Nervous System (Brain & Spinal Cord)
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Cerebrum
largest part of the brain consisting of a right and left hemisphere that provides higher mental functions
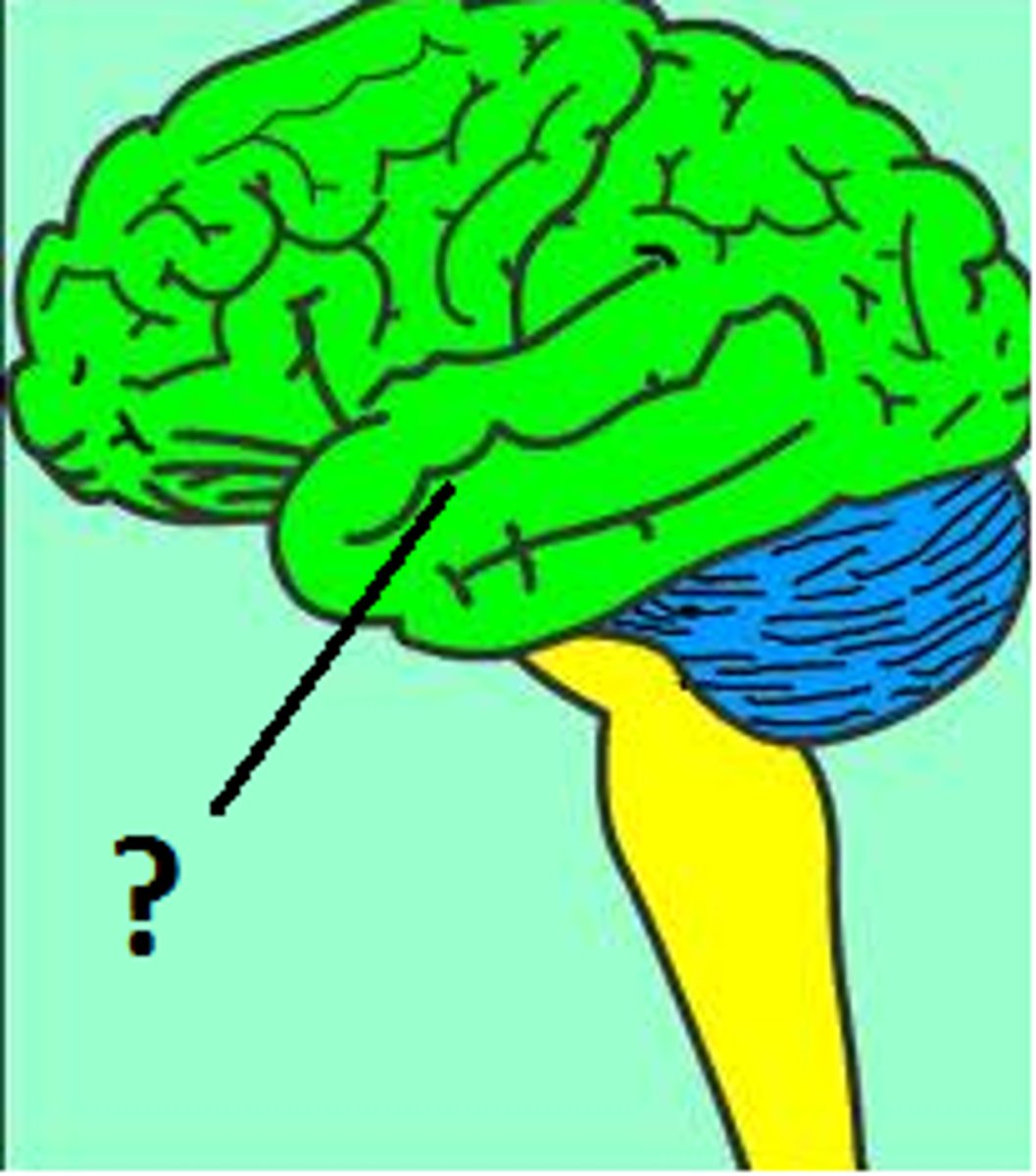
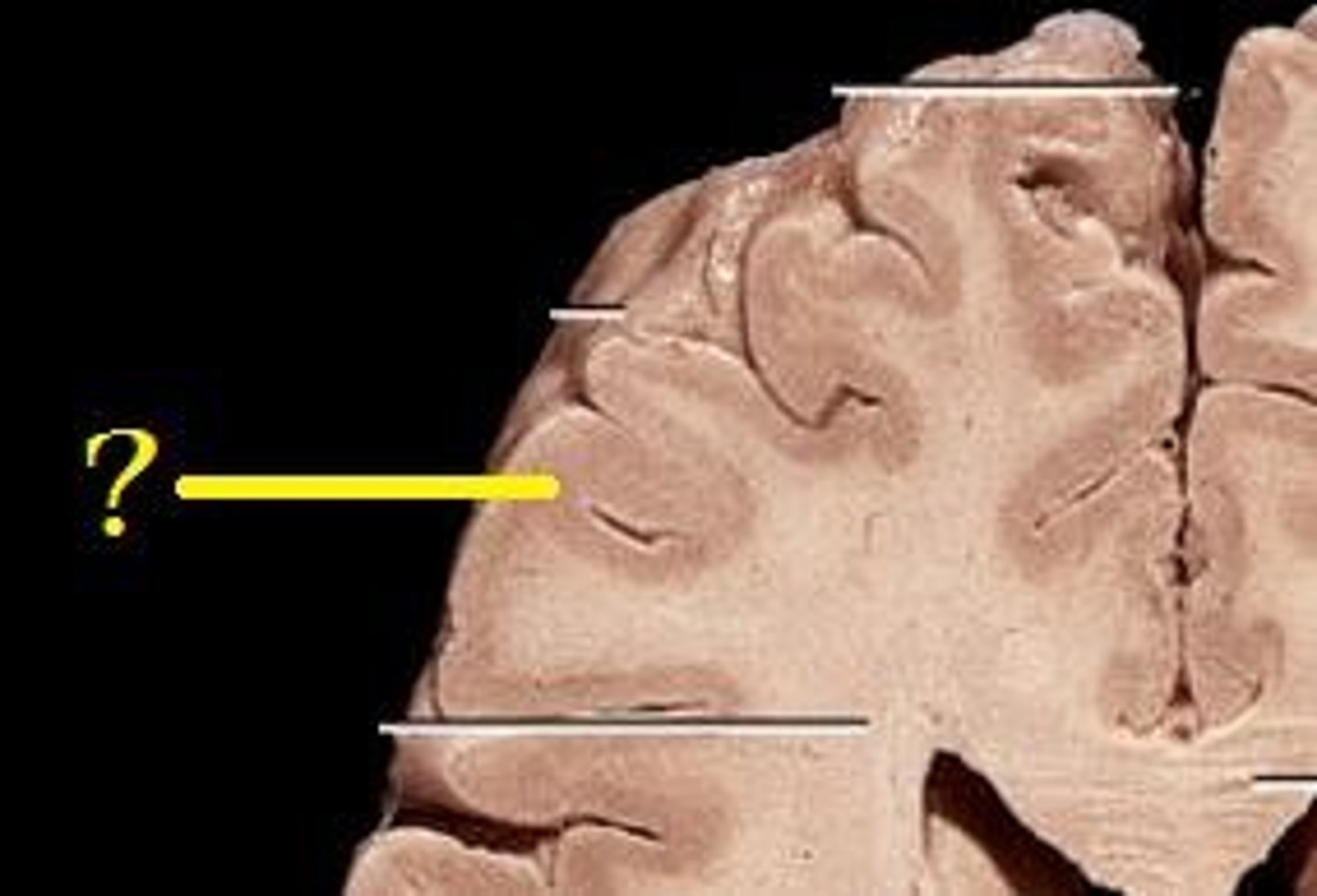
Gyri
Ridges (convolutions) on the surface of the brain
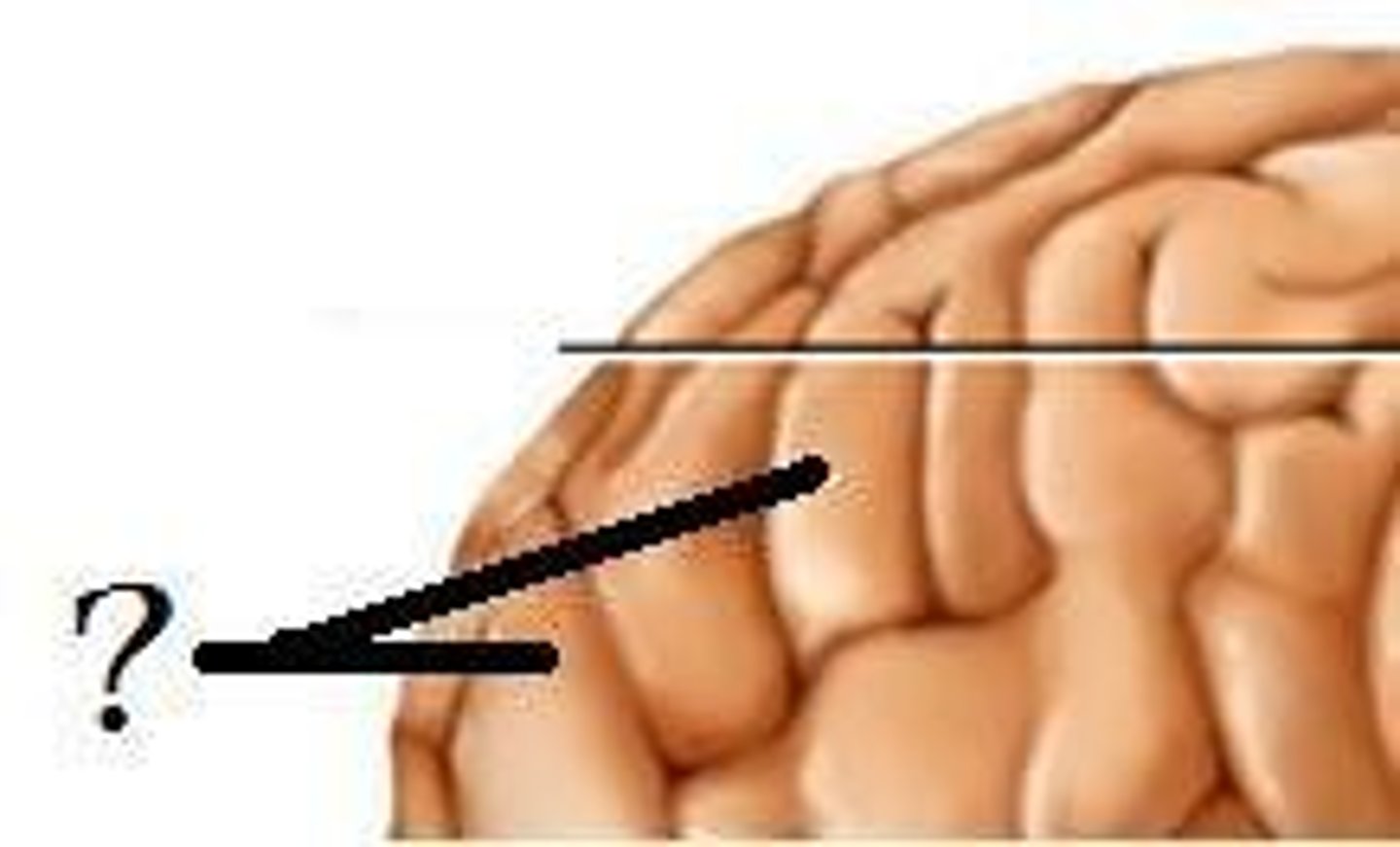
Sulci
Shallow grooves between gyri
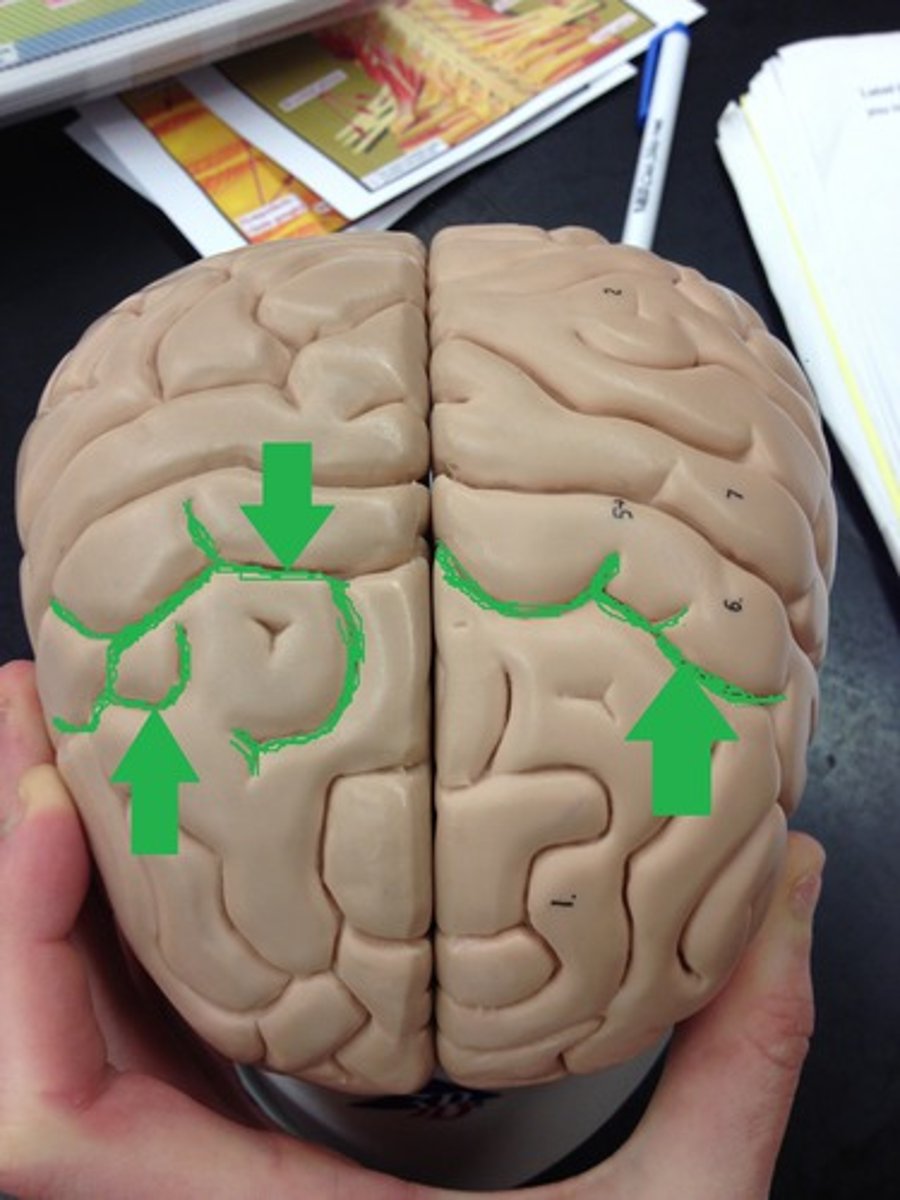
Fissure
Deep grooves that separates parts (such as lobes)
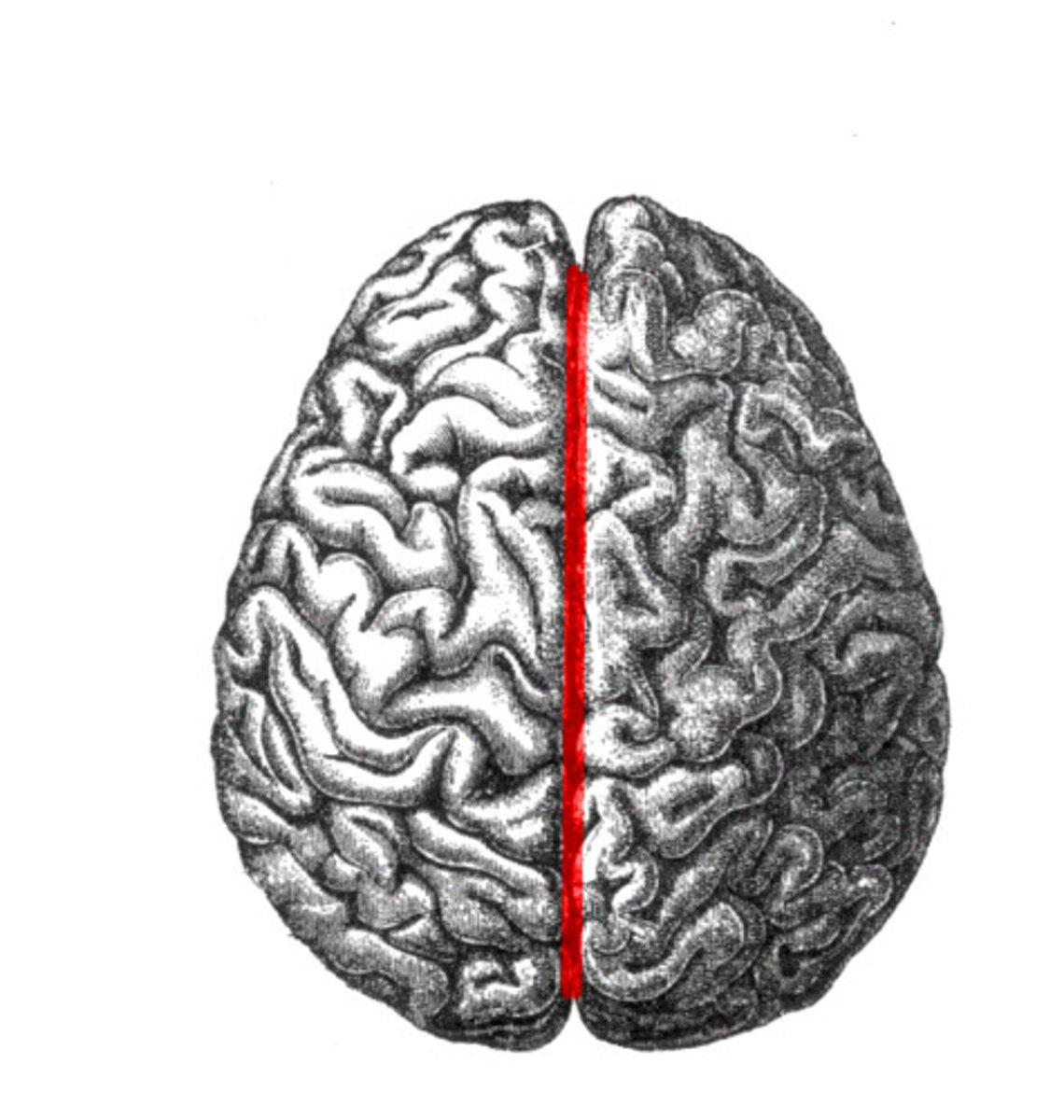
Corpus Callosum
Broad, flat bundle of axons that connects the cerebral hemispheres
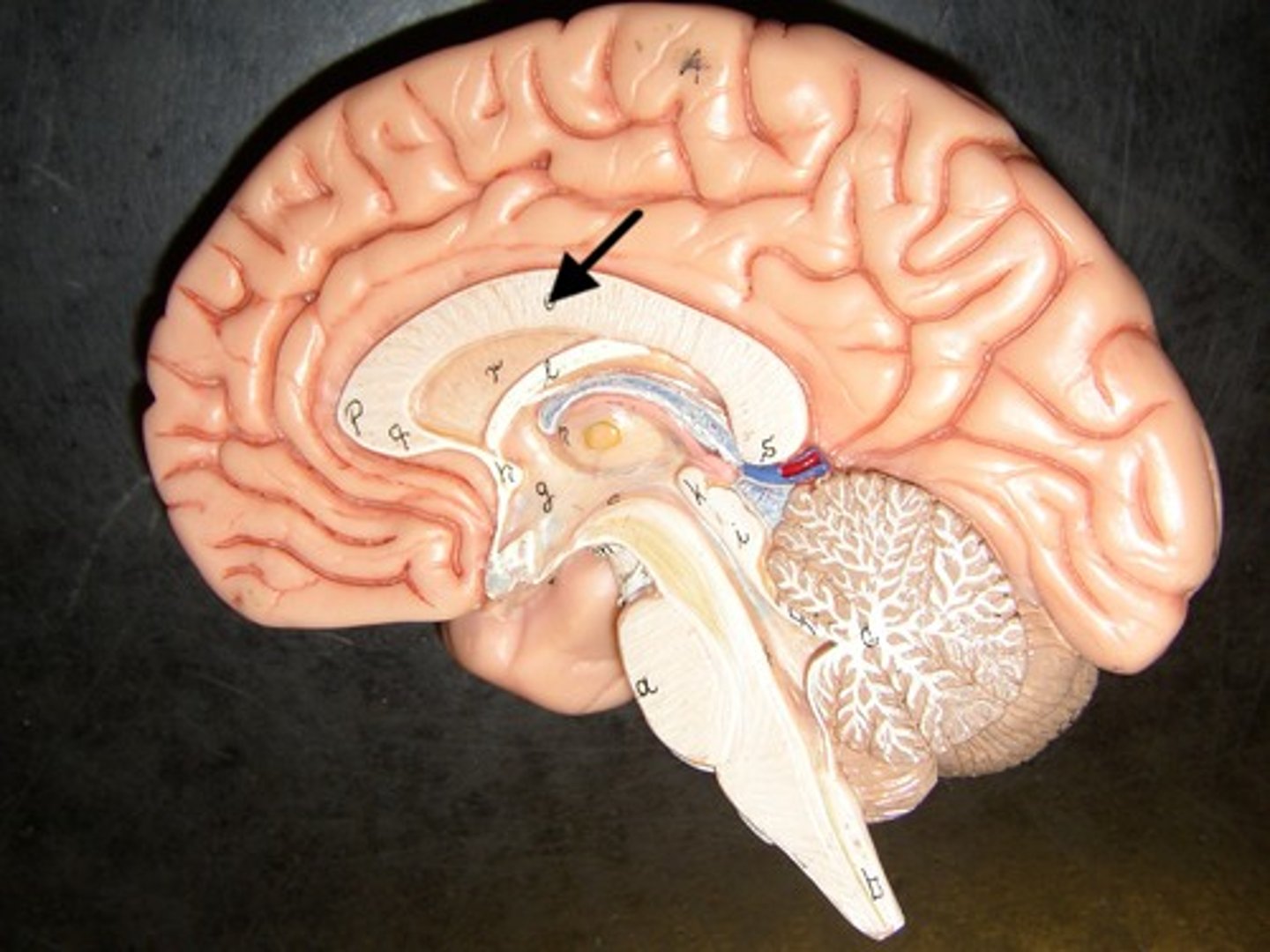
Frontal Lobe
Lobe of the brain that is responsible for executive functions, motor control, and personality & emotions. Important in decision-making, concentration, planning, problem-solving, voluntary movements, emotional regulation, and social behavior.
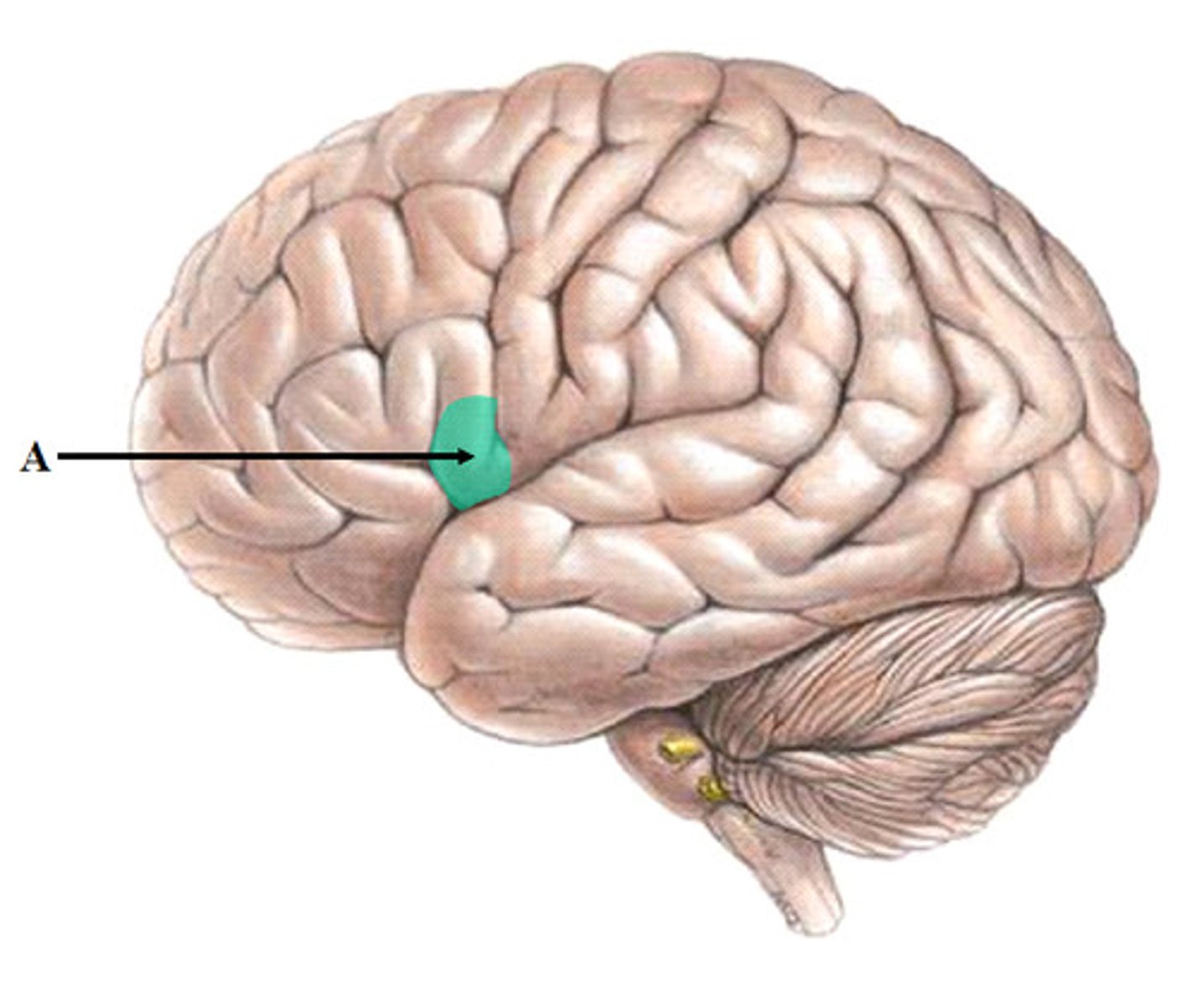
Broca's Area
Area of the brain responsible for speech production; provides motor instructions to muscles necessary for speech (mouth, tongue, and larynx)
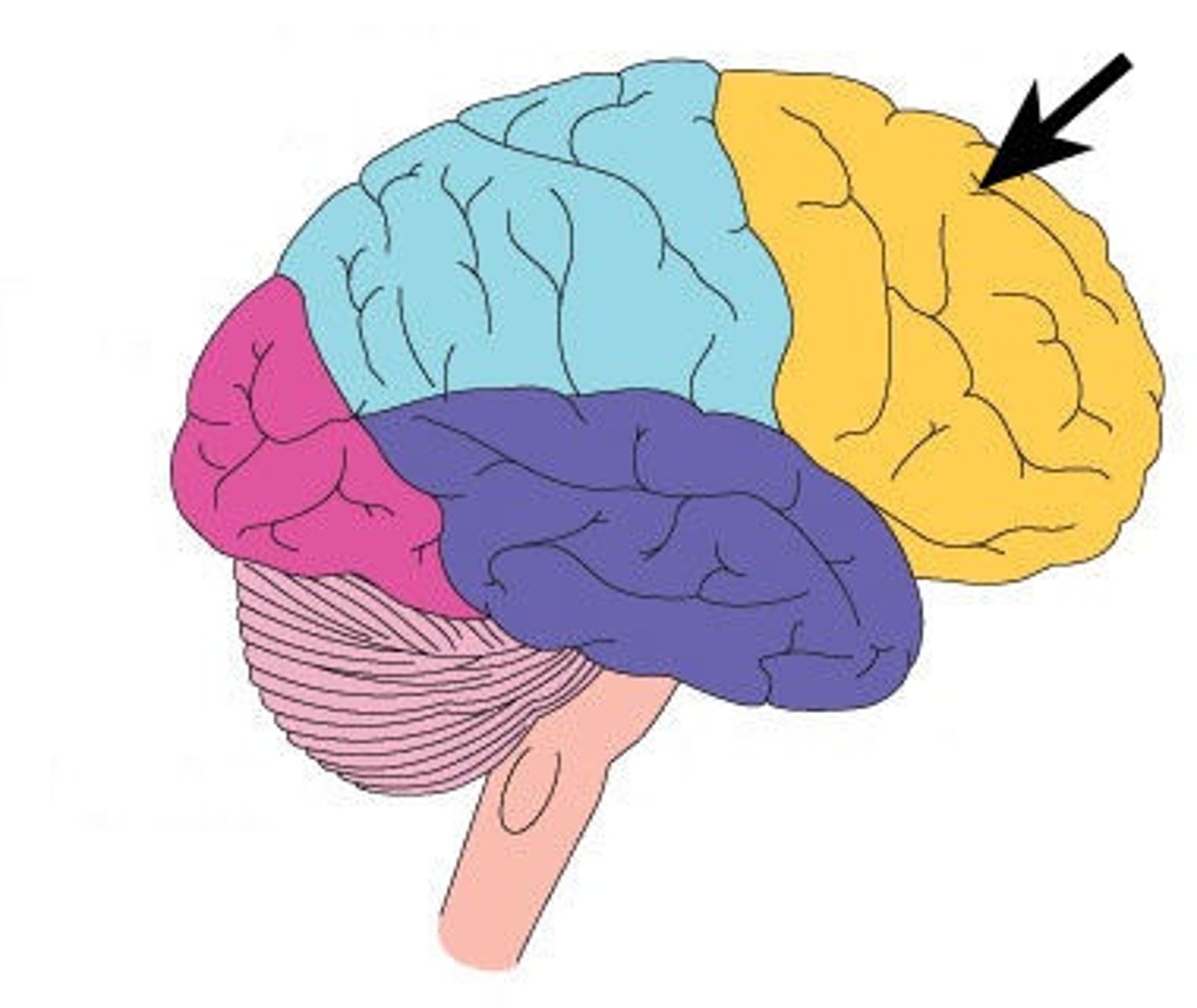
Parietal Lobe
Lobe of the brain that is responsible for sensory processing, spatial awareness, visual-spatial functions, and understanding speech and using words.
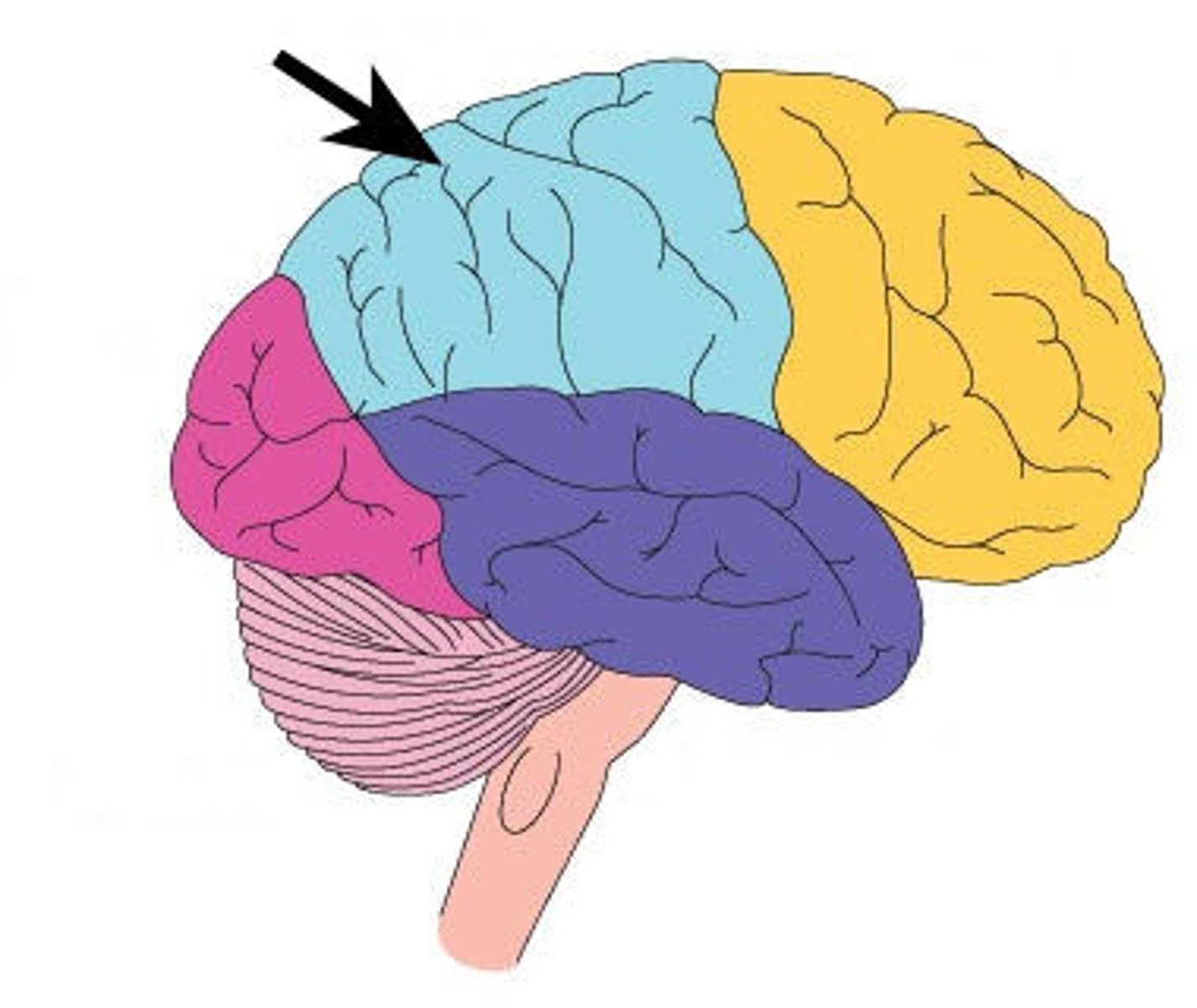
Somatosensory Cortex
Area of the brain responsible for sensations of touch, pressure, temperature, and pain
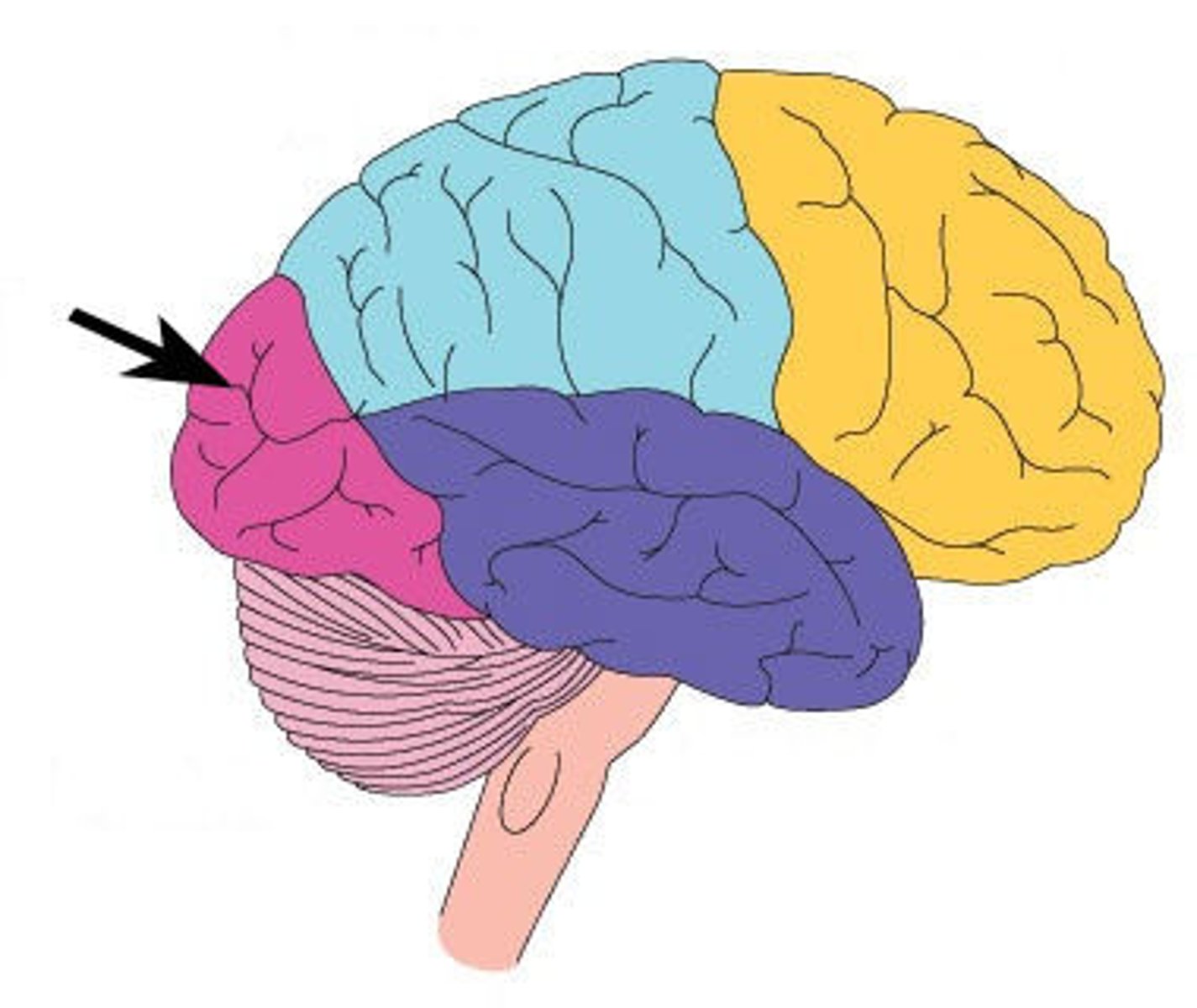
Occipital Lobe
Lobe of the brain that combines visual images and visual recognition
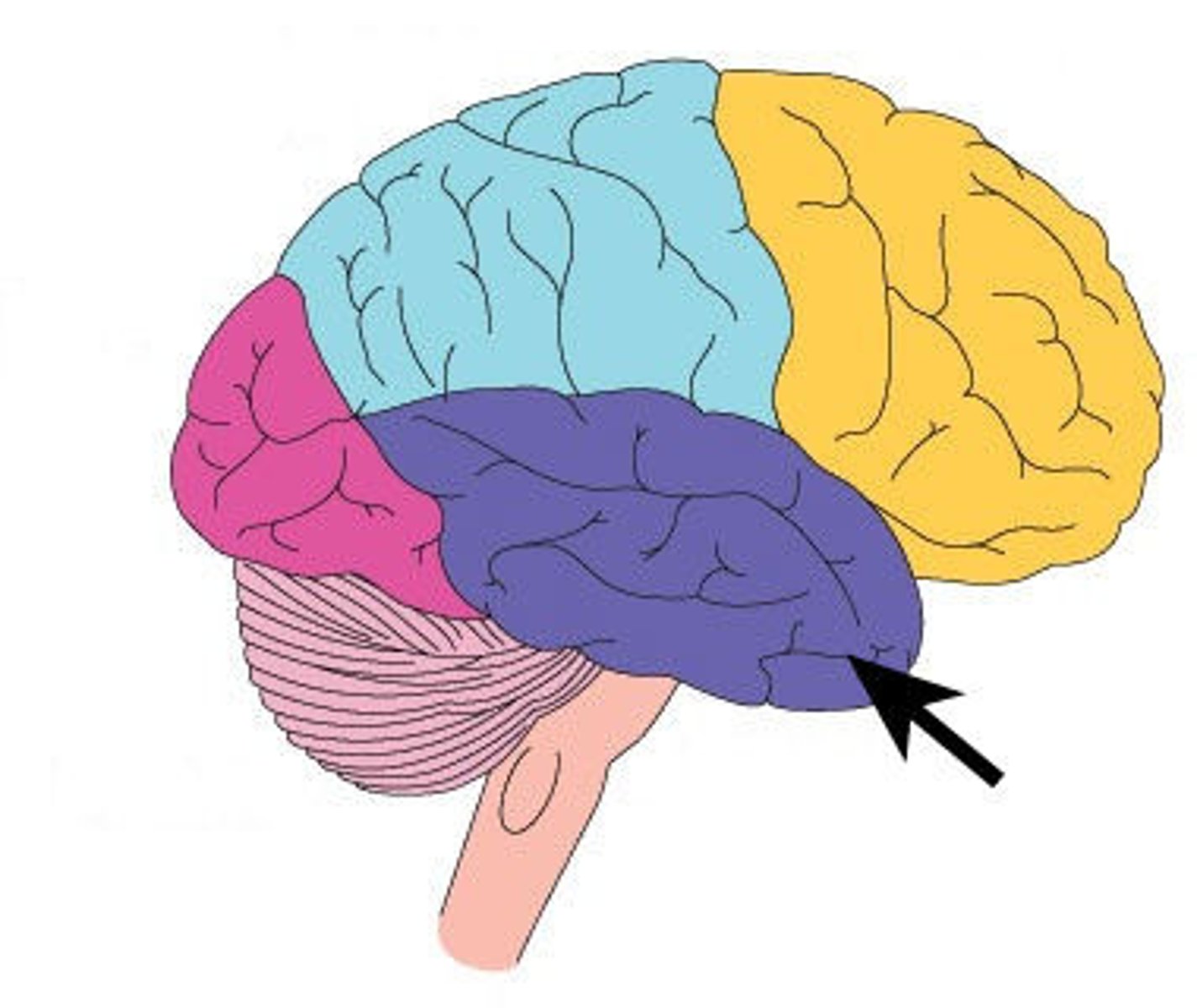
Temporal Lobe
Lobe of the brain responsible for auditory processing, memory, emotion, and language.
Wernicke's Area
Area of the brain that receives and relays input from the visual and auditory cortex; important for understanding written and spoken language
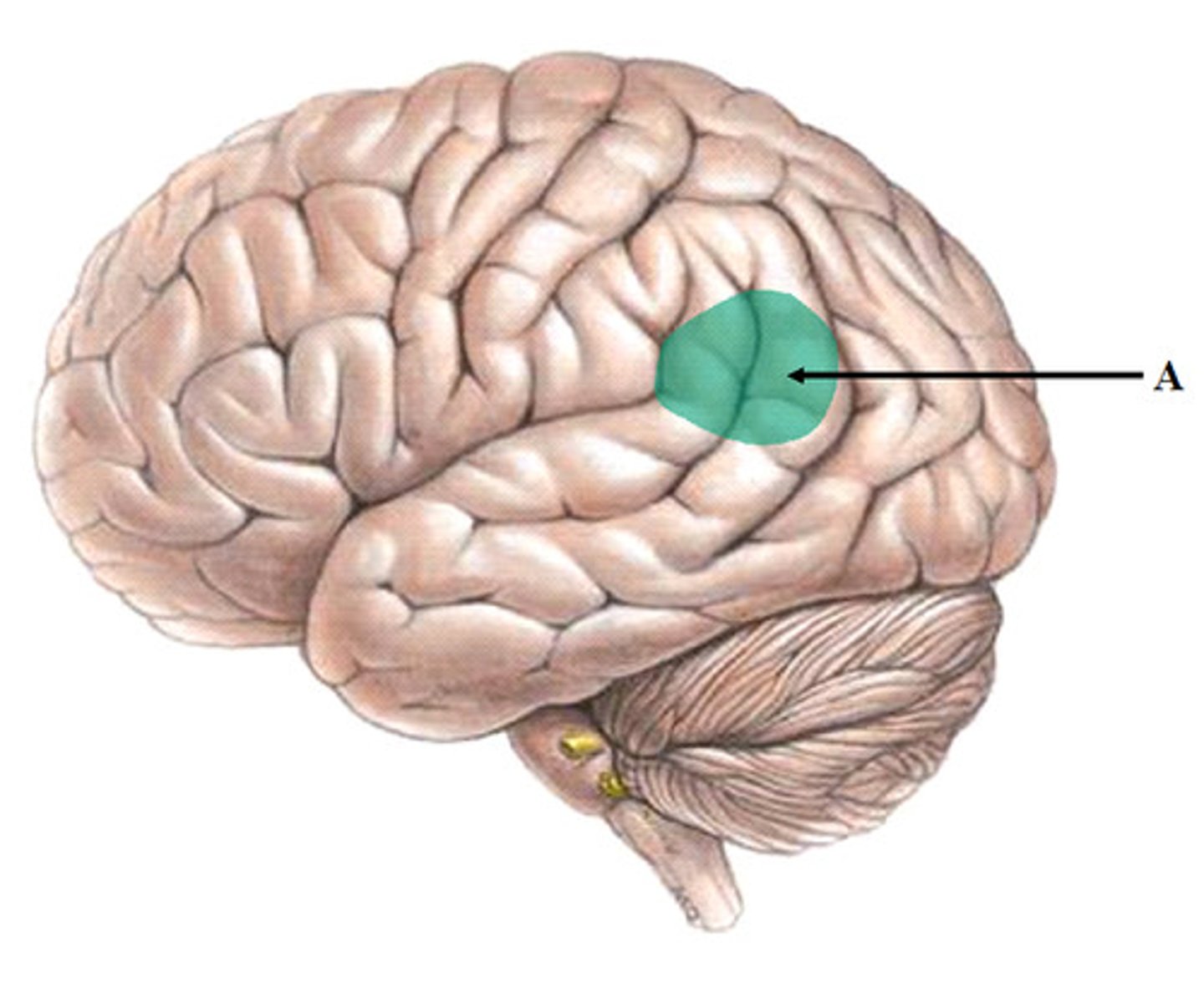
Cortex
The outer or surface portion of the cerebrum; responsible for integration and contains nearly 75% of all neuron cell bodies
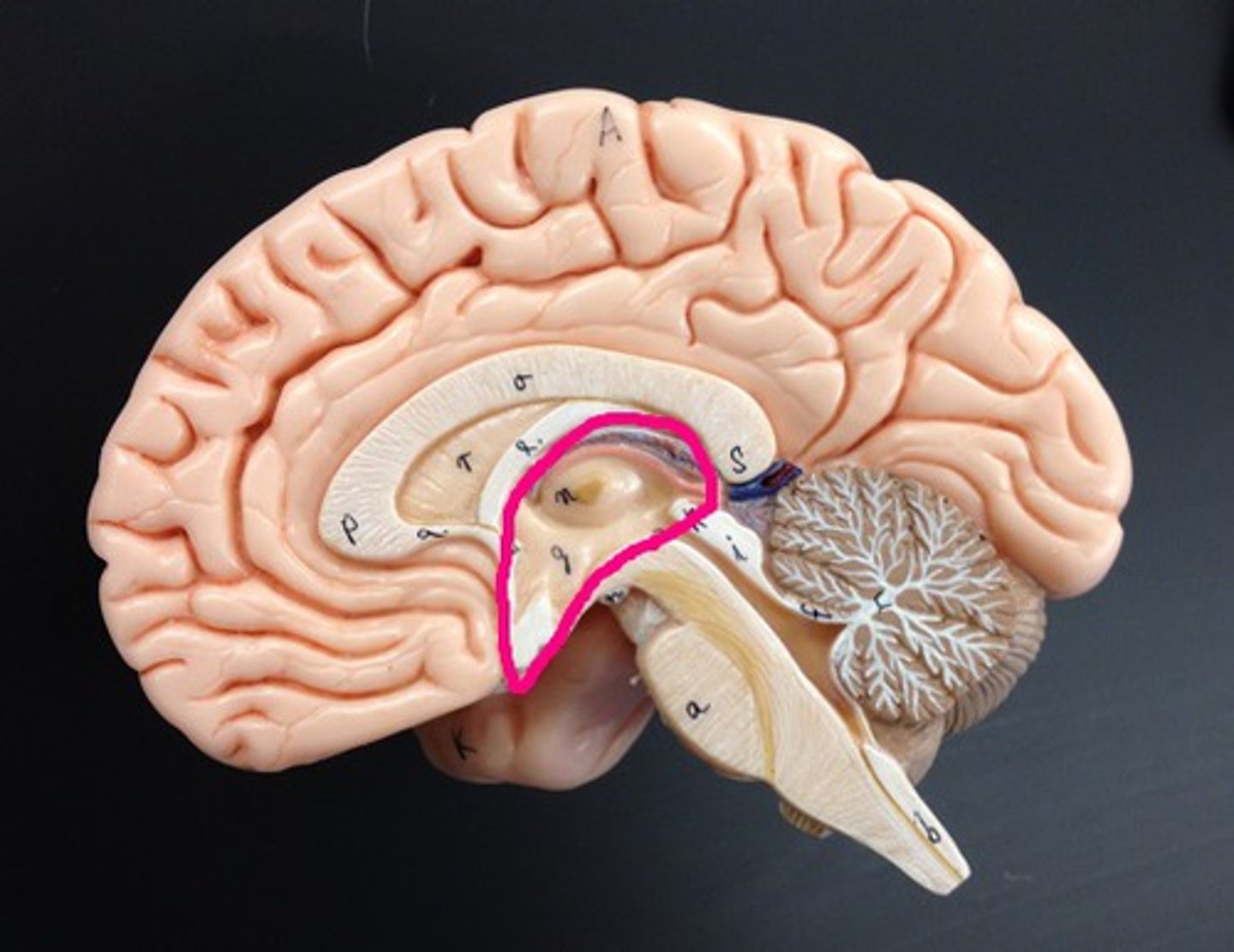
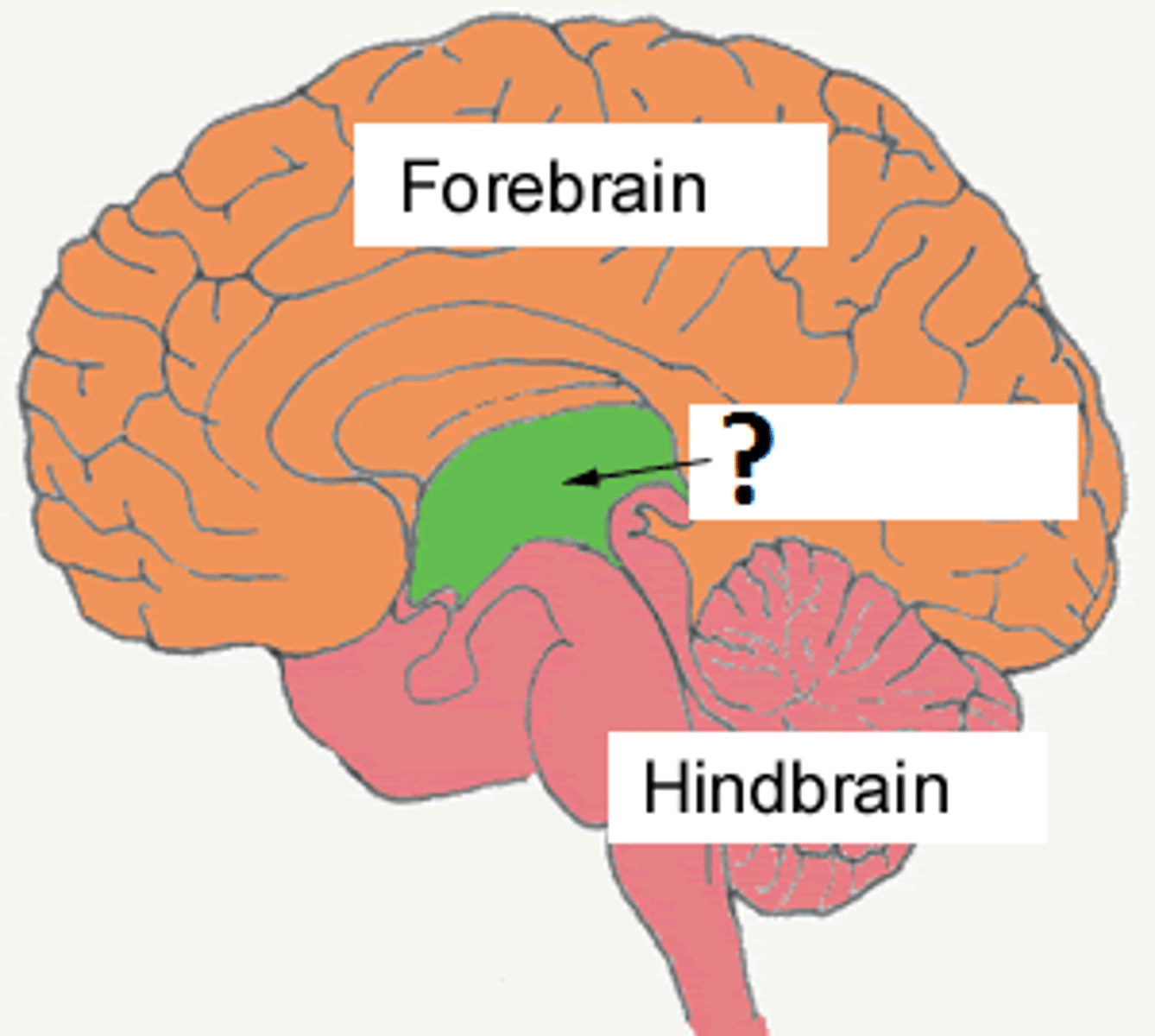
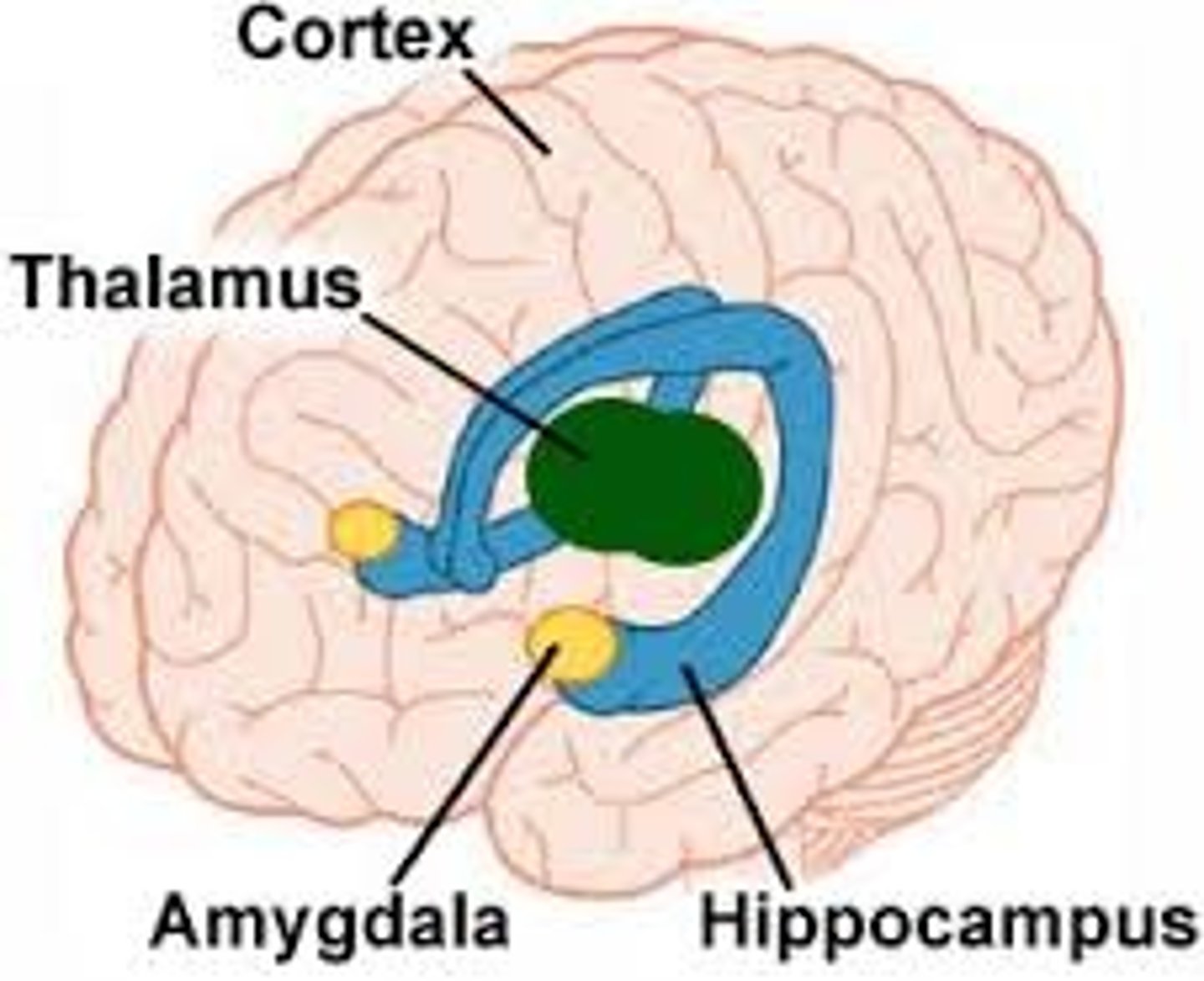
Diencephalon
Part of the brain located between the cerebral hemispheres and above the midbrain; includes the thalamus, hypothalamus, pineal gland, and other structures
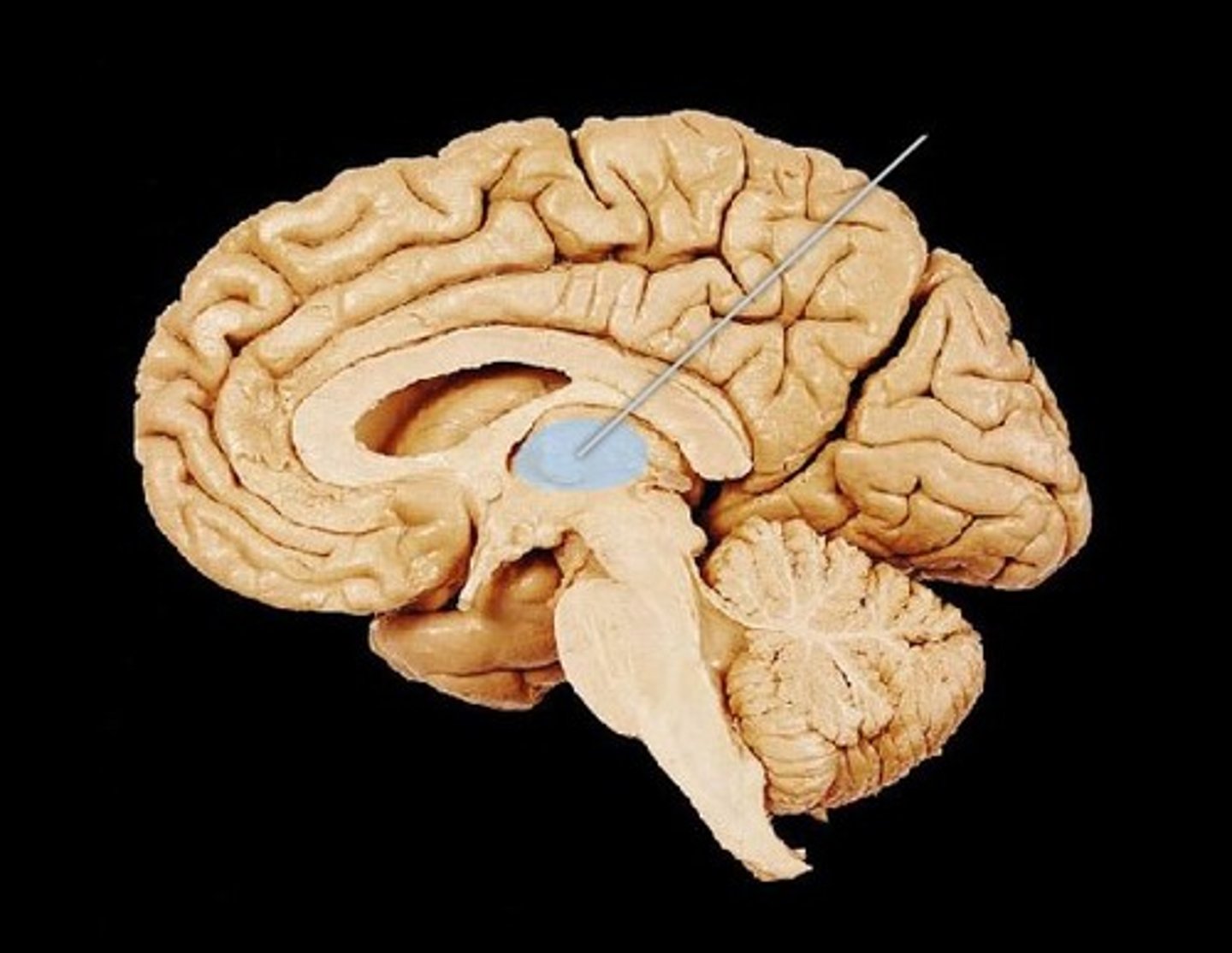
Thalamus
Structure of the brain that acts as a processing and relay center for almost all sensory information (except smell); produces an awareness of sensations
Hypothalamus
Structure of the brain that links the nervous system and the endocrine system; maintains homeostasis
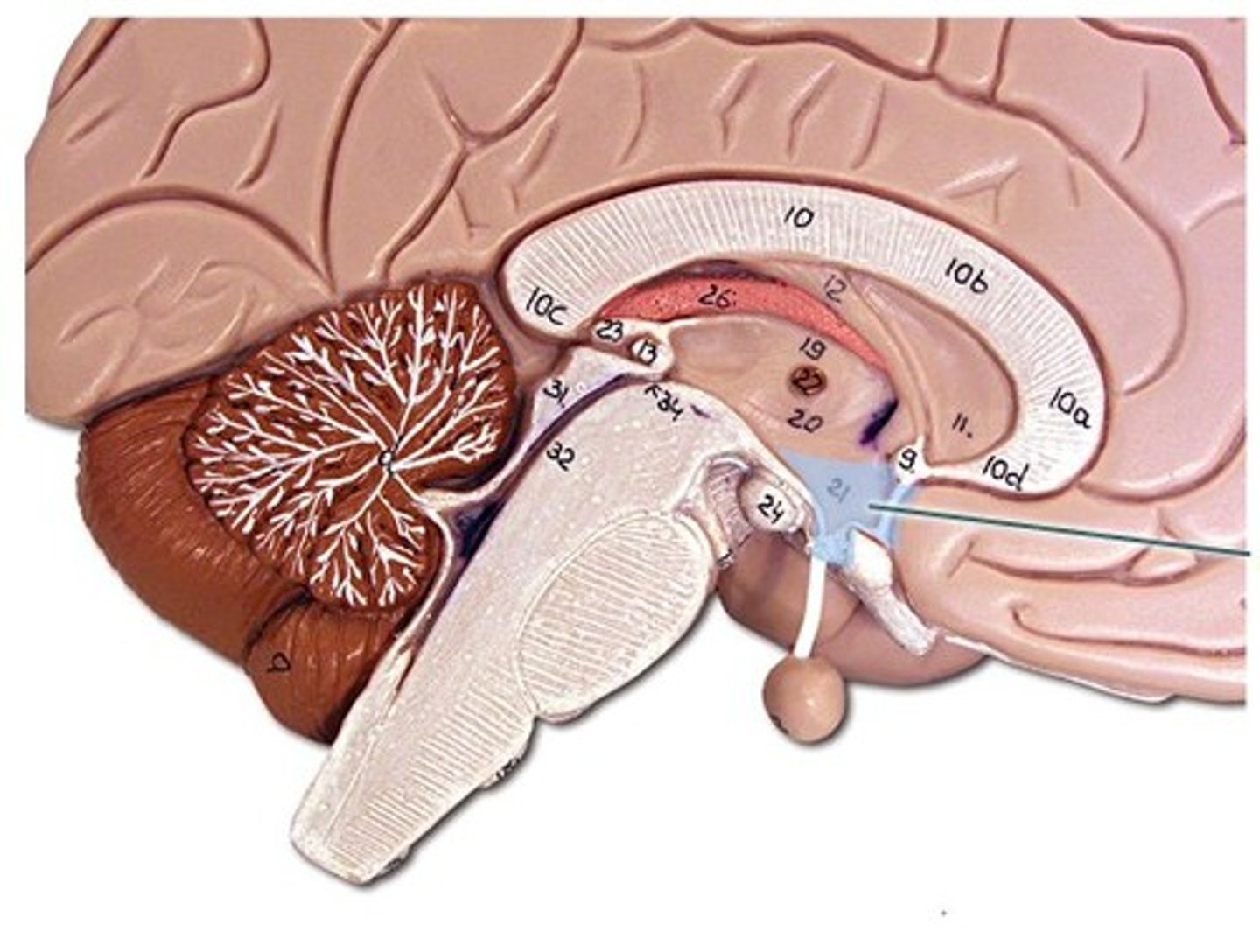
Brainstem
Bundle of nervous tissue that connects the cerebrum, diencephalon, and cerebellum to the spinal cord; contains three structures: midbrain, pons, and medulla oblongata
Midbrain
Small region of the brainstem between the diencephalon and the pons that contains myelinated axons that connect the spinal cord to higher parts of the brain
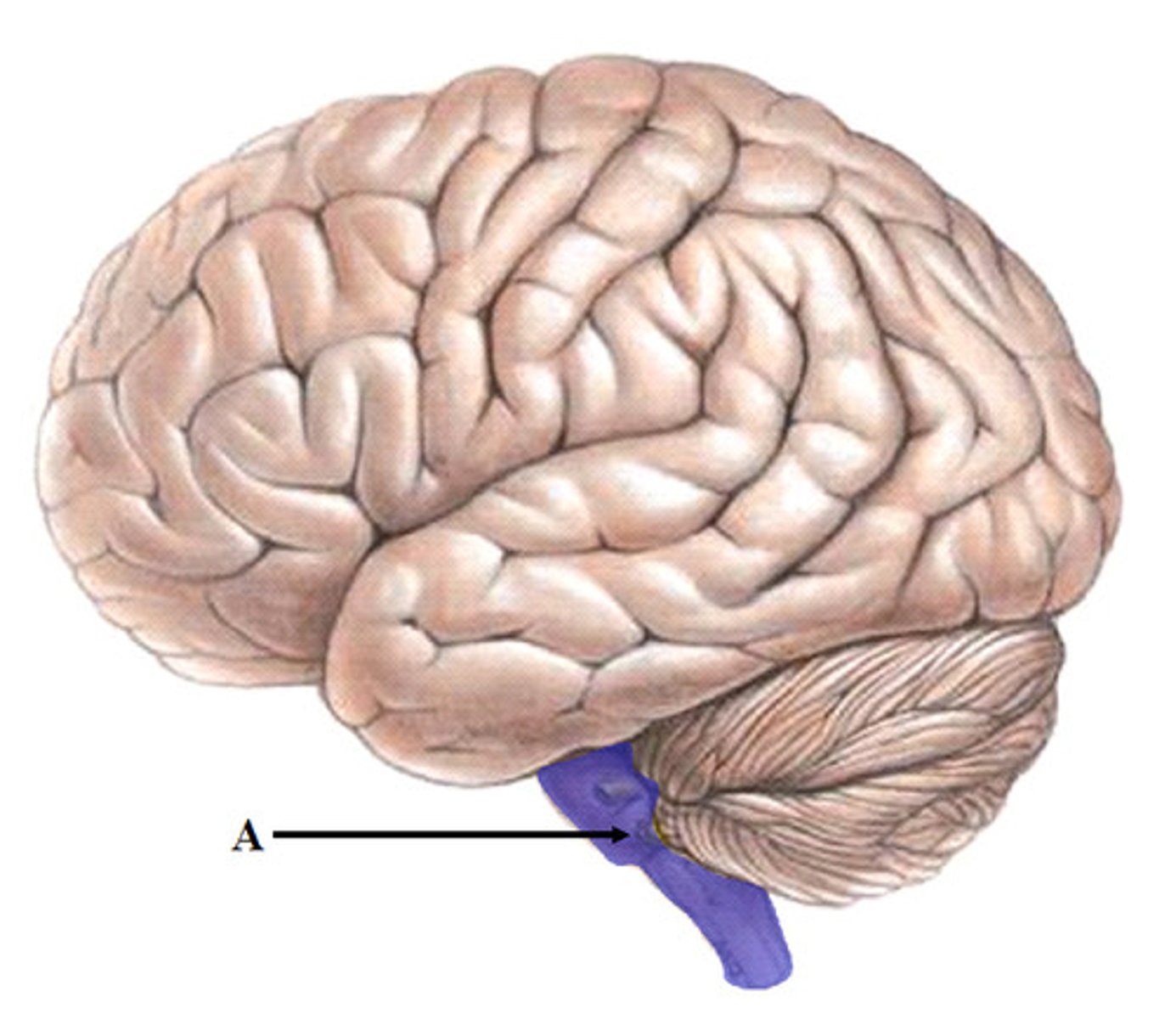
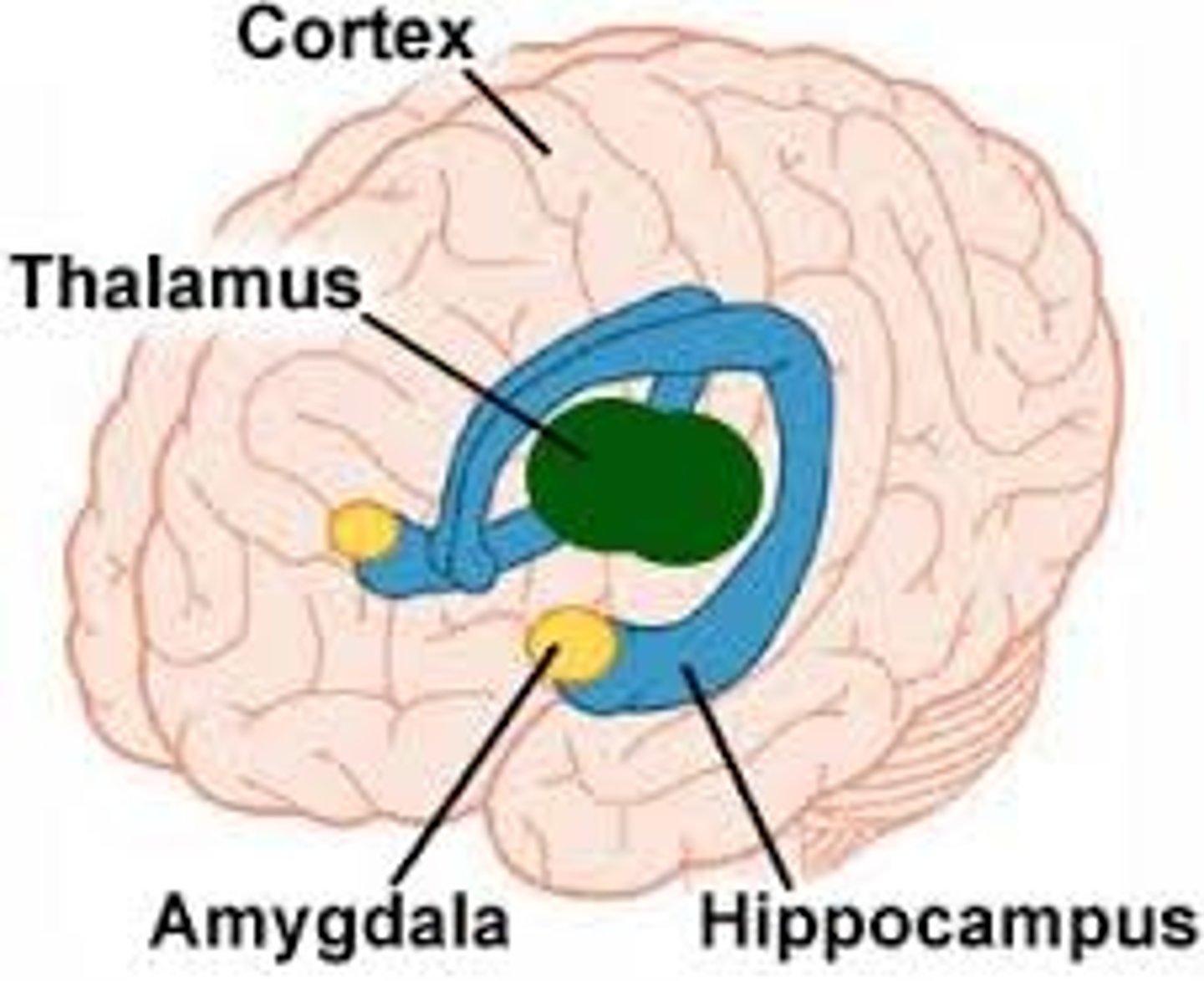
Hippocampus
Portion of the brain associated with learning and memory; consolidates information from short-term memory to long-term memory; plays a role in spatial navigation
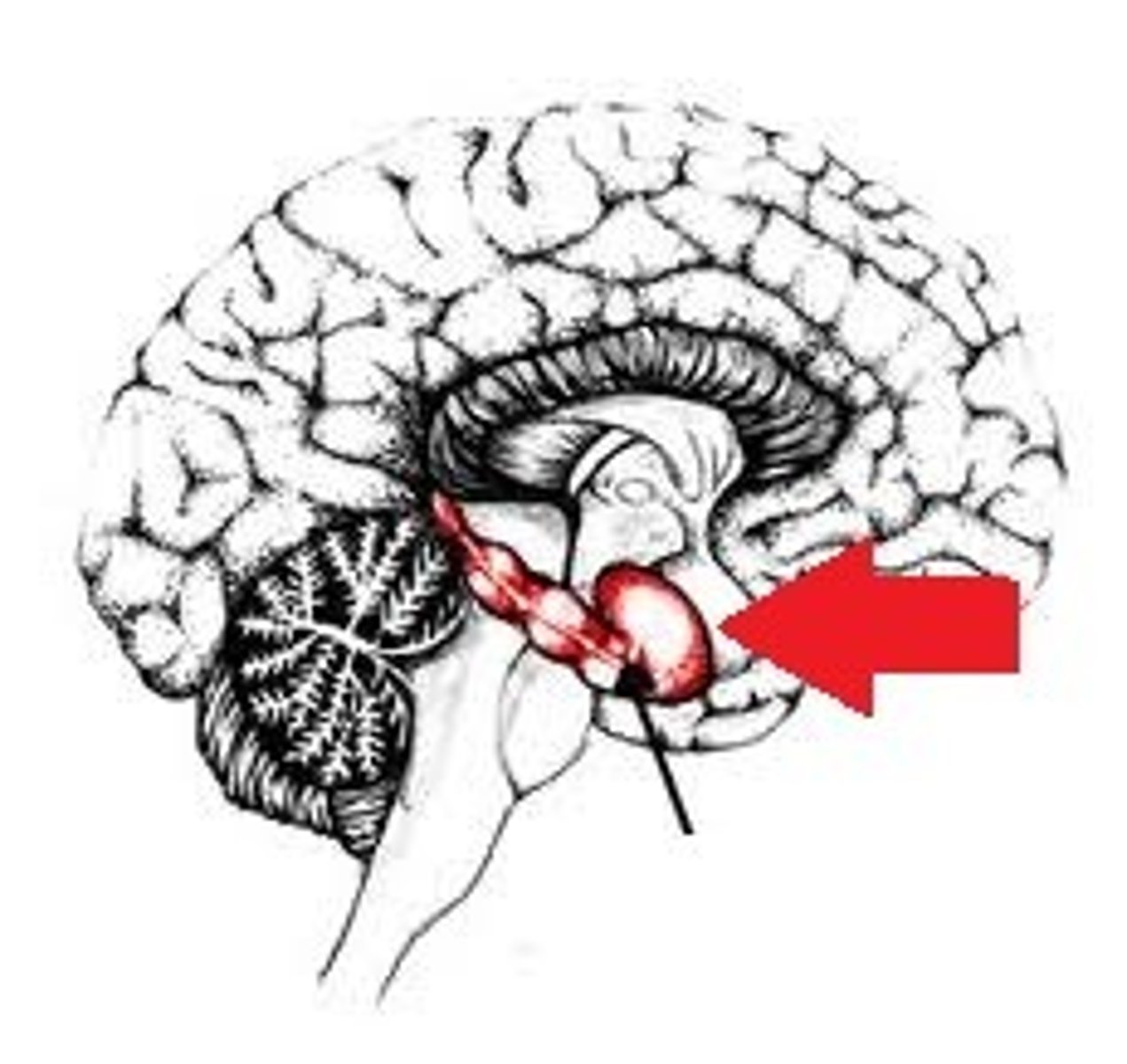
Amygdala
Portion of the brain linked to emotion and memory; controls emotional experience and expression
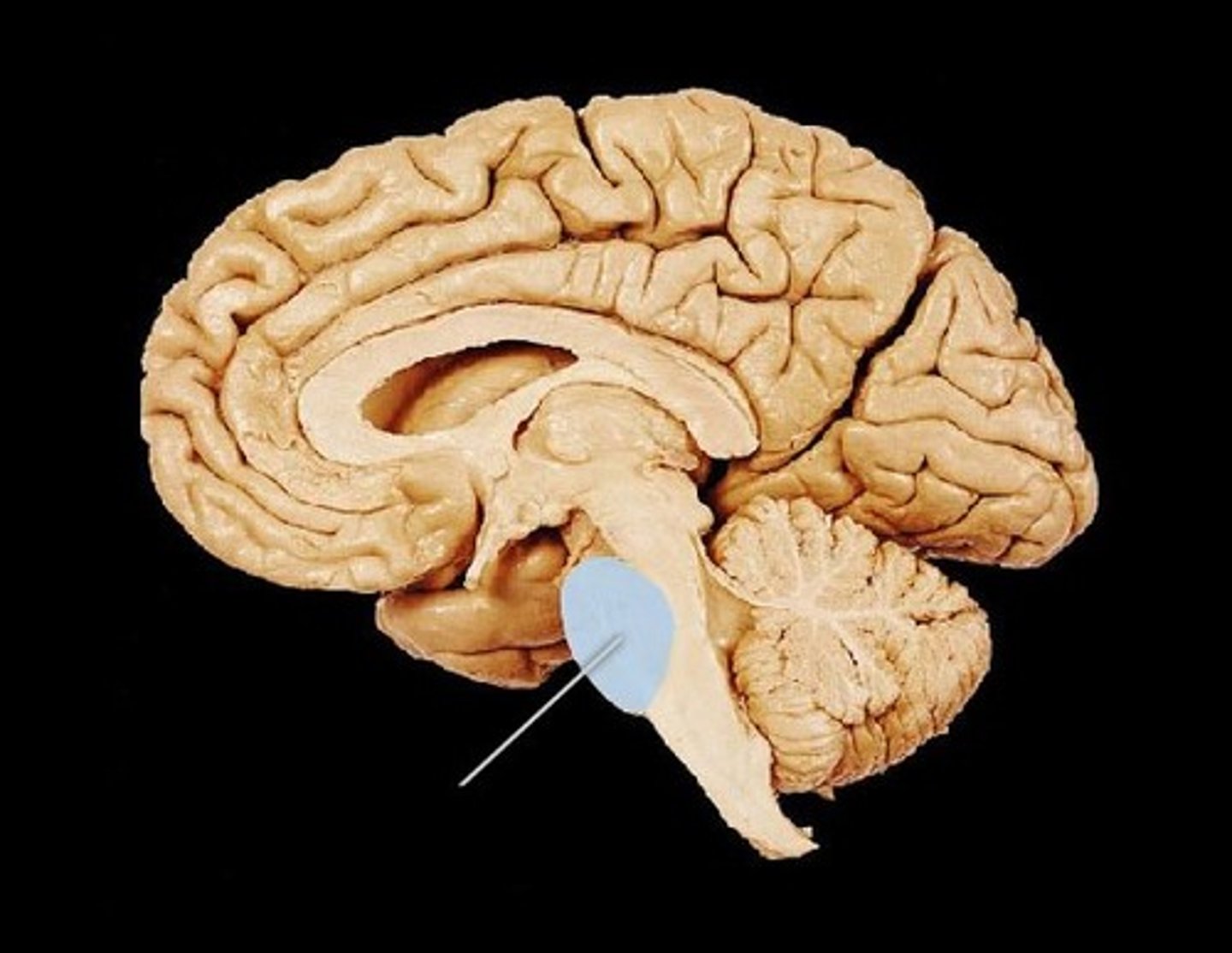
Pons
Part of the brainstem that contains centers for respiration and serves as a relay station; relays sensory impulses to the cerebrum; handles unconscious processes and jobs such as REM and breathing
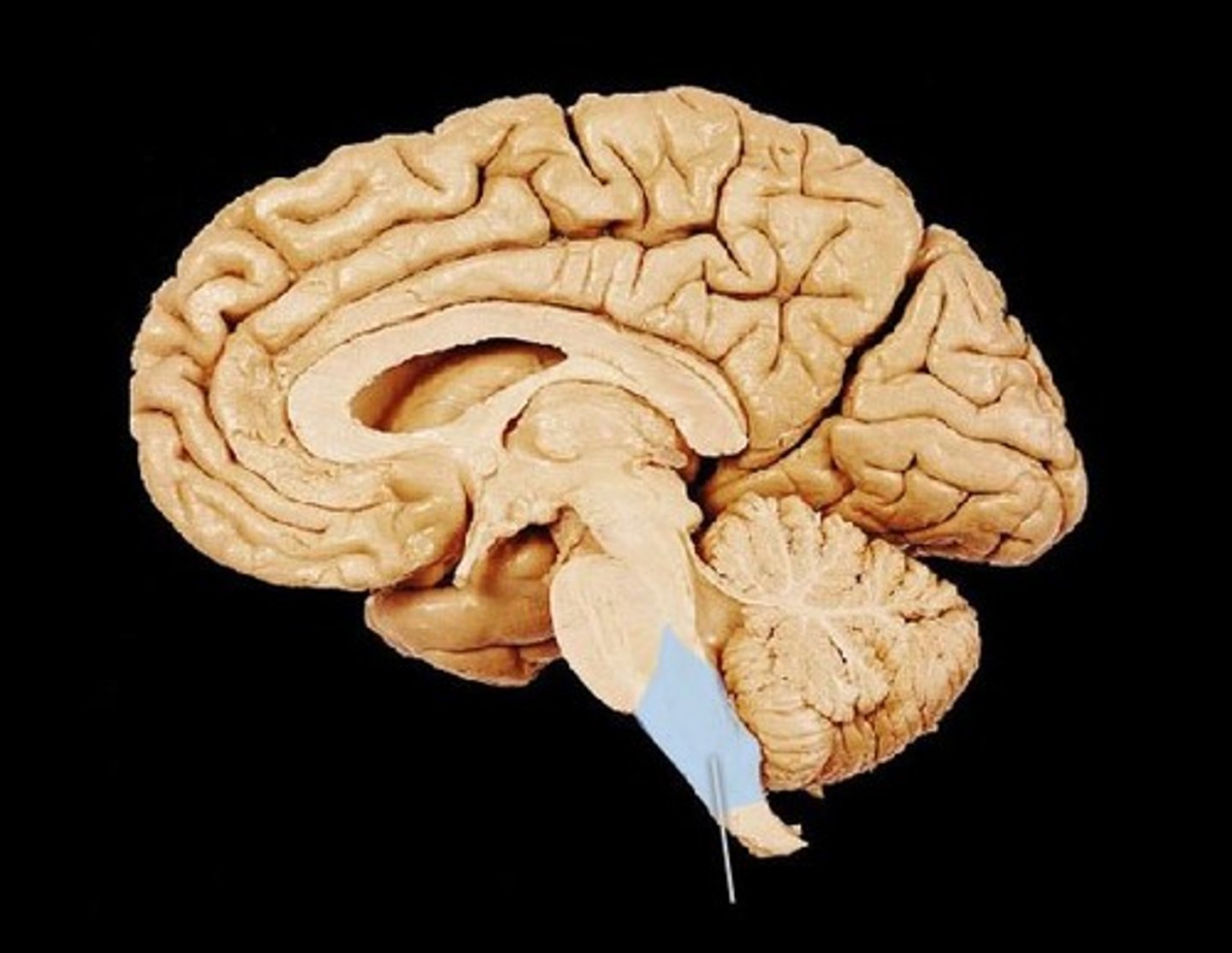
Medulla Oblongata
Portion of the brainstem that contains centers for breathing, cardiovascular control, swallowing, and other involuntary functions; all ascending and descending nerve tracts pass through this structure
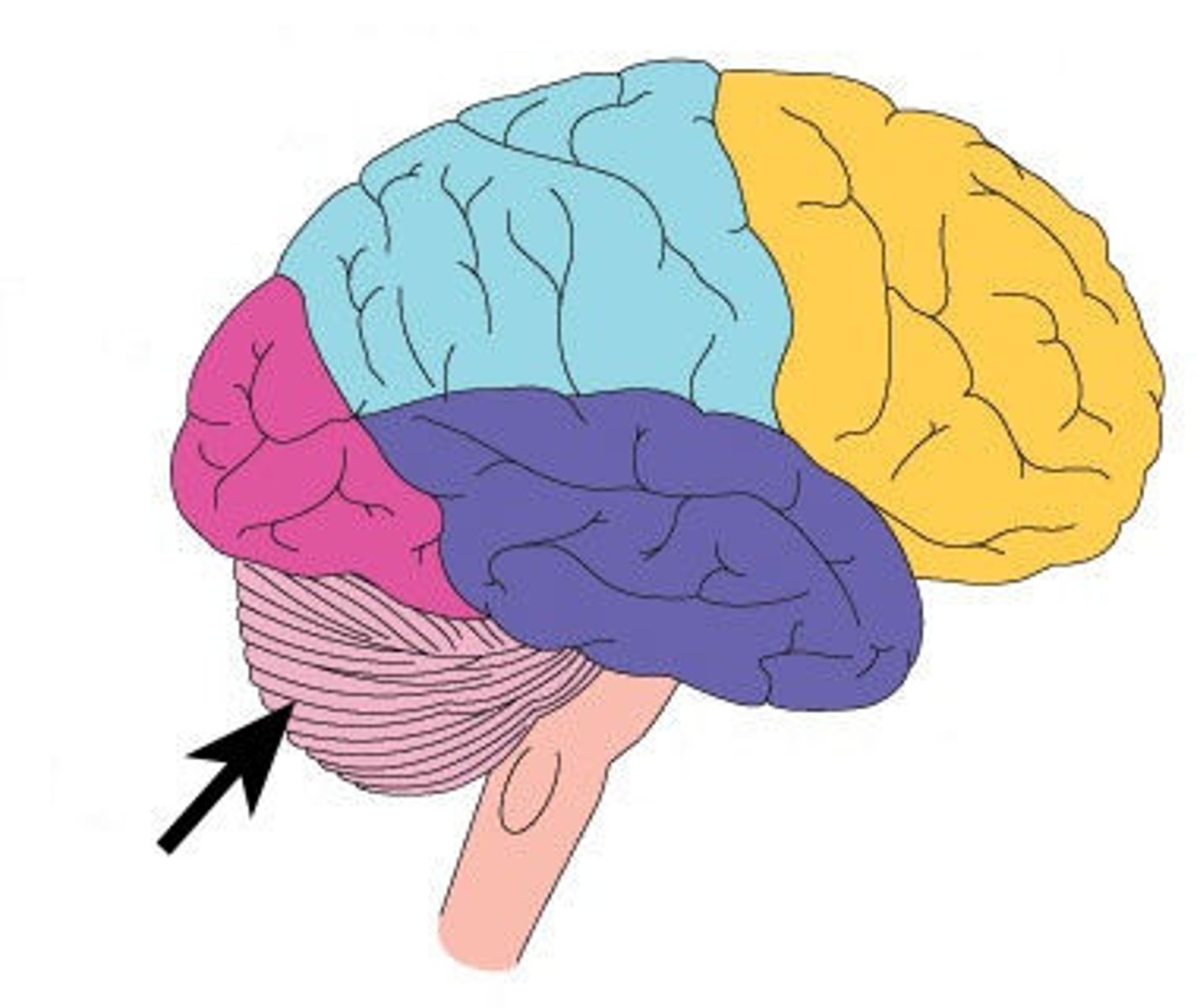
Cerebellum
Part of the brain that coordinates skeletal muscle movement and is responsible for motor learning, balance, and equilibrium; located beneath the occipital lobe
Anterior Horn
Part of the spinal cord that contain cell bodies of motor neurons that carry signals to muscles/glands; gray matter
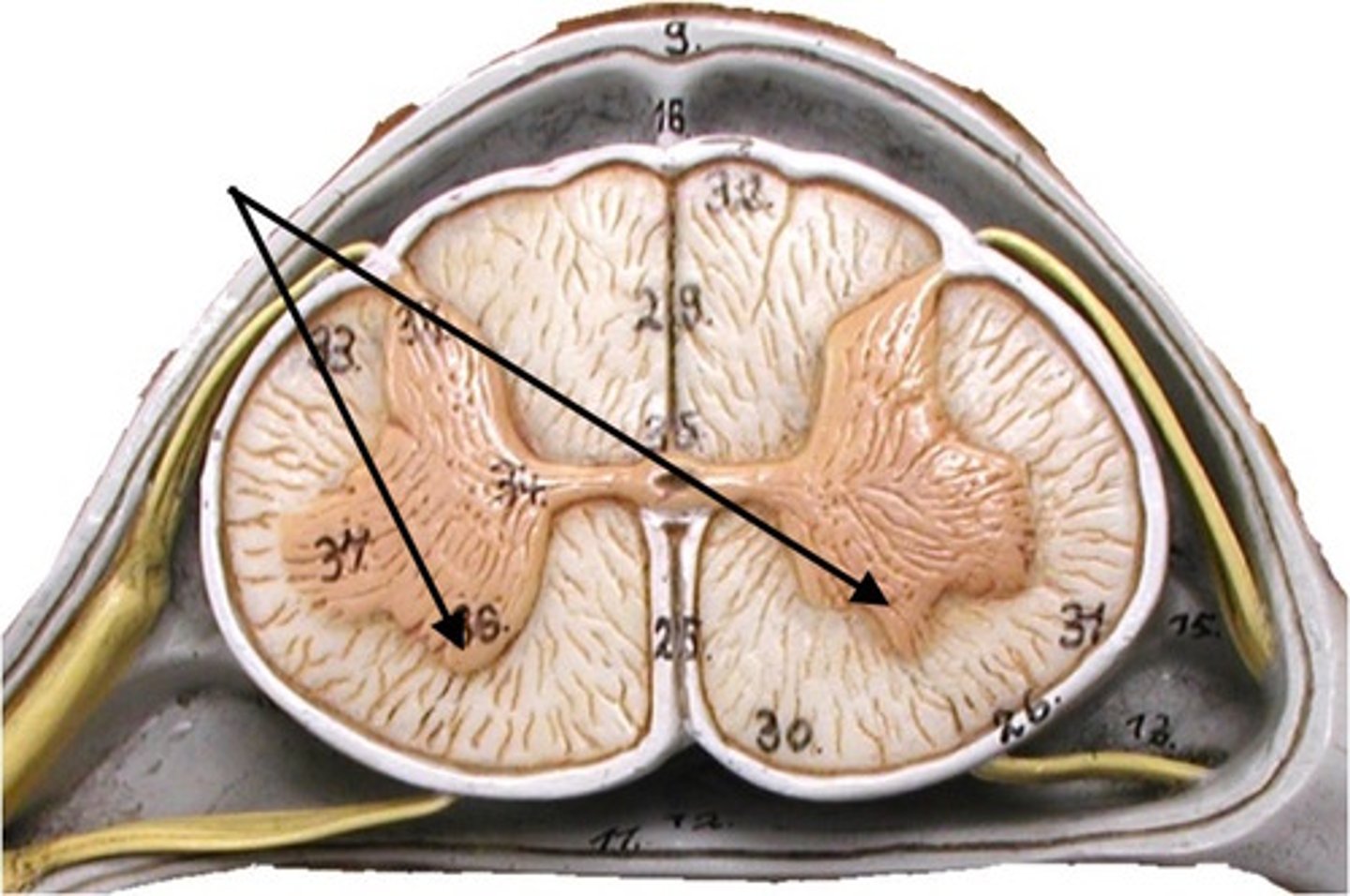
Posterior Horn
Part of the spinal cord that contain interneurons that receive sensory information from sensory neurons; gray matter
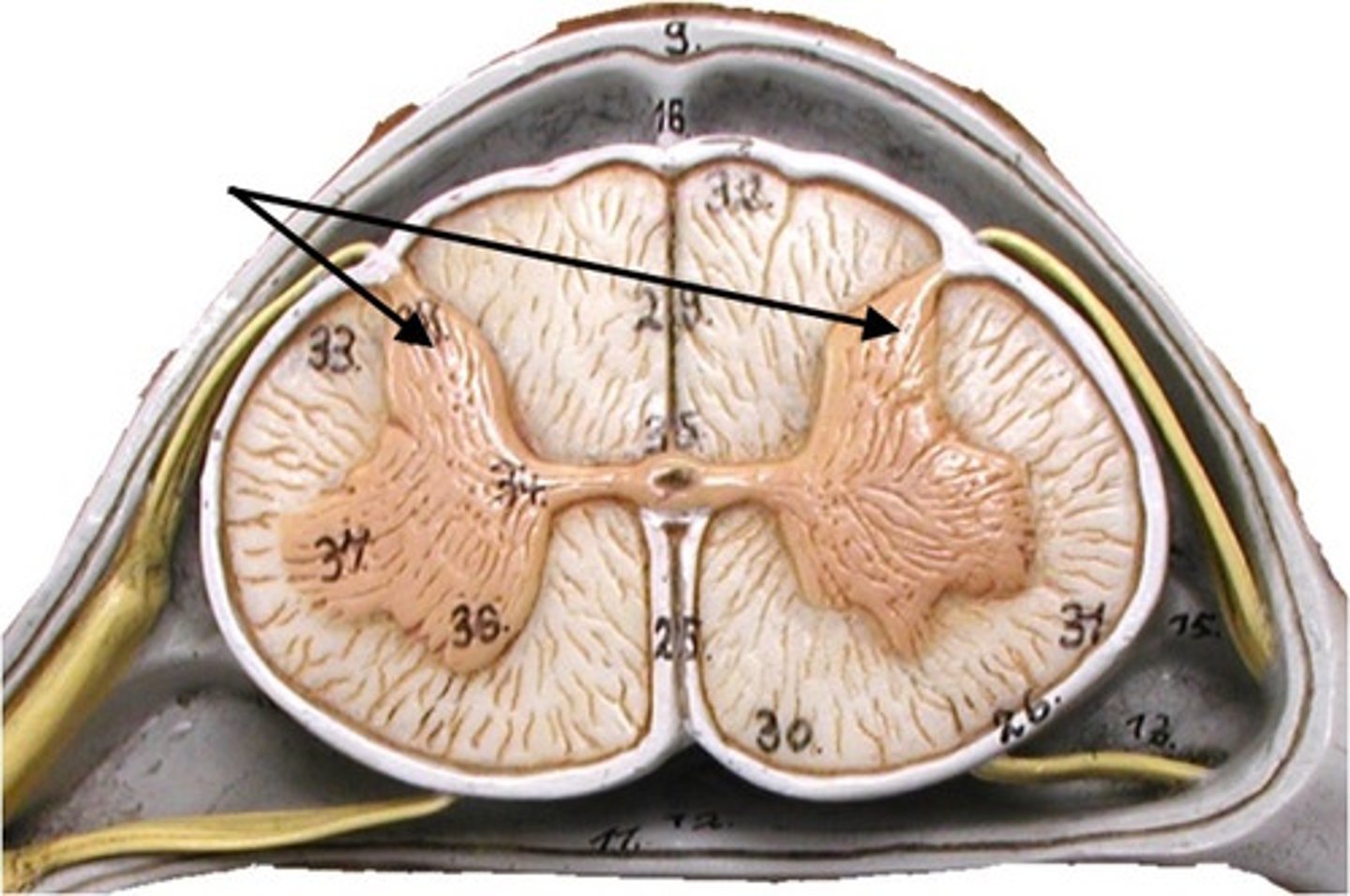
Gray Matter
A type of nervous tissue that is composed of neuron cell bodies, dendrites, and unmyelinated axons, along with synapses
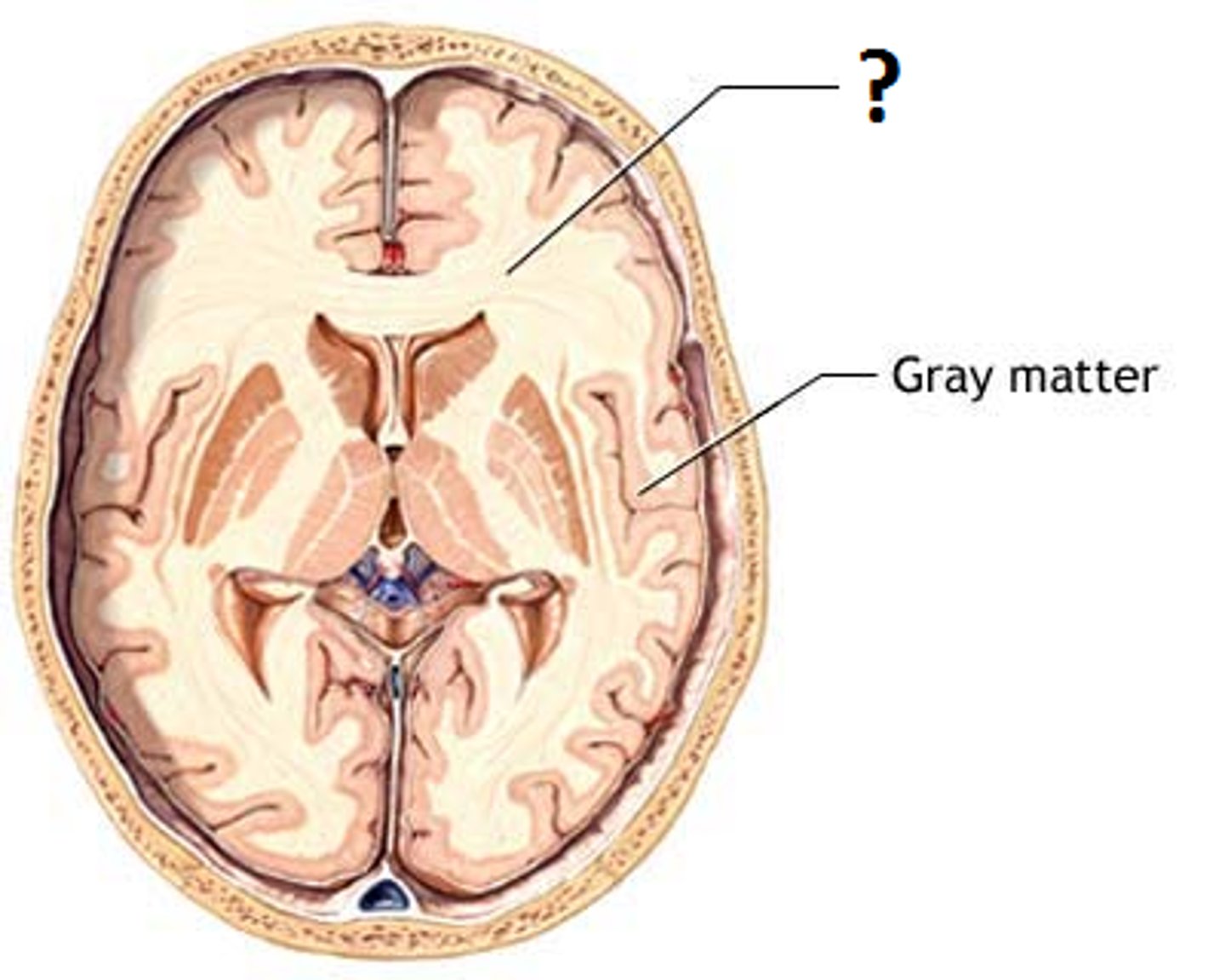
White Matter
A type of nervous tissue that is composed of myelinated nerve fibers (axons) that facilitate communication between different regions of the brain
Nerve Tracts
Longitudinal bundles of myelinated axons within funiculi, forming significant neural pathways in the central nervous system
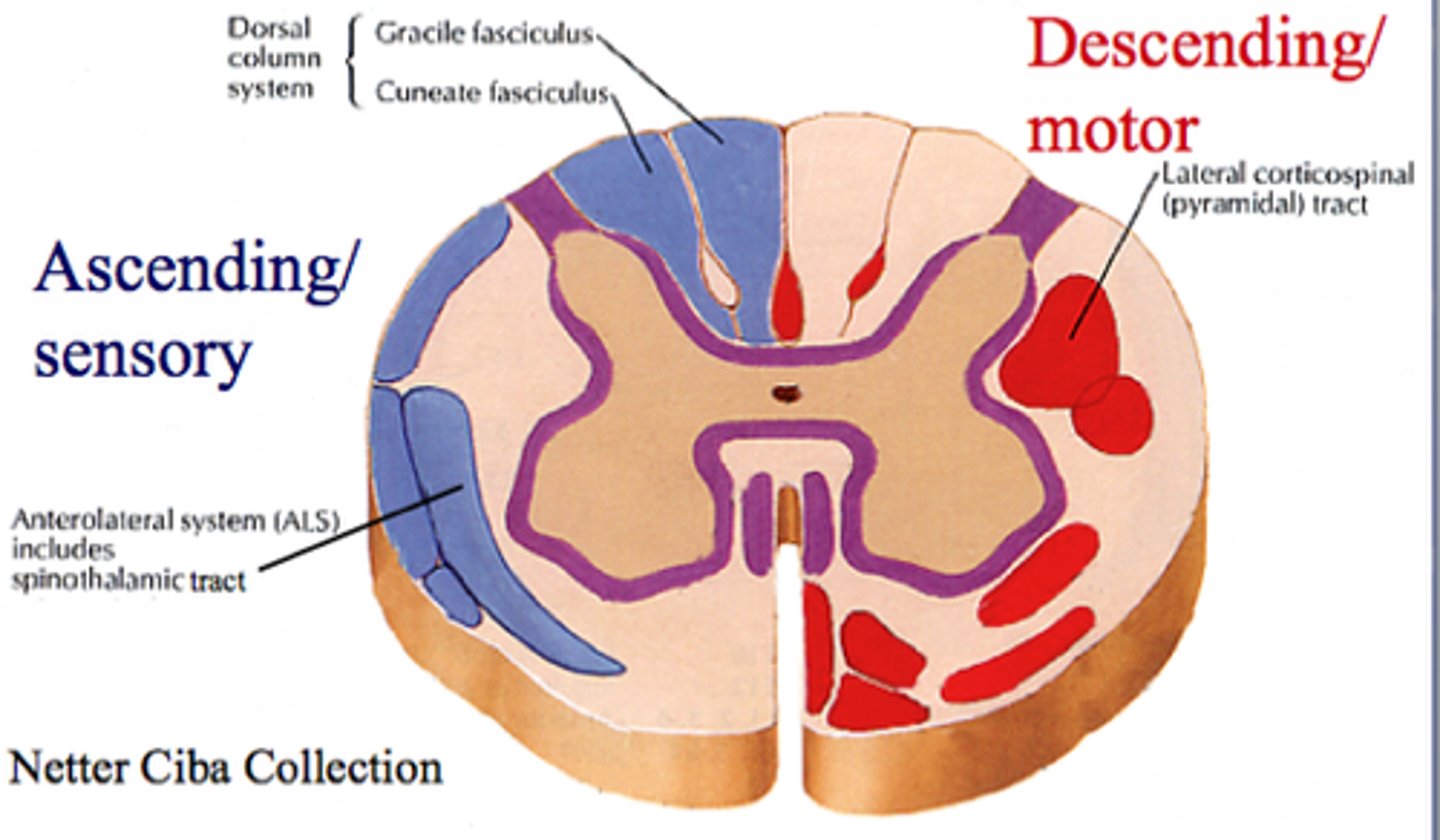
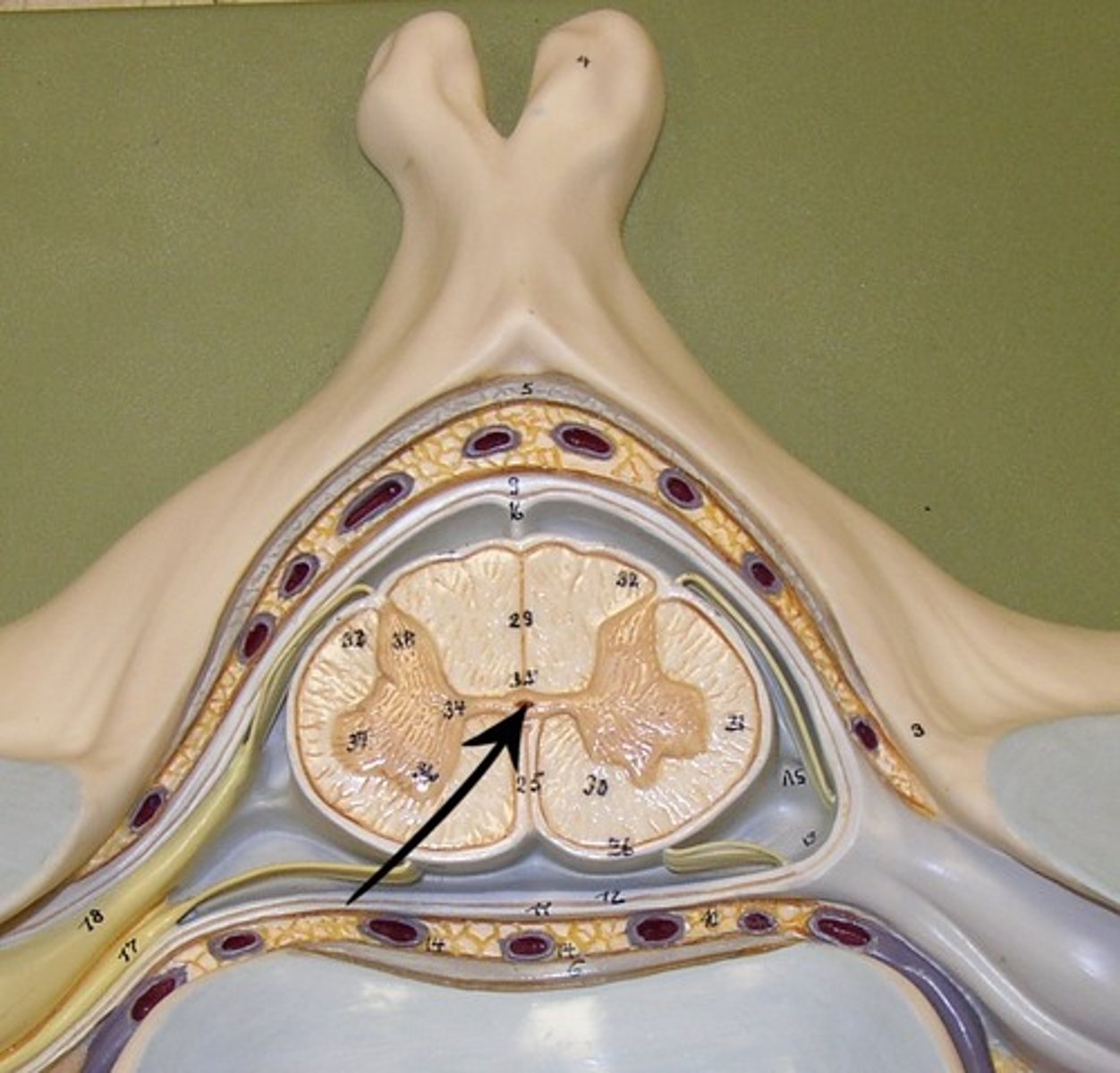
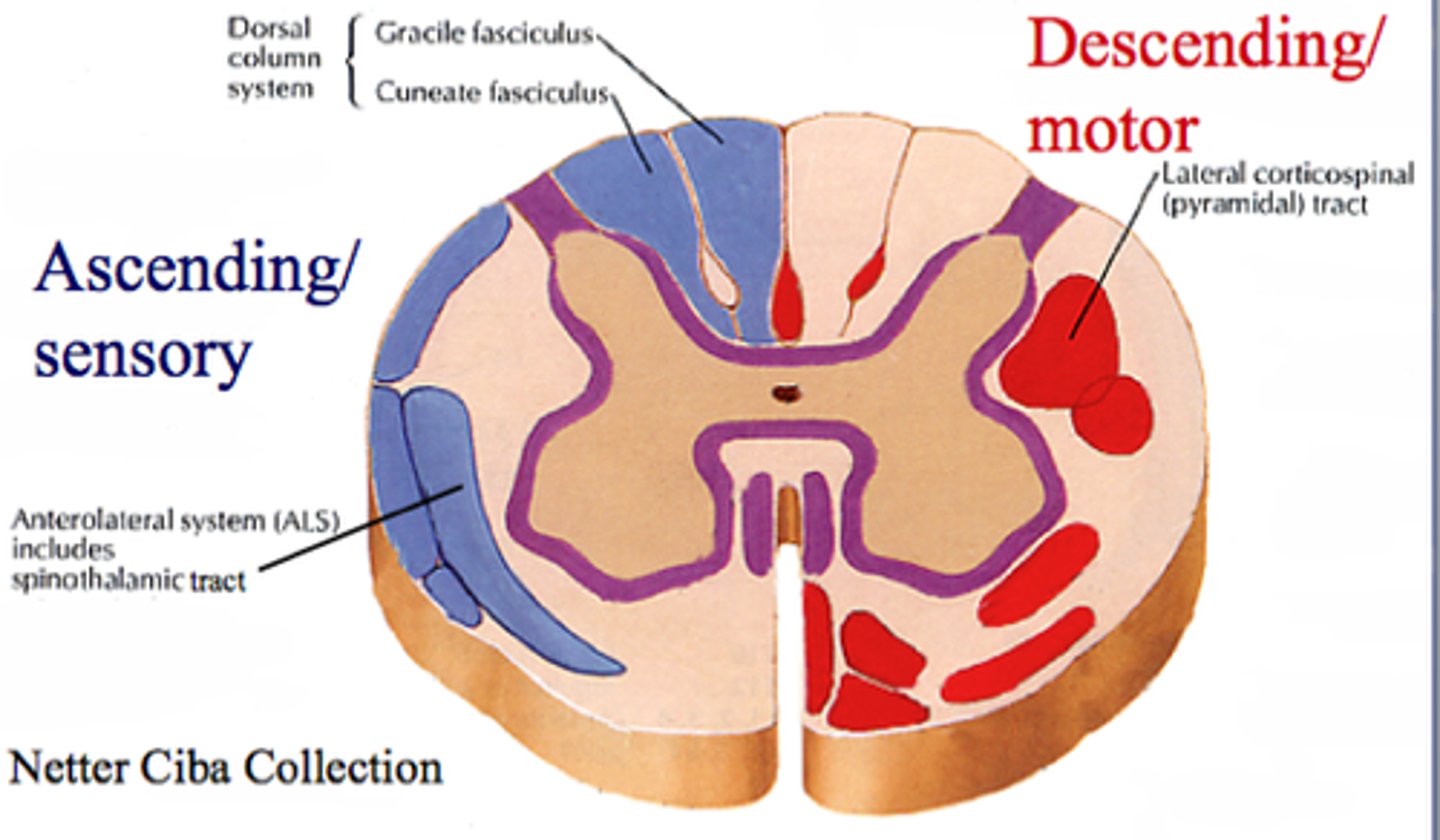
Central Canal
The tube in the spinal cord that contains cerebrospinal fluid
Ascending Tracts
Nerve tract that carries sensory information from the PNS to the CNS
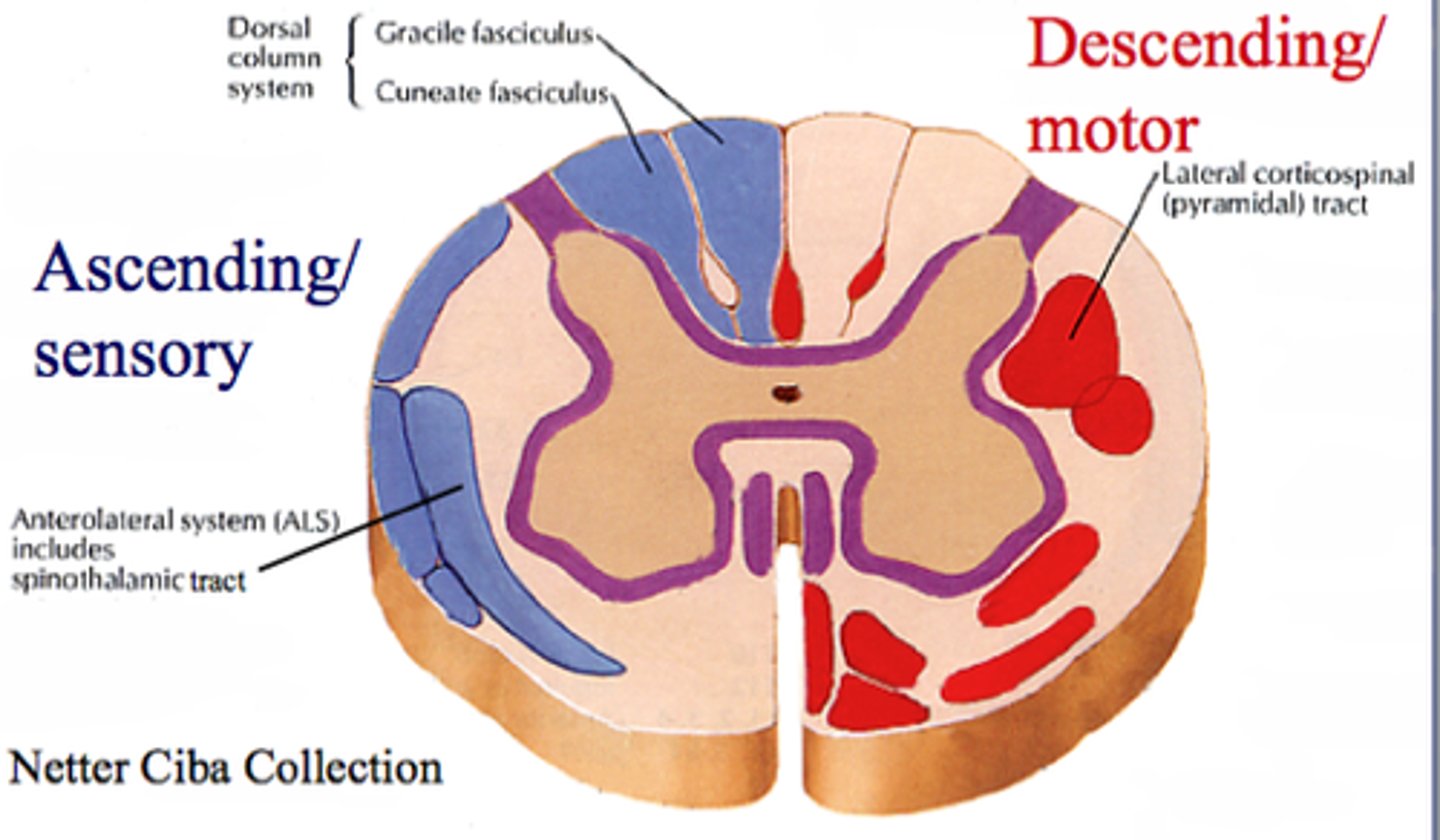
Descending Tracts
Nerve tract that conducts motor impulses from the CNS to the PNS
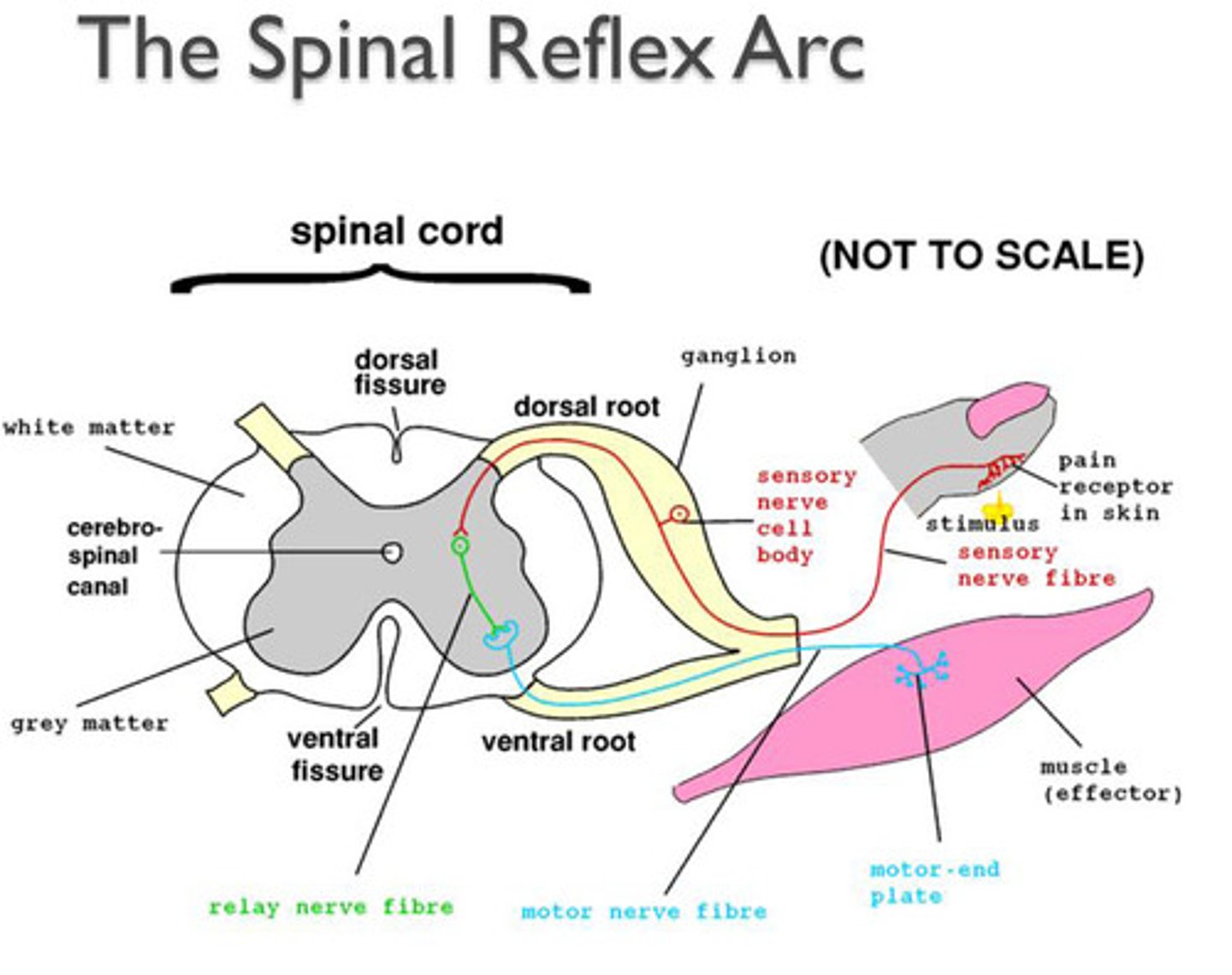
Spinal Reflex
Reflex arc that passes through the spinal cord; arcs from one neuron to another for a quick reaction without thinking
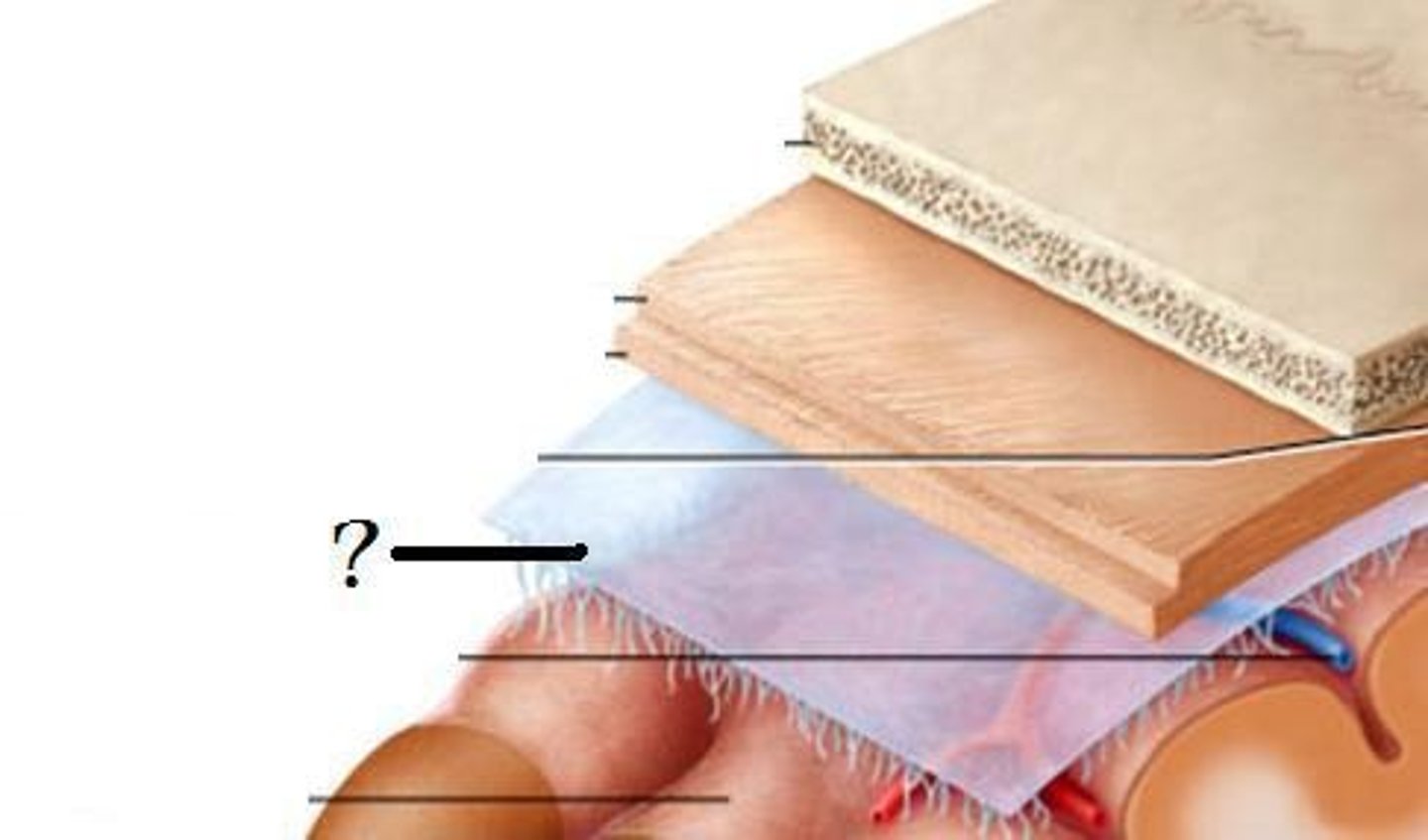
Meninges
Three layers of membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord; located between the bone and soft tissues of the nervous system; protects the brain and spinal cord
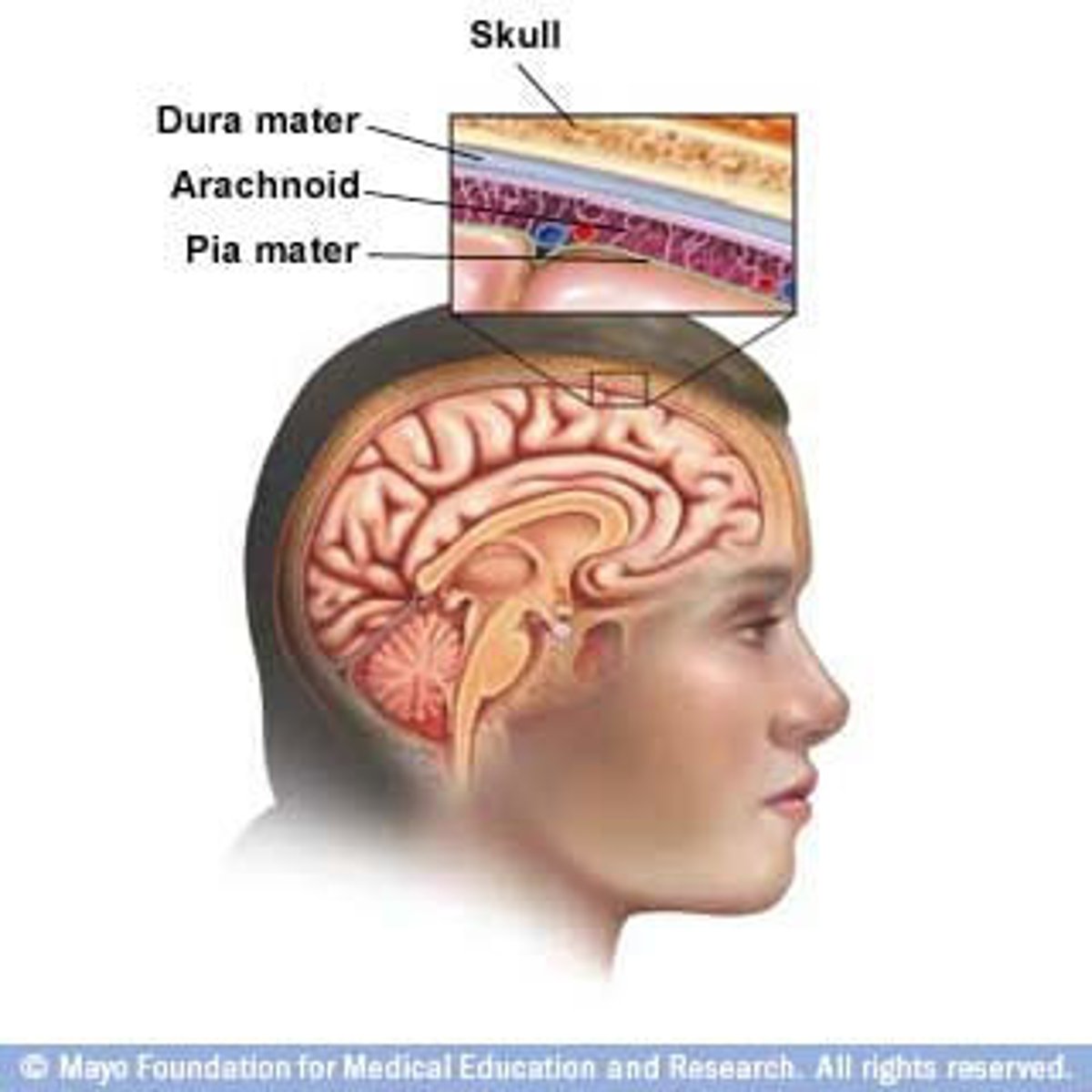
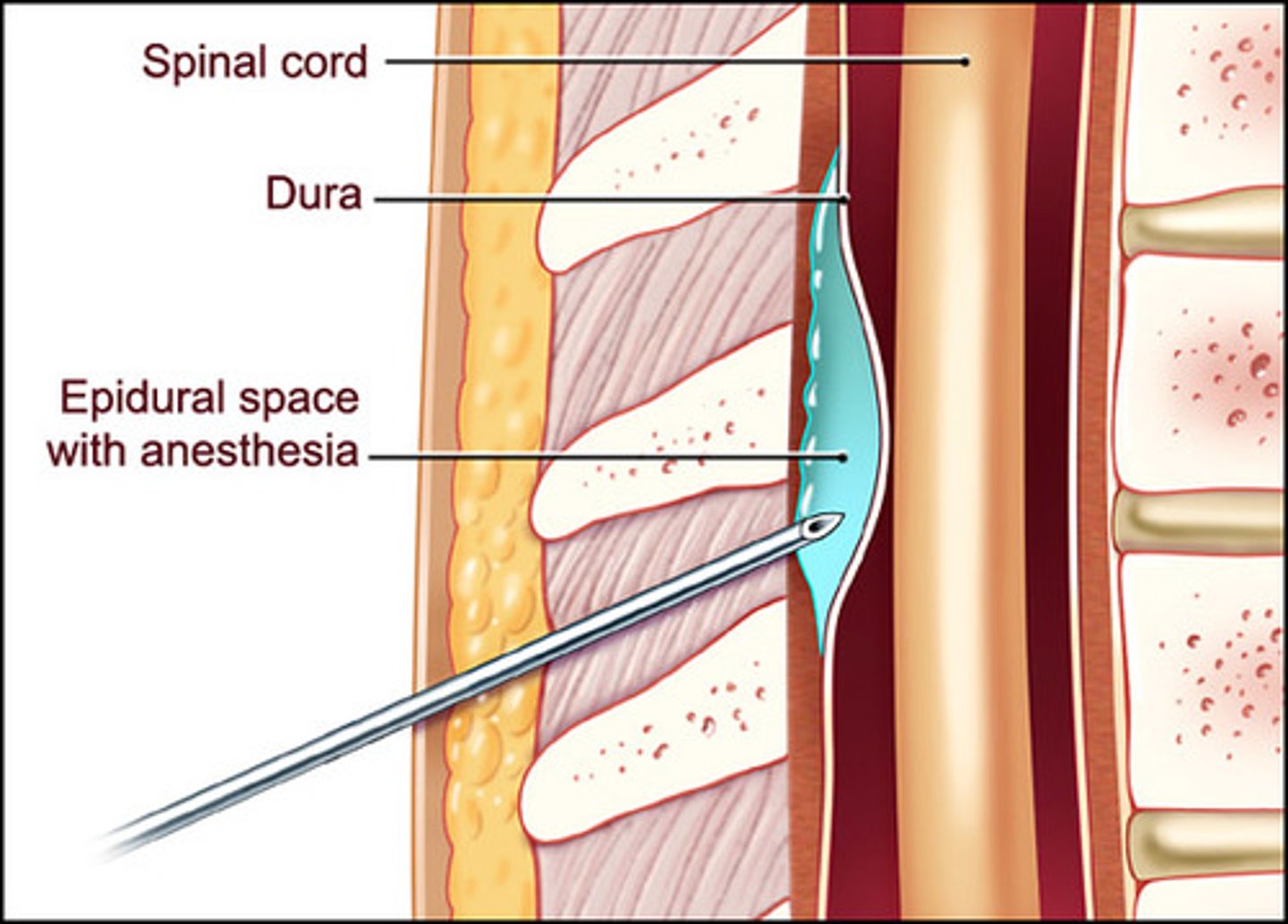
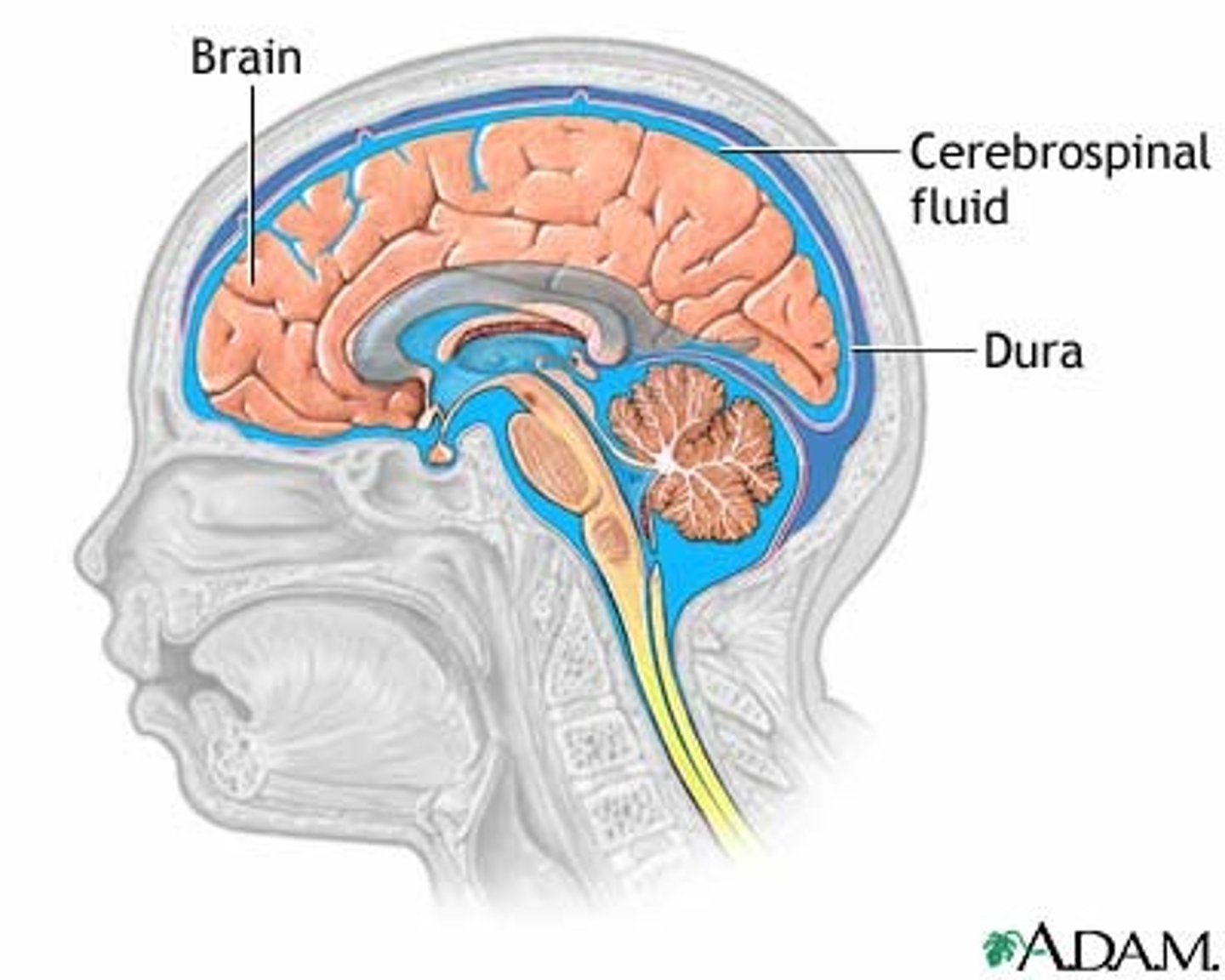
Dura mater
Outermost layer of the meninges and contains blood vessels and nerves; composed of tough connective tissue
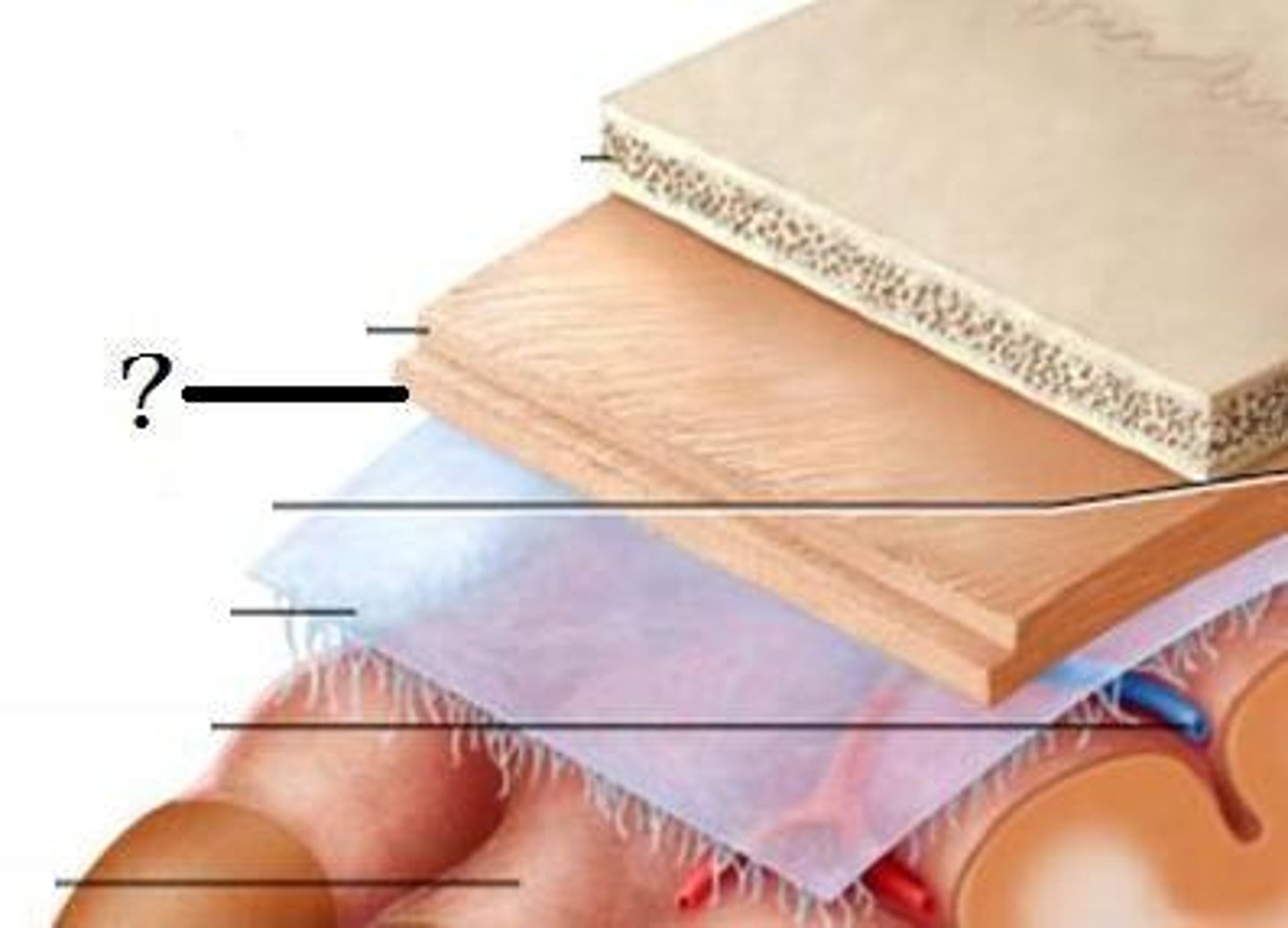
Epidural space
The space between the dural sheath and the bone of the vertebral canal; contains loose connective tissue and adipose tissue that provides a protective pad around the spinal cord
Arachnoid mater
Delicate, web-like middle layer of the meninges that lacks blood vessels
Cerebrospinal Fluid
Clear, watery fluid in the ventricles of the brain and central canal of the spinal cord that delivers nutrients to the CNS, provides protection, and removes waste
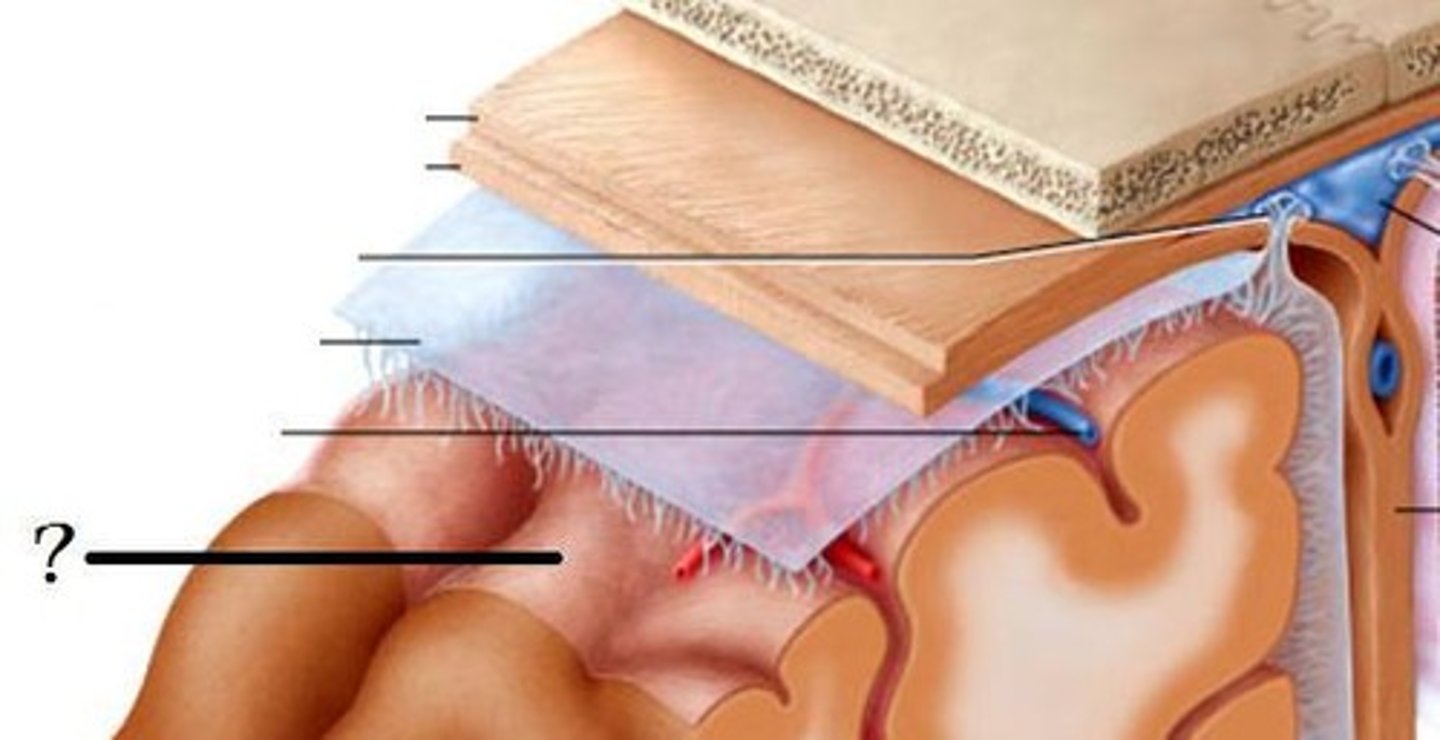
Pia mater
Innermost, thin layer of the meninges that is in direct contact with the brain and the spinal cord
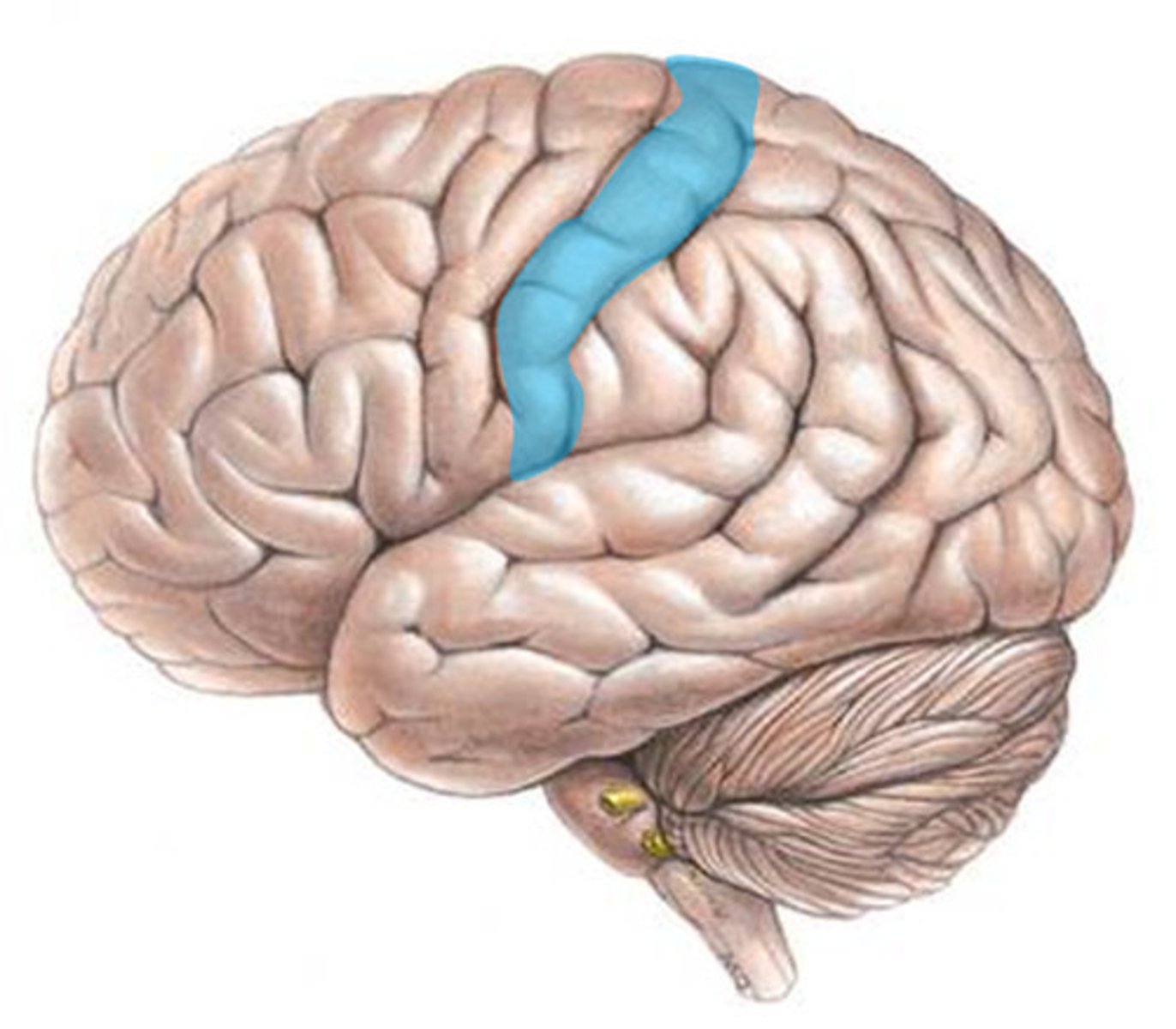
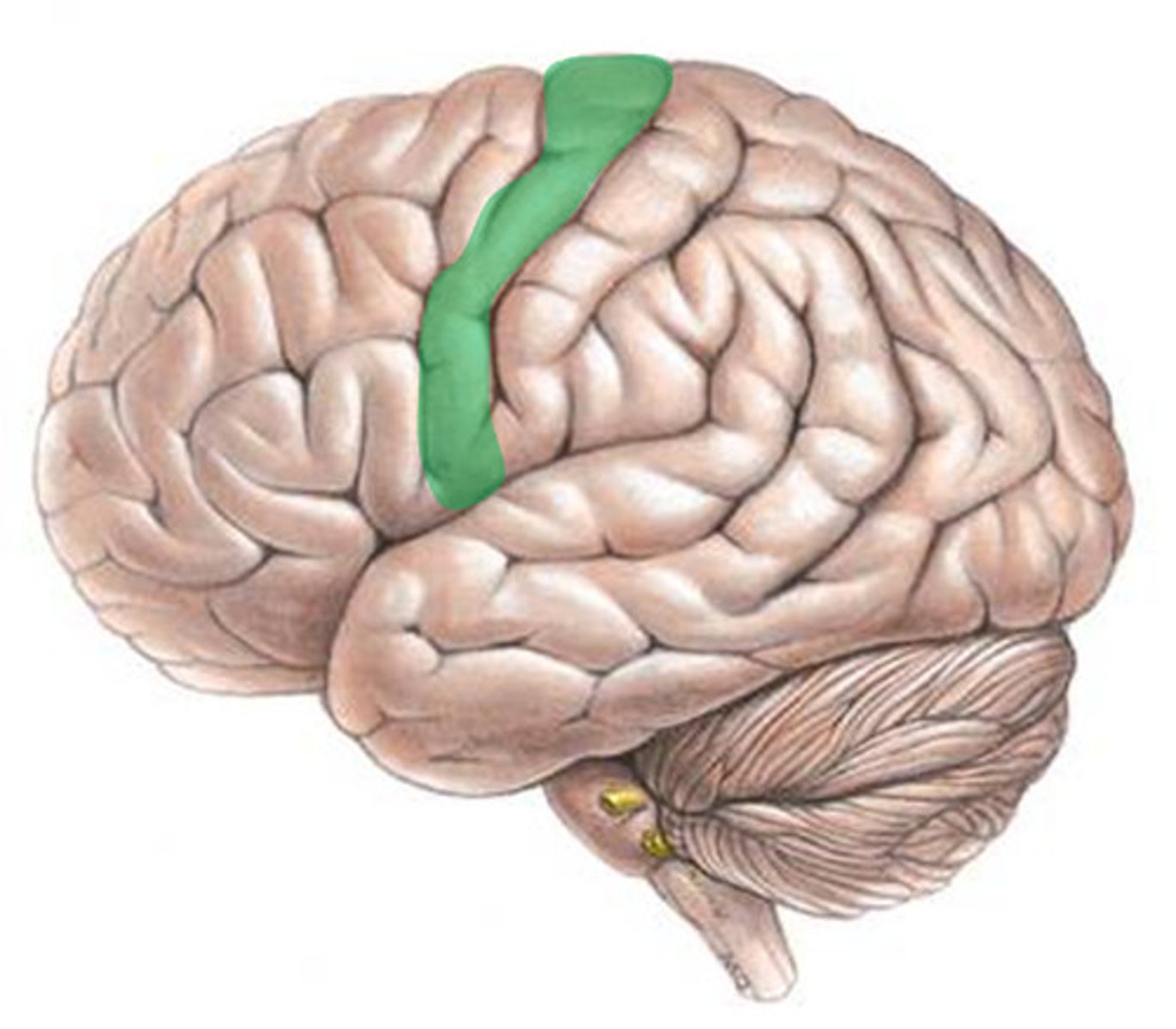
Motor Cortex
Area of the brain responsible for generating signals to direct the voluntary movement of the body
Limbic System
Connected structures in the brain that produce emotions; contains the thalamus, hypothalamus, amygdala, hippocampus, etc.
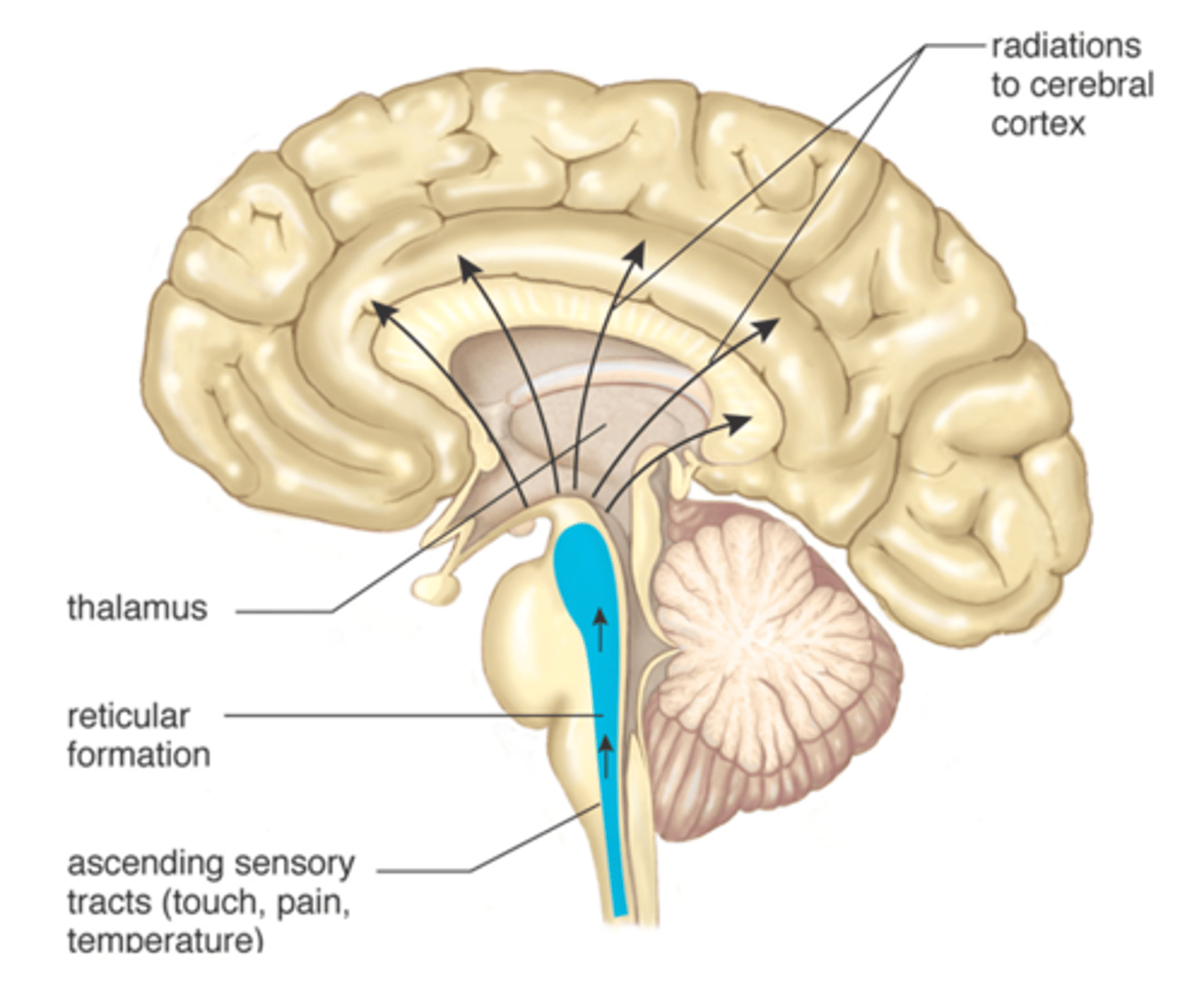
Reticular Formation
Complex network of nerve fibers in the brainstem that arouses the cerebrum to a wakeful state
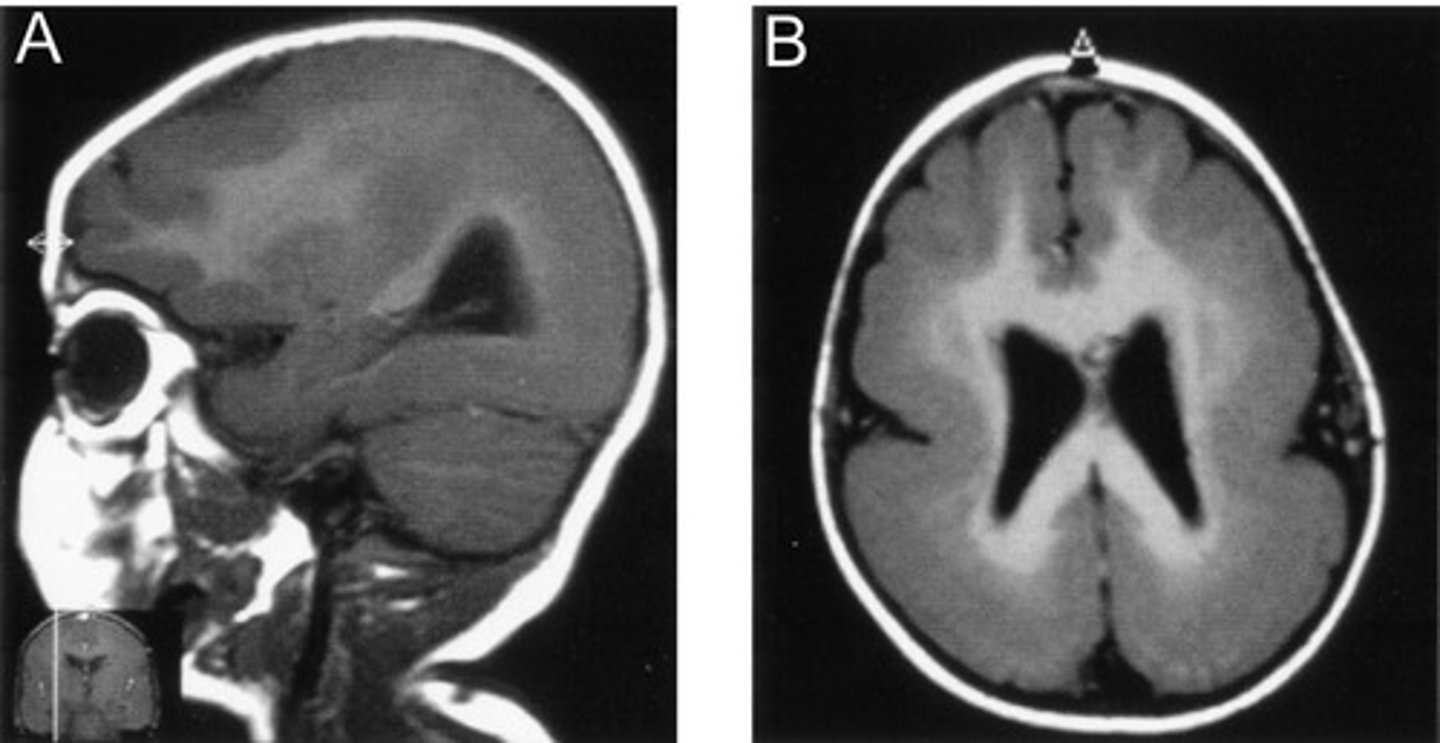
Lissencephaly
A rare brain malformation where the brain's surface lacks the normal ridges and grooves; also known as "smooth brain"
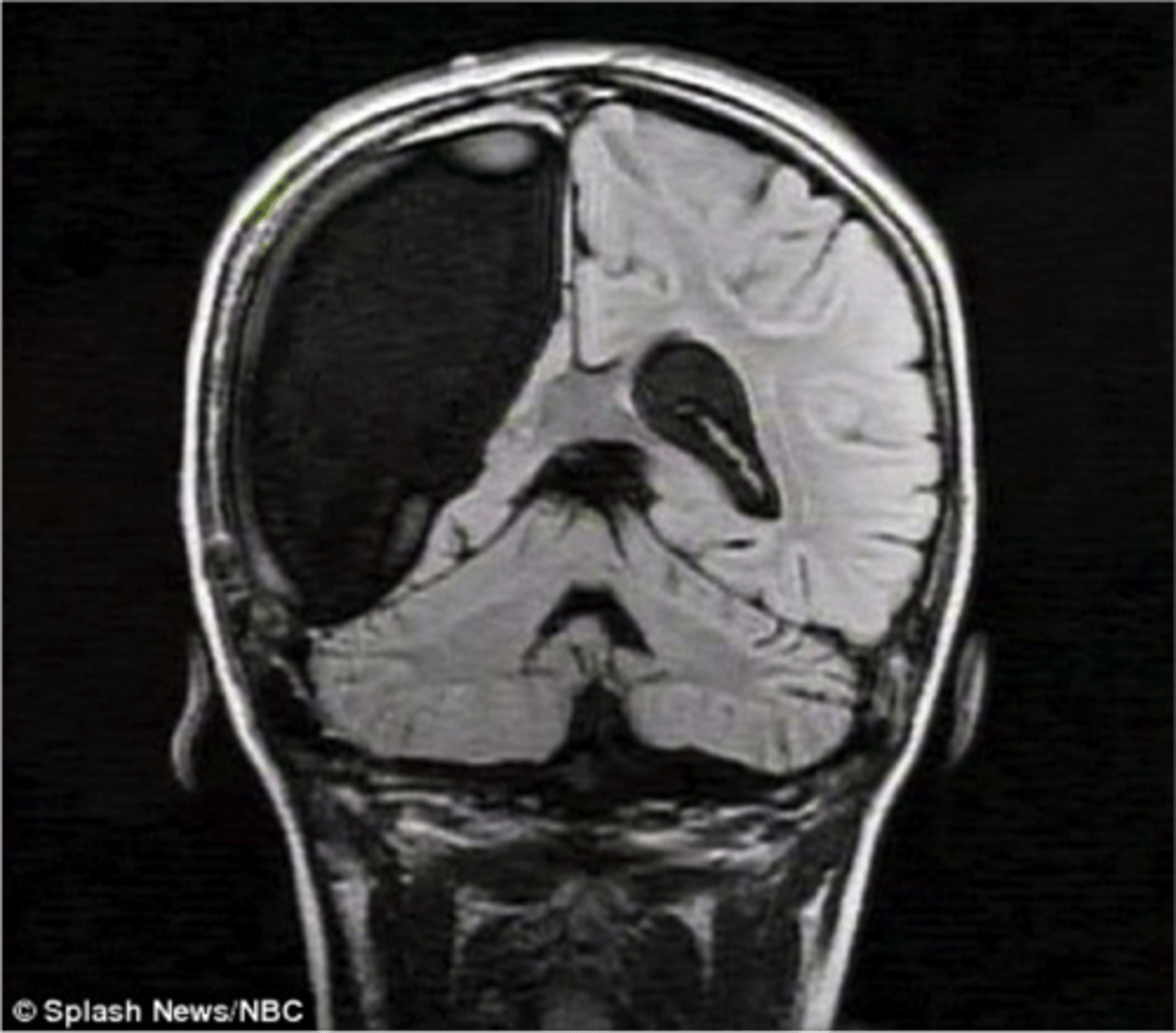
Hemispherectomy
A rare and complex surgical procedure where one hemisphere of the brain is either partially or completely removed
Spinal Cord
Slender column of nervous tissue extending downward from the brain into the vertebral canal
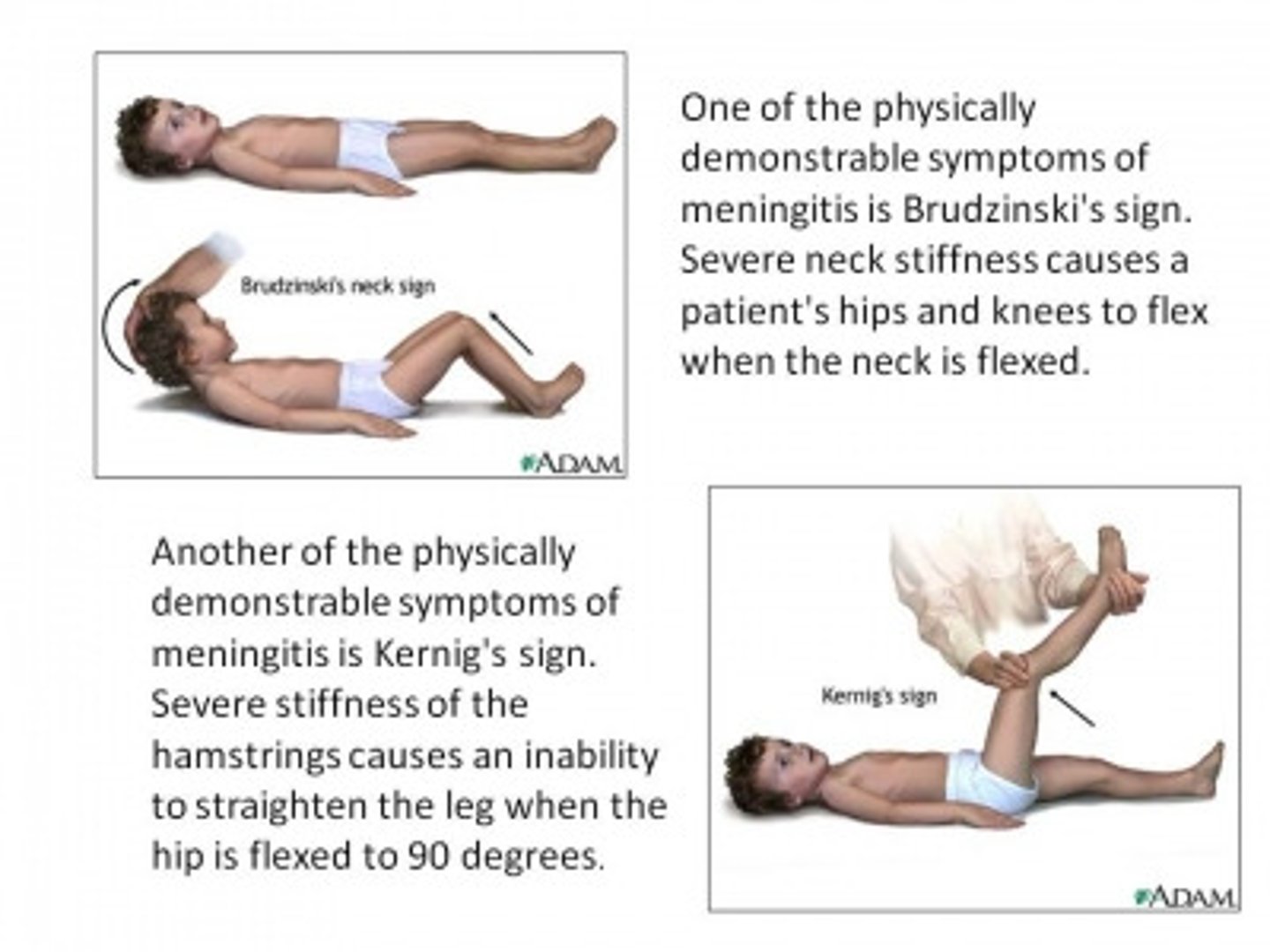
Meningitis
Inflammation of the meninges