BIOLOGY 11: Microscope
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Microscope
It is an instrument that produces magnified images of tiny structures.
Dissecting Microscope
It is a microscope used for dissecting specimens. It provides a magnified, 3D view that allows the person performing the dissection to see the specimen clearly. With the right magnification and resolution, finer details can also be observed.
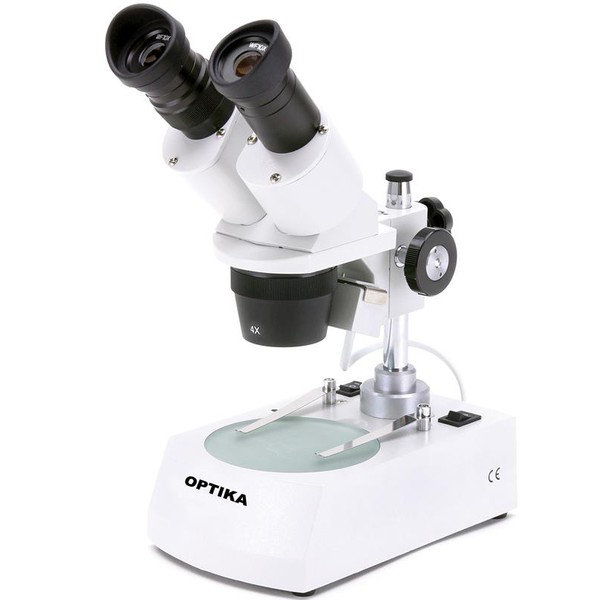

Electron Microscope
It is a high-powered, high-resolution microscope that uses a focused beam of electrons and electromagnetic lenses to produce images at the nanoscale, allowing magnification of up to 10,000,000x.
This type of microscope can be further classified into two types: transmission and scanning.
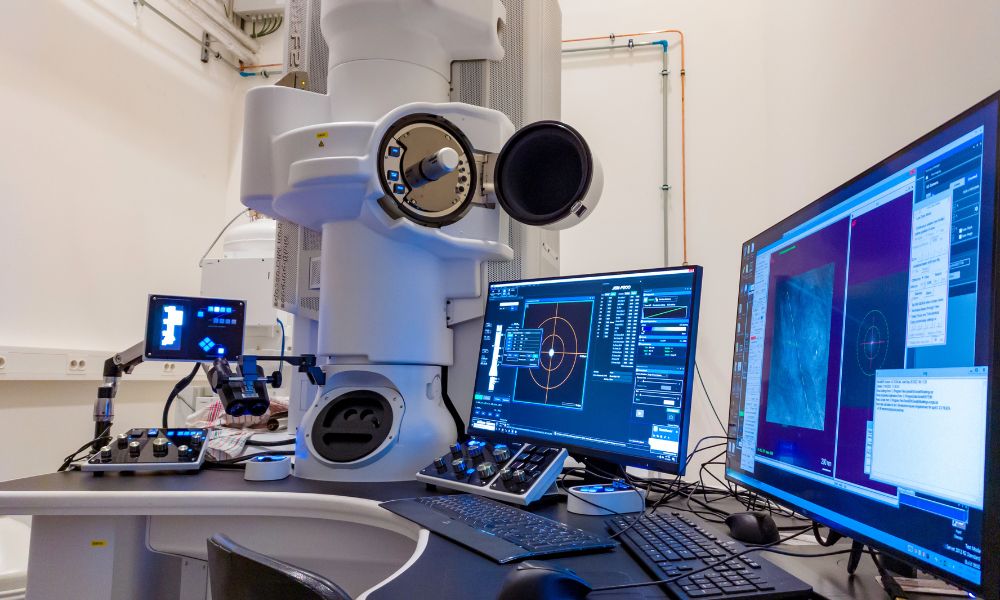

Transmission Electron Microscope
It is a type of microscope that uses a beam of electrons transmitted through a very thin specimen to produce highly detailed images of its internal structures at extremely high resolution.
Scanning Electron Microscope
It is a type of microscope that uses a focused beam of electrons to scan the surface of a specimen, creating detailed images that show the surface structure and give a three-dimensional appearance.
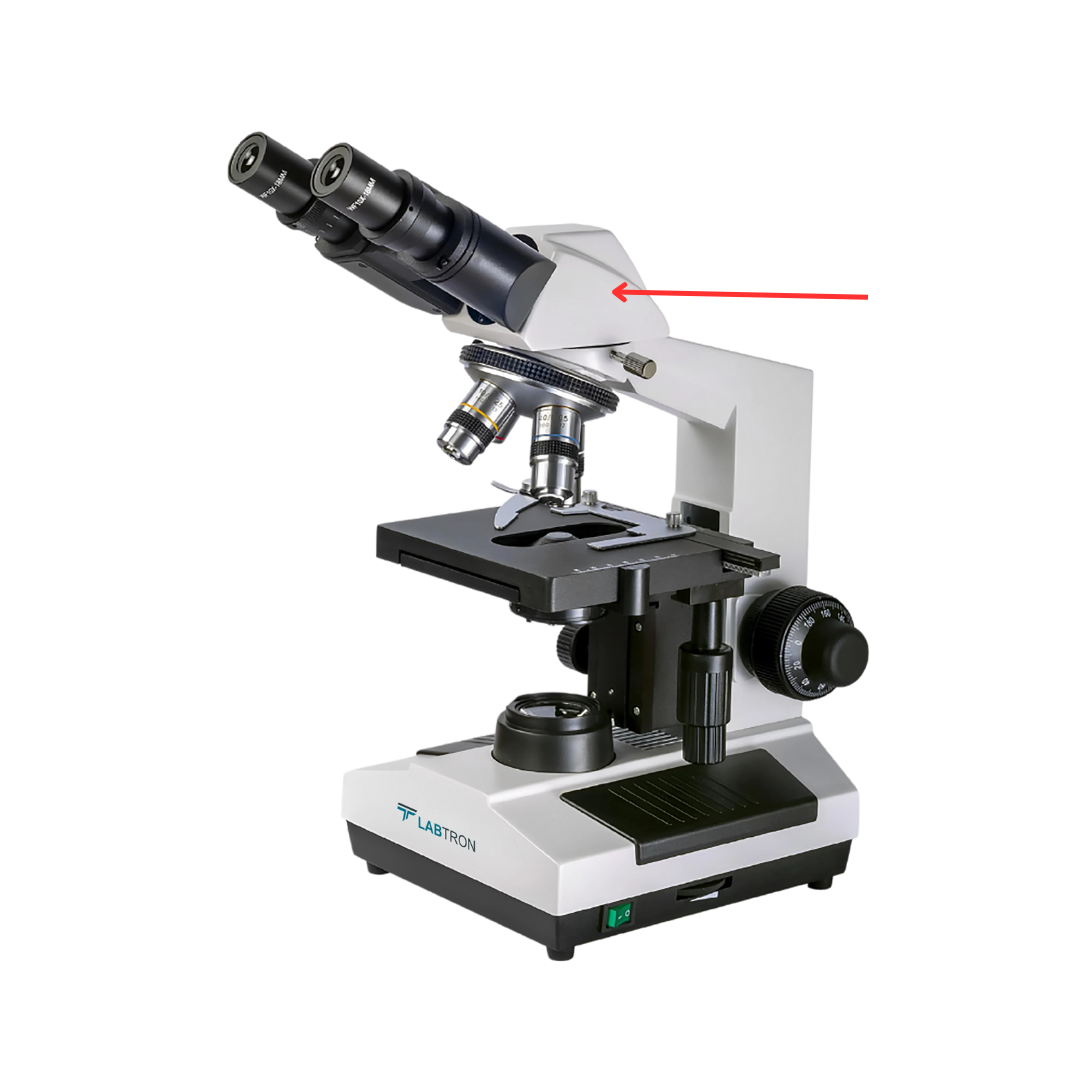
Compound Microscope
It is a type of microscope that uses visible light and multiple lenses to magnify small specimens, allowing the observer to see fine details of cells and tissues at moderate to high magnification.

3 main parts of a microscope
Optical
Illuminating
Mechanical
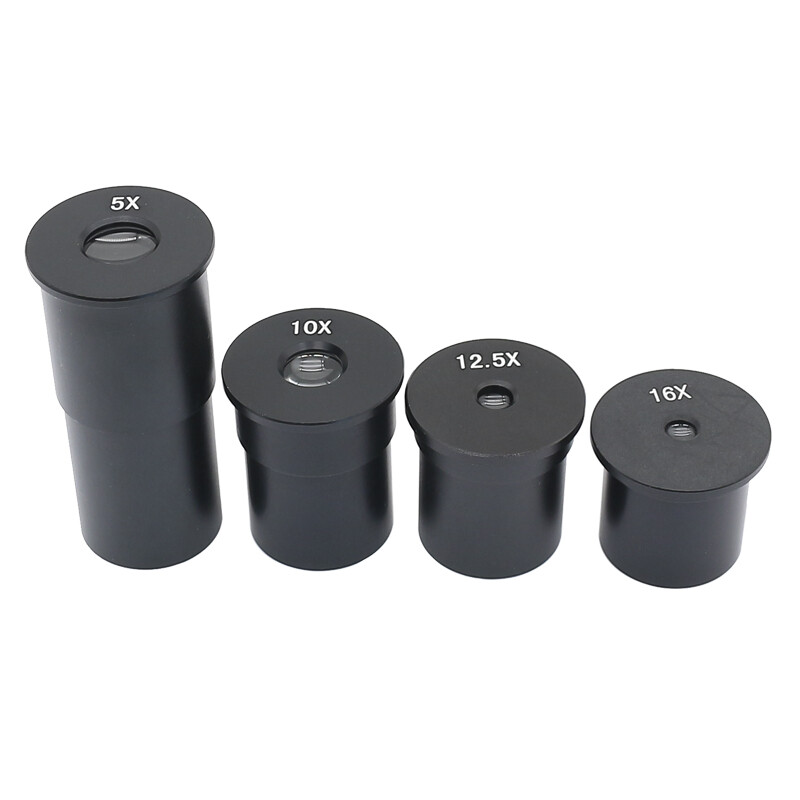
Ocular Eyepiece
It is the lens closest to the viewer’s eye, used to look at the specimen, and it ranges from 5x to 30x magnification.

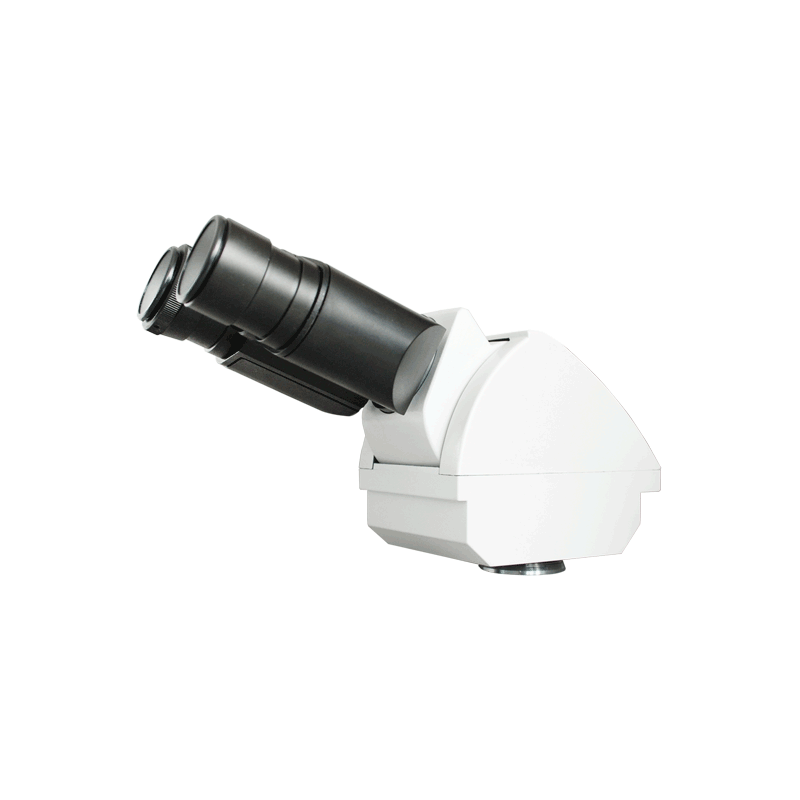
Eyepiece Tube
Holds the eyepiece lens in place above the objective lens, positioning it for viewing.

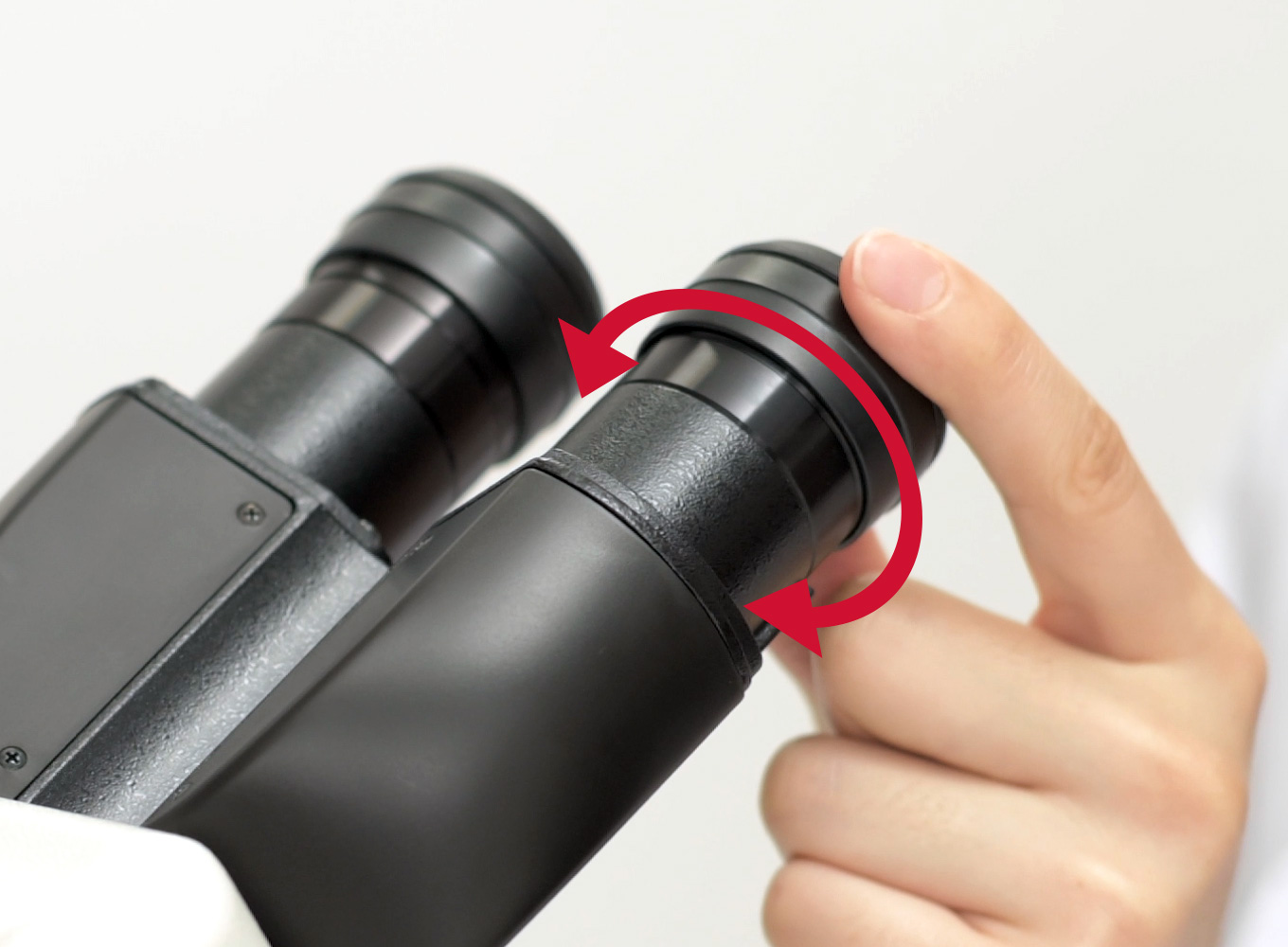
Diopter Adjustment
A control knob that is present only if the microscope has 2 eyepieces. It is used to change focus on 1 eyepiece and to correct any difference in vision.

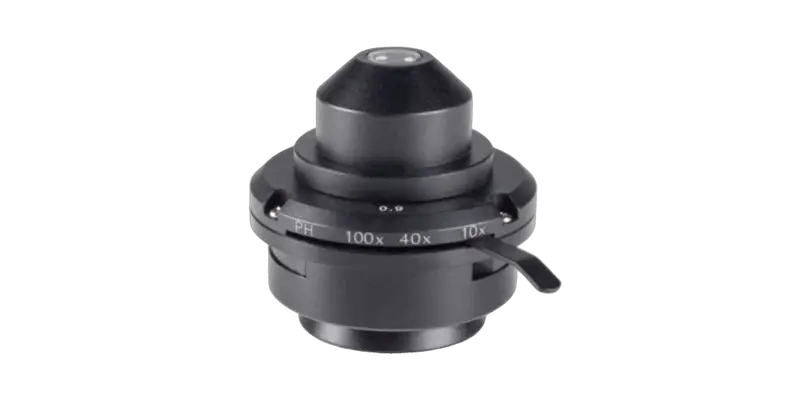
Nosepiece/Revolving Turret
It holds multiple objective lenses (typically 3-5) and rotates to allow the user to easily switch between different magnification levels.
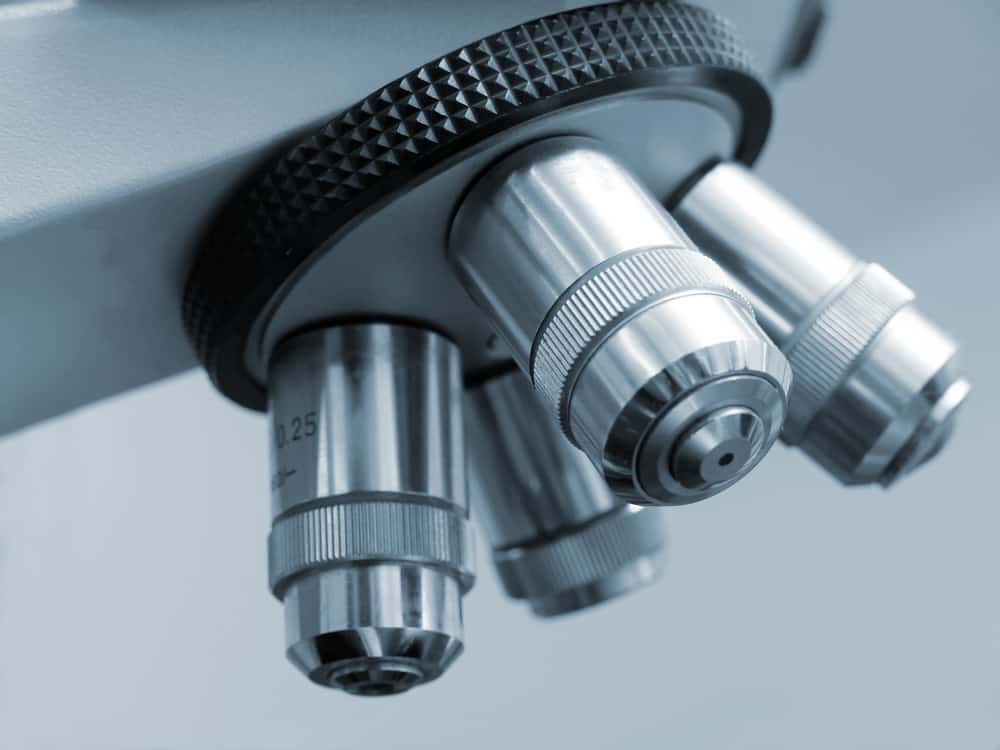

Objective Lenses
The primary lenses closest to the object being looked at in a microscope.
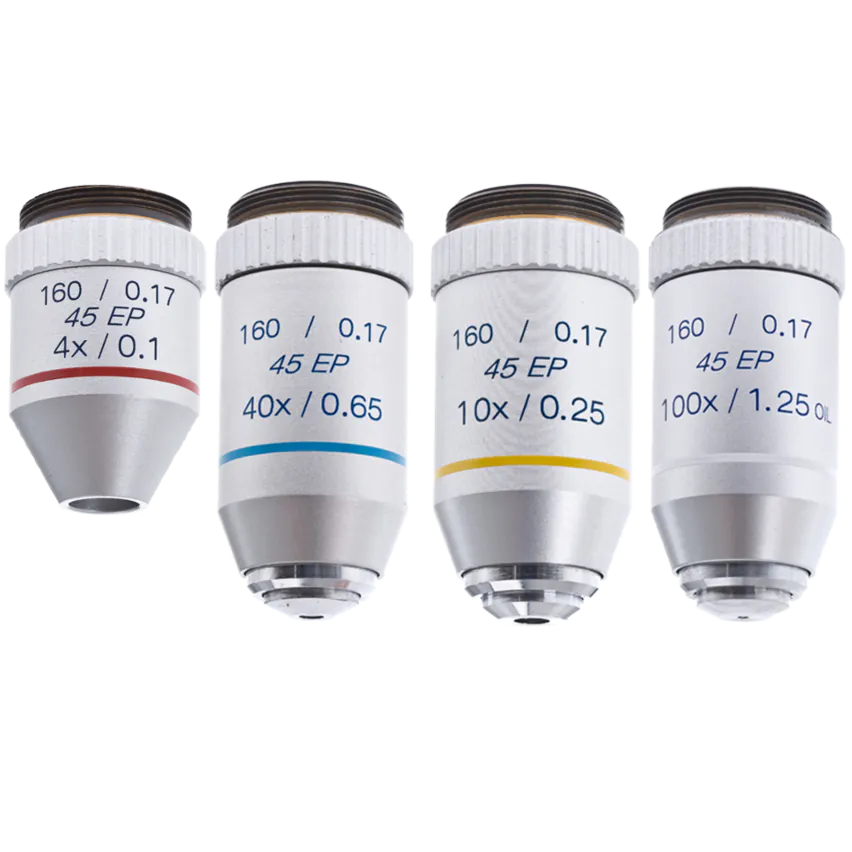

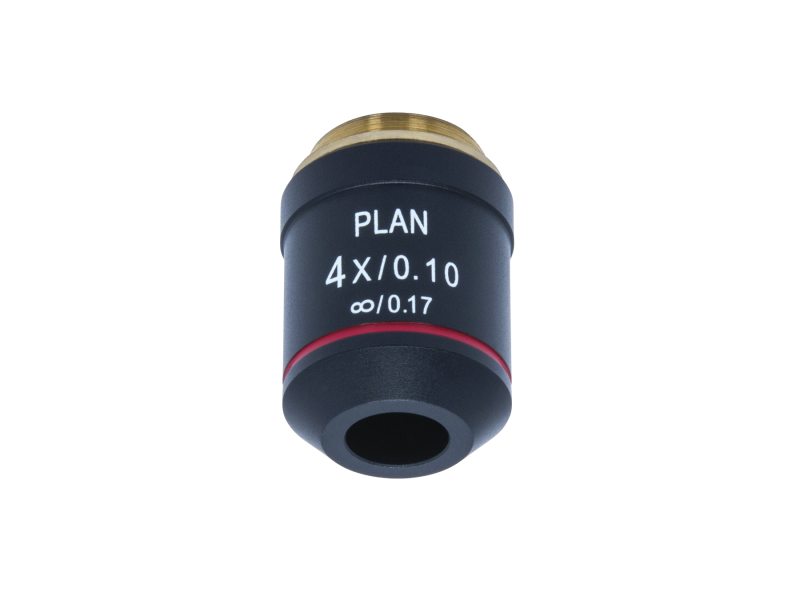
SPO (Scanning Power Objective)
Lowest magnification lens (4x)
Used to get a wide view of the specimen and to locate the area you want to examine.

LPO (Low Power Objective)
Low magnification lens (10x)
Used for general viewing and to see more details than the scanning lens.

HPO (High Power Objective)
High magnification lens (40x)
Used to see fine details of the specimen.

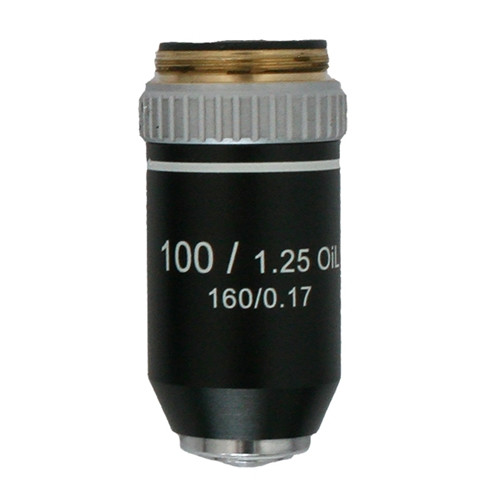
OIO (Oil Immersion Objective)
Highest magnification lens (100x)
Used with immersion oil to increase clarity and resolution for very small details.

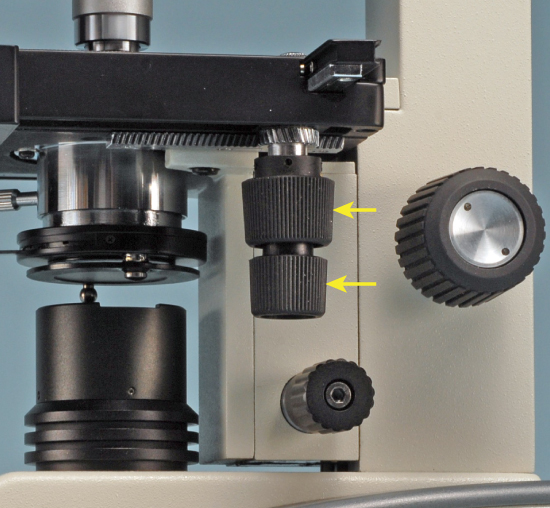
Fine Adjustment Knob
It is the smaller knob used for making very precise focus adjustments, helping to sharpen the image and improve clarity, especially when using the high power objective.
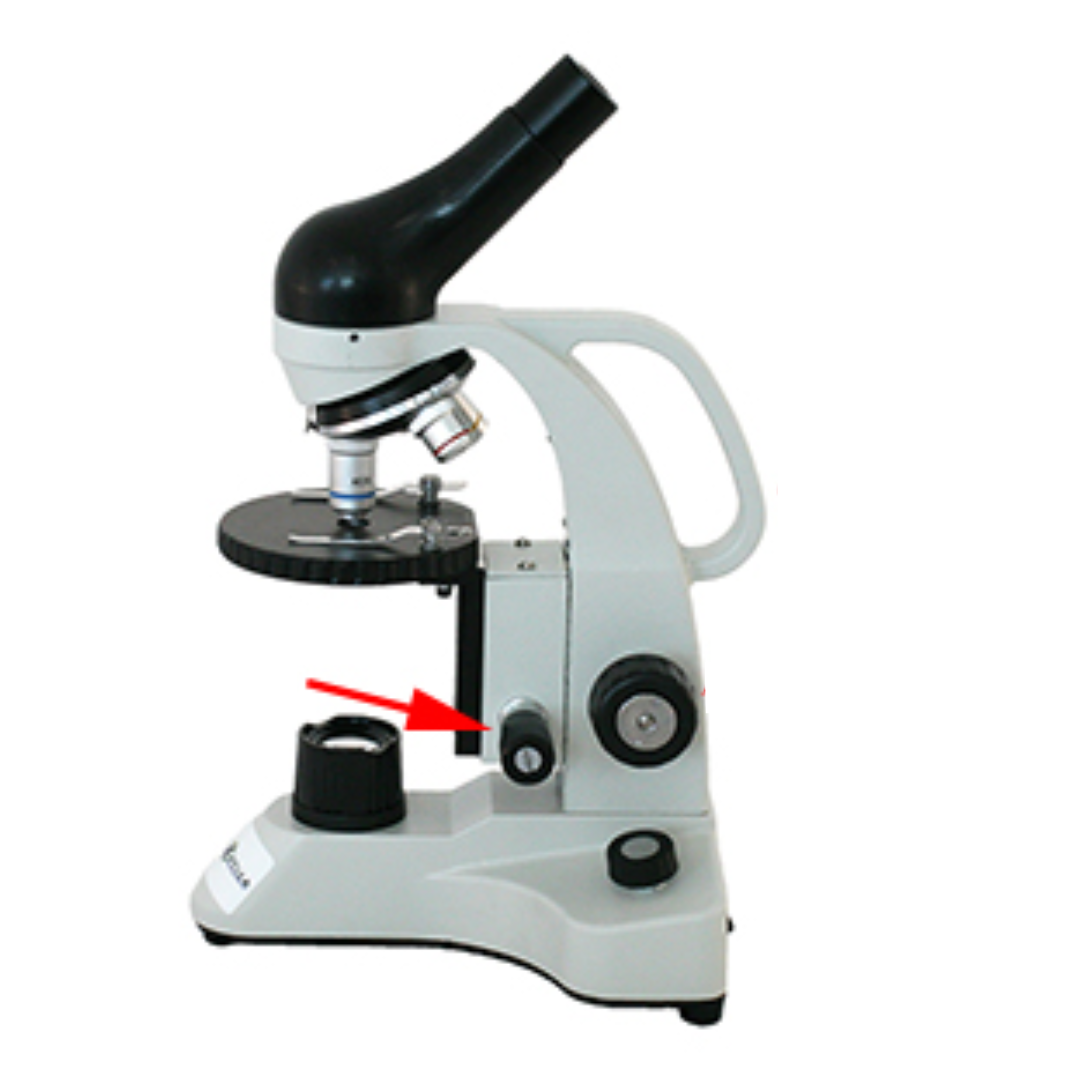

Coarse Adjustment Knob
It is the bigger knob used to adjust the stage higher or lower, helping to bring the specimen into general focus, especially when using the low power objective.
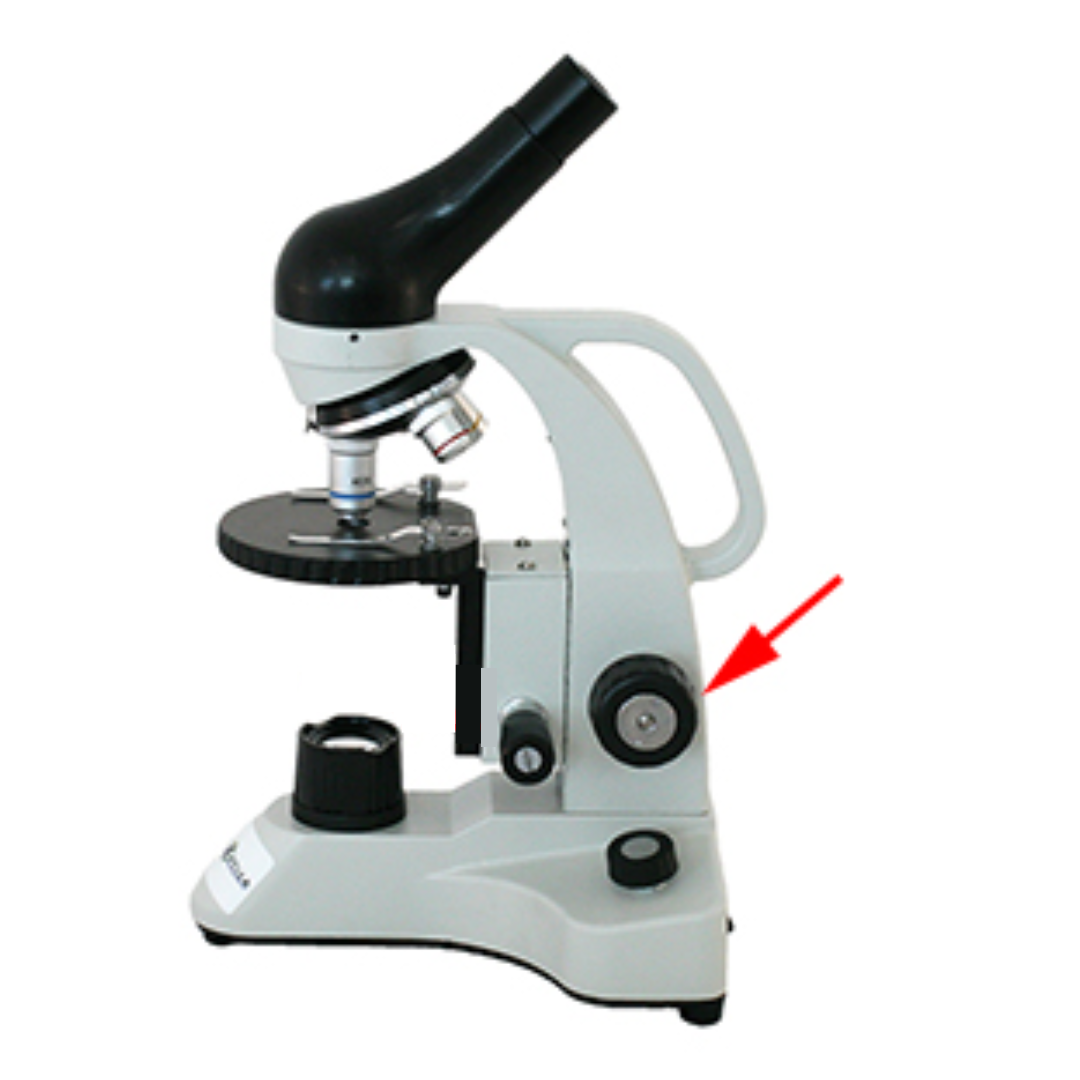
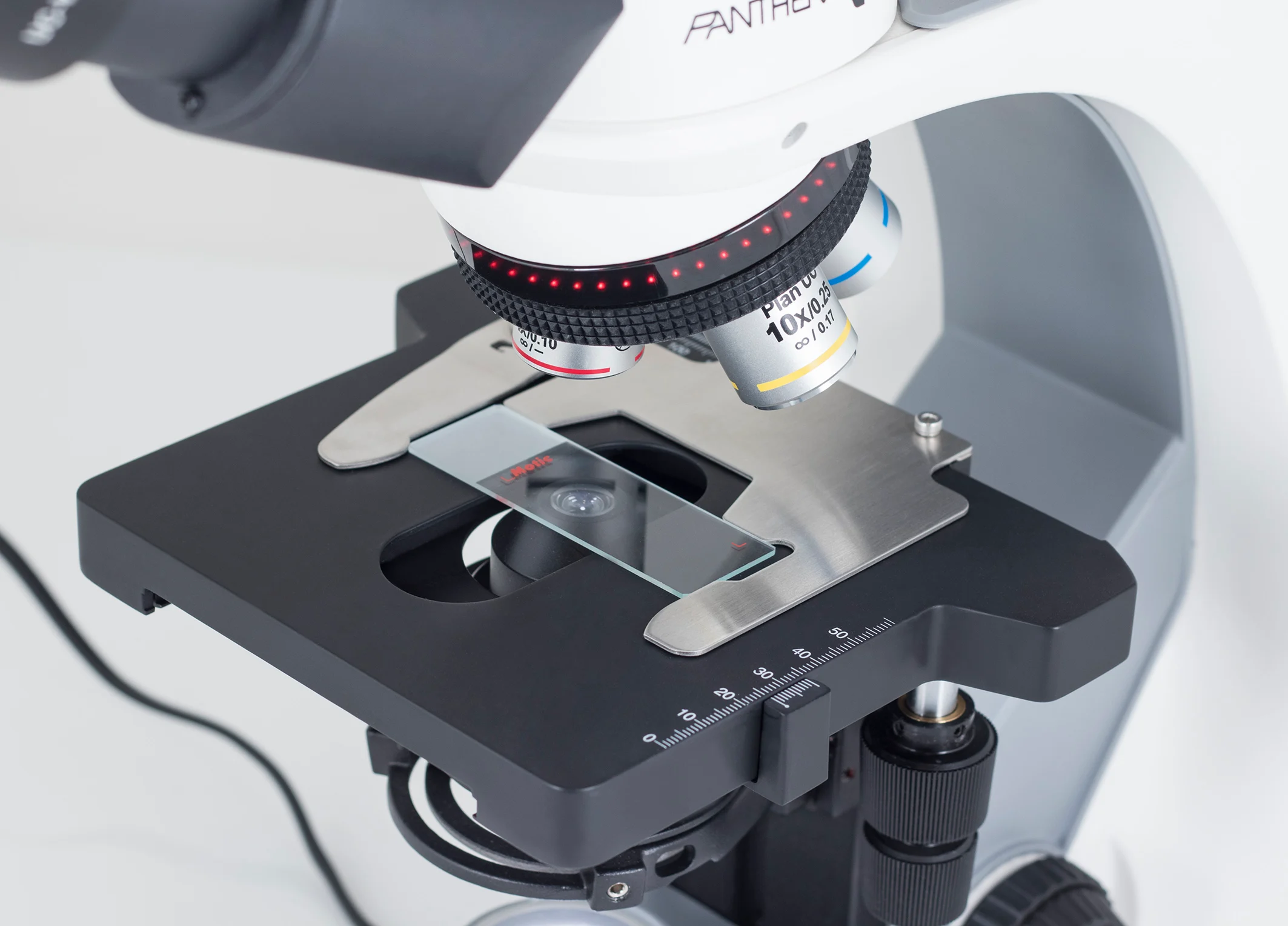
Stage
This is the platform where specimen slides are placed for viewing. It uses stage clips to secure said slides in place.

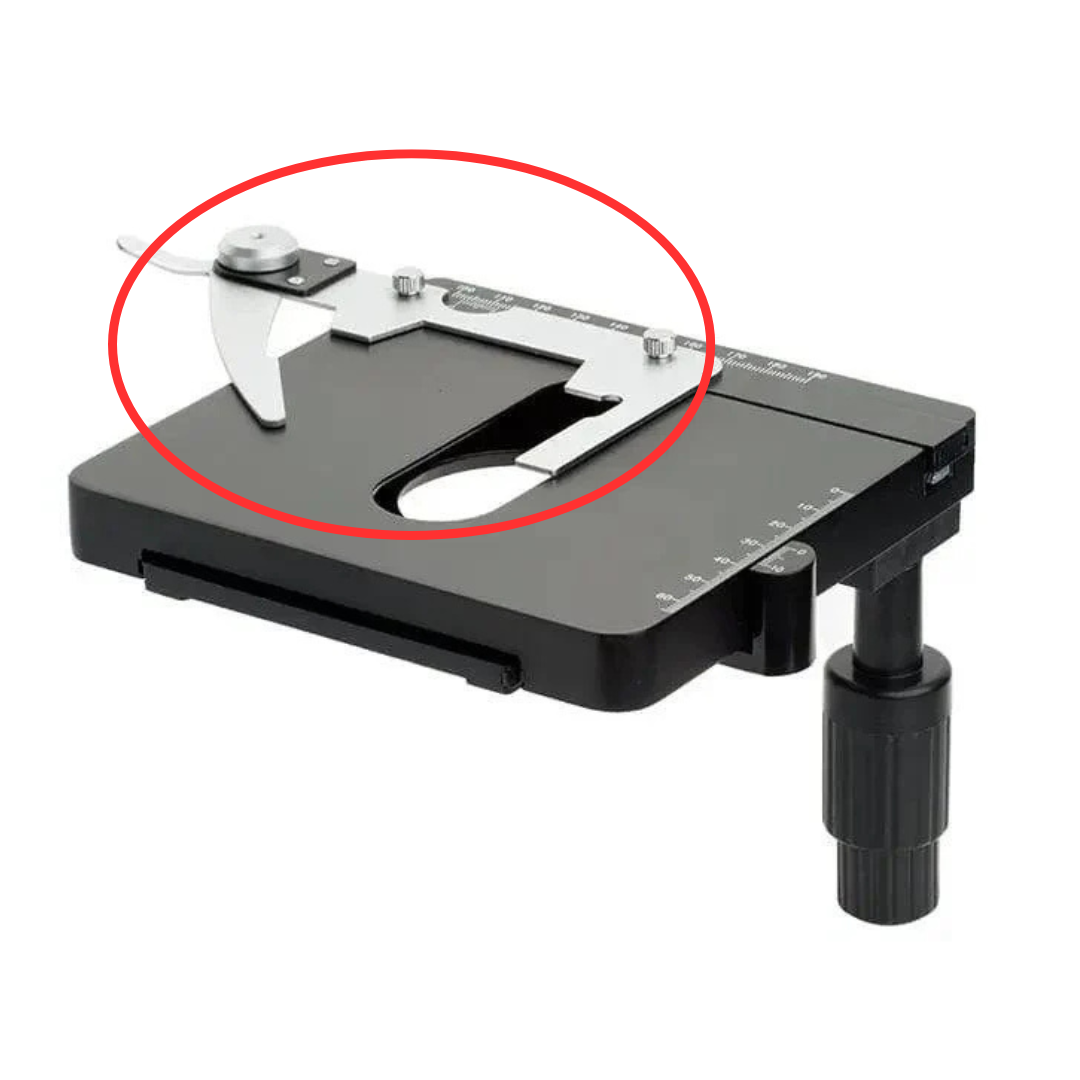
Stage Clips
These are small, metal, or plastic spring-loaded clamps on a microscope stage that secure the slide, ensuring the specimen remains steady and properly positioned over the aperture for accurate, stable viewing.

Stage Control Knob
It is a knob used to move the stage mechanically either forward and back or left and right.
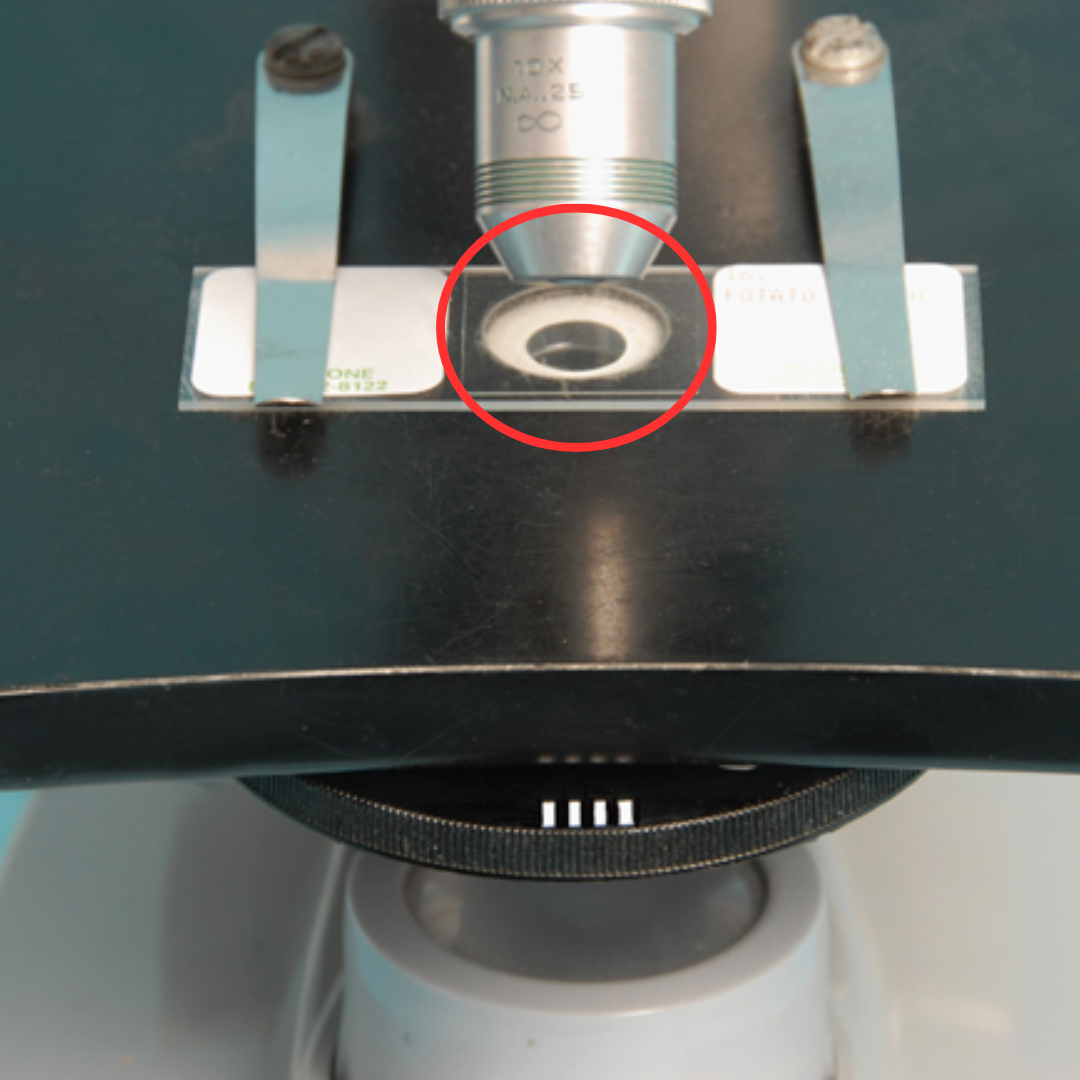
Aperture
It is a hole in the stage that enables light to pass through.
Condenser
It is the lenses used to collect and focus light from the illuminator into the specimen.

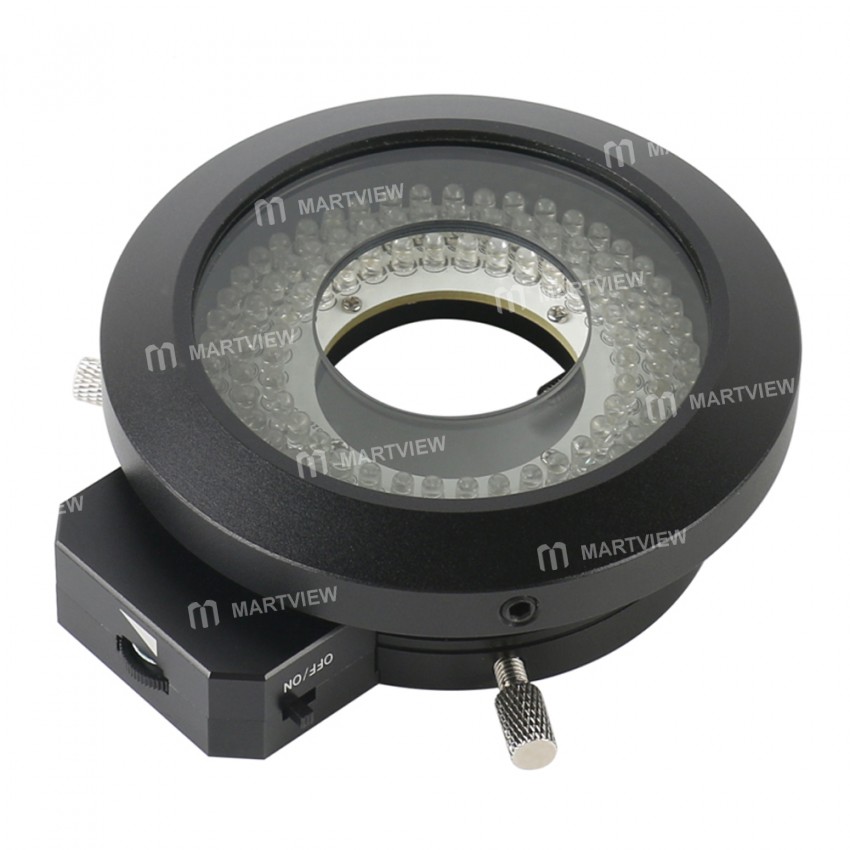
Illuminator
The light source for a microscope.

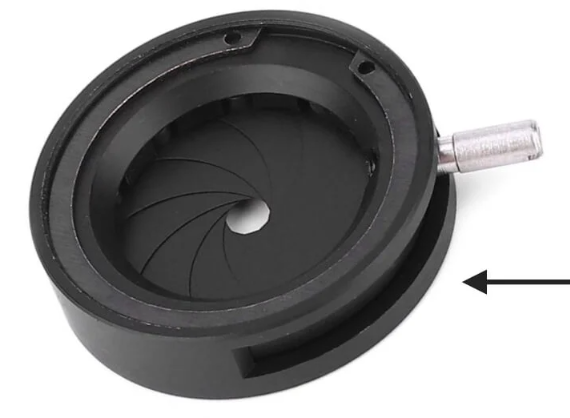
Diaphragm/Iris
It is found under the stage and is used to control the amount of light that reaches the specimen.

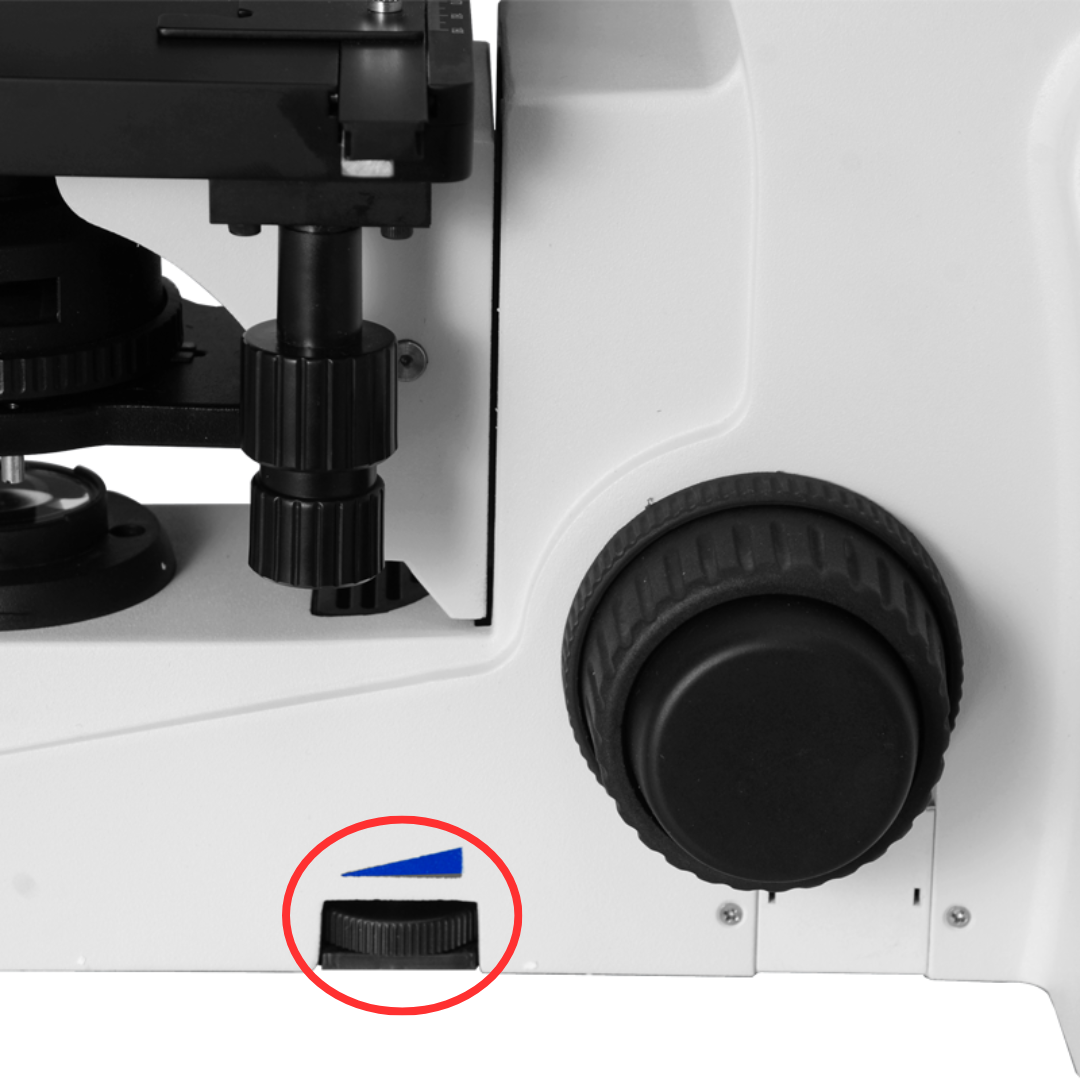
Condenser Focus Knob
It is used to move the condenser up or down to control the focus of light.
Abbe Condenser
It is a condenser found on high-quality microscopes that focuses and concentrates light onto the specimen, improving illumination and contrast, and it can be used for magnification up to 900x.
Rack Stop
It prevents the objective from hitting the specimen.
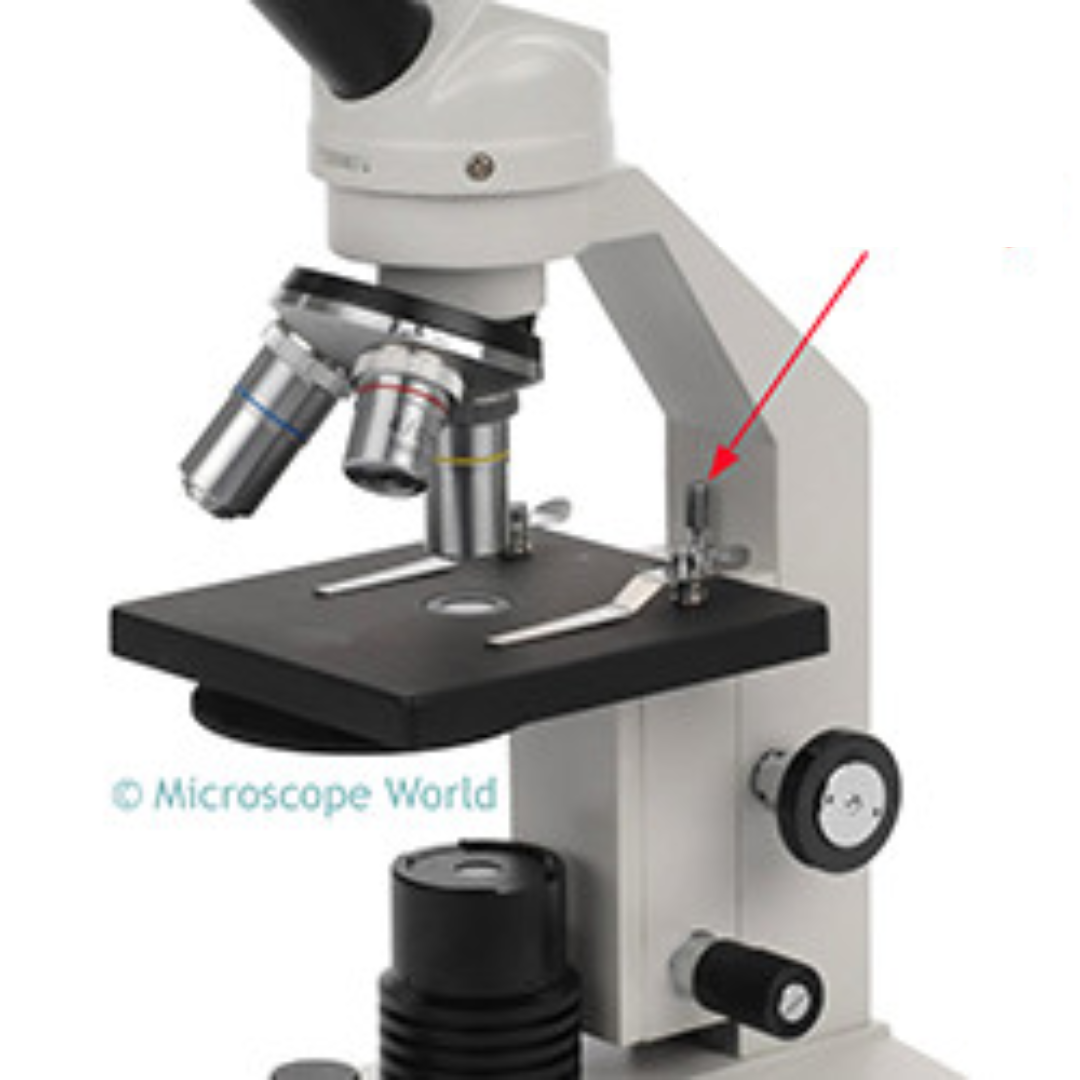
Light Switch
Turns the microscope’s light on or off.
Brightness Adjustment
It is used to adjust the light intensity, making the specimen easier to view by making the illumination brighter or dimmer.

Mirror
It is used to reflect and direct light from an external source onto the specimen, providing illumination for viewing.

Base
Allows the microscope to stand.
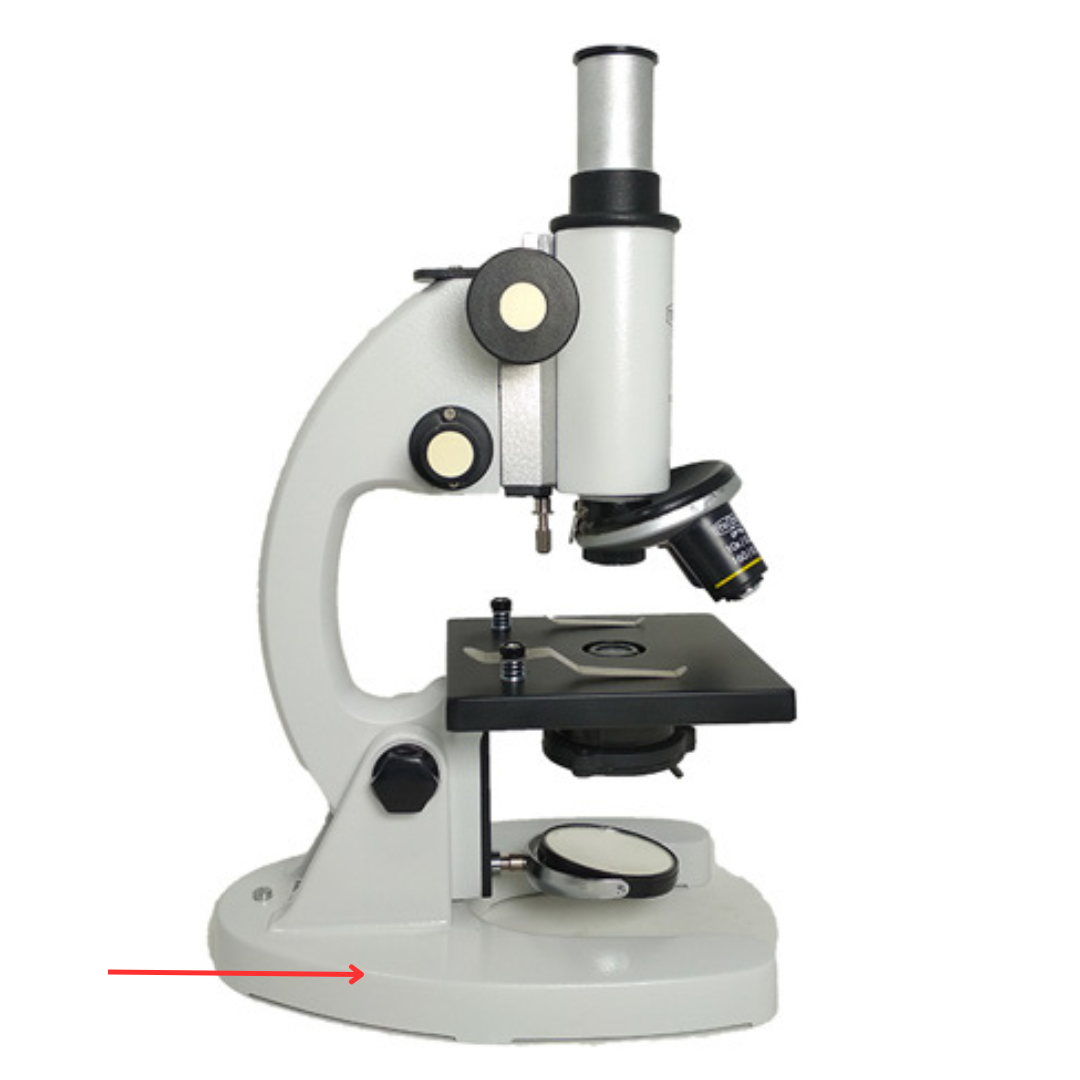

Pillar
Supports the stage.
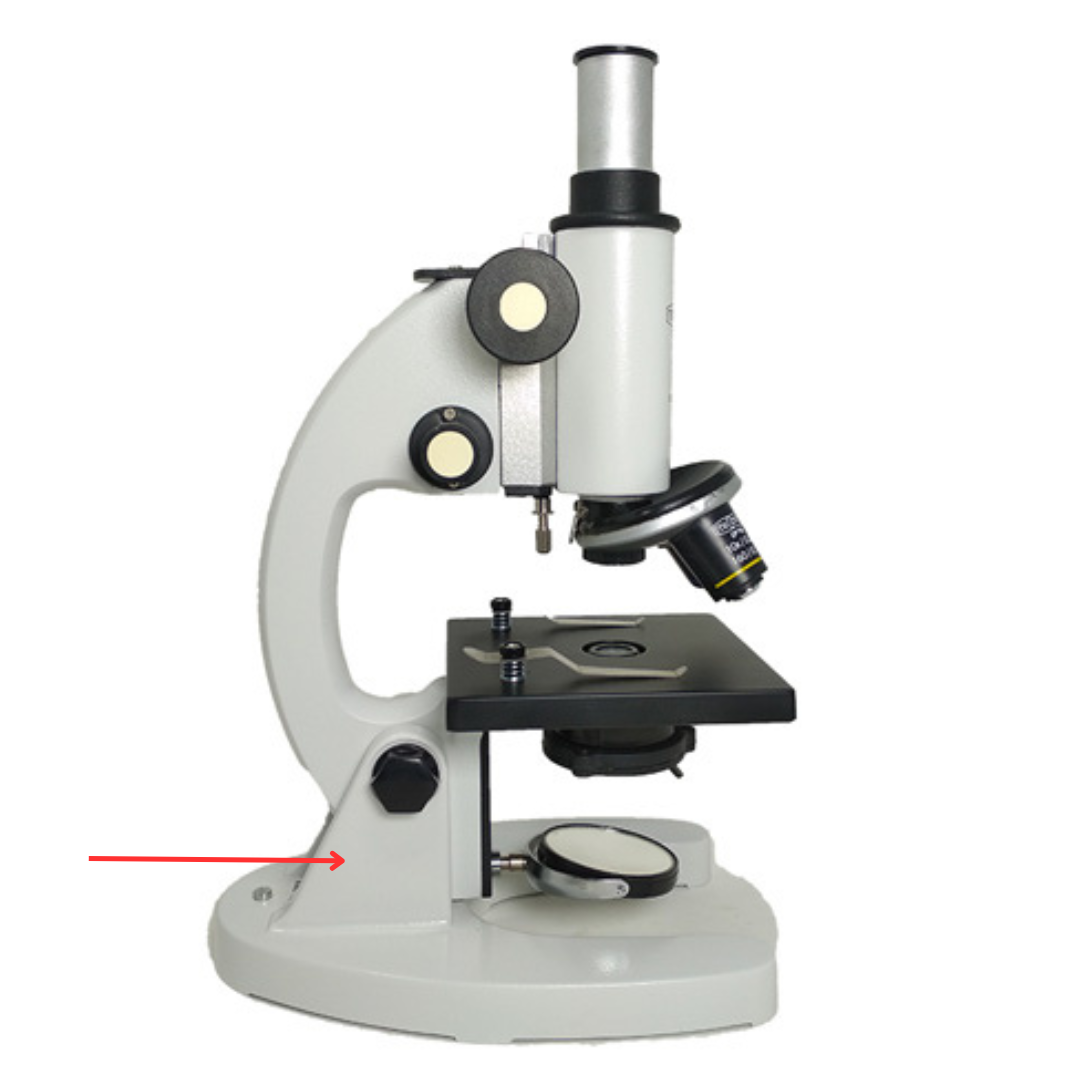

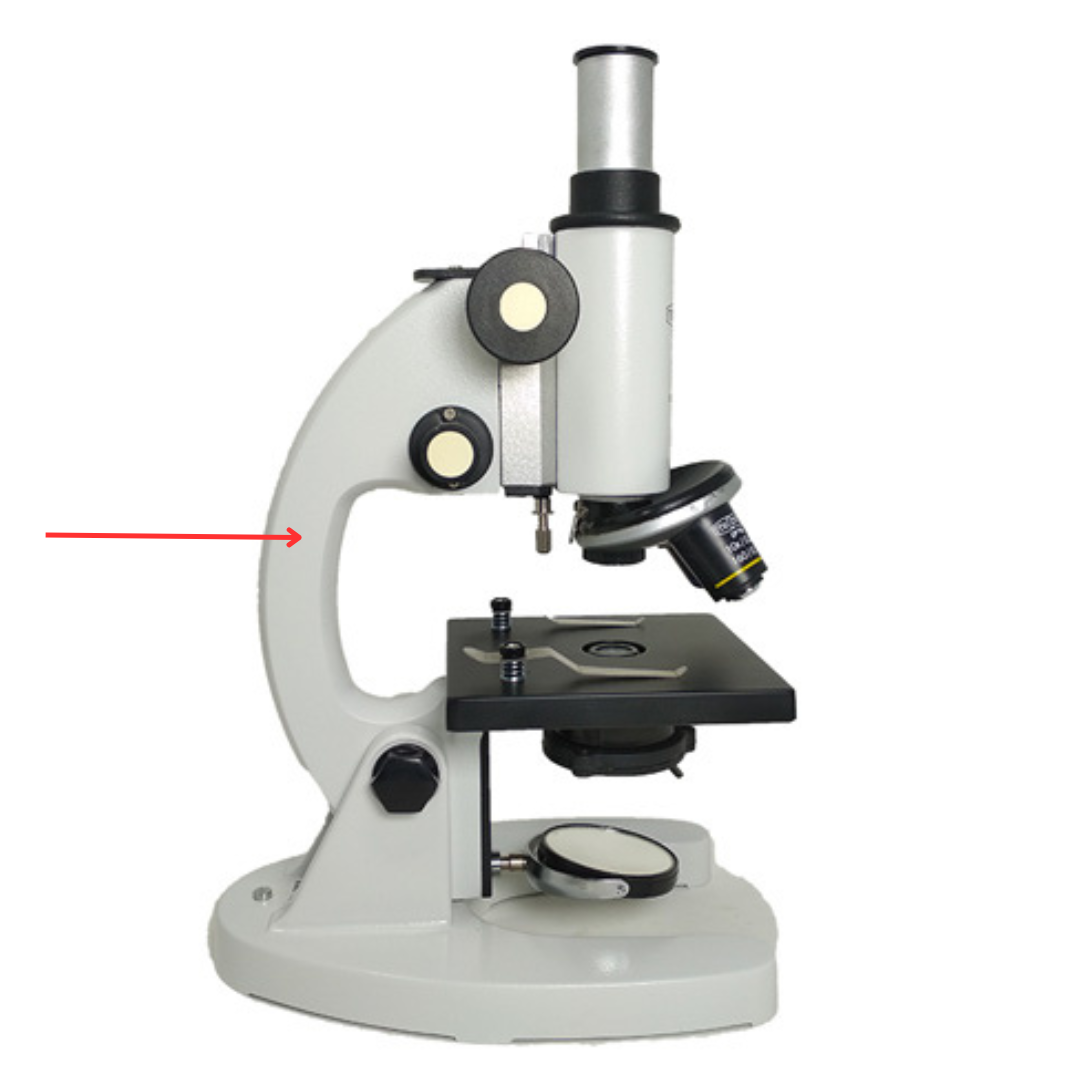
Arm
Curved part grasped when carrying the microscope.

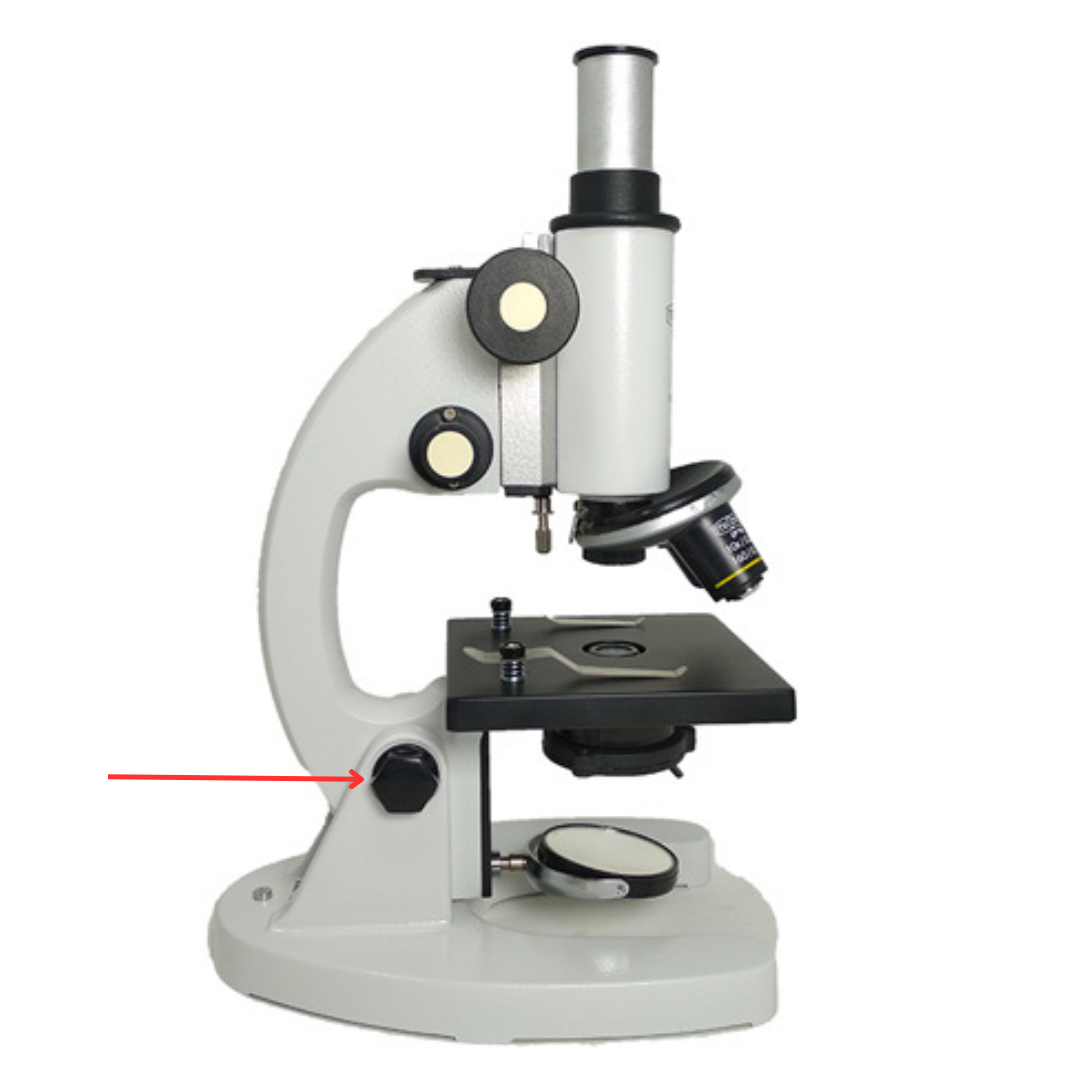
Inclination Joint
It is used to allow tilting of the microscope so the user can view the specimen at a more comfortable angle.

Mirror Rack
Holds the mirror in place.
Head
It supports and connects the eyepieces to the objective lenses, ensuring proper alignment for image viewing.
