BIOL 162 -Chapter 5: Reflexes and Reaction Times
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
Neuron
A single cell that specializes in communication via electrical impulses.
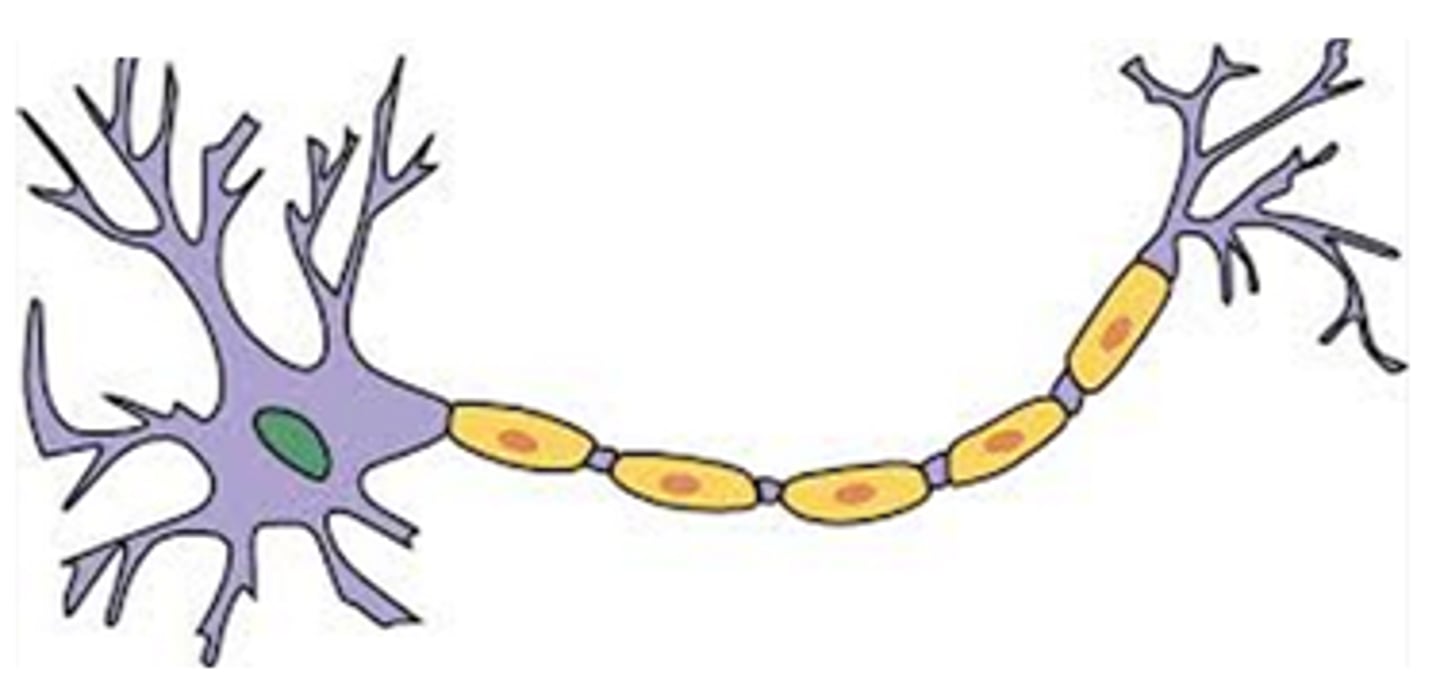
Cell Body/Soma
The largest part of the neuron containing the nucleus and organelles.
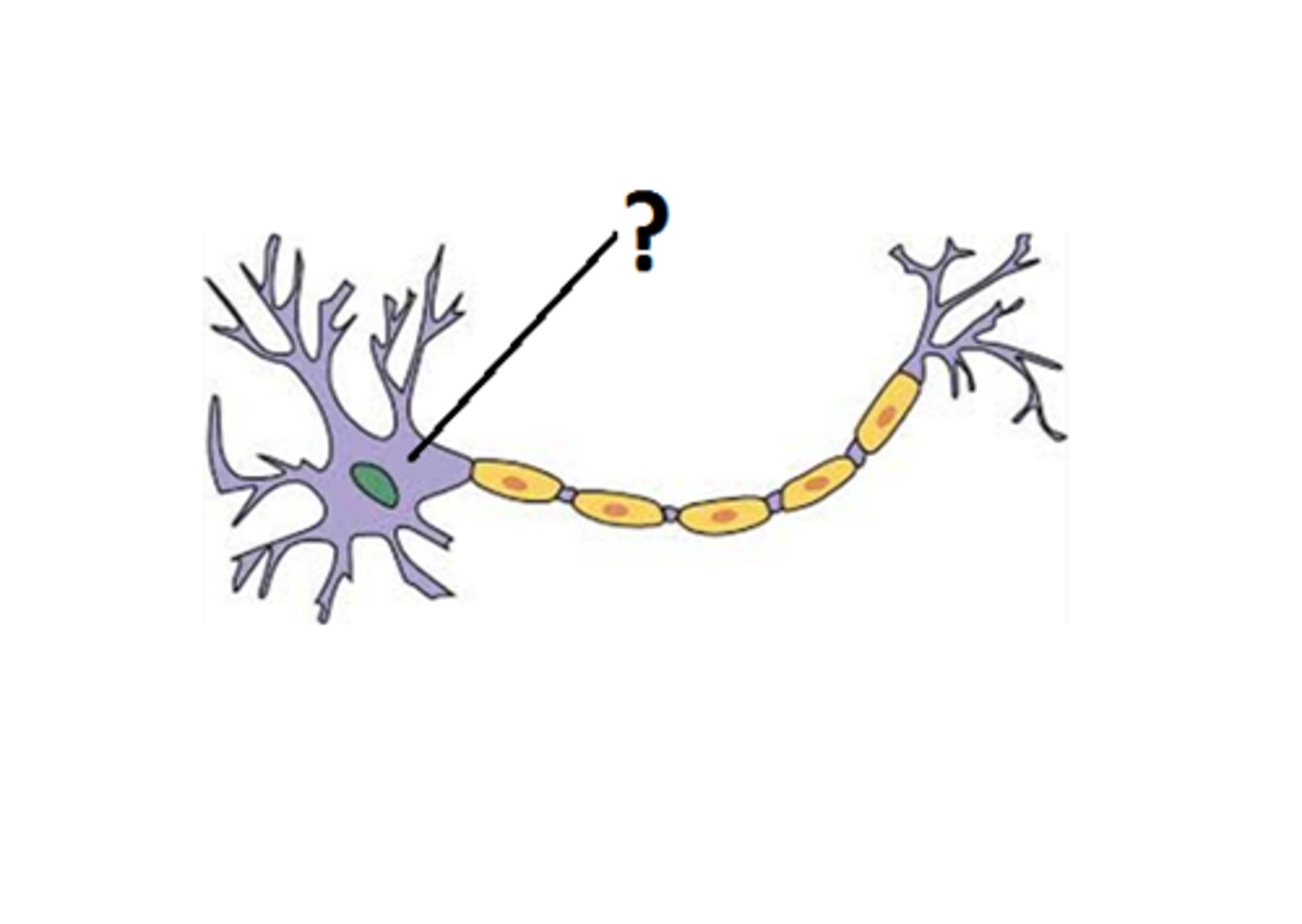
Dendrites
Short projections continuous with the soma and function to receive information.
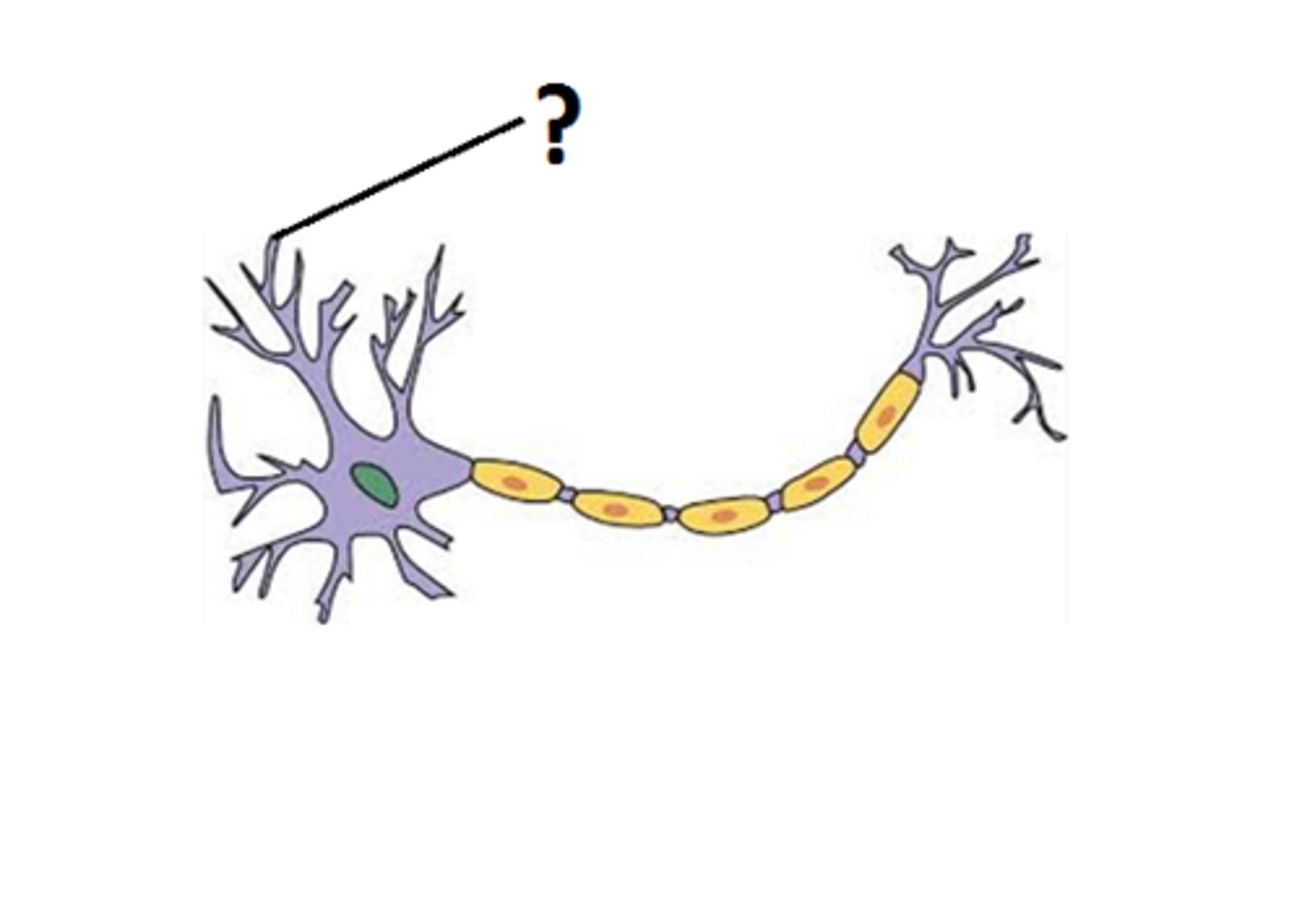
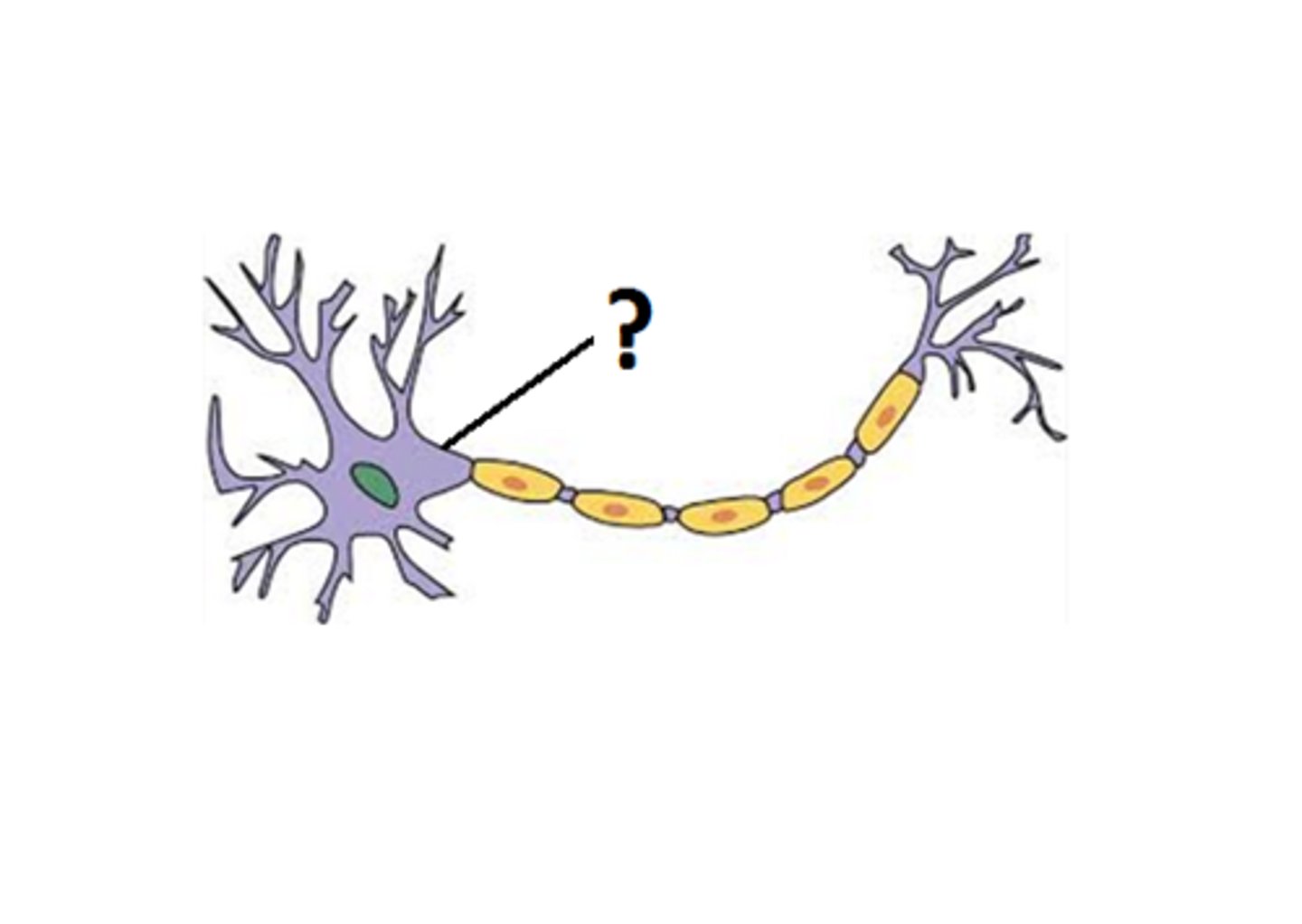
Axon
The single long projection responsible for transmitting information from the cell body to the next cell.
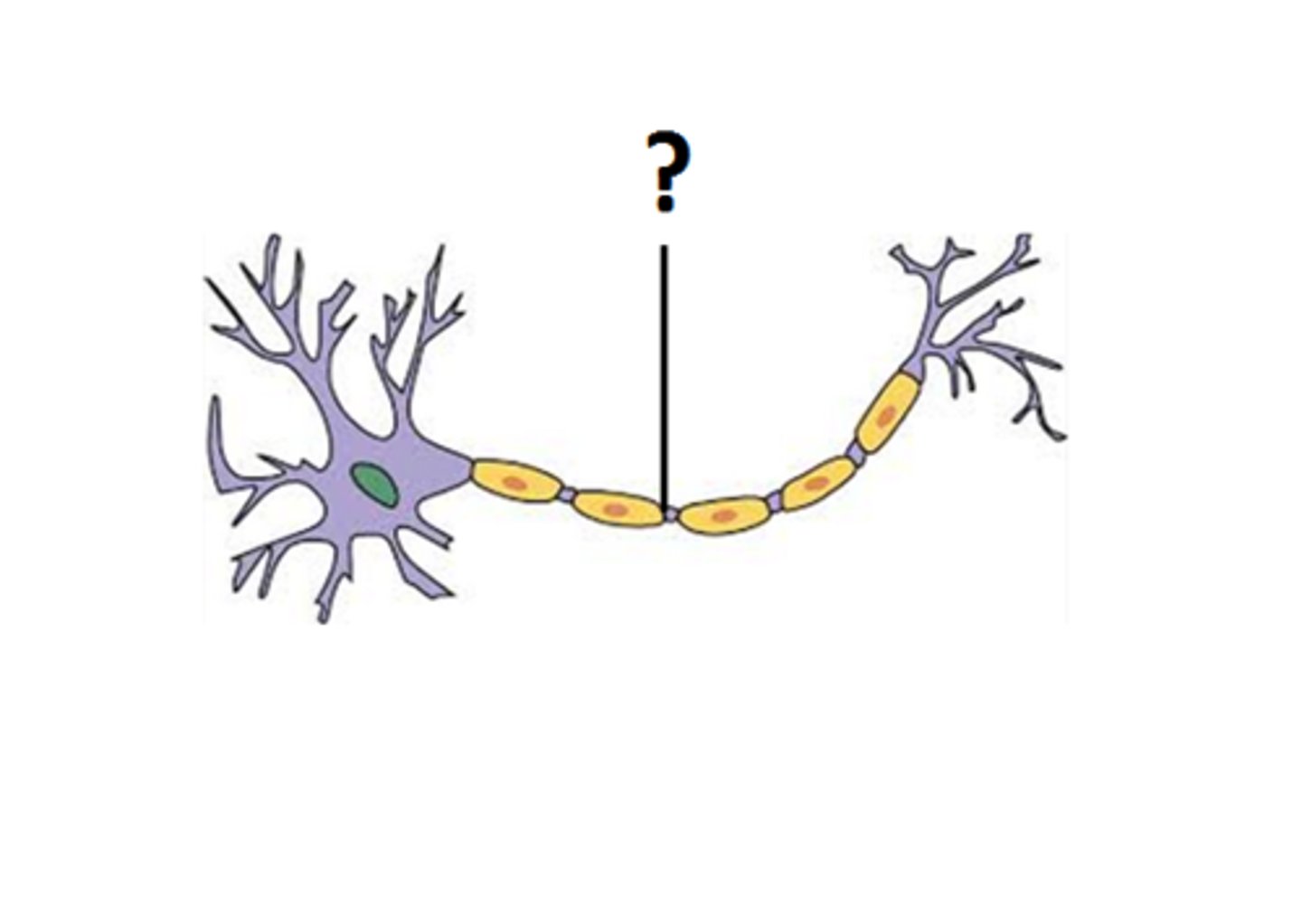
Axon Hillock
The portion of the axon connecting the cell body, often swollen, the site of action potential generation.
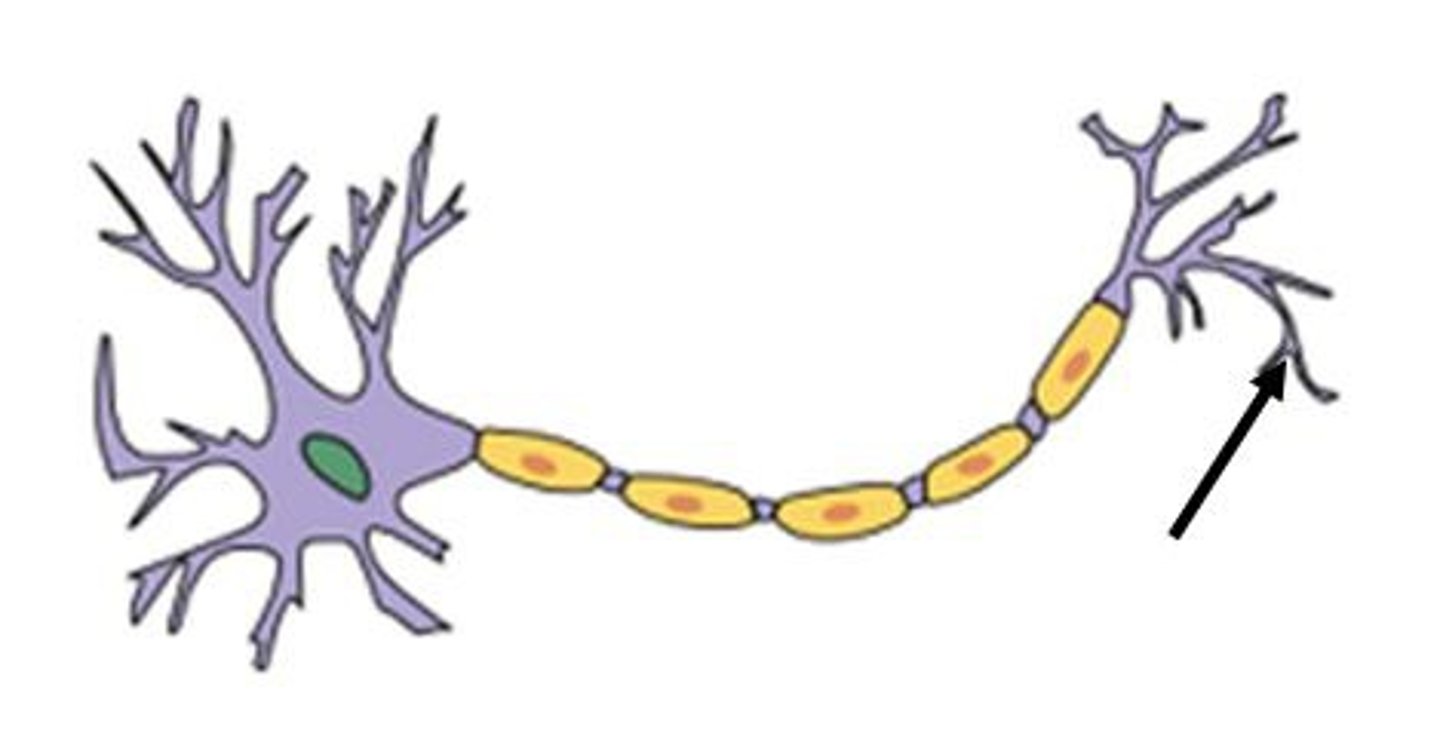
Axon Terminals
The end of an axon that is branched.
Synapse
A junction between two nerve cells.
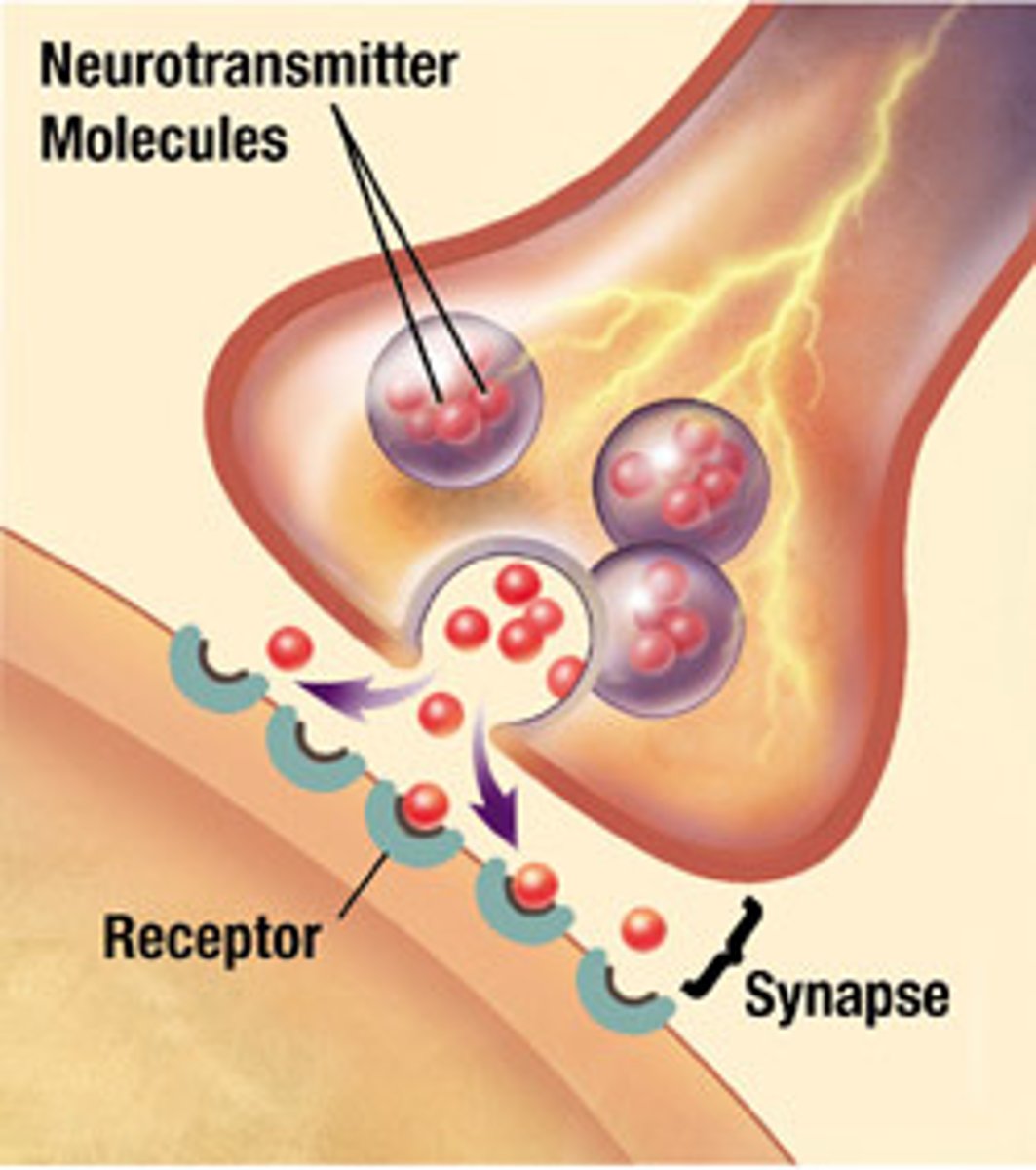
Pre-Synaptic Neuron
The neuron sending a signal.
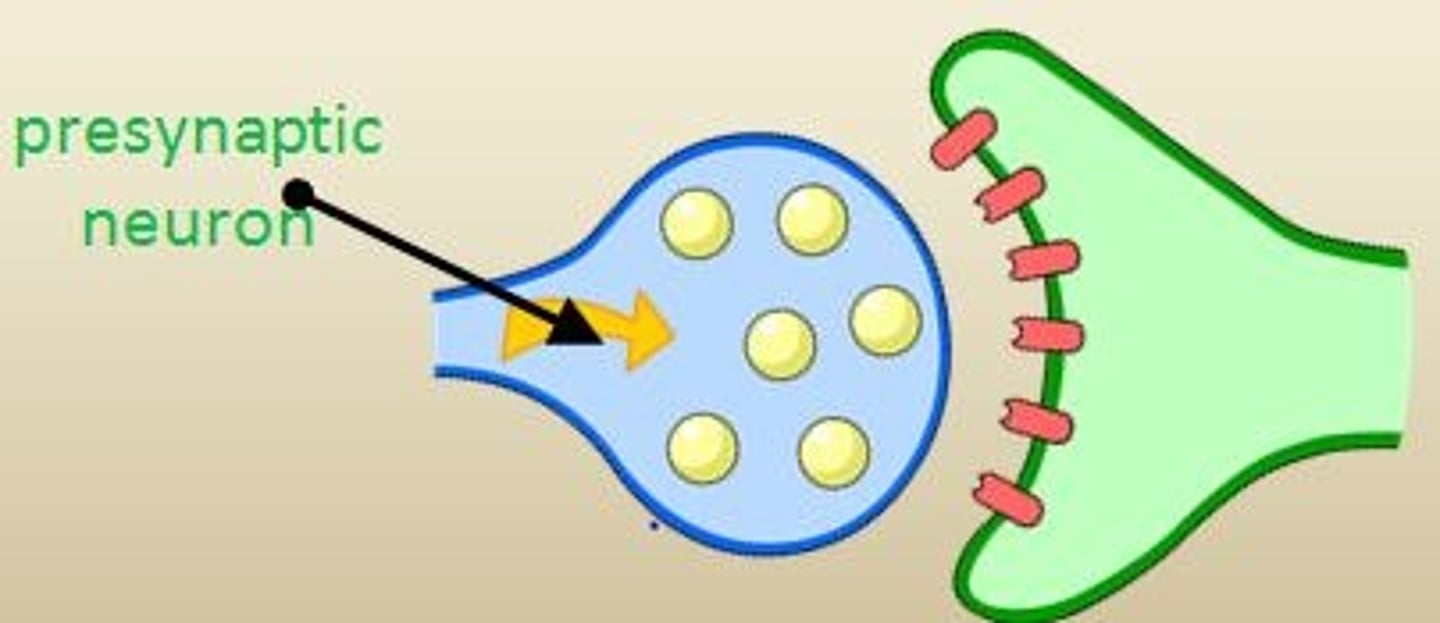
Post-Synaptic Neuron
The neuron receiving the signal.
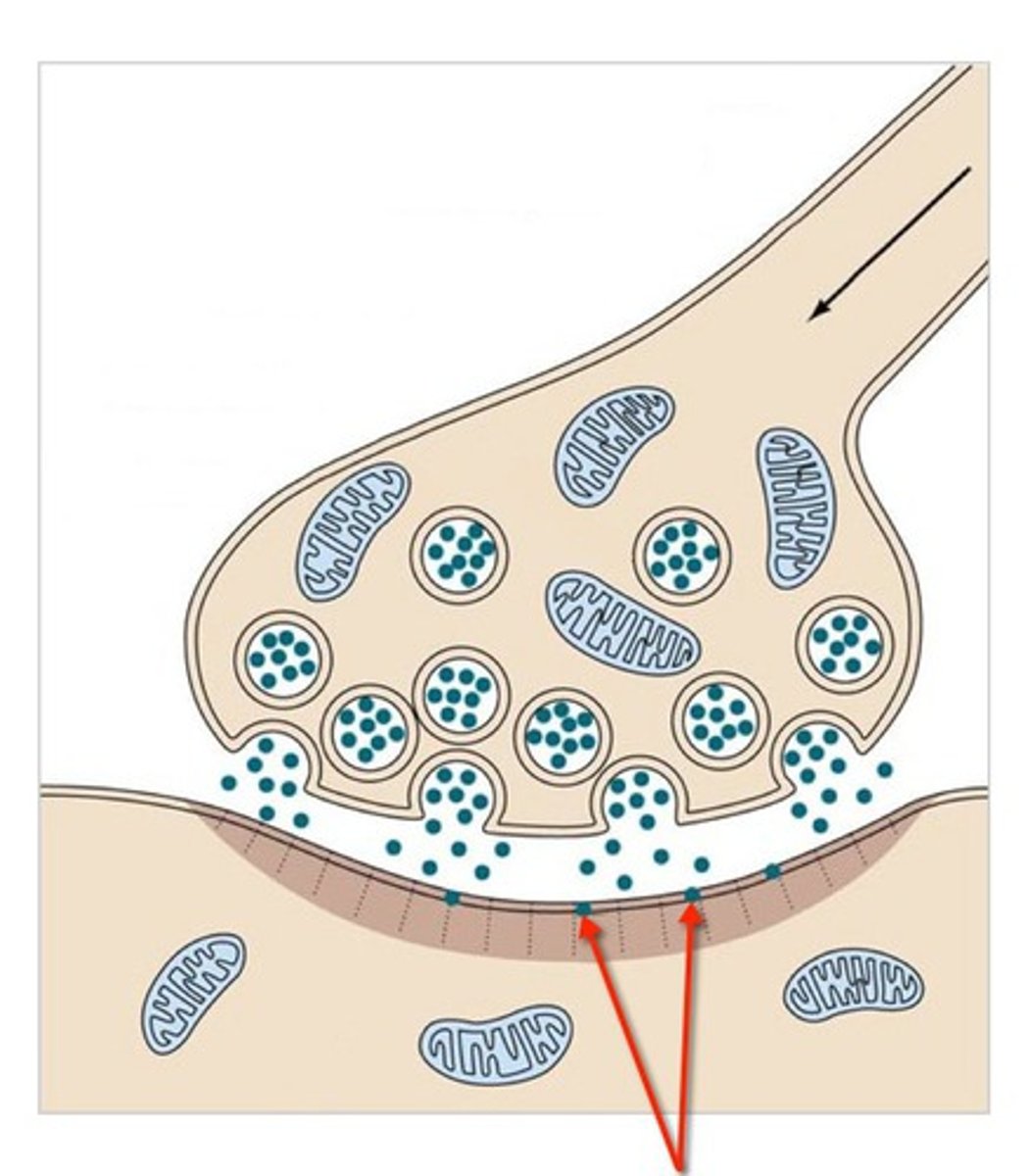
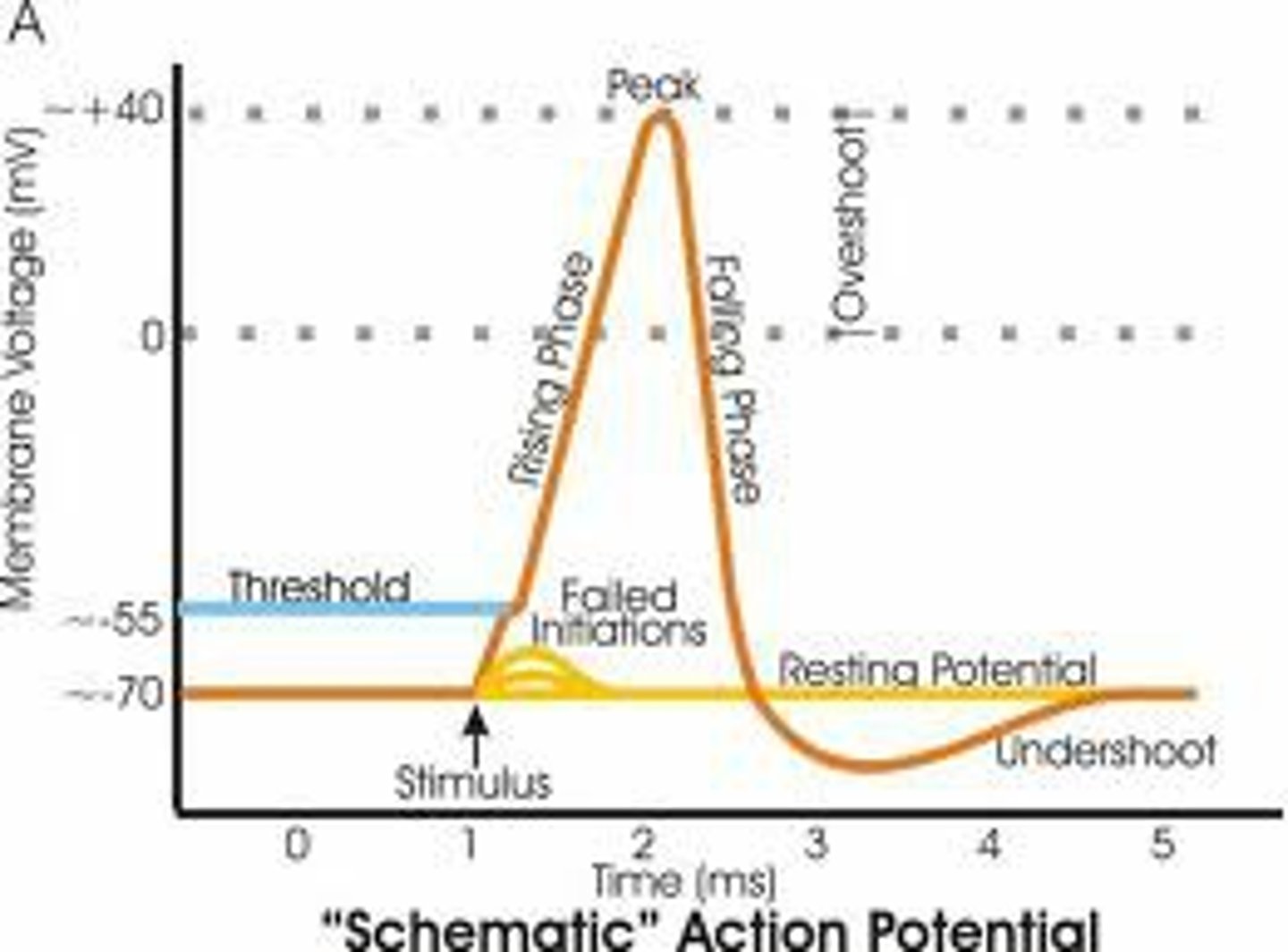
Action Potential
An electrical impulse that travels down the axon of a neuron.
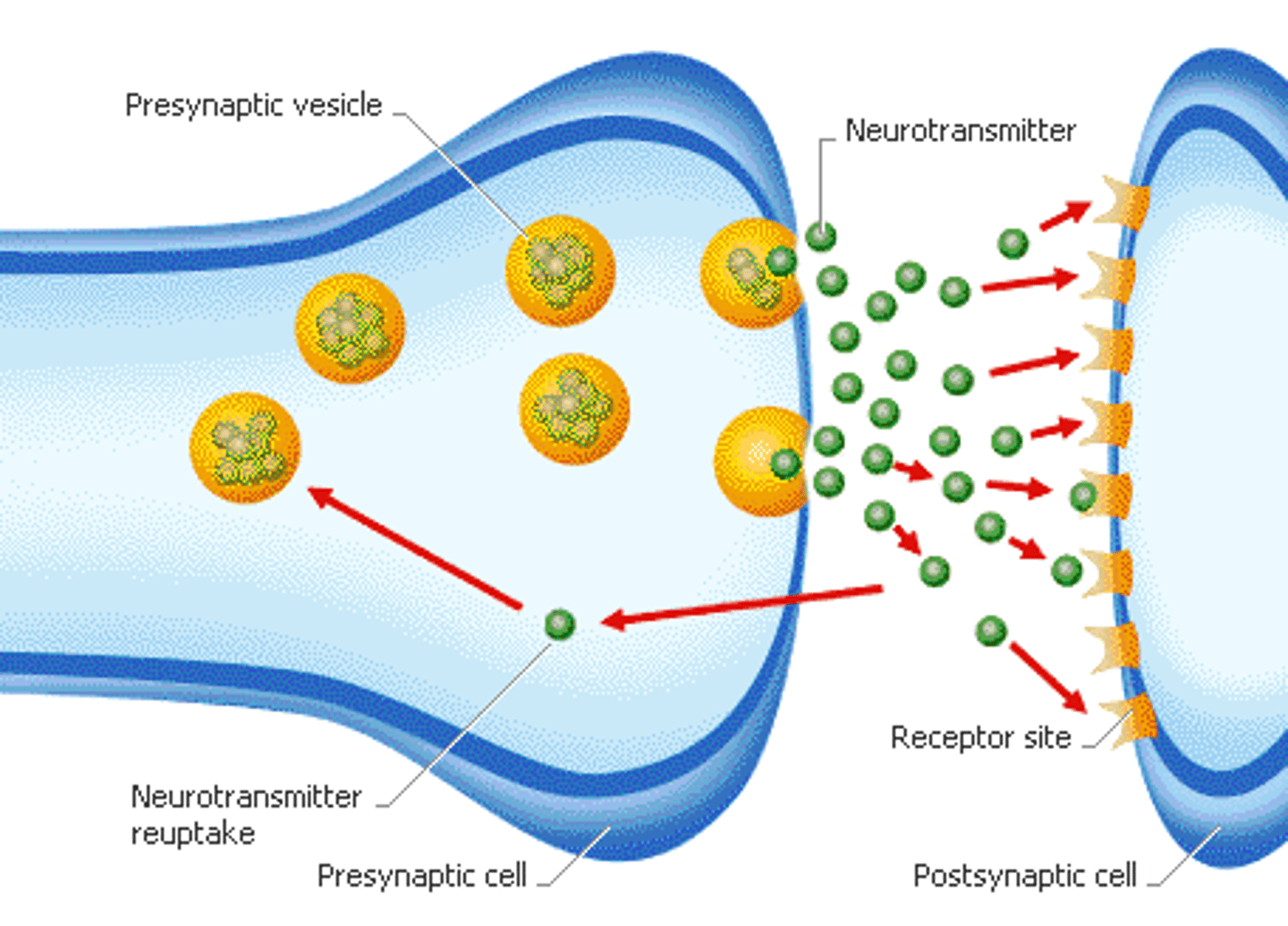
Neurotransmitter
A chemical that is used to communicate between neurons.
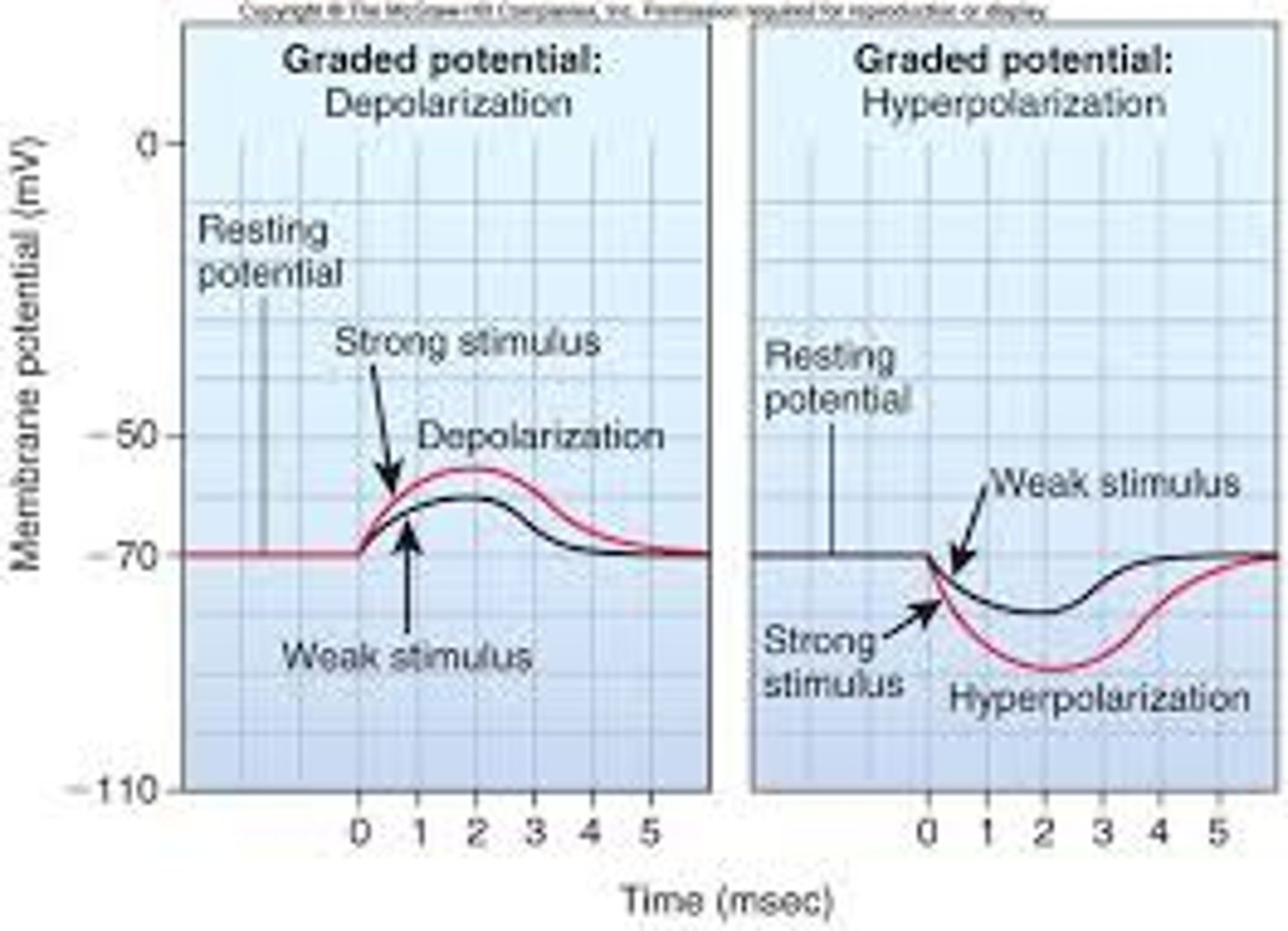
Graded (Local) Potential
A small electrical impulse that fades over distance.
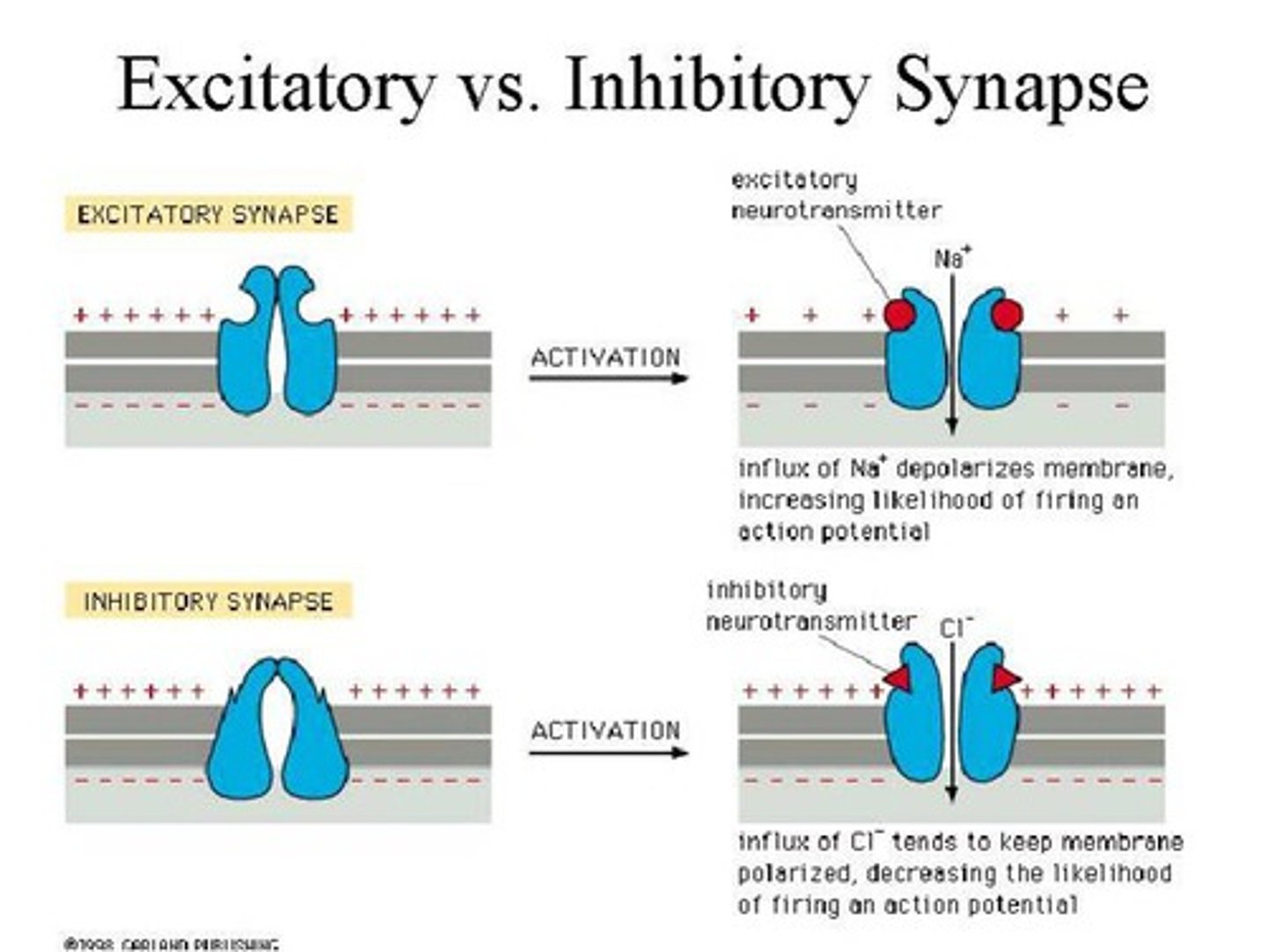
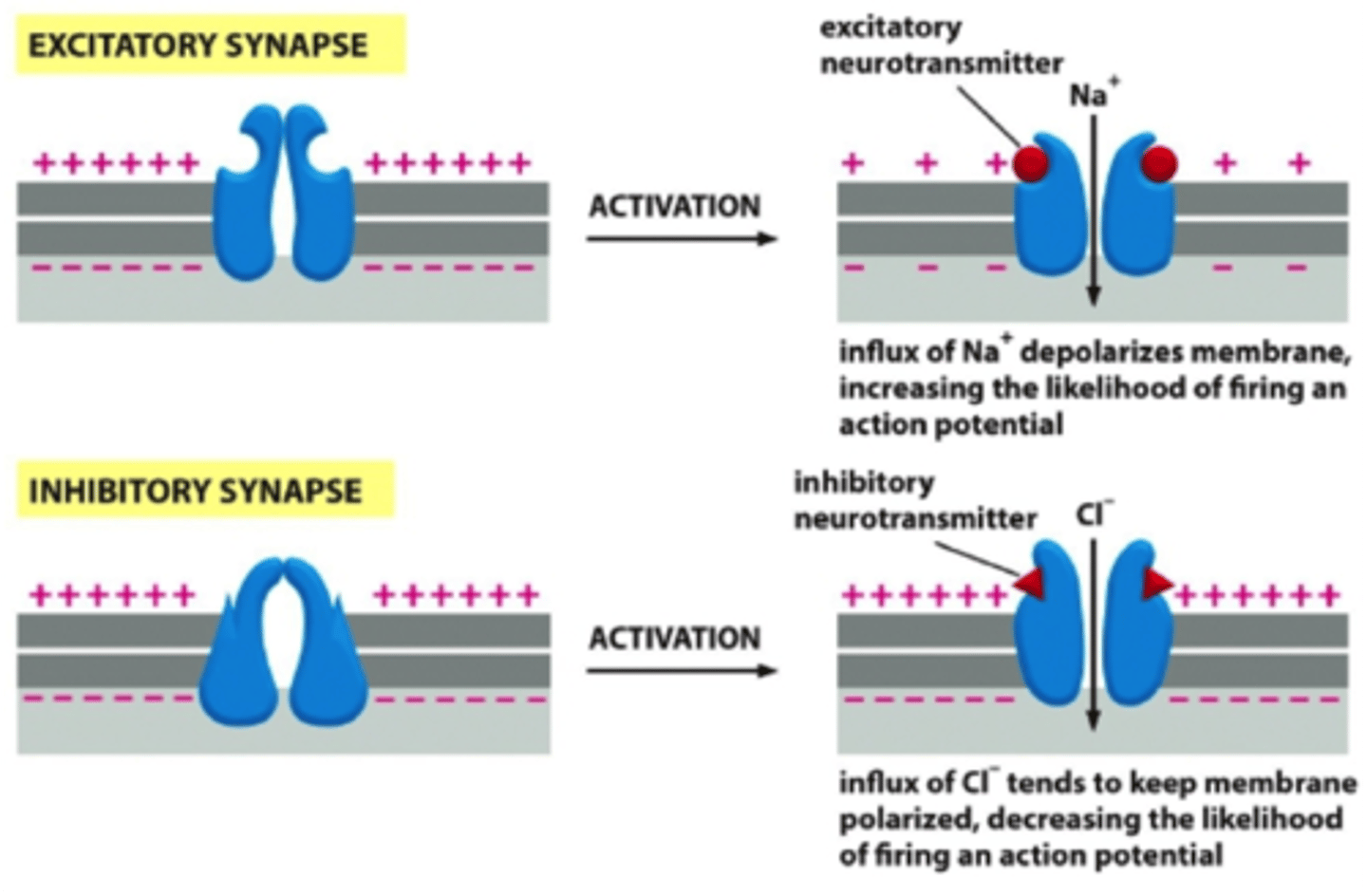
Excitatory
Can cause that neuron to initiate an action potential in its axon.
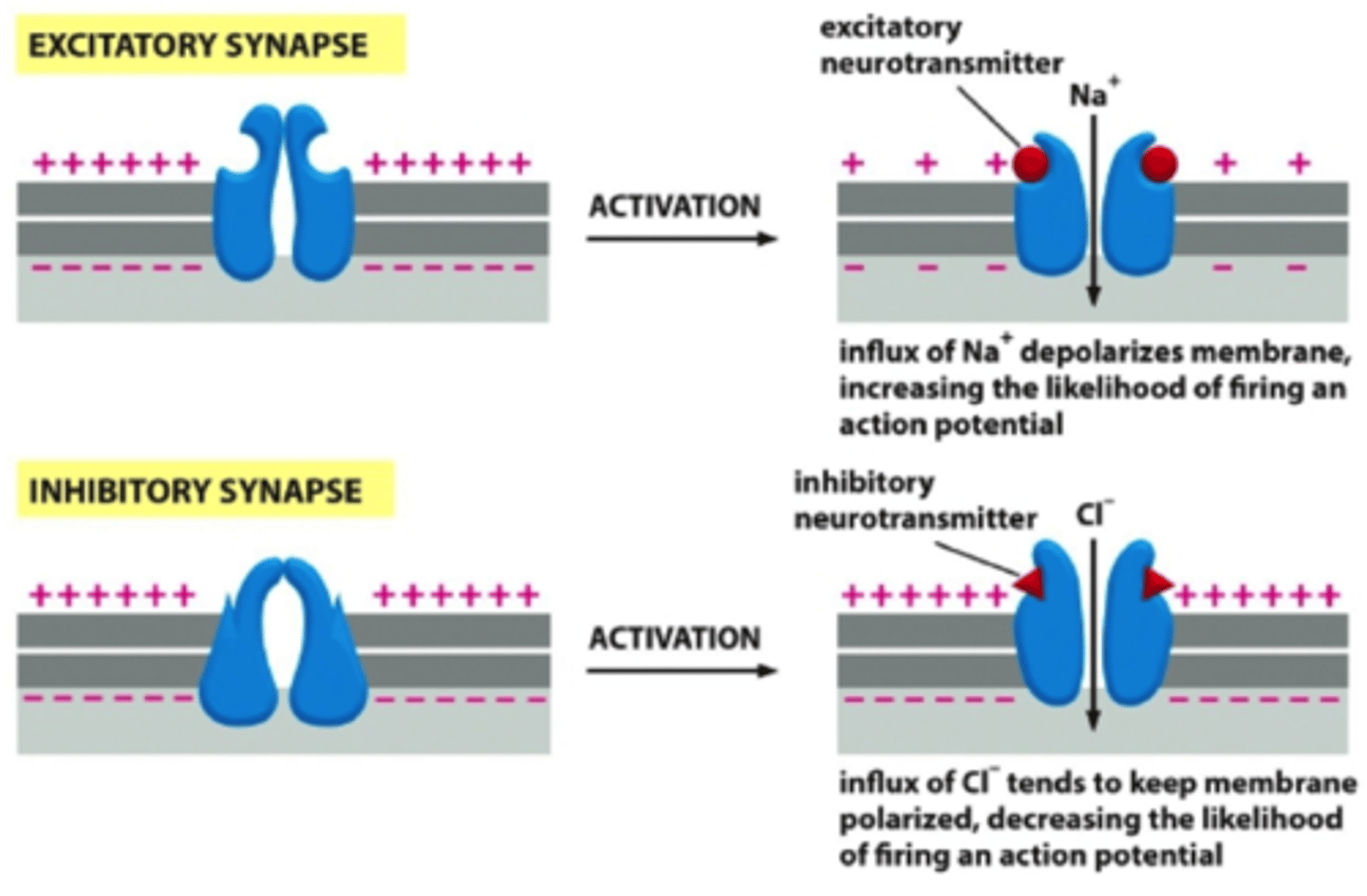
Inhibitory
Can cause that neuron to be less likely to initiate an action potential.
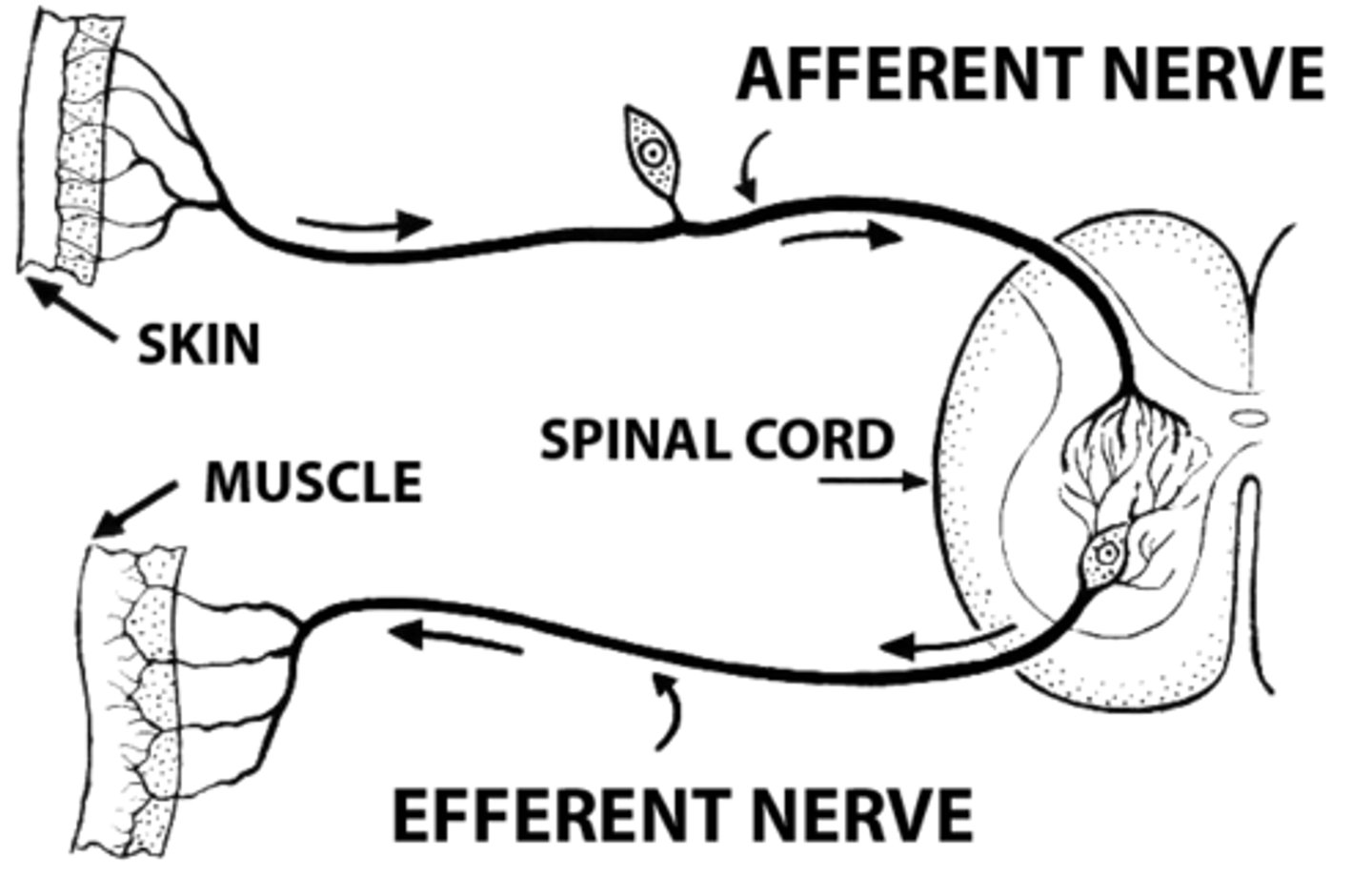
Afferent Neurons
Sensory neurons, convey impulses towards the CNS from sensory receptors found throughout the body.
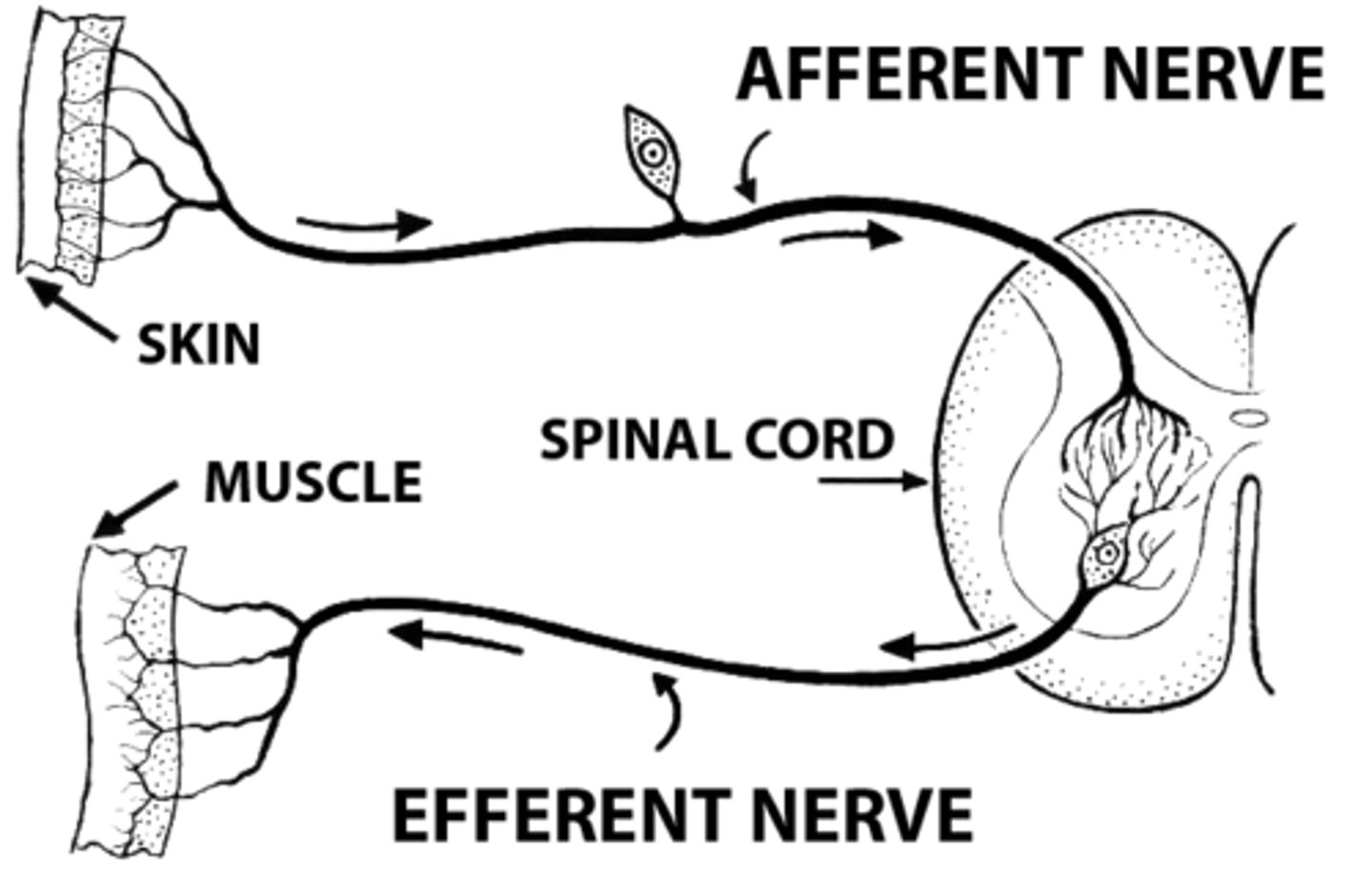
Efferent Neurons
Motor neurons, convey impulses away from the CNS to a target, which can be a muscle or a gland.
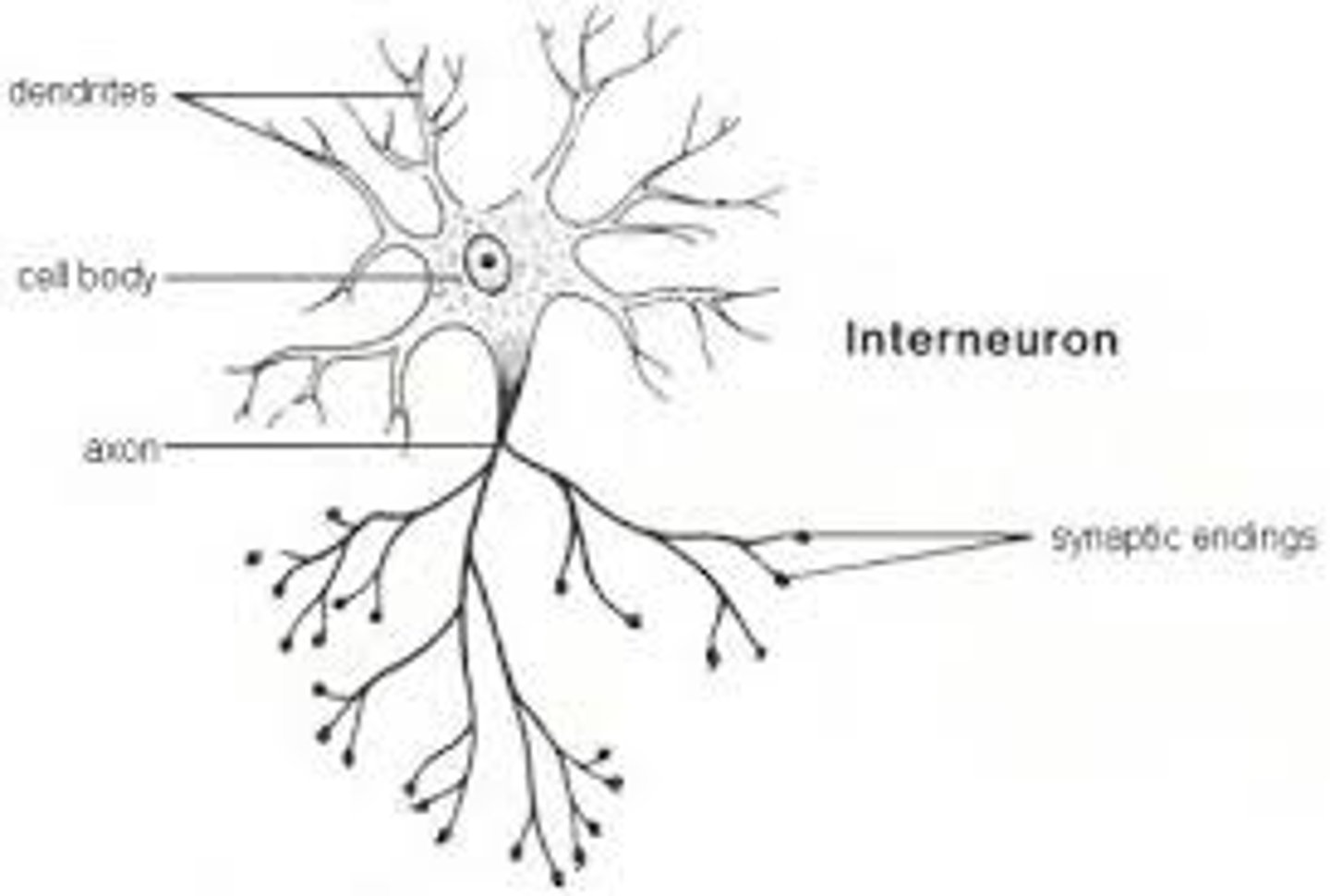
Interneurons
Found within the CNS, connect efferent and afferent neurons and integrate sensory input and motor output.
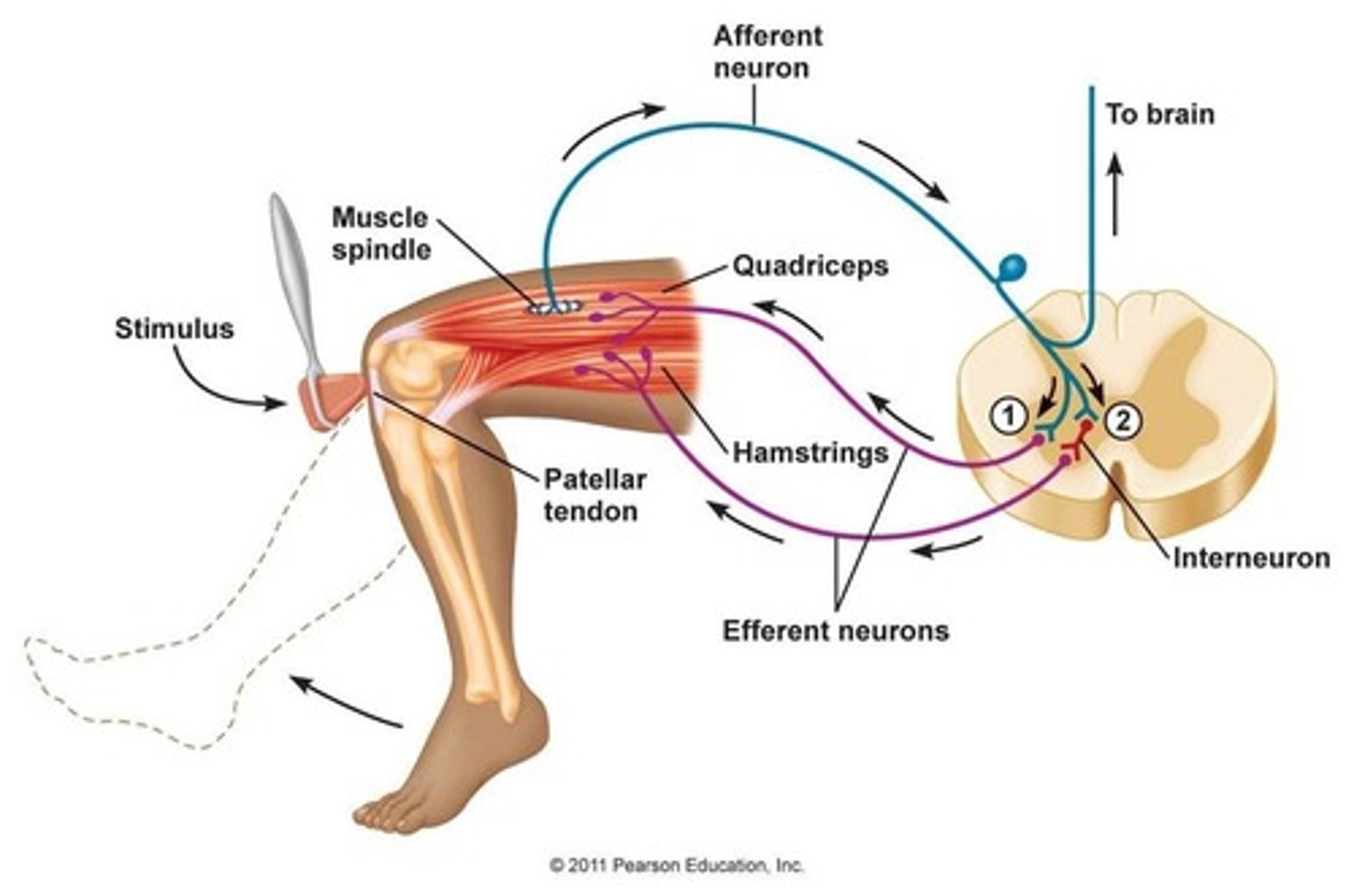
Reflex
A very fast, involuntary response to a stimulus.
Latency
The amount of time that passes between the initial stimulus and the response of a reflex.
Muscle Stretch Reflex
Follows the five steps of a typical reflex arc and is triggered when a muscle is rapidly stretched.
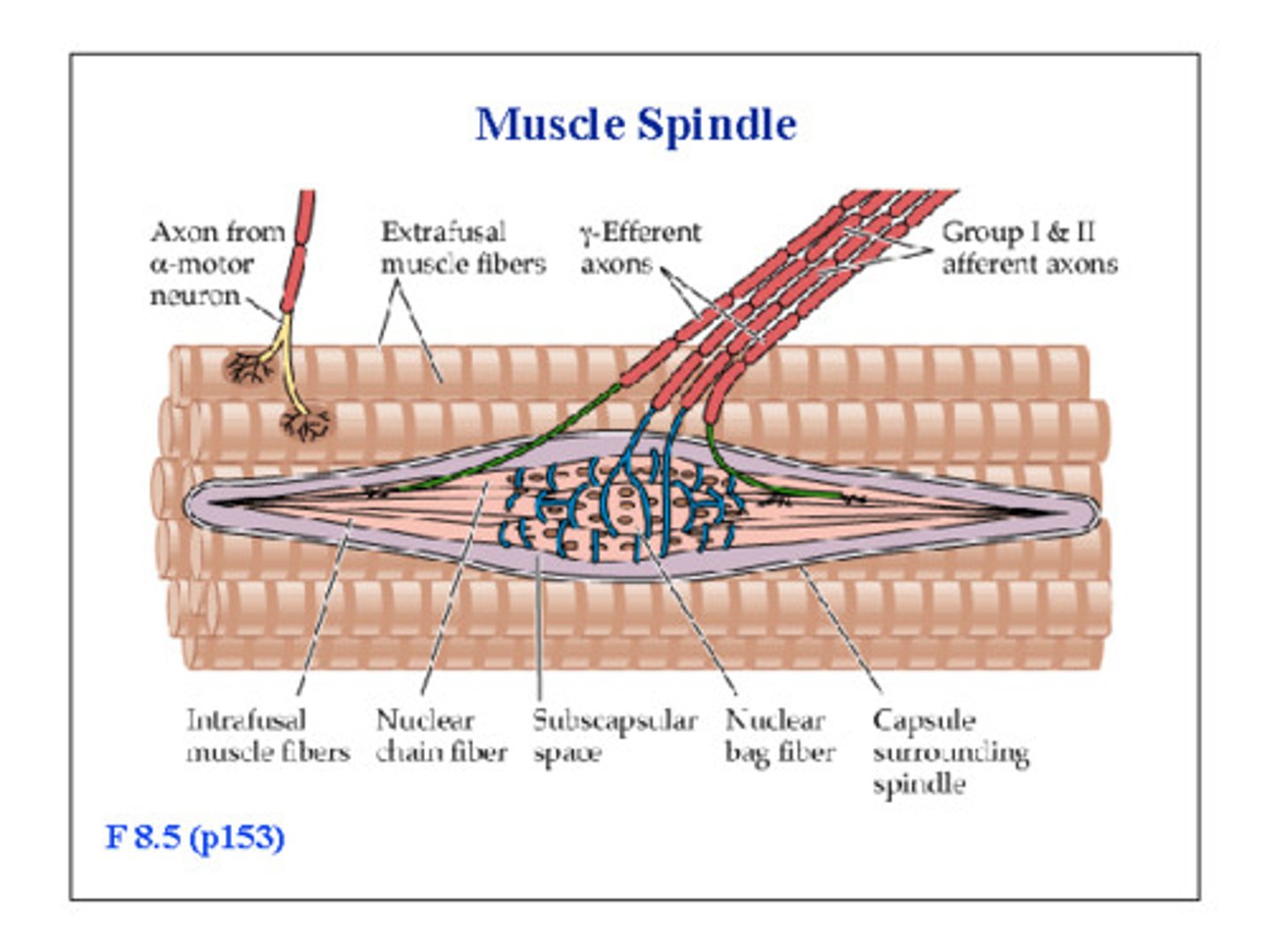
Muscle Spindles
Muscle fibers with sensory neuron axon terminals wrapped around them.
Excitatory Synapse
A synapse in which an action potential in a presynaptic neuron increases the probability of an action potential occurring in a postsynaptic cell.