MCAT: Organ Systems
1/728
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
729 Terms
parts of the nervous system
central and peripheral
central nervous system
brain and spinal cord
peripheral nervous system
nerves and ganglia
ganglia
clusters of cell bodies in the PNS
cerebral hemispheres
The right and left halves of the cerebrum
cerebrum
Area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body
afferent neurons
Nerve cells that carry impulses towards the central nervous system
efferent neurons
Nerve cells that conduct impulses away from the central nervous system
midbrain
A small part of the brain above the pons that integrates sensory information and relays it upward.
pons
A brain structure that relays information from the cerebellum to the rest of the brain
medulla
the base of the brainstem; controls heartbeat and breathing
cerebellum
A large structure of the hindbrain that controls fine motor skills.
hindbrain
medulla, pons, cerebellum
forebrain
The largest and most complicated region of the brain, including the thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system, and cerebrum.
thalamus
the brain's sensory switchboard, located on top of the brainstem; it directs messages to the sensory receiving areas in the cortex and transmits replies to the cerebellum and medulla
hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
limbic system
neural system located below the cerebral hemispheres; associated with emotions and drives
cranial nerves
12 pairs of nerves that carry messages to and from the brain
spinal nerves
31 pairs of nerves arising from the spinal cord
basic functions of the nervous systems
motor control, sensory detection, automatic responses
syndromes
patterns of nervous system abnormalities
higher functions of the nervous systems
cognition, emotions, and consciousness
motor functions
Complex muscle-and-nerve acts that produce movement (walking, writing, typing running etc.)
sensory functions
sending and processing sensory info. ( hearing, seeing, touch,etc)
automatic responses
things that don't require conscious involvement, like reflexes, respiration, circulation, digestion
cognition
the thinking functions of the brain, learning, language, memory, executive functions
emotions
feelings created in response to thoughts, remarks, and events
consciousness
our awareness of ourselves and our environment
somatosensory tracts
position, vibration, fine touch, pain, temperature, and gross touch
position sense
awareness of static position
vibration sense
subclass of tactile sense, sensed by deformation of tactile receptors
fine touch sense
provides specific information about a touch sensation, such as exactly what point on the body is touched plus the shape, size, and texture of the source of stimulation
pain sense
activated by any factor that damages the tissues
temperature sense
sense hot and cold
gross touch sense
non-localizable
autonomic nervous system
A subdivision of the peripheral nervous system. Controls involuntary activity of visceral muscles and internal organs and glands.
somatic nervous system
the division of the peripheral nervous system that controls the body's skeletal muscles
Sympathetic Nervous System (SNS)
The component of the autonomic nervous system that responds to stressful situations by initiating the fight-or-flight response.
-norepinephrine
parasympathetic nervous system
the division of the autonomic nervous system that calms the body, conserving its energy
-also uses acetylcholine
Acetylcholine (ACh)
A neurotransmitter that enables learning and memory and also triggers muscle contraction; somatic nervous system
motor unit
A motor neuron and all of the muscle fibers it innervates
lower motor neurons
axons leave the CNS, extend through PNS to skeletal muscles. Cell bodies in anterior horns of spinal cord and in cranial nerve nuclei of brainstem
neuromuscular junction
point of contact between a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle cell
atrophy
(n.) the wasting away of a body organ or tissue; any progressive decline or failure; (v.) to waste away
fasciculations
Involuntary contractions or twitchings of muscle fibers
hypotonia
a condition in which there is diminished tone of the skeletal muscles
hyporeflexia
absence of a reflex
muscle stretch reflex
causes a muscle to contact after it's stretched, as a protective response; rubber hammer hitting knee
Upper motor neurons
motor neurons in the central nervous system that control the lower motor neurons in the peripheral nervous system; somas found in cerebral cortex
corticospinal tract
connections between brain and spine
tract
collection of axons in CNS
corticobulbar tract
Controls all voluntary movement for speech production. Descends from motor cortex through internal capsule but terminates at cranial nerves.
upper motor neuron signs
hyperreflexia, clonis, hypertonia, extensor plantar response
Hyperreflexia
Exaggerated reflex response
lower motor neuron signs
atrophy, fasciculations, hypotonia, hyporeflexia
clonis
The rapid repetitive response to stretch.
hypertonia
increased muscle tone
Extensor Plantar Response
if you take a hard object and scrape along bottom of foot, normal response is flexor - toes will come down on the object. But with extensor, toes extend up.
Autonomic Nervous System
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms.
- efferent neurons
-smooth muscle
-cardiac muscle
-gland cells
ganglia
clusters of cell bodies in the PNS
forebrain
The largest and most complicated region of the brain, including the thalamus, hypothalamus, limbic system, and cerebrum.
pituitary gland
The endocrine system's most influential gland. Under the influence of the hypothalamus, the pituitary regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands.
forebrain function
thinking, sensing,memory, emotions, hunger, sleep, fullness
hindbrain functions
balance, motor coordination, breathing, digestion, general arousal processes (sleeping and waking); "vital functioning"
neural cells
neurons and neuroglia
neurons
a nerve cell; the basic building block of the nervous system
neuroglia
cells that support and protect neurons
neuron structure
cell body/soma, dendrites, axon, myelin sheath
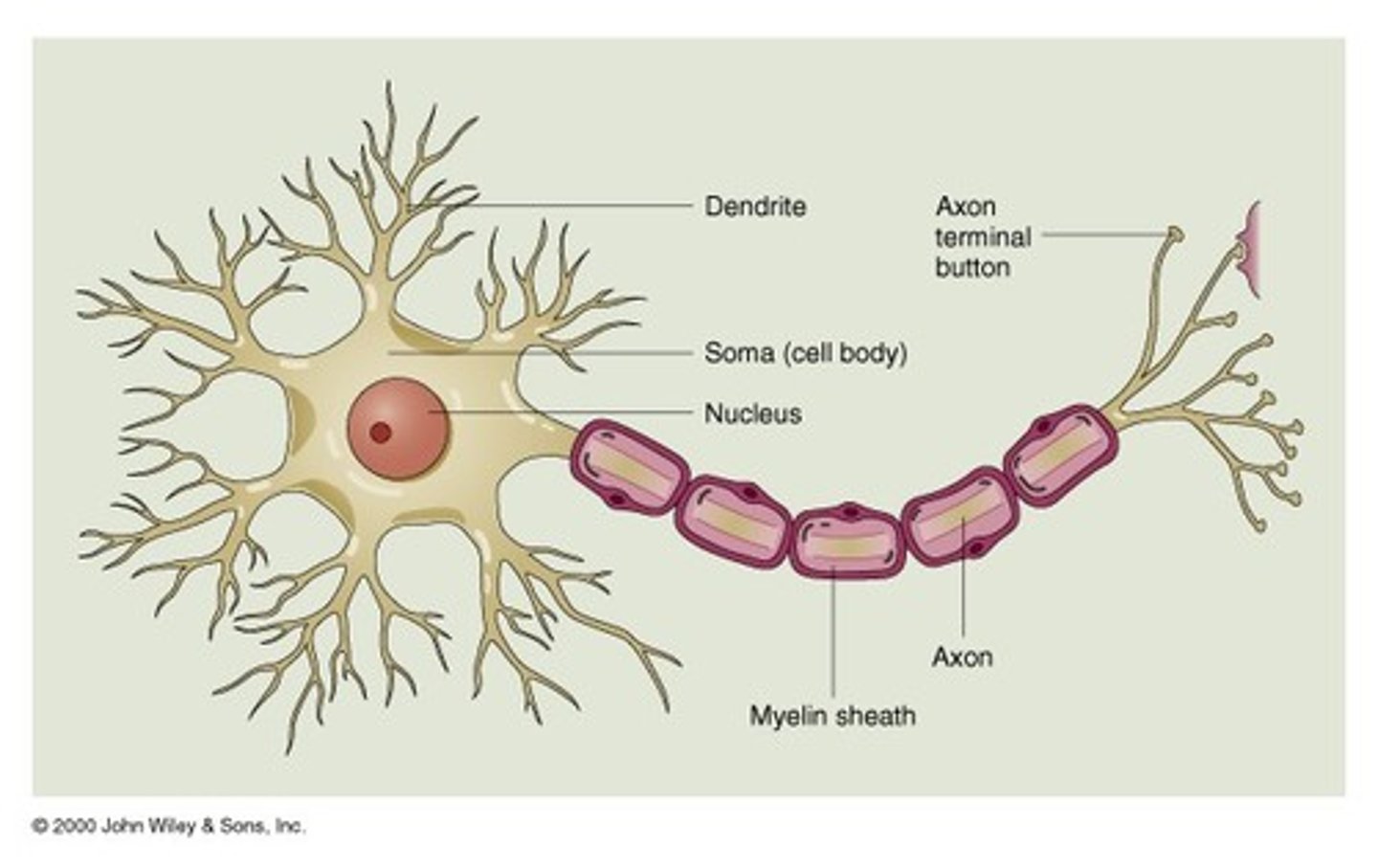
myelin sheath function
Protect and electrically insulate the axon
Increase speed of nerve impulse transmission
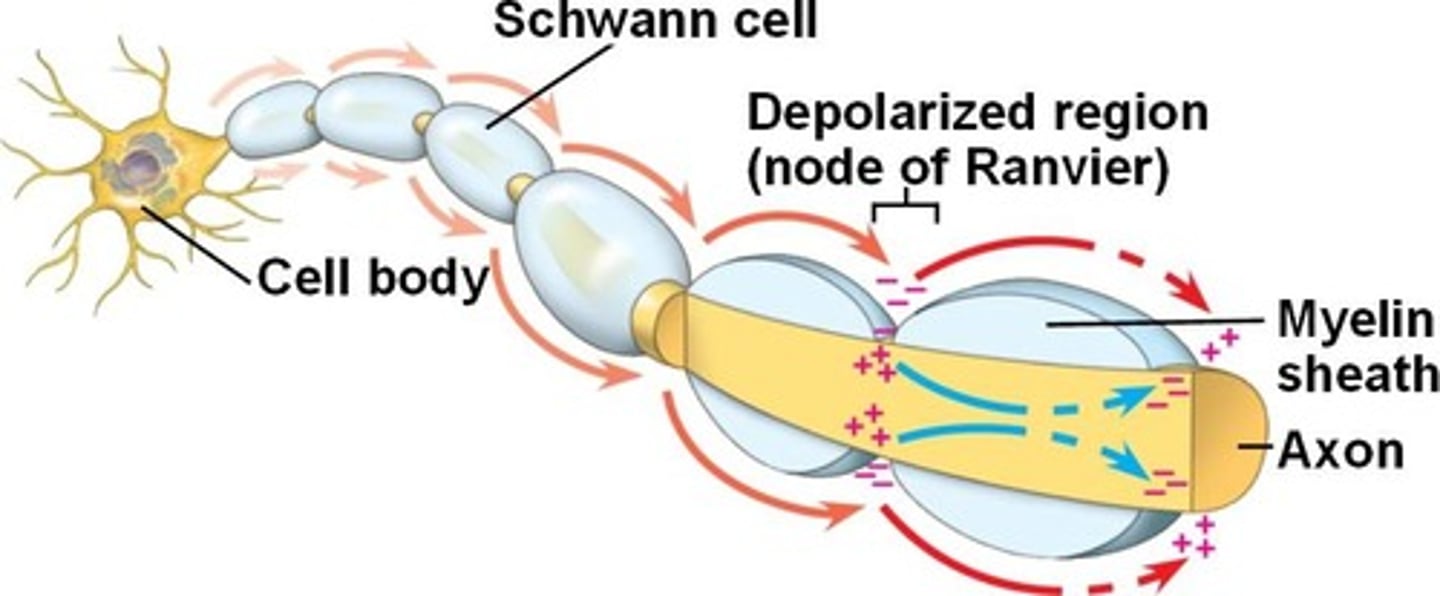
node of Ranvier
A gap between successive segments of the myelin sheath where the axon membrane is exposed.
synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron
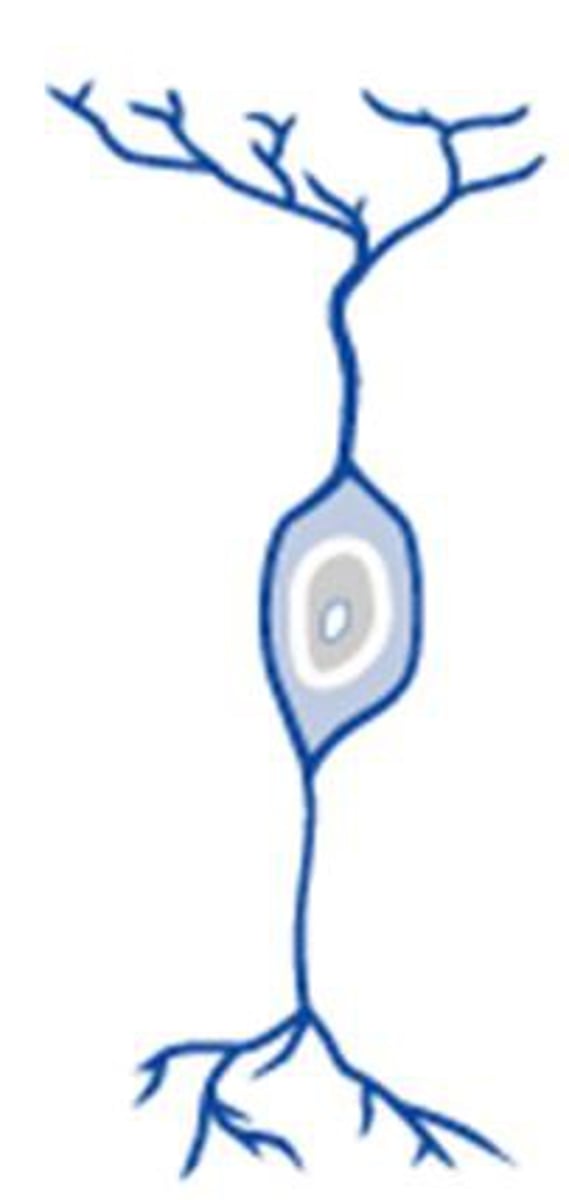
unipolar neuron
a neuron with one process extending from its cell body
bipolar neuron
a neuron with one axon and one dendrite attached to its soma
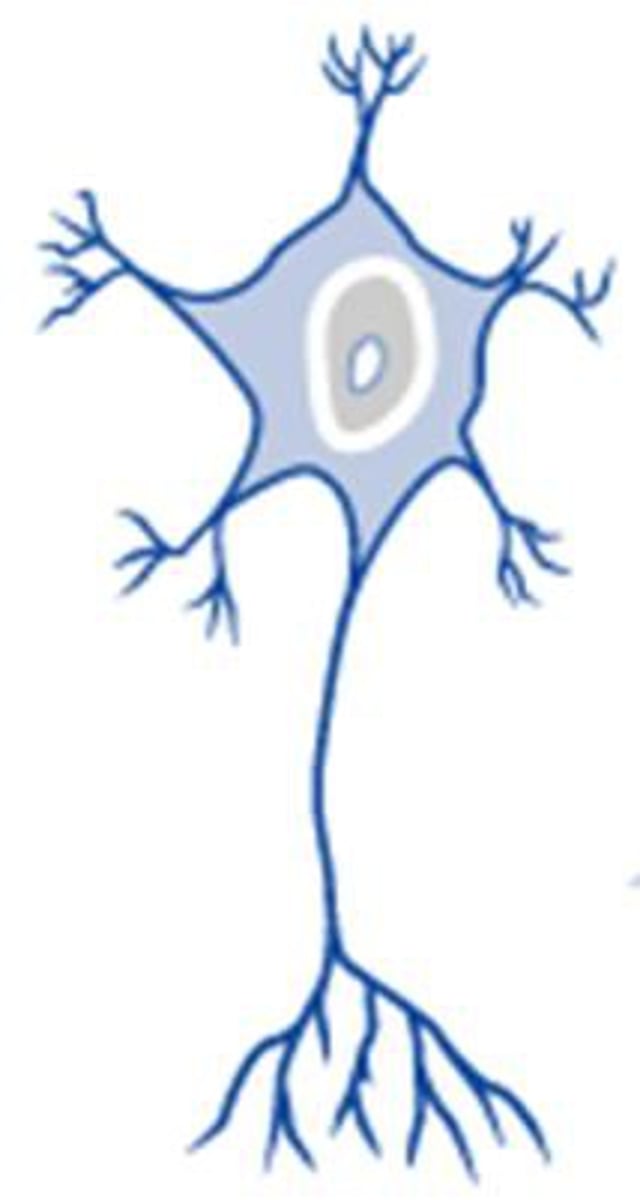
multipolar neuron
A neuron with a single axon and multiple dendrites; the most common type of neuron in the nervous system.
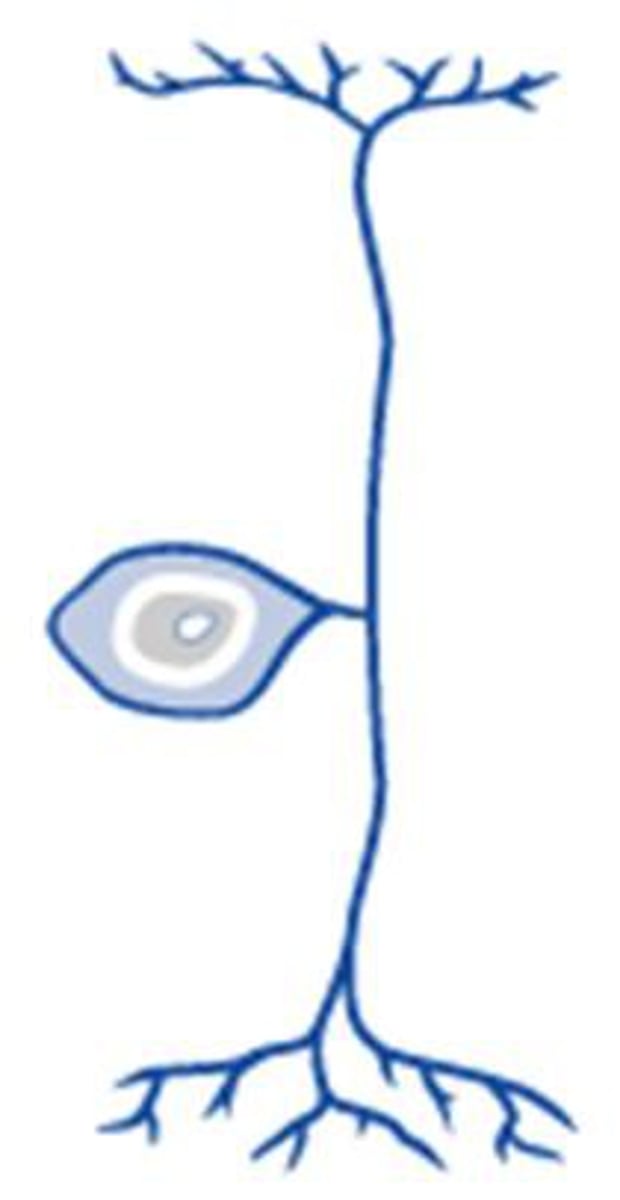
pseudo-unipolar neuron
One axon that splits into two branches
Sensory neurons
neuron function
Neurons are highly irritable
Respond to adequate stimulus by generating an action potential (nerve impulse)
Impulse is always the same regardless of stimulus
resting membrane potential
the electrical charge of a neuron when it is not active
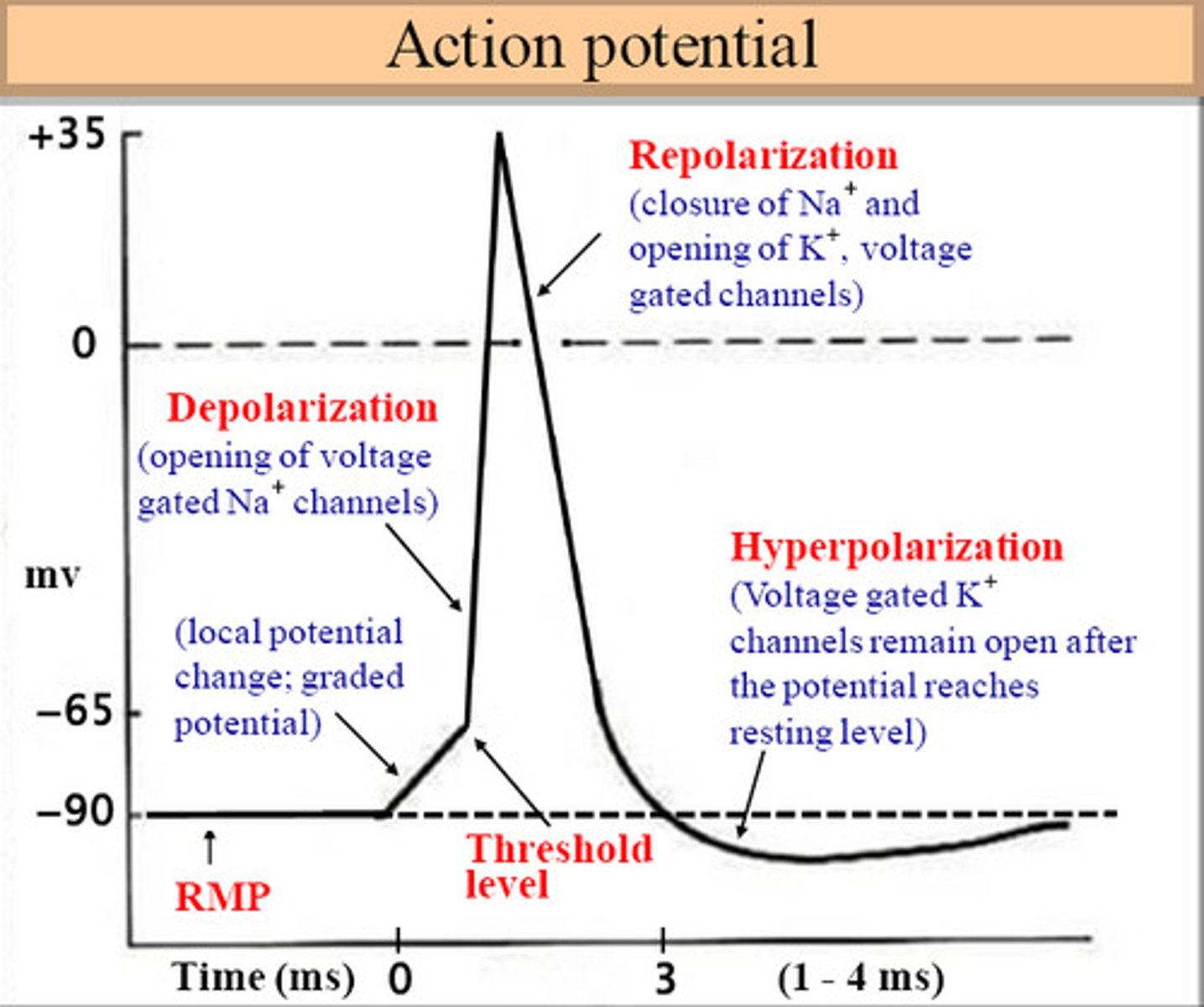
action potential
a neural impulse; a brief electrical charge that travels down an axon
graded potential
a shift in the electrical charge in a tiny area of a neuron
threshold potential
The minimum membrane potential that must be reached in order for an action potential to be generated.
interneuron
a neuron that carries nerve impulses from one neuron to another
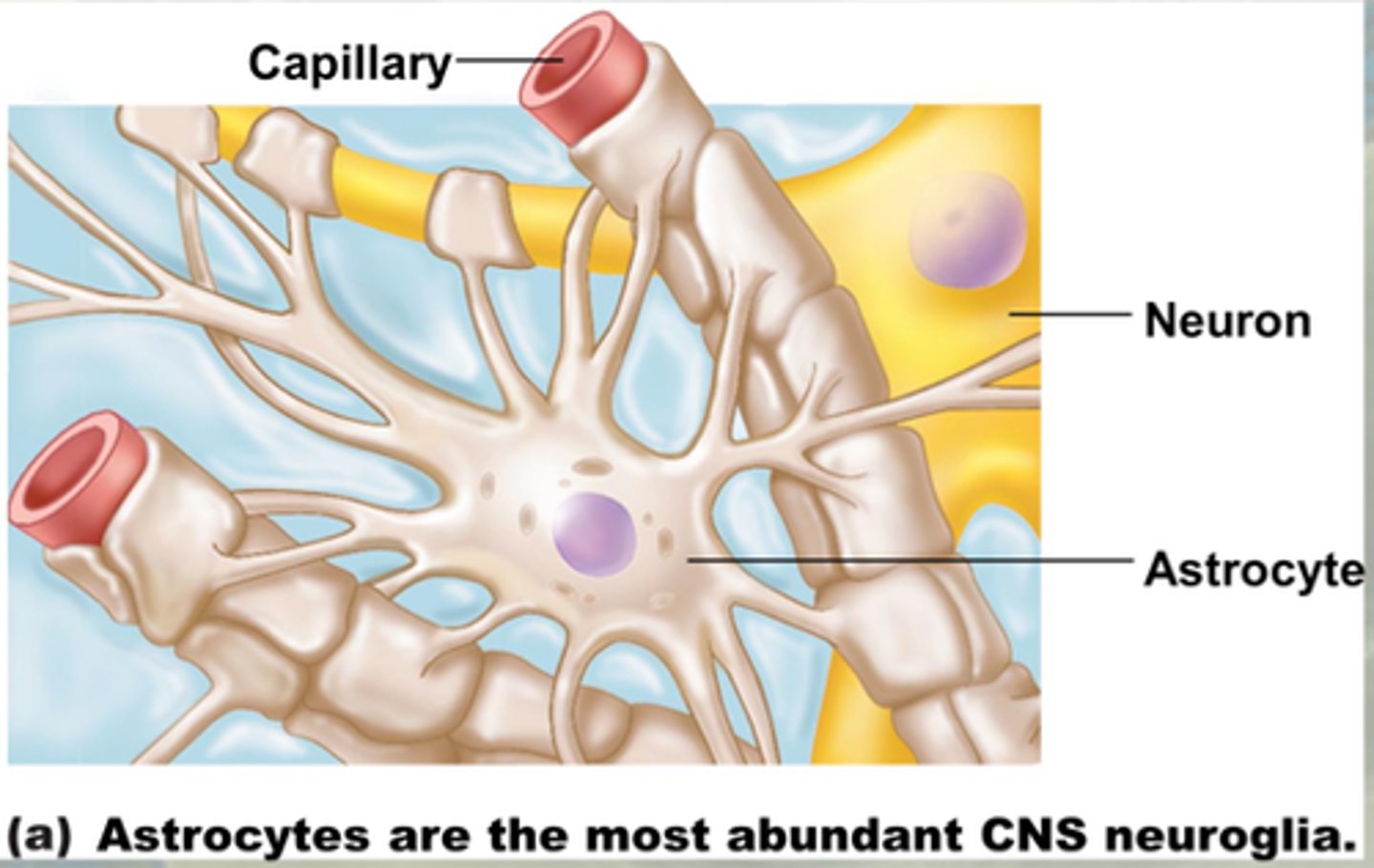
Astrocytes
Provide structural and metabolic support for neurons; they migrate to areas of injury and wall off the area almost like a "scar"; astrogliosis/glial scar; homeostasis; blood-brain barrier
"star cells"
- end feet
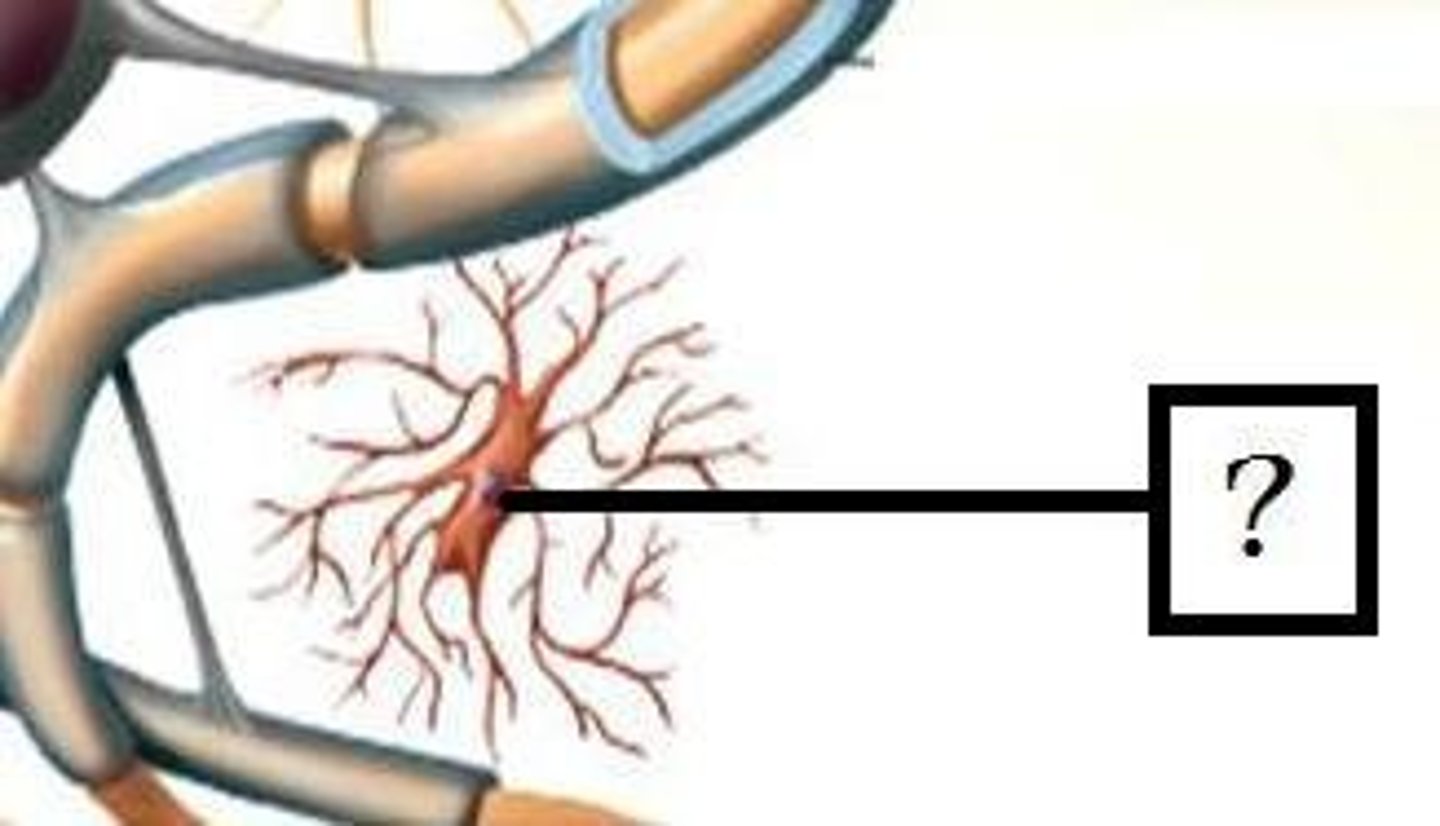
Microglia
phagocytic cells that ingest and break down waste products and pathogens in the CNS; turn into blob and look for bacteria/etc., kill it, ingest the debris (phagocytosis); antigen presentation
antigen presentation
the display of the antigen fragment in an exposed groove of the MHC protein
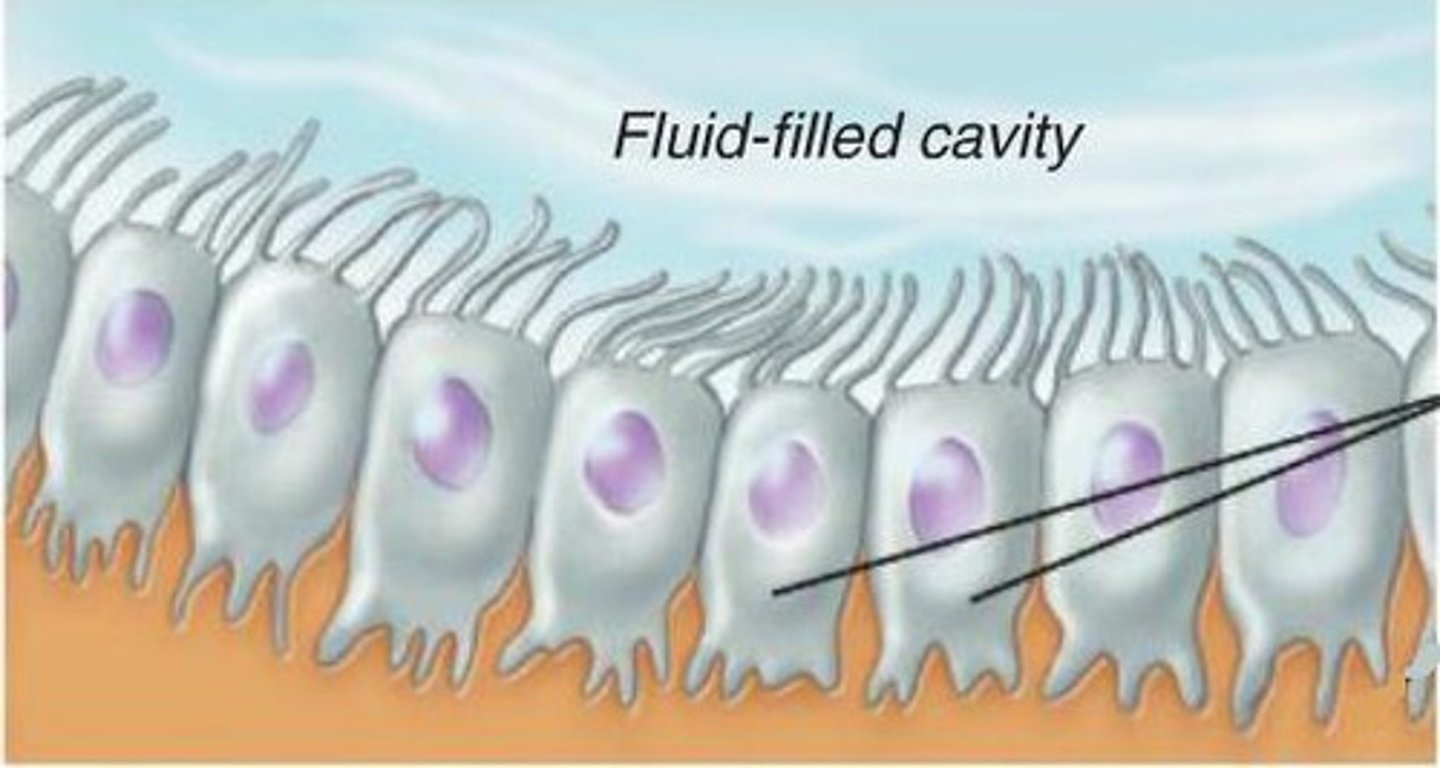
ependymal cells
line cavities of the brain and spinal cord, circulate cerebrospinal fluid; microvilli and cilia;
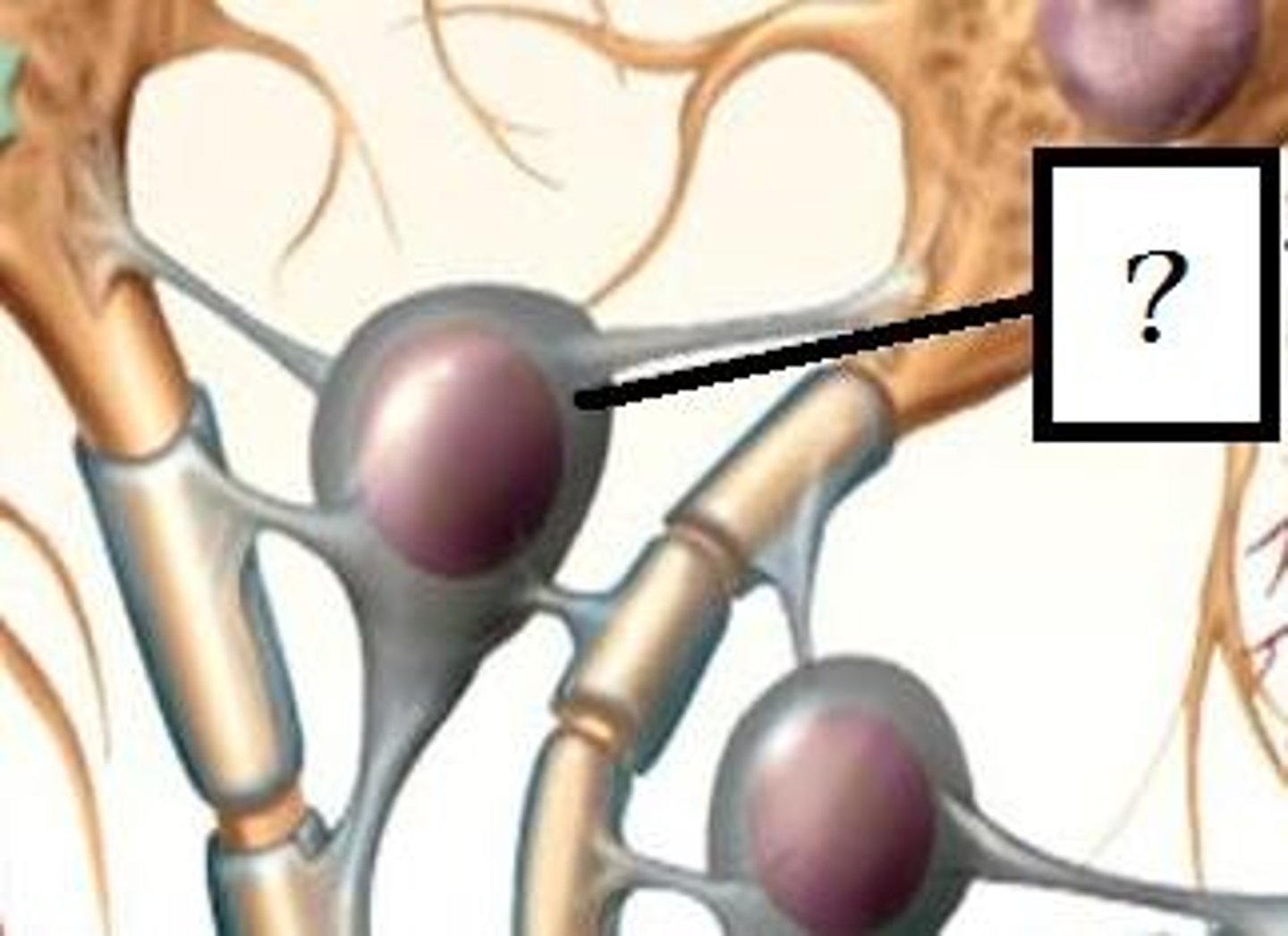
Oligodendrocytes
Type of glial cell in the CNS that wrap axons in a myelin sheath.
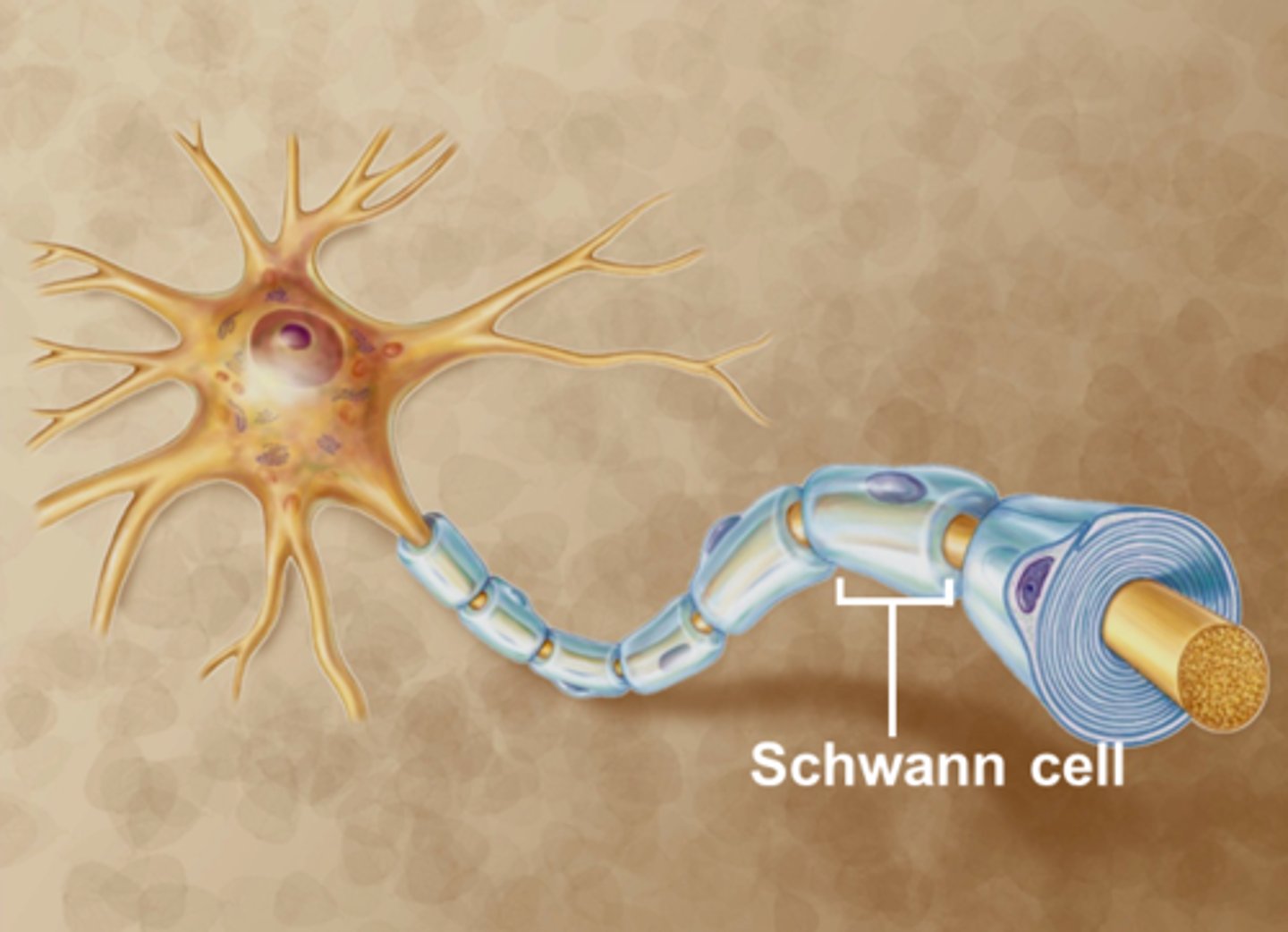
Schwann cells
Supporting cells of the peripheral nervous system responsible for the formation of myelin.
sodium-potassium pump
a carrier protein that uses ATP to actively transport sodium ions out of a cell and potassium ions into the cell
ion leak channels
allow ions to cross the plasma membrane down their electrochemical gradient
Chloride Potassium Symporter
Integral membrane protein that uses potassium leaving cell to push out chloride
action potential figure
saltatory conduction
sending a message in a myelinated neuron, the impulse jumps from node to node
hyperpolarization
The movement of the membrane potential of a cell away from rest potential in a more negative direction.
repolarization
Return of the cell to resting state, caused by reentry of potassium into the cell while sodium exits the cell.
refractory period
a period of inactivity after a neuron has fired
axon diameter
the larger the diameter, the faster the impulse because it offers less resistance; higher probability that the ions will travel further before colliding into things
proprioception
our sense of body position; very fast acting nerves
conduction velocity
the speed at which an action potential is propagated along the length of an axon
synaptic cleft
The narrow gap that separates the presynaptic neuron from the postsynaptic cell.
pre-synaptic cell
The cell SENDING information (from axon); where the NTs are stored