Interactions - CYTOCHROME P450 ENZYMES
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What are cytochrome P450 enzymes responsible for?
Metabolism of most drugs in the body"
Which CYP450 isoenzymes metabolise about 90% of drugs?
CYP3A5
CYP3A4
CYP2D6
CYP2C19
CYP2C9
CYP1A2
Which two CYP450 enzymes are the most clinically significant?
CYP3A4 and CYP2D6
What are the four CYP2D6 metaboliser phenotypes?
CYP2D6 Polymorphisms:
Poor Metabolisers
Intermediate Metabolisers
Extensive Metabolisers
Ultrarapid Metabolisers
What is the consequence of being a CYP2D6 poor metaboliser for active drugs?
Inability to metabolise drug, INCREASED RISK of adverse drug reaction
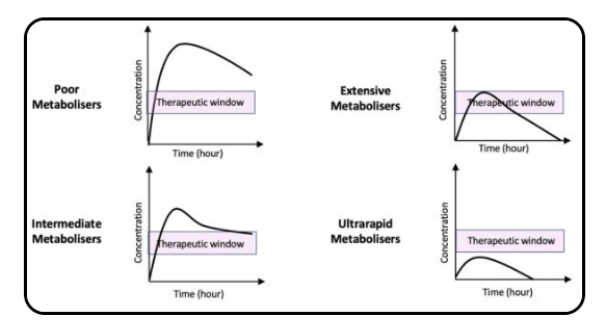
What is the consequence of being a CYP2D6 ultrarapid metaboliser for active drugs?
Very RAPID metabolism, LACK of Therapeutic Response SINCE therapeutic dose isn't achieved!

How do CYP2D6 enzymes respond to prodrugs?
Poor metabolisers fail to CONVERT the prodrug into active form, leading to lack of therapeutic response.
—
Ultrarapid metabolisers RAPIDLY convert into active form, causing potential toxicity e.g. CODEINE.
List examples of important CYP450 substrates.
Statins → Reduce LDLs (Bad Cholesterol)
Theophylline → Long-acting bronchodilator
Phenytoin → Anti-epileptic (Anticonvulsant)
Warfarin → Vit K Antagonist
SSRIs → Antidepressant
Amitriptyline → Tricyclic antidepressant
Codeine
Caffeine
What is the effect of CYP450 enzyme INDUCERS on drug levels?
INDUCERS = Increased enzyme activity
—
↑ Enzyme expression
↑ Drug Metabolism
↓ Drug concentration
RISK of treatment FAILIURE
List examples of key CYP450 inducers
Anticonvulsants: Phenytoin, Carbamazepine, Phenobarbitone
Steroids: Dexamethasone, Prednisolone, Glucocorticoids
Antibiotics: Rifampicin, Griseofluvin
Others [Food, Drink and Smoking Interactions]: Nicotine, Alcohol, Cigarette smoke, St Johns Wort
—
CRAP GPS
What are major CYP450 inducers?
Mnemonic: CRAP GPS
C → Carbamazepine (SSRi)
R → Rifampicin
A → Alcohol
P → Prednisolone OR Phenytoin (Anticonvulsant)
G → Griseofulvin (Antifungal)
P → Phenobarbital (Anticonvulsant)
S → St John's Wort
What is the effect of CYP450 enzyme inhibitors on drug metabolism?
Inhibitors REDUCE enzyme activity
—
↓ Enzyme activity
↓ Drug Metabolism Rate
↑ RISK of Toxicity
Effect is rapid and dose-related
List examples of key CYP450 inhibitors.
Azoles: Ketoconazole, fluconazole
Antibiotics: Sulfonamides, metronidazole, ciprofloxacin, chloramphenicol, macrolides, isoniazid
H₂ Receptor Antagonist: Cimetidine → Treating GERD
PPI: Omeprazole
Anticonvulsant: Sodium Valporate → Treating Epilepsy / Bi-Polar
SSRis: Fluoxetine / Sertraline / Citalopram
Grapefruit Juice
—
SICKFACES.COM
What are major CYP450 inhibitors?
Mnemonic: SICKFACES.COM
S → Sulfonamides / SSRIs
I → Isoniazid [INH] (Treats and prevent tuberculosis (TB))
C → Cimetidine
K → Ketoconazole
F → Fluconazole
A → Amiodarone (Class 3 Anti-arrhythmic → Potassium channel blockers)
C → Chloramphenicol, Ciprofloxacin
E → Erythromycin
S → Sodium Valproate
.
C → Ciprofloxacin
O → Omeprazole
M → Metronidazole / Macrolides
In SICKFACES.COM, what does the S stand for?
Sulfonamides / SSRIs
SSRis: Fluoxetine / Sertraline / Citalopram
In SICKFACES.COM, what does the I stand for?
Isoniazid [INH - Isonicotinic acid hydrazide]
Treats and prevent tuberculosis (TB)
In SICKFACES.COM, what does the first C stand for?
Cimetidine"
In SICKFACES.COM, what does K stand for?
Ketoconazole"
In SICKFACES.COM, what does F stand for?
Fluconazole"
In SICKFACES.COM, what does A stand for?
Amiodarone, acetaminophen"
In SICKFACES.COM, what does the second C stand for?
Ciprofloxacin / Chloramphenicol
In SICKFACES.COM, what does E stand for?
Erythromycin"
In SICKFACES.COM, what does the S before .COM stand for?
Sodium valproate"
In SICKFACES.COM, what does the C in .COM stand for?
Cimetidine"
In SICKFACES.COM, what does O stand for?
Omeprazole"
In SICKFACES.COM, what does M stand for?
Macrolides, metronidazole"
Why can St John's wort cause oral contraceptive failure?
St Johns wort is CYP3A4 inducer
↑ CLEARANCE & METABOLISM of oral contraceptives
↓ effectiveness CAUSING treatment FAILIURE
AFFECTS Oral contraceptive pills
—
Such as Levonogestrel, Northestisoe, Ethinylestradiol and Desogesterel
Name oral contraceptive components affected by St John's wort
AFFECTS Oral contraceptive pills:
—
Levonogestrel
Progestogen-only pills
Progestogen-only implants
Combined hormonal contraceptives (pill, patch, ring)
Northestisoe
Ethinylestradiol
Desogesterel
What contraceptive advice is given for patients on St John's wort?
Avoid COMBINED use
—
Use OTHER CONTRACEPTIVE METHODS such as:
Intrauterine devices [IUD] → Copper / Hormonal
Barrier methods → External (male) condoms, Internal (female) condoms // Diaphragms [A shallow, dome-shaped cup inserted into the vagina before sex to cover the cervix. Used with spermicide] // Cervical caps [A smaller silicone cup that fits snugly over the cervix, also used with Spermicide]
Depot contraception → [Long-acting hormonal injections] such as Depo-Provera (12 weeks) // Sayana Press (13 weeks, self-injectable) // Noristerat (8 weeks, short-term use
How does miconazole interact with warfarin?
Miconazole (prescribed in thrush) is a CYP450 2C9 enzyme inhibitor
DECREASING Warfarin clearance
INCREASING TOTAL warfarin concentration
INCREASING INR [International Normalised Ratio - How long it takes for your blood to clot IN COMPARISON to the avg human]
What monitoring and dose adjustment are needed when miconazole is used with warfarin?
Monitor INR closely and reduce warfarin dose as needed.
Mr A is a 45-year-old ex-smoker with a history of chronic asthma. He is a regular patient at your pharmacy. Today he brings in a prescription for erythromycin 500mg tablets, one to be taken every 6 hours for 5 days.
He explains that he has developed a bad chest infection. His patient medication records shows that he is allergic to penicillin and that he is taking the following medication:
Salbutamol 100mcg/dose inhaler, two puffs four times daily when required,
Seretide 250 Evohaler (fluticasone propionate 250 mcg, salmeterol xinafoate 25mcg/metered inhalation), two puffs twice daily,
Uniphyllin Continus (theophylline) modified-release tablets, one tablet every 12 hours.
You decide to contact his GP to discuss your concerns.
—
Question: Which of the following points would be most important to discuss with Mr A’s GP?
a. Symptoms of theophylline toxicity include bradycardia and breathlessness
b. Smoking can decrease the plasma concentration of theophylline
c. Theophylline has a narrow therapeutic index and therefore Mr A will be at risk of sub-therapeutic treatment of his condition.
d. Erythromycin will decrease the plasma concentration of theophylline
e. Erythromycin will increase the plasma concentration of theophylline
Erythromycin will increase the plasma concentration of theophylline.
—
Theophylline is a high-risk drug - look into it's therapeutic range
Plasma levels of 10-20 mg/L (55-110 micromol/L) achieve bronchodilation; lower (5-15 mg/L) may suffice in some. Toxicity risk rises >20 mg/L; adverse effects possible even at 10-20 mg/L.
