3. The Eye
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Energy can be described using ________.
Wavelength (measured in nm)
The visible spectrum for humans ranges from _______ nm,
400 - 700 nm
Light enters through the _____ and is focused the _____ and _____ to a sharp image on the _____.
Pupil, cornea and lens, retina
What are the 2 visual receptors that contain visual pigment?
Rods and Cones
What nerve carries information from the retina to the brain?
Optic Nerve
The eye had ~120 million ______ and ~6 million ______.
Rods, Cones.
The _______ consists entirely of cones, which are key for high acuity vision and colour.
Fovea
The _______ mostly consists of rods, which are key for vision in low light environments.
Peripheral Retina
Macular Degeneration
The fovea and small surrounding area are destroyed (particular implications for high acuity vision). This creates a dead zone on the retina.
Retinitis Pigmentosa
Rods are destroyed first (particular implications for night vision). Foveal cones can also be attacked. Severe cases can lead to complete blindnessl
The Blind Spot
The location where the optic nerve exits the eye; this area contains no receptors.
The Blind Spot - How is Top-Down Processing Involved?
The brain fills in missing information by extrapolating what’s around it (via top-down processing).
Myopia (Nearsightedness)
The inability to see distant objects clearly.
Occurs when the image gets focused in front of the retina. This can be caused by:
Refractive Myopia: Cornea or lens bends too much light.
Axial Myopia: Eyeball is too long.
Hyperopia (Farsightedness)
The inability to see nearby objects clearly.
Occurs when the image gets fo used behind the retina.
Typically caused by an eyeball that is too short.
Presbyopia (Old Eye)
Occurs when the lens can not longer adjust for close objects.
Caused by the hardening of the lens and weakening biliary muscles.
The outer segment of receptors contain ______ ______ molecules.
Visual Pigment
Visual Pigment Molecules Consist of 2 Components:
Retinal: Light sensitive molecules
Opsin: A large protein
Visual Transduction
Occurs when the retinal absorbs one photon, causing it to change shape (a process referred to as isomerization).
A Chain Reaction
Occurs when a visual pigment absorbs a single photon of light.
Each visual pigment molecule activates hundreds more molecules, which each activate ~ 1000 more molecules.
This creates a cascade effect, which eventually results in the activation of the receptor.
Dark Adaptation
The process of increasing visual sensitivity after switching from high to low lighting conditions.
Process needed for Transduction
Retinal molecule changes shape
Opsin molecule separates
The retina shows visual pigment bleaching
Retinal and opsin must then recombination in a process called regeneration, in order to be capable of responding to light again.
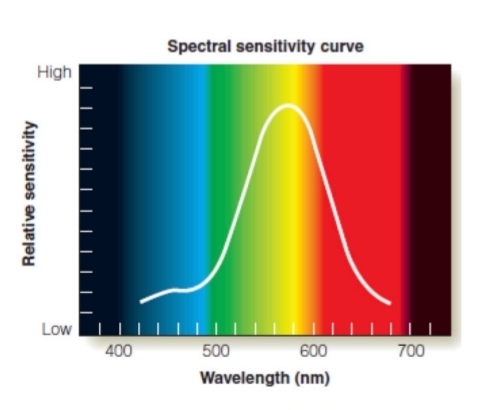
Spectral Sensitivity
Refers to the sensitivity of rods and cones to different parts of the visible spectrum.
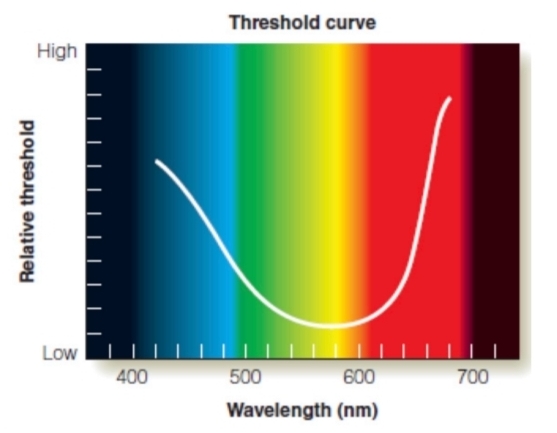
Threshold vs Sensitivity
Threshold and Sensitivity mean similar things, but are essentially reciprocal concepts.
1/Threshold = Sensitivity
Spectral Sensitivity
A spectral sensitivity curve is shown in the upper right.
Threshold Curve
Humans are most sensitive to what portion of the visible light spectrum?
The central range (greenish/yellow light); this corresponds to the spectrum that they have the lowest threshold for.
Rods are more sensitive to _____-wavelength light (_____ nm)
Short-wavelength light, (500 nm)
Cones are more sensitive to _____ nm (on average).
560 nm
Purkinje Shift
Enhanced sensitivity to short wavelengths during dark adaptation when the shift from cone to rod vision occurs..
Rods and cones send signals vertically through 2 types of cells:
Bipolar Cells
Ganglion Cells
Rods and cones send signals horizontally:
Between receptors by horizontal cells
Between bipolar and between ganglion cells by amacrine
Rods (as compared to cones) are:
More sensitive to light
Requires less light to respond
Have greater convergence
This greater convergence = summation of the inputs of many rods into ganglion cells, increasing the likelihood of a response.
Less convergence of cones = ?
Better Acuity
All cone foveal vision results in high visual acuity. This relates to:
The difference in convergence, in which fewer cones are connected to any one ganglion cell (i.e. have less convergence).