Unit 4 Part 2 - Cellular Respiration (Biology 9H)
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Cellular respiration
Process by which molecules (glucose & oxygen) are broken down to release energy (ATP) for the cell.
Either aerobic (with oxygen) or anaerobic (w/o oxygen)
3 stages for aerobic= glycolysis, Krebs cycle, & electron transport chain
2 stages for anaerobic = glycolysis and fermentation
Biochemical pathway : series of chemical reactions where products of one become reactants for the next
2 ways to convert glucose into ATP
Fermentation (anaerobic respiration) - makes 2 ATP & doesn’t need oxygen
Aerobic respiration - makes 36 ATP & needs oxygen
Mutualism
Win-win relationship
Ex.: bacteria benefit from living in our intestines since they get food & a warm environment.
We benefit from having bacteria since we get short chain fatty acids which we digest.
Fermentation
Occurs in the cytoplasm
Lactic acid fermentation
Produces 2 lactic acid & 2 ATP
Occurs in bacteria & mammals
I.e. cheese, kimchi, yogurt, sauerkraut
Alcoholic fermentation
Produces 2 alcohol (ethanol) & 2 CO2 & 2 ATP
Occurs in yeast
Fermentation recycles NAD+ back to glycolysis
Important bc it results in glycolysis producing ATP even if there’s no oxygen (anaerobic)
Aerobic respiration equation & where it occurs
C6H12O6 + 6O2 ==> 6H2O + 6CO2 + ~36 ATP
Occurs in the mitochondria
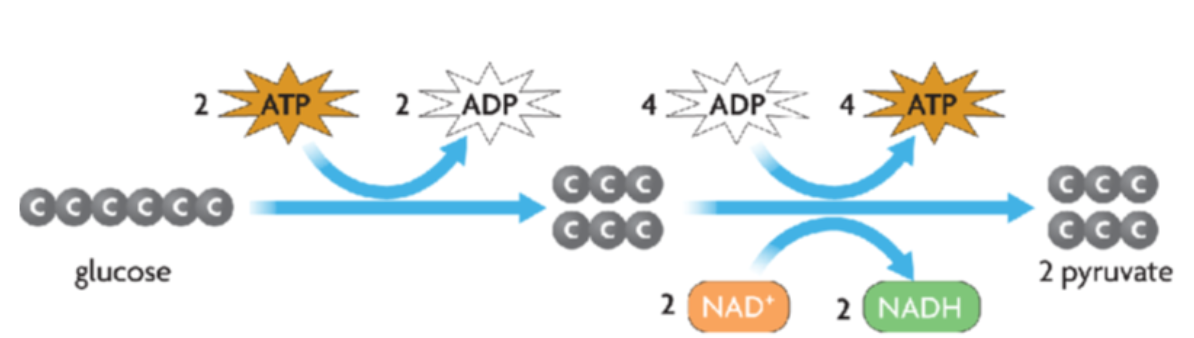
Glycolysis
First stage of cellular respiration
Occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell
Breaks down glucose into 2 3-C pyruvate molecules (used in aerobic respiration)
Produces ATP and NADH
NADH = carries electrons to the Electron Transport Chain (final stage of aerobic respiration)
Doesn’t use oxygen (anaerobic)
Krebs cycle
Second stage of aerobic respiration
Occurs in the matrix of mitochondria
Adds electrons to NAD and FAD
Produces NADH, FADH2, ATP, CO2
NADH and FADH2 → go to Electron Transport Chain
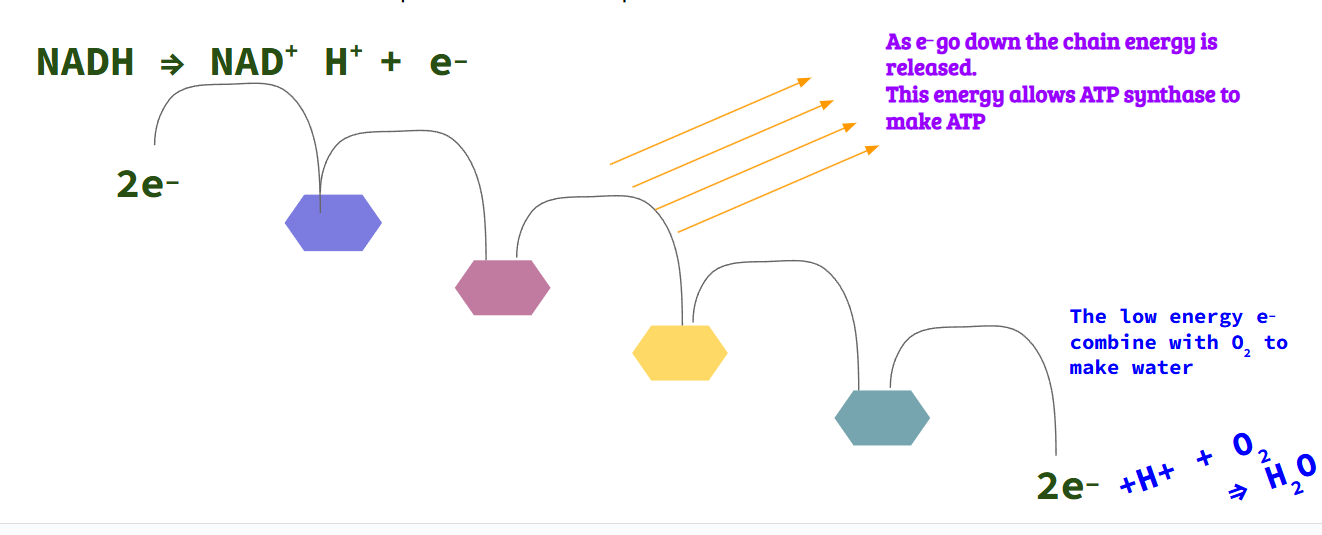
Electron Transport Chain
Third stage of aerobic respiration
Is a series of proteins
Uses reactant O2 which is not from Krebs cycle
Occurs in inner membrane of mitochondria
Uses electrons carried by NADH and FADH2 molecules from Krebs cycle
Produces ATP and water
NADH ⇒ NAD+ H+ + e_
As the e- (electron) goes down the chain → energy released
→ATP synthase (enzyme) makes ATP
Low energy electron @ the bottom of the chain combines w/ O2 and H+ to make water.
When is glucose used?
Glycolysis
When is oxygen used?
Electron Transport Chain
When is water made?
Electron Transport Chain
When is carbon dioxide (CO2) made?
Krebs cycle
When is ATP made?
Throughout cellular respiration, but mostly in the ETC for aerobic respiration
Why do you die when you are deprived of oxygen?
You need oxygen for cellular respiration in order to sustain your body, as the amount of ATP made by fermentation (anaerobic respiration), which doesn’t need oxygen, is not enough energy to survive.
What elements are sugar molecules made of?
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
Why do organisms perform respiration instead of just using glucose?
Glucose is better for energy storage, while ATP is better for fuel and serves as an energy currency (fuels cellular processes) as it can be directly used.
What will happen if you forget to add yeast to your bread?
A) Dough will not taste sweet
B) Dough will contain alchohol
C) It will not rise
D) All of the above
C
How is it possible for plants to release carbon dioxide and oxygen at the same time? (About chemical reactions & the speed they occur)
Plants do photosynthesis (O2) and cellular respiration (CO2) simultaneously, but they do photosynthesis at a higher rate. The oxygen produced in photosynthesis is used in respiration; the oxygen they don’t use is then released by the plant to the atmosphere.
This means that during the daylight, there is more O2 being released than CO2 is being taken in.
What role do photosynthesis and cellular respiration play in forming carbon-based compounds?
Carbon-based compounds = glucose
Photosynthesis: makes glucose by taking CO2 from the atmosphere & bonding the carbons (w/ other elements) together
Cellular respiration: breaks down glucose to release energy. CO2 is a waste product & returned to the atmosphere.
For photosynthesis and cellular respiration, are they endothermic or exothermic?
Photosynthesis - endothermic
Cellular respiration - exothermic
How is breathing related to cellular respiration?
When you breathe, you let in oxygen to your body which you need to perform cellular respiration to produce ATP. You also release the excess CO2 (product of respiration) when you exhale.
You take in O2 and get rid of CO2 through your lungs.
Do skin cells or the cells in your bicep muscles have more mitochondria? Why?
Bicep muscles because you use your muscles more often when you exercise. When exercising, you have to breathe in more oxygen to produce enough energy in respiration, and respiration occurs in the mitochondria. Your muscle cells use more ATP when exercising.
Why does a person breathe faster and deeper when they are exercising? Use the fact that when a person exercises, their muscle cells use much more ATP.
In order for aerobic respiration, the person needs to breathe in oxygen so they can make enough ATP, which they need more of when exercising. If they don’t breathe enough oxygen, they would have to do anaerobic respiration which doesn’t produce enough ATP/energy.
More carbon given off by respiration & decomposition than taken in by photosynthesis.
Is it a carbon source or sink, and is the Net Ecosystem Exchange (NEE) positive or negative? When does this occur?
Carbon source
NEE is positive
Usually happens at night & in the winter, since photosynthesis doesn’t occur.
More carbon taken in by photosynthesis than given off by respiration & decomposition
Is it a carbon source or sink, and is the Net Ecosystem Exchange (NEE) positive or negative? When does this occur?
Carbon sink
NEE is negative
Usually happens during the summer and day since there is a lot of light and photosynthesis occurs.