Rabbit Consultation - History Taking and Clinical Examination
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What types of diseases are common in rabbits?
Subclinical Disease - acute presentation of a chronic condition, since clinical signs are often missed by owners until the disease are very advanced, due to being prey animals
What types of medical conditions in rabbits are emergencies?
ALL emergencies
• Gl stasis rabbit
• Dyspnoeic rabbit
• Collapsed rabbit
• Quiet rabbit
Ideally, how should rabbits arrive in the practice?
• Ideally a separate waiting area
Away from predator species
• Not to be carried in hand
• Secure carrier, with hay to nibble
• Bonded companion
• Dark (covered - careful with ventilation)
• Minimal travelling time
• Familiar food ('packed lunch')
• Familiar bedding
What guides the type of clinical history taken when seeing a rabbit based on their condition?
• Stable
Systematic approach
History and Clinical Examination
• Unstable
Prioritise key history points
Prioritise focal clinical assessment (Completing a full clinical exam once more stable)
What key details should be prioritized when taking a history during an emergency?

In the case of a non-diseased animal, how should the history be taken (ie what details should be taken)?
Can be good to have history forms to reduce time of history taking

If dental disease is suspected in the rabbit, what questions should guide this history taking?

Continue Previous Card:

What are the most important aspects when it comes to safely handling rabbits?
Remember rabbits have:
- Delicate skeletons
- Powerful and muscular hind limbs
- Can jump unpredictably
- Confident and secure handling is key → they will mock you
We want to avoid injury. Inappropriate handling can lead to:
- Spinal trauma
- Fractures
How should rabbits NOT be handled?
No to trancing, where the rabbit is on it’s back
Rabbits enter state = tonic immobility (Which is stressful for rabbits)
Still used by some breeders to assist grooming, or for cute photos
What are features of the ideal clinical exam room?
Towel/VetBed on the weigh scales or consult table
Describe the systematic approach for clinical exam of a rabbit.
• Demeanour
• 'TPR'
• Nose to Tail
Head
Body
Thoracic compliance
Abdominal palpation
• Limbs
•Ventral examination
• Weight and BCS
• Otoscopic Examination
Dental Examination
Aural (Ear) Examination
When observing demeanor, what features or observations are you looking to make?
Observations
• Mentation
• Posture
• Activity prior to examination
• Respiratory effort and rate
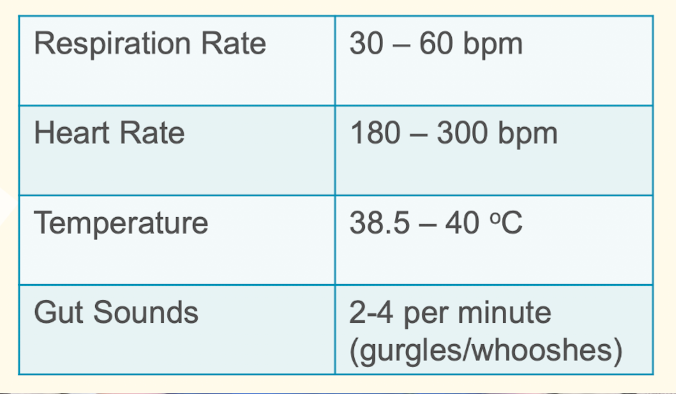
When taking TPR - auscultations of heart, lungs, and temperature, what are the normal fields and rates?
1. Heart
Rate and rhythmn
Murmurs
Pulse deficits
Central Auricular
Femoral
2. Respiratory
• Lung fields
• Trachea
• Sinuses
3. Gut Sounds
• Both sides for 1 minute
When performing head to nose examination, what primary observations are you looking to make?
Head to Nose
Assessing:
• Symmetry
• Presence/absence of discharge (Check rabbits hands for crusties)
• Normal 'twitching'
• No nostril 'flailing'
What sort of symptoms might be seen with damage to facial nerve?
Asymmetry, facial nerve damage, can be a sign of inflammation associated with otitis media
Unilateral:
• Contracture
• Loss of palpebral
• Loss of nose twitching
What are common eye abnormalities in rabbits?
Abnormalities:
• Corneal trauma
Large area of fluorescein dye → uptake into superficial corneal ulcer
• Conjunctivitis
Inspissated Meibomian gland (Chalezia)
• Prominence of third eyelids
• Exophthalmos or buphthalmos
• Abnormal eyes position
Nystagmus, strabismus, etc
• Uveitis
• Lens abnormalities
Underlying dental disease at what two locations may cause a blockage of the nasolacrimal duct?
Upper first molar or upper incisor are locations which tend to place pressure on nasolacrimal duct and may cause blockage, may overspill into the eyes
What are common abnormalities associated with ears of rabbits?
• Headshaking or scratching
• Lesions
• Alopecia
• Skin colour
• Discharge
• Erythema
• Oedema
• Palpate for ear base swellings
What are you observing when examining the ears of rabbits?
• Wax
• Parasites
• Foreign body
• Masses
• Tumour
• Polyp
How should the jaw/dentition be palpated and examined?
Palpate lower jaw - mandible
Palpate laterally on mandible and maxilla to check for sharp points and pain
Evaluate lateral jaw movement (if hospitalized, observe eating)
Check Incisors
Angle, Malocclusion, Fractures
Mucous membrane colors
Once examination of the head is complete, you can use the _______ lymph nodes to then transition into looking at the body.
What lymph nodes should also be examined?
Submandibular (lentil sized, next to large salivary glands)
Usually good if not felt
• Prescapular (usually palpable)
• Popliteal (usually palpable)
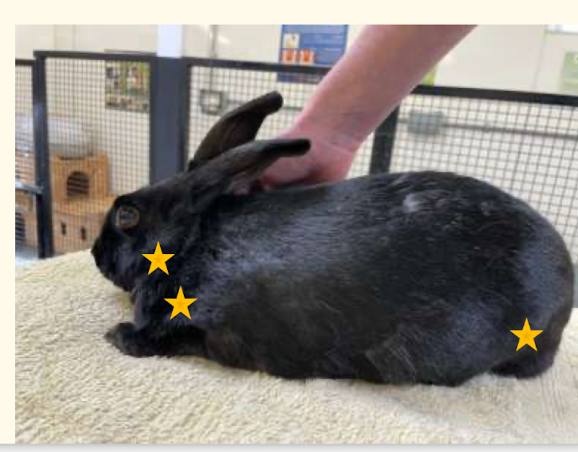

When evaluating the limbs, neck and back, what features are important to examine?
- Claw length
- Swellings
- Muscle atrophy
- Arthritis
- Easier palpating both at same time for forelimb
- Can be easier to assess hindlimbs during ventral exam
What is chest compliance and how is this examined in rabbits?
Applying pressure to chest twice, abnormal size of thymus may compress or move the heart
Gives indication for listening to chest again, or radiographs
In the abdominal palpation, what organs should be able to palpated?
• GI - Stomach, Small Intestines, Caecum, Distal Colon
• Urinary - Kidneys, Bladder
In the abdominal palpation, what organs should NOT be able to palpated, unless concerning?
• Concern if can palpate: Liver, spleen, non-pregnant uterus
What does stomach size (Abdominal palpation) tell you?
Feeding habits, are they full, bloated
What observations are important to note when performing the ventral examination?
• Hygiene
• Mammary gland palpation
• Sex determination
• Inguinal scent glands
• Hindlimbs
Claw length
Limb palpations
Pododermatits check
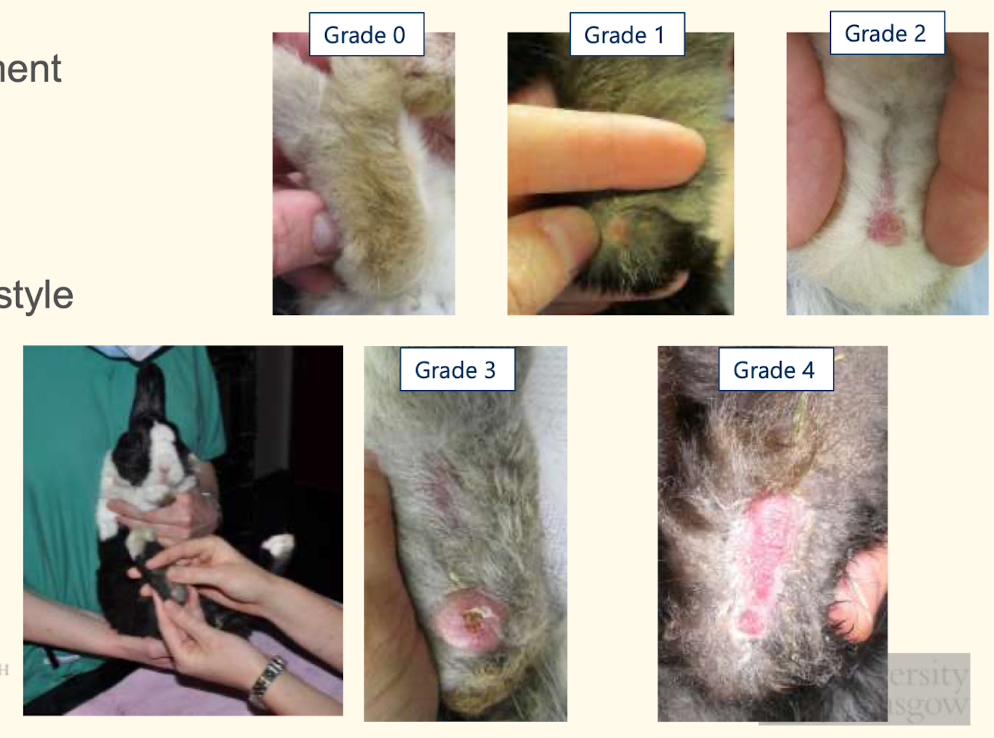
What region of the rabbit is most likely to be affected by pododermatitis?
Point of hocks
What are predispositions for pododermatitis?
- Dirty environment
- Hard flooring
- Obesity
- Rex breed
- Sedentary lifestyle
How can pododermatitis be graded?
What are the most important features of the otoscopic examination?
• Left until last - ears and teeth
• Metal cone (Plastic - sharp edges)
• Correct restraint - ask owner to hold, bum toward owner, or bunny burrito
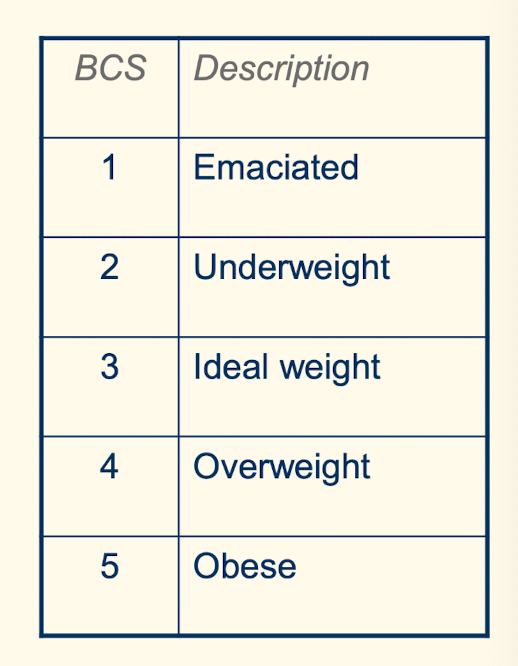
How are the weights and BCS scores of rabbits measured?
• Weigh - towel on scales - less important than BCS as tumours and cysts may alter weight - making it inaccurate
• BCS:
- prominence of:
Ribs
Dorsal spinous processes
Pelvic bones
- Assessment of abdominal and subcutaneous fat
Obesity can prevent ______ of the _______.
expansion, caecum