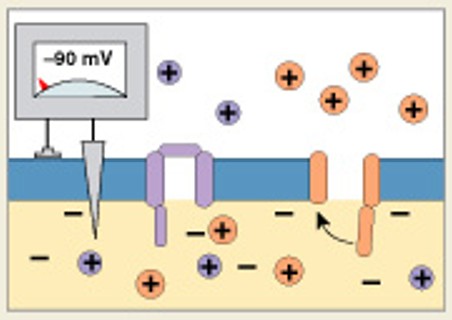
What is the refractory period?
What occurs from beginning of action potential to return to resting state?
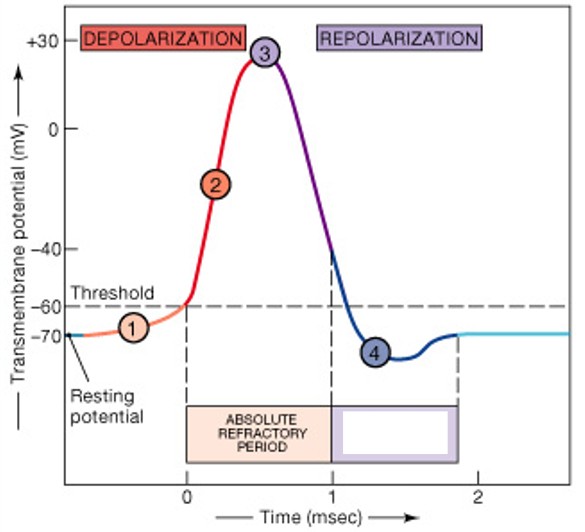
What is absolute refractory period?
Which type of refractory period have:
Sodium channels open or inactivated
No action potential possible
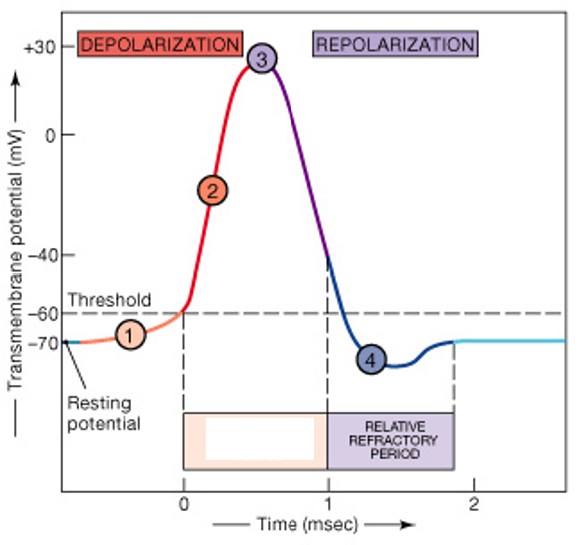
What is relative refractory period?
Which type of refractory period have:
Membrane potential almost normal
Very large stimulus can initiate action potential
What is continuous propagation?
Which propagation of action potentials is:
Action potential spread across membrane in small steps
Unmyelinated axons
What is saltatory propagation?
Which propagation of action potentials is:
Action potential leaps from node to node
Myelinated axons
Faster and uses less energy than continuous propagation
What are type A fibers of axons?
Which fiber type of axon is:
Myelinated, large diameter, high speed (140 m/s), carry rapid information to/from CNS
Position, balance, touch, and motor impulses
What are type B fibers of axons?
Which fiber type of axon is:
Myelinated, small diameter, medium speed (40 m/s), carry intermediate signals
Sensory information, peripheral effectors
What are type C fibers of axons?
Which fiber type of axon is:
Unmyelinated, very small diameter, slow speed (1 m/s), carry slower information
Pain, involuntary muscle, gland controls
What are nerve impulses in synaptic activity?
What are action potentials transmitted from presynaptic neuron to postsynaptic neuron (or other postsynaptic cell) across a synapse?
What are electrical synapses?
Which type of synapses is:
Direct physical contact between cells
Produces continuous local current and action potential propagation
Found in the brain & eye
What are chemical synapses?
Which type of synapses is:
Signal transmitted across a gap by chemical neurotransmitters
Are found in most synapses between neurons
All synapses between neurons and other cells
What are excitatory neurotransmitters?
Which class of neurotransmitters:
Cause depolarization of postsynaptic membranes
Promote action potentials
What are inhibitory neurotransmitters?
Which class of neurotransmitters:
Cause hyperpolarization of postsynaptic
Suppress action potentials
What is the process and steps of cholinergic synapse?
What is this the process of:
Action potential arrives, depolarizes synaptic knob
Calcium ions enter synaptic knob, trigger exocytosis of ACh
ACh binds to receptors, depolarizes postsynaptic membrane
AChE breaks ACh into acetate and choline
What is the first step of cholinergic synapse?
Which step of cholinergic synapse:
Action potential arrives, depolarizes synaptic knob

What is the second step of cholinergic synapse, after action potential arrives, depolarizes synaptic knob?
Which step of cholinergic synapse:
Calcium ions enter synaptic knob, trigger exocytosis of ACh
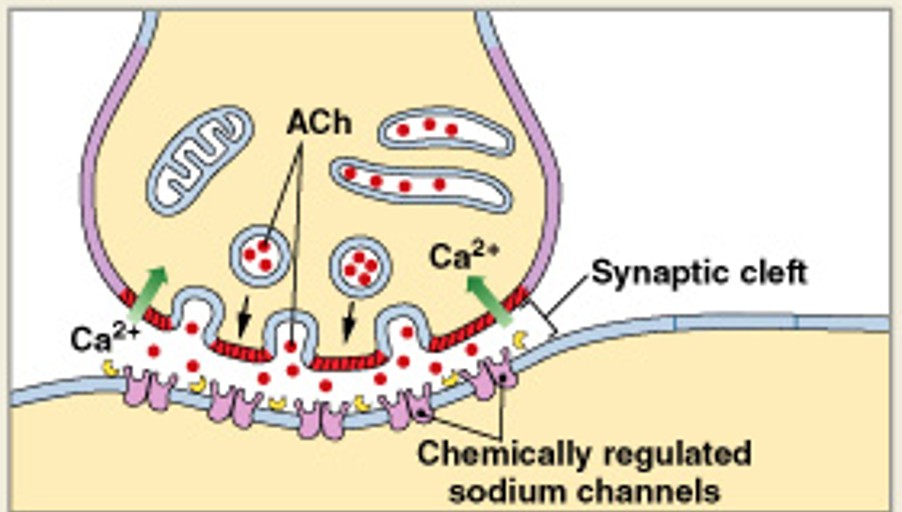
What is the third step of cholinergic synapse, after calcium ions enter synaptic knob, trigger exocytosis of ACh?
Which step of cholinergic synapse:
ACh binds to receptors, depolarizes postsynaptic membrane
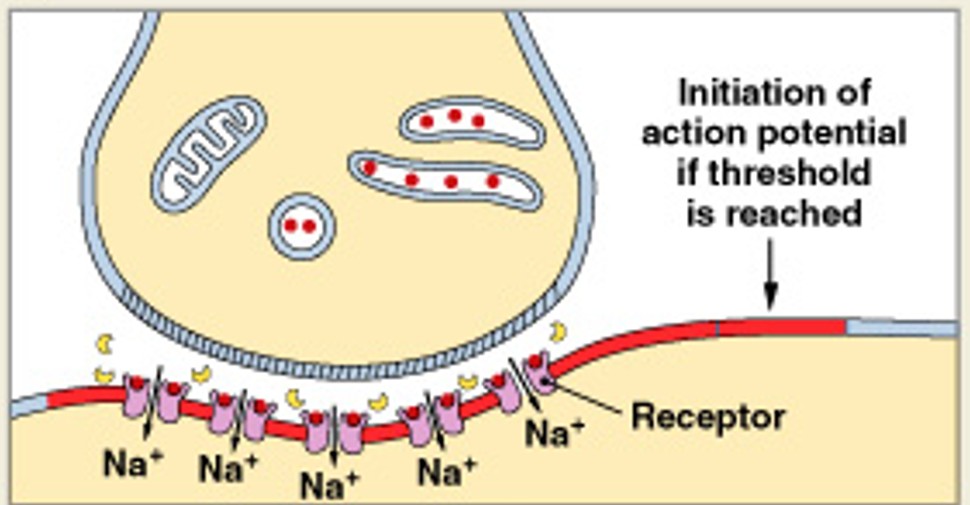
What is the fourth step of cholinergic synapse, after ACh binds to receptors, depolarizes postsynaptic membrane?
Which step of cholinergic synapse:
AChE breaks ACh into acetate and choline
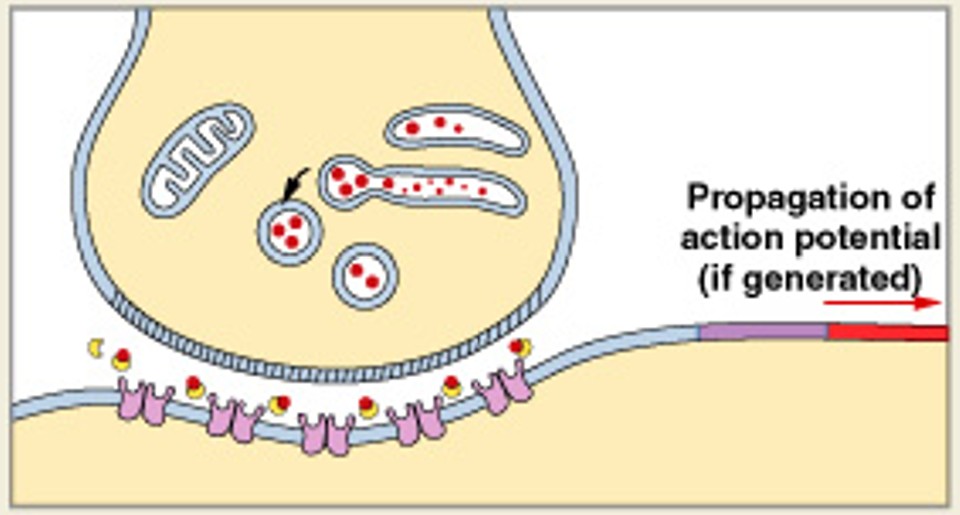
What is synaptic fatigue?
What occurs when neurotransmitter can’t recycle fast enough to meet demands of intense stimuli?
What is norepinephrine (NE) of neurotransmitters?
Which type of neurotransmitters is:
Released by adrenergic synapses
Excitatory and depolarizing effect
Found in brain and portions of ANS
What is dopamine of neurotransmitters?
Which type of neurotransmitters is:
A CNS neurotransmitter
May be excitatory or inhibitory
Involved in Parkinson’s disease, cocaine use
What is serotonin of neurotransmitters?
Which type of neurotransmitters is:
A CNS neurotransmitter
Affects attention and emotional states
What are neuromodulators (opioids)?
What are chemicals released by synaptic knobs and bind to the same receptors as opium or morphine?
What are postsynaptic potentials?
What are graded potentials developed in a postsynaptic cell in response to neurotransmitters?