Unit 4: External Dynamic Forces Shaping Our Planet
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|

20 Terms
Weathering
The breaking down of rocks and other materials on the Earth's surface.
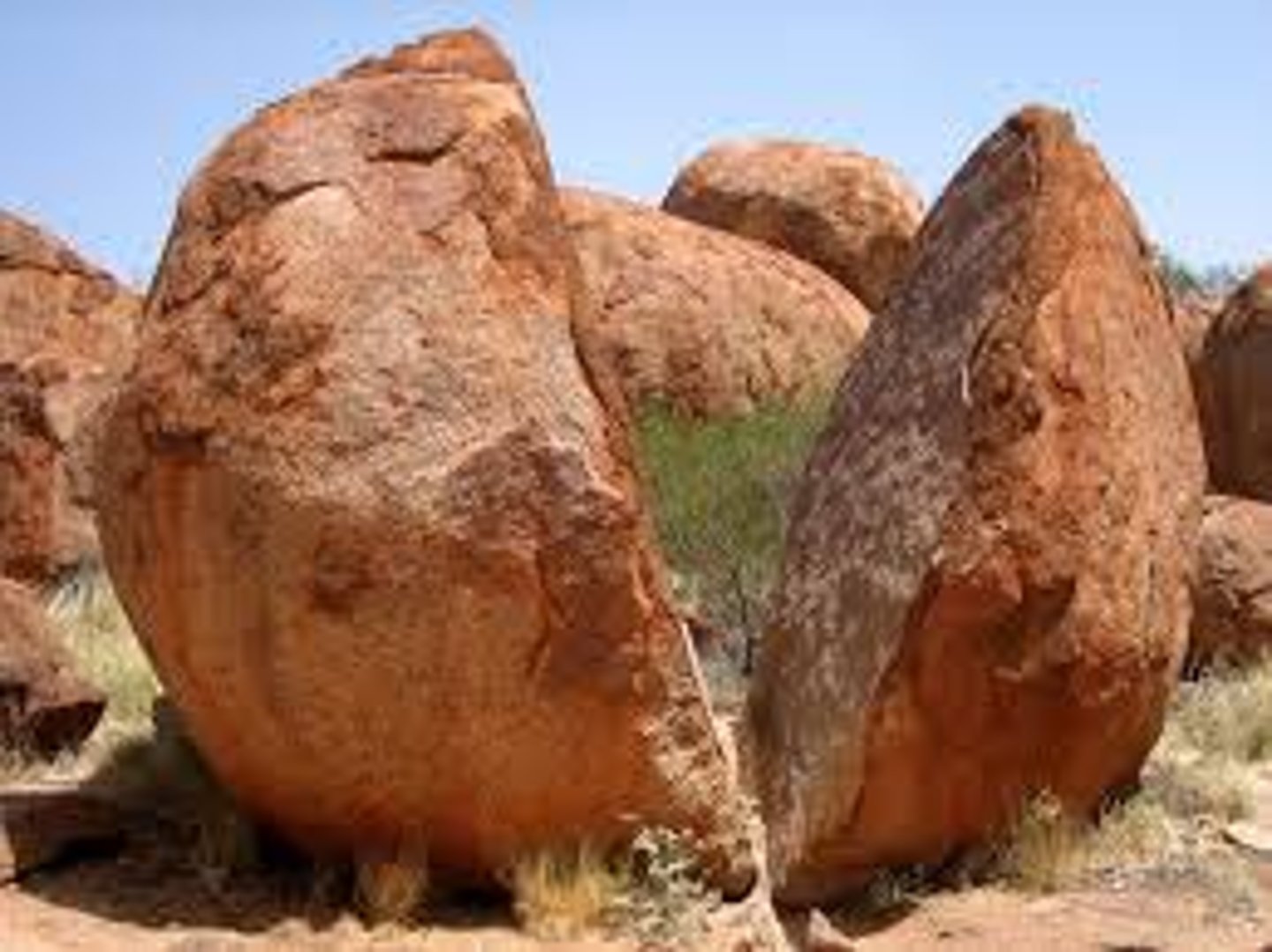

Erosion
The process by which wind, water, ice, or gravity transports soil and sediment from one location to another

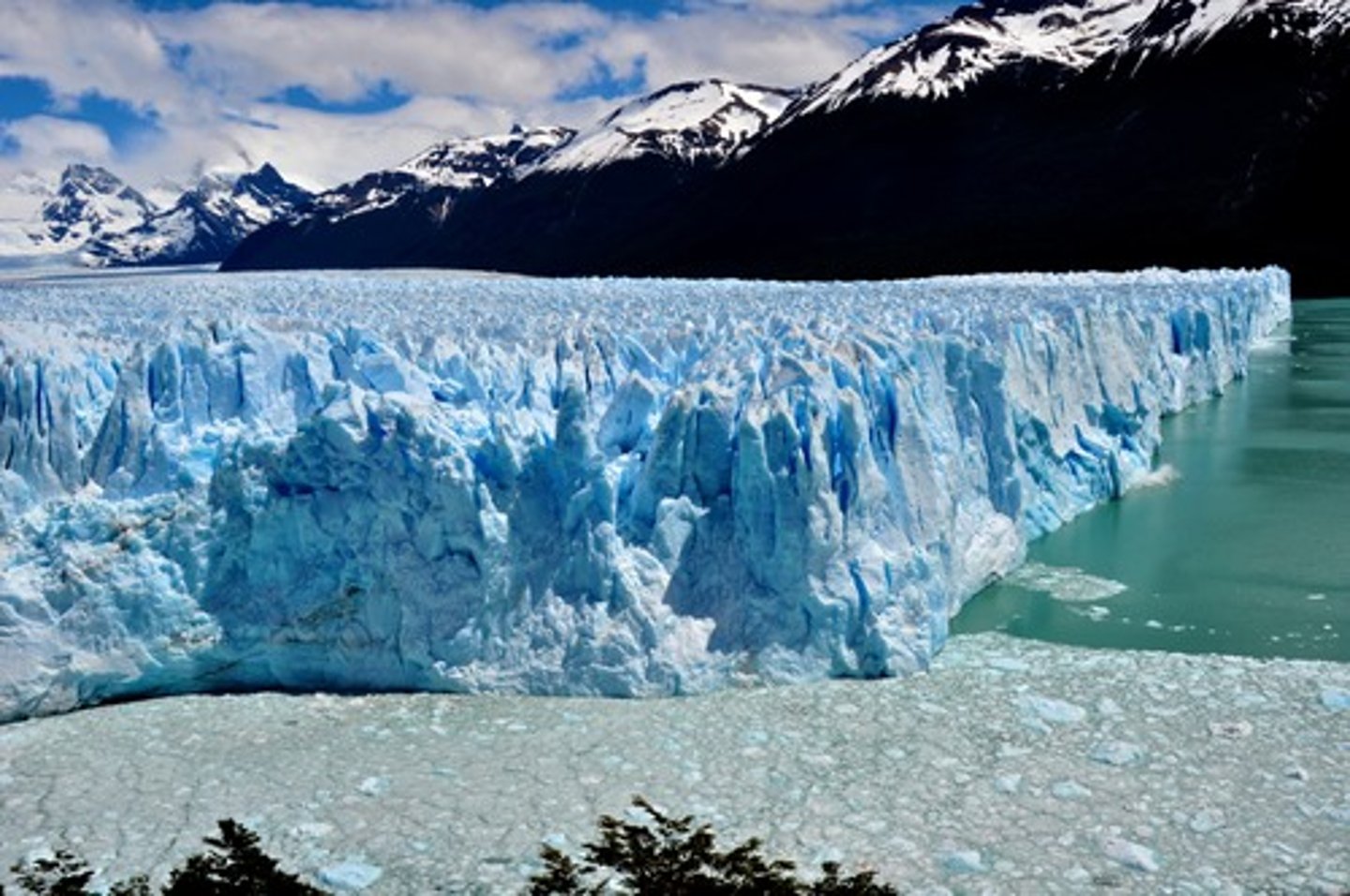
Glacier
A slowly moving mass or river of ice formed by the accumulation and compaction of snow on mountains or near the poles.

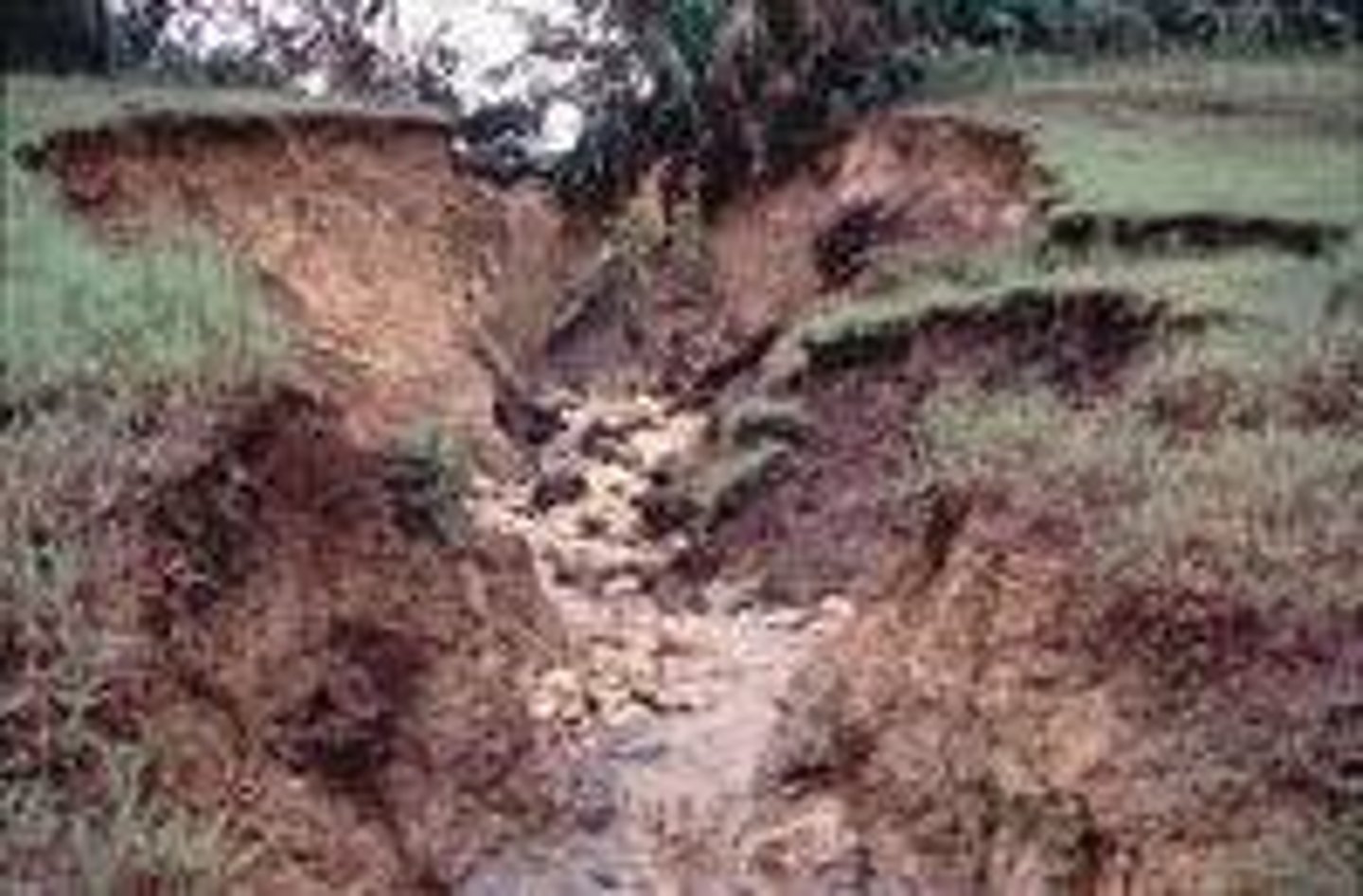
Mechanical weathering
The type of weathering in which rock is physically broken into smaller pieces
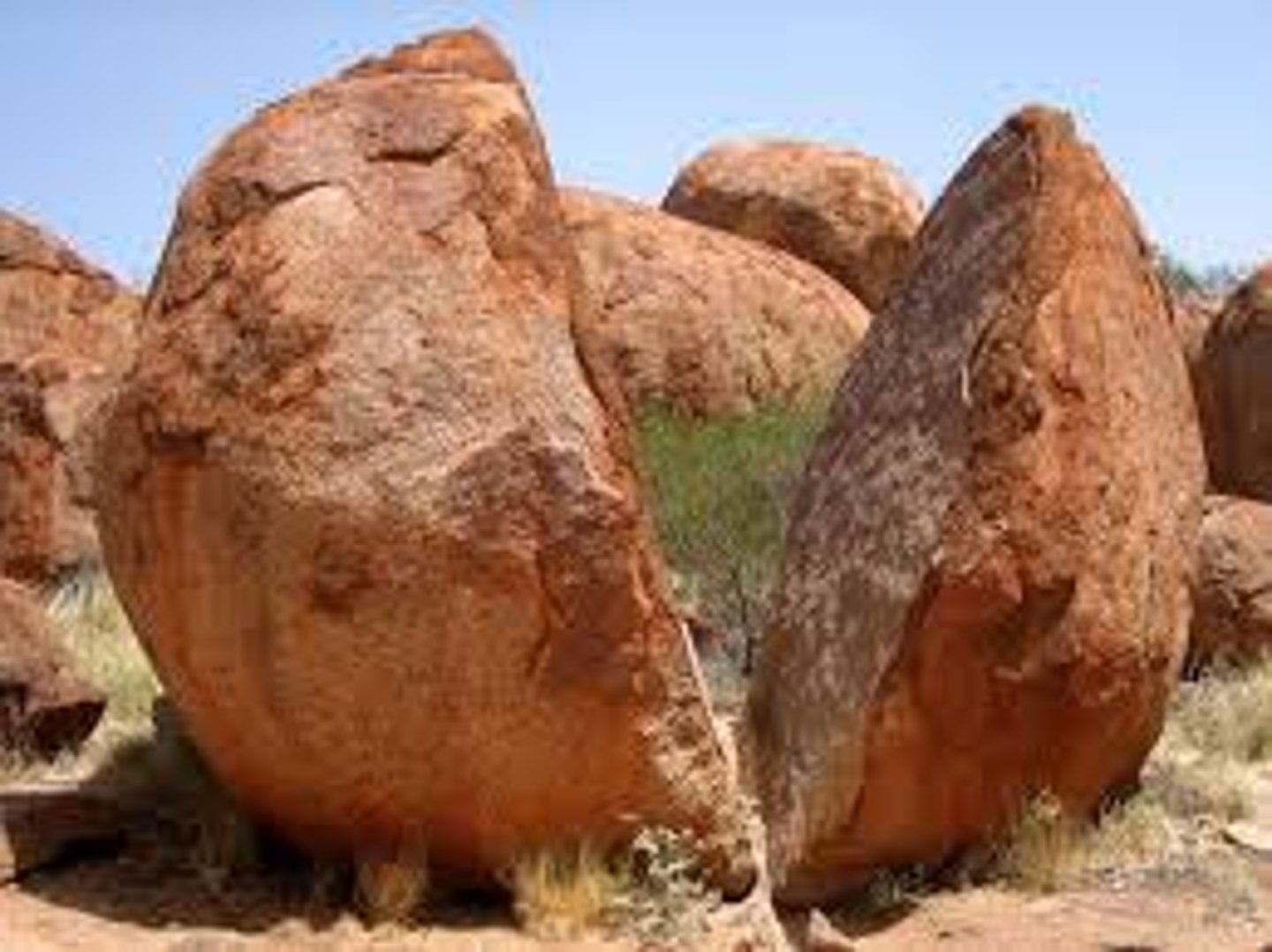

Chemical weathering
The process that breaks down rock through chemical changes.
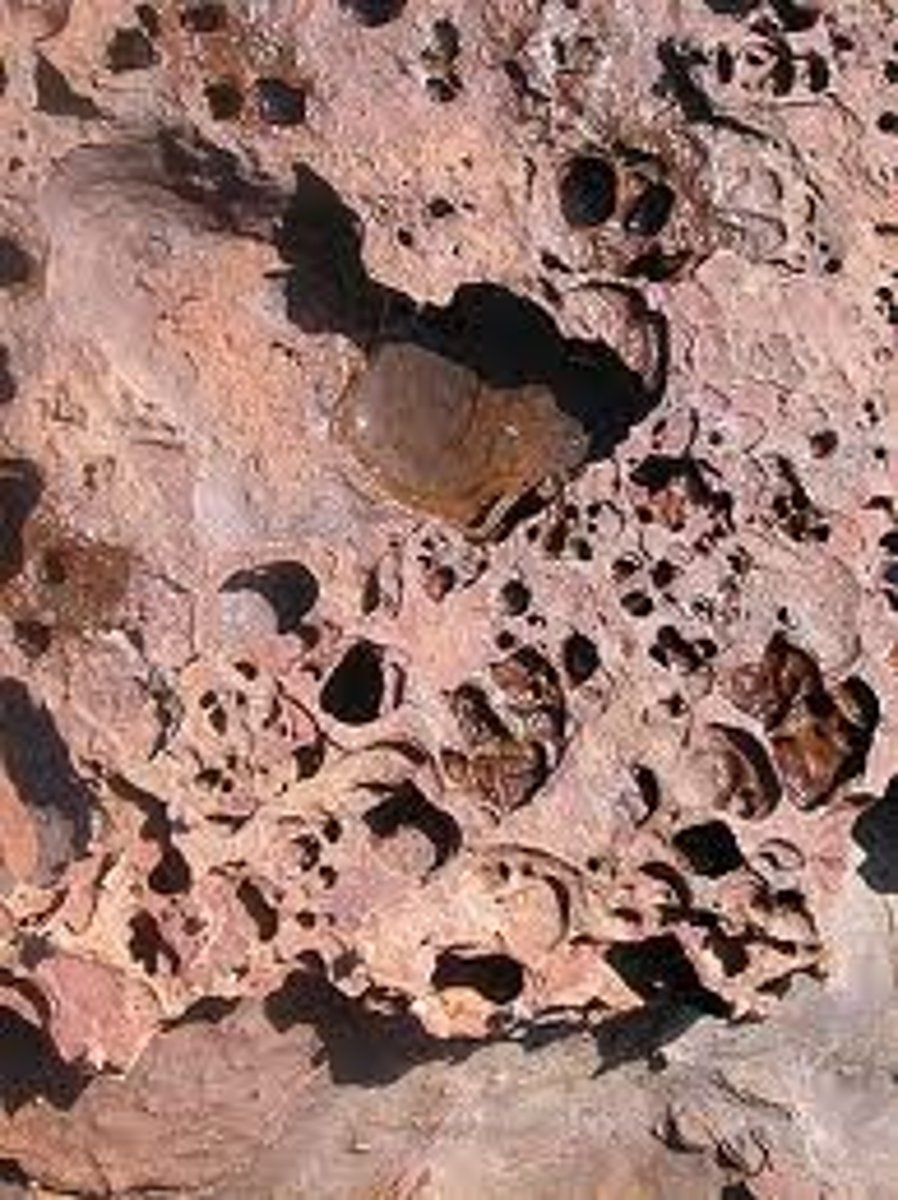

Biological weathering
Any weathering that's caused by the activities of living organisms.

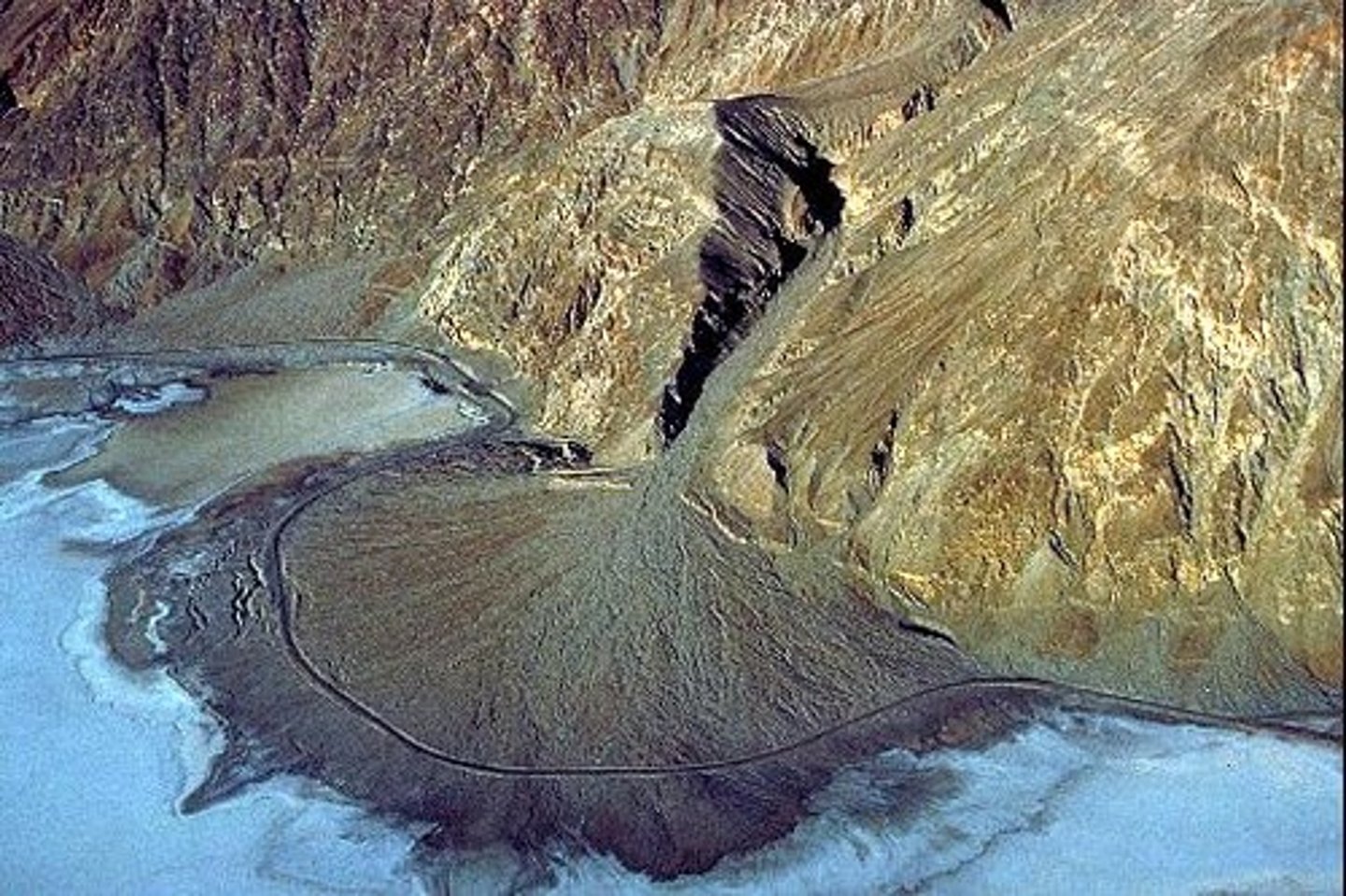
Deposition
Process in which sediment is laid down in new locations.

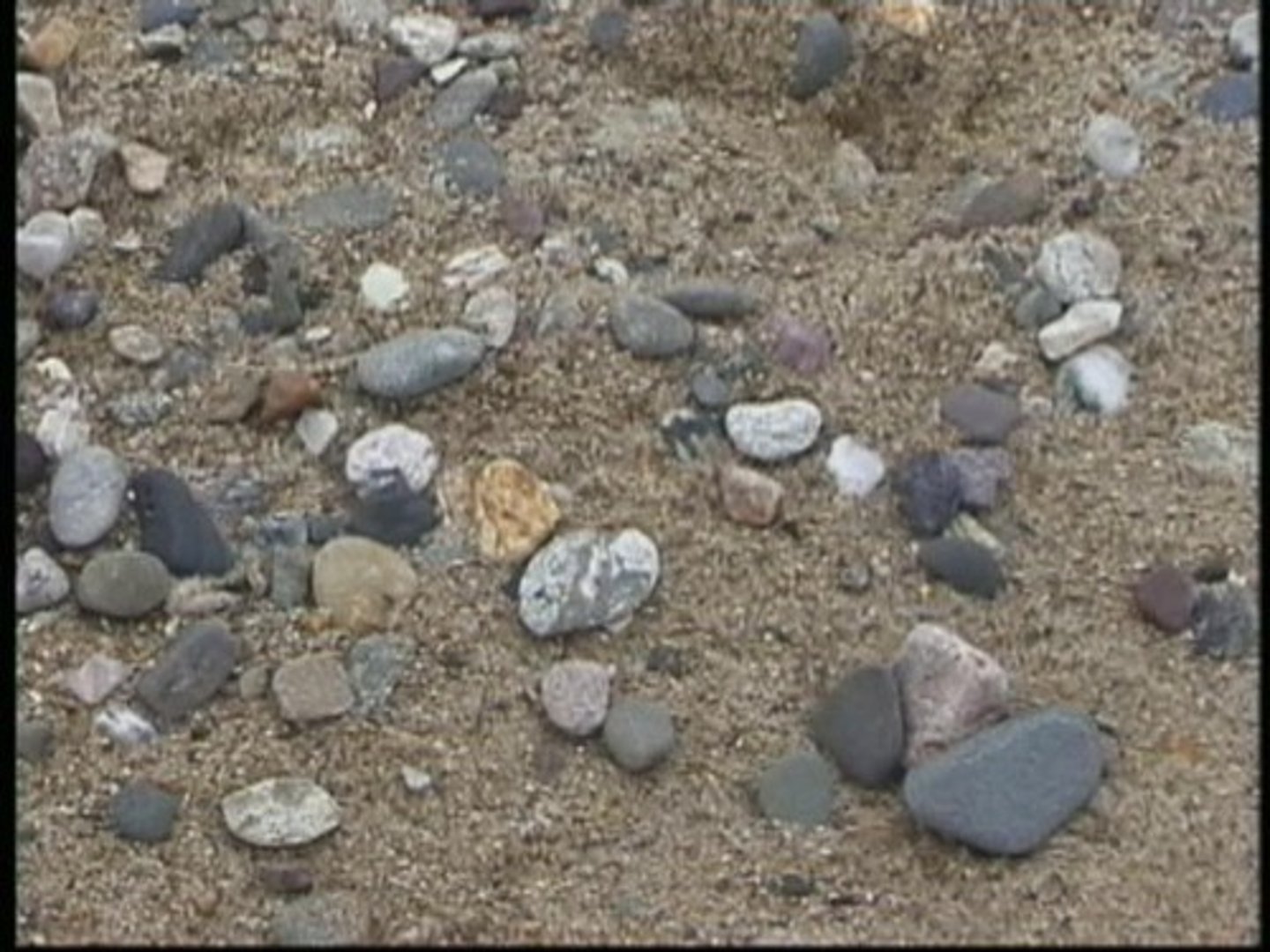
Sediment
Small, solid pieces of material that come from rocks or living things.

Abrasion
A type of mechanical weathering where the grinding away of rock occurs by rock particles carried by water, ice, wind or gravity
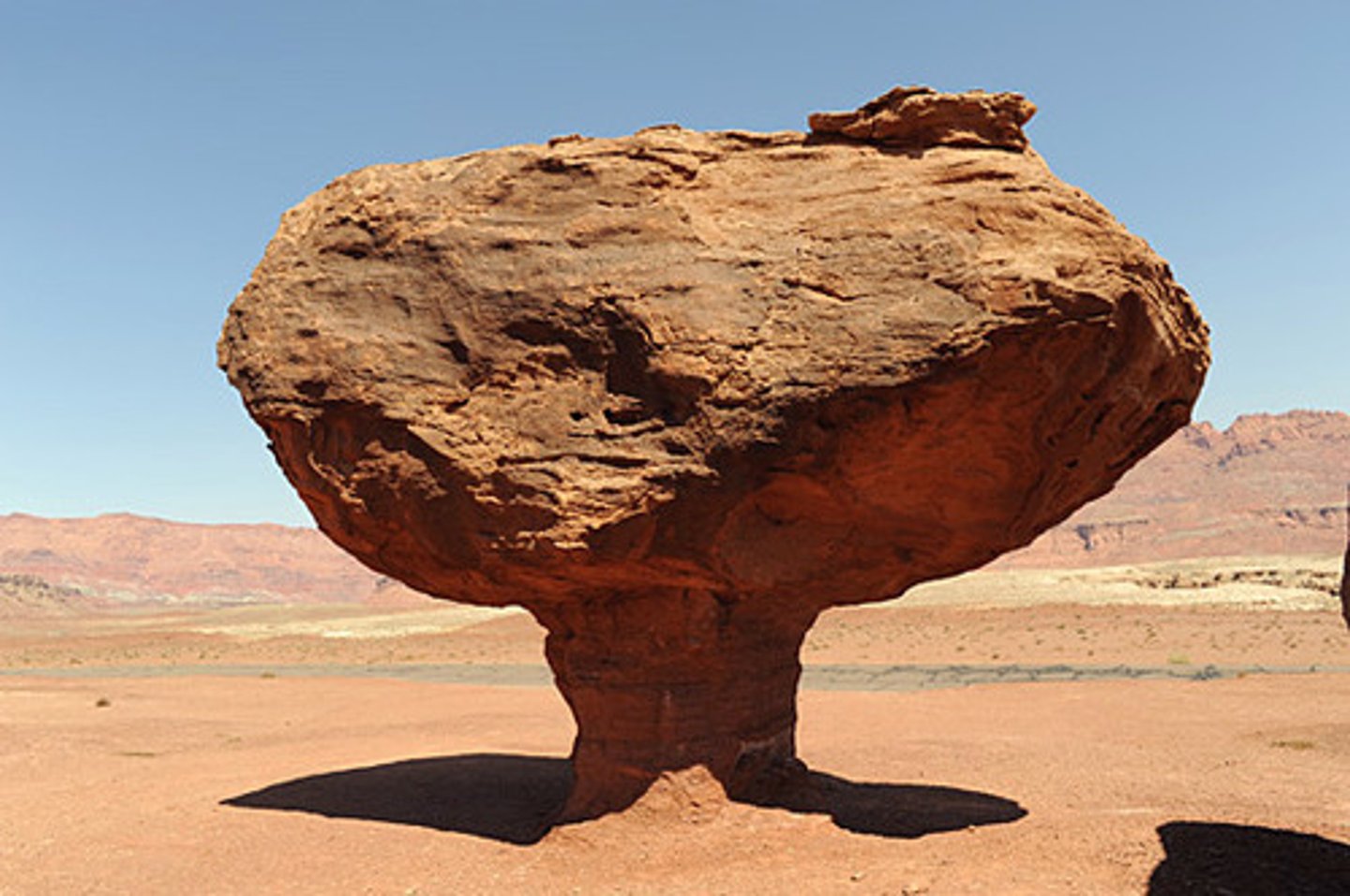

Ice wedging
Process that splits rock when water seeps into cracks, then freezes and expands.
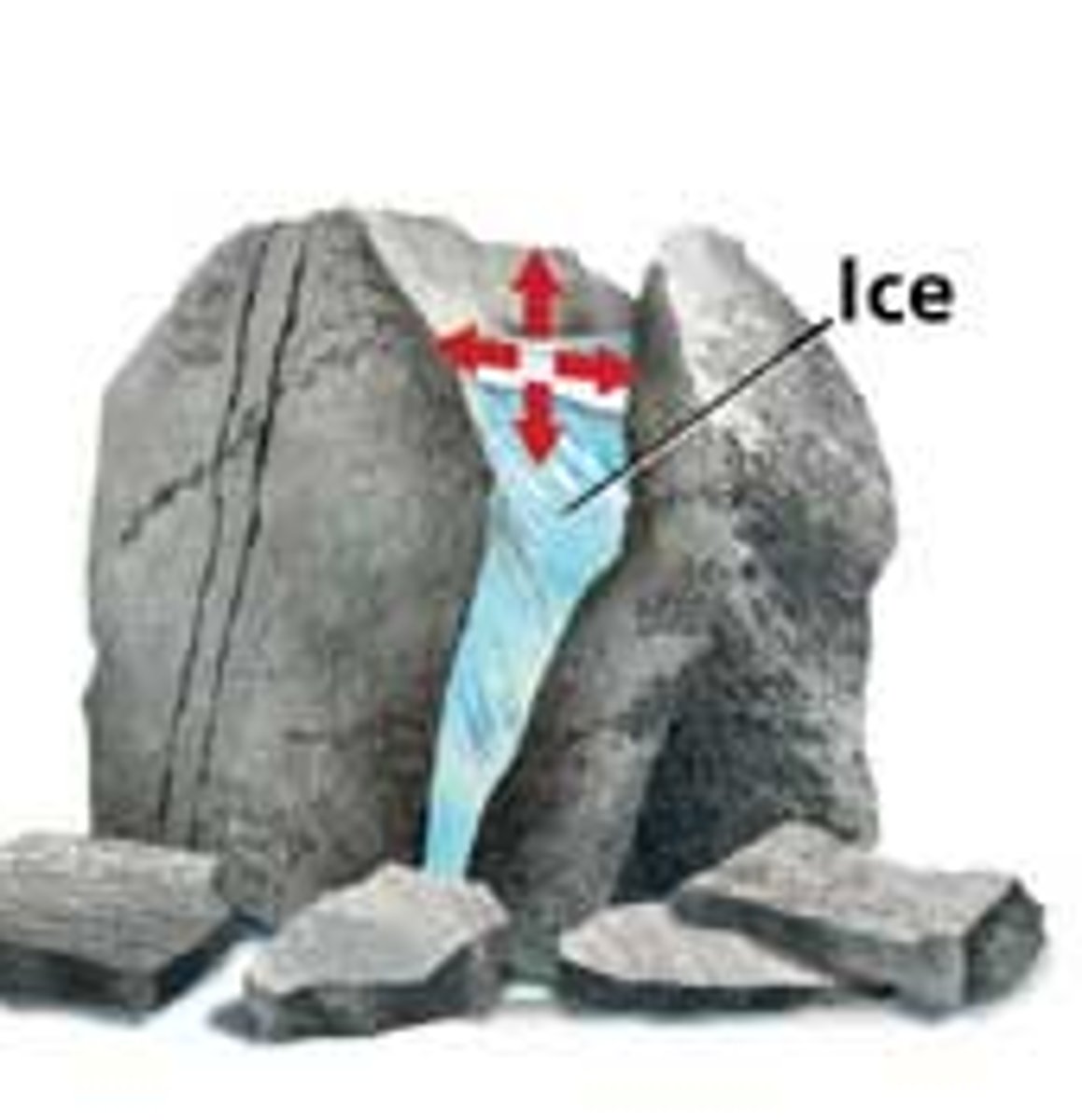

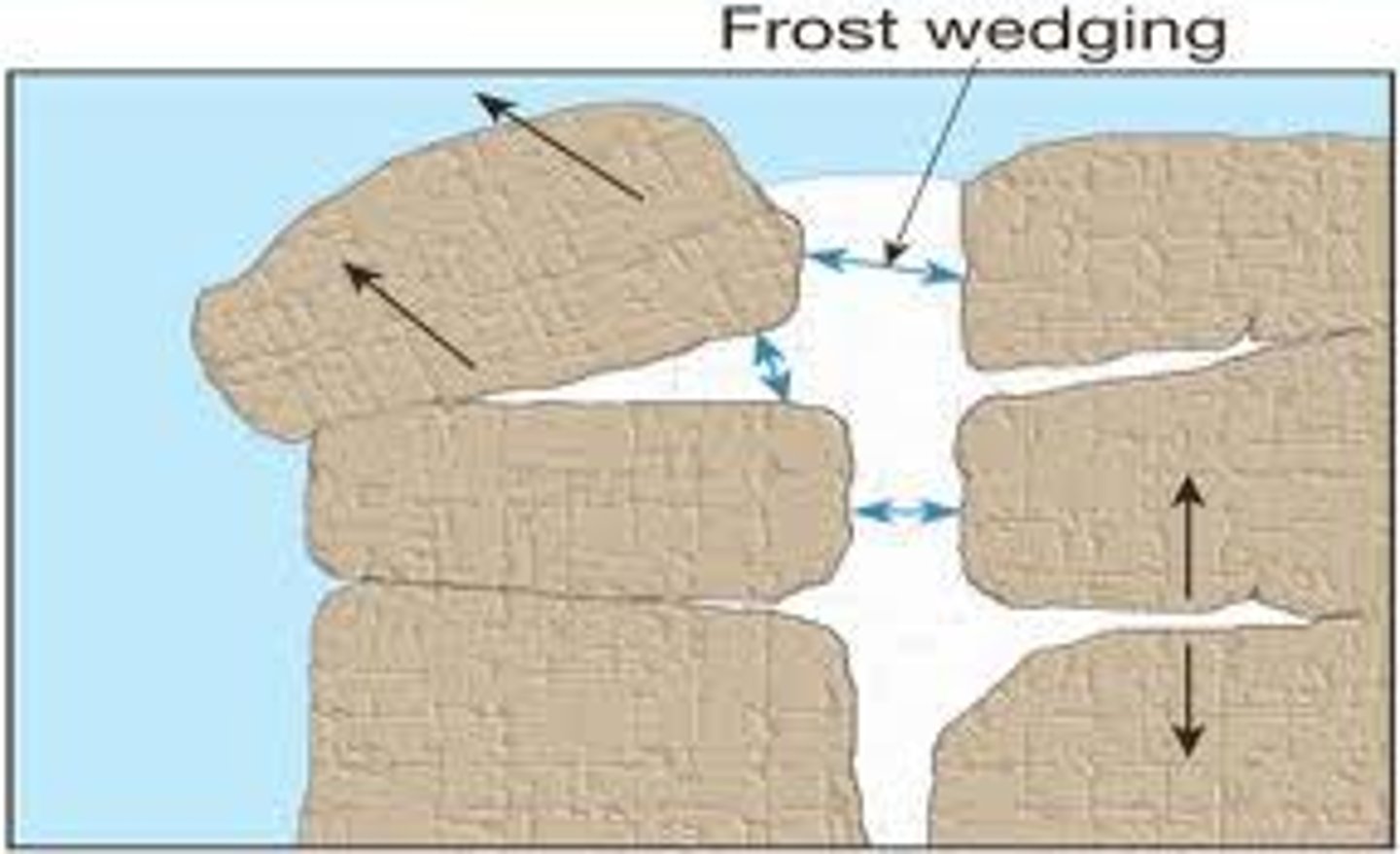
Frost wedging
The mechanical breakup of rock caused by the expansion of freezing water in cracks and crevices.
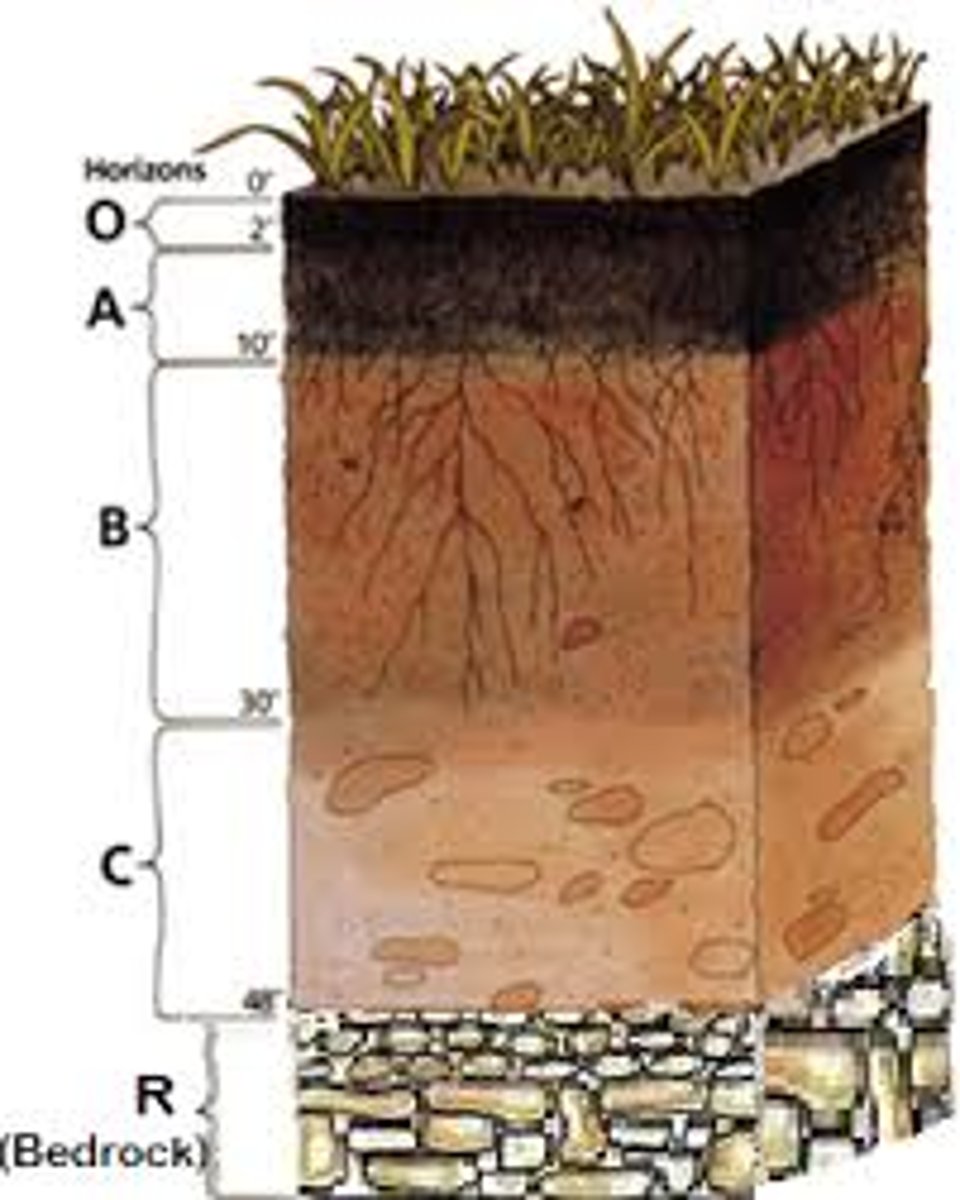
Soil
A loose mixture of rock fragments, organic material, water, and air that can support the growth of vegetation
Wind erosion
When wind moves sand, dust and soil from one place to another.

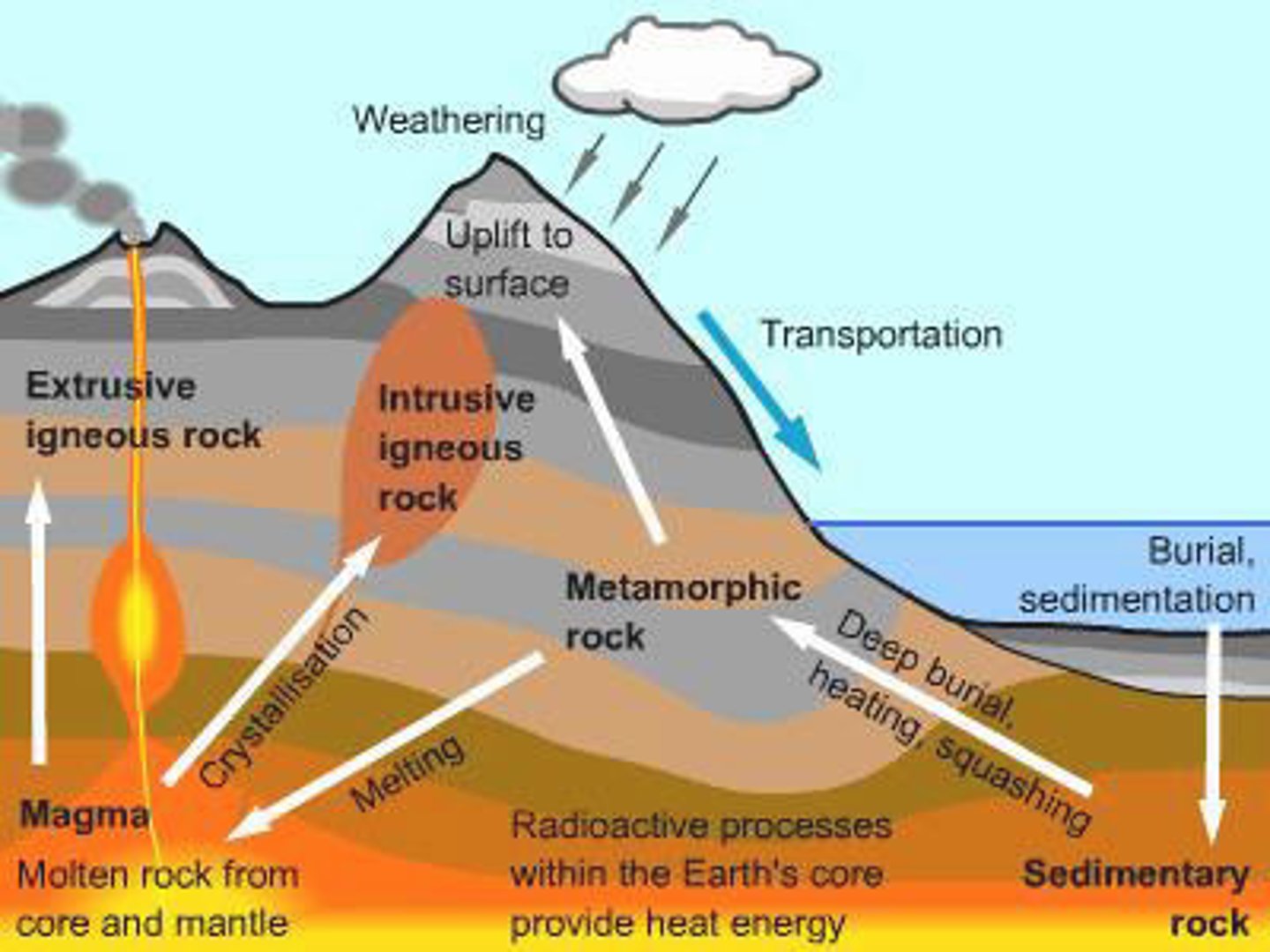
Rock cycle
A series of processes on the surface and inside Earth that slowly changes rocks from one kind to another.
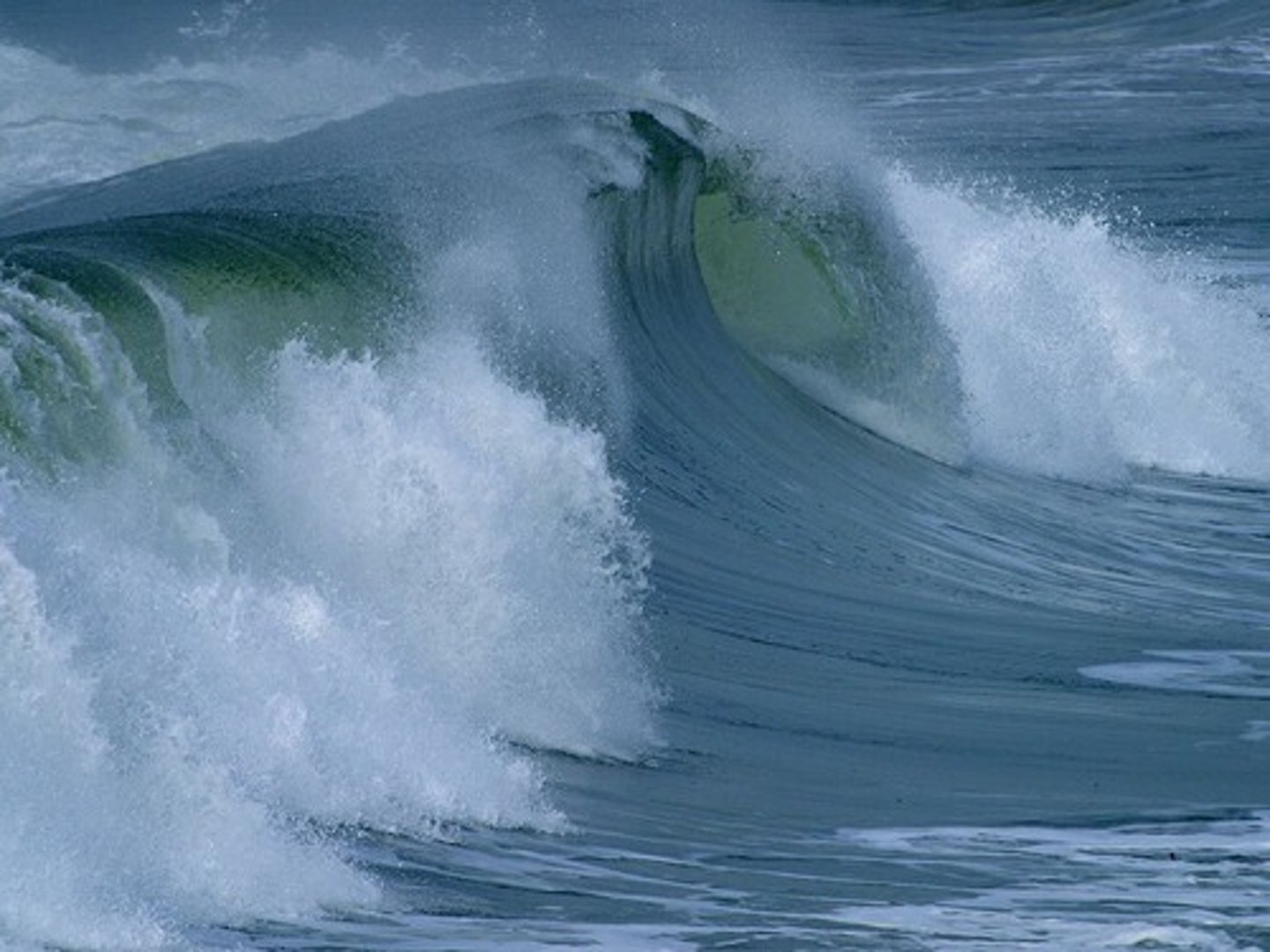
Ocean waves
Moving ridges of water on the surface of the ocean caused by wind and constantly cause weathering along the shoreline.

Oxidation
A chemical weathering process where iron combines with oxygen when water is present and creates rust.
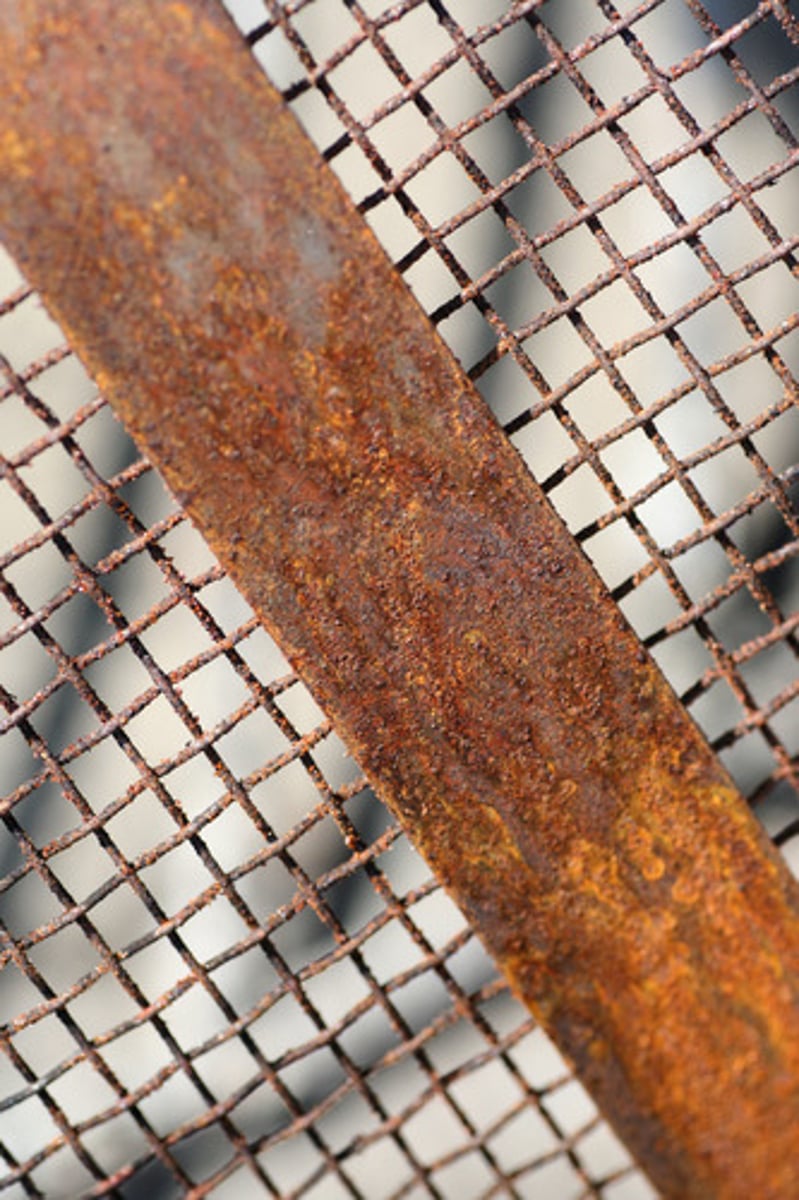

Acid rain
A type of rapid chemical weathering caused by the burning of fossil fuels to create air pollution which then mixes with precipitation and falls to Earth.

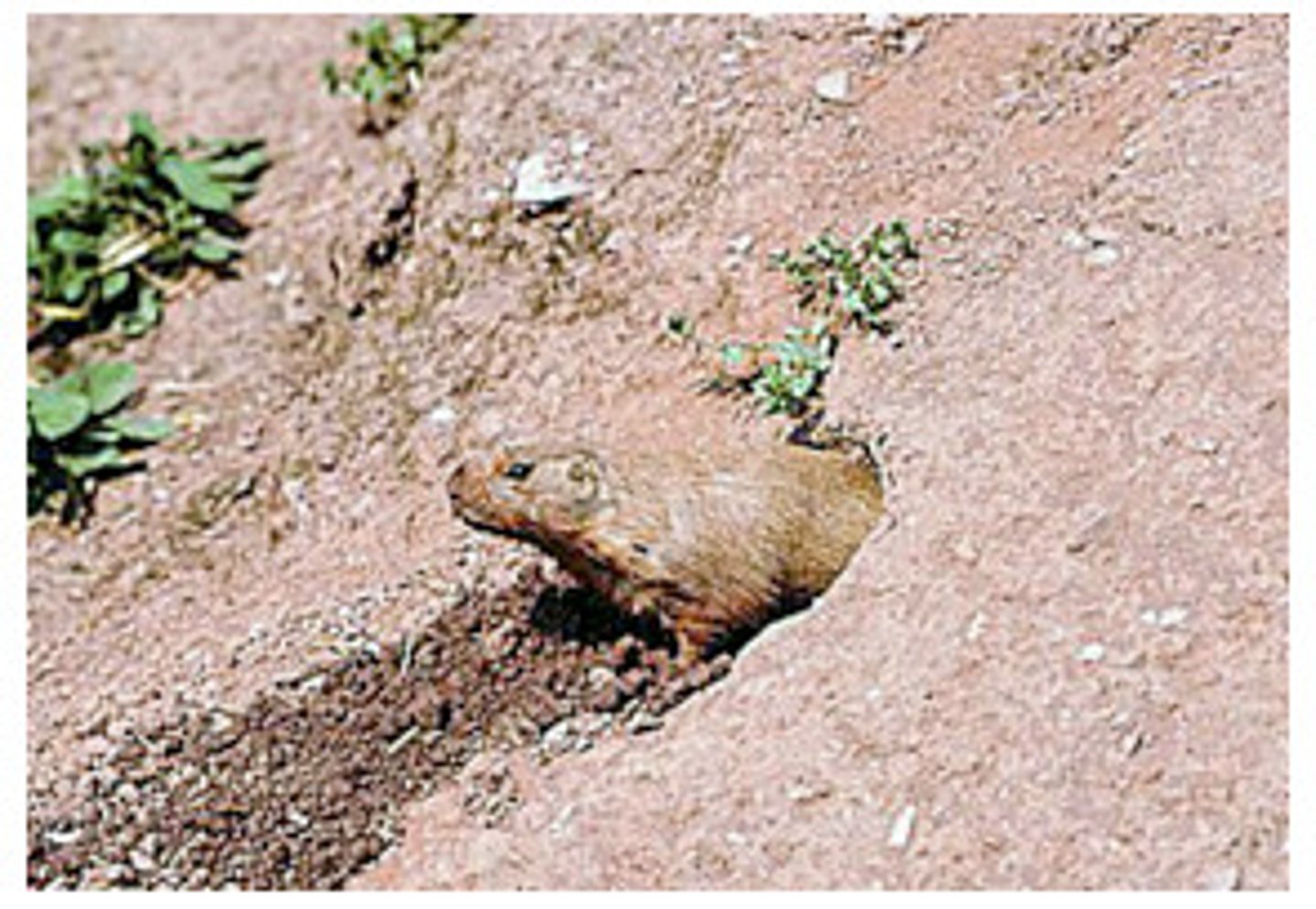
Animal actions
Type of mechanical weathering where animals that burrow into the ground can break up rocks as they build their burrows.

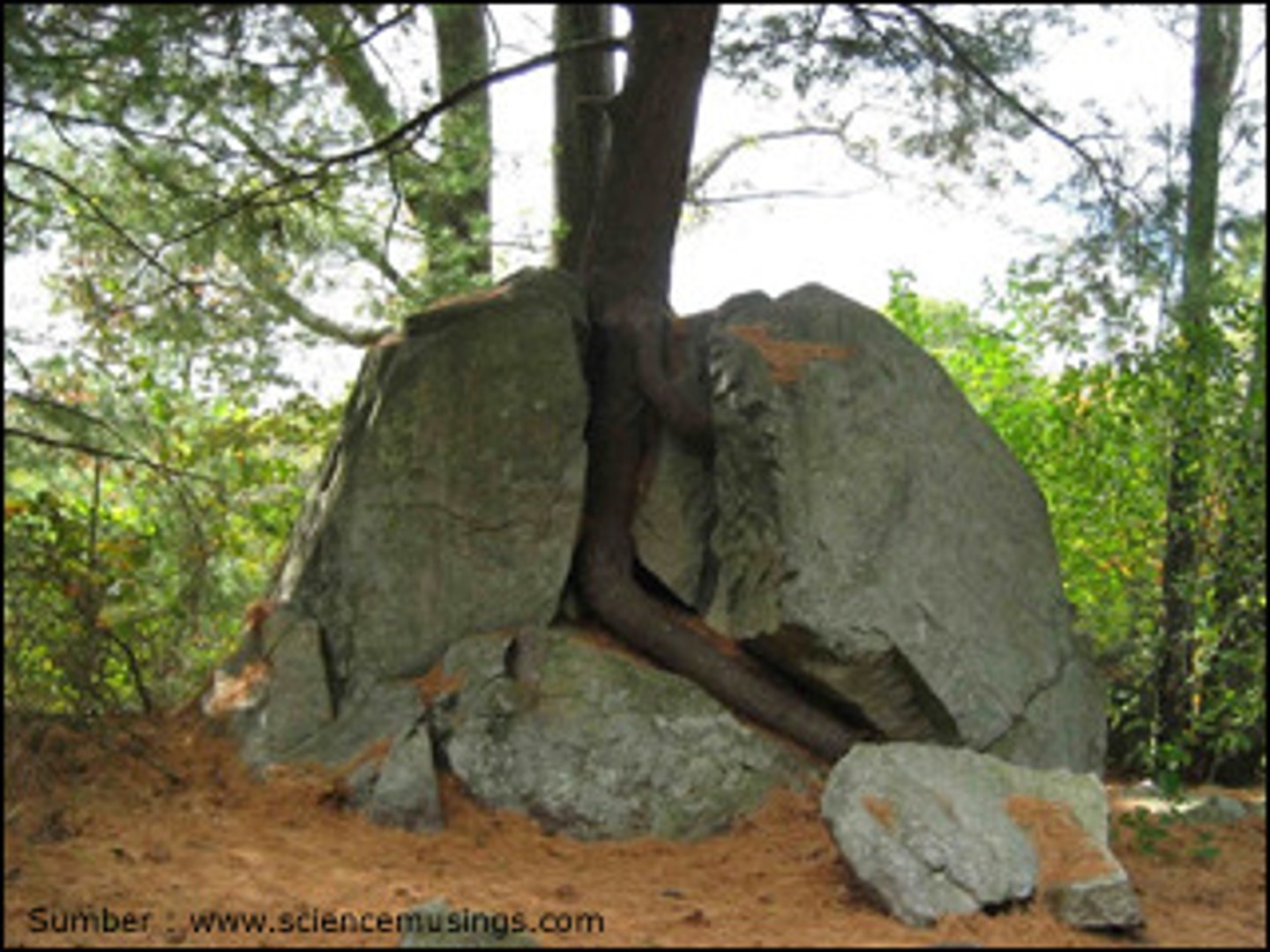
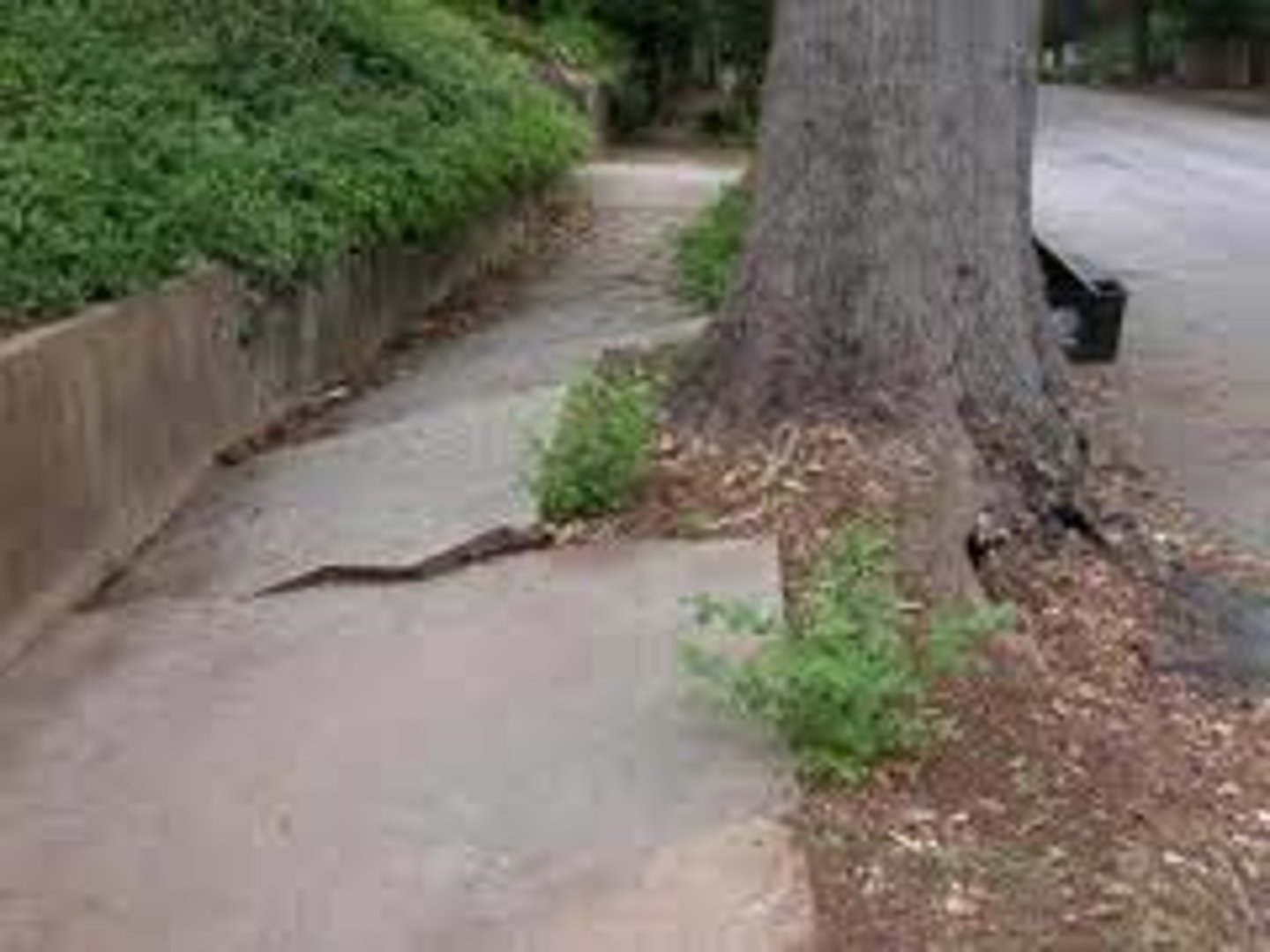
Plant growth
Type of mechanical weathering where plants roots grow into cracks in rocks and as they grow they break the rock down.

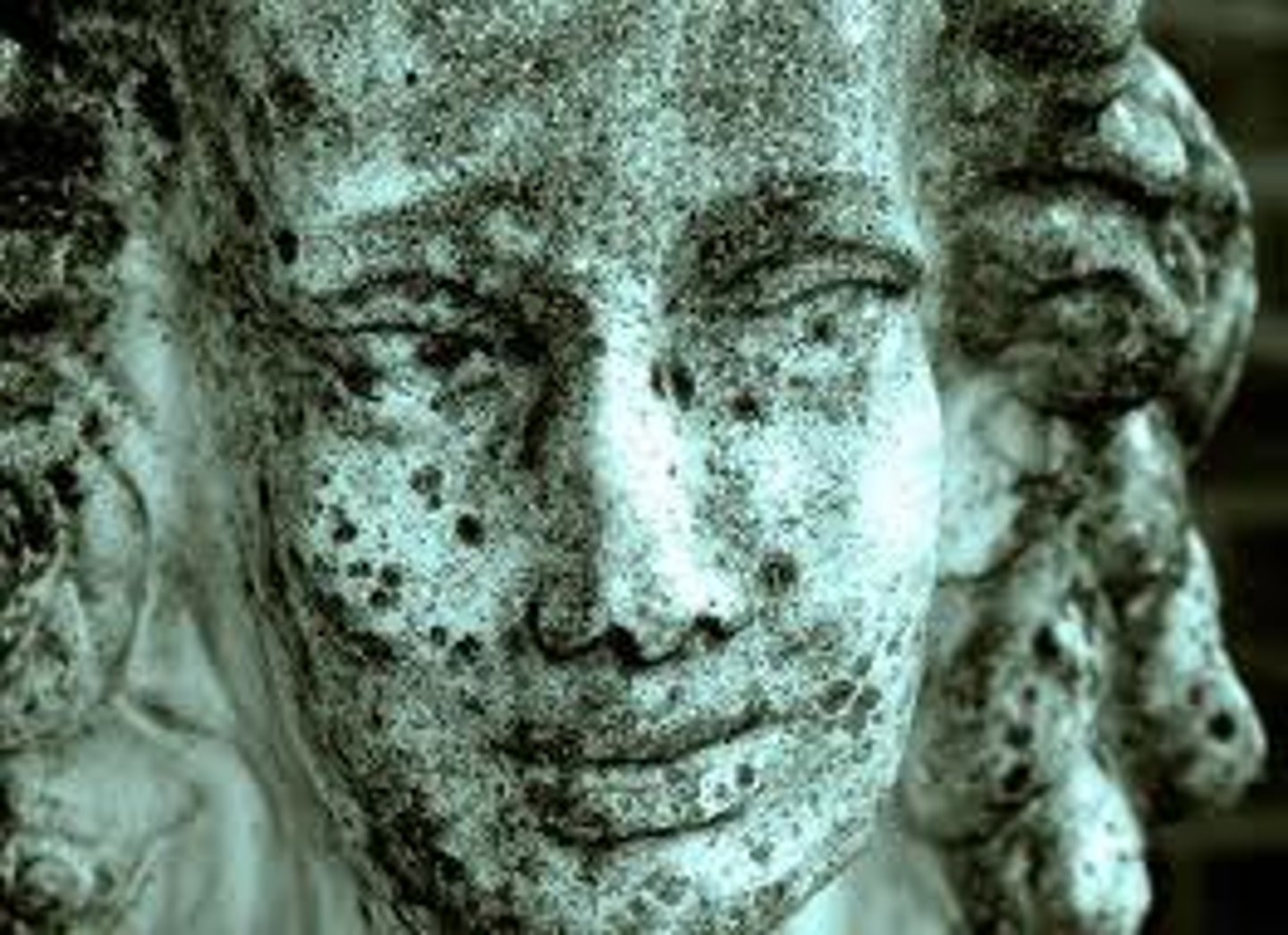
Lichen weathering
Chemical weathering of rocks by the excretion of various organic acids, particularly oxalic acid, which can effectively dissolve minerals and chelate metallic cations.