Full Anatomage Week 2 pa 534
1/206
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
207 Terms
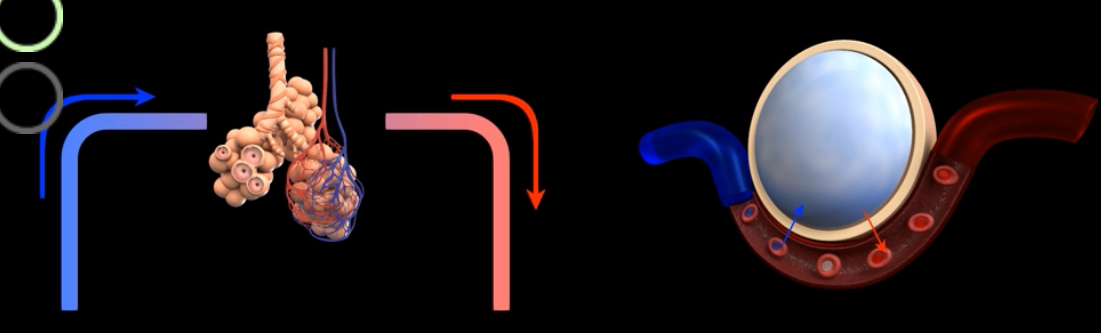
What is this?
External respiration or alveolar gas exchange- exchange of gases between alveoli and blood
What this this?
Gas transport- movement of respiratory gases between alveoli and systemic cells of the body
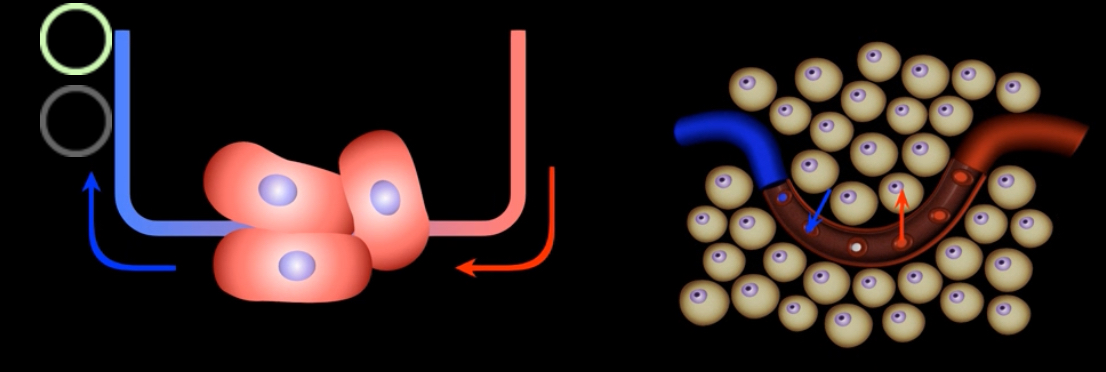
What this this?
Internal respiration/ systemic gas exchange- exchange of gases between blood and the cells of the body
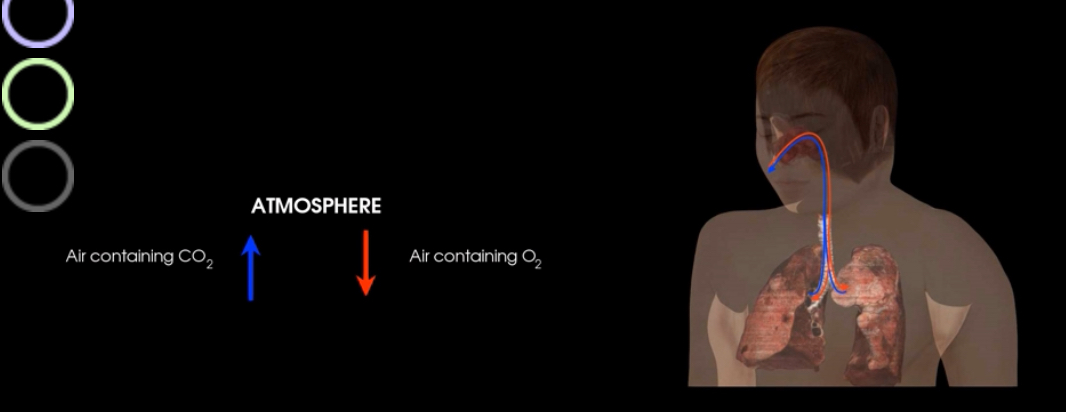
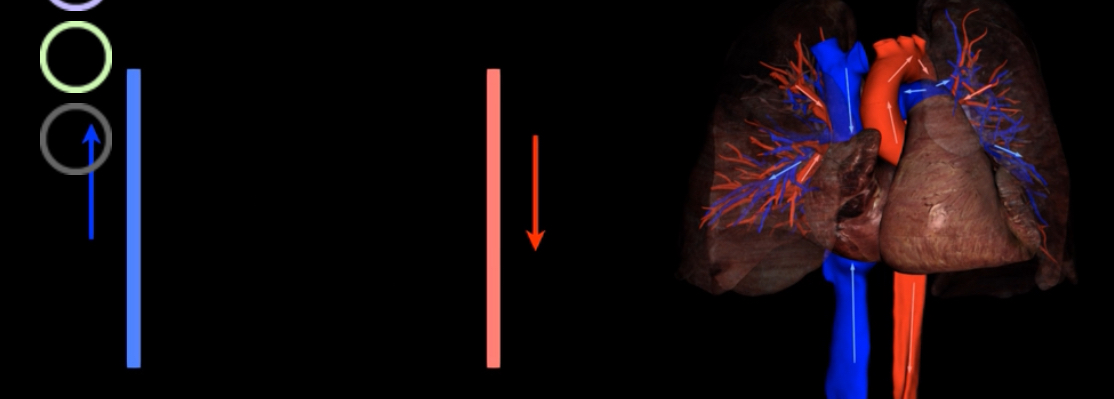
What is this?
Pulmonary ventilation (breathing)- movement of air (gases)between the atmosphere and alveoli of lungs
What are the steps in ventilation?
During pulmonary ventilation oxygen rich air is inhaled into alveoli
Oxygen diffuses from alveoli into blood of the pulmonary capillaries during external respiration
Systemic arrives transport oxygen from lungs to the tissue
Oxygen diffuses from the below into the systemic cells
CO2 diffuses out of the systemic cells and into the blood
Systemic veins transports CO2 for tissues back to lungs
CO2 diffuses out of blood and into alveoli during external respiration
Air containing CO2 is exhaled during expiratory phase of pulmonary ventilation
What are the actions of inspiration and expiration?
Actions of skeletal muscles of respiration
Changes in volume of thoracic cavity and lungs
Changes in pressure of air within the lungs
Pressure gradients between regions
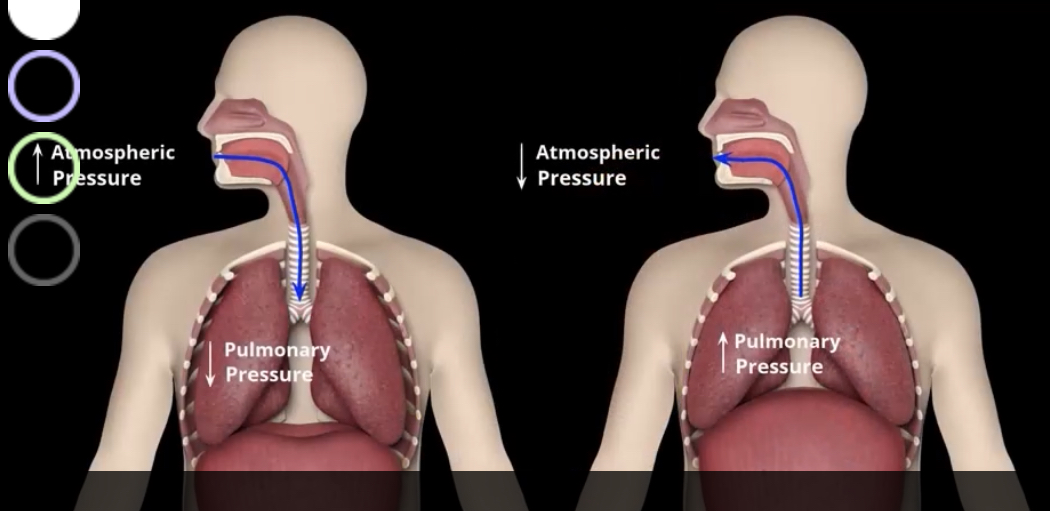
How is inspiration and expiration driven?
By the pressure differences between atmosphere and lungs
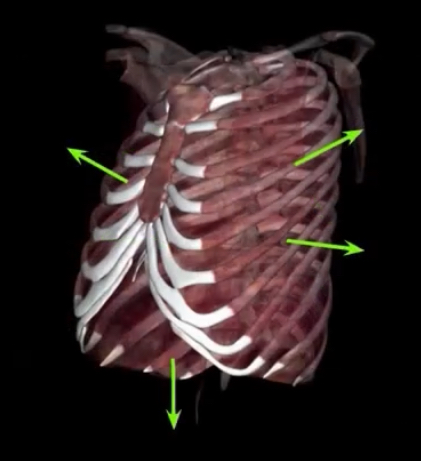
What is occurring?
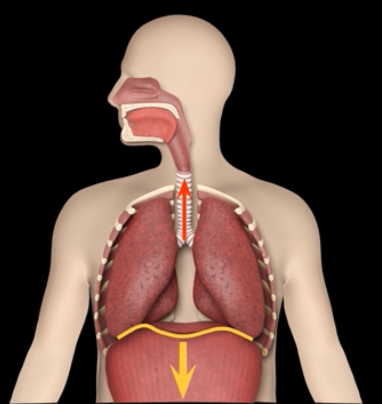
Inspiration - active process requiring muscle contraction to increase dimensions of thoracic cavity
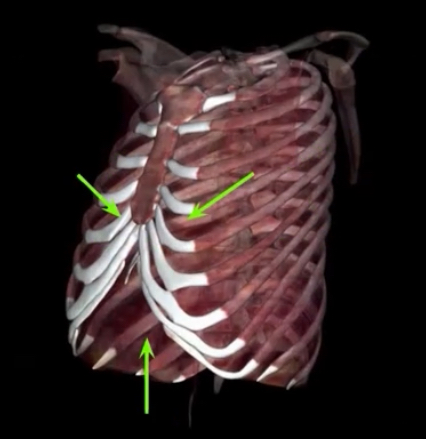
What is occurring?
Quiet Expiration- passive as a result of muscles returning to relaxed state (forced expiration is active process causing muscle contraction)
What is Eupnea?
quiet breathing occurring at rest without added effort
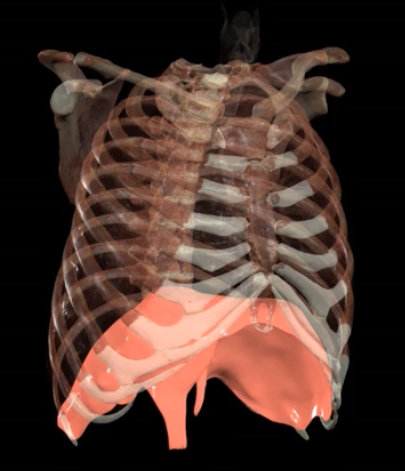
What is this?
Diaphragm
What is this?
External intercostals
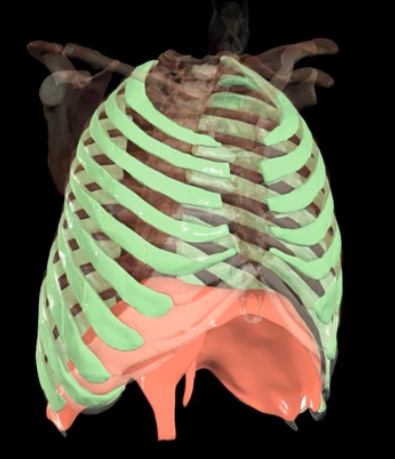
What is occurring during contraction?
Causes diaphragm to flatten and pull lungs and expand thoracic cavity downwards
What occurs during contraction?
External intracoastal elevate ribs and expand thoracic cavity outward
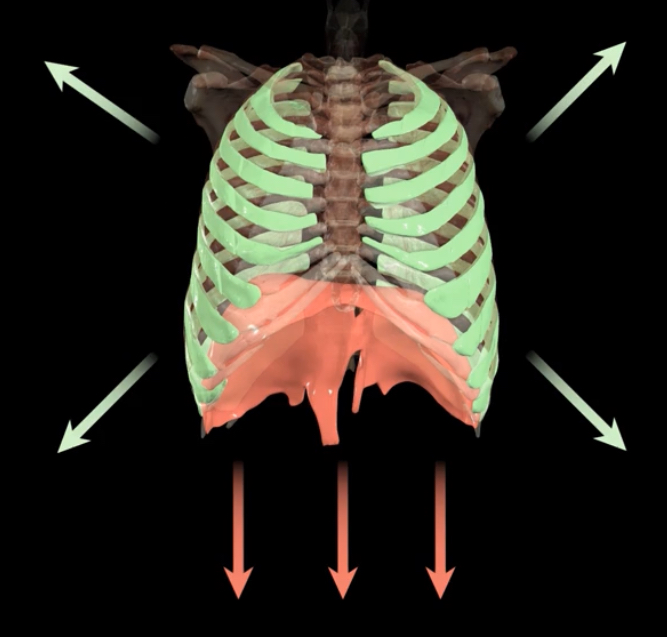
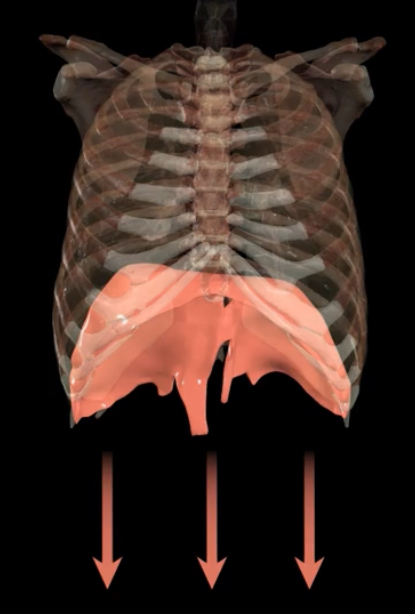
What is occurring?
Active process of quiet inspiration-There is a decrease in pressure causing air to move down pressure gradient and into the lungs
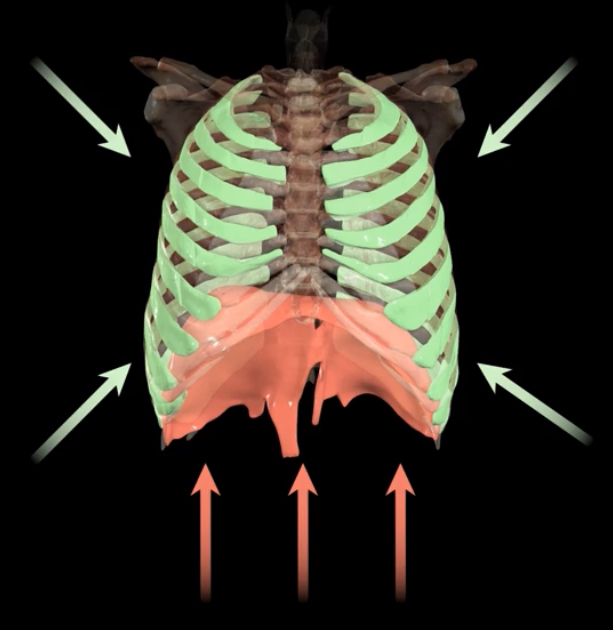
What is occcuring?
During quiet expiration, and passive process, the muscles relax and increase in pressure pushes air out of the lungs
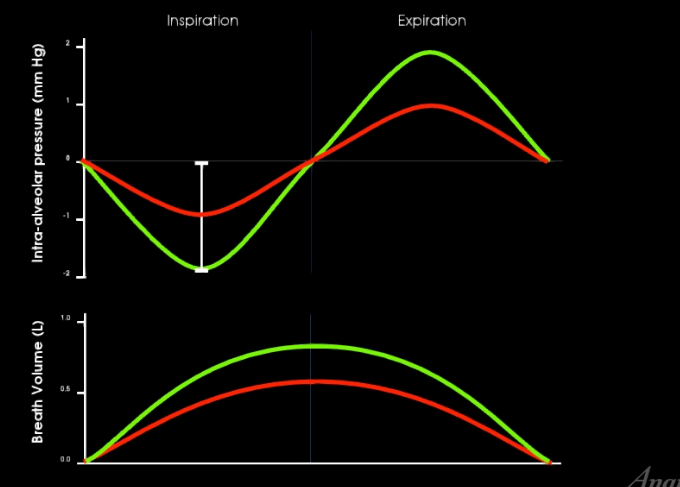
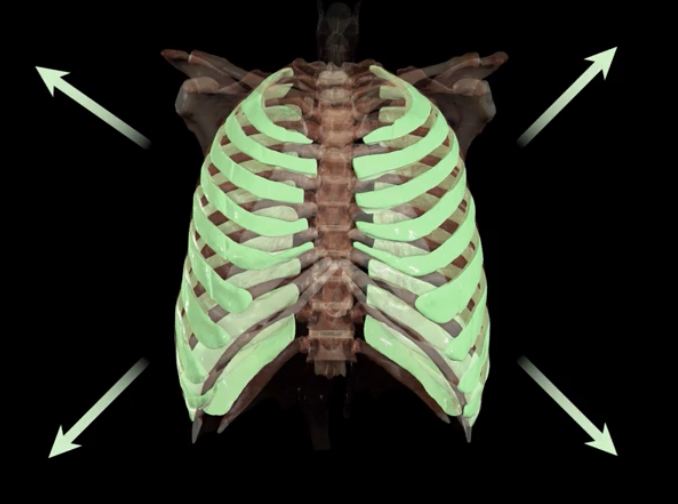
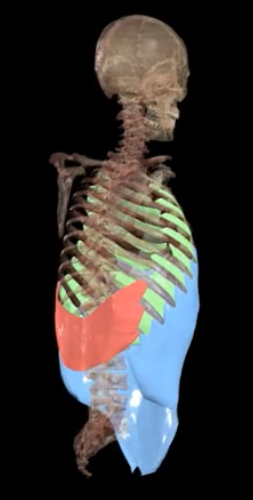
Which is quiet breathing and which is forced breathing?
Red- quiet breathing
Green- forced breathing
What type of breathing is forced breathing?
Inspiration and expiration are active, requiring muscle contraction
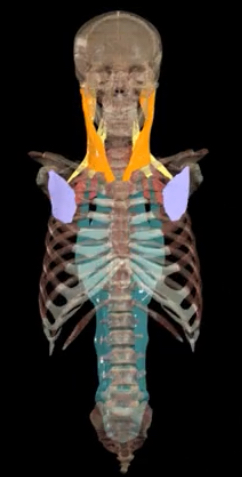
What muscles contract during forced inspiration?
Purple- pectoral minor
Orange- sternocleidomastiod
Yellow- scalenes
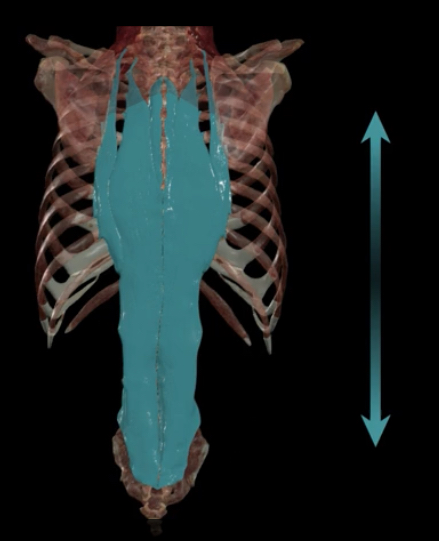
Red- serratus posterior superior
Blue- erector spinae
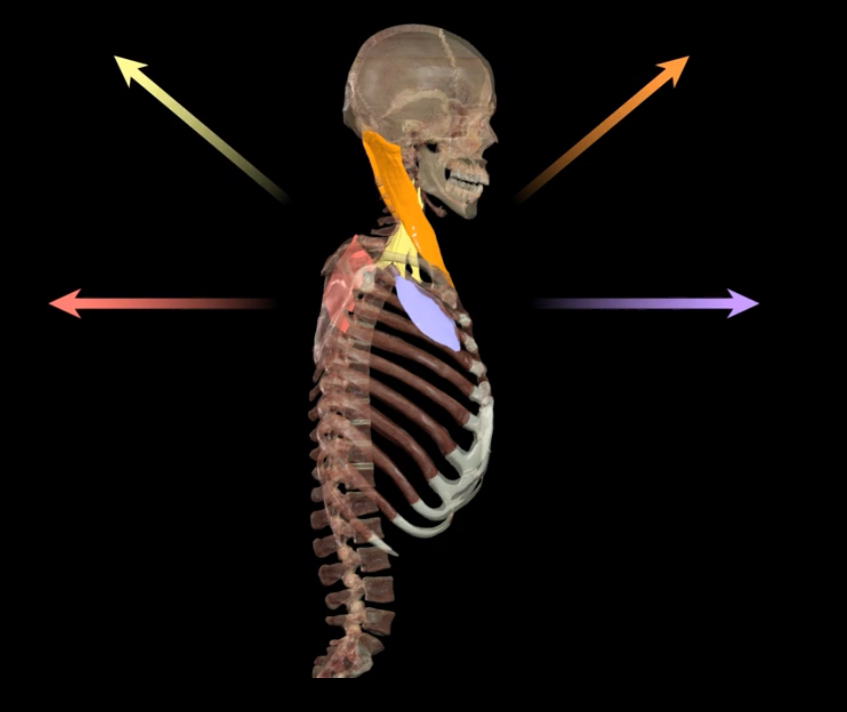
What muscles expand the thoracic cavity?
Sternocleidomastiod
Scalenes
Pectoral minor
Serratus posterior superior
What muscle elevates the rib cage?
Erector spinae
What muscles contract in forced expriration?
Red-Serratus posterior inferior
Green- internal intercostals
Blue- abdominal muscles
Transverse thoracic (not shown)
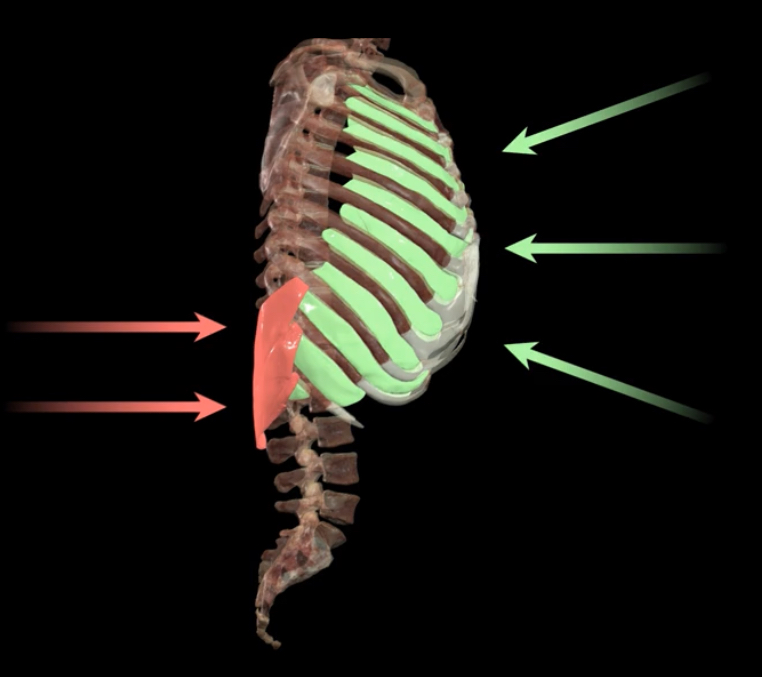
What muscles compress the thoracic cavity beyond normal resting state?
Serratus posterior inferior
Internal intercostals
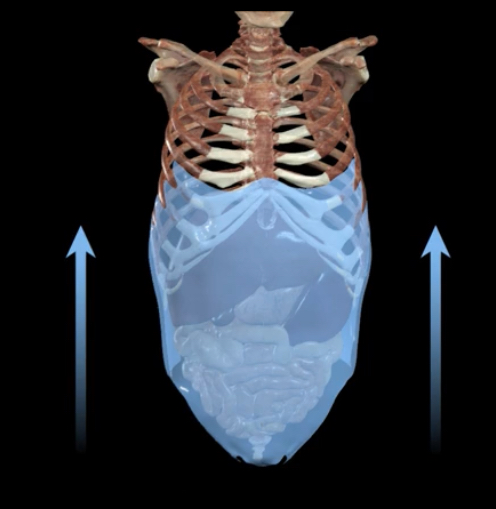
What occurs to the abdominal muscle during forced expiration?
Compresses abdominal viscera against diaphragm, pushing it more superiorly into t thoracic cavity
What is boyle’s law?
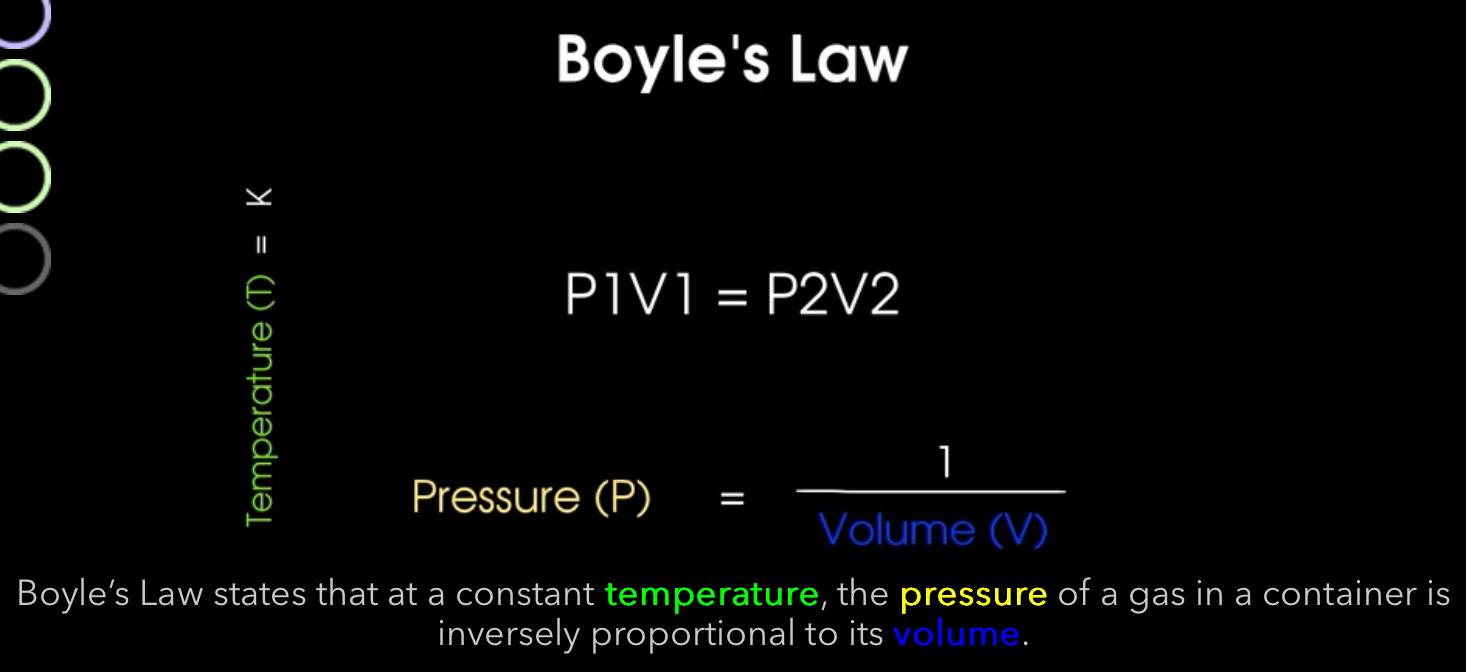
What’s the relationship between pressure and volume in Boyle’s law?
Inverse
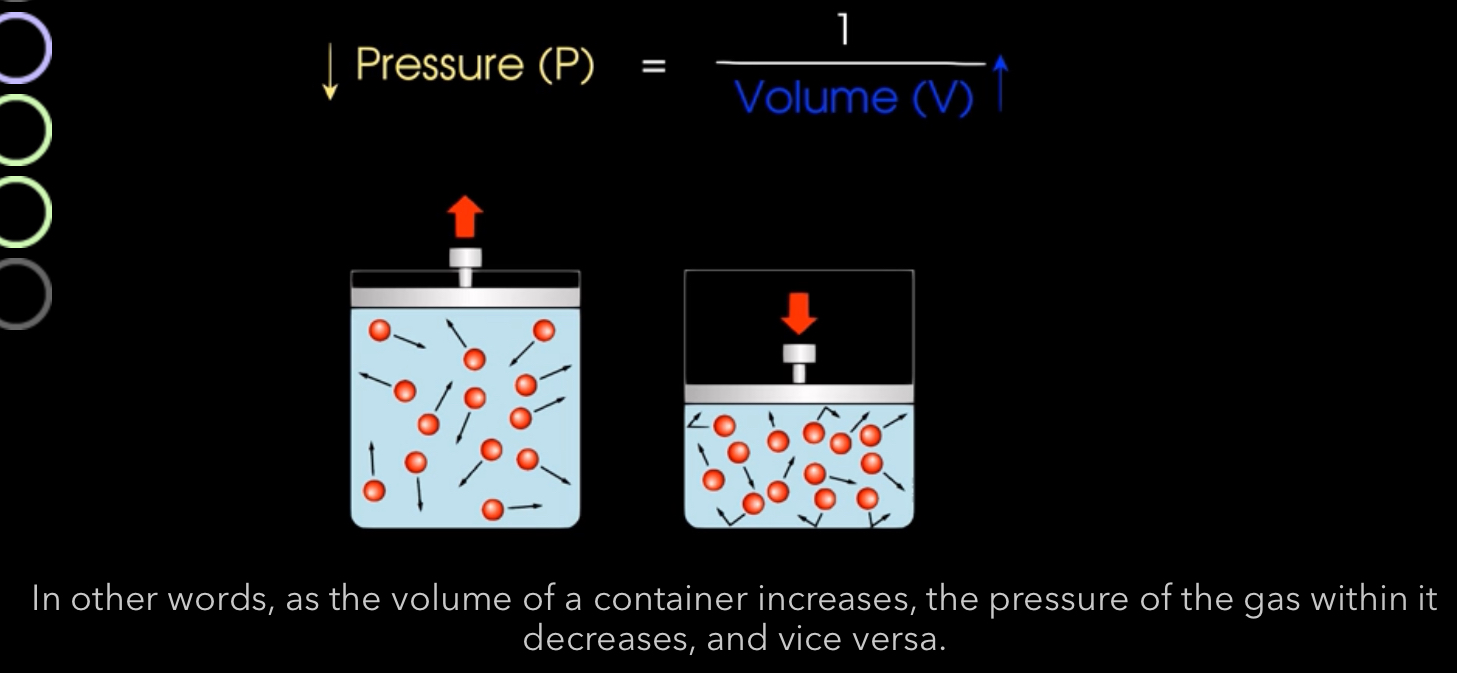
How does Boyle’s law work with respirations?
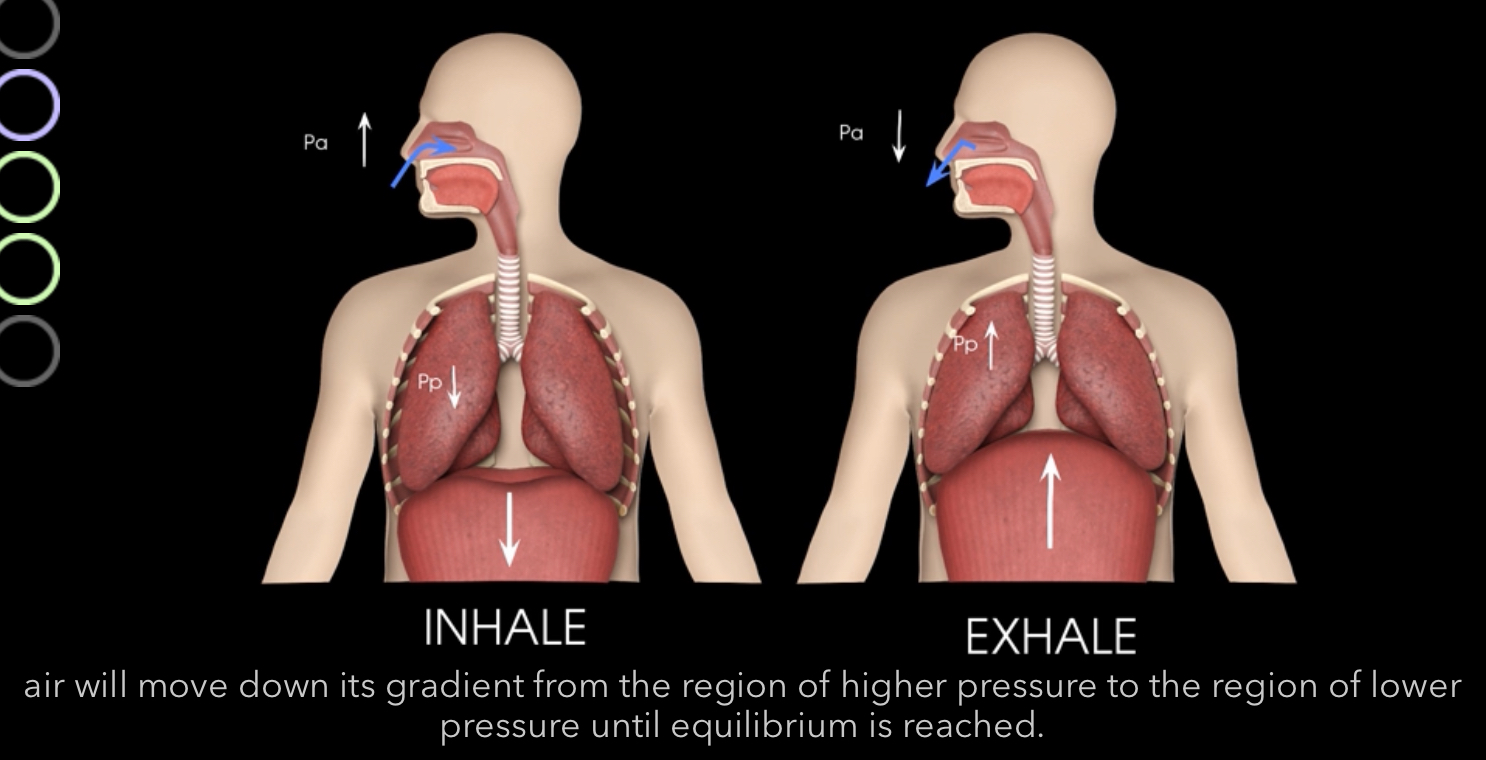
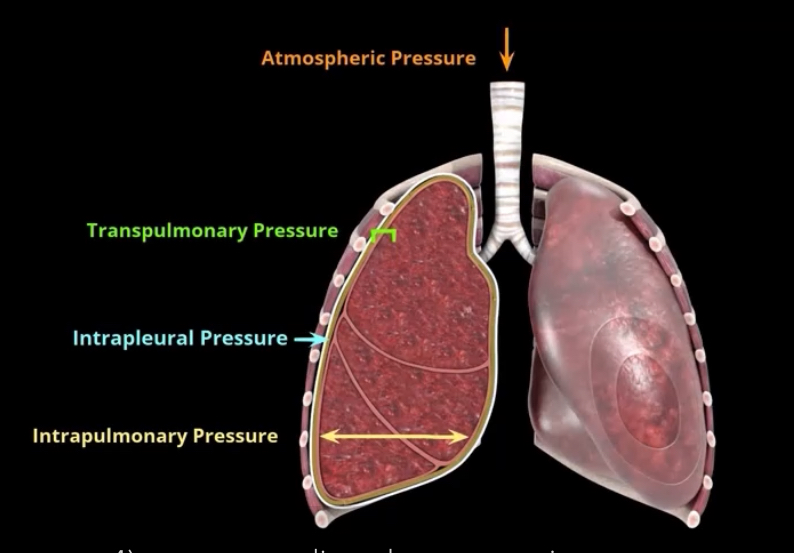
What are the major pressures that influence pulmonary ventilation?
Atmospheric pressure
Intrapulmonary (intra-alveolar) pressure
Intrapleural pressure
Transpulmonary pressure
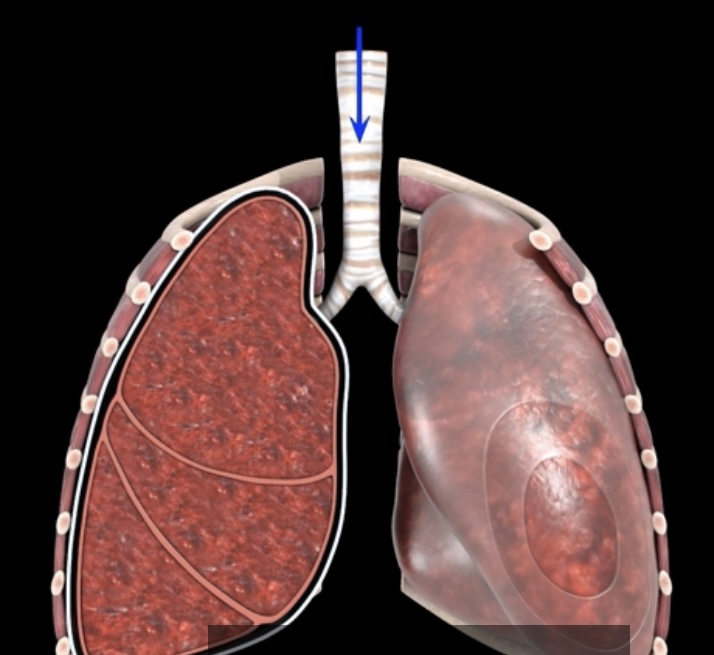
What pressure is this? What is it?
Atmospheric pressure- pressure of gases in air in external environment (based at sea level)
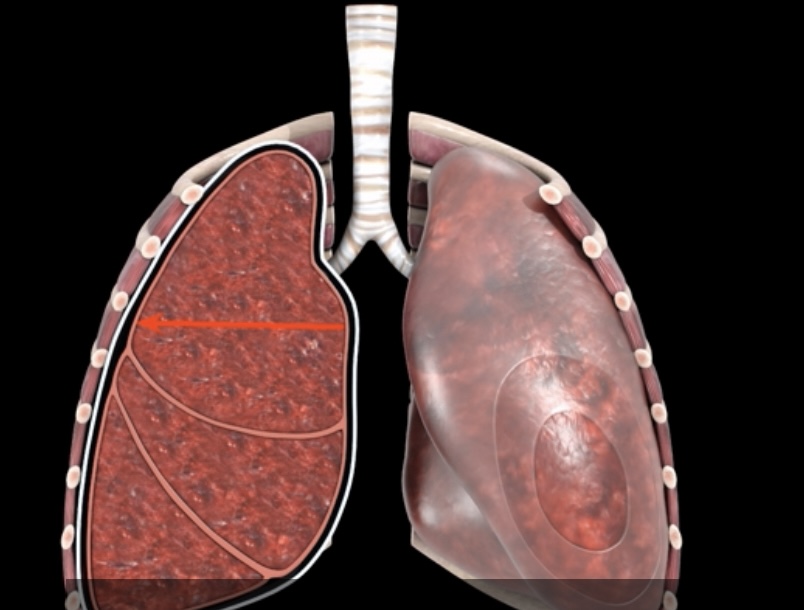
What pressure it this? What is it?
Intra-pulmonary pressure (intraalveolar)- pressure within the alveoli and changes with alveolar volume with breathing
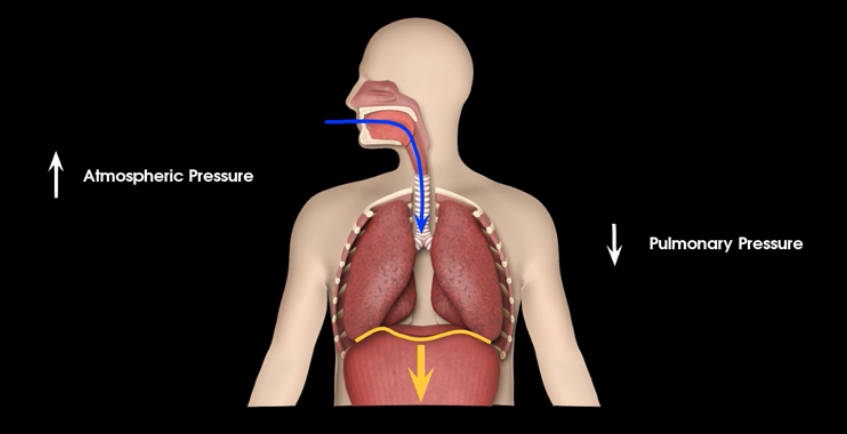
an increase in lung volume decreases intrapulmonary pressure decreases below atmospheric pressure producing a pressure gradient that pulls air into lungs and vice versa
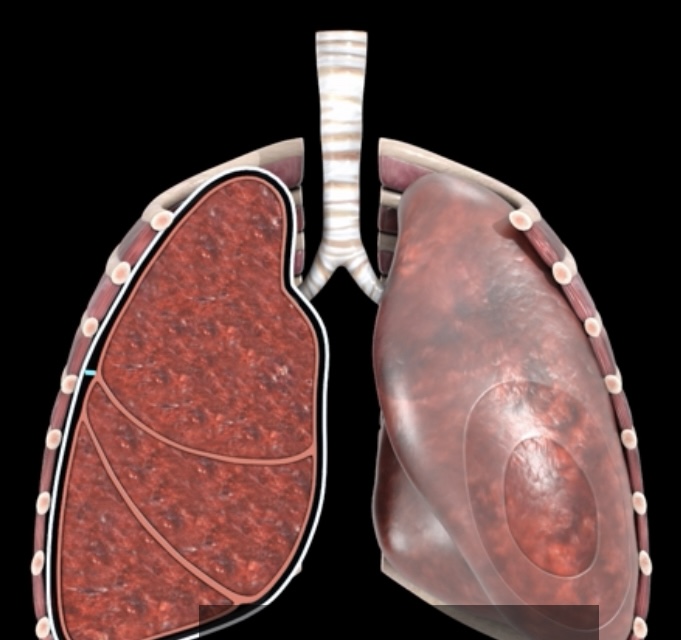
What pressure is this? What is it?
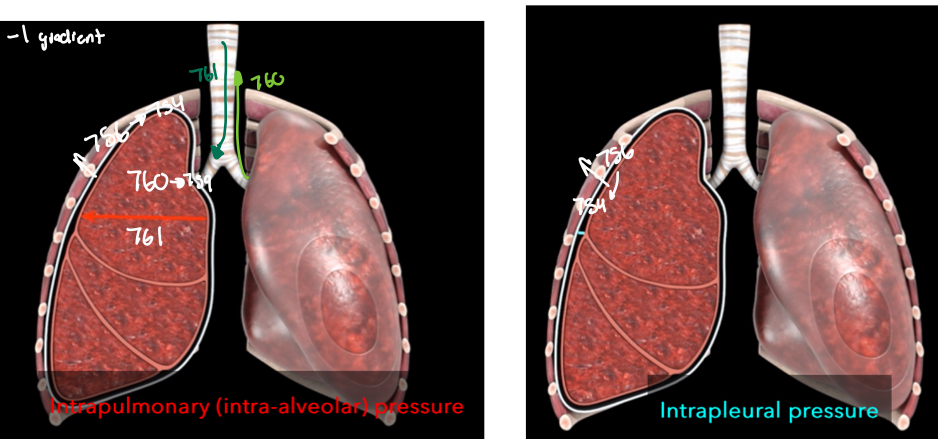
intrapleural pressure- fluctuates with breathing and is 4mmHg lower than intrapulmonary pressure (negative pressure) from opposing forces on the pleural fluid
Alveolar surface tension pulls inward of lungs
Elastic recoil is slightly stronger outward pull at 756mmHg
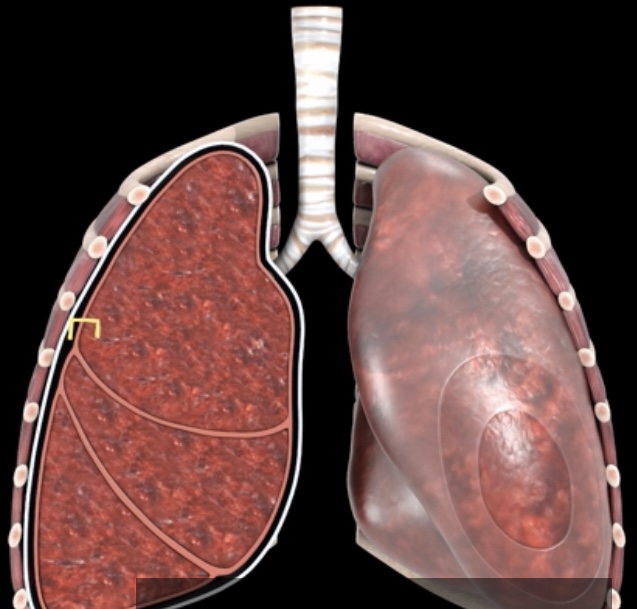
What pressure is this? What is it?
Transpulmonary- 4mmHg difference between the intrapulmonary and Intrapleural pressures
What’s the relationship between altitude and atmospheric pressure

how does the pressure gradient work when breathing?
Intrapulmonary pressure is at 760mmHg and Intrapleural pressure is at 756
when inspiration and muscles contract, intrapulmonary pressure decreases to 759mmHg and Intrapleural pressure decreases to 754mmHg creating a -1 mmHg gradient
When diaphraphm and intracostals relax, Intrapleural pressure returns to 756mHg
When lungs recoil, intrapulmonary pressure increases to 761mmHg creating a pressure gradient of +1mmHg
During expiratory intrapulmonary pressure returns to 760mmHg
What 2 factors effect airflow?
pressure gradient
Resistance
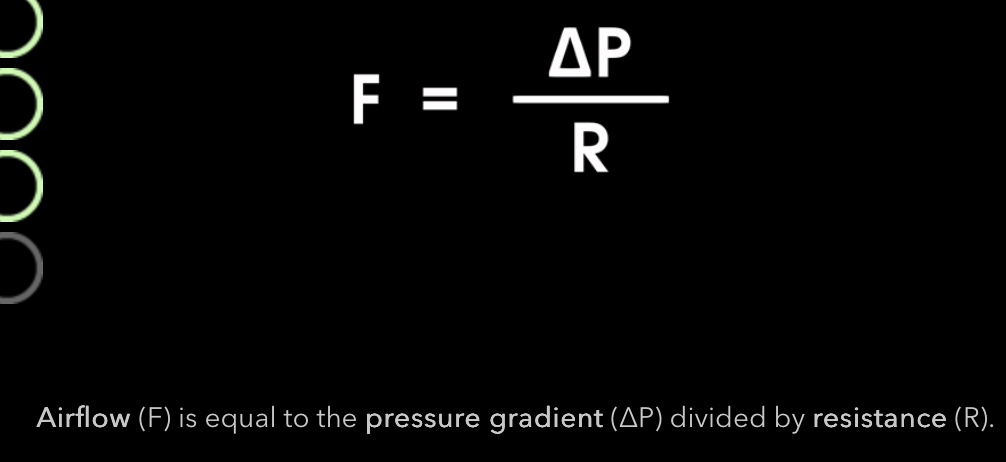
What is the airflow equation?
Airflow is directly related to the pressure gradient
inversely related to resistance
What factors contribute to respiratory restiance?
elasticity of lungs, chest wall, airway diameter, alveolar surface tension

How is elasticity and resistance related? And as we age?
Inversely
Occurs as we age, from diseases (pulmonary fibrosis), skeletal abnormalities affecting thoracic cage or vertebral column (fractures or arthritis, vertebral malformations-> scoliosis)
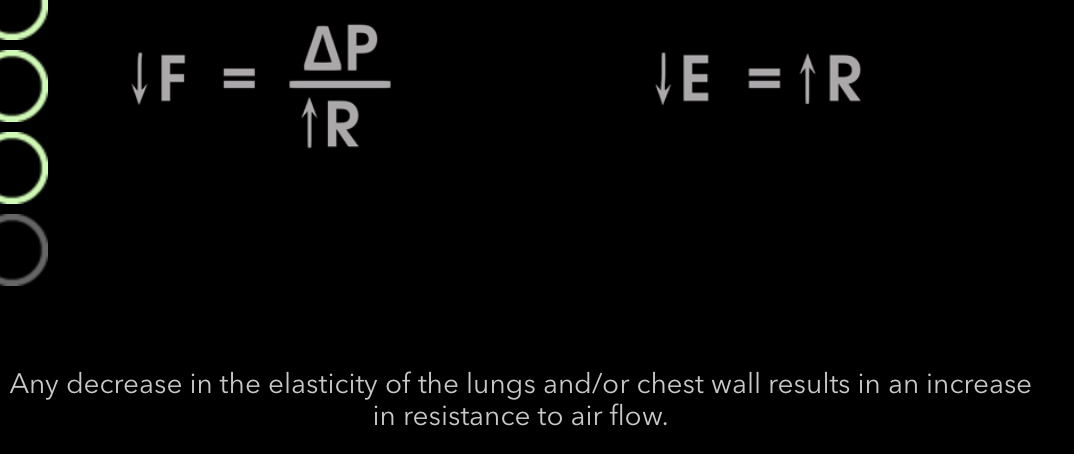
How is bronchonstriction and resistance related? When does it occur?
Inveresly
Occurs in parasympathetic
• histamine release
• Cold temperatures
• excess mucus
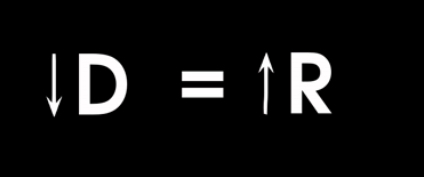
What causes bronchodilation?
Sympathetic system
release of epinephrine
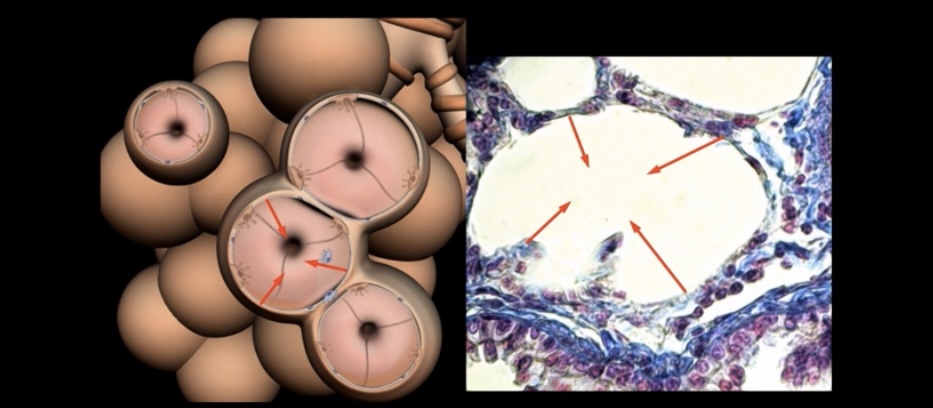
What is the effect of increased alveolar surface tension?
Causes alveoli to collapse in oneself and Increased resistance
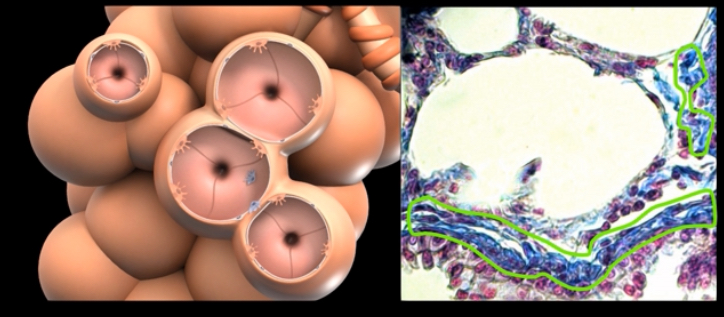
What is this and whats its function?
Type 2 alveolar cells produce pulmonary surfactant helping reinflating of alveoli →ARDs in premature infants → artificial surfactant or and CPAP
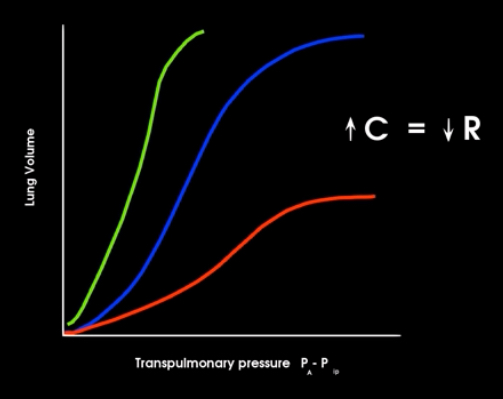
What’s makes up compliance?
Elasticity and alveolar surface tension
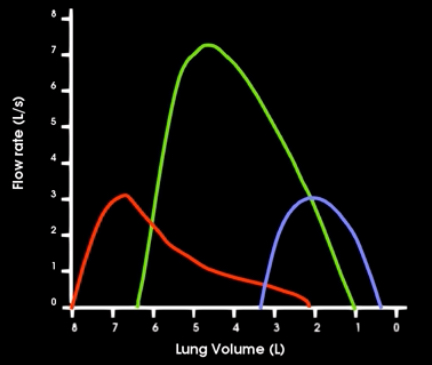
What type os disorders are shown?
Red- obstructive lung disorders (asthma, bronchitis, emphysema)= resistance is increased due to obstruction
Purple- restrictive lung disorders (pneumonia, pulmonary fibrosis)= compliance of lungs is decreased making the lungs stiffer and harder to inflate
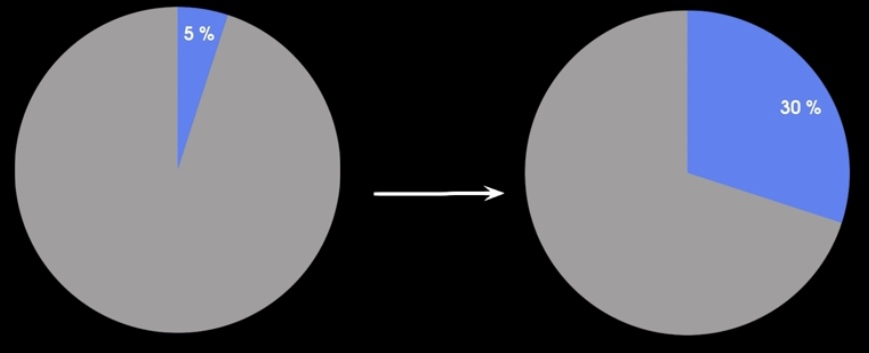
How does resistance effect breathing?
Increases difficulty of breathing 20-30%
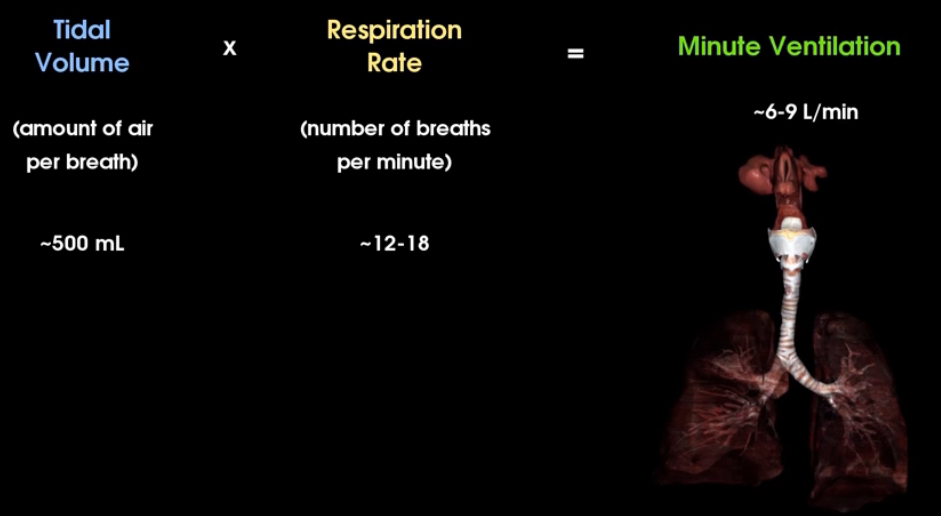
What is tidal volume, respiration rate, and minute ventilation? What are the average numbers of each?
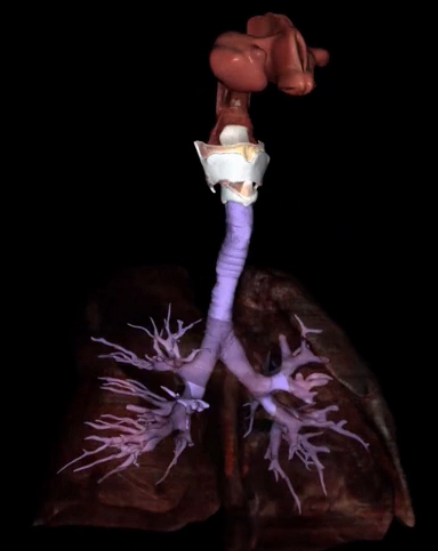
What is this and what does it hold?
Anatomic dead space and contains air that doesn’t reach the alveolis
How does the dead space affect alveolar ventilation?
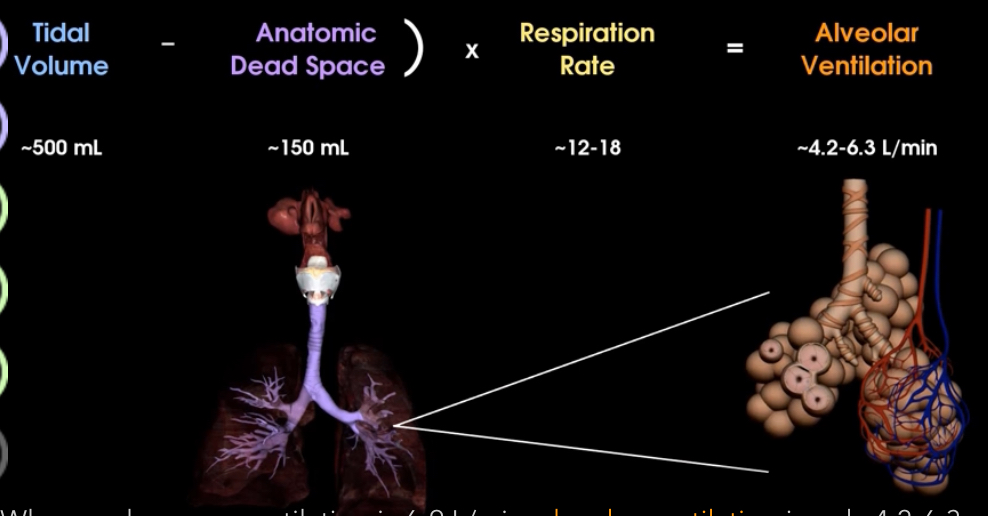
What is physiologic dead space and what is it made up of?
Alveoli not able to participate in gas exchange due to a disease. It is made up of anatomic dead space and nonfunctional alveoli

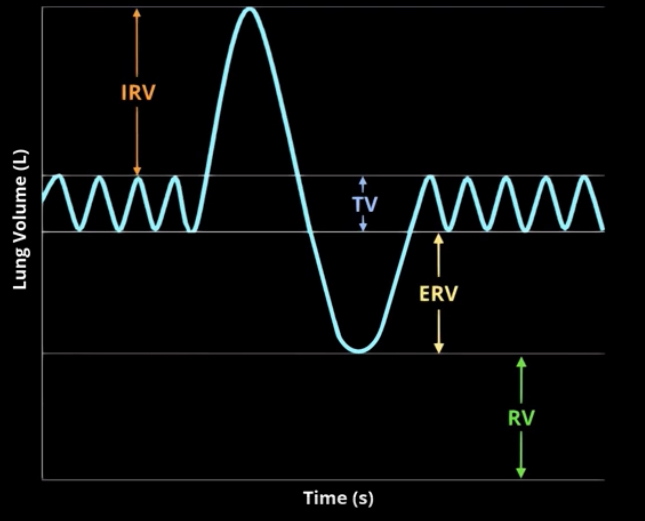
What volumes are measured in spirometery?
tidal volume- air that is inhaled or exhaled during quiet breathing
Inspiratory reserved volume- volume of air that can be forcibly inhaled beyond tidal volume
Expiratory reserved volume-volume of air that can be forcibly exhaled beyond tidal volume
Residual volume- volume of air that remains in lung after forced expiration
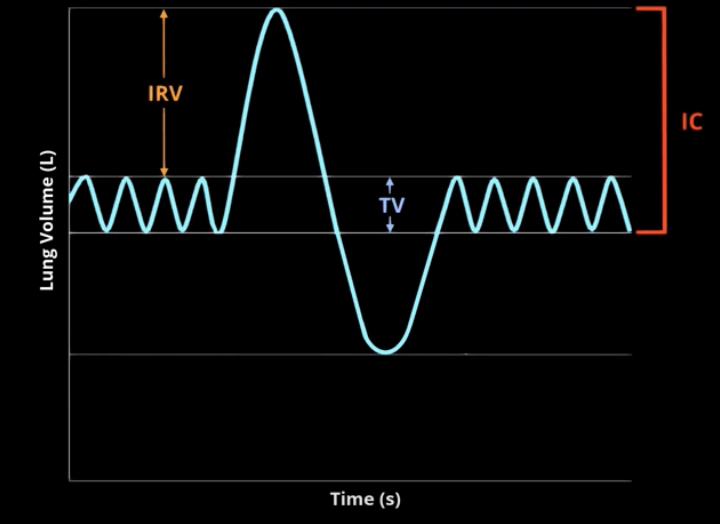
What is inspiratory capacity?
Maximum volume of air that can be inhaled from resting rate
Equal to sum of tidal volume and inspiratory reserve volume
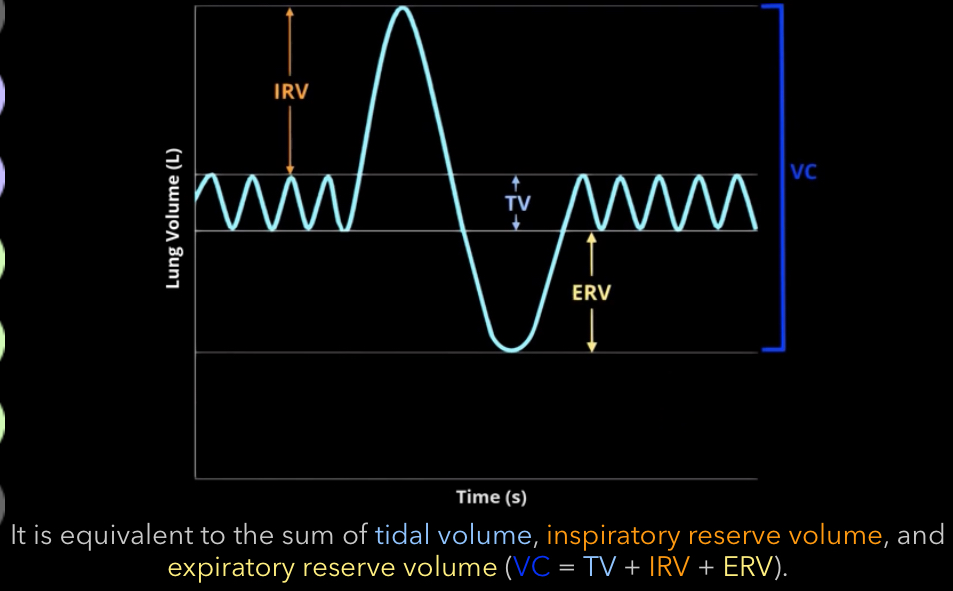
What is vital capacity?
Total volume of air that can be exhaled after maximum inhalation
equal to tidal volume + inspiratory reserve volume + expiratory reserve volume
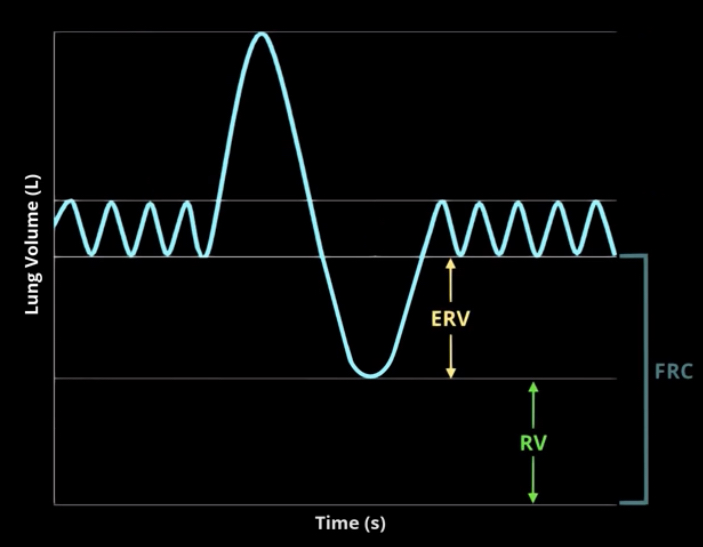
What is functional residual capacity?
Amount of air remaining in lungs after normal exhalation
expiratory reserve volume + residual volume
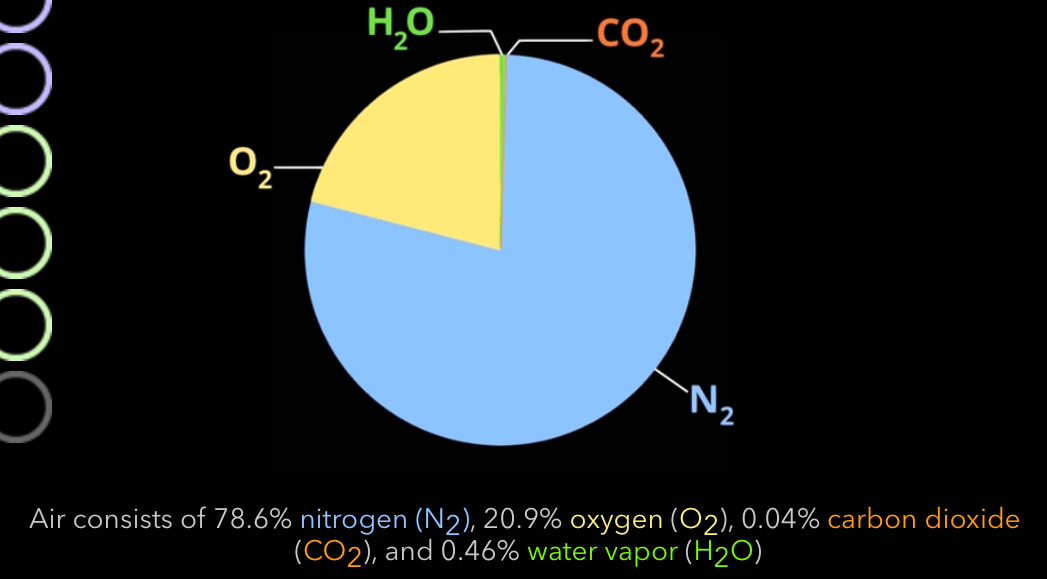
What gases are contained in air? What percent? What mmHg?
O2- 159
N2- 597
CO2-0.3
H2O- 3.5
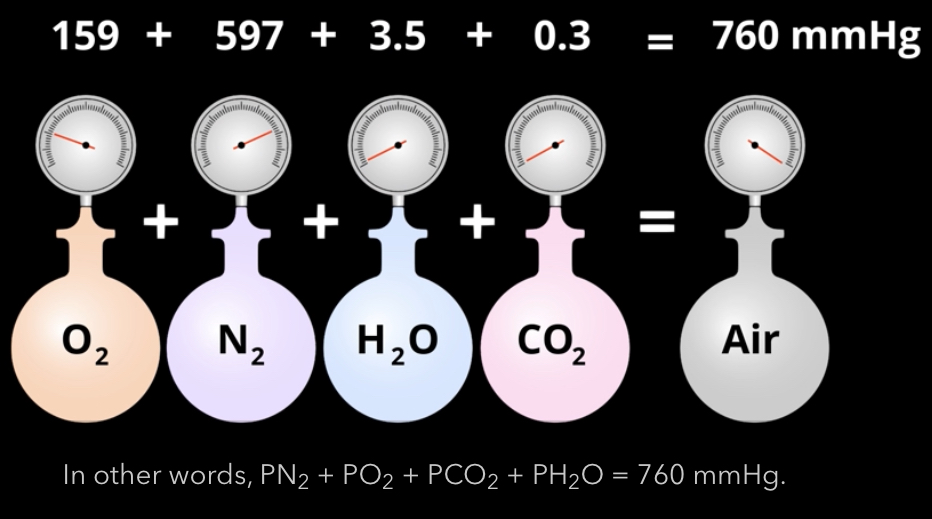
What is atmospheric pressure at sea level? How do you find the partial pressure of each gas in the air?
760mmHg
multiple by the percent
What drives the force between gas exchange?
Oxygen and CO2 partial pressure gradient
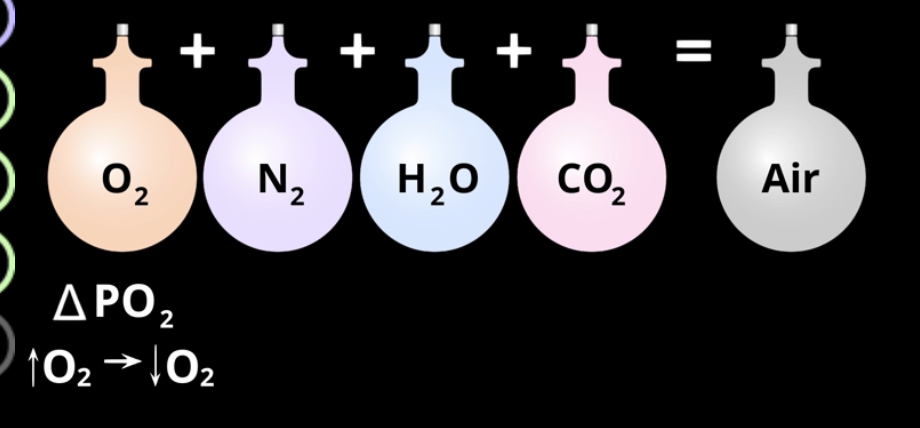
what is the pressures in the inhaled air vs alveoli?
Alveoli and blood?
Blood and systemic body?
In the capillaries?

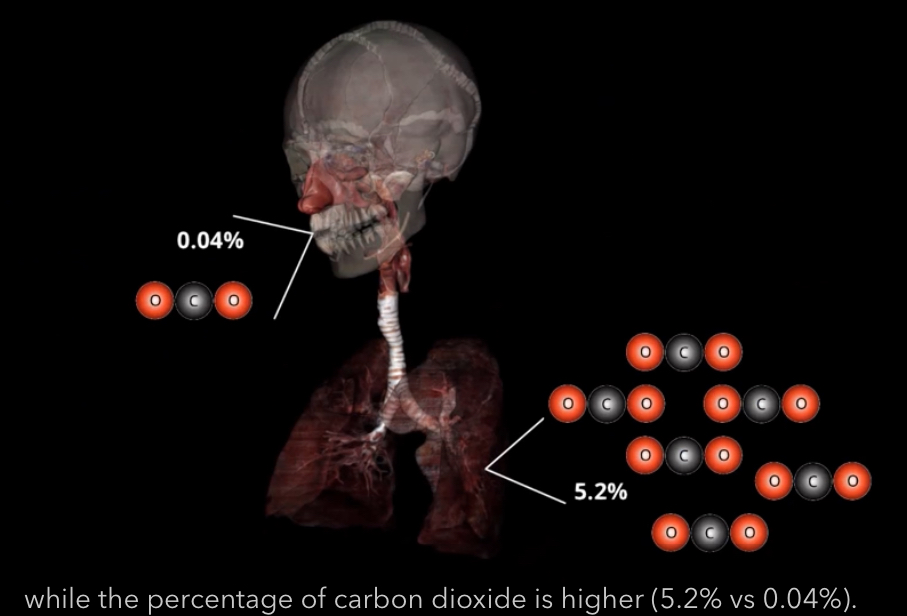
What is the percent of oxygen outside the body and in the alveolar?

What is the percent of CO2 outside the body and in the alveolar?
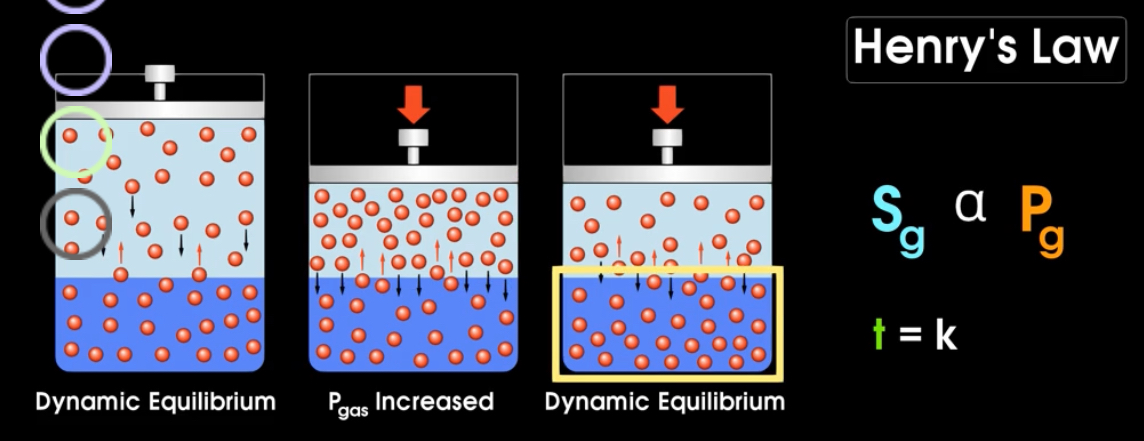
What is Henry’s law?
Higher the pressure of a gas above a liquid, the more gas will be forced into the liquid
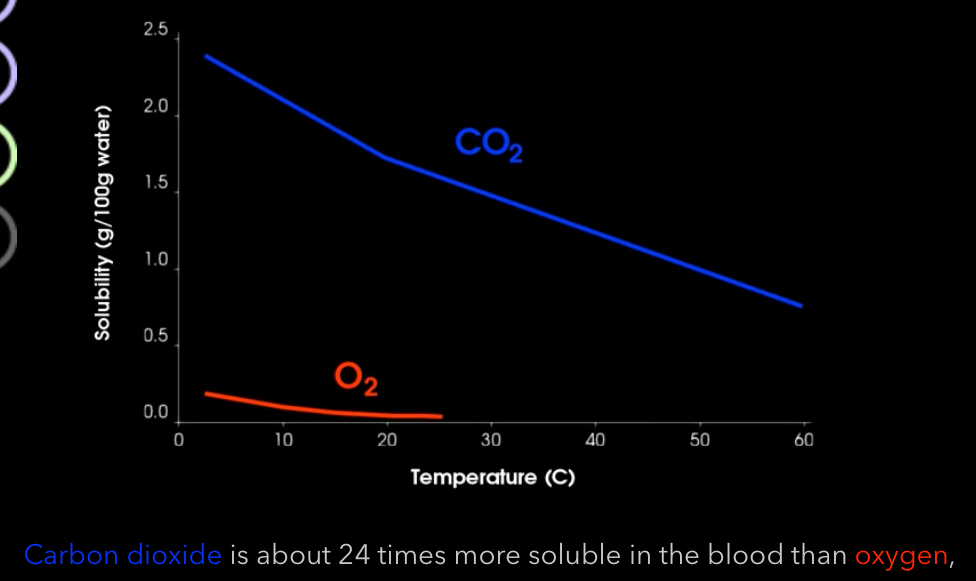
What is the solubility of CO2 compared to Oxygen?
Requiring oxygen to have a higher pressure gradient to “push” it down its gradient than CO2
What factors contribute to the efficiency of gas exchange? What the size of each?
large surface tension (70m)
Thinness (0.5microliters)
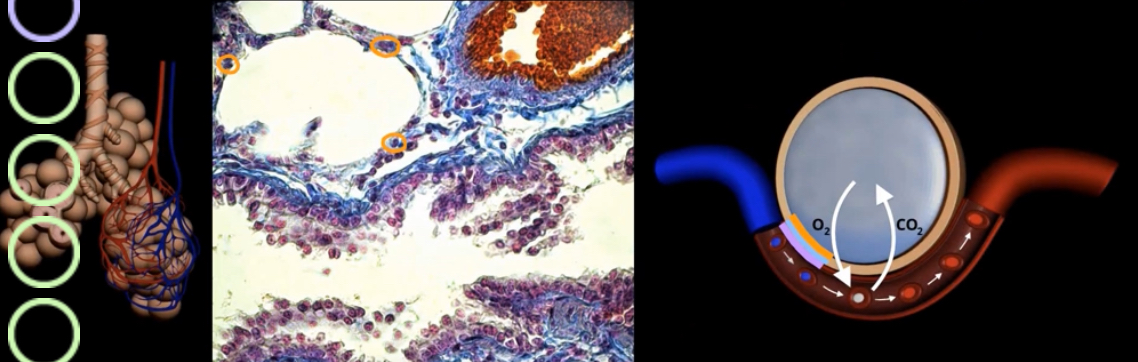
What’s orange, blue, purple?
Orange- type 1 alveolar cells
Purple- endothelial cell
Blue- basement membrane
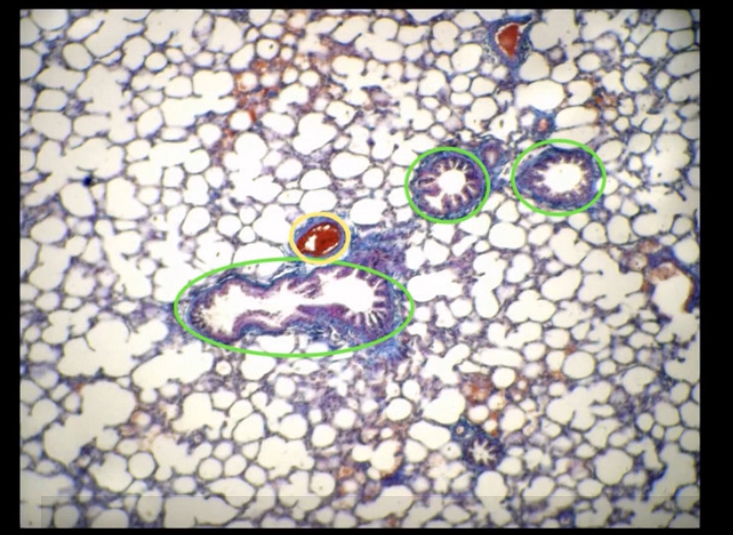
Green?
Yellow?
Green-bronchioles
Yellow- arteriole
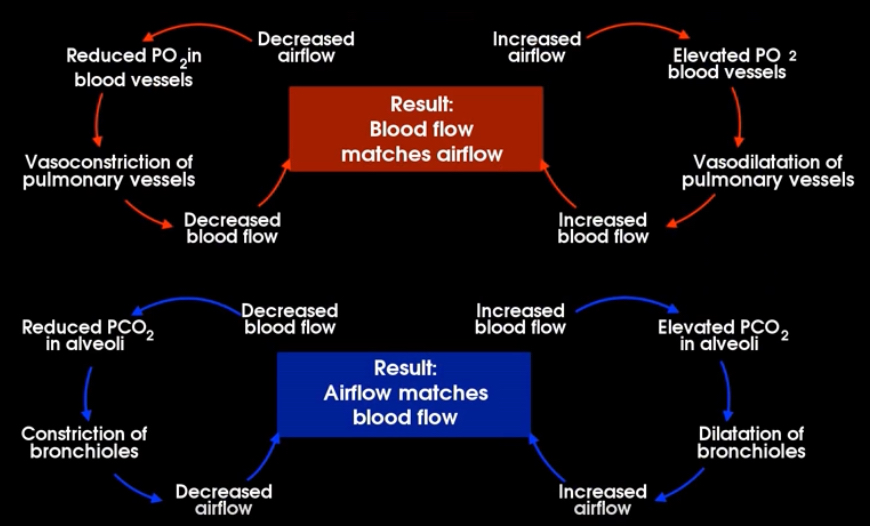
What is this?
Ventilation-perfusion coupling
both should match
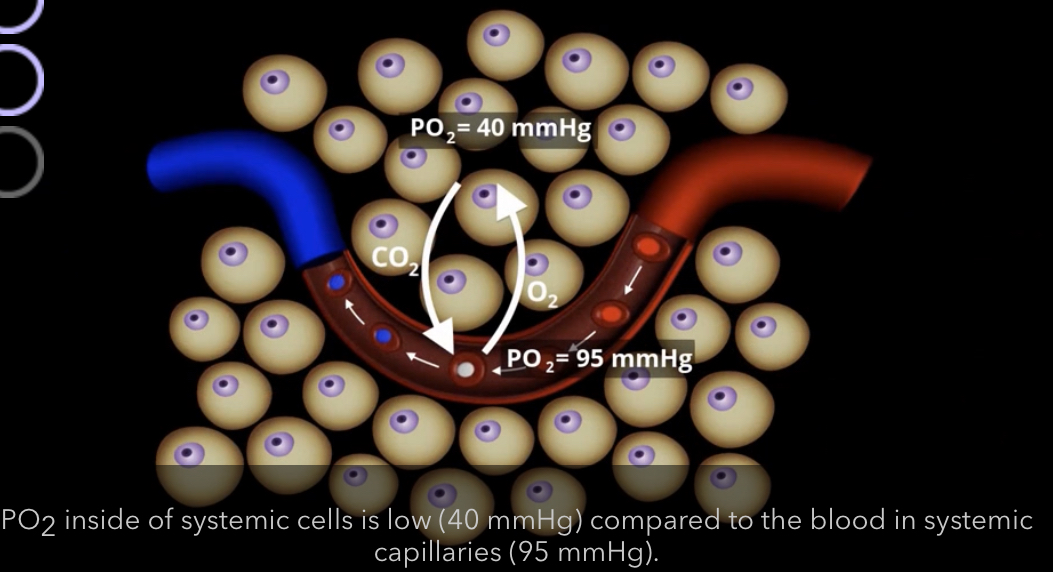
What gas exchange is occuring systemically?
CO2 is going into the blood and O2 is going into the body/tissue
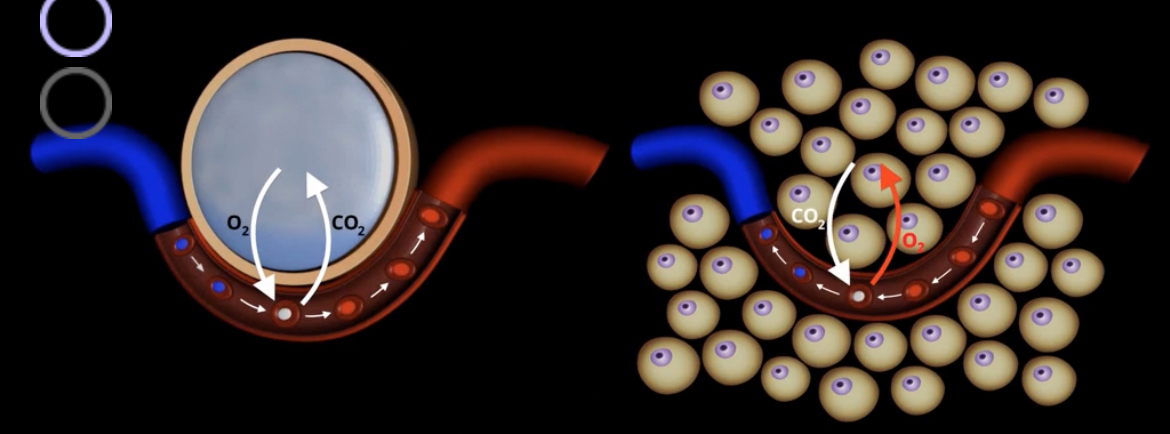
What is the partial pressure of oxygen systemic cells and blood in systemic capillaries?
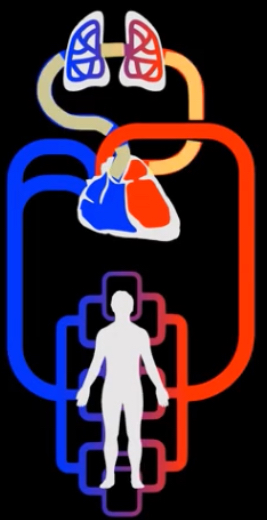
What circuit is the blue? The rest?
Blue- pulmonary
Rest- systemic
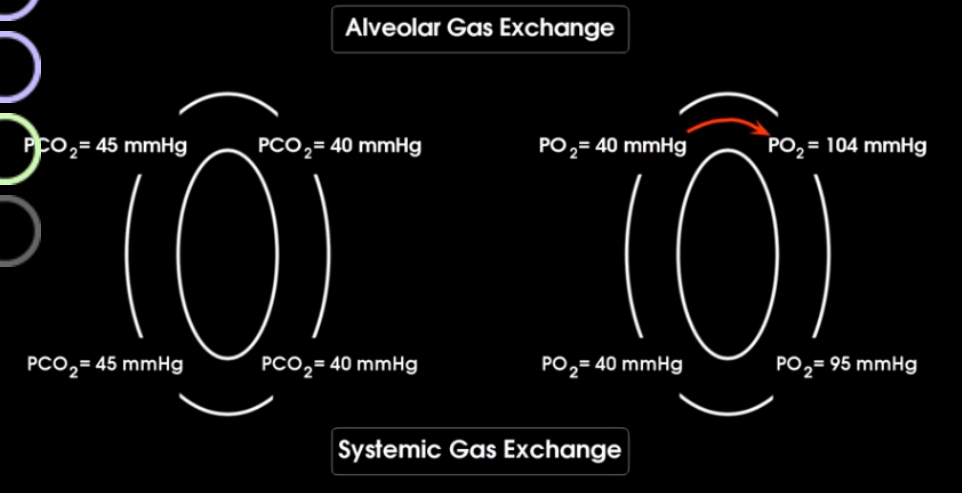
Explain the pressures of oxygen and CO2 throughout the body in the alveolar gas exchange and the systemic gas exchange
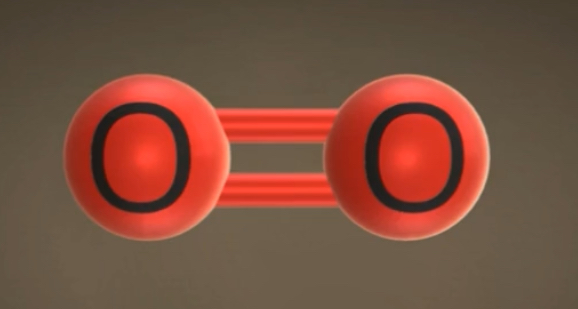
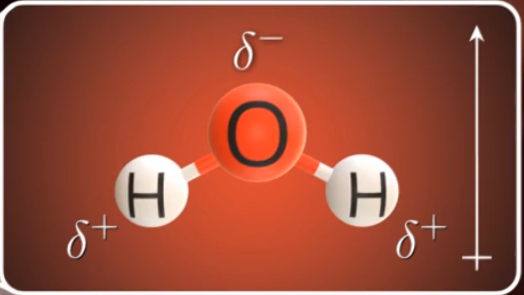
What molecule is this? Polar or nonpolar?
Oxygen, non polar
What’s this? Polar or nah
What’s this?
Hemoglobin
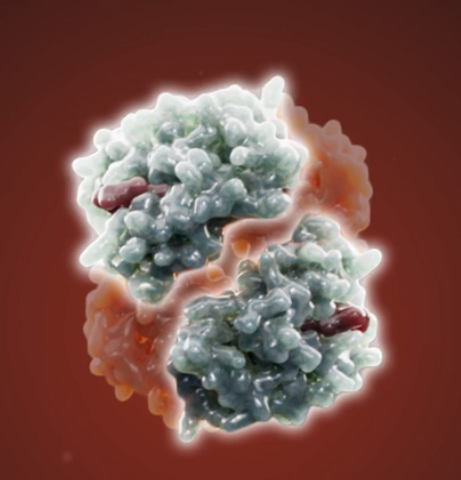
What part is this?
2 alpha subunits
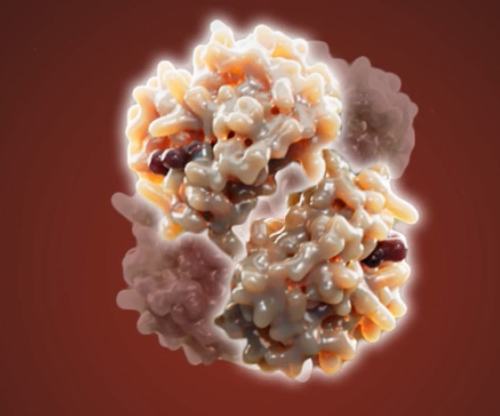
What’s this?
2 beta subunits
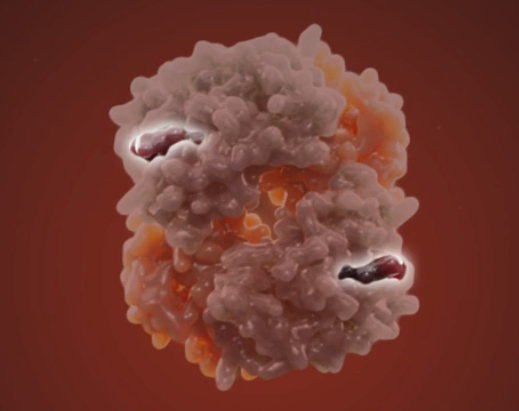
What’s this? Function?
2 heme groups carrying Iron, gives color, binds to oxygen
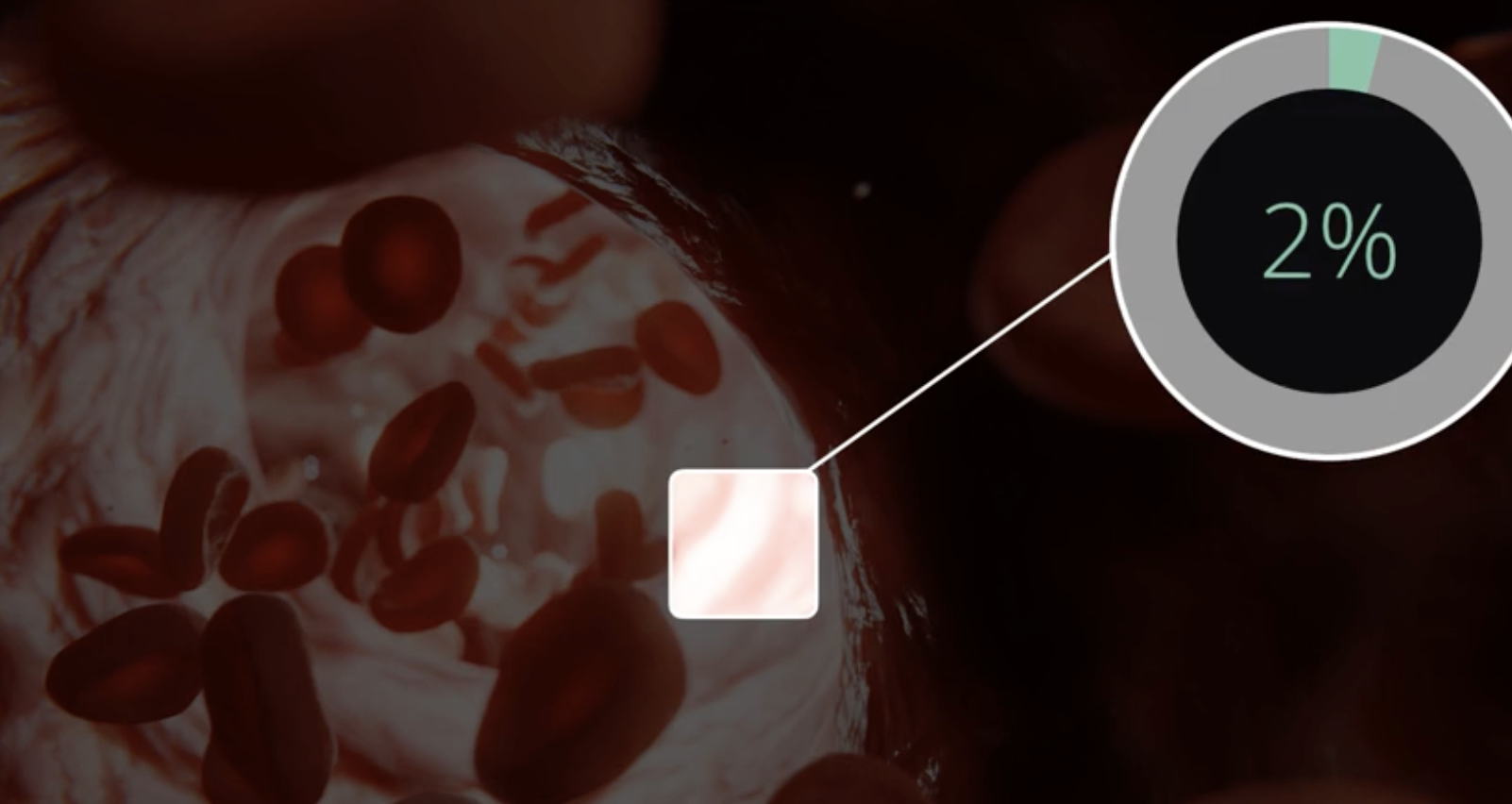

2% of what is dissolved in plasma
oxygen

7% of what is dissolved in plasmsa
CO2
what percentage of CO2 enters RBC and binds to what forming what?
23%
hemoglobin
form carbaminohemoglobin (hbco2)
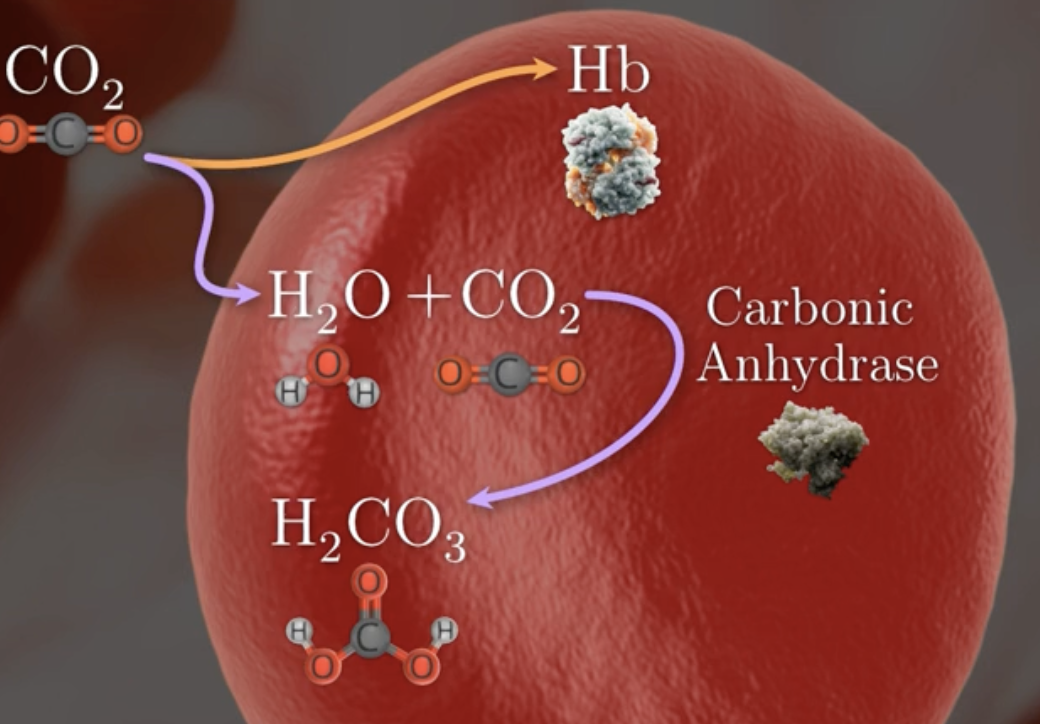
what percentage of CO2 binds to water in RBC ?
70%
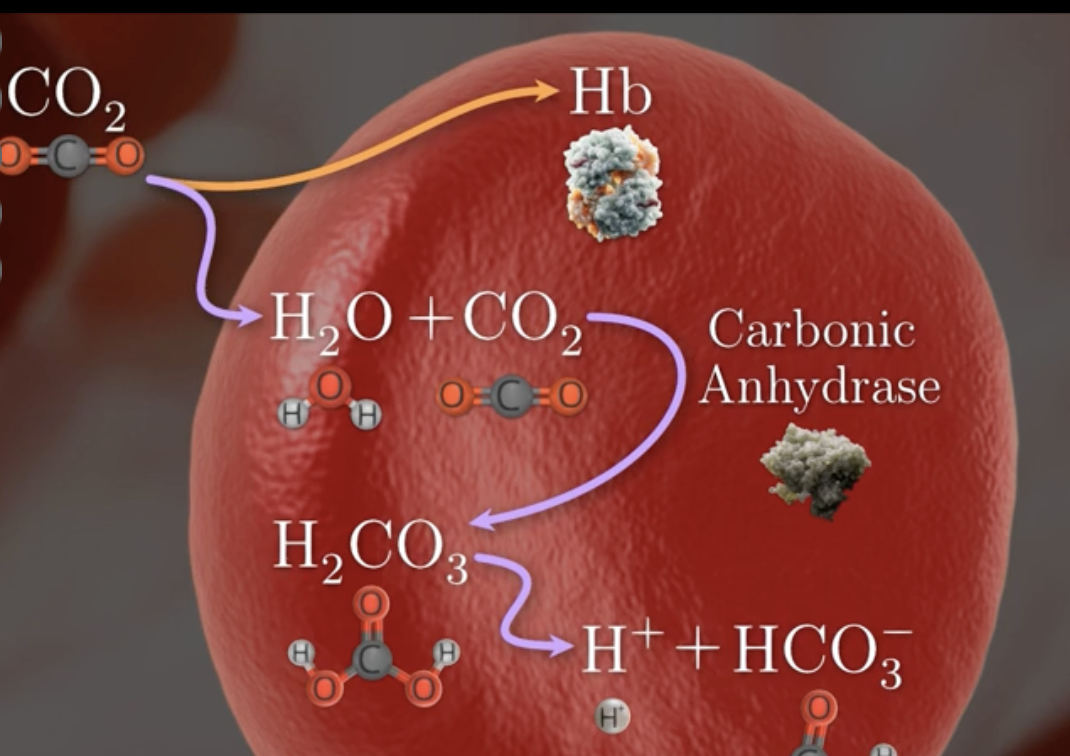
describe process of co2 binding to water in rbc
CO2 binds to H2O
catalyzed by carbonic anhydrase
to form carbonic acid h2co3
which dissociates forming H+ + bicarbonate Hco3-
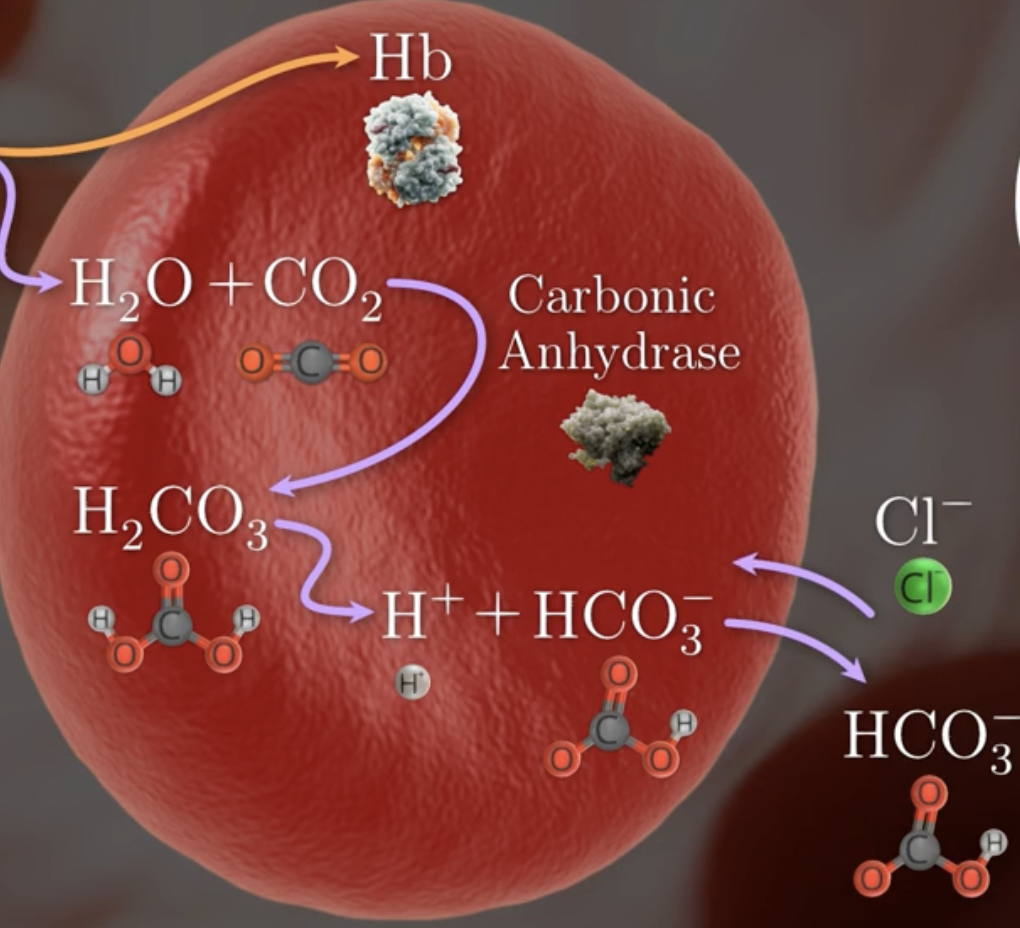
how is the charge of RBC maintained
bicarbonte HCO3- diffuse out of cell
chloride CL- ion diffuse in
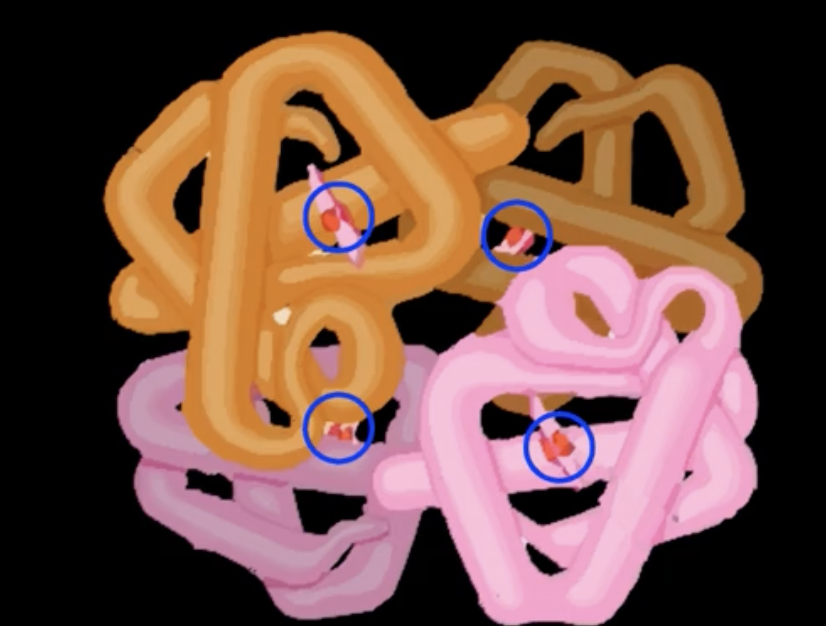
one hb molecule can carry how many o2 molecules
4
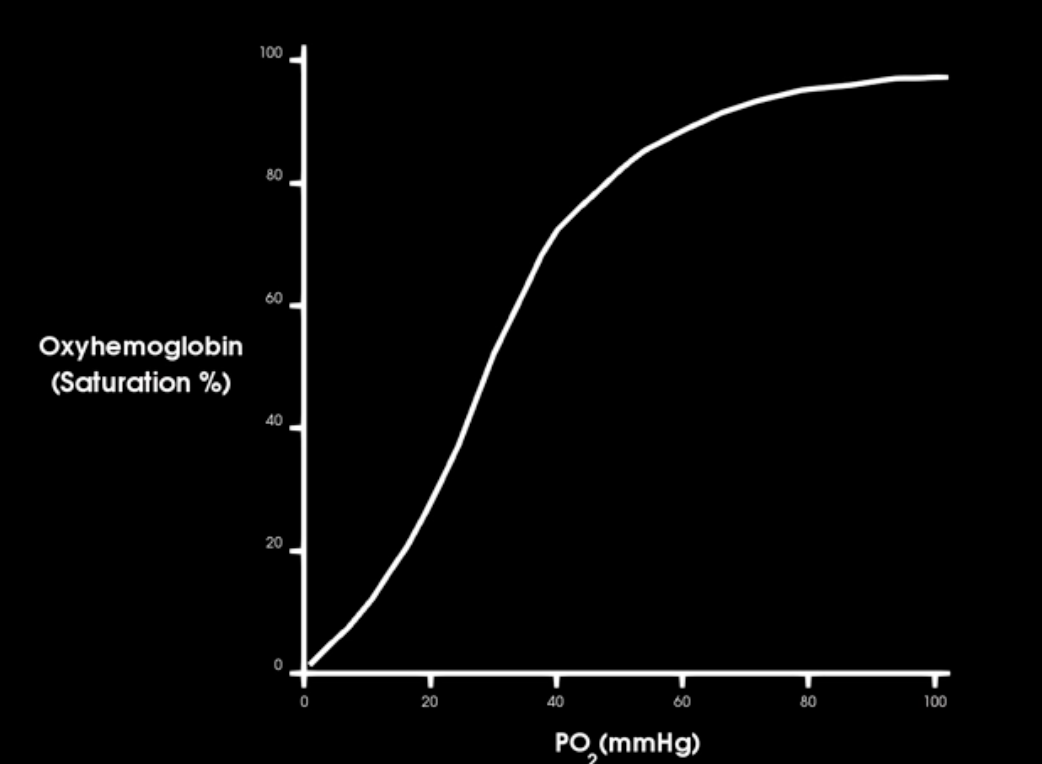
what is the the most important variable affecting hemoglobin affinity for o2
pressure of o2 PO2
as PO2 increase, hb affinity for o2 increase
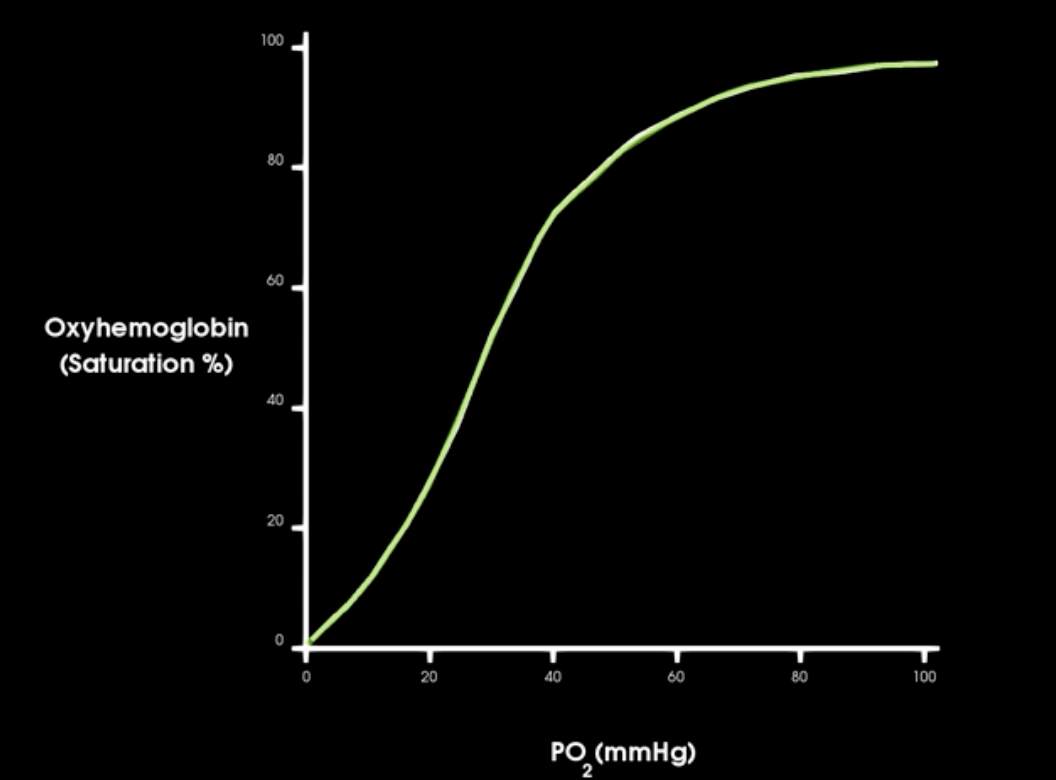
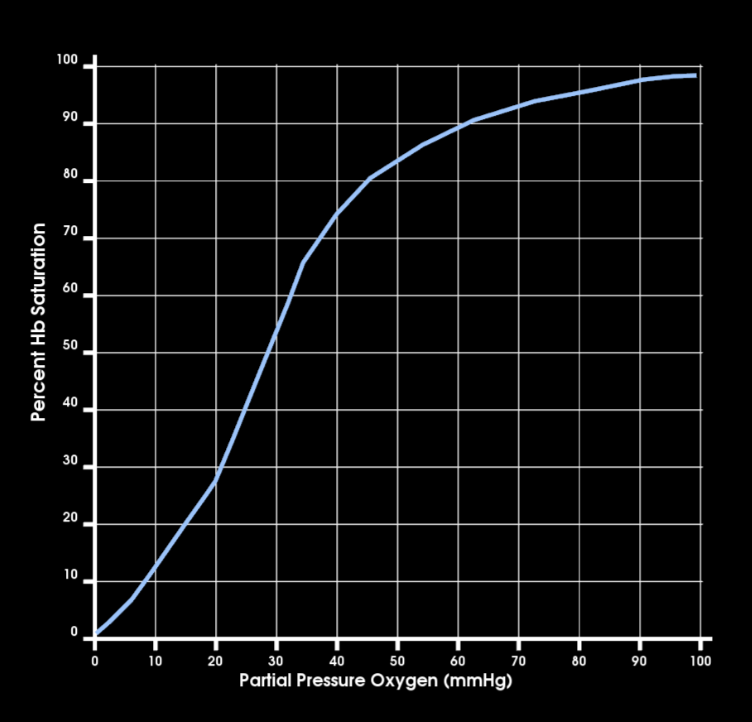
what is this curve and describe
oxygen hemoglobin saturation curve
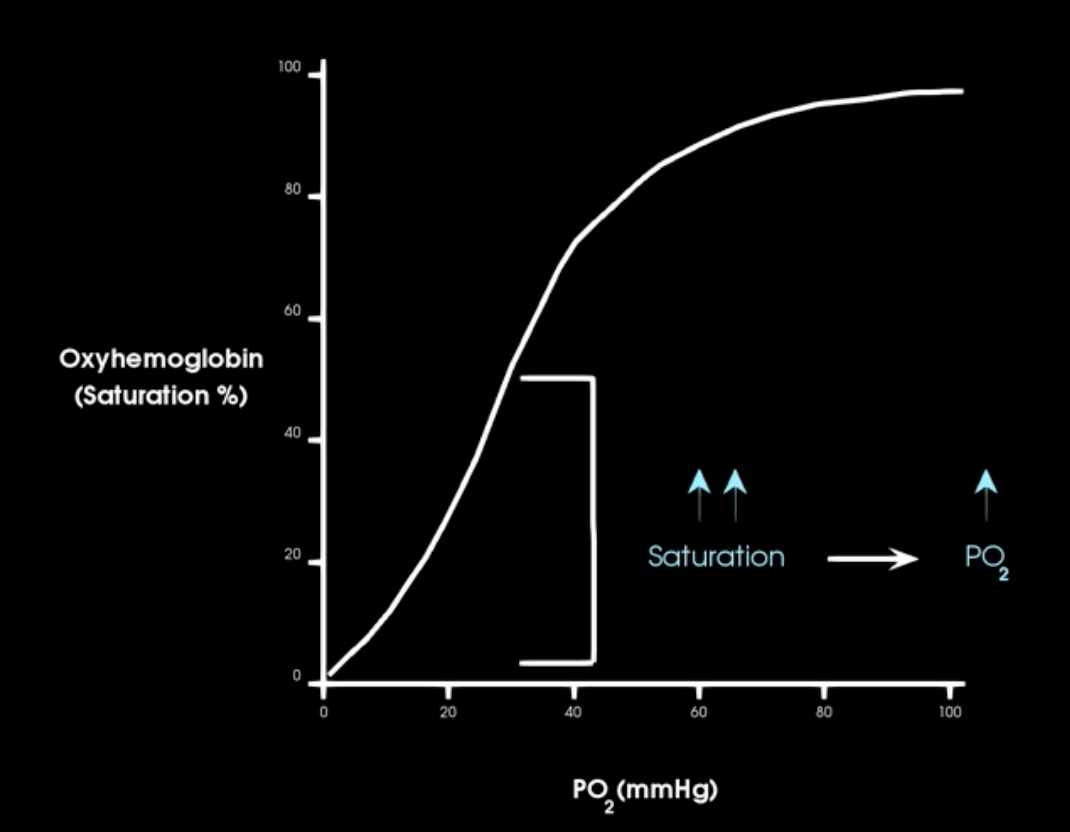
what occurs in the beginnign of o2-hb satur. curve
initially: large changes in saturation occur w/ small changes in PO2
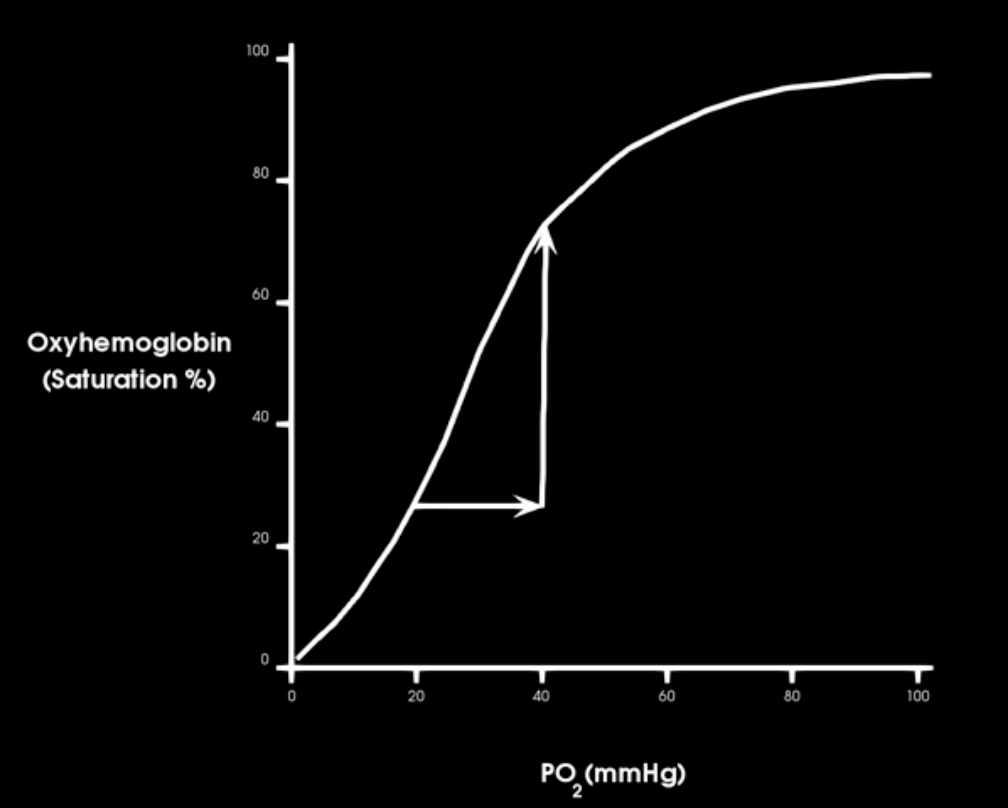
hgb is 90% saturate at what Po2
60 mm hg

large changes in altitutde result in and trigger the release of what
significant decrease in PO2 = hypoxemia
triggers release of erythropoietin (EPO) from kidneys
at systemic venous PO2 how satured is hb w/ o2? `
75%
pO2 = 40 mm hg
A right shift of o2-hb sat. curve indicates what?
More O2 is being released to the tissues at any given po2

if hgbs affinity for oxygen is increased what happens to release of o2
its ability to release o2 to tissue is decreased
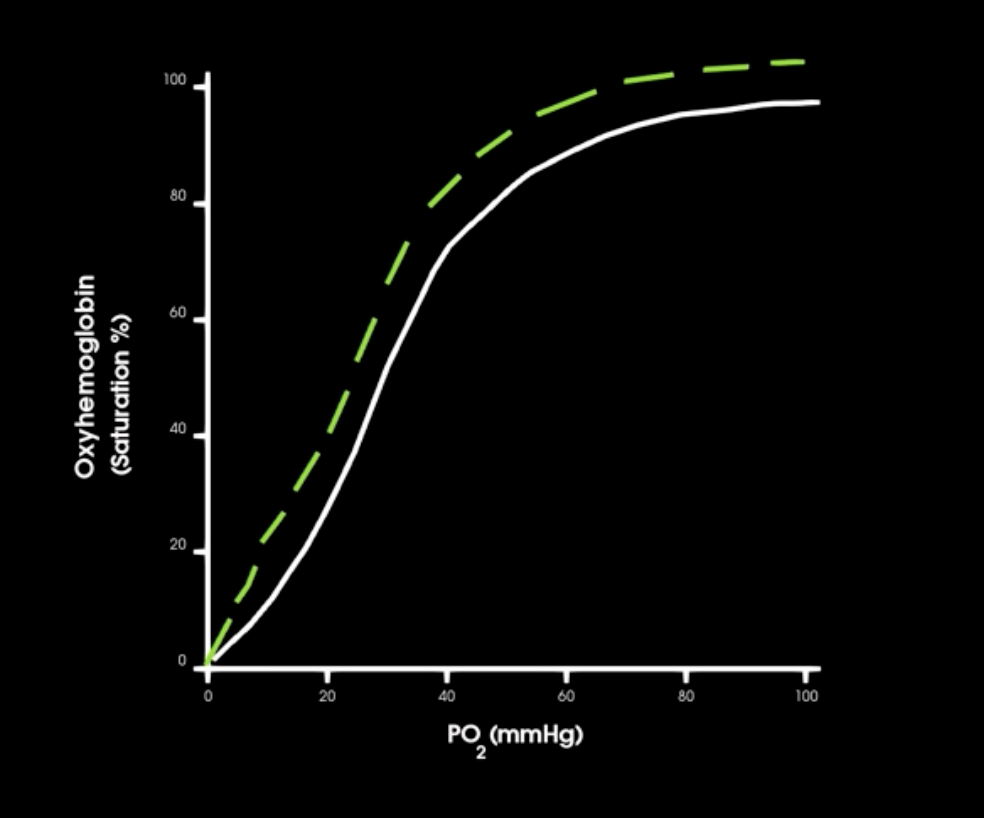
left shift in saturation curve indicates what
increase in hgb affinity for o2
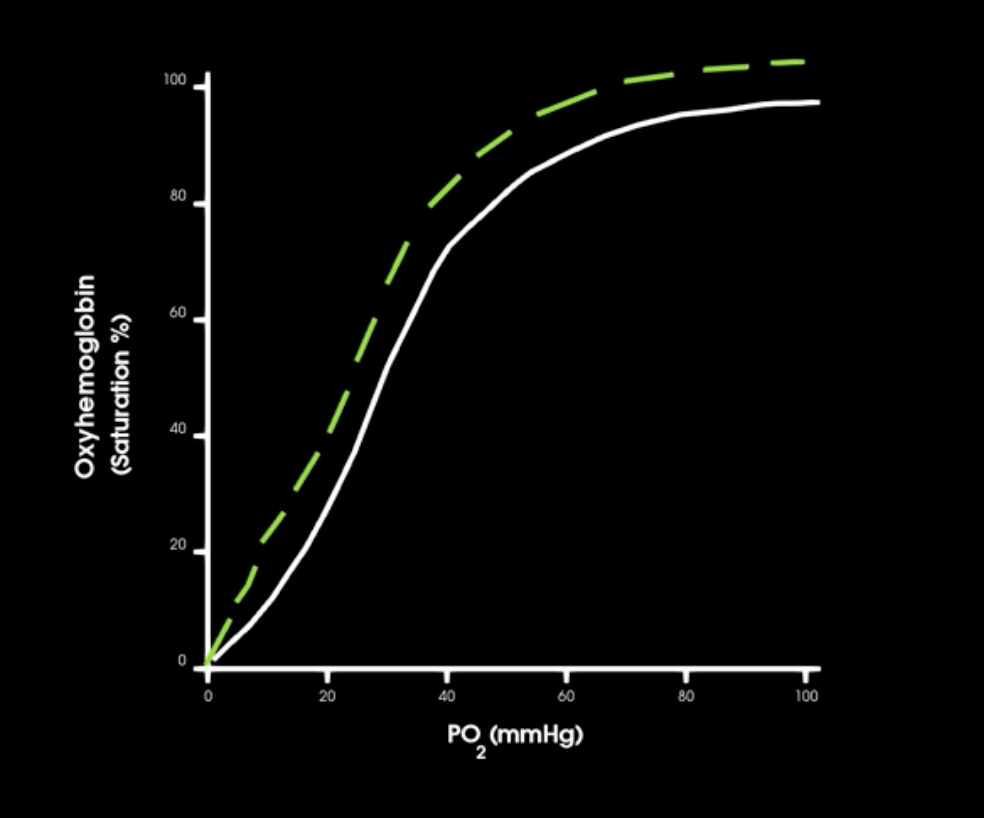
right shift in curve indicates what in hgb affinity
decrease in hgb-o2 affinity
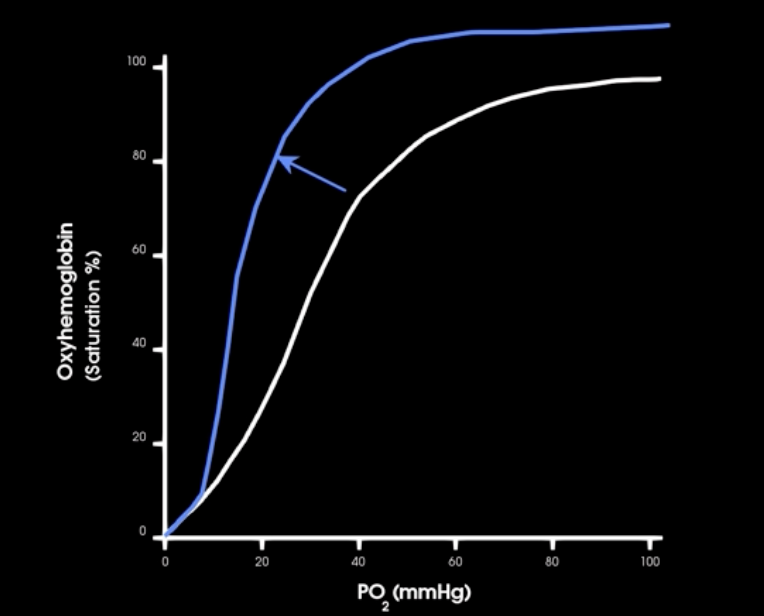
how does increase in emperature affect hgb-o2 affinity
increase in body temp causes decrease in hgb-o2 affinity and allow more o2 to be released to cells
how does decrease in temp affect hgb-o2 affinity
decrease in body temp increases o2 binding and less o2 released
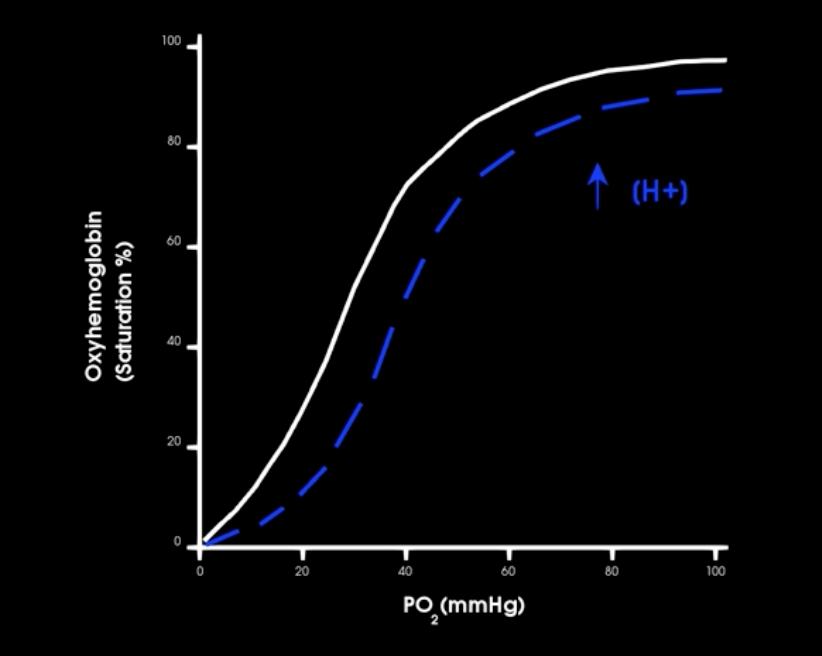
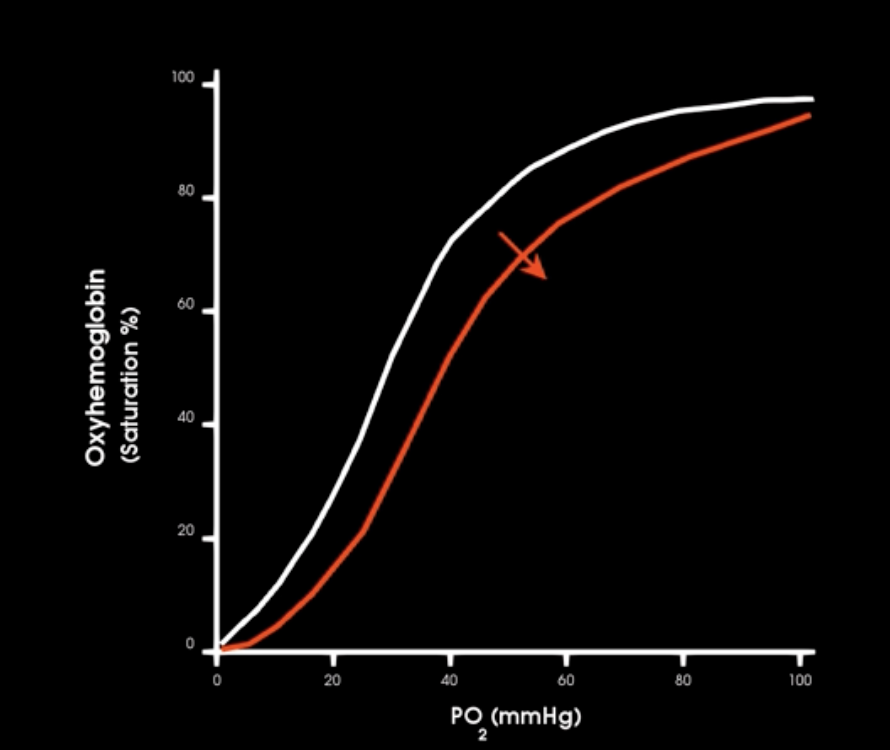
if co2 production increases how does this affect hgb-o2 affinity
which way is curve shifted
what is this affect called
shifts curve to the right, more o2 unloaded to tissues
BOHR EFFECT
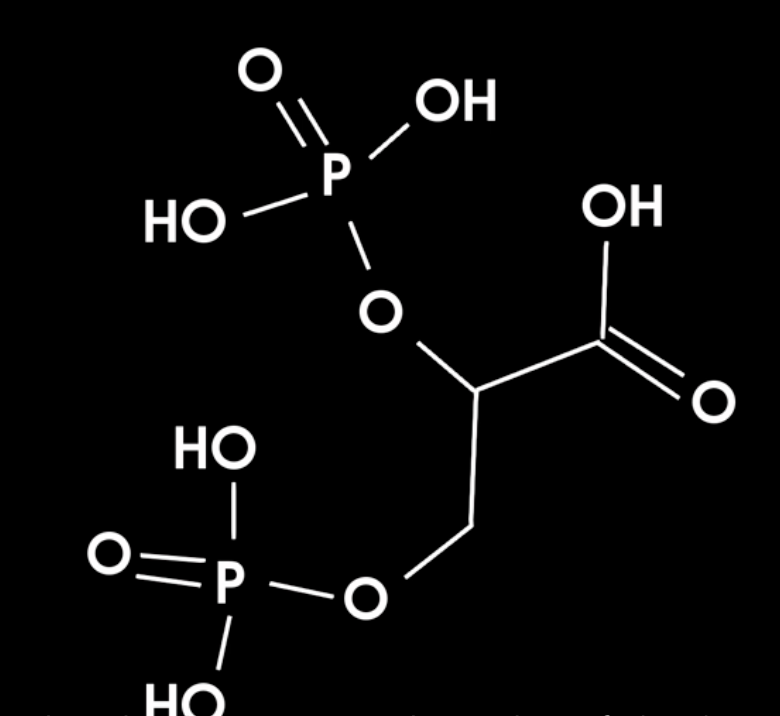
what is this and fxn?
what stimulates its production
2,3-BPG - product of glycolysis in erythrocytes
production stimulated by thyroid hormone, growth hormone, epinephrine, and testosterone
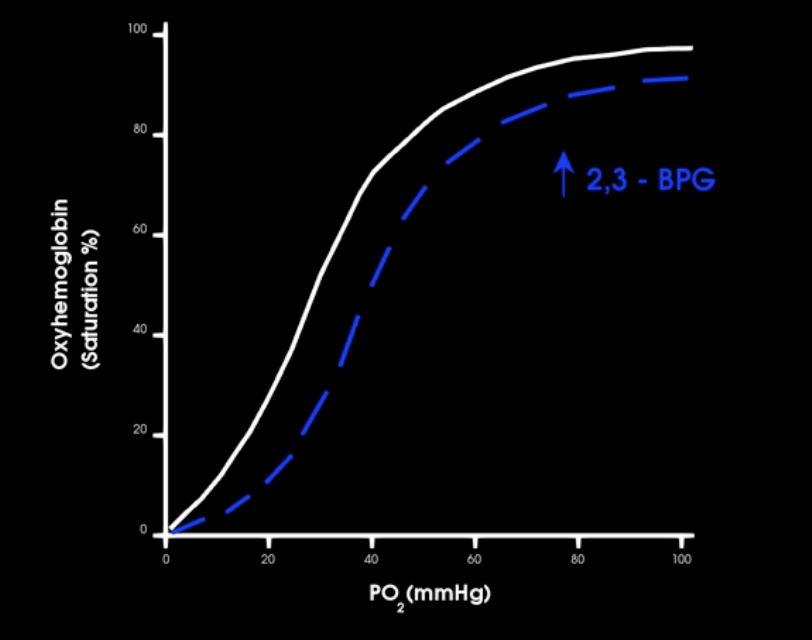
when 2,3 BPG bind to hb what happens to affinity for o2
, it decreases its affinity for O2 causing additional O2 to be released to tissues
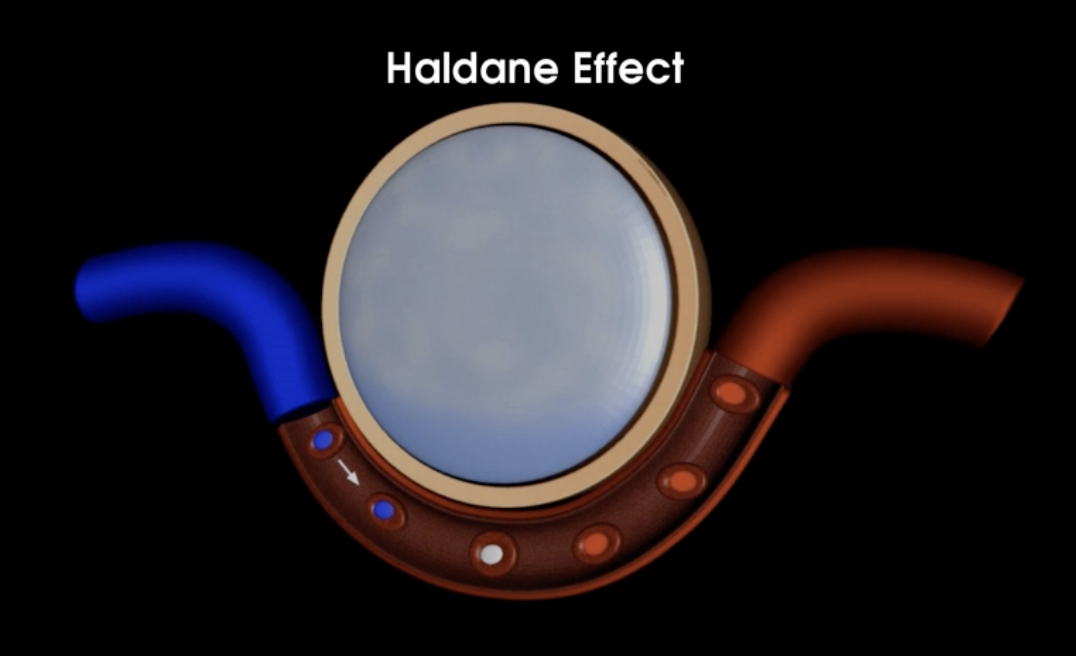
What is the Haldane effect?
the binding of o2 to hb decreases its affinity for co2
as more o2 binds to hb in pulmonary capillaries, more co2 is unloaded to be exhaled from body
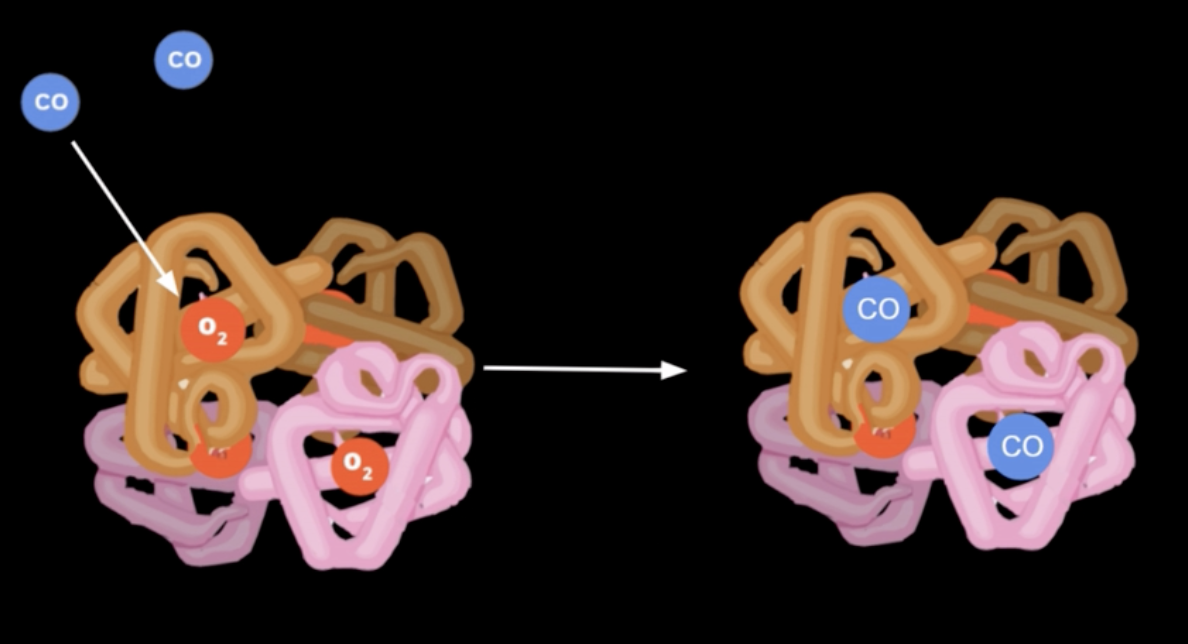
How does carbon monoxide (CO) affect o2 binding to hb
CO bind more strongly than O2
CO to hb creates carboxyhemoglobin (hbCO)
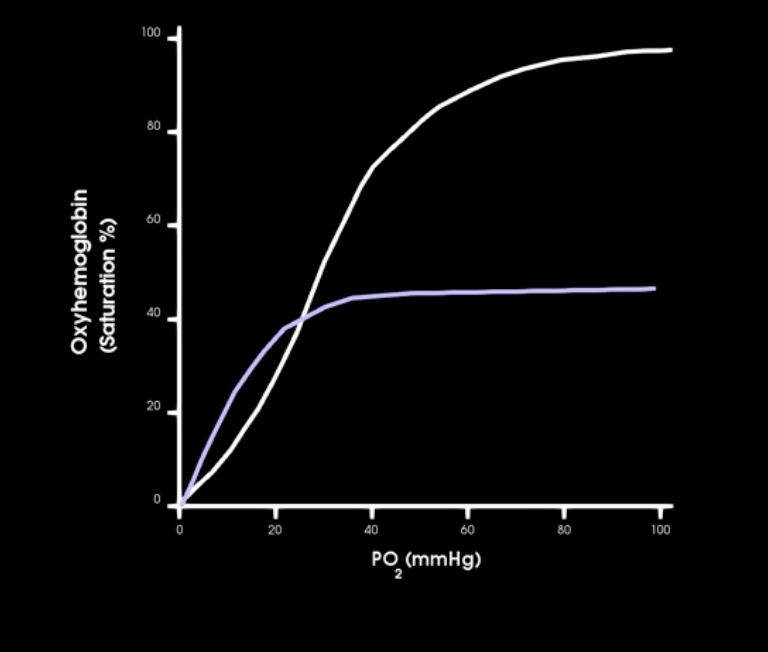
how does CO affect o2-hgb sat curve
CO binding results in lower o2 sat curve at any given PO2