GENOMICS & SEQUENCING OF GENOMES
1/12
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
13 Terms
Genomics
the study of an entire genome(s)
Subfields of genomics
functional genomics
comparative genomics
Functional genomics
examines relationship between genotypes or sequences at any loci with the resulting phenotype
ex: GWAS heart disease
Comparative genomics
align genome sequences between two or more group (e.g. species) to identify differences or similarities)
ex: comparing wooly mammoth + modern elephant genomes
Medical genomics
identification of gene variants that make cancers aggressive
sequence DNA from diff breast cancers, some w/ good prognosis & some w/ poor prognosis
identify & compare mutations between the two groups
compare genome from patient’s tumor to the known genomes
Personalized medicine
tailor treatment of disease to a person’s specific genome profile
Pharmacogenetics
identify drug treatments that correspond w/ a person’s genome profile
Human genome project
done using the whole-genome shotgun approach
create genomic library → sequence each clone
Sanger sequencing (dideoxy sequencing)
sequence DNA using one relatively short piece of DNA at a time
still used today to sequence one or a few segments of DNA
based on PCR amplification of the DNA you want to sequence
template can be linear or circular
Taq polymerase adds nucleotides starting from a primer based on complementary sequences
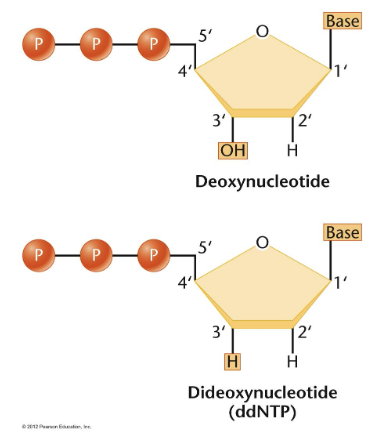
Chain-terminating reaction
Both dNTPs and ddNTPs are added to the reaction
Polymerase can add either dNTP or ddNTP equally well (doesn’t favor one over the other)
Incorporation of ddNTP causes synthesis of that one new strand to stop
Another base can’t be added to its 3’ carbon
Each ddNTP is labeled a different fluorescent color
Reaction products are a mixture of different length products, each with the last nucleotide labeled according to the identity of the base
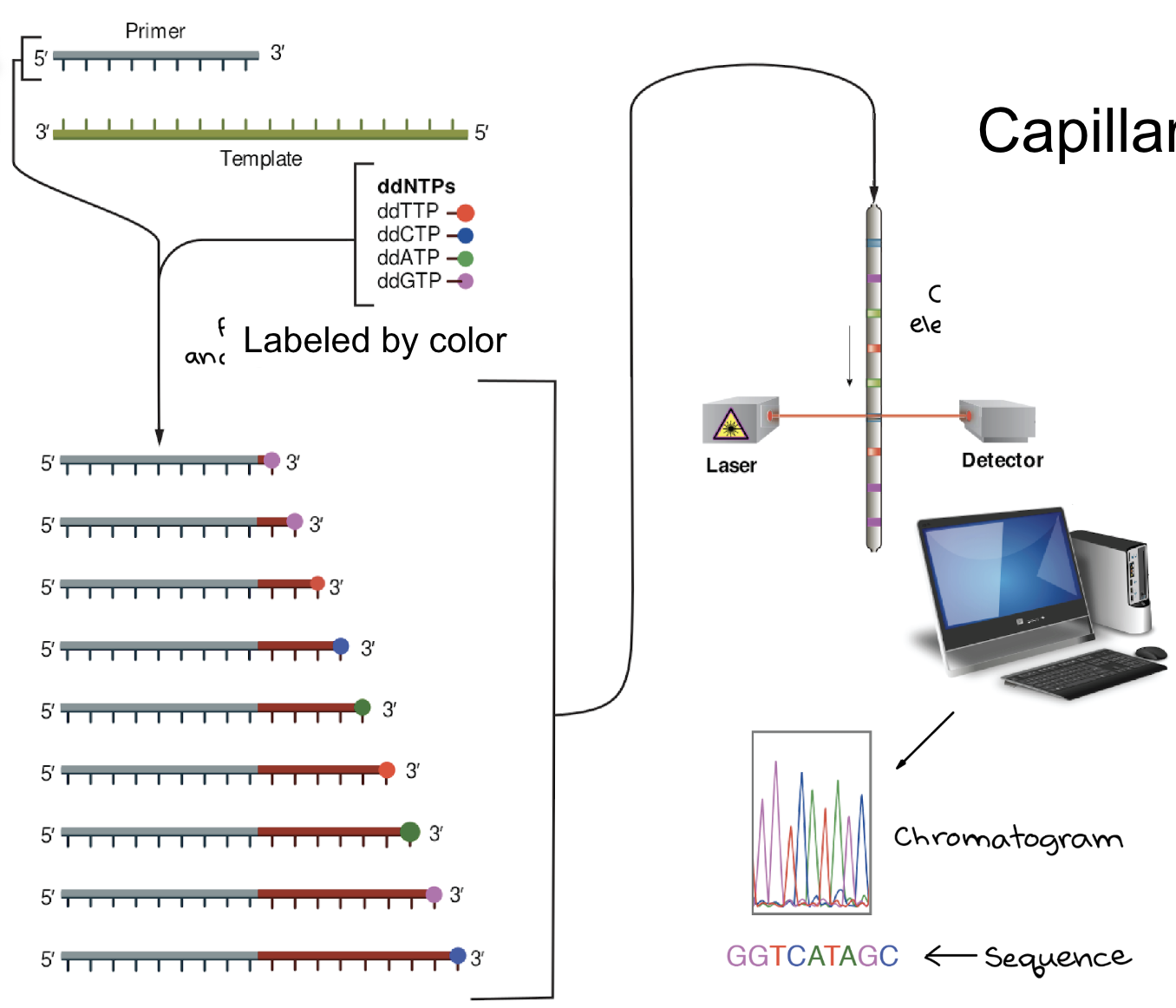
Capillary Sanger sequencing
reaction products are separated by capillary gel electrophoresis
products come out the bottom of the capillary in size order
laser at the bottom of the capillary excites fluorescence and the emission is detected
order of fluorescence dictates order of bases
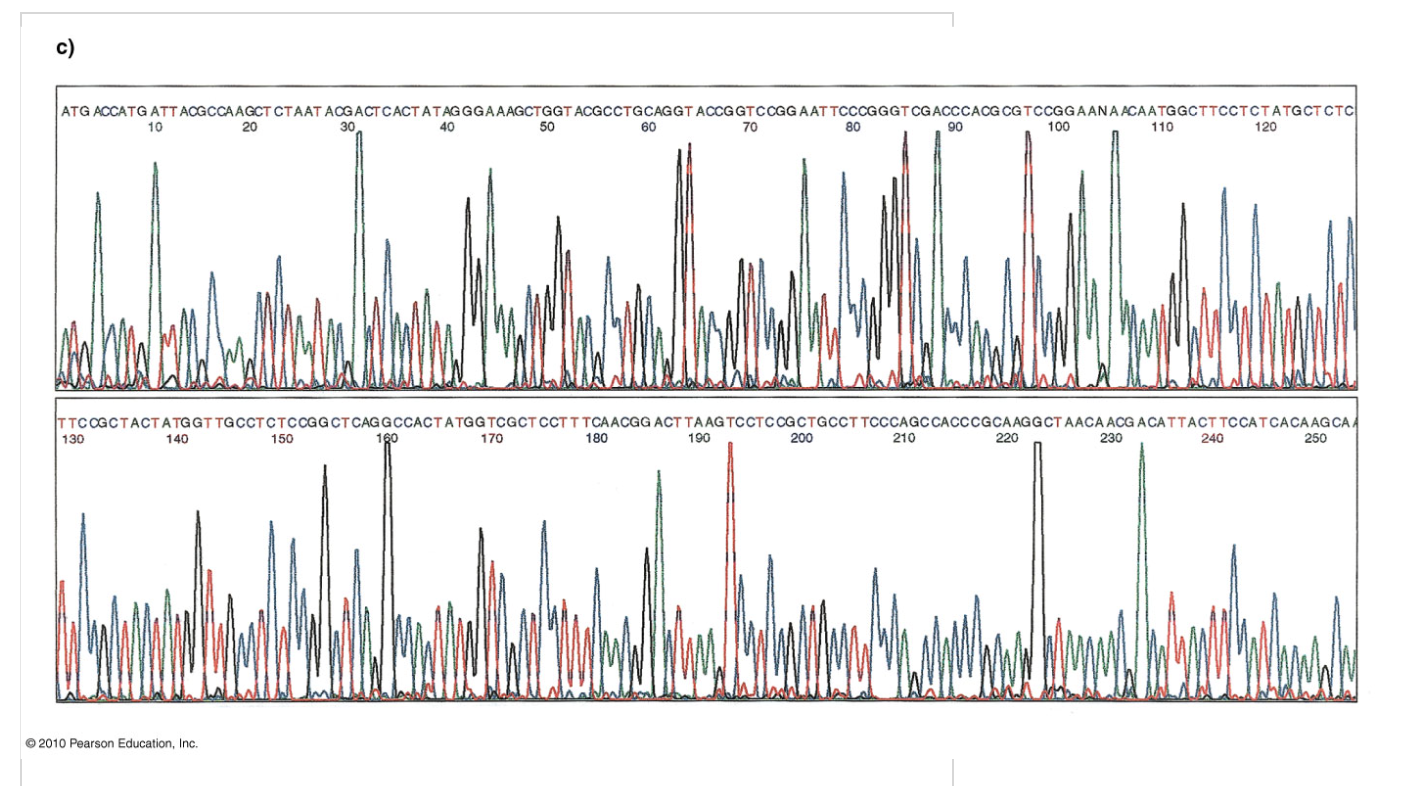
Chromatogram
different colored peaks represent different bases
A = green
T = red
C = blue
G = yellow (black)
read the order of the colored peaks to deduce sequence
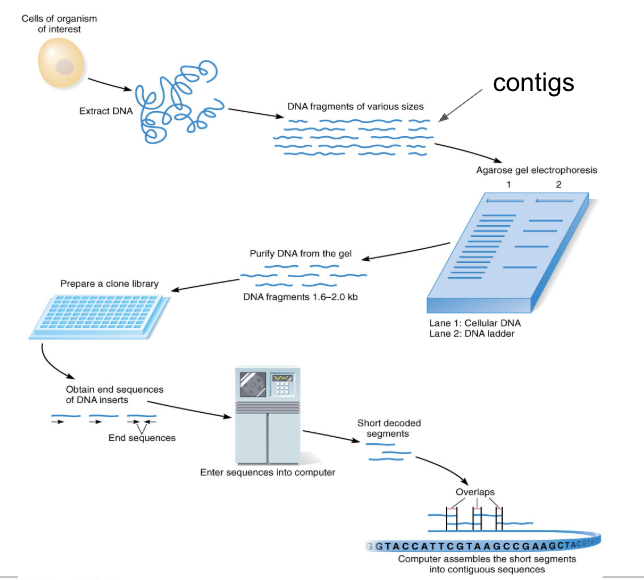
Shotgun genome sequencing
extracted DNA from many individuals
cut DNA into small, overlapping fragments (called contigs)
cut DNA using restriction digestions done in suboptimal conditions so that the R.E. didn’t cut at every site of DNA
made a genomic library from contigs
each clone contains a different contig
isolated each clone
sequenced each clone using Sanger sequencing
got sequence of each contig
reassembled contig sequences by puzzling together overlapping sequences
created one continuous sequence for each chromosome
deposited info in NCBI database