VCE Biology (Unit 1)
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Cell
The basic unit of structure and function in organisms (living things)
Cell Theory
The widely accepted theory that all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things, and new cells are produced from existing cells
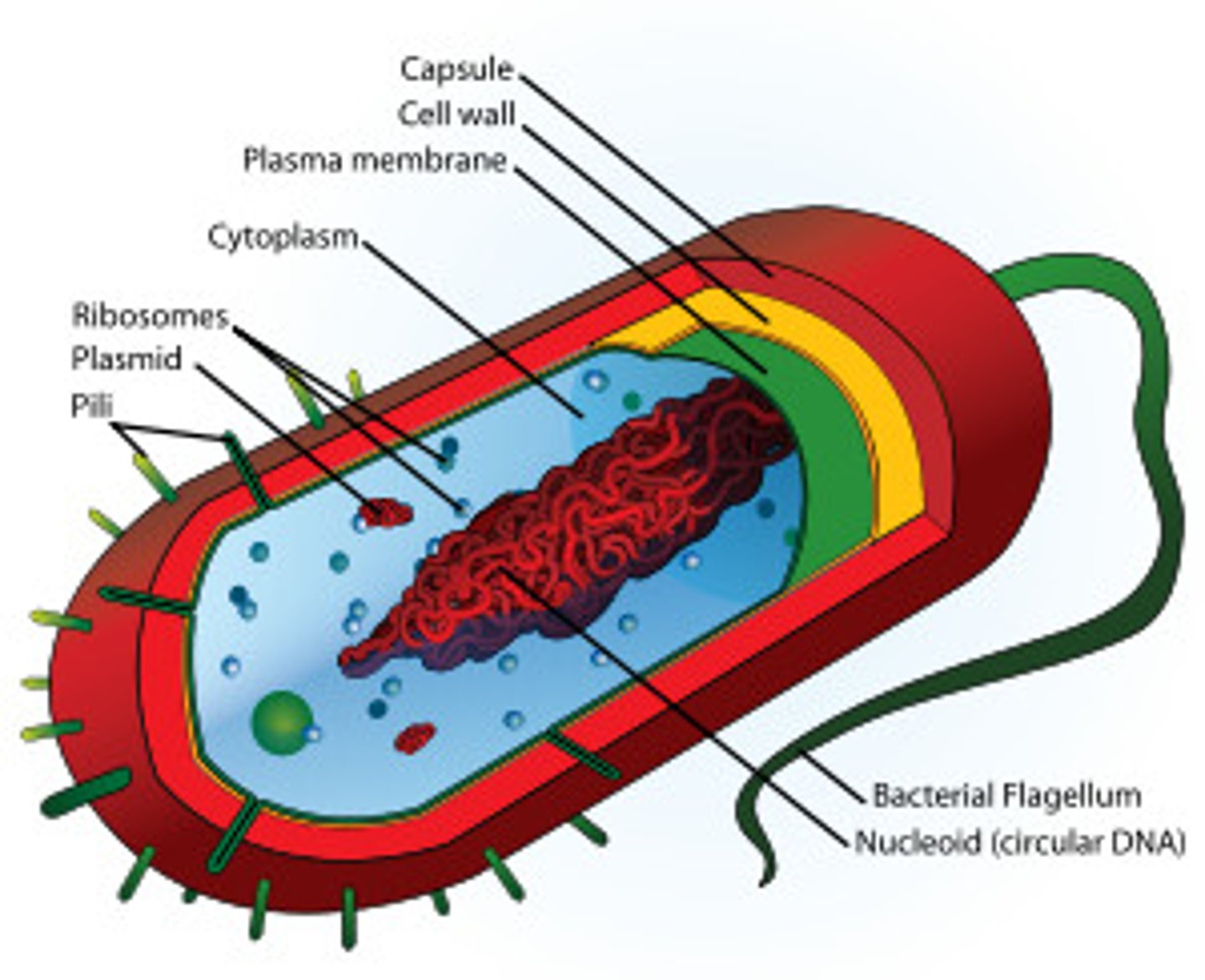
Prokaryote
Simple type of cell that lacks a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
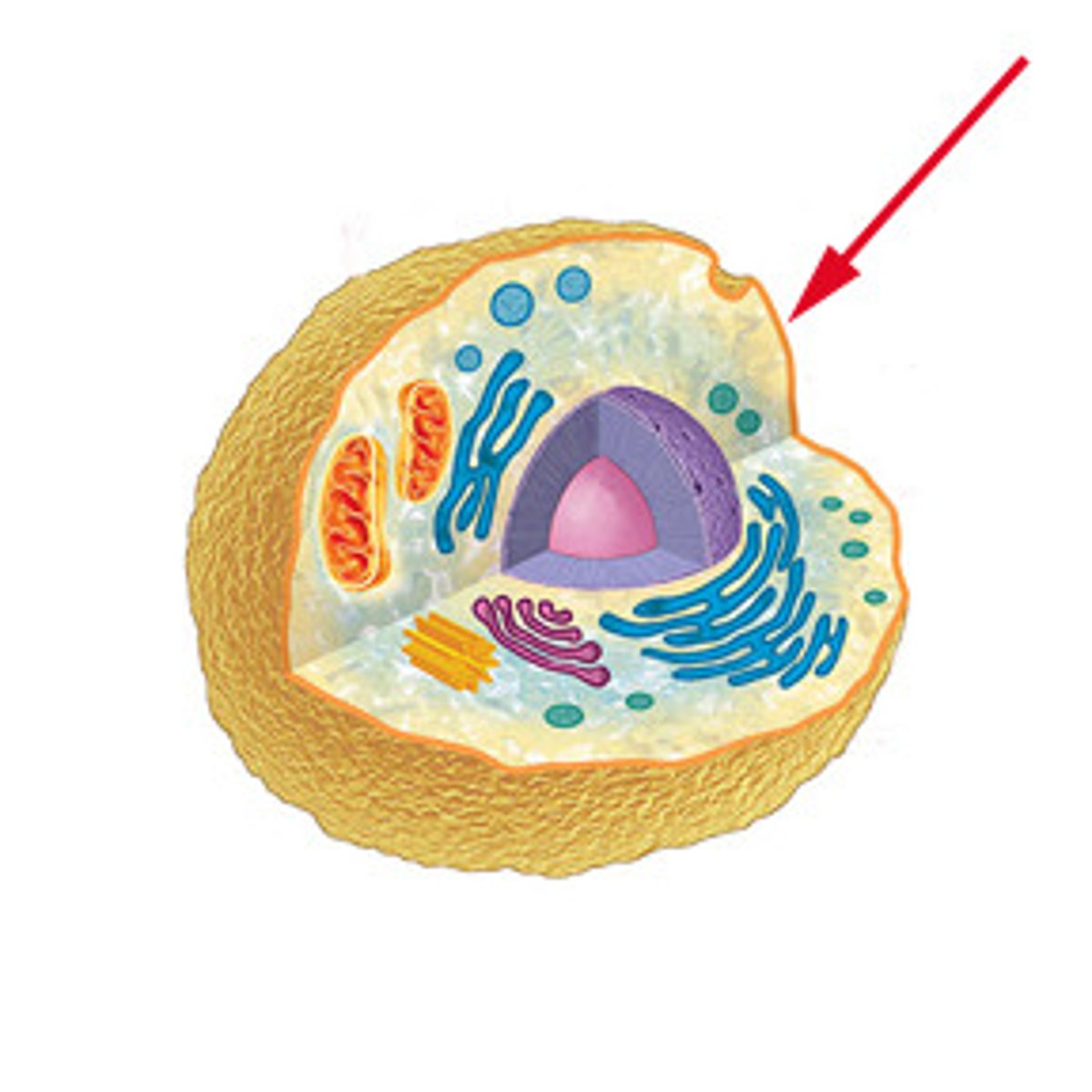
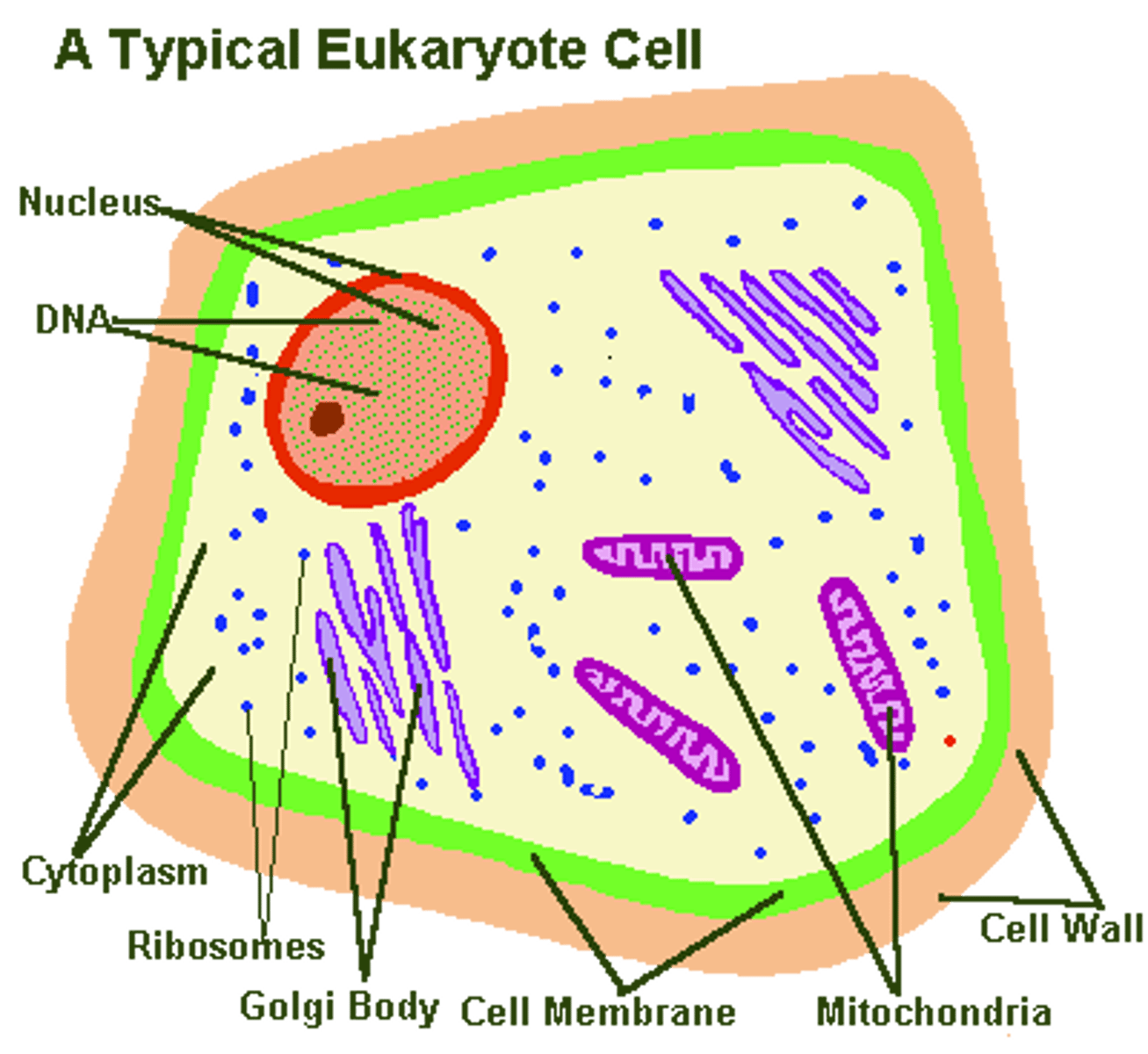
Eukaryote
A cell that contains a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Cytoskeleton
Network of protein filaments within some cells that helps the cell maintain its shape and is involved in many forms of cell movement
Cytoplasm
A jellylike fluid inside the cell in which the organelles are suspended
Cytosol
Fluid portion of cytoplasm
Chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
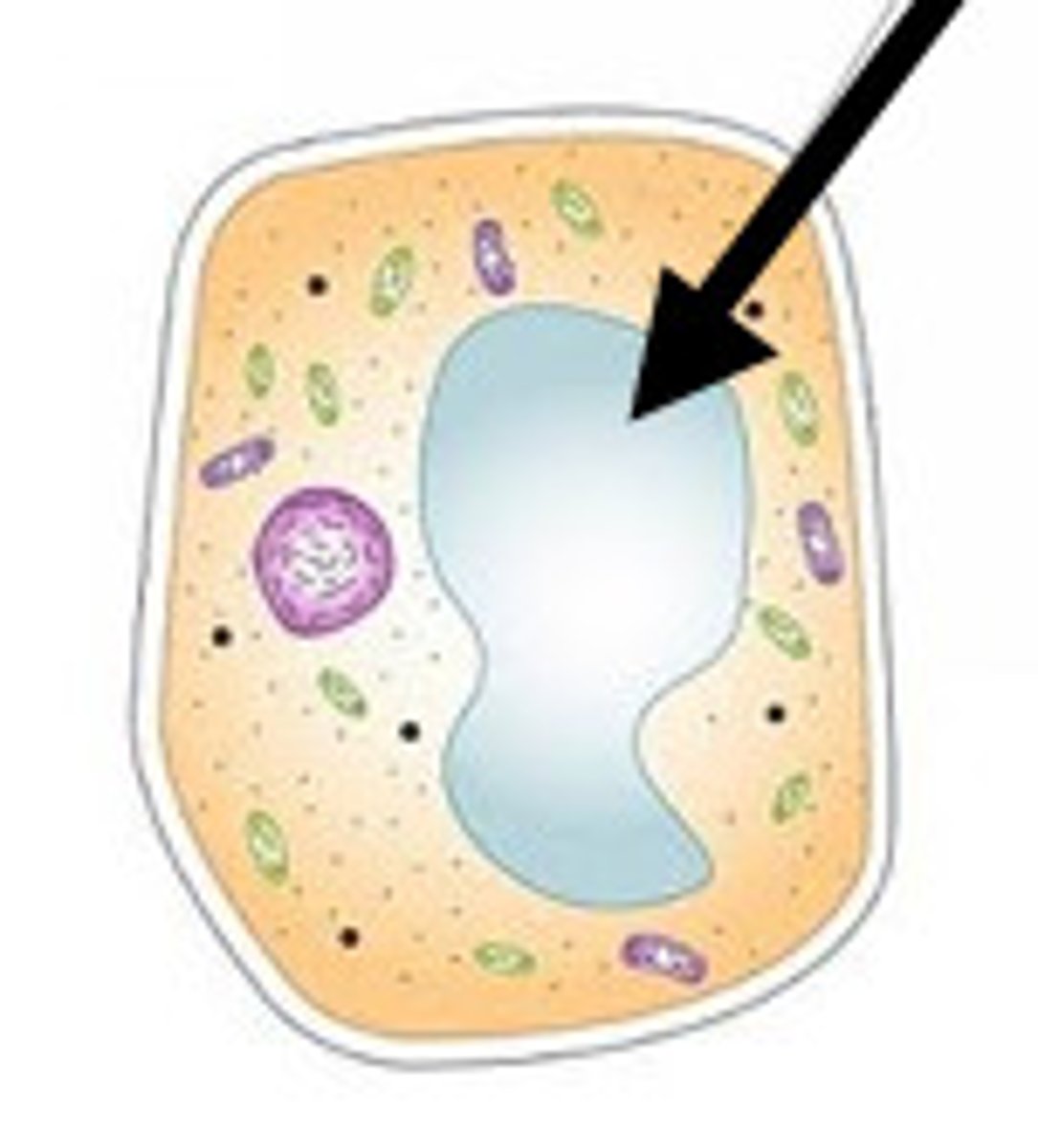
Vacuole
Cell organelle that stores materials such as water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates
Cell wall
A rigid structure that surrounds the cell membrane and provides support to the cell
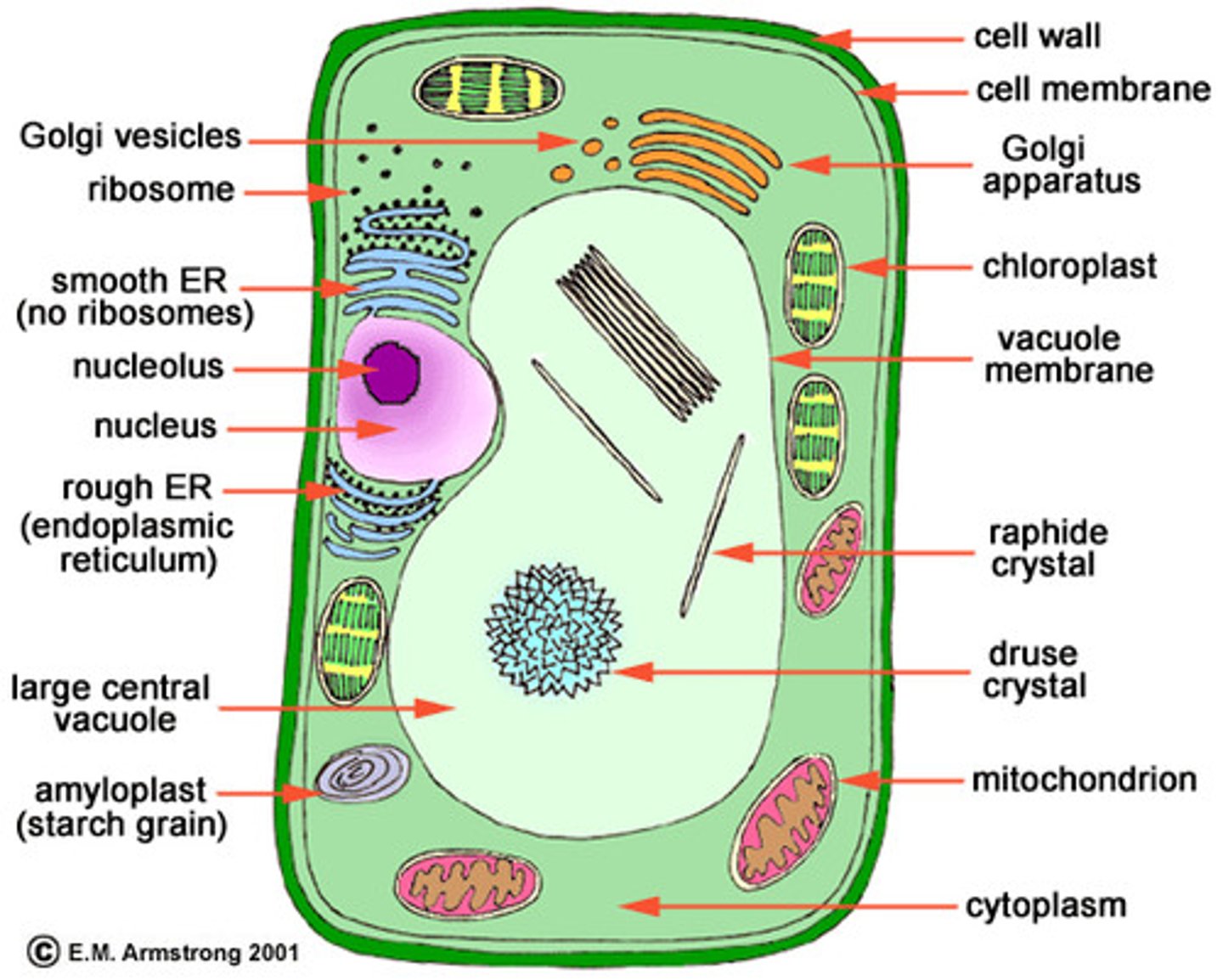
Cellulose
A substance (made of sugars) that is common in the cell walls of many organisms
Nucleus
An organelle of the cell containing DNA and RNA and responsible for growth and reproduction
Nuclear envelope
Double membrane perforated with pores that control the flow of materials in and out of the nucleus
Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA)
A complex molecule containing the genetic information that makes up the chromosomes
Nucleolus
Found inside the nucleus and produces ribosomes
Mitochondria
An organelle found in large numbers in most cells, in which the biochemical processes of cellular respiration occur
Ribosome
Site of protein synthesis
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
An extensive membranous network in eukaryotic cells, continuous with the outer nuclear membrane and composed of ribosome-studded (rough) and ribosome-free (smooth) regions.
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
An endomembrane system covered with ribosomes where many proteins for transport are assembled.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
An endomembrane system where lipids are synthesized, calcium levels are regulated, and toxic substances are broken down.
Golgi apparatus
A system of membranes that modifies and packages proteins for export by the cell
Vesicle
Small membrane-bound sac that functions in moving products into, out of, and within a cell
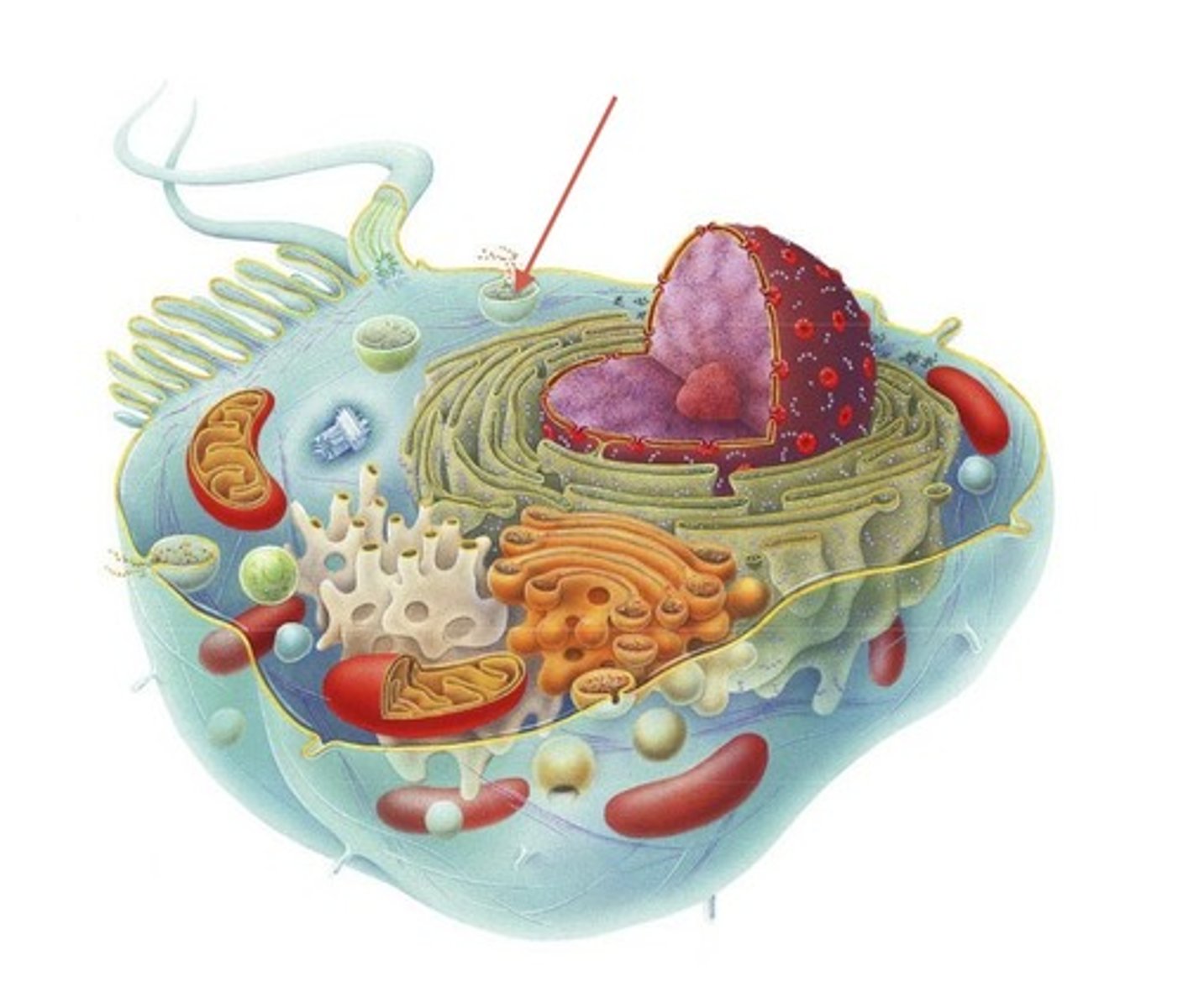
Lysosome
An organelle containing digestive enzymes
Peroxisomes
Contain oxidase enzymes that detoxify alcohol, hydrogen peroxide, and other harmful chemicals
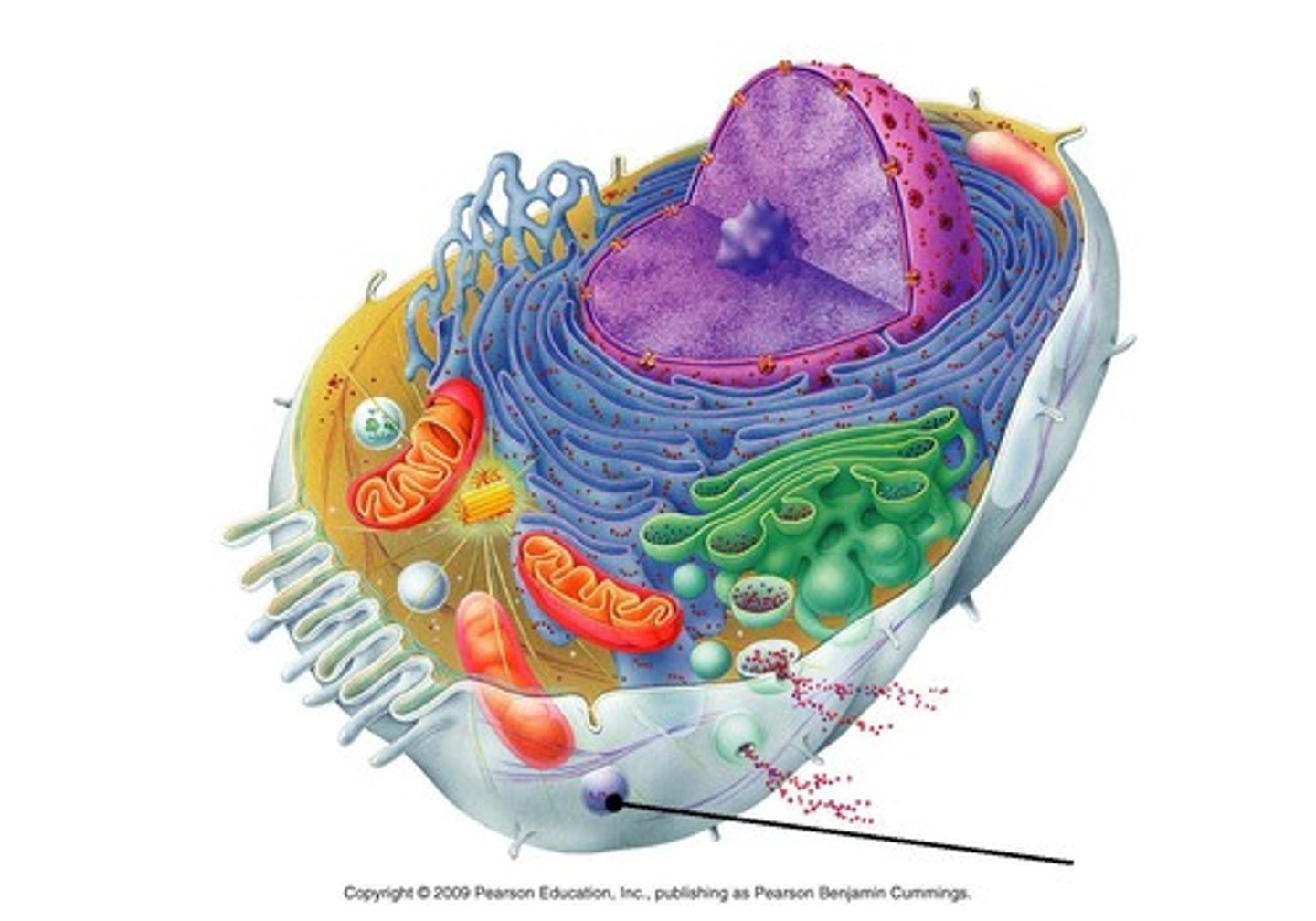
Cilia
Hairlike projections that extend from the plasma membrane and are used for locomotion
Flagellum
A long, hairlike structure that grows out of a cell and enables the cell to move
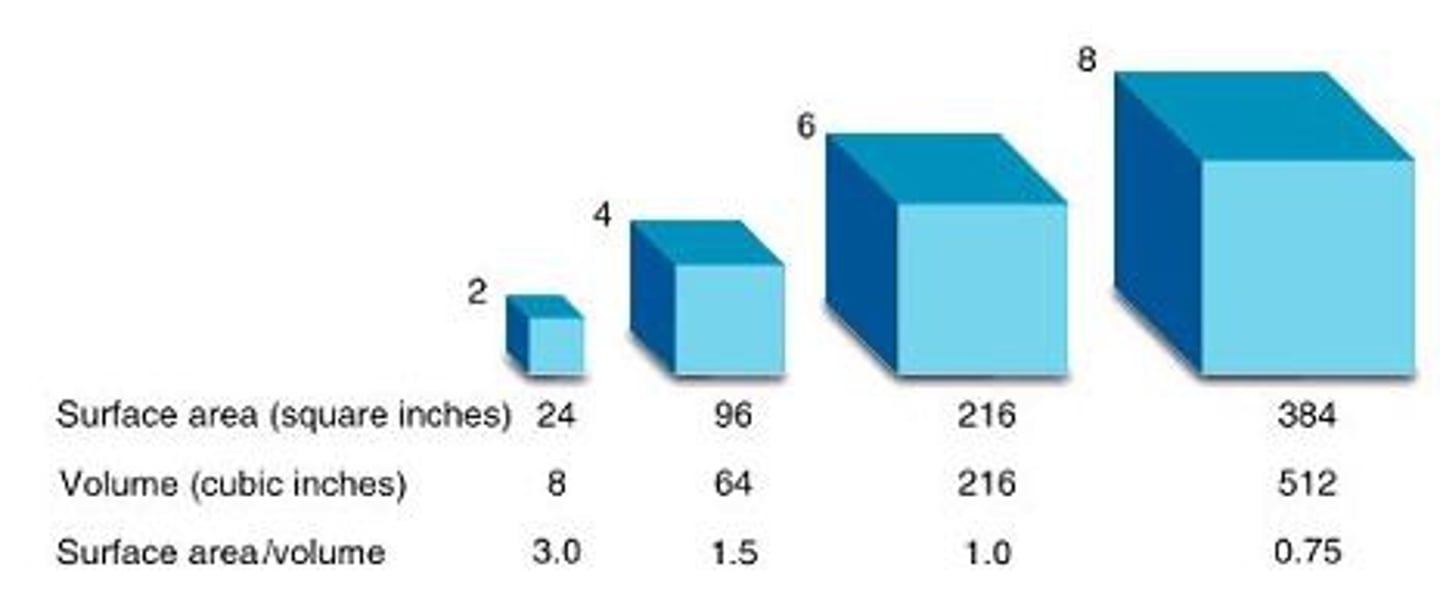
Surface area to volume ratio
Ratio of a cell's outside surface area to its internal volume
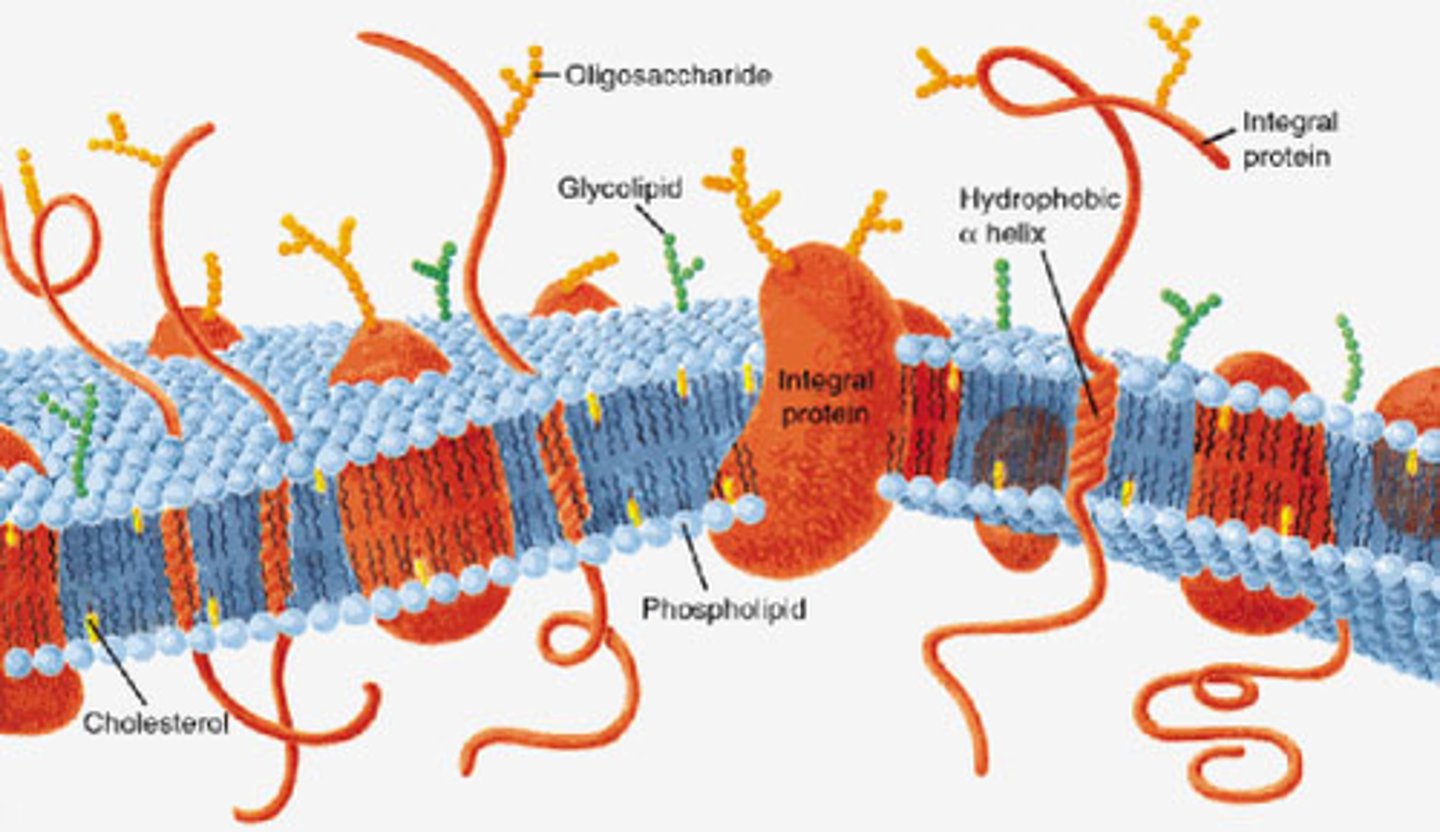
Plasma membrane
A selectively-permeable phospholipid bilayer forming the boundary of the cells and controlling transport of substances into/out of a cell
Semipermeable
Membranes that allow some substances through but not others
Phospholipids
A molecule that is a constituent of the inner bilayer of biological membranes, having a polar, hydrophilic head and a nonpolar, hydrophobic tail
Glycoproteins
A protein in the membrane that is involved in intercellular communication
Glycolipids
Lipids with a carbohydrate attached, found in the cell membrane, and are involved in intercellular communication
Fluid mosaic model
Model that describes the arrangement and movement of the molecules that make up a cell membrane
Diffusion
The net movement of a substance from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration, towards equilibrium (down the concentration gradient)
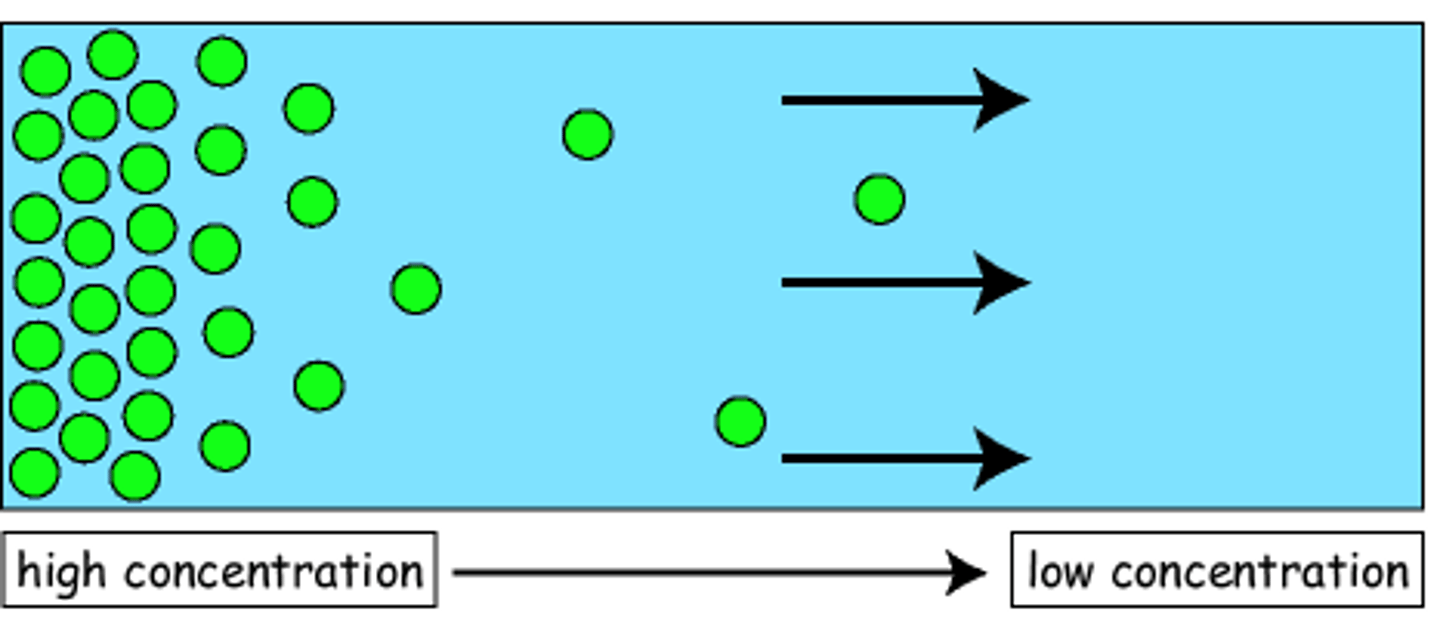
Concentration gradient (diffusion)
The direction of movement of a substance from higher concentration to lower concentration
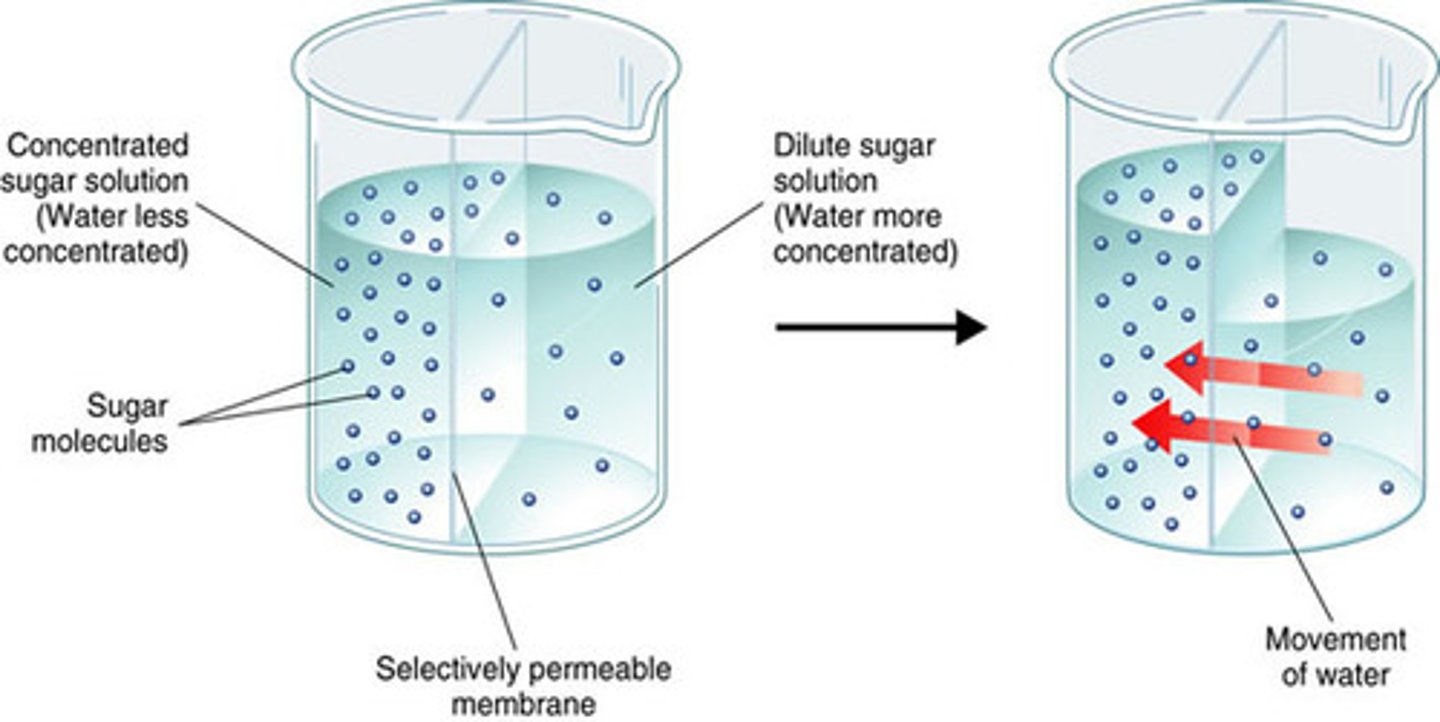
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a selectively permeable membrane from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration
Facilitated diffusion
The transport of substances through a cell membrane along a concentration gradient with the aid of channel or carrier proteins
Isotonic
Describes a solution whose solute concentration is equal to the solute concentration inside a cell
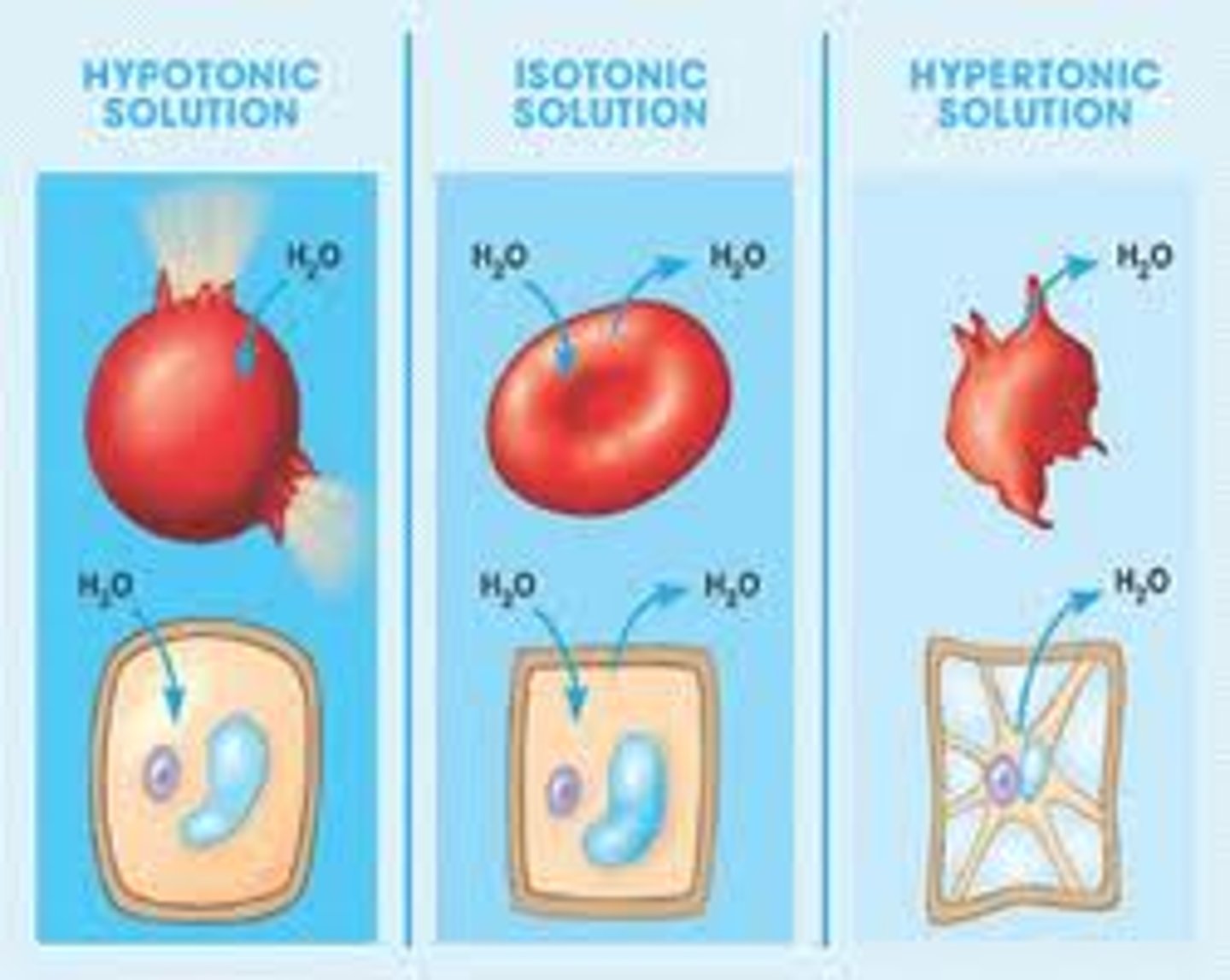
Hypotonic
Describes a solution whose solute concentration is lower than the solute concentration inside a cell
Hypertonic
Describes a solution whose solute concentration is higher than the solute concentration inside a cell
Carrier proteins
Proteins that bind solutes and transport them across the plasma membrane
Channel proteins
Proteins that provide passageways through the membrane for certain hydrophilic (water-soluble) substances such as polar and charged molecules
Active transport
The movement of a substance across a cell membrane from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration, requiring cellular energy (ATP)
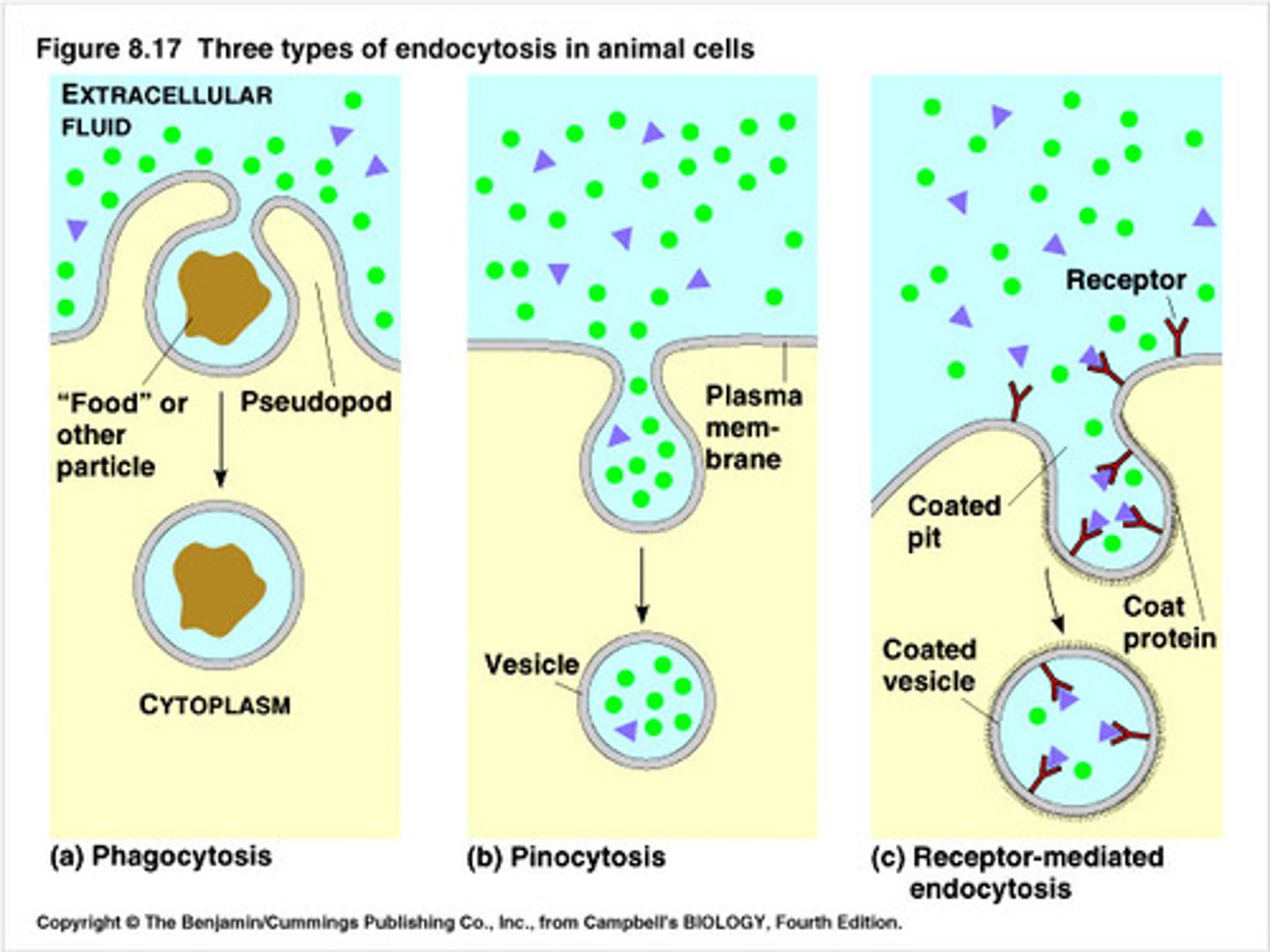
Endocytosis
Process by which a cell takes material into the cell by infolding of the cell membrane
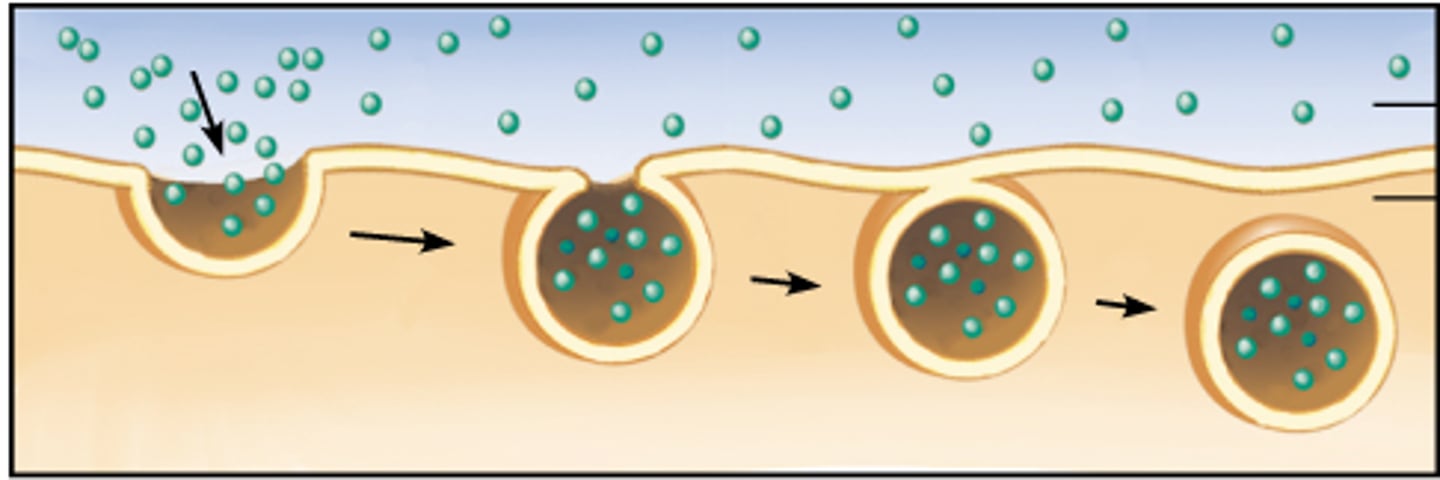
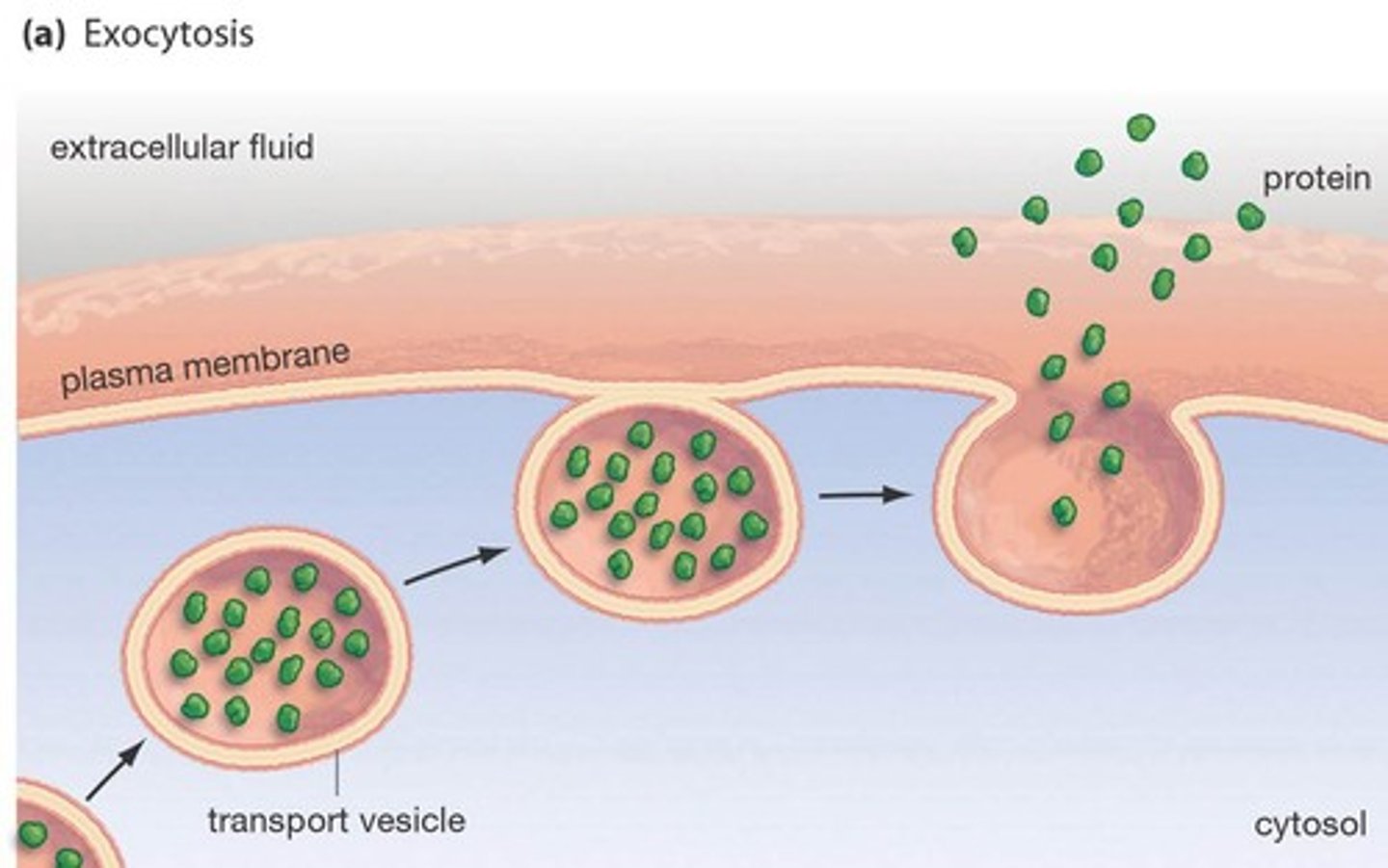
Exocytosis
Release of substances out a cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the membrane
Pinocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which the cell ingests extracellular fluid and its dissolved solutes
Phagocytosis
A type of endocytosis in which a cell engulfs large particles or whole cells (solid matter)
Autotroph
An organism that is able to form nutritional organic substances from simple inorganic substances such as carbon dioxide.
Heterotroph
Organism that obtains energy from the foods it consumes; also called a consumer
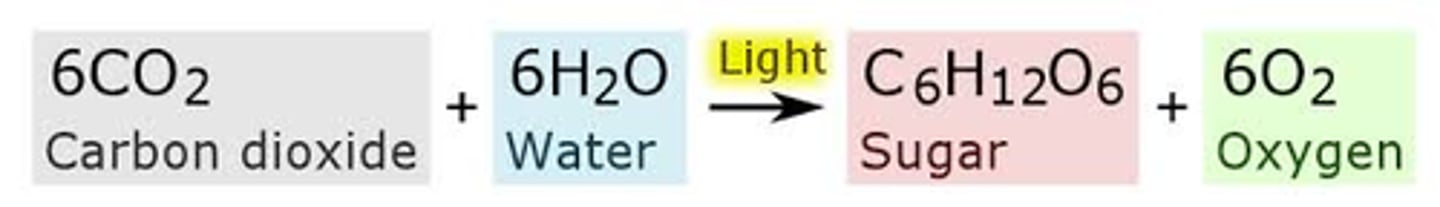
Photosynthesis
Process by which plants and some other organisms use light energy to convert water and carbon dioxide into oxygen and high-energy carbohydrates such as sugars and starches
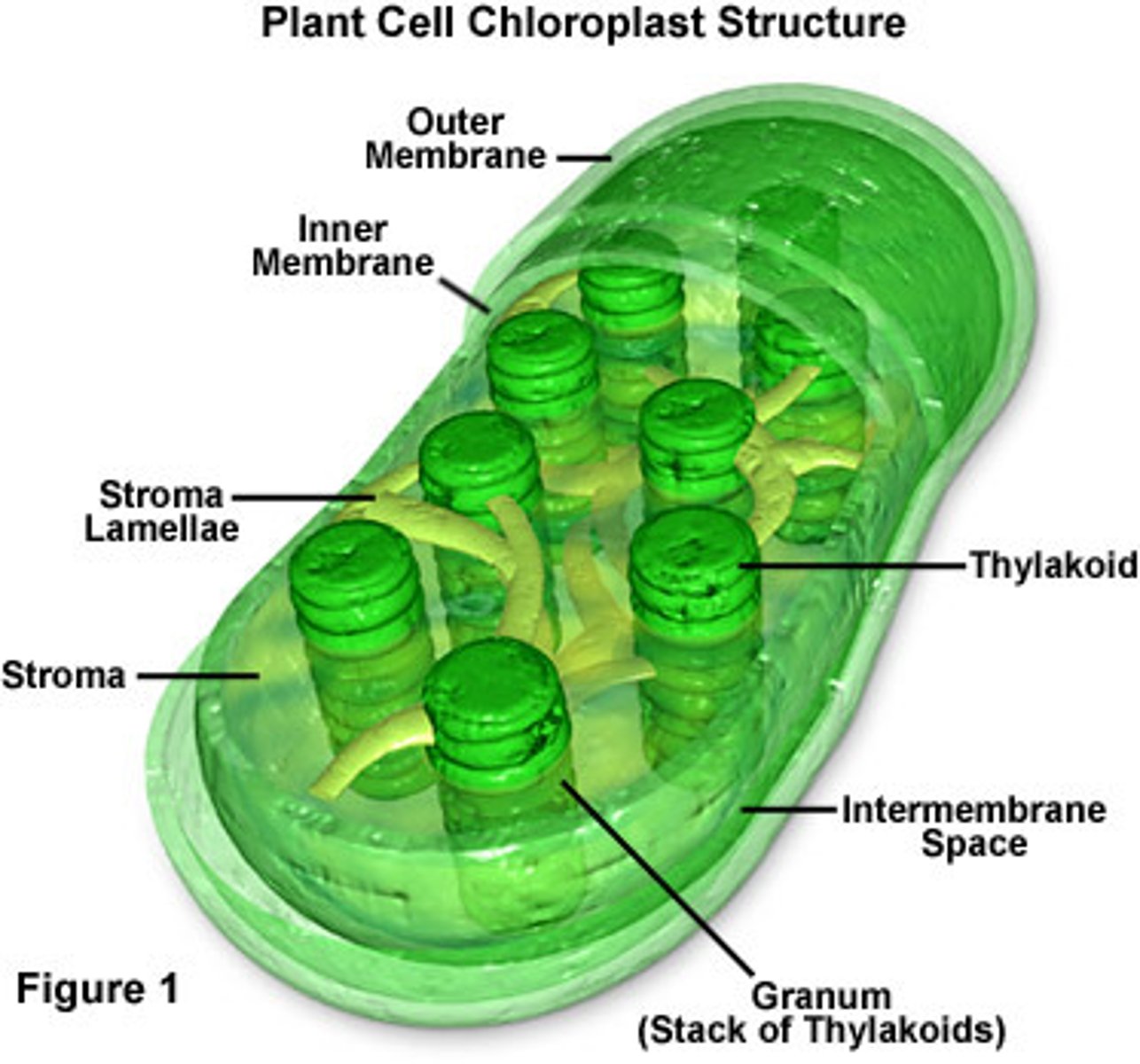
Chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
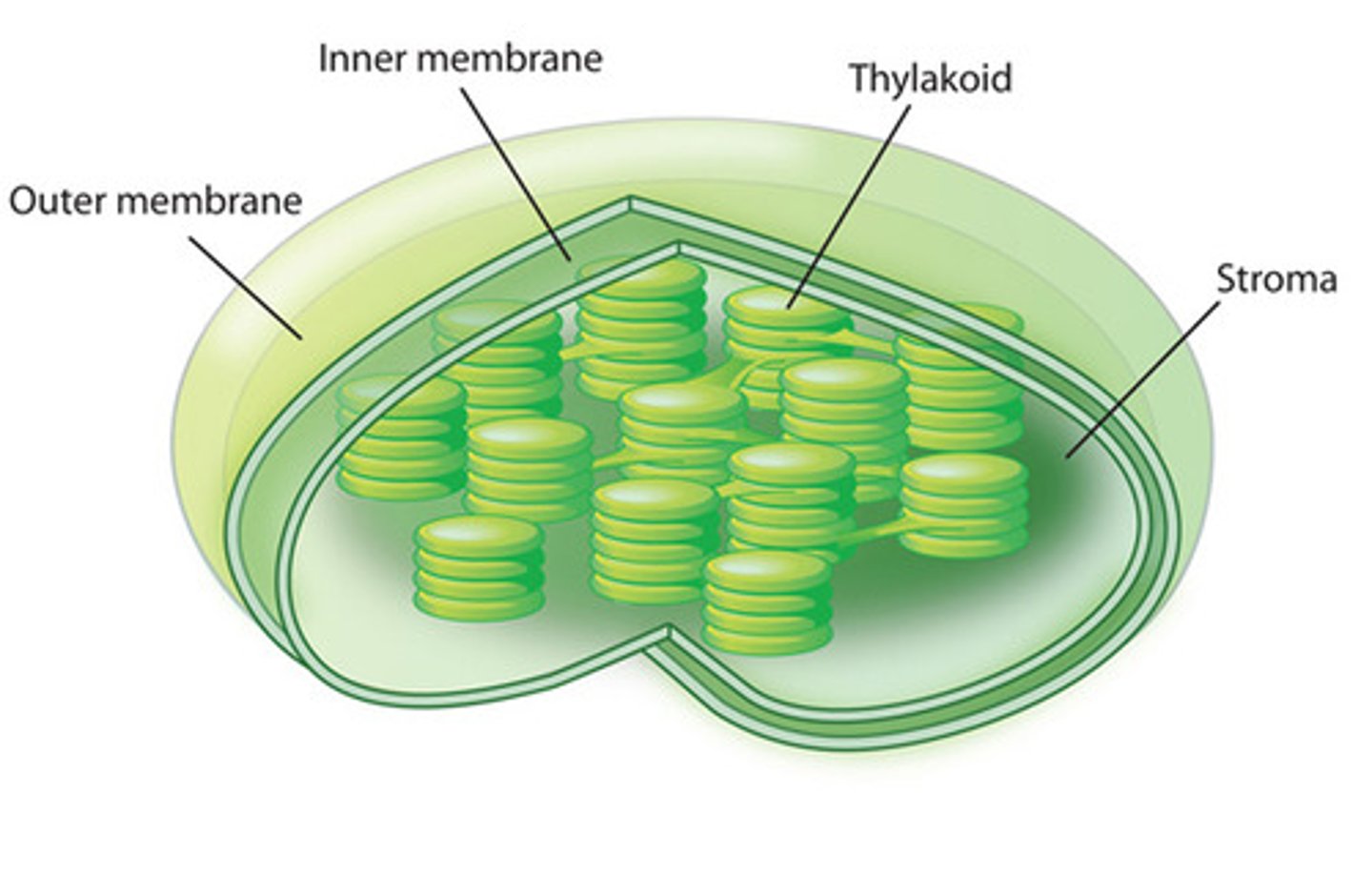
Grana
The stacks of thylakoids embedded in the stroma of a chloroplast
Stroma
Fluid portion of the chloroplast; outside of the thylakoids
Chlorophyll
A green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plants, algae, and some bacteria
Accessory pigments
Pigment that absorbs light at different wavelengths and then pass energy onto chlorophyll
Thylakoid
A flattened membrane sac inside the chloroplast, used to convert light energy into chemical energy
Light-dependent reactions
Set of reactions in photosynthesis that use energy from light to produce ATP and NADPH
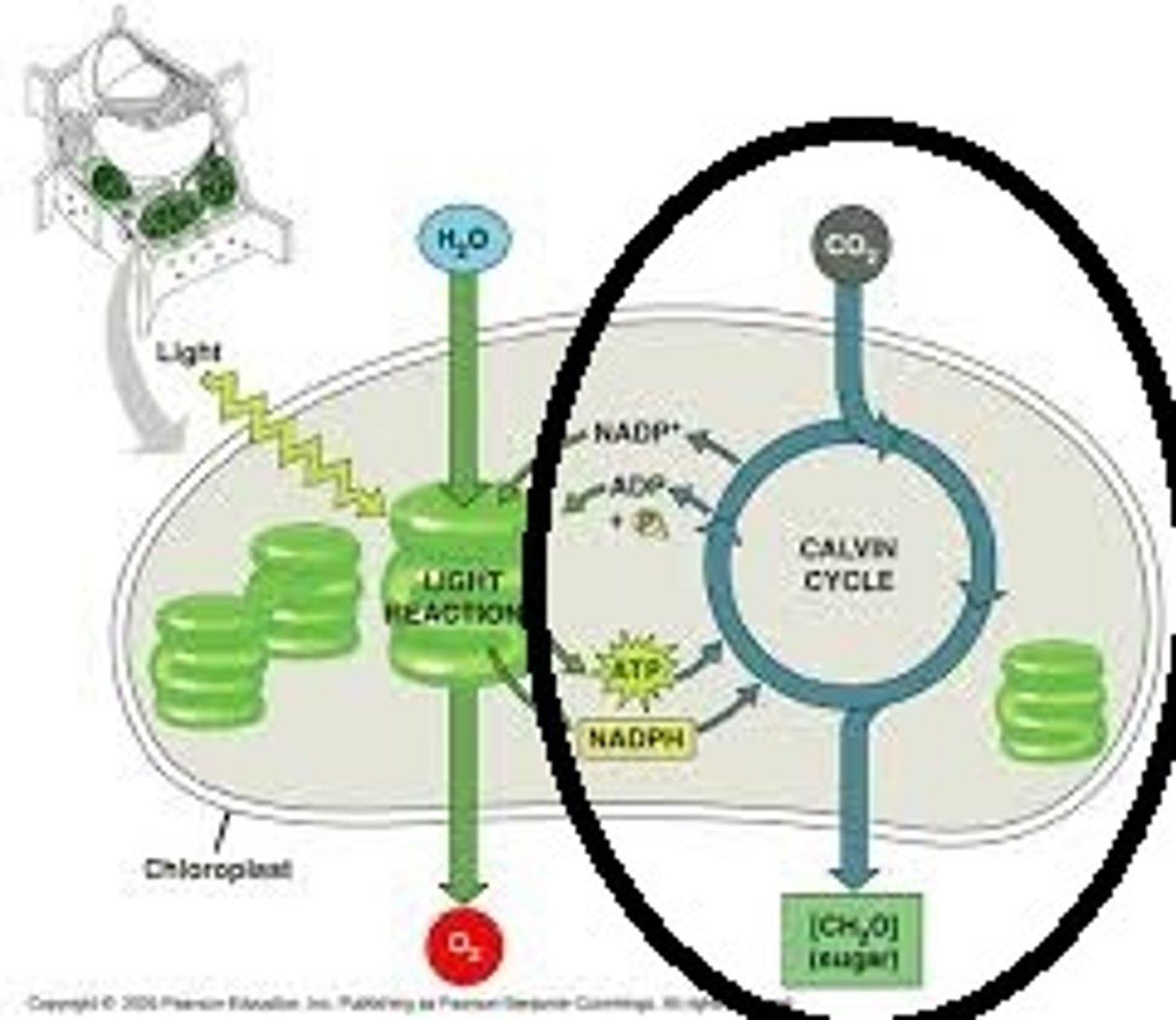
Light Independent Reactions (Calvin Cycle)
Reactions of photosynthesis in which energy from ATP and NADPH is used to produce glucose
Cellular respiration
Process that releases energy by breaking down glucose and other food molecules in the presence of oxygen

Aerobic respiration
Respiration that requires oxygen

Anaerobic respiration
Respiration in the absence of oxygen
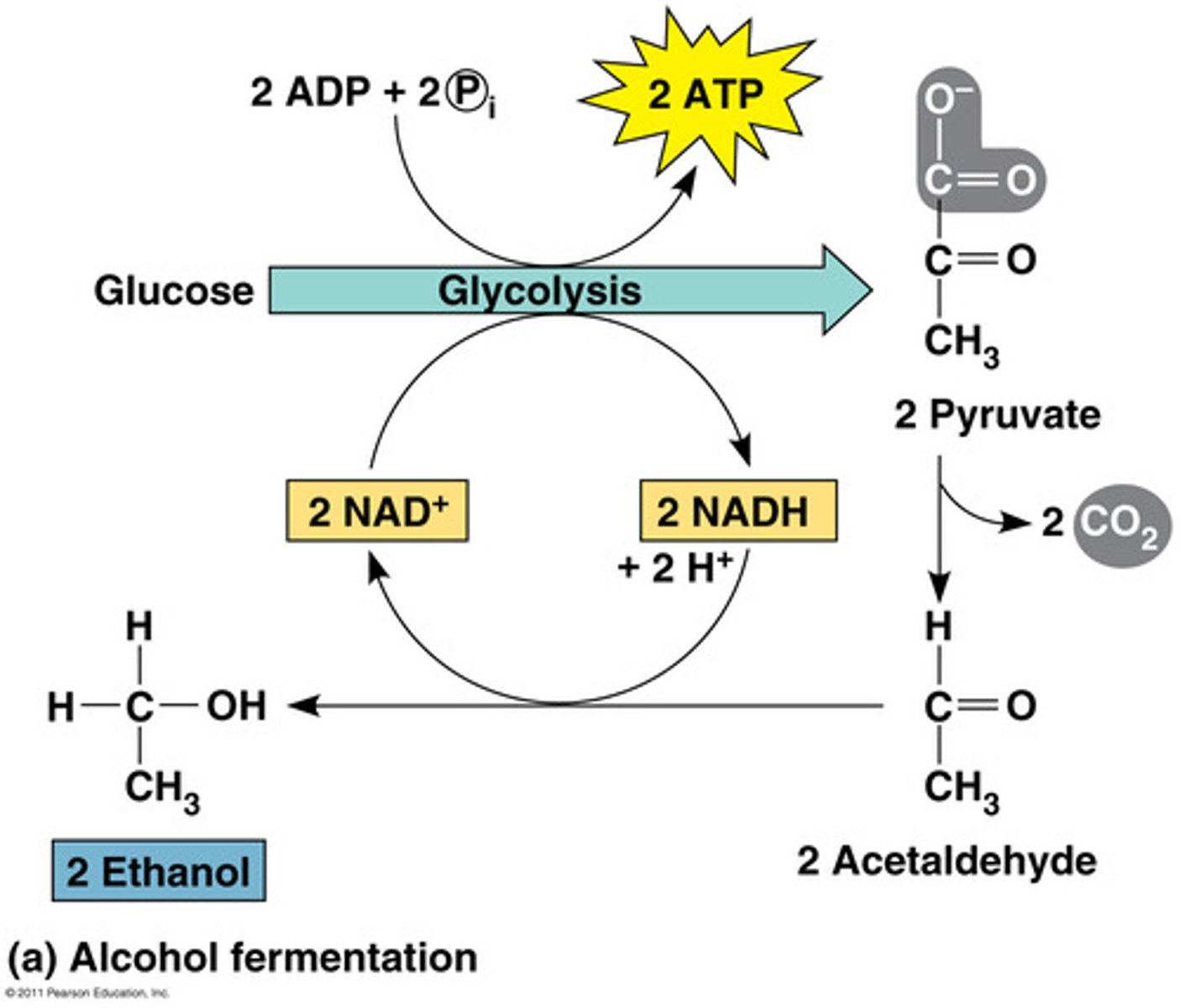
Glycolysis
A metabolic process that breaks down carbohydrates and sugars through a series of reactions to either pyruvic acid or lactic acid and release energy for the body in the form of ATP
Krebs cycle
Second stage of cellular respiration, in which pyruvic acid is broken down into carbon dioxide in a series of energy-extracting reactions
Electron transport chain
A sequence of electron carrier molecules (membrane proteins) that shuttle electrons during the redox reactions that release energy used to make ATP.
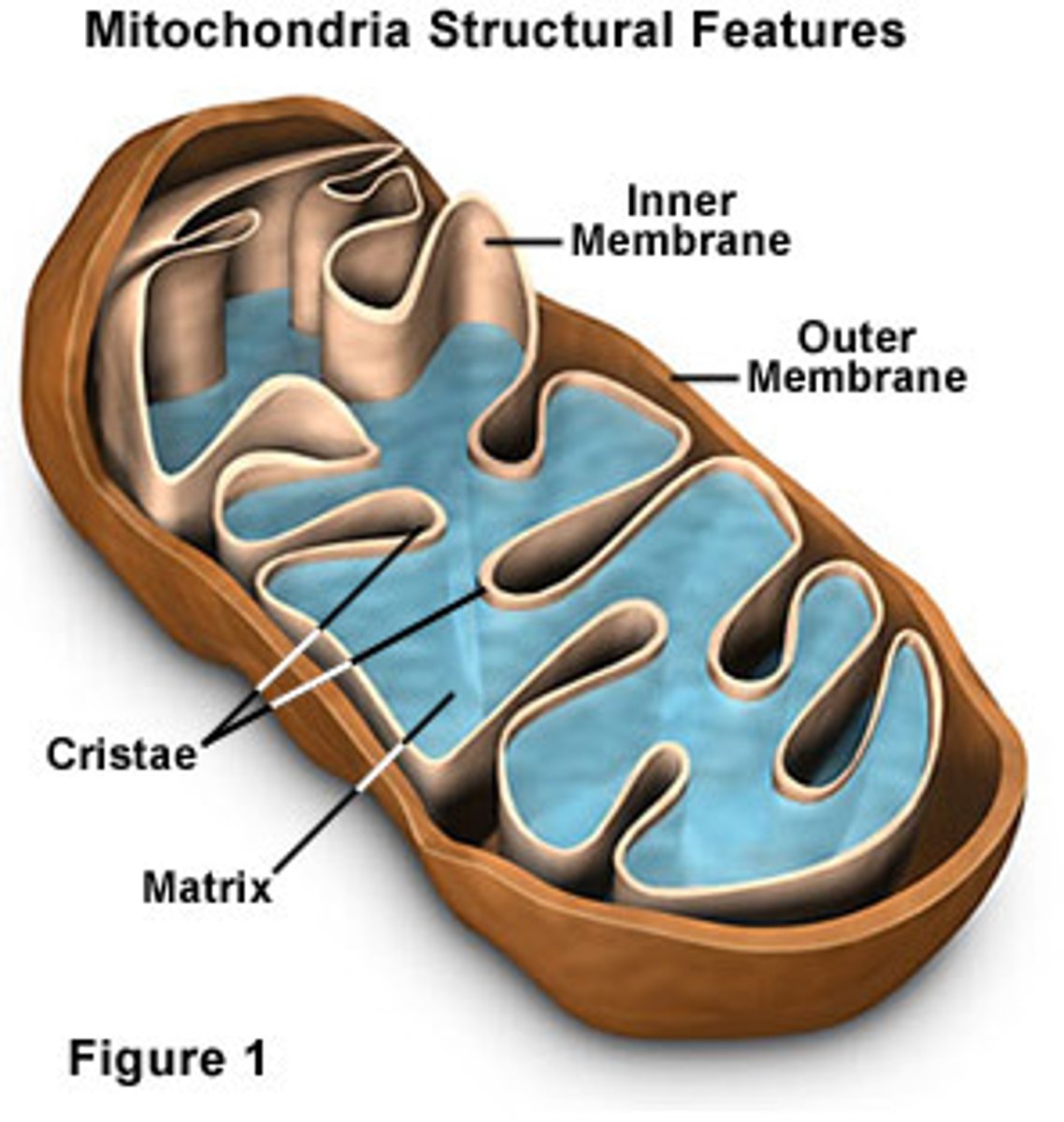
Matrix
Innermost compartment of the mitochondrion
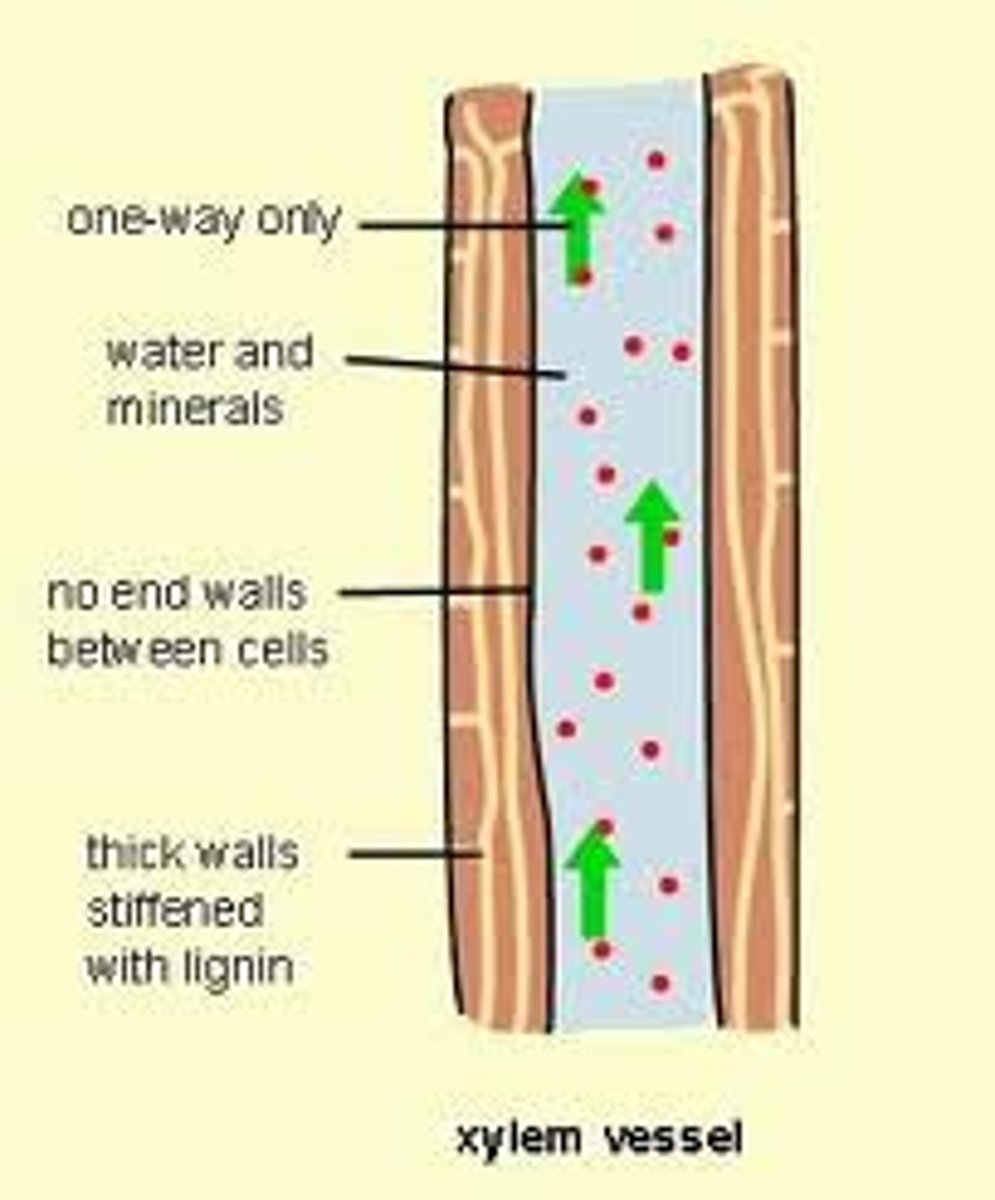
Vascular plants
Have tissues made of cells that transport water and nutrients throughout the plant
Xylem
Vascular tissue that carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant
Phloem
Living vascular tissue that carries sugar and organic substances throughout a plant
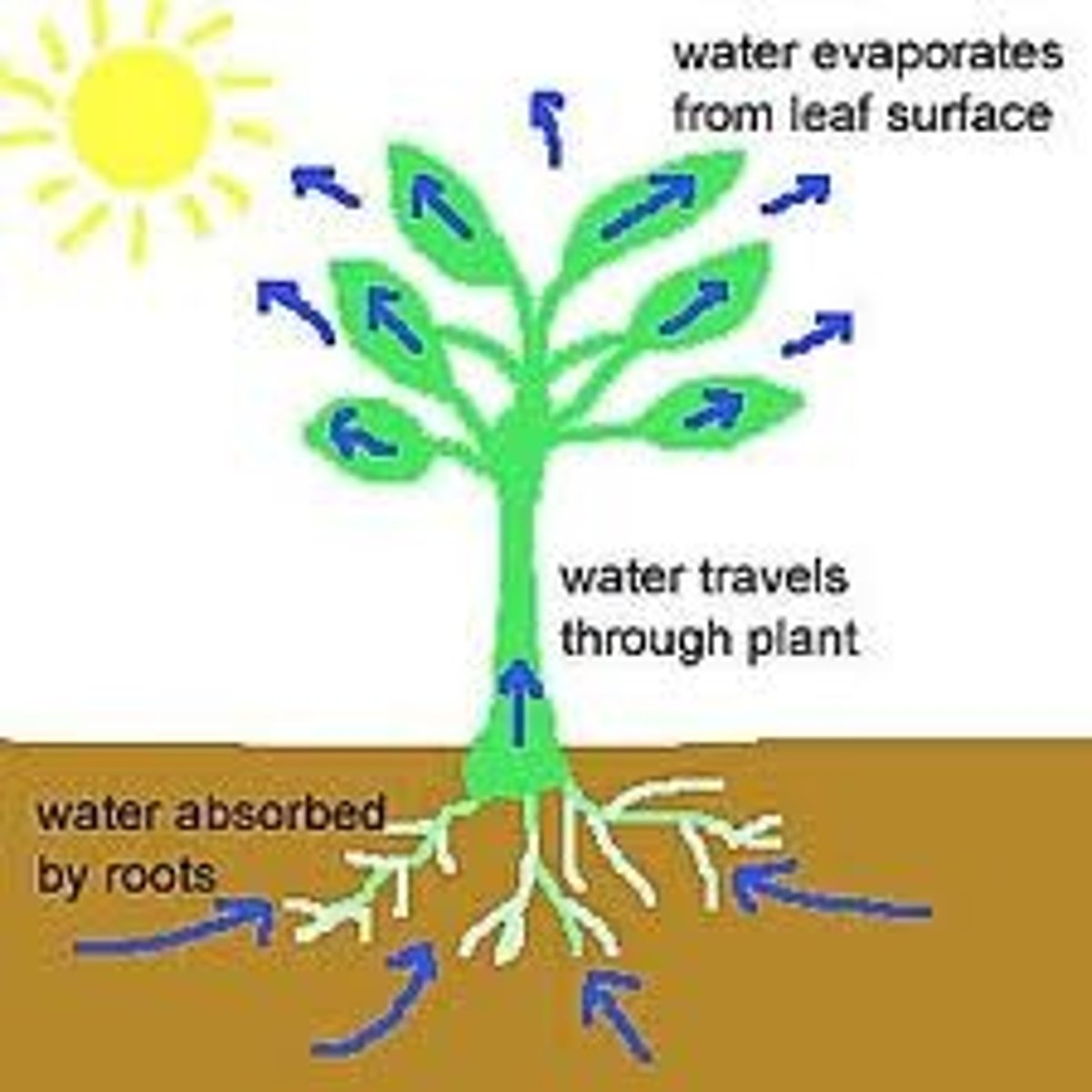
Transpiration
Evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant
Circulatory system
Transports oxygen, waste, nutrients, hormones, heat, etc... around the body

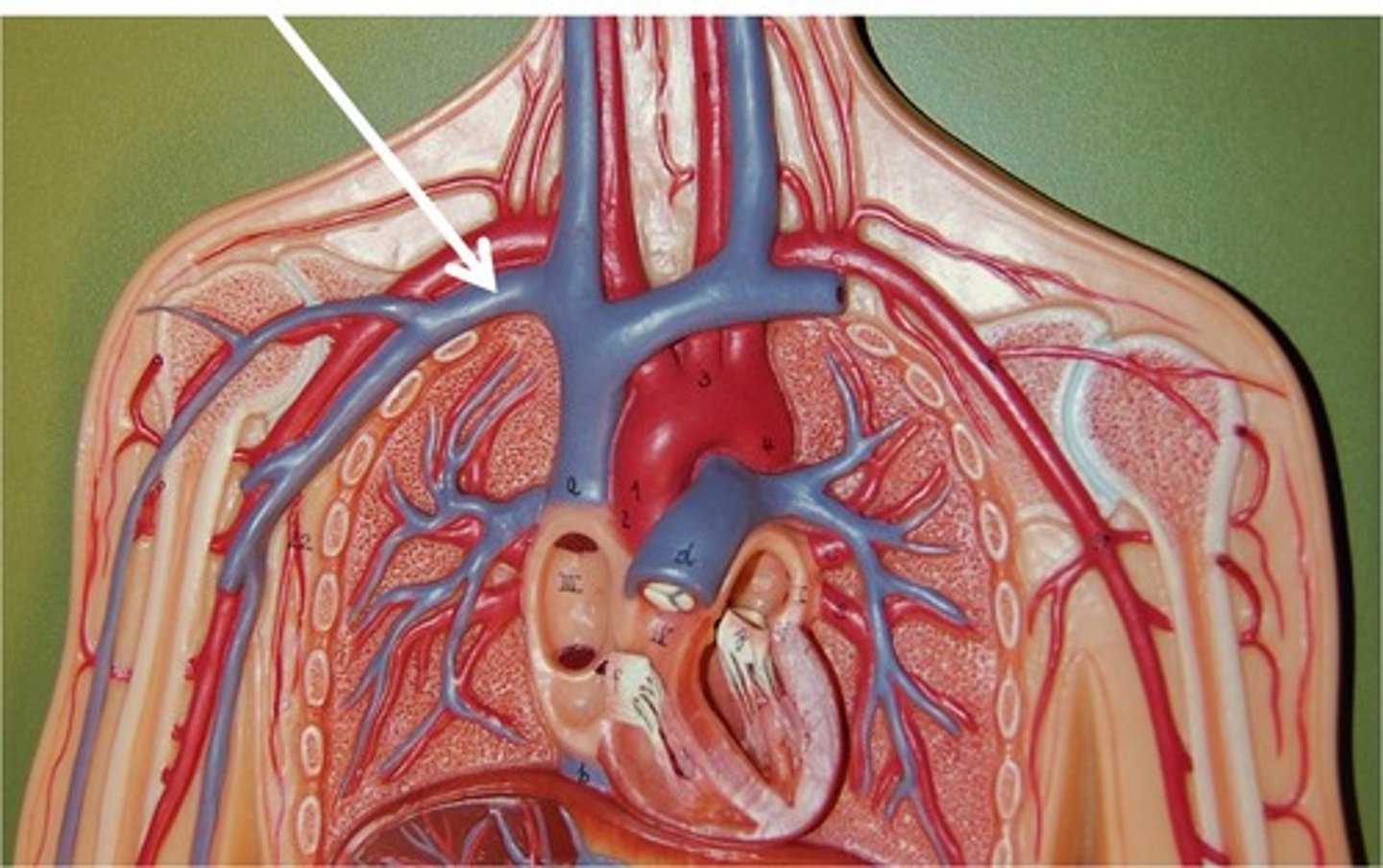
Arteries
Carry blood away from the heart
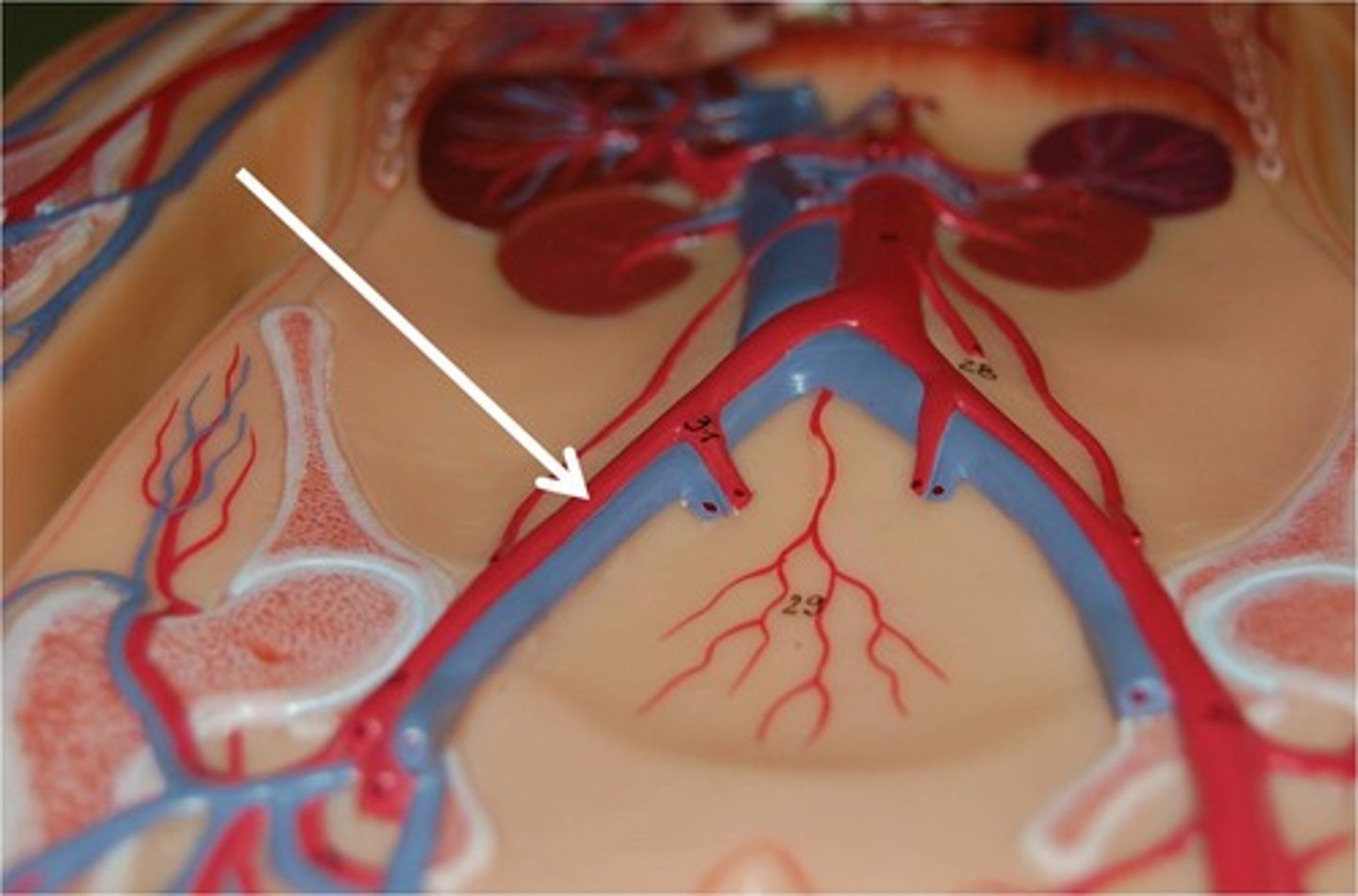
Veins
Carry blood back to the heart
Capillaries
Microscopic vessel through which exchanges take place between the blood and cells of the body
Structural adaptation
A physical feature of an organism's body having a specific function that contributes to the survival of the organism
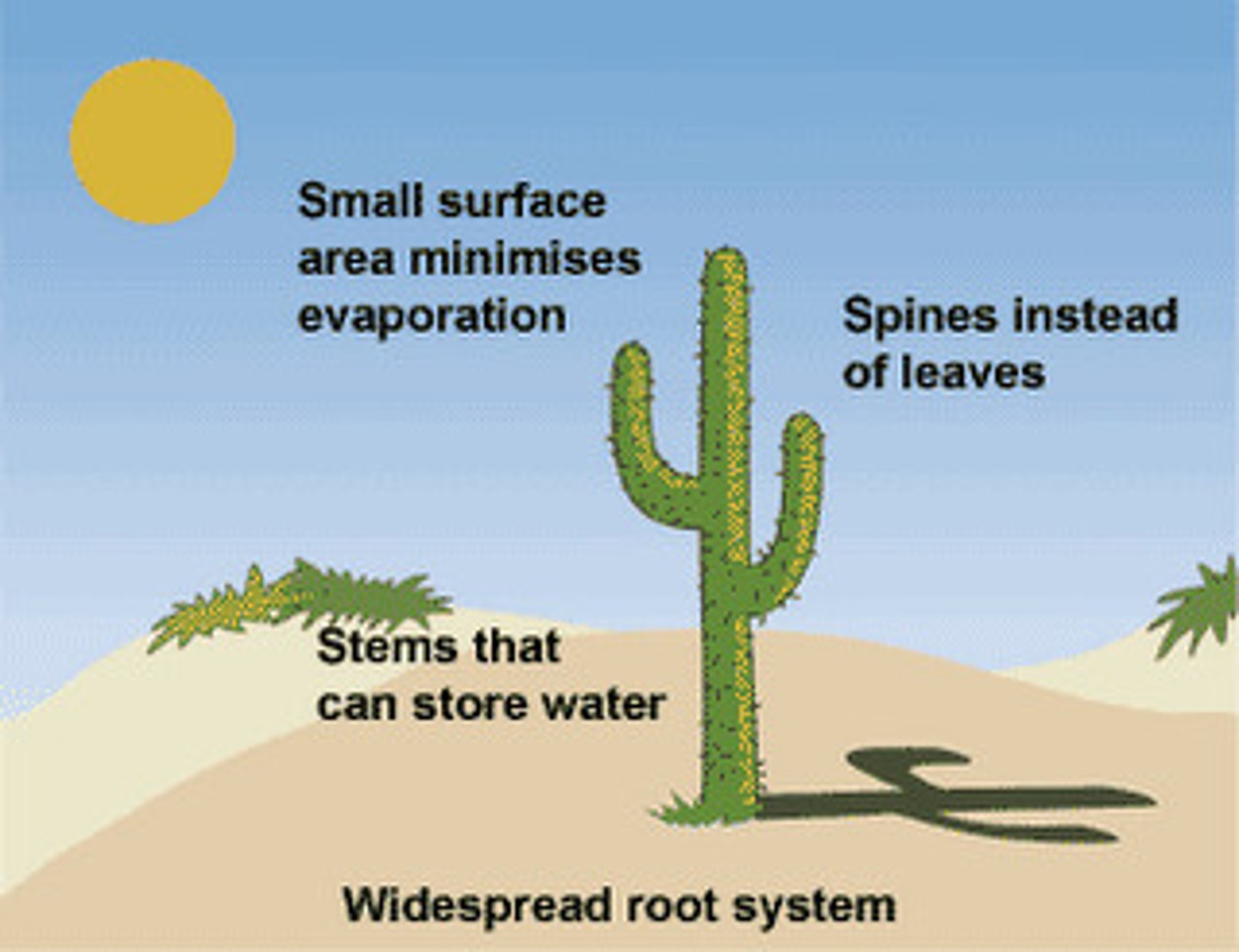
Physiological adaptation
A physical or chemical event that occurs within the body of an organism and enables survival
Behavioural adaptation
Actions of individuals or groups which increase the chances of survival and reproduction

Tolerance range
Range of an abiotic factor in the environment in which an organism can survive
Abiotic factors
Nonliving components of environment.
Biotic factors
All the living organisms that inhabit an environment
Biomimicry
The design and production of materials, structures, and systems that are modelled on biological entities and processes
Homeostasis
Maintenance of a relatively constant internal environment within narrow limits/ a tolerance range
Hypothalamus
A neural structure lying below the thalamus; it directs several maintenance activities (eating, drinking, body temperature), helps govern the endocrine system via the pituitary gland, and is linked to emotion and reward.
Negative feedback
A primary mechanism of homeostasis, whereby a change in a physiological variable that is being monitored triggers a response that counteracts the initial fluctuation.
Positive feedback
A physiological control mechanism in which a change in some variable triggers mechanisms that amplify the change
Thermoregulation
Process of maintaining an internal temperature within a tolerable range
Osmoregulation
Regulation of solute concentrations and water balance by a cell or organism
Vasodilation
A widening of the diameter of a blood vessel to release more heat to the external environment
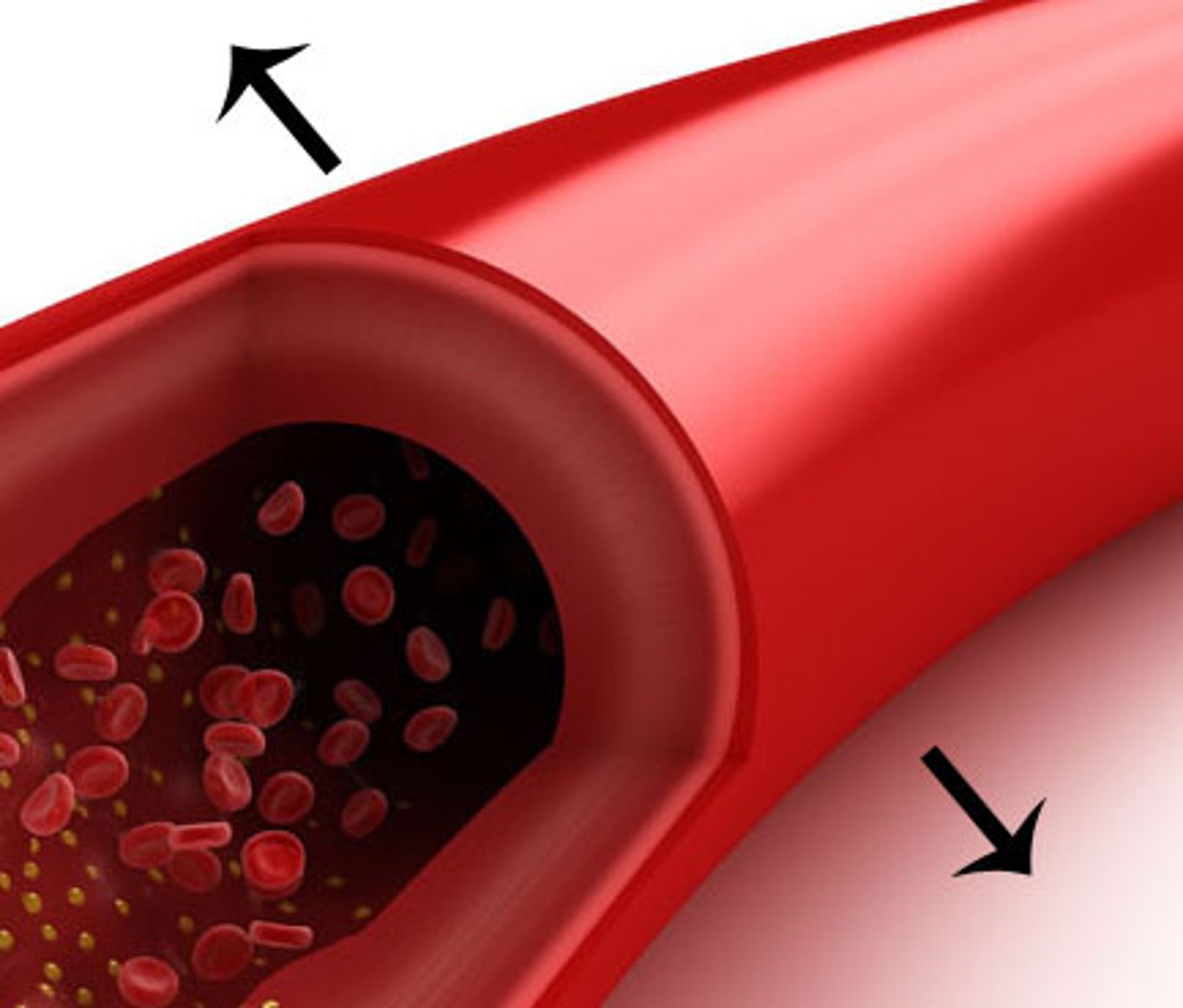
Vasoconstriction
The constriction of blood vessels, which reduces heat loss to the external environment
Thyroxine
Also called thryoid hormone, thyroxine is produced and secreted by follicle cells in the thyroid gland. it targets all cells in the body and increases overall body metabolism. This increases body temperature.
Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)
Hormone produced by the neurosecretory cells in the hypothalamus that stimulates water reabsorption from kidney tubule cells into the blood and vasoconstriction of arterioles.
Pancreas
Regulates the level of sugar in the blood
Insulin
A hormone produced by beta cells in the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels by facilitating the uptake of glucose into tissues (lowers blood sugar)
Glucagon
A hormone secreted by the pancreatic alpha cells that increases blood glucose concentration