Exam I - Duplex Retina
1/156
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
157 Terms
bleached
When rhodopsin absorbs light it has become _______, meaning it cannot capturing any more light until the original quantum is transmitted.
Duplicity theory
theory that above a certain luminance cones mediate photopic vision and below a certain luminance rods mediate scotopic vision. Allows for smooth adaptation to varying luminance levels.
10-6 to 106 cd/m2
the range of light levels visible by the human visual system.
10
Adaptive range of the eye is how many log units?
1
Pupillary changes account for how many log units of adaptive range?
1-2
Neural responsiveness accounts for how many log units of adaptive range?
photoreceptors
The majority of the adaptive range of the eye is due to...
photoreceptor adaptation
pupil size
concentration of photopigments
neural responsiveness
four mechanisms of light adaptation of the visual system
3.4
Cones mediate pure photopic vision at luminance levels above _______ cd/m2
0.034
Rods mediate pure scotopic vision at luminance levels below ______ cd/m2
mesopic vision
Vision mediated when both rods and cones are working simultaneously. Creates a smooth transition between photopic and scotopic vision.
1.2
Pupillary response changes retinal illuminance by ______ log units
scotopic vision
Rod mediated vision occuring at luminance levels of 10−2 to 10−6 cd/m². Poor visual acuity of 20/200 and absence of color discrimination
photopic vision
cone mediated vision at luminance levels of 102 to 106 cd/m². Excellent visual acuity of 20/200 and color discrimination.
Discs
structures present in the rod and cone outer segments that contain photopigments that absorb light quanta
rods
which photoreceptor has free floating discs?
cones
which photoreceptor does not have free floating discs?
RPE
discs of photoreceptors are phagocytized by which retinal structure?
Ciliary process
structure located between the inner and outer segments of rod and cone photoreceptors. Generates the outer segment that regenerates every 24 hrs.
rods
which photoreceptor has discs that are shed during the day?
cones
which photoreceptor has discs that are shed during the night?
inner segment
part of the photoreceptor that contain all cellular organelles except the cell nucleus.
outer plexiform layer
Both rods and cones synapse at this layer of the retina
Spherule
synaptic ending of a rod
Pedicle
synaptic ending of a cone
Retinitis pigmentosa
absence of phagocytosis of the photoreceptor discs by the RPE results in an accumulation of metabolic waste damaging rods and cones. This results in night blindness. Vitamin A supplement slows down the progression. Possible tissue transplantation, gene therapy, etc. in the future.
Retinal prosthesis
camera mounted to a spectacle frame transmits an image to a microelectrode attached to the retinal nerve fiber layer. These microelectrodes stimulate ganglion cells axons mimicking signals produced when photoreceptors are activated. Can be used to restore vision in patients with damage due to RP and other retinal disease. Does not completely imitate retinal processing.
Epiretinal design
design of retinal prosthesis where the microelectrode is attached to the nerve fiber layer stimulating ganglion cell axons.
Subretinal design
design of retinal prosthesis where the microelectrode is attached to the depth of damaged photoreceptors stimulating outer aspects of ganglion and bipolar cell layers.
Subfoveal
Placement of subretinal implant that results in better visual outcome
retinal processing
subretinal and epiretinal prosthesis are severely limited because they ignore...
Post receptor coding
design of retinal prosthesis where encoded messages produced by post-receptor retinal processing is determined, replicated and provided directly to the ganglion cells. May produce an image remarkably similar to that produced by a healthy retina.
120
there are about _____ million rods in the human retina
6
there are about _____ million cones in the human retina
20
rods are most tightly packed ______ degrees from the fovea
cones
the number of these photoreceptors remains stable with age
rods
the number of these photoreceptors decreases with age
fovea
L and M cones are most concentrated in the...
5
the percent of total cones located in the fovea. also similar to teh percent of retinal ganglion cells located in the fovea
5,10
s cones consitute ___ to ____ percent of the cone population
0.3, 0.4
s cones are not found in the central _____ to _____ degrees of the fovea
0.5
s cones have a peak density at _____ degrees from the fovea
scotopic system
which visual system has excellent spatial summation?
photopic system
which visual system has poor spatial summation?
scotopic system
which visual system has poor temporal resolution?
photopic system
which visual system has excellent temporal resolution?
scotopic system
which visual system has excellent temporal summation?
photopic system
which visual system has poor temporal summation?
Rhodopsin
the rod photopigment contained within the discs of the rod outer segment. Is capable of absorbing one photon of light in order to activate the rod. About 10^15 molecules found in the eye contributing to scotopic vision.
1000
each rod contains how many discs?
10,000
each disc contains how many molecules of rhodopsin?
10^15
how many molecules of rhodopsin are found in the eye?
transmission
the absorption spectrum for rhodopsin is the reciprocal of the ______ curve
507 nm (blue green)
the peak absorption for rhodopsin and therefor the scotopic system. Other quanta will be absorb as well, but with less probability.
1
how many quanta of light are required to bleach a molecule of rhodopsin?
5.2 minutes
half time of rhodopsin
Principle of univariance
once a quantum of light is absorbed by rhodopsin, all information regarding its wavelength is lost. This is why rods do not have color discrimination.
Spectral sensitivity
the relative efficiency of detection of light as a function of wavelength of the signal.
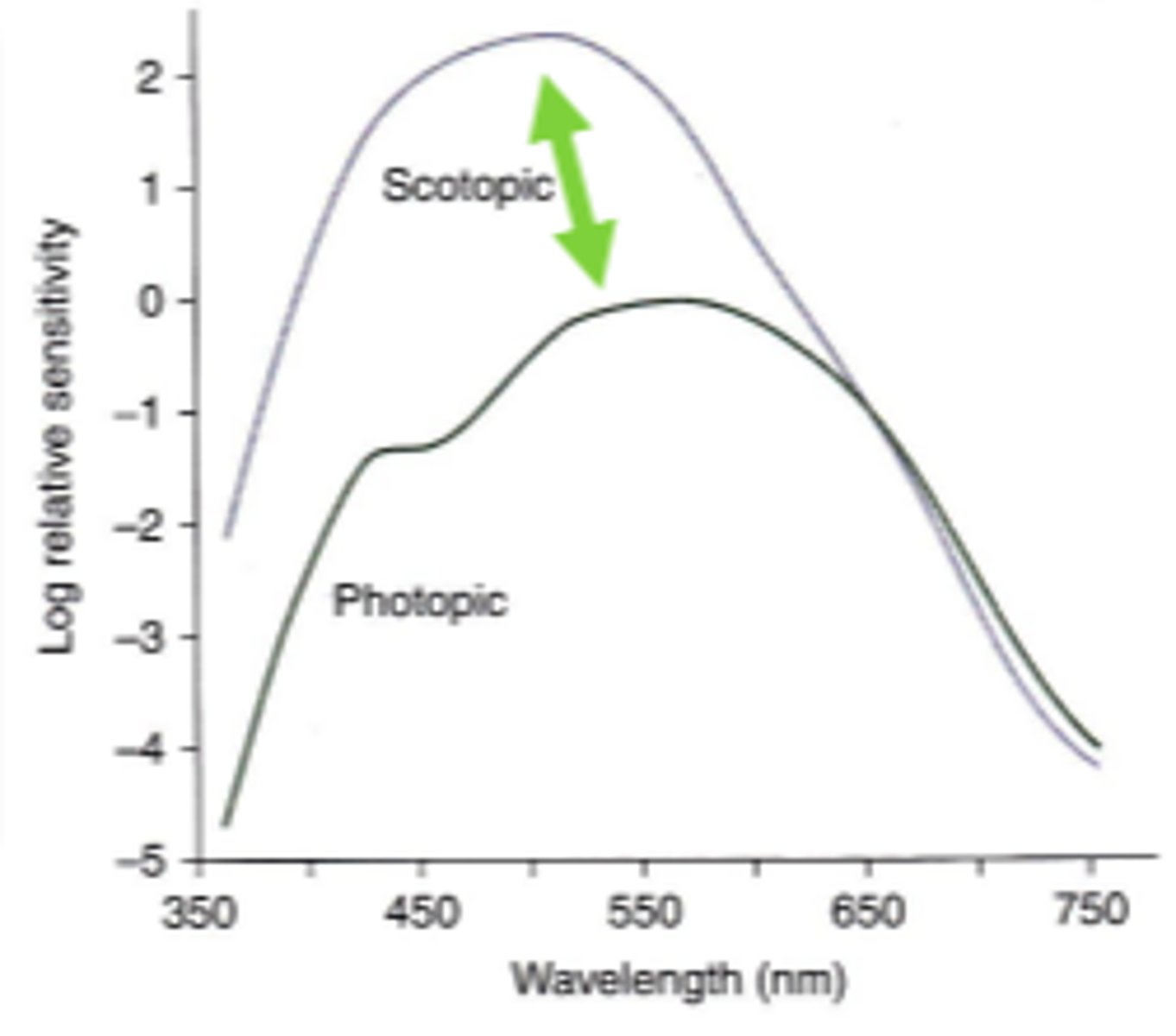
Scotopic spectral sensitivity
ability to detect light stimuli under scotopic condition. Determined by the rhodopsin absorption curve. Demonstrated by dark adapting a subject and measuring the minimum amount of energy required to detect stimuli of various wavelengths. Very similar to the rhodopsin absorption spectrum because rhodopsin is the only photopigment present in the scotopic system.
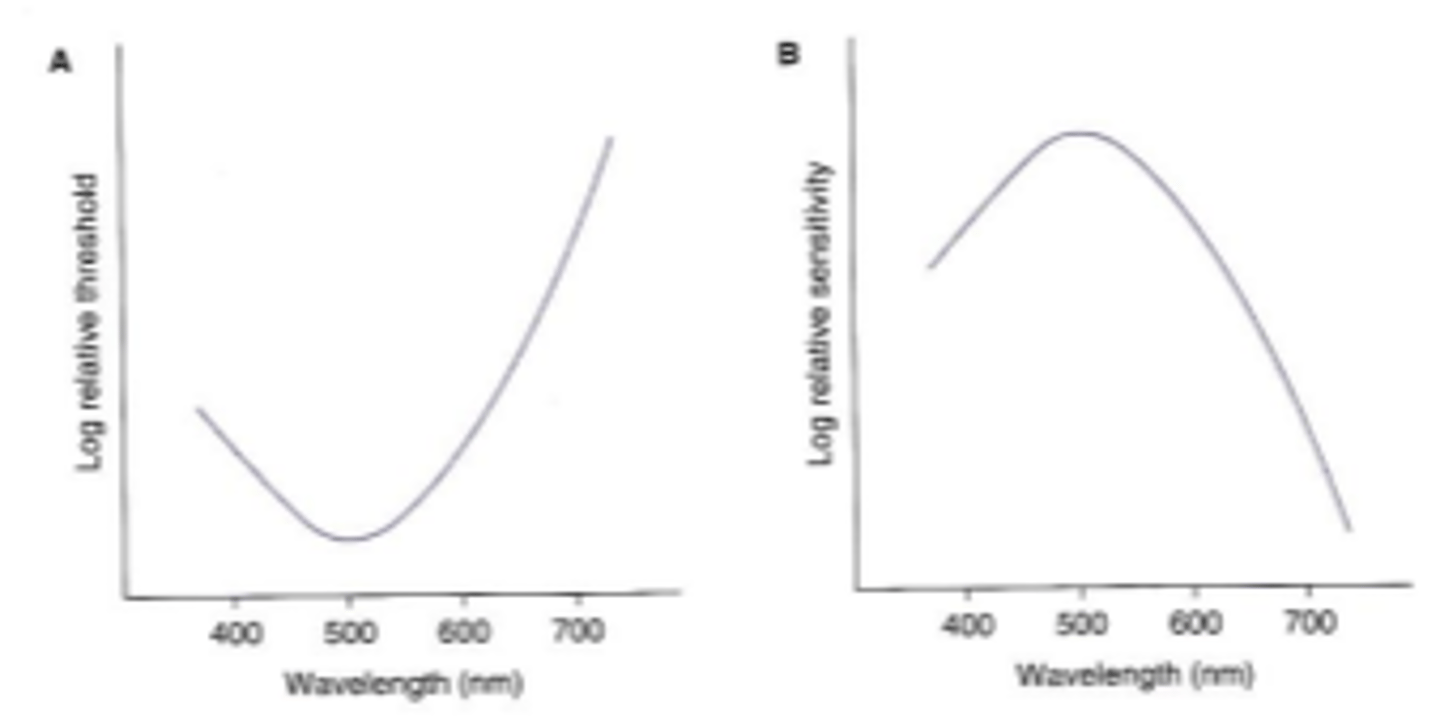
Threshold
the minimum amount of energy required to detect stimuli
Sensitivity
the inverse of threshold.
10
how many rods are required to activate a single ganglion cell?
1
how many activated ganglion cells are required for stimulus detection?
20
Less than what percent of quanta incident on the retina are absorbed by rhodopsin?
Spatial and temporal summation
two conditions required for the detection of light quanta by rhodopsin. Quanta must occur within a certain space and time constraint.
555 nm
the maximal sensitivity of the photopic system
cyanolabe
chlorolabe
erythrolabe
the three fundamental cone photopigments
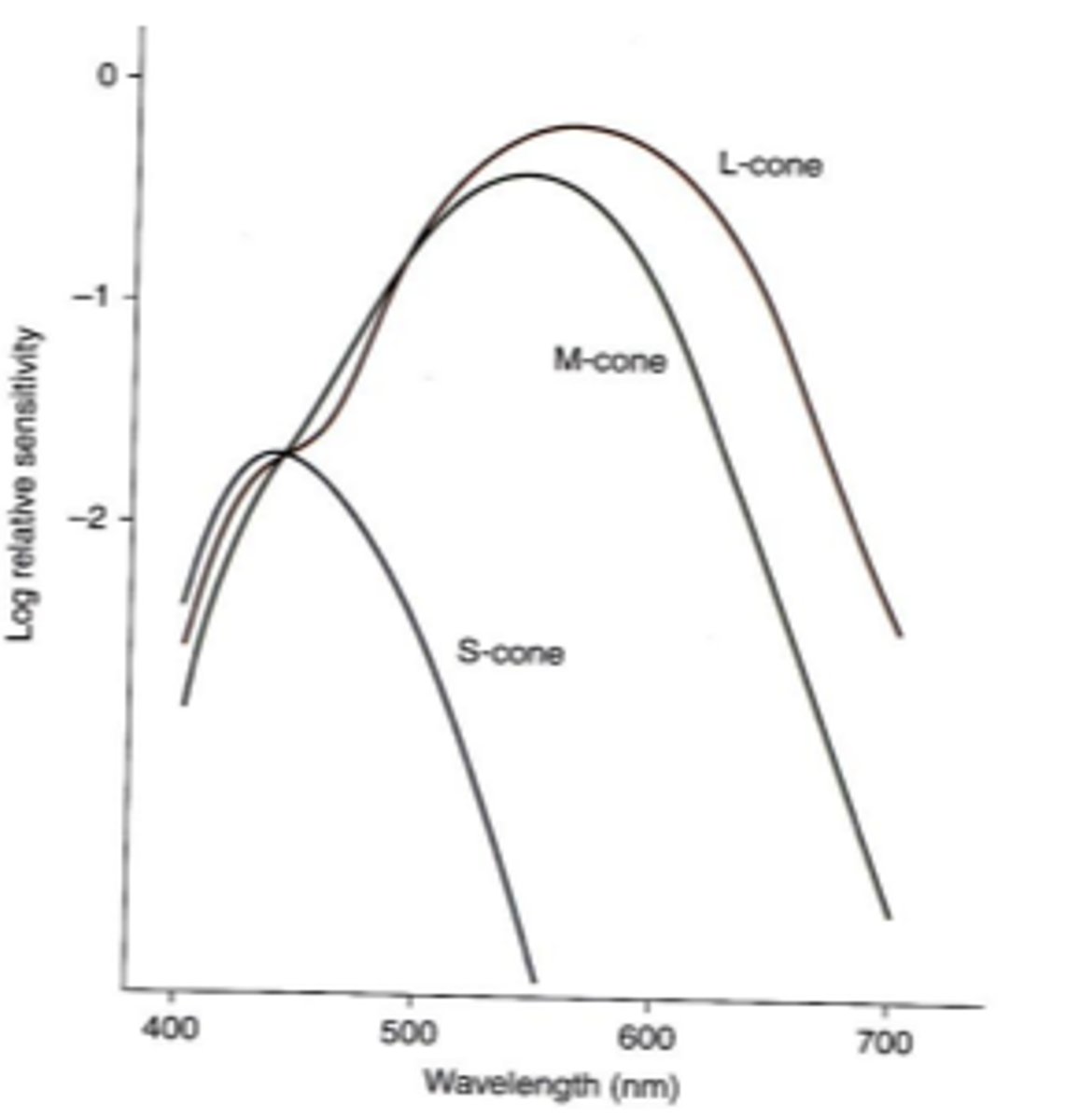
426 nm
peak absorption of cyanolabe s cone photopigments
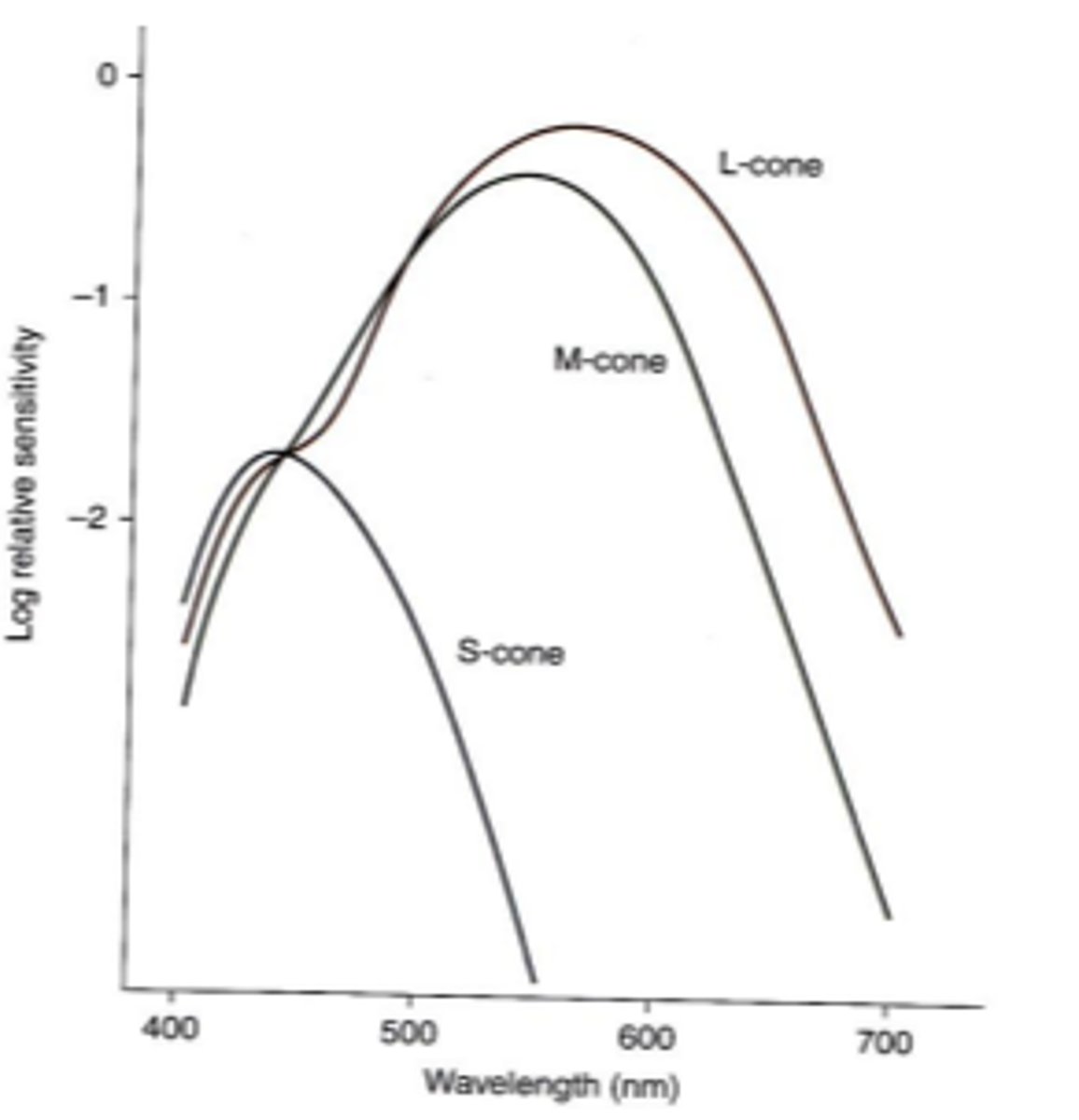
530 nm
peak absorption of chlorolabe m cone photopigments
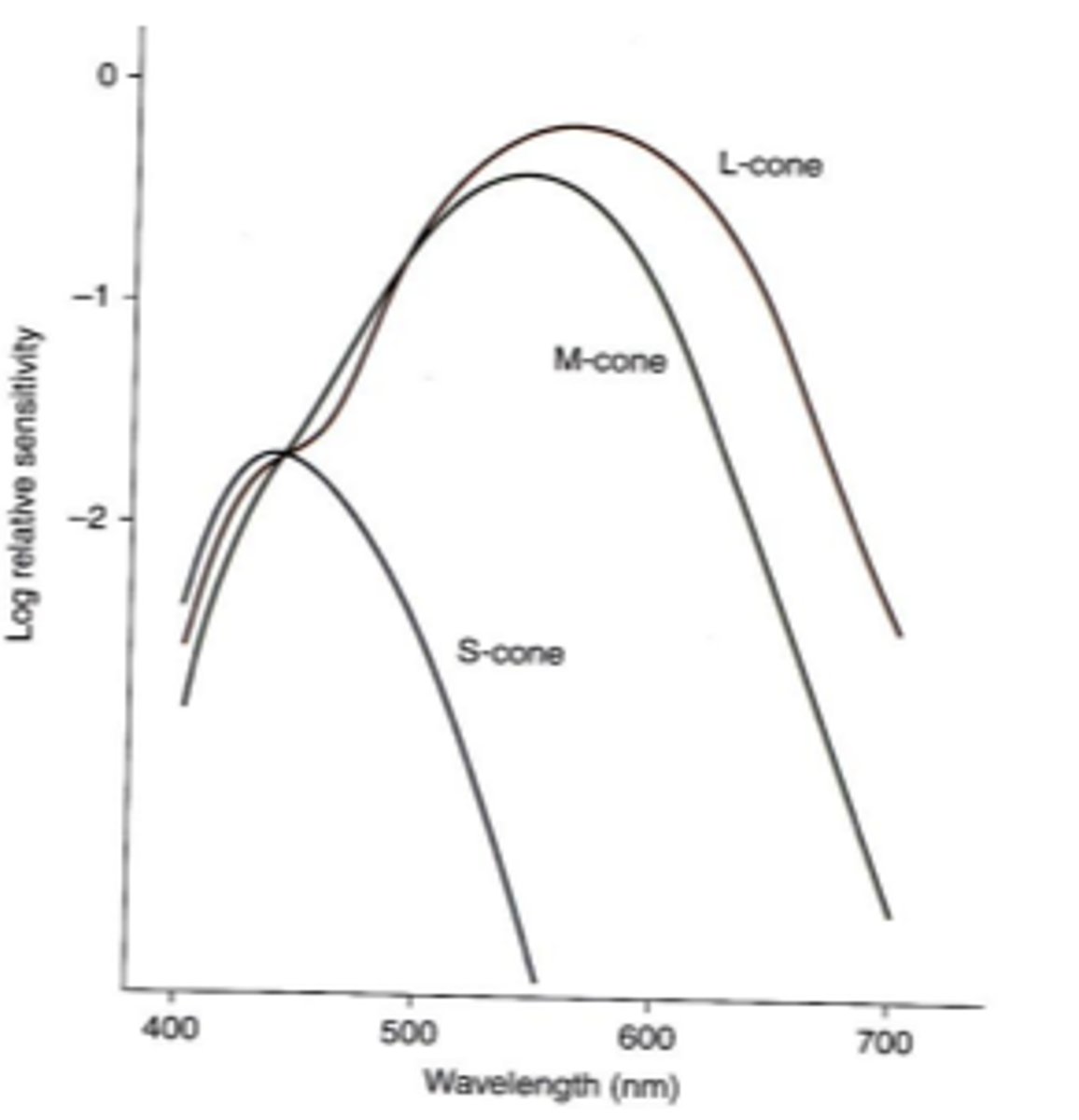
552and 557 nm
peak absorption of erythrolabe l cone photopigments (2)
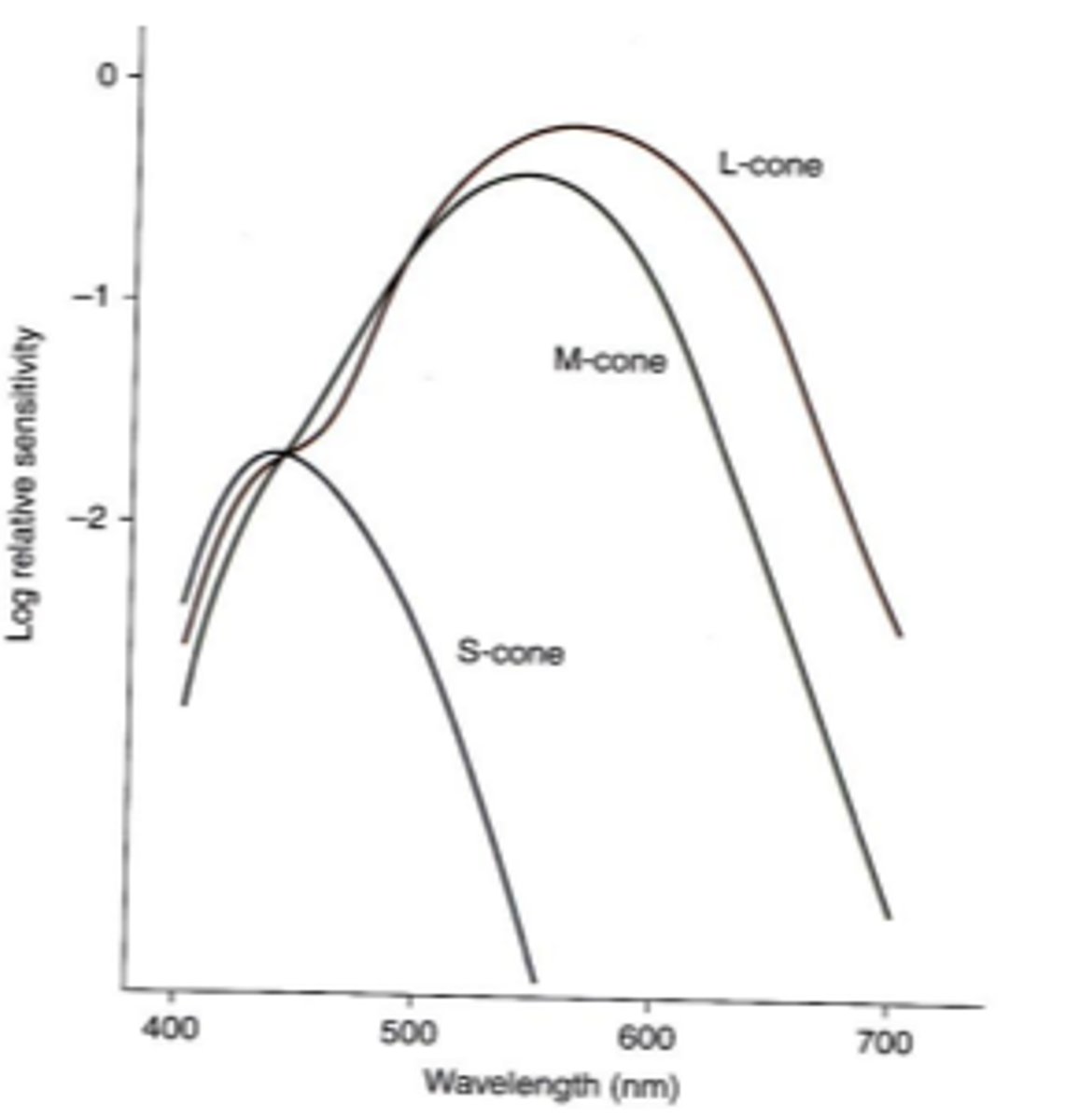
cone photopigments
do cone photopigments or rhodopsin recover at a faster rate from bleaching?
1.5 min
half time of cone photopigments
L, M, S
the photopic spectral sensitivity curve represents the addition of ____ and ____ cones because _____ cones make little to no contribution to photopic spectral sensivity
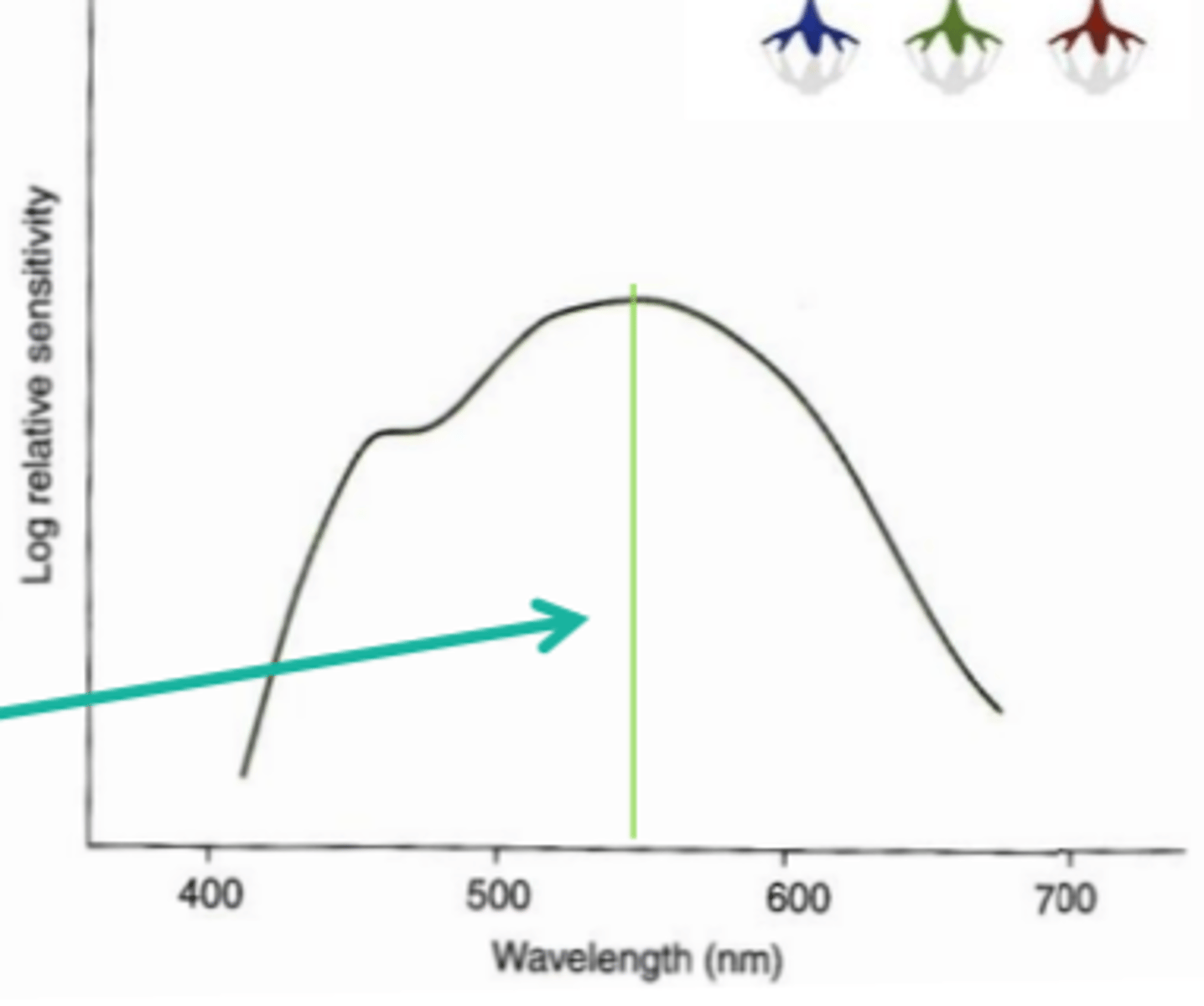
Photochromatic interval
difference in sensitivity between scotopic and photopic systems for a given wavelength.
long (red)
In this wavelength the photochromatic interval is zero because rods and cones are equally sensitive to this wavelength.
more
in all wavelengths but red and beyond, the scotopic system is (more/less) sensitive.
650
beyond what wavelength is the photopic system slightly more sensitive?
Purkinje shift
as lighting conditions change from scotopic to photopic, the wavelengths to which we are sensitive increases from 507 to 555 nm. Results in a relative increase in brightness of longer wavelength stimuli as lighting changes.

Visual adaptation
process whereby the visual system adjusts its operating level at the prevailing light level. A brief change in sensitivity or perception when exposed to a new or intense stimulus.
Light adaptation
the process that decreases the visual system's light sensitivity in response to adapting light.
Dark adaptation
processes that increases light sensitivity in response to time in darkness.
Bleaching
process that causes reduction in sensitivity of photoreceptors in response to light stimulus. Photopigments become almost transparent, then regenerate to regain their pigmentation. Cannot absorb any more light quanta
Dark adaptation curve
graphical representation of rod and cone recovery dynamics after light exposure/bleaching. Represents the lowest threshold at any given point of time for both rods and cones. Useful in clinical diagnosis of various retinal disorders
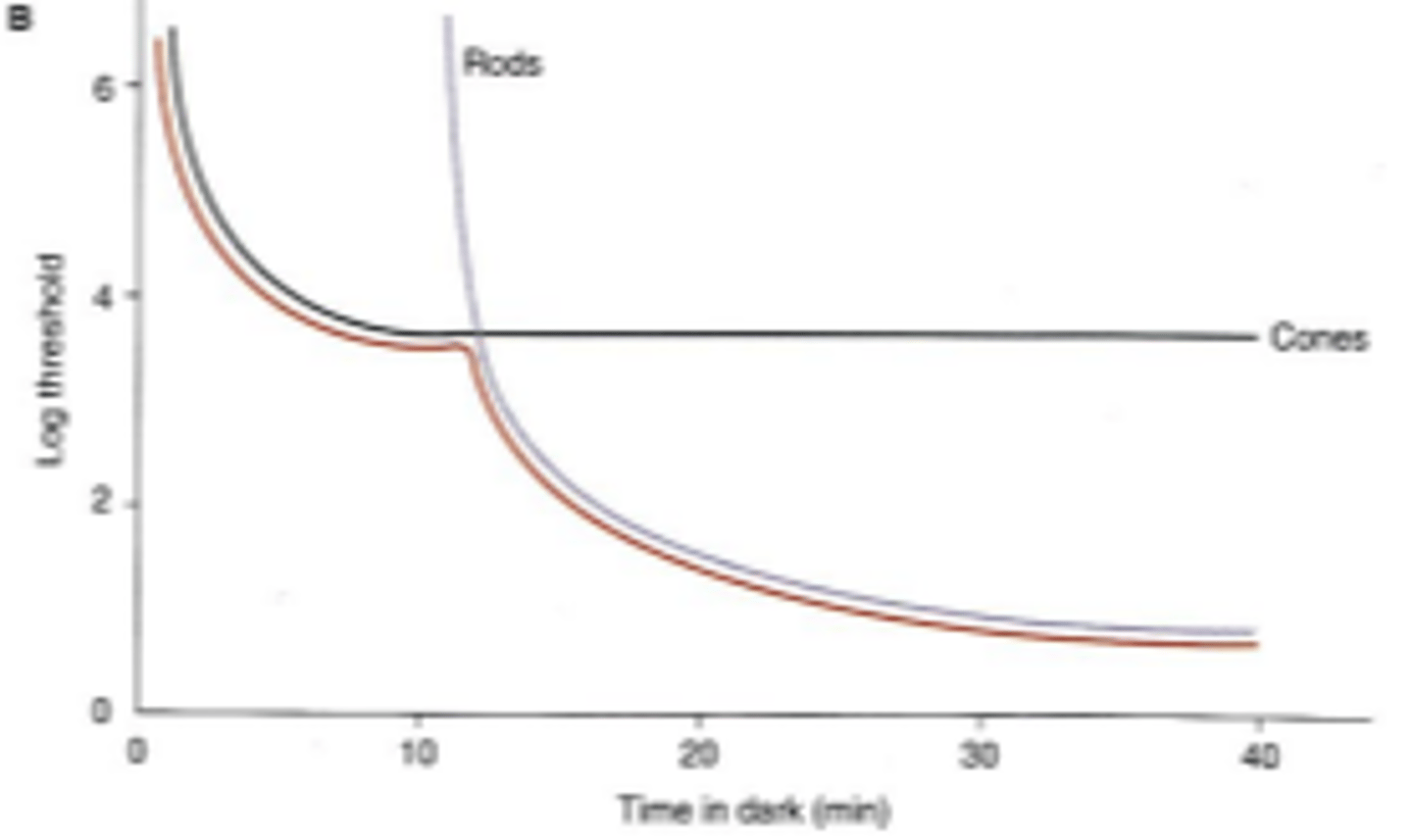
infinitely high
in early dark adaption, the threshold for rods is...
Adapting light
bright light used to initially bleach all photoreceptors to generate the dark adaptation curve.
Detection threshold
determined as a function of time for a stimulus flashed against a totally dark background after adapting light is turned off. Used to generate the dark adaptation curve.
420 nm short wavelength
wavelength used to generate the dark adaptation curve because it stimulates both rods and cones
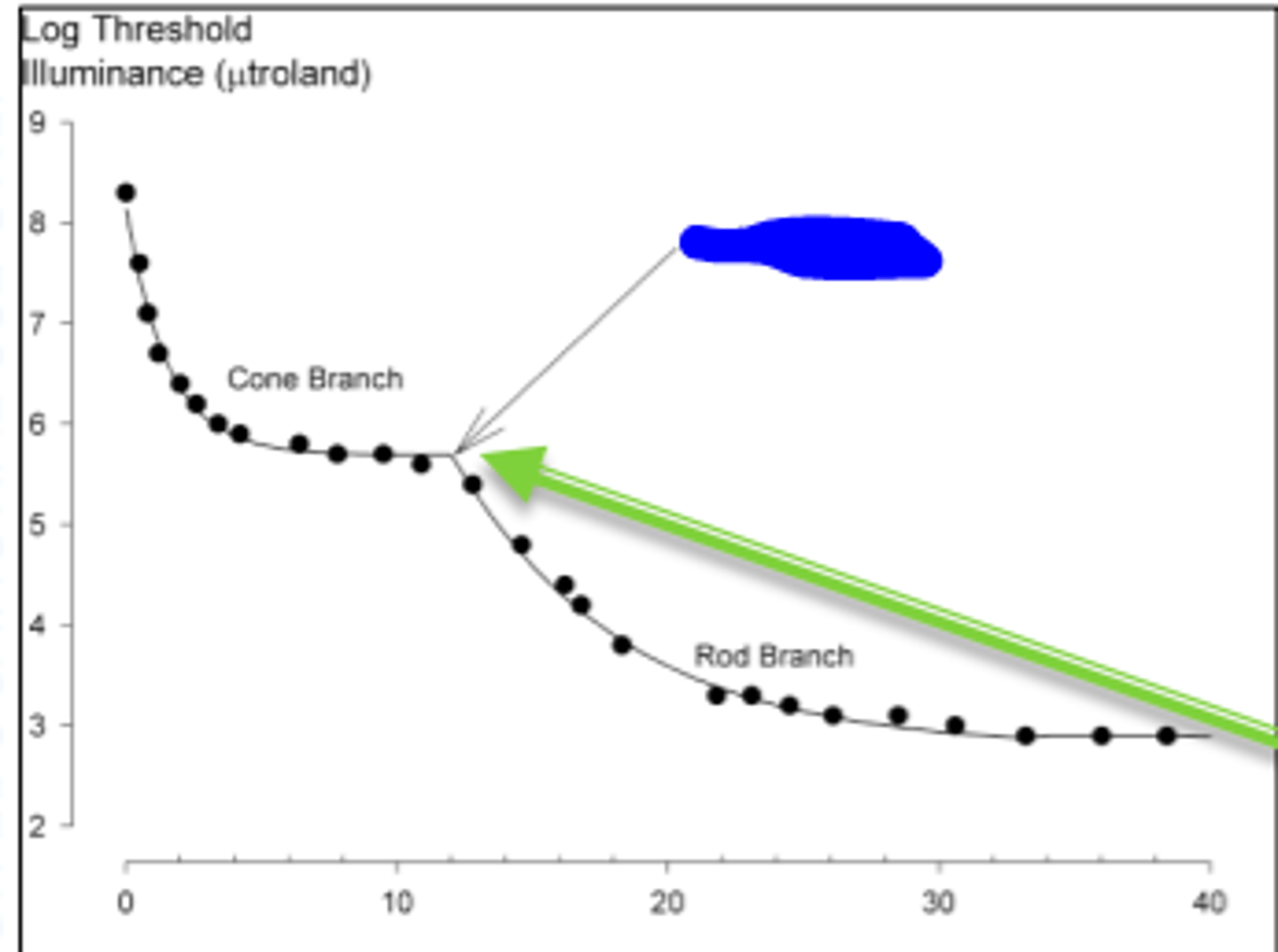
cone branch
branch of the dark adaptation curve occuring during the first ten minutes. Color can be detected during this part of the dark adaptation curve. Cones are more sensitive than rods because they recover faster from bleaching
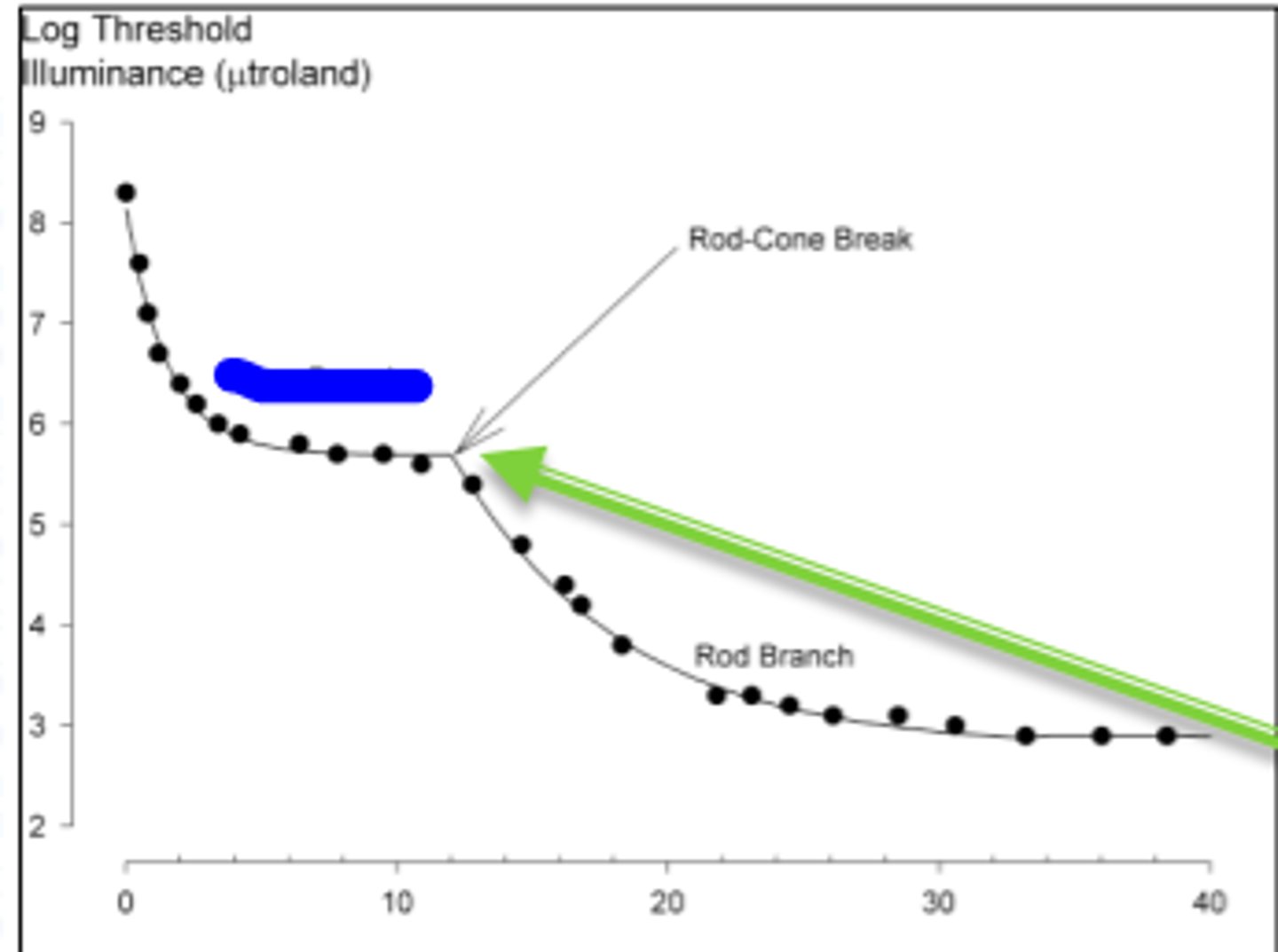
cone branch
branch of the dark adaptation curve occuring after about 12 minutes. At this point, rods are more sensitive than cones.
rod cone break
point in the dark adaptation curve where rods become more sensitive than cones. Divides the portion of the dark adaptation curve where the patient detected the test flash using cones, and the where the patient detected the test flash using rods. Occurs at about 12 minutes
35
Rods are fully dark adapted when the dark adaptation curve reaches a plateau. This occurs after approximately how many minutes?
rod cone break, rod
the dark adaptation curve for a rod monochromat will exhibit no _______, and only a ______ branch
5
when rods are fully dark adapted, threshold of the dark adaptation curve reduces by _____ log units.
remains constant
how does the rod cone break of the dark adaptation curve change with age?
2,3
After 40 years of age, each additional decade increases threshold of rods and cones by ____ to _____ log units. This results in a decreased ability to recover visual sensitivity from bright lights.
cone branch only
How does a small, centrally fixated test stimulus affect the dark adaptation curve?
rod
a dark adaptation curve with a 650 nm stimulus will show no _____ branch. This is because rods are no more sensitive than cones to this wavelength.
10
50% bleaching of rhodopsin increases threshold by _____ log units. This accounts for slow recovery in sensitivity that follows exposure to a bright adapting light.
Rod monochromats
patients having only rods, no cones. Extremely photophobic. Patients are essentially blind under photopic conditions. Can wear dark sunglasses to lessen the bleaching of rhodopsin and preventing rod saturation. Red tints can also be used because long wavelengths are not effective at bleaching rhodopsin.
no cone branch
If the adapting light of the dark adaptation curve is very dim or red colored, the rods are not stimulated and are immediately dark adapted and sensitive to the stimulus. This will show...