anatomy unit 11 endocrine and excretory systems
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
The Second greatest controlling system of the human body.
Function:
Coordinates and directs the activity of the body's cells.
Organs:
Hypothalamus
Pituitary Gland
Pineal Gland
Parathyroid Glands
Thyroid
Adrenal Glands
Pancreas
Ovaries
Testes
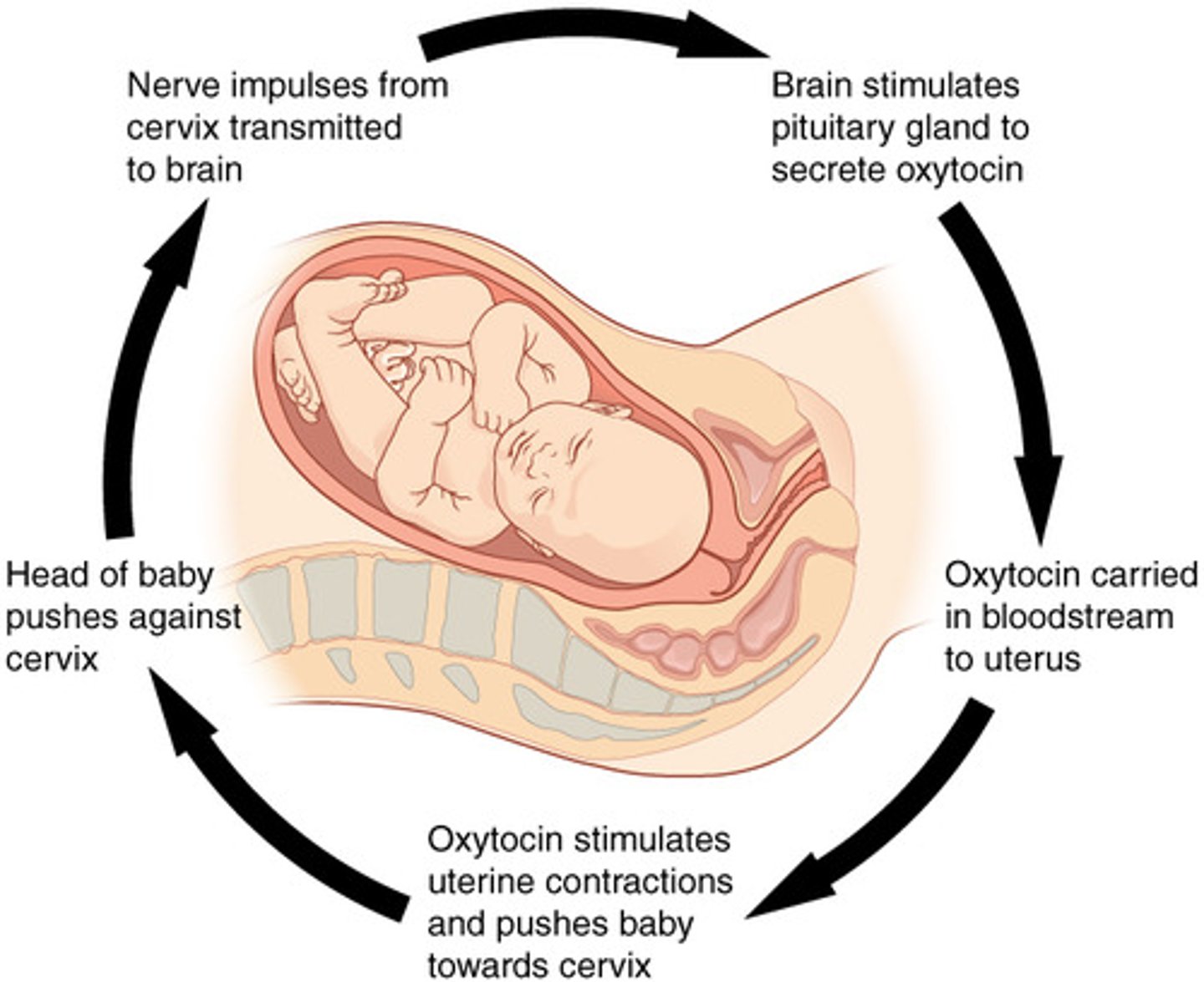
Positive Feedback
a process in which an initial change will bring about an additional change in the same direction.
Examples:
Childbirth
Blood clotting
Negative Feedback
when a process influences the operation of the process itself in such a way as to reduce changes
Examples:
Regulating Blood Pressure
Regulating Blood Glucose Levels
Body Temperature Regulation
Hormone Regulation
Hormone
a class of regulatory biochemicals produced in specialized cells then transported by the bloodstream to other parts of the body.
Influences:
Digestion
Metabolism
Growth
Reproduction
Mood control
Target Cells
cells that have receptors for a particular hormone

target organs
organs that respond to a particular hormone
Growth Hormone-
a general metabolic hormone secreted from the pituitary gland. Plays a role in determining final body size.
Growth of skeletal muscles
Growth of long bones
Antidiuretic hormone
"against the flow of urine from the kidney" prevents excessive water loss in the urine, secreted by the pituitary gland. Travels in the blood to the kidneys. (no pee)
Aldosterone
Allows water loses and regulates the sodium ion content in the Extracellular Fluid, secreted by the adrenal glands. (pee)
Melatonin
- involved in rhythmic activities, secreted by the pineal gland.
Regulated by light/dark cycles
Calcitonin
reduces blood calcium levels by returning the calcium to the bones, secreted by the thyroid gland.
Parathyroid hormone
raises the blood calcium level by taking the calcium from the bones, secreted by the parathyroid glands.
Epinephrine and Norepinephrine
Secreted by the Adrenal glands. Together form Adrenaline. Released in response to a threat or stress. Fight or flight response.
Glucagon
raises blood glucose by taking it out of storage (liver), secreted by the pancreas.
Insulin
reduces blood glucose by telling body cells to use it, secreted by the pancreas.
ductless glands
endocrine glands that produce hormones that they release into the blood or lymph
- Endocrine glands have a very rich blood supply.
Pineal Gland
located in the brain behind the thalamus, very small and cone shaped. Somewhat a mystery; only secretes melatonin.
Pituitary Gland
approximately the size of a grape located in the brain. Master gland, controls other endocrine glands.
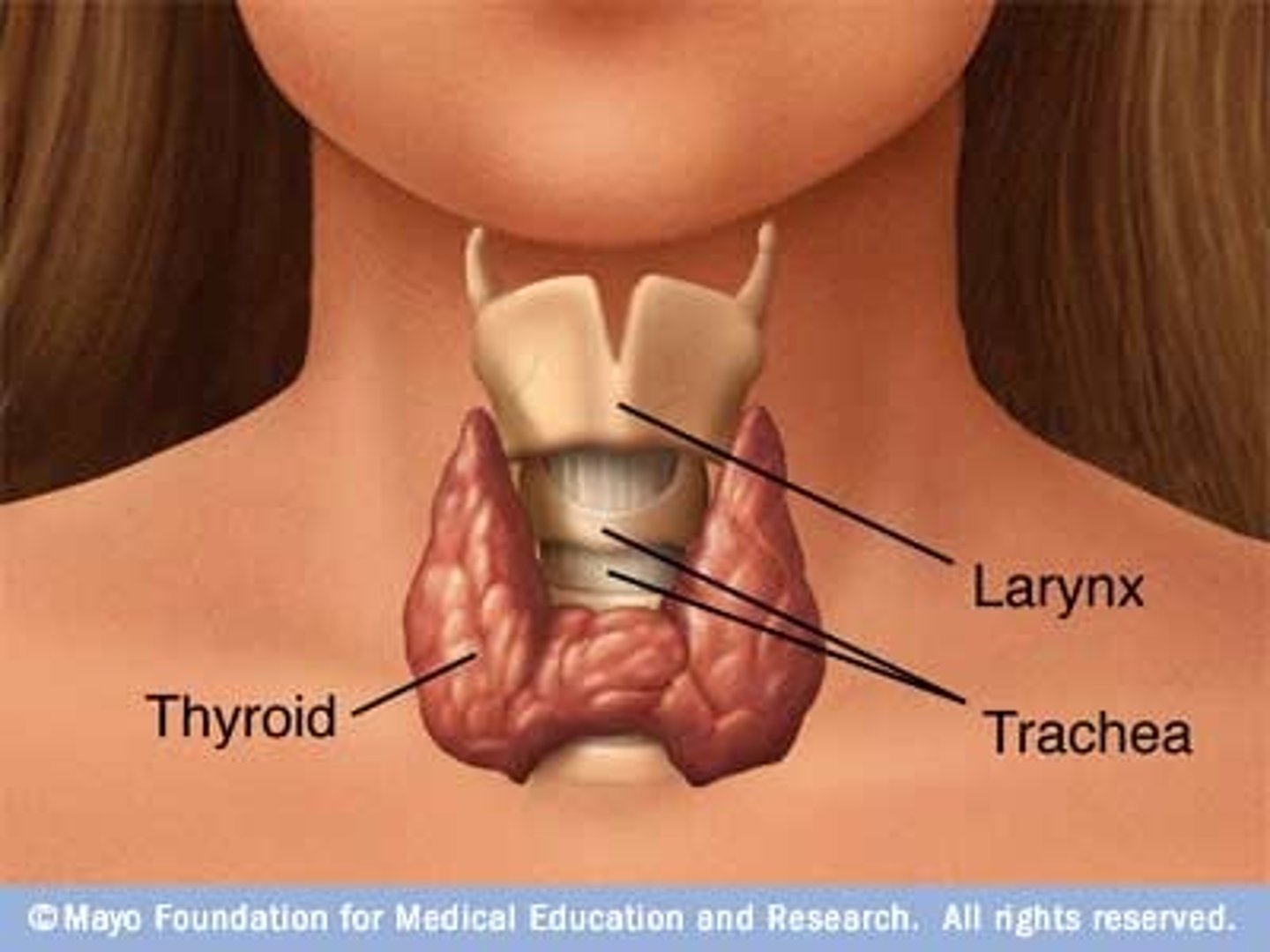
Thyroid Gland
located at the base of the neck, looks like a butterfly with two lobes.
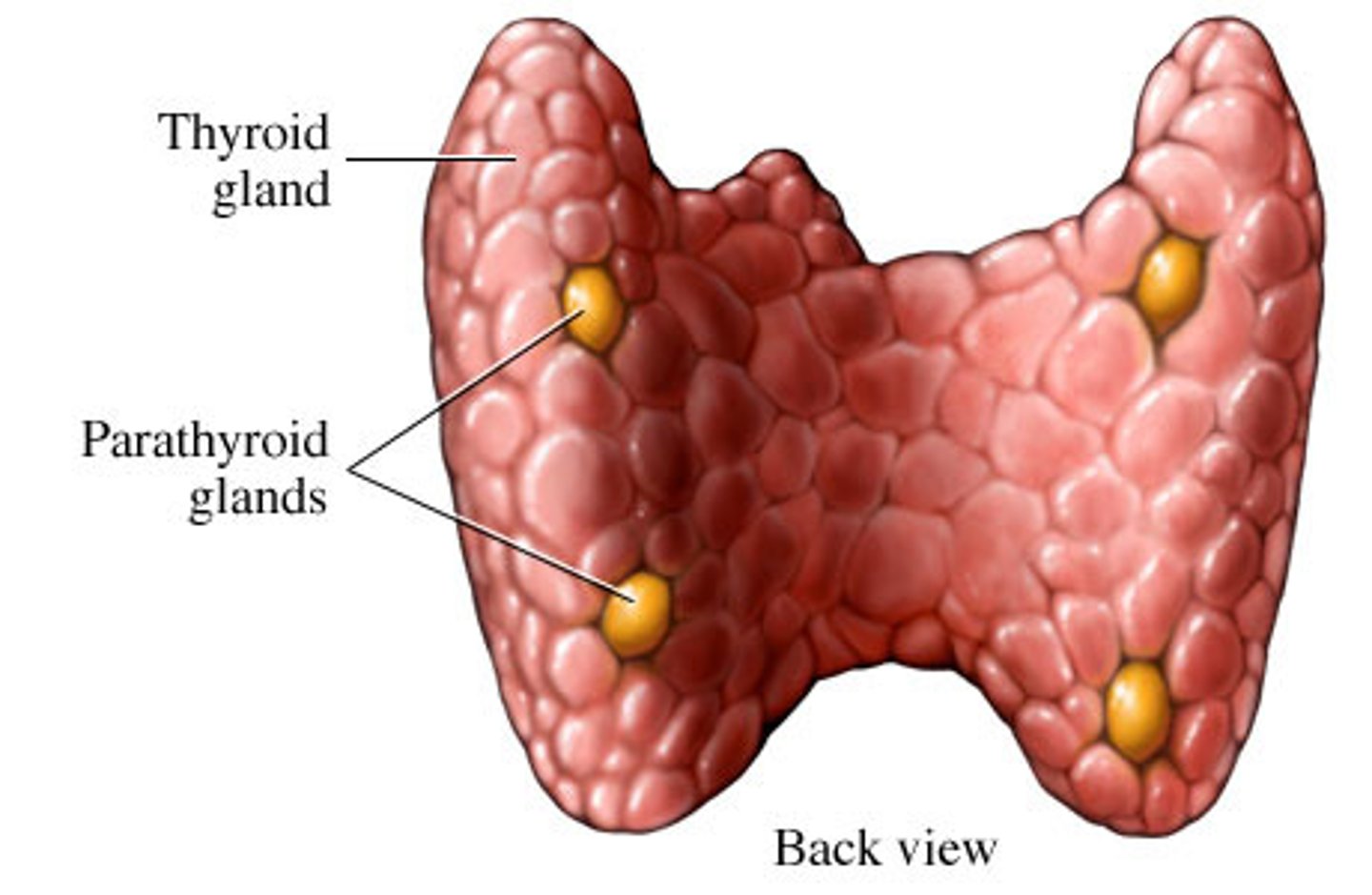
Parathyroid glands
tiny masses
imbedded in the thyroid gland
at the base of the neck, two
glands in each lobe of the thyroid.
Thymus
located in the upper thorax, posterior to the sternum. Large in infants and children, gets smaller as you grow older. Helps WBCs mature
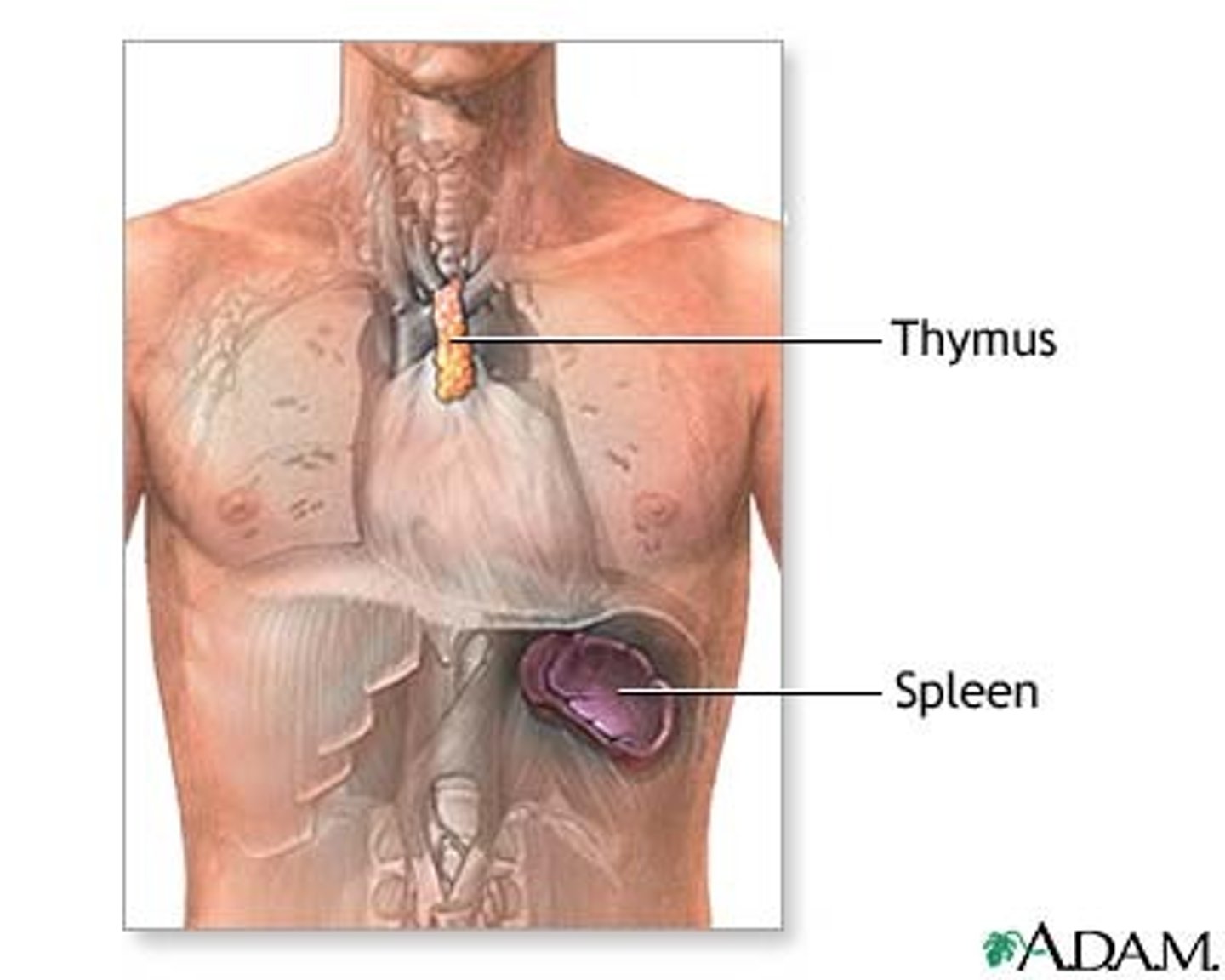
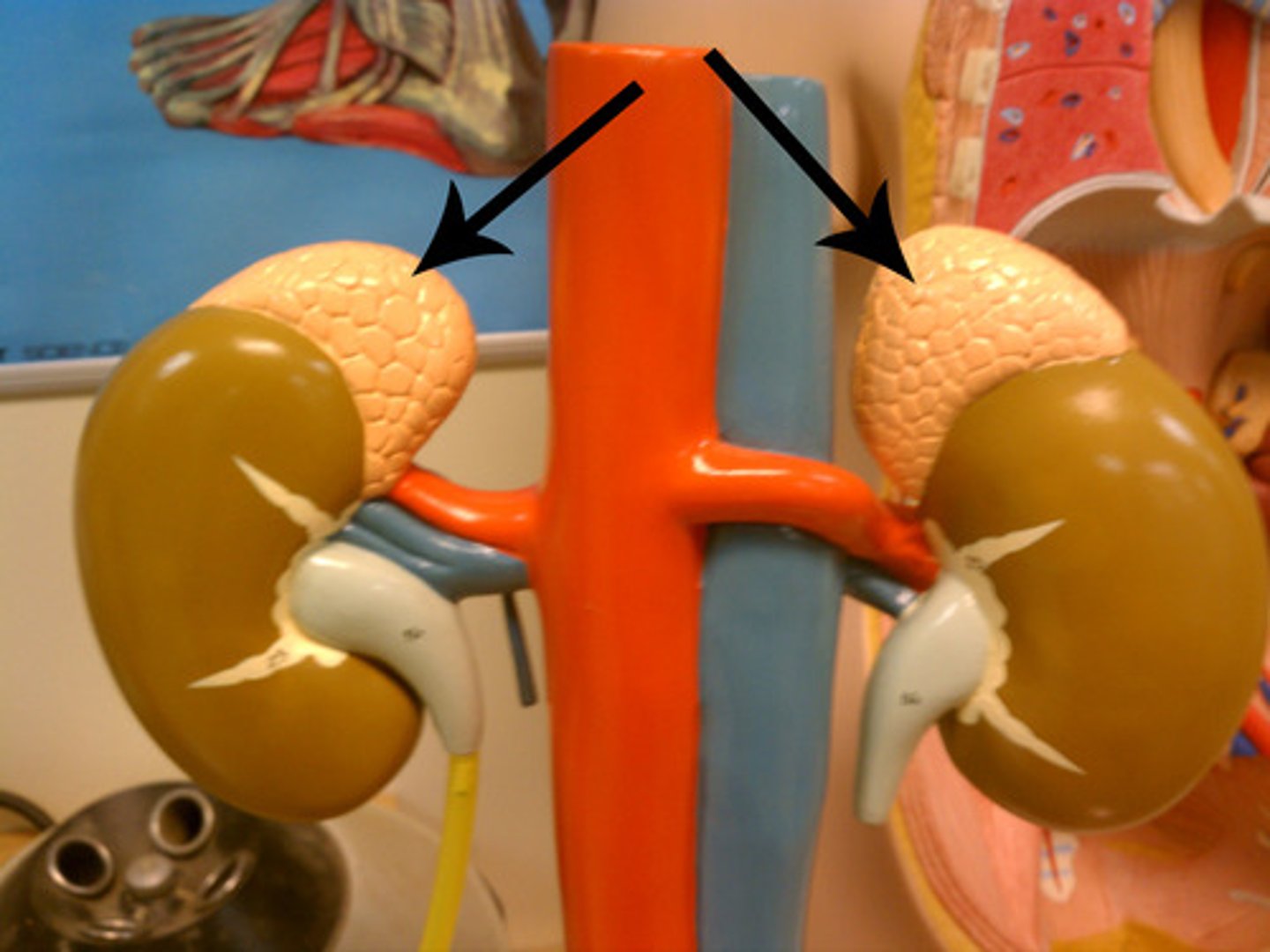
Adrenal glands
- two bean-shaped glands that curve over the top of the kidneys.
- produce essential hormones that regulate metabolism, immune response, blood pressure, stress, and sexual development
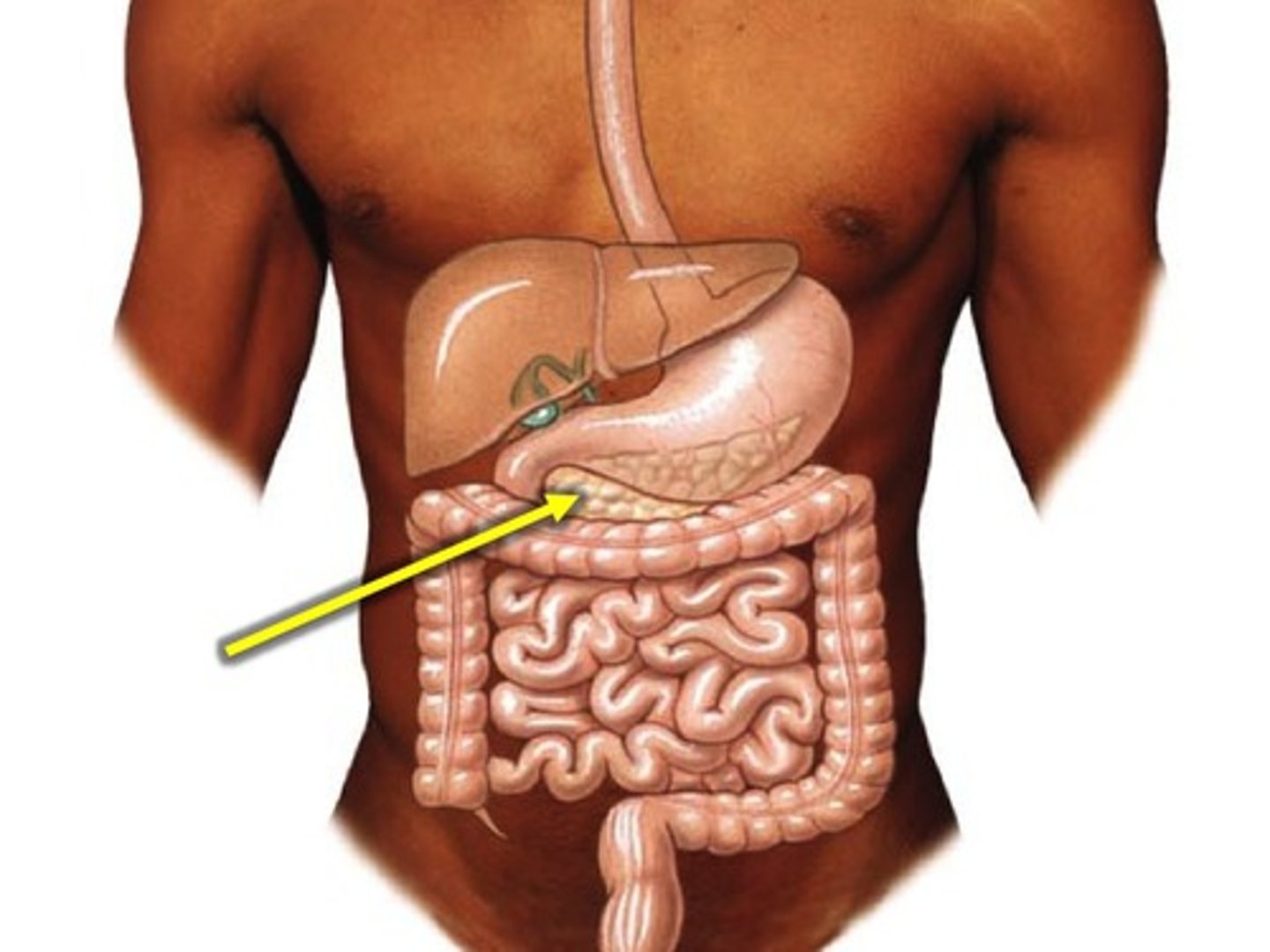
Pancreas
located close to the stomach in the abdominal cavity, is a mixed gland.
Gonads
Ovaries and Testes, overlaps with the reproductive system. Ovaries produce Estrogen and Progesterone. Testes produce Testosterone.
EXCRETORY SYSTEM
Disposes of waste and excess ions
Regulates blood volume and chemical makeup.
Provide temporary storage reservoirs for urine or serve as transportation channels to carry it from one body region to another.
Organs: Kidney, Ureter, Bladder, and Urethra
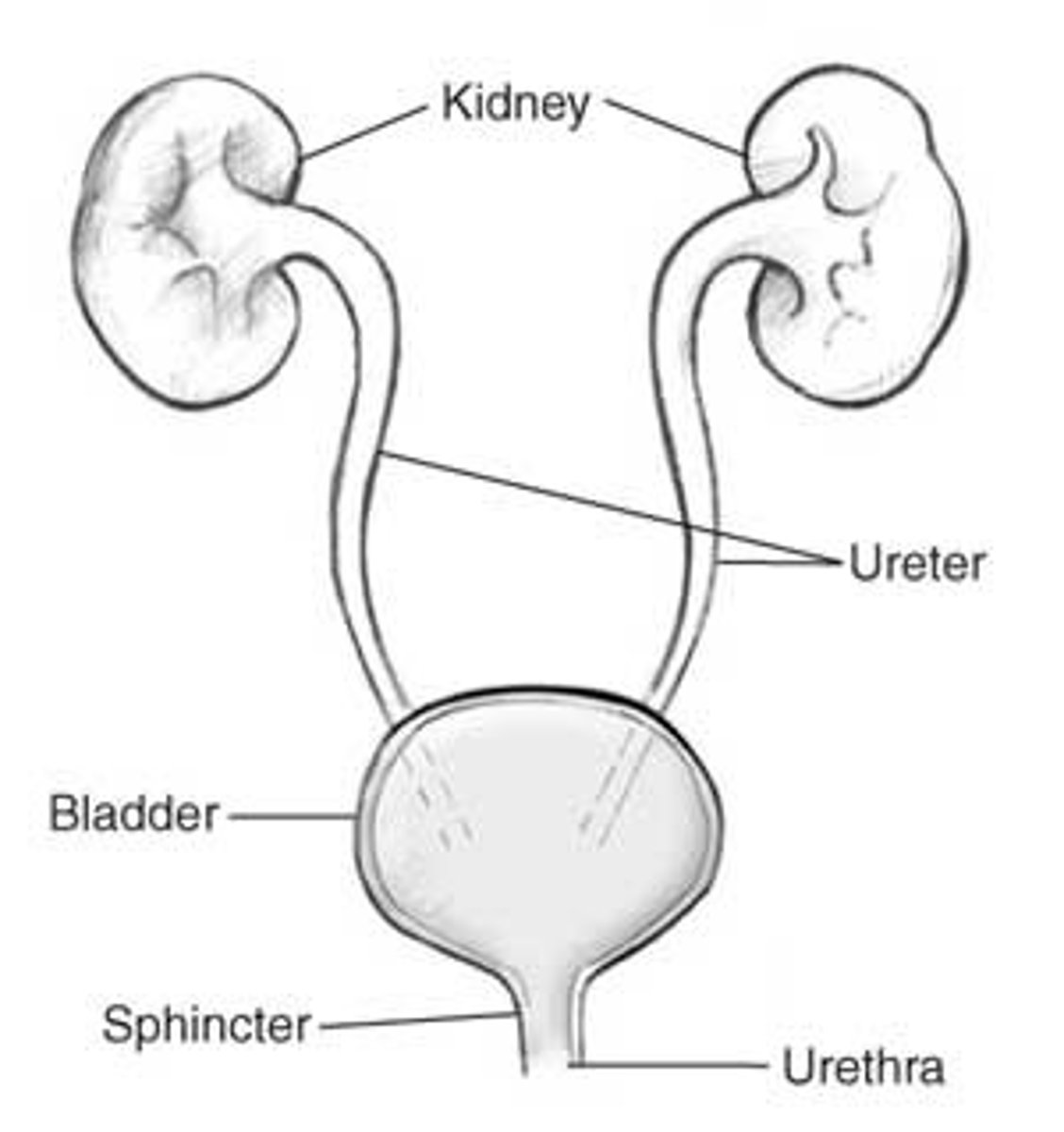
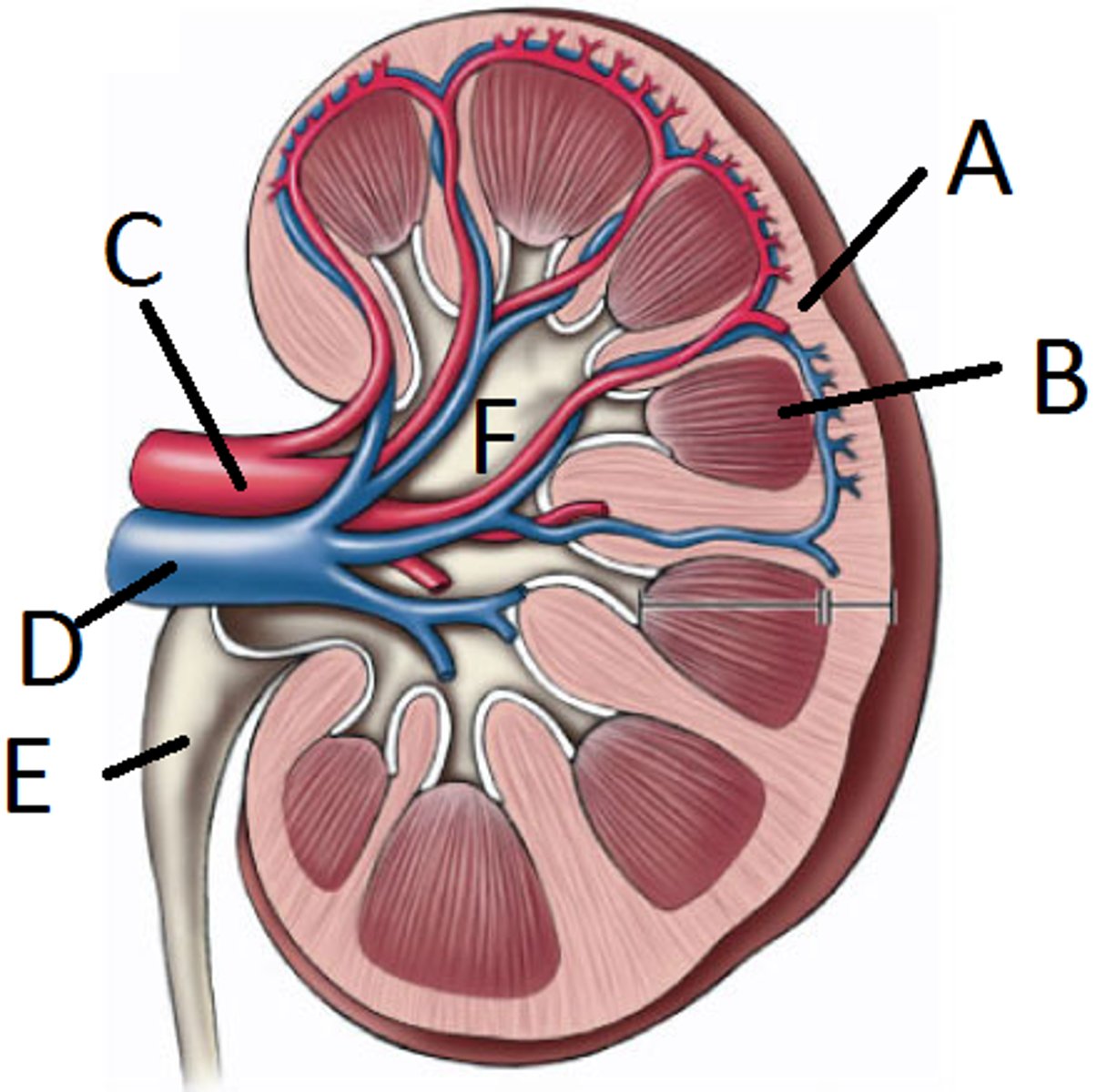
Kidney
filters blood and extracellular fluid for excess water and ions; about 12cm long and 6cm wide, located abdominal cavity in the back wall.
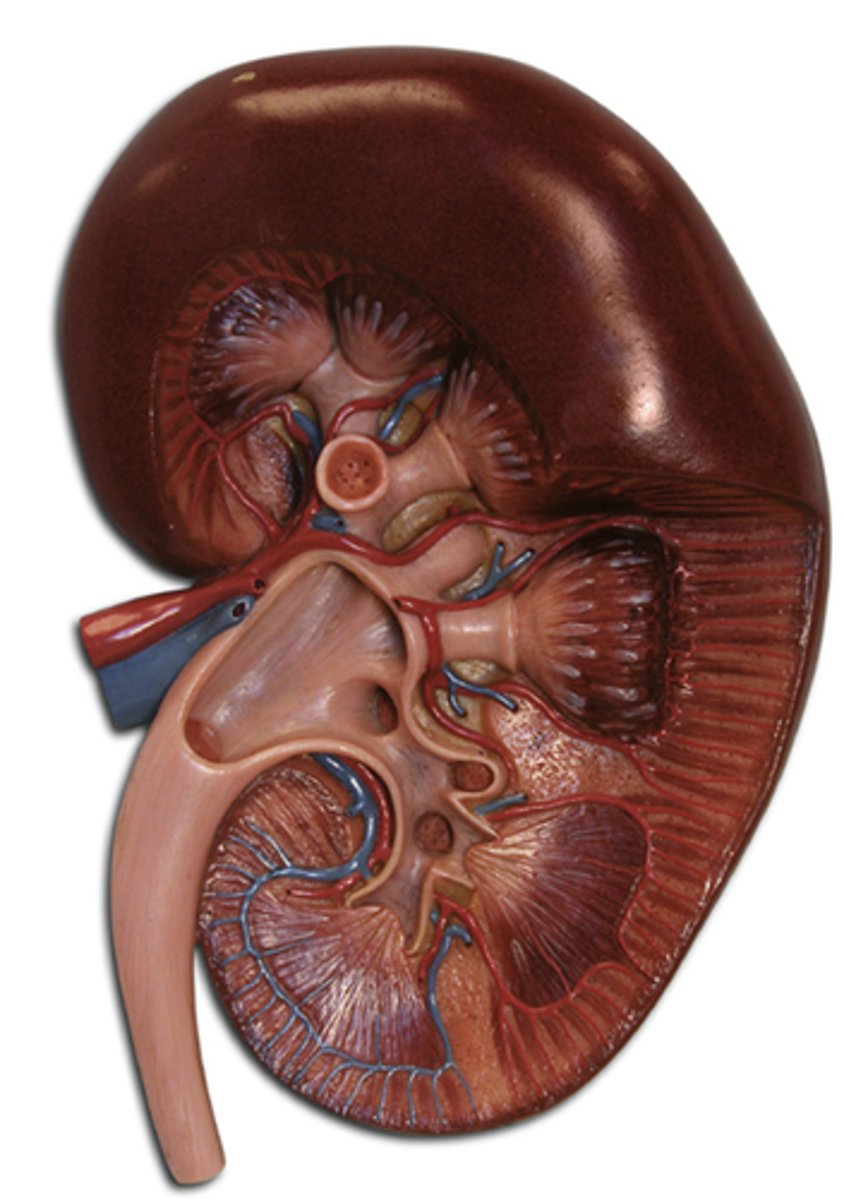
Renal Capsule
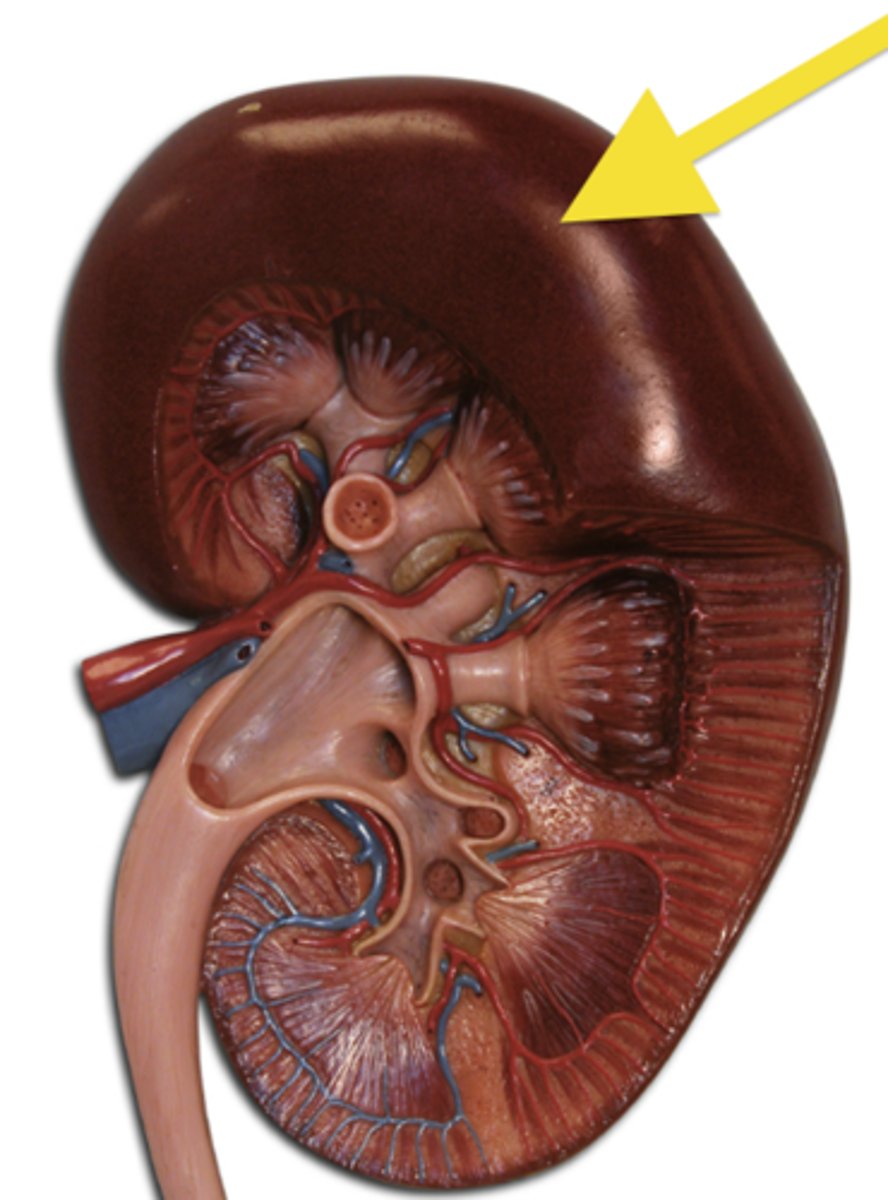
fibrous transparent membrane that encloses the kidney.
Renal Cortex
the outer region, found just under the renal capsule.
Medullary pyramid
triangular regions with a striped appearance. The broader bases faces toward the cortex, the tip points towards the inner region.
Renal columns
the area in between each of the medullary pyramids.
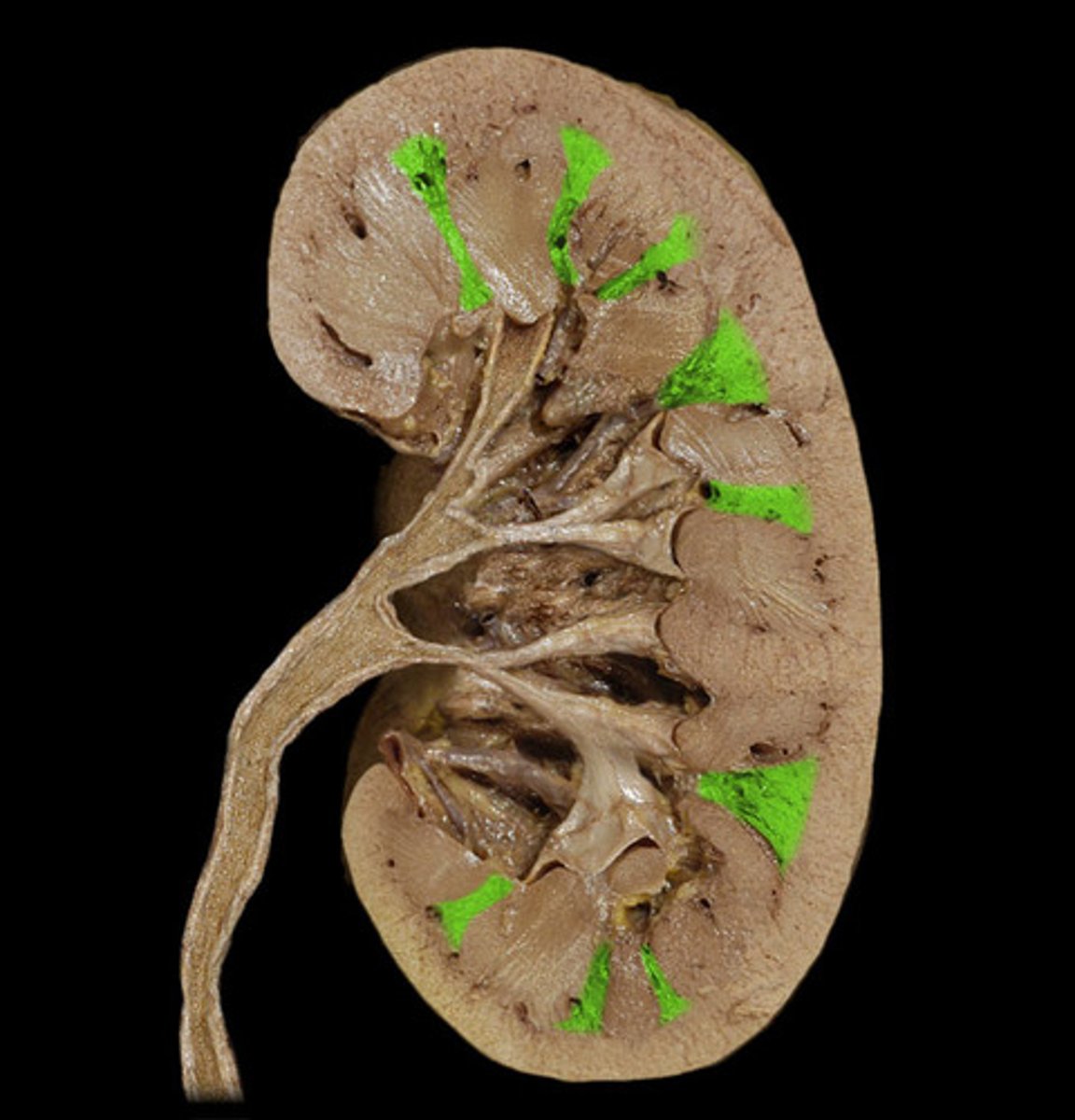
Renal Artery
the arterial supply of each kidney.
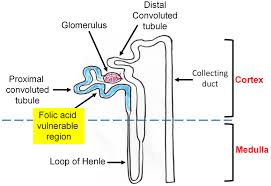
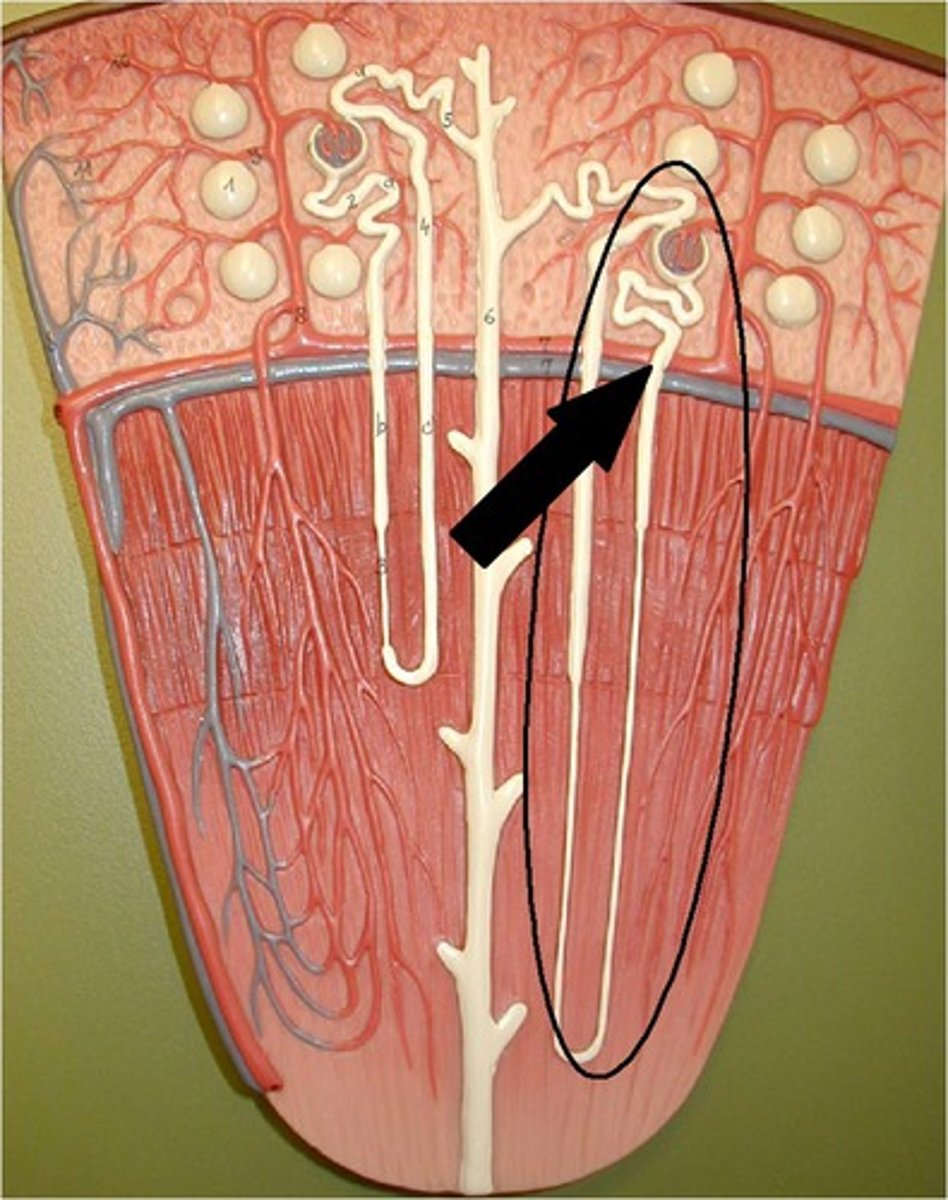
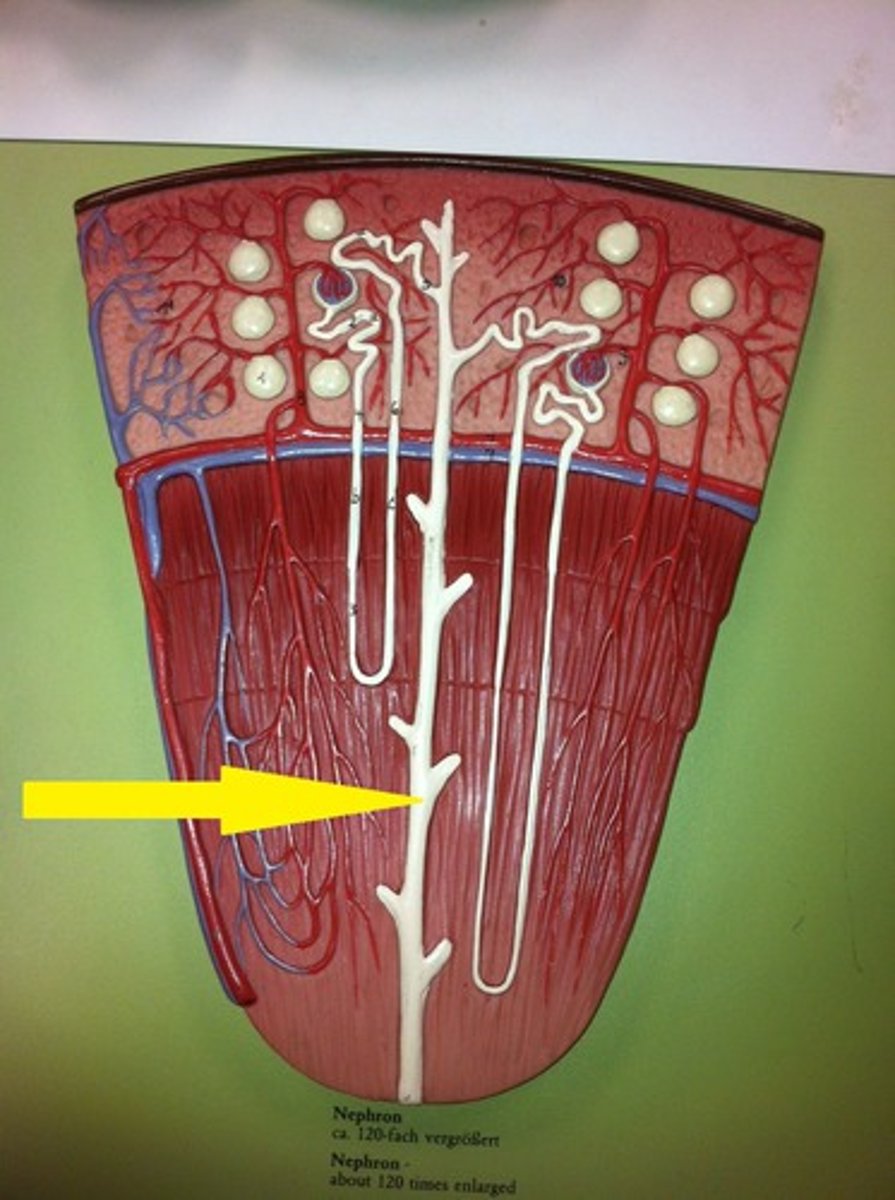
Nephrons
millions of tiny structures in each kidney, which are the structural and functional units of the kidneys. Responsible for forming urine.
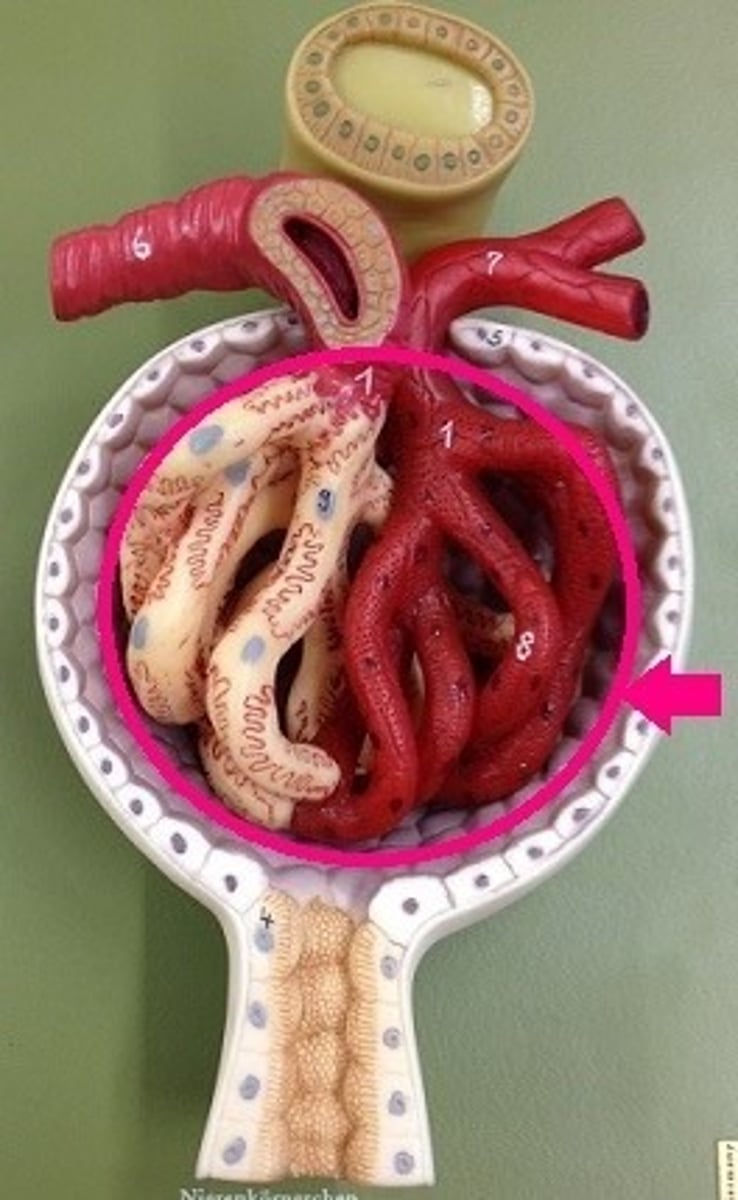
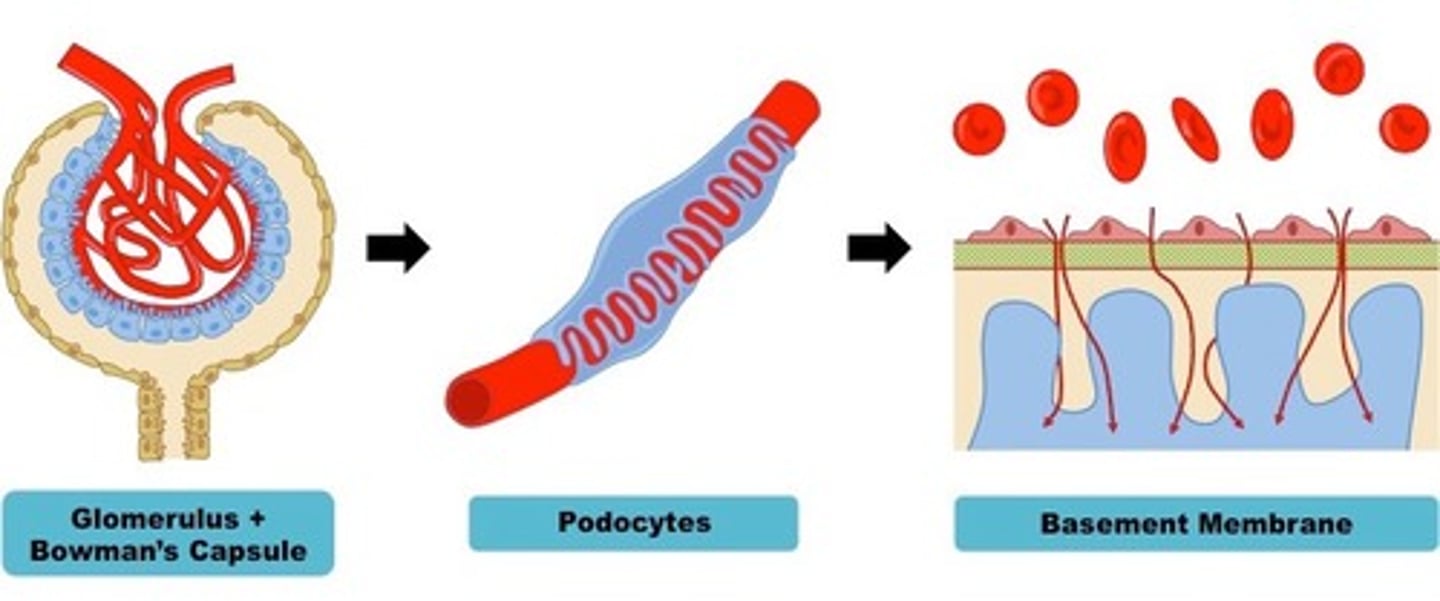
Glomerulus
a knot of capillaries within the nephron. (start filtering
blood)
Renal tubule
the long tube
that makes up the greater
part of the nephron.
Produces and filters the
urine.
Bowman's Capsule
part of the renal tubule that
performs the first step
of filtration of blood.
Loop of Henle
main function is to create a concentration gradient in the medulla of the kidney.

Collecting Duct
collects urine after filtration and sends it to the ureter.
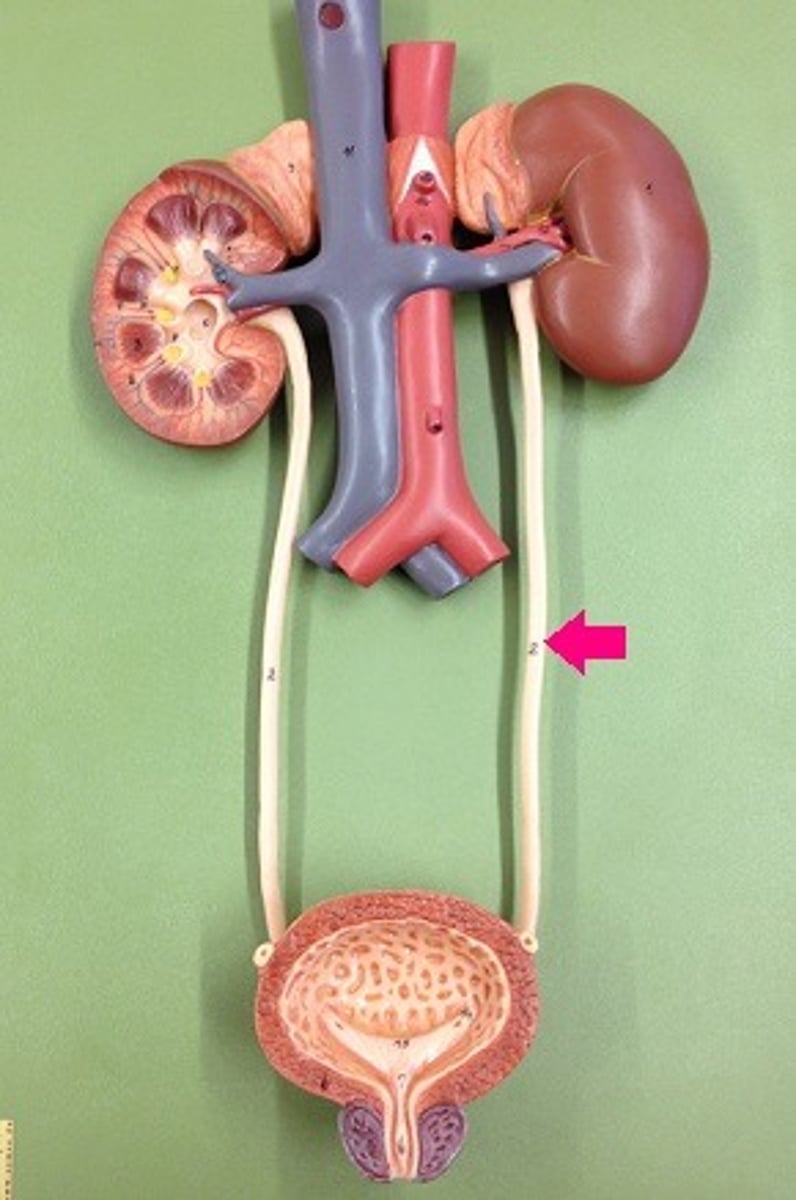
Ureter
brings urine from the kidneys to the bladder
Bladder
storage tank for urine. Normally holds approximately 500mL.
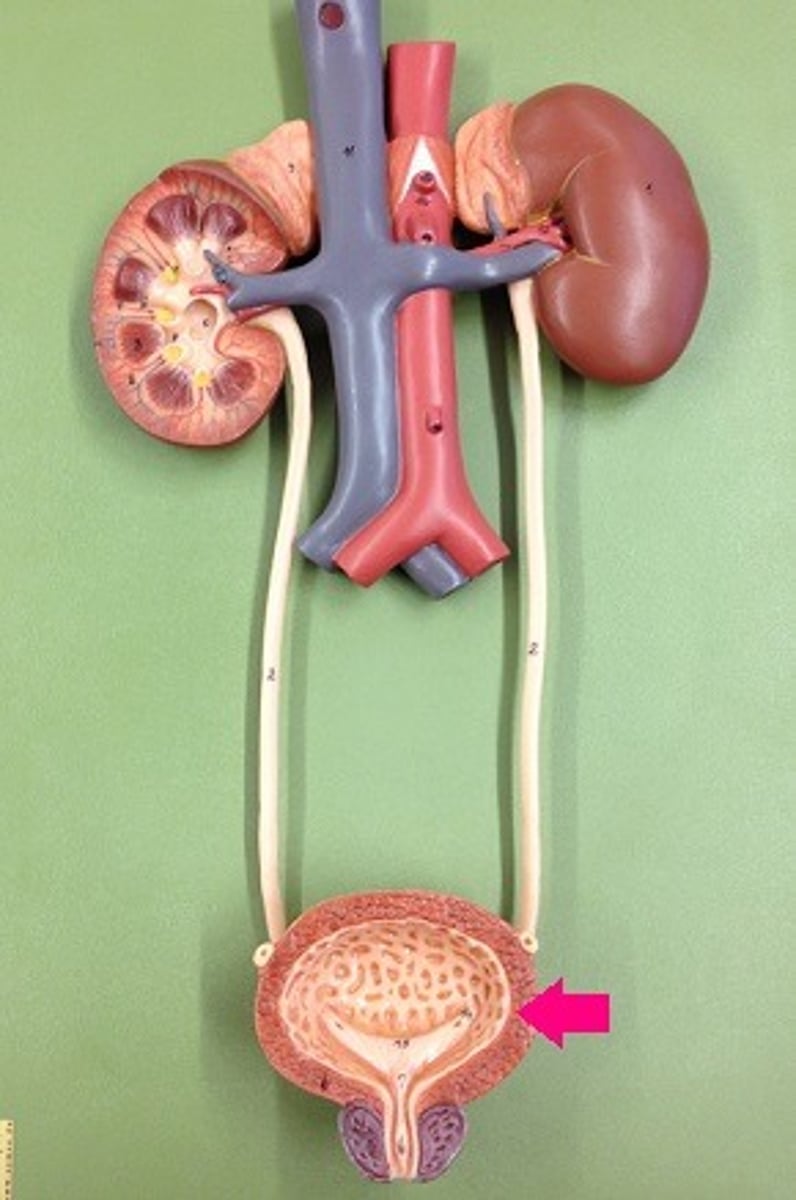
Urethra
urine exits the bladder into the urethra,which carries urine out of the body.
Electrolyte balance
the solute concentrations in the various fluid compartments, cause excess water and ions to move into the kidneys.
Acid-Base Balance
the optimum level of H+ ions that are present in the blood. We want to keep this balance, not too acidic, not too basic; just right.
Most hydrogen ions originate as by-products of cellular metabolism, which continuously adds substances to the blood.
Alkalosis
Whenever the pH of arterial blood rises above a pH of 7.45.
Acidosis
Whenever the pH of arterial blood falls below a pH of 7.35.
7.35 is not acidic from a chemical standpoint, however a pH of 7.35 represents a higher-than-optimal H+ concentration for the functioning of most body cells.
Bicarbonate buffer system
is a mixture of carbonic acid and bicarbonate ion. Helps maintain the pH of the blood.
characteristics of urine
Usually pale to deep yellow.
The normal yellow color is due to urochrome, a pigment that results from the body's destruction of hemoglobin.
The more solutes there are in the urine, the deeper the yellow its color.
Urine is sterile
Urine is slightly acidic (pH around 6)
Abnormal Urinary things
Glucose- diabetes
protein- kidney issues
WBCs and bacteria- infection
RBCs and Hemoglobin- kidney/bladder stones or infection
bile pigment- liver problems
urochrome
pigment that makes urine yellow
proximal convoluted tubule
reabsorbs most water, glucose, amino acids, and ions (like 80% of water)

Distal Convoluted Tubule
fine-tunes electrolyte/water balance (more "optional" reabsorption) under hormones like aldosterone