Fungi - Chp 21 just practical nf
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
Mycology
the study of fungi
What are the characteristics of fungi?
eukaryotic/have membrane bound organelles
reproduces asexually + sexually
heterotrophic
have cell walls made from chitin
made up of many tubes called hyphae which form a visible mycellium
multinucleate
Hypha
tube or filament in a fungus
Mycelium
visible mass of hypha
Parasitic Fungus + Example
live in or on another living orgnanism causing harm
athlete’s foot
What is an obligate parasite?
lives on a host and does not cause it harm or kill eg mildew
What is a facultative parasite?
kills the host and feeds on the dead remains eg soft rots in fruit
Saprophytic Fungus + Example
live on dead organisms: decomposers eg mould
Examples of edible fungi
standard fiel mushroom - above ground
truffle - below ground
Examples of poisonous fungi
death cap + destroying angel
How is food digested by fungus?
digested extracellularly
enzymes are secreted onto the food
nutrients are absorbed into the hyphae
What is a method of identification of fungi
spore prints
What does Aseptate mean?
nuclei in the fungus are not separate by walls and can move freely in the hyphae
What is the name of common bread mould?
Rhizopus
What type of fungus is rhizopus?
saprophytic
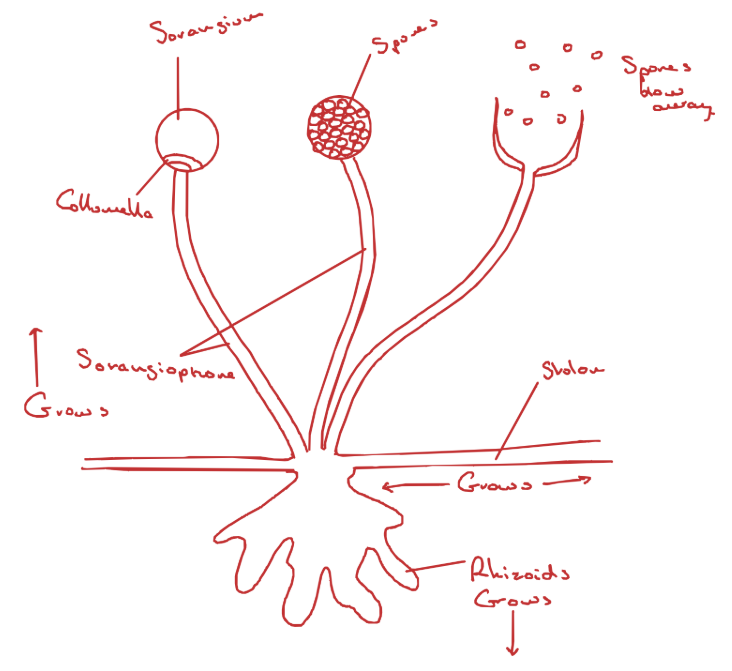
Rhizopus diagram
Hyphae - function
secrete digestive enzymes + absorb the digested food
Stolon - structure
aerial hyphae growing horizontally that spread over the surface + turn downward to create rhizoids
Rhizoids - function + structure
branched hyphae that penetrate the food source + anchor the fungus
releases digestive enzymes + absorbs the digested food
Sporangiophore - structure
hyphae that grow up from the surface of the substrate vertically
Sporangium - structure
swelling at the ip of a sporangiophore containing spores which divide by mitosis
What are spores
small light asexual reproductive structures that are carried by the wind
Columella
a cross wall pushin up into the sporangium from below + separate spores from the sporangiophores
Apophysis
swelling below the sporangium
Outline the 3 types of hyphae:
Rhizoids - grow down
Stolon - grows across
Sporangiophore - grows up
How does rhizopus normally reproduce + why does it change method?
normally asexual by sporulation
sexual reproduction occurs in adverse conditions such as dehydration
Describe asexual reproduction of rhizopus:
sporangium divides by mitosis to produce haploid cells
each cell develops a wall and becomes a spore
sporangium bursts in dry conditions to release spores
spores dispersed by wind
germinate if they land on a suitable substrate
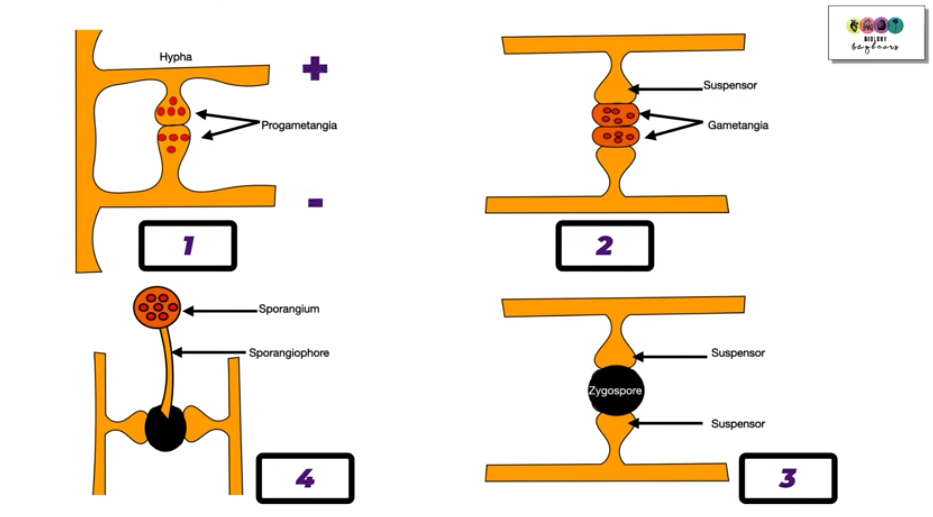
Describe sexual reproduction of rhizopus:
2 chemically opposite hyphae (+ and -) come into contact
swellings form and eventually touch
nuclei move into swellings to form progametangia
cross walls form behing the progametangia to produce gametangia + block other nuclei from entering
suspensors support the gametangia
walls break down between the gametangia allowing the nuclei to fuse to form a diploid zygote
a tough, black wall forms around the zygote to produce the zygospore
zygospore germinates by meiosis when conditions are suitable
hypha grows out of zygospore to produce sporangium, which releases many haploid spoires to produce new hyphae
What is another name for yeast cells?
saccharomyces
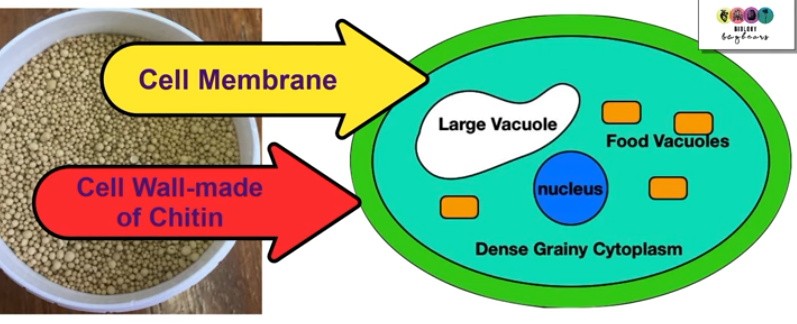
Describe the structure of a yeast cell:
single celled
round or ovular
cell walls made from chitin
has a dense cytoplasm that contains many food storage vacuoles + one large vacuole
food stored as glycogen
has one nucleus
How do yeast cells reproduce?
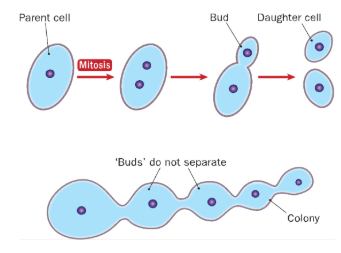
asexually by a process called budding
Describe the process by which yeast cells reproduce
a small extension called a bud appears on a parent cell
the parent nucleus divides by mitosis
one nucleus and some cytoplasm enter the bud
the bud breaks away from the parent cell or may remain attached
Name 2 economic benefits of fungus:
mushrooms are a source of food that are sold
yeast is used for fermentation to produce alcohol and in baking
Name 2 economic disadvantages of fungus:
can destroy materials such as food, crops and wood
can cause diseases such as athlete’s foot
What is asepsis?
all pathogens destroyed
How can asepsis be achieved?
washing hands before and after
hair tied back
disinfect bench before and after
do not put hands near mouth
keep all containers closed
What does sterile mean?
all micro-organisms are destroyed
Techniques for sterilisation
flaming
swabbing with disinfectant
immersion in liquid disinfectant