7.4 What Are Intelligence & Creativity, Assessing Intelligence, Problems with Assessing Intelligence
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
General Intelligence (“g” factor)
British psychologist Charles Spearman believed intelligence consisted of one general factor, called g, which could be measured and compared among individuals.
Crystallized Intelligence
characterized as acquired knowledge and the ability to retrieve it. Helps you overcome concrete, straightforward problems.
Fluid Intelligence
encompasses the ability to see complex relationships and solve problems. Helps you tackle complex, abstract challenges in your daily life,
Triarchic Theory of Intelligence
intelligence as comprised of three parts (Sternberg, 1988): practical, creative, and analytical intelligence
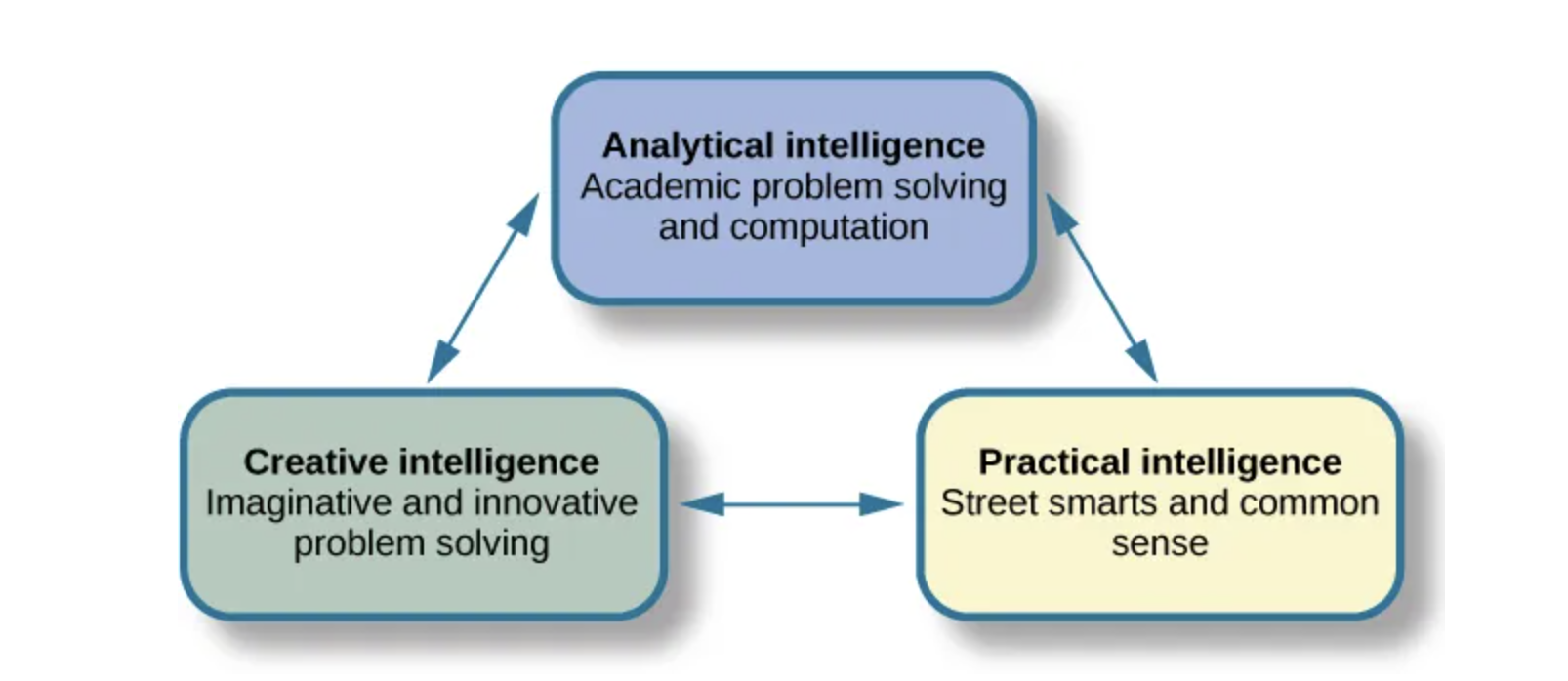
Practical Intelligence
Being practical means you find solutions that work in your everyday life by applying knowledge based on your experiences. This type of intelligence appears to be separate from traditional understanding of IQ; individuals who score high in practical intelligence may or may not have comparable scores in creative and analytical intelligence
Analytical Intelligence
closely aligned with academic problem solving and computations. Sternberg says that analytical intelligence is demonstrated by an ability to analyze, evaluate, judge, compare, and contrast.
Creative Intelligence
marked by inventing or imagining a solution to a problem or situation. Creativity in this realm can include finding a novel solution to an unexpected problem or producing a beautiful work of art or a well-developed short story.
Multiple Intelligences
developed by Howard Gardner, a Harvard psychologist and former student of Erik Erikson. In Gardner’s theory, each person possesses at least eight intelligences. The eight intelligences are linguistic intelligence, logical-mathematical intelligence, musical intelligence, bodily kinesthetic intelligence, spatial intelligence, interpersonal intelligence, intrapersonal intelligence, and naturalistic intelligence.
Emotional Intelligence
encompasses the ability to understand the emotions of yourself and others, show empathy, understand social relationships and cues, and regulate your own emotions and respond in culturally appropriate ways
Creativity
the ability to generate, create, or discover new ideas, solutions, and possibilities. Very
Divergent Thinking
can be described as thinking “outside the box;” it allows an individual to arrive at unique, multiple solutions to a given problem.
Convergent Thinking
describes the ability to provide a correct or well-established answer or solution to a problem
Achievement Tests
intended to reflect what you have learned,
Aptitude Tests
intended to predict your ability to learn a new skill.
Intelligence Quotient (IQ)
a person’s mental age divided by chronological age and multiplied by 100 to get rid of the decimal point.
defined originally as the ratio of mental age (ma) to chronological age (ca) multiplied by 100 (thus, IQ = ma/ca × 100). On contemporary intelligence tests, the average performance for a given age is assigned a score of 100.
Standardization
If you then take the test following the same procedures, your score will be meaningful when compared with others. This process is called standardization.
Stanford-Binet
the widely used American revision (by Terman at Stanford University) of Binet’s original intelligence test.
Wechsler-Adult Intelligence Scale (WAIS)
most widely used individual intelligence test.
Flynn Effect
Intelligence test performance has improved over time. This worldwide phenomenon is called the Flynn effect.
Normal Curve
If we construct a graph of test-takers’ scores, the scores typically form a bell-shaped pattern called the bell curve, or normal curve.
Validity
High reliability does not ensure a test’s validity—the extent to which the test actually measures or predicts what it promises.
Mental Age
a measure of intelligence test performance devised by Binet; the level of performance typically associated with children of a certain chronological age. Thus, a child who does as well as an average 8-year-old is said to have a mental age of 8.
Content Validity
Tests that tap the pertinent behavior, or criterion, have content
validity. The road test for a driver’s license has content validity
Construct Validity
the degree to which a test or instrument is capable of measuring a concept, trait, or other theoretical entity.
Threatened by: (a) mismatch between the construct and its operational definition, (b) various forms of bias, and (c) various experimenter effects and other participant reactions to aspects of the experimental situation.
Predictive Validity
the success with which a test predicts the behavior it is designed to predict; it is assessed by computing the correlation between test scores and the criterion behavior. (Also called criterion-related validity.)
Reliability
the extent to which a test yields consistent results, as assessed by the consistency of scores on two halves of the test, on alternative forms of the test, or on retesting.
Test-Retest Reliability
test with alternative forms of the test, or retest with the same test
Split-Half Reliability
To check a test’s reliability, researchers test people many times. They may split the test in half. Agreement of odd-question scores and even-question scores
Test-retest reliability
To check a test’s reliability, researchers test people many
times.
Stereotype Lift
When a positive stereotype aids the ability or worth of an outgroup, people may experience stereotype lift--a performance boost that occurs when downward comparisons are made with a denigrated outgroup.
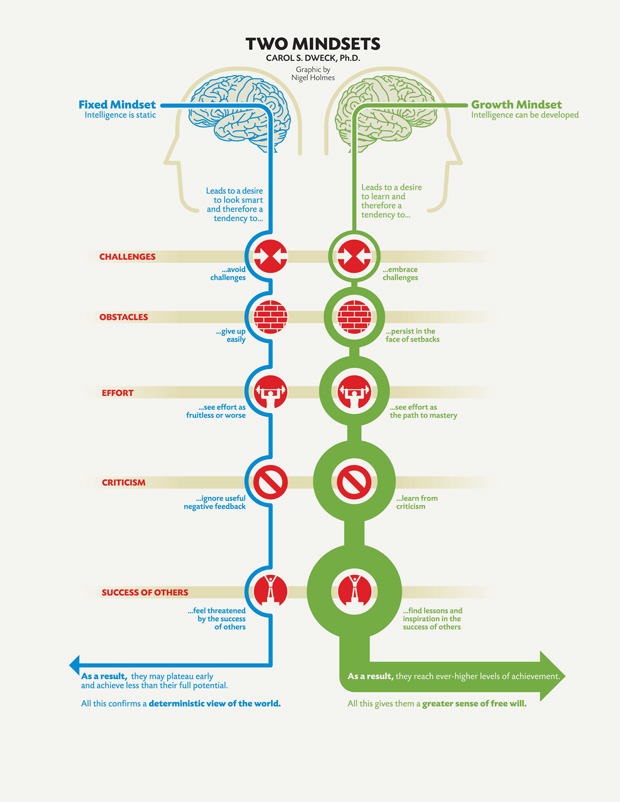
Fixed Mindset
If you believe that your qualities are unchangeable — the fixed mindset — you will want to prove yourself correct over and over rather than learning from your mistakes.
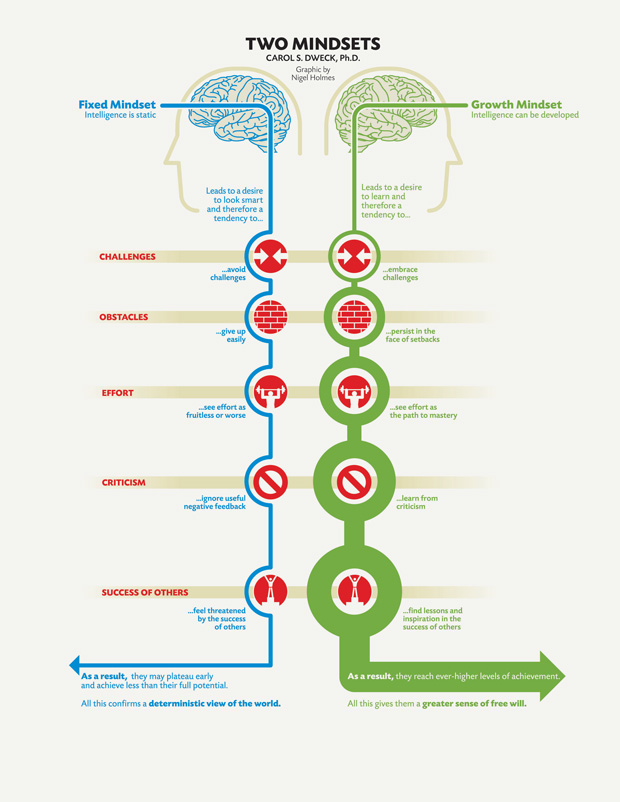
Growth Mindset
This growth mindset is based on the belief that your basic qualities are things you can cultivate through your efforts.