Week 2 Physics
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Pulsed & continuous ultrasound, PRP & PRF, PD, DF, SPL, bandwith
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
Pulsed wave ultrasound
Uses short pulses of sound separated by gaps of no sound.
Ability to perform echo location and generate images by assigning pixels to echoes.
Commonly utilized in sonography and most Doppler ultrasound.
Continuous wave ultrasound
Does not allow for echo location, distance measurement, or image formation.
Characteristics of Pulsed Wave Ultrasound
Consists of few cycles of compressions and rarefactions.
Key components include:
Ringing Period: Short periods during which sound is emitted.
Listening Period: Longer gaps where no sound is emitted.
Each pulse creates a single scan line, leading to image formation.
Characteristics of Continuous Wave Ultrasound
Continuous flow of sound wave; does not allow for localization of echoes.
Used primarily for accurate measurement of high-velocity flows but has poor range resolution.
Continuous Wave Vs Pulsed Wave Ultrasound
Pulsed Wave offers good range resolution but has limitations on maximum velocity.
Continuous Wave is beneficial for high speeds but sacrifices depth accuracy.
PRP (Pulsed Repetition Period)
The time duration from the beginning of one pulse to the beginning of the next, which affects the maximum imaging depth and the frame rate i.e. once cycle
Measured in seconds (sec), milliseconds (ms), or microseconds (μs).
PRP is influenced by
The depth of imaging.
The speed of sound in soft tissue.
Examples: Typical PRP values in diagnostic ultrasound range from 0.08 to 0.5 μs.
Non-adjustable: The PRP value is not operator adjustable; it is determined by the transducer/ultrasound system.
Period (T) vs. Pulse Repetition Period (PRP)
Period measures the duration of a single oscillation.
PRP measures the time for completing one echo segment (includes ringing and listening time).
Pulse Repetition Frequency (PRF)
The number of pulses transmitted per second, which influences the image quality and temporal resolution.
Commonly expressed in Hertz (Hz) or Kilohertz (KHz).
PRF is essentially how often the ultrasound transducer emits a pulse.
PRF indicates how many scan lines can be produced in one second, influencing frame rate
Relationship between PRP and PRF
Inversely proportional
PRP (ms) = 1/PRF (kHz)
Field of View (FOV) Impact
Affects the number of scan lines required and, subsequently, the frame rate:
Curved Linear Transducer: Larger FOV requires 400-600 scan lines.
Linear Transducer: Smaller FOV requires 300-400 scan lines.
Sector Transducer: Smallest FOV requires 200-300 scan lines.
Pulse Duration (PD)
The time it takes for a single pulse emitted from the ultrasound transducer.
Typically in microseconds (μs).
PD (us) = T (us) x n
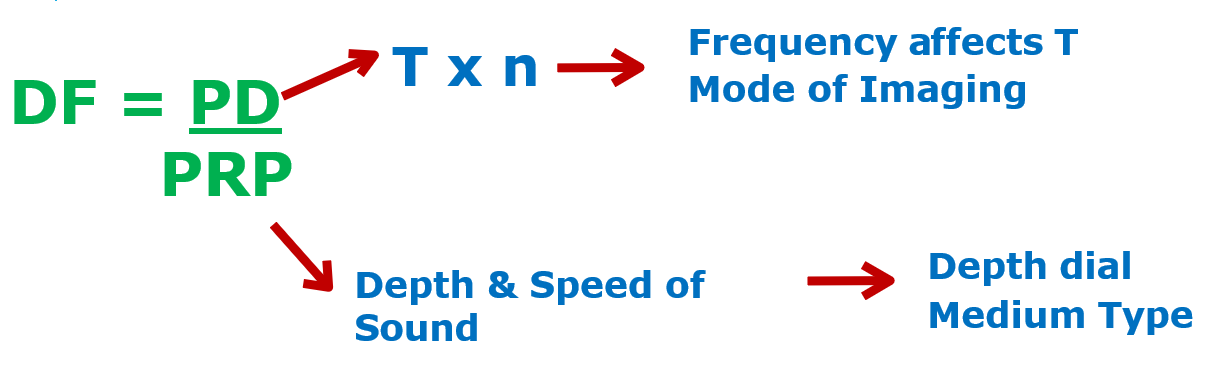
Duty factor (DF)
The percentage of time that the ultrasound system is actively emitting a pulse compared to the total time (ringing + listening).
Provides insight into how often ultrasound is used in imaging versus listening time.
Duty factor formula
DF = PD/PRP
Spatial Pulse Length (SPL)
The physical space that a pulse occupies in the medium.
Unit: Millimeters (mm).
SPL = λ x n
SPL impact on image quality
Smaller SPL = Better Image Resolution
Very long pulses lead to poor resolution because they cannot differentiate between closely located objects.
Bandwidth
The range of frequencies contained within a pulse. The shorter the pulse, the broader the bandwidth