Development of the Cardiovascular System 1
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
trilaminar disc
from lateral plate mesoderm
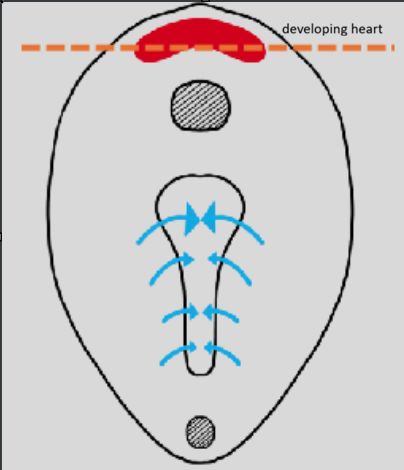
differentiation of mesoderm into cardiac tissue
mesoderm undergoes vasculogenesis:
angioblasts (endothelium of embryonic blood vessels)→ outer part
hemocytoblasts (elements of blood itself)→ inner part
endoderm secretes growth factor→ causes splanchnic division of lateral place mesoderm to diferentiate into cardiac tissue
form:
pericardial cavity
heart
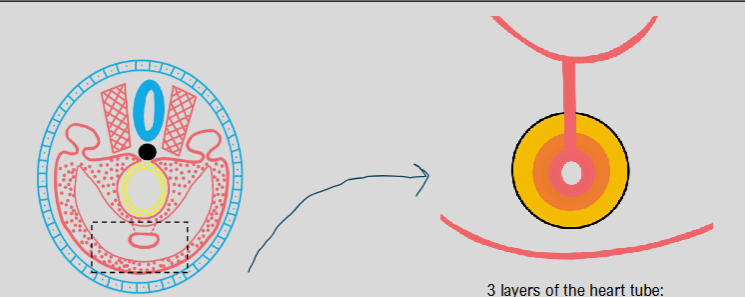
lateral folding
formation of single heart tube and single pericardial cavity
3 layers of heart tube:
endocardium
cardiac jelly
myocardium
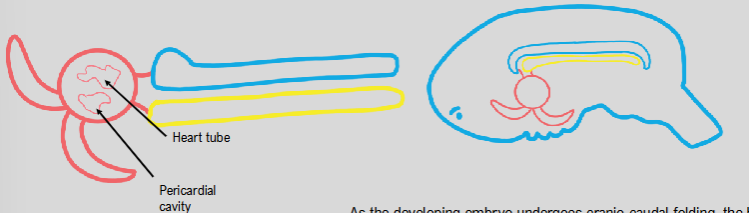
craniocaudal folding
heart moves from top of head to lie in the thoracic region
during this folding, heart tube is pulled inside pericardial cavity
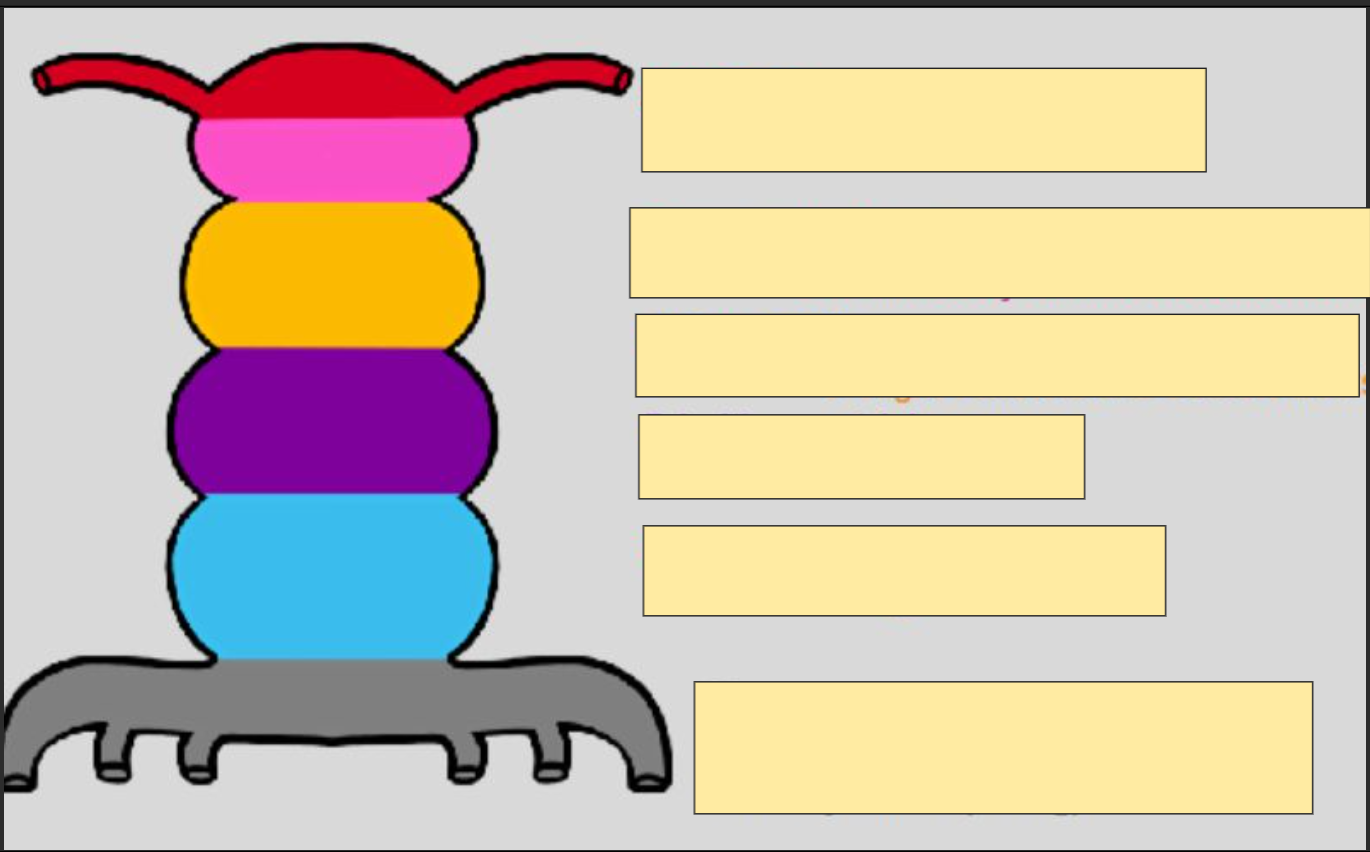
segments of the heart tube
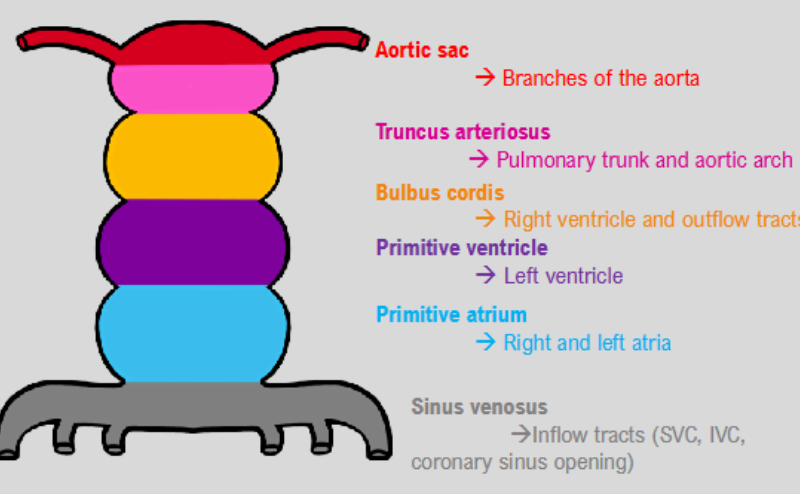
folding of heart tube
bulbous cordis begins to grow
insufficient space to grow→ moves down and to the right
displaced primitive ventricle→ moves to the left and up
as ventricle moves up, primitive atria dragged out of the way
primitive atria will displace to move to the top
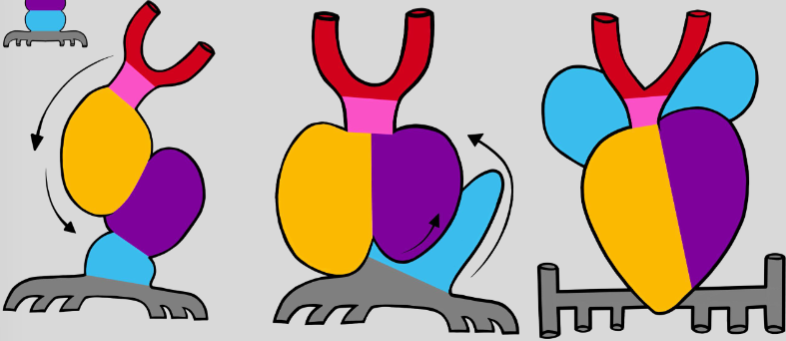
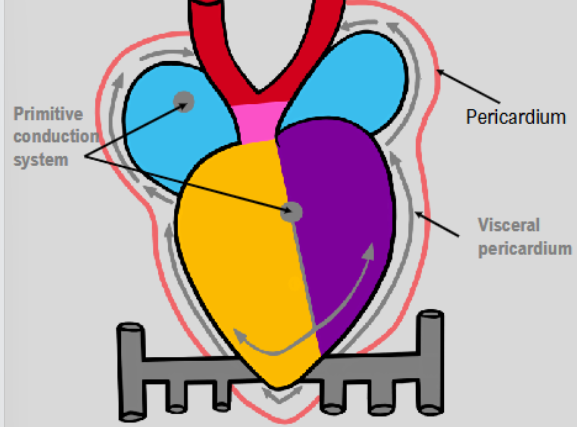
day 22→ differentiation of sinus venosus
some cells from sinus venosus move into pericardial cavity and begin to form visceral pericardium
other cells move into heart itself and begin to form primitive conduction system→ heart can now technically beat
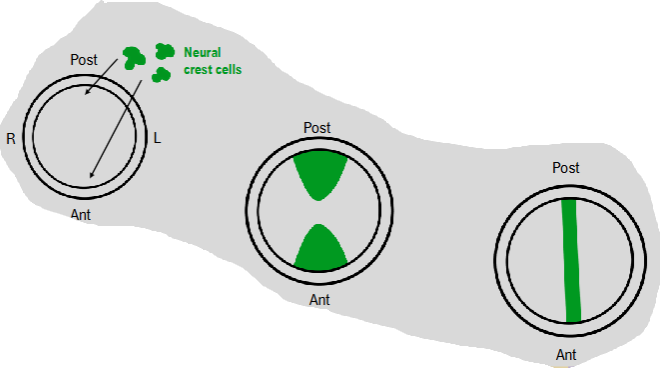
formation of atrioventricular canal
neural crest cells migrate into heart tube and begin to form endocardial cushions
eventually endocardial cushions unite to form septum intermedium
forms right AV canal and left AV canal
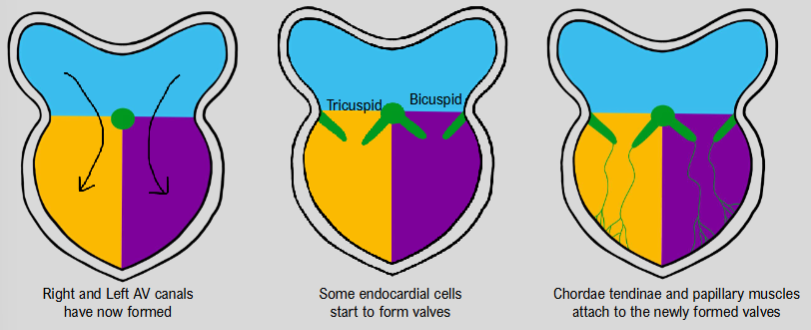
formation of valves
right and left AV canals have now formed
neural crest cells move in to form valves
chordae tendineae and papillary muscles attach to newly formed valves
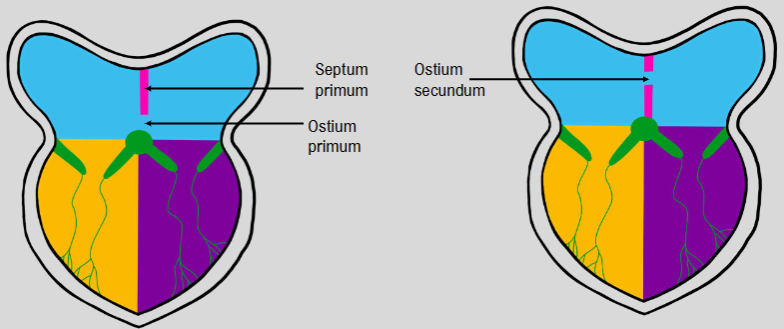
formation of separate atria
septum primum grows from the top to ostium primum
apoptosis happens to form ostium secundum→ forms a gap
septum secundum’ blocks ostium secundum→ still a small space (foramen ovale) for blood to travel through
when baby is born, gap closes leaving fossa ovalis
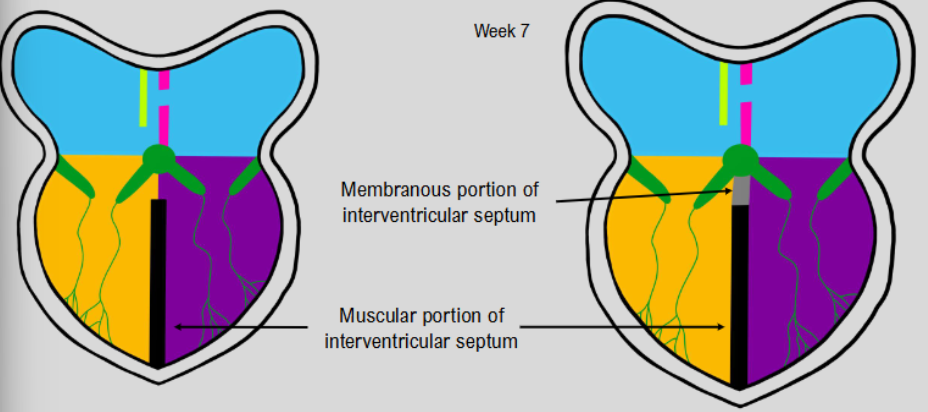
formation of separate ventricles
muscular portion of interventricular septum
as is reaches septum intermedium, membrane forms and fuses to muscular portion
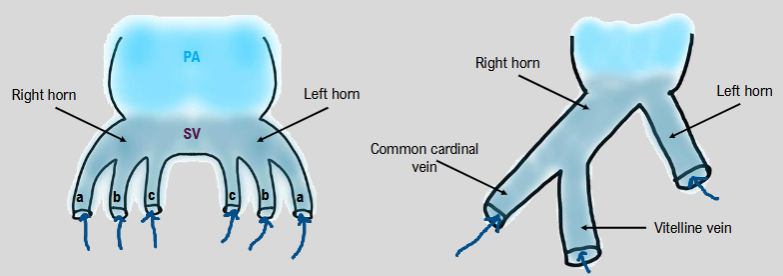
development of inflow tracts
sinous venousus divides into left and right horns, each having
a. common cardinal vein
b. umbilical vein
c. vitelline vein
all 3 of the veins feeding into the left form break down, leaving just the horn
right umbilical vein also breaks down
formation of vena cava
left horn shifts to right and is absorbed into right horn
sinus venosus is then absorbed into primitive atria:
right common cardinal vein forms SVC
left horn becomes coronary sinus
right vitelline vein becomes IVC
whilst right horn is absorbed into right atrium, outgrowth from left atrium forms single pulmonary vein
further branches into 4 veins
week 5→ pulmonary veins incorporated into left atrial wall→ intussusception
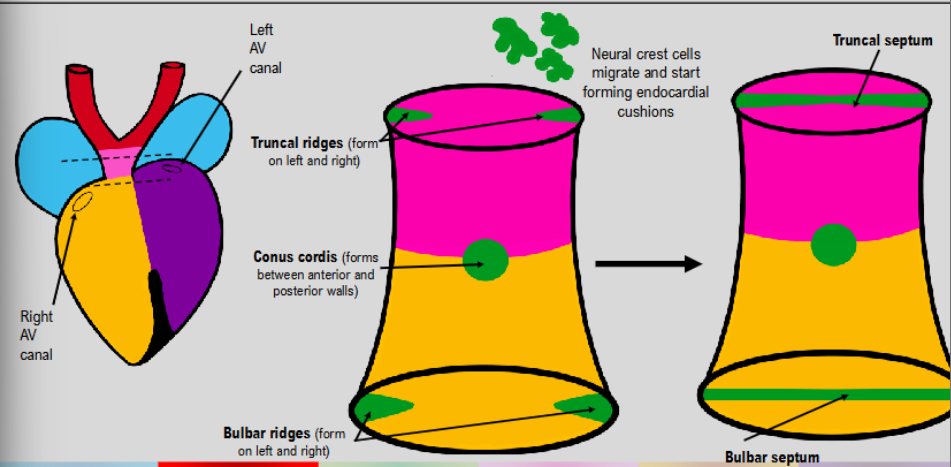
formation of outflow tracts
neural crest cells form truncal ridges in truncus arteriosus and bulbar ridges in bulbous cordis→ left and right
bulbar ridges from bulbar septum
as ridges converge to form septa→ structures twist around its central axis
creates corkscrew formation for blood leaving ventricles to navigate
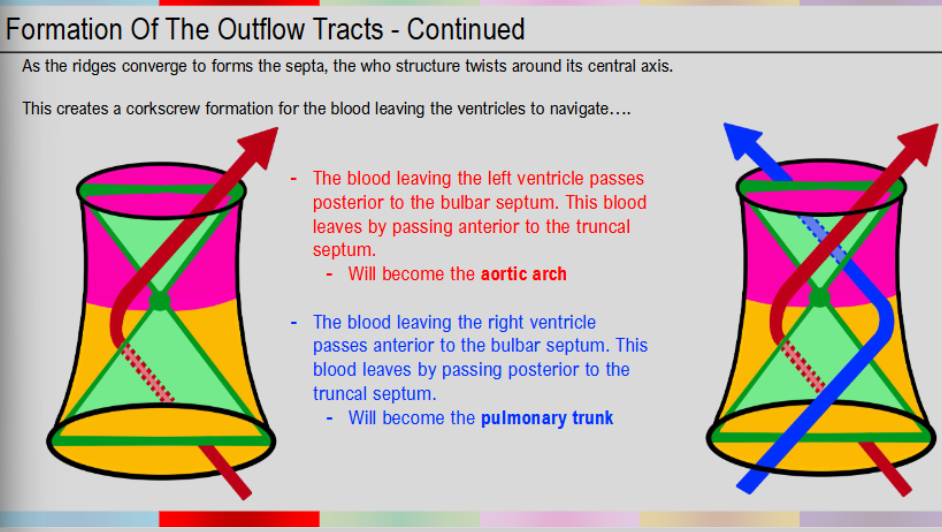
navigation of blood leaving the ventricles
blood leaving left ventricle passes posterior to bulbar septum
blood leaves by passing anterior to truncal septum
will become aortic arch
blood leaving right ventricle passes anterior to bulbar septum
leaves by passing posterior to truncal septum
will become pulmonary trunk
rotation of outflow tracts
once septa have formed further rotation takes place
separates structure into aortic arch and pulmonary trunk
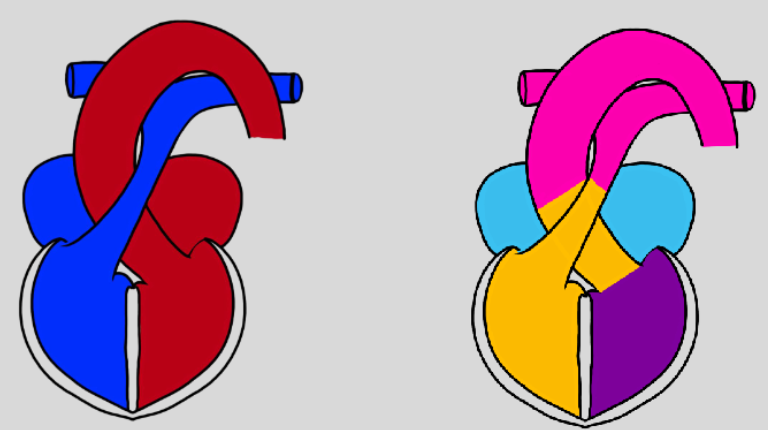
foetal circulation
oxygenated blood enters through umbilical vein
some blood enter foetus’ liver, rest enters ductus venosus→ lets blood bypass liver and enter IVC
IVC drains blood to right atrium
due to foramen ovale, blood passes from right to left atrium, bypassing right ventricle
blood moves into left ventricle and exits heart via aorta
any blood that passes into right ventricle passes through ductus arteriosus as it exits heart→ not necessary for blood to travel to lungs in the foetus
circulation after birth
umbilical circulation no longer necessary
ductus venosus and closes and becomes ligamentun venosum
once newborn takes its first breath, pulmonary arteries dilate and alter pressure in the atria
this causes increased pressure in left atrium→ forces septum primum to push against more stable septum secundum
foramen ovale is now closed→ seen as fossa ovalis in adults
blood flows into right ventricle and exits via pulmonary arteries
first breath alters oxygen saturation in ductus arteriosus→ constructs and forms ligamentum arteriosum
means blood will travel to lungs