Long-Term Memory + Memory Errors
5.0(2)
Card Sorting
1/174
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Chapter 6-8
Last updated 11:53 PM on 5/17/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
175 Terms
1
New cards
**What is explicit memory?**
memories we are aware of
2
New cards
**What is long-term memory?**
system that is responsible for storing info for long periods of time
3
New cards
**What is known as “archive” of information about past events in our lives and knowledge we have learned.**
long-term memory
4
New cards
**Giving directions to a lost traveler is an example of what?**
explicit memory
5
New cards
**What is the serial position curve?**
created by presenting a list of words to a participant, one after another -→ after the last word, the participant writes down all the words he or she remembers, in any order
6
New cards
**When you remember events from the previous weekend is an example of what type of memory?**
episodic
7
New cards
**When you remember the capitals of state is an example of what type of memory?**
semantic memory
8
New cards
**What is episodic memory?**
memory for events of your life
9
New cards
**What is semantic memory?**
memory for facts
10
New cards
**We do many things without being able to explain how we do them is an example of what type of memory?**
implicit memory
11
New cards
**What is implicit memory?**
occurs when learning from experience is not accompanied by conscious remembering
12
New cards
**Mirror imaging is an example of what?**
procedural memory
13
New cards
**What is procedural/skill memory?**
memory for doing things that usually involve learned skills
14
New cards
**What is priming?**
occurs when the presentation of one stimulus (the priming stimulus) changes the way a person responds to another stimulus (the test stimulus)
15
New cards
**This is an example of what: You are presented with the word 'doctor'. A moment later, you will recognize the word 'nurse' much faster than the word 'cat' because the two medical workers are closely associated in your mind.**
priming
16
New cards
**What is classical conditioning?**
occurs when the following two stimuli are paired: (1) a neutral stimulus that initially does not result in a response and (2) a conditioning stimulus (more commonly called an unconditioned stimulus) that does result in a response
17
New cards
**This example: Presenting a tone to a person followed by a puff of air to the eye that causes the person to blink. The tone initially does not cause an eyeblink, but after a number of pairings with the puff of air, the person blinks in response to the tone.**
conditioning
18
New cards
**What is the recency effect?**
better memory for the stimuli presented at the end of a sequence
19
New cards
**What is the priming effect?**
participants are more likely to remember words presented at the beginning of a sequence
20
New cards
**What is coding?**
refers to the form in which stimuli are represented
21
New cards
**What is proactive interference?**
decrease in memory that occurs when previously learned information interferes with learning new information
22
New cards
**What is repetition priming?**
occurs when the test stimulus is the same as or resembles the priming stimulus
23
New cards
**This is an example of: a difficulty in remembering a friend's new phone number after having previously learned the old number**
proactive interference
24
New cards
**This is an example of: seeing the word bird may cause you to respond more quickly to a later presentation of the word bird than to a word you have not seen, even though you may not remember seeing bird earlier**
repetition priming
25
New cards
**What is the propaganda effect?**
participants are more likely to rate statements they have read or heard before as being true, simply because they have been exposed to them before
26
New cards
**This is an example of: A campaign might claim that most people support their candidate, even if this is not true**
propaganda effect
27
New cards
**This is an example of: holding a phone number in memory by repeating it over and over**
maintenance rehearsal
28
New cards
**What is elaborative rehearsal?**
Using meanings and connections to help transfer information from STM to LTM
29
New cards
**What is maintenance rehearsal?**
Repetition of stimuli that maintains information \n in STM but does not transfer it to LTM
30
New cards
**What is deep processing?**
involves close attention and elaborative rehearsal focuses on item's meaning and its relationship to something else
31
New cards
**What is shallow processing?**
little attention to meaning
32
New cards
**This is an example of: When a phone number is repeated over and over or attention is focused on a word’s physical features such as whether it is printed in lower-case or capital letters**
shallow processing
33
New cards
**What is cued recall?**
when the participant is presented with retrieval cues to aid in recall of previously experienced stimuli
34
New cards
**What is transfer-appropriate processing?**
better performance when the type of processing matches in encoding and retrieval
35
New cards
**What is consolidation?**
the process that transforms new memories from a fragile state in which they can be disrupted to a more permanent state resistant to disruption
36
New cards
**What is synaptic consolidation?**
takes place over minutes or hours involves structural changes at synapses
37
New cards
**What is systems consolidation?**
takes place over months or even years, involves the gradual reorganization of neural circuits within the brain
38
New cards
**“Cells that fire together, wire together” is considered to be what?**
synaptic consolidation
39
New cards
**After encoding, activity of hippocampus fades with time, is considered to be what?**
systems consolidation
40
New cards
**What type of amnesia happens for events after injury (inability to form new memories?**
anterograde amnesia
41
New cards
**What is loss for memory for event before trauma?**
retrograde amnesia
42
New cards
**What is the loss for memory for recent events is more fragile than for remote events?**
graded amnesia
43
New cards
**What is the standard model of consolidation?**
is when memory unfolds according to sequence of steps which the hippocampus is involved in encoding new memories and makes connection with higher cortical areas --> connections between hippocampus and cortical areas weaken and strengthen and HC is not involved
44
New cards
**What is the multiple model of consolidation?**
the hippocampus communicates with cortical areas and proposes that the hippocampus remains in active communication with the cortical areas, even for remote memories
45
New cards
**What is reconsolidation?**
idea that when a memory is retrieved (remembered), it becomes fragile, like it was when it was originally formed, and that when it is in this fragile state, it needs to be consolidated again
46
New cards
**What is autobiographical memory?**
Memory for specific experiences from our life, which \n can include both episodic and semantic components
47
New cards
**The first time learning to drive a car is an example of what type of memory?**
autobiographical memory
48
New cards
**What is the reminiscence bump?**
The enhanced memory for adolescence and young adulthood found in people over 40
49
New cards
**What is a flashbulb memory?**
refer to a person’s memory for the circumstances surrounding shocking, highly charged events
50
New cards
**This is an example of: The memories I have described about how I heard about the 9/11 attack, and the people and events directly associated with finding out about the attack, are still vivid in my mind more than 16 years later**
flashbulb memory
51
New cards
**What is the illusory truth effect?**
The enhanced probability of evaluating a statement as being true upon repeated presentation
52
New cards
**This is an example of: People who hear a false statement like “Leopards are the fastest land animal” multiple times are more likely to think that it is true**
illusory truth effect
53
New cards
**This is an example of: Imagine that there’s a movie you can’t wait to see because you heard it’s really good. But when you try to remember what first turned you on to the movie, you’re uncertain.**
source monitoring
54
New cards
**What is source monitoring?**
the process of determining the origins of our memories, knowledge, or beliefs
55
New cards
**What is the source monitoring error?**
misidentifying the source of a memory
56
New cards
**If you decided searching for interest of the movie was the review you read online but in reality you first heard about it from your friend is an example of what type of error?**
source monitoring error
57
New cards
**Harrison’s problem was that he thought he was the source of the melody, when the actual source was someone else is an example of?**
cryptomnesia
58
New cards
**What is cryptomnesia?**
unconscious phenomenon of work of others
59
New cards
**What is a schema?**
person’s knowledge about some aspect of the environment
60
New cards
**Having the knowledge about what a bank is and what it includes is an example of a?**
schema
61
New cards
**What is a script?**
our conception of the sequence of actions that usually occurs during a particular experience
62
New cards
**Your coffee shop ________ might be waiting in line, ordering a drink and pastry from the barista, receiving the pastry, paying, and waiting near “pickup” for your drink**
script
63
New cards
**What is the misinformation effect?**
misleading information presented after a person witnesses an event can change how the person describes that event later
64
New cards
**This is an example of what: using the word "smashed" instead of "hit" could change how the participants remembered the accident**
misinformation effect
65
New cards
**What is misleading post information?**
misleading information
66
New cards
**What is eyewitness testimony?**
testimony by someone who has witnessed a crime.
67
New cards
**What is constructive nature of memory?**
what people report as memories are constructed based on what actually happened plus additional factors, such as the person’s knowledge, experiences, and expectations
68
New cards
**This is an example of: how a lawyer can call various witnesses to recall the happenings of a crime. The witnesses cannot all tell the same story.**
constructive nature of memory
69
New cards
**What is the Ebbinghaus’ savings curve?**
decrease in savings (remembering) with increasing delays indicates \n that forgetting occurs rapidly over the first 2 days and then \n occurs more slowly after that
70
New cards
**What was the task of the serial position curve?**
1). Read list of words 2). After the last word, write down 3). all words remembered
71
New cards
**Memory is better for words presented at the beginning of the** \n **list is?**
primacy effect
72
New cards
**Memory is better for words presented at the end of the** \n **list is?**
recency effect
73
New cards
**What was the task of the primacy effect?**
Repeat words out loud between 5-sec intervals; write down list after last word
74
New cards
**What were the results of the primacy effect?**
More repetitions for words at beginning
75
New cards
**What was the task for the recency effect?**
Count backwards by 3 after last word
76
New cards
**Why did the recency effect occur?**
Effect due to storage of last items in STM
77
New cards
**Holding an image in the mind to produce a visual pattern that was just seen is an example of what type of coding?**
STM visual memory
78
New cards
**Visualizing what the Lincoln Memorial at Washington D.C. looked like when you saw it last summer is an example of what type of coding?**
LTM visual coding
79
New cards
**Representing the sounds of letter in the mind just after hearing them is an example of what type of coding?**
STM auditory coding
80
New cards
**Repeating a song you have heard many times before over and over in your mind is an example of what type of coding?**
LTM auditory coding
81
New cards
**Placing words in STM task into categories based on their meaning is an example of what type of coding?**
STM semantic coding
82
New cards
**Recalling the general plot of a novel you read last week is an example of what type of coding?**
LTM semantic coding
83
New cards
**What was the finding of Wickens experience?**
proactive interference
84
New cards
**What were the result of Wikens experiment?**
The Fruits group showed reduced performance on trials 2, 3, and 4 caused at least partially by proactive interference (indicated by blue points)
85
New cards
**What happened in trials 2 & 3 in the Wikens experiment?**
Professions group showed similarly reduced performance on trials 2 and 3
86
New cards
**Why was their increased performance on trial 4?**
represents a release from proactive interference because the \n names of fruits, rather than professions, were presented on trial 4
87
New cards
**What was HM double dissociation?**
when there was surgery removed hippocampus bilaterally -→ Retained short-term memory (STM) but unable to transfer info to long-term memory (LTM)
88
New cards
**What was KF double dissociation?**
accident damaged parietal lobe -→ Impaired STM (reduced digit span) but functional LTM \n (able to form and hold new memories)
89
New cards
**What is tied to personal experience, remembering is reliving, and “mental time travel?”**
episodic memory
90
New cards
**Episodic memory is**
“self-knowing”
91
New cards
**Your experience moving in to your dorm at UCSC is an example of what?**
an episodic memory
92
New cards
**Semantic memory is**
“knowing”
93
New cards
**The capital of California is Sacramento is**
semantic memory
94
New cards
**What double dissociation study had no episodic memory and semantic was intact?**
KC’s damaged hippocampus
95
New cards
**What double dissociation study had episode memory, but no semantic?**
italian woman
96
New cards
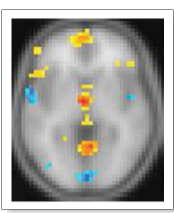
**What areas are involved with episodic memories and semantic memories?**
yellow areas represent brain regions = episodic & ; the blue areas represent regions associated = semantic
97
New cards
**Forgetting increases**
with longer intervals after encoding
98
New cards
**Forgetting is not**
an “all-or-nothing” process
99
New cards
**What is familiarity associated with?**
semantic memories
100
New cards
**What is recollection associated with?**
episodic memories