BIOL practical
1/137
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
138 Terms
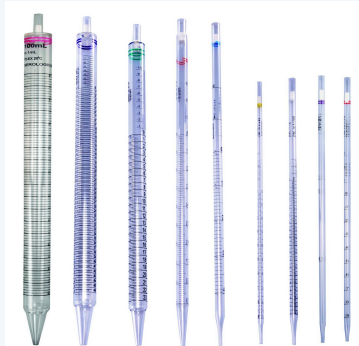
Graduated Pipet
used to measure 1.0ml to 25.0ml volumes of liquids precisely
Pipettor
suction device used with graduated pipet to transfer liquid

Graduated Cylinder
used to precisely measure 5.0ml to 1000.0ml volumes of liquids

beaker
used to measure approximate volumes (+/-5%) of liquids. Generally used to measure 20.0ml to 1000.0 ml volumes

Conical Flasks
Generally used to store or measure approximate volumes of liquids (+/-5%)

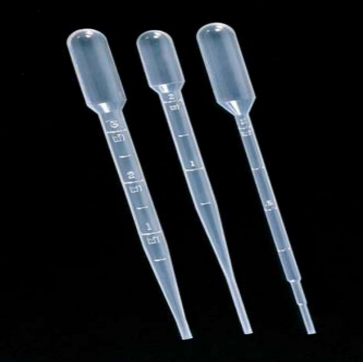
Transfer Pipet
used to transfer small (approximately 1.0ml or less) volumes of liquids. Typically used to measure approximate drops of liquid
Dropper Bottle
generally used to store small quantities of liquids and to dispense approximate small amounts such as a dropper full or X-number of drops; dark bottles can be used to store light sensitive liquids
Bead Bath
used to heat or boil solutions

Tongs and test tube holder
used to hold laboratory container that may be hot to the touch
Test tube
glass tubes used to carry out reactions in a contained environment. they do NOT fit in Spec20
Cuvette
small containers used to hold solutions to be measured using the spectrophotometer they are SMALLER than test tubes
Spectrophotometer
Equipment used to measure the absorbance/O.D. of a particular solution
Scientific Method
foundation of all universal experiments and designed to eliminate personal, social, cultural, religious, racial, sexual, and other biases of a scientist and provide a standard for exploring accurate and reproducible explanation of natural phenomenon
Scientific Method DO
a way to ask and answer specific questions by making observations and doing experiments
Scientific Method HOW
step by step process
Steps to scientific method
observation
background
hypothesis
experiment
results
discussion
conclusion
communicate
Scientific method step 1
observe and ask questions about the underlying question
Scientific method step 2
do background research to found out what is already known about it
Scientific method step 3
if there is a gap in information and you are still interested make an educated guess about the process
Scientific method step 4
list of materials, method, control groups
Scientific method step 5
data obtained from experiment represented in tables or graphs with a caption
Scientific Method step 6 and 7
results are explained and conclusions are drawn
Scientific Method step 8
once you have conclusive findings you want to share it with the world in a publication in an authentic journal
First microscope
long tube

Dissection/Simple Microscope
single objective lens, has light microscope
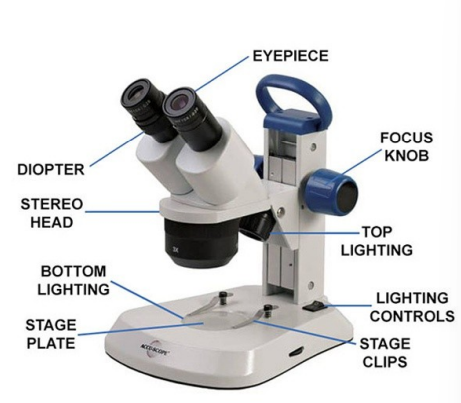
Compound Microscope
has several objective lenses and provides higher magnification than dissection scopes, is a light microscope
Electron Microscope
observing extremely minute structures like viruses and cell details, electrons used to create the image

Microscope parts
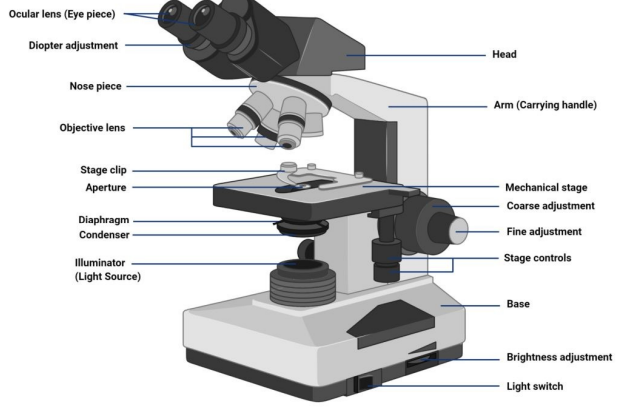
Magnification
ability to enlarge an image times life size or X
Resolving power
ability to clearly separate two objects close together
Total Magnification Power
combined magnification of the ocular lens and objective lens (objective lens is 10x)
Prokaryotes
they have genetic material but no true nucleus
no nucleus
smaller in size
no membrane bound cell-organelles
genetic material is circular
Eukaryotes
membrane-bound genetic material (true nucleus) and other membrane bound organelles
nucleus present
bigger in size
have membrane bound cell-organelles
genetic material is linear
Both cells
contain genetic material, are filled with cytosol/cytoplasm, and surrounded by plasma membrane, contain ribosomes
common cell organelles between animal and plant cells
nucleus
mitochondria
golgi apparatus
endoplasmic recticulum
vacuoles
plant cell specific organelles
chloroplast
central vacuole
cell wall
Hierarchy of life
atoms, molecules, macromolecules, cells
Major components of most organic molecules
carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, nitrogen
Formation of polymers
polymers are made up of monomers with a carbon backbone, monomers are linked together by removing water (dehydration reaction) to produce polymers
Macromolecules
carbohydrates
proteins
lipids
nucleic acids
Carbohydrates
Building blocks: monosaccharides and disaccharides | complex: amylose and amylopectin
ex: glucose and sucrose
linked by: glycosidic bonds
functional group: carbonyl
Redox reaction
oxidation is a loss of hydrogen
reduction is a gain of hydrogen
Proteins
Building blocks: amino acids
linked by: peptide bonds
functional group: amino and carboxyl
made up of: polypeptides
detection of carbohydrates
simple carbs: benedict’s test
positive: orange-red (needs to be heated)
complex carbs: iodine test
positive: bluish black-black
detection of proteins
biuret test
positive: violet
Lipids
building blocks: fatty acids and glycerol
linked by: ester linkage
functional group: carboxyl and hydroxyl
detection of fats
hydrophobic test
positive: two layers
Nucleotides
monomers of DNA
Membrane structure
Fluid mosaic model: describes cell membrane as a mosaic of several types of molecules that are constantly moving
Phospholipid bilayer
hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails
components of bio membranes: integral (intrinsic) proteins
channel proteins
components of bio membranes: peripheral (extrinsic) proteins
primarily receptors
components of bio membranes: cholesterol
maintains structure and fluidity
components of bio membranes: surface sugars (glycoproteins or glycolipids)
cell to cell recognition
Membrane functions
serve as cell barriers
helps to compartmentalize the cell for proper organelle function
semi-permeable membranes allow regulated movement of molecules
Passive transport
movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration (along the concentration gradient, natural movement)
examples of passive transport
diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion
active transport
movement of molecules from an area of lower concentration to higher concentration (against the concentration gradient, low to high) with the expense of energy
Diffusion
the movement or transport of molecules along the concentration gradient
Facilitated Diffusion
The movement or transport of molecules along the concentration gradient with the help of a protein carrier/channel
osmosis
the movement or transport of water along the concentration gradient across a semipermeable membrane
Tonicity
the concentration of a solution as compared to another solution
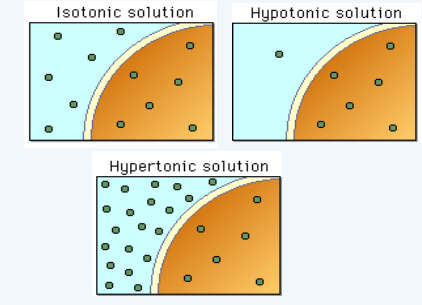
Tonicity on an animal cell
hypotonic: lysed H2O in
isotonic: normal H2O in and out
hypertonic: shriveled H2O out
Tonicity on a plant cell
hypotonic: turgid (normal) H2O in
isotonic: flaccid H2O in and out
hypertonic: plasmolyzed H2O out
Plant cell in hypertonic solution
plasmolysis
Plasmolysis definition
the shrinking of the cell membrane away from the cell walls because of loss of water to the outside hypertonic solution
Percent solutions
the amount (grams) or of chemical or compound (solute) per 100ml of a solution (solvent)
Solute
what is being dissolved
Solvent
the dissolver
Active Transport
transport of a solution against the concentration gradient by spending energy
What is the difference between meiosis and mitosis
meiosis: sex cells
mitosis: body cells (regeneration)
What is metabolism
all chemical reactions happening in a cell
What is anabolism
Synthesis of bigger molecules from smaller molecules
What is catabolism
Breakdown of larger molecules into smaller molecules to liberate energy
What is cellular respiration
it is a catabolic process by which carbohydrates are broken down and the energy released is used to make ATP
What is anaerobic respiration (fermentation)
the breakdown of glucose
no oxygen required
low atp yield
quick energy yield
starts and finishes in the cytoplasm
occurs in bacteria, muscle, yeast cells
What is aerobic cellular respiration
breakdown of glucose
oxygen required
high atp yield
slow energy yield
starts in cytoplasm and finishes in mitochondria
occurs in animal and plant cells
Cellular Respiration formula
C6H12O6 + 6O2 → 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water + energy
Aqueous environment formula
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3
carbon dioxide + water → carbonic acid
Aerobic respiration steps
glycolysis
citric acid cycle
oxidative phosphorylation
What happens during glycolysis
glucose → 2 pyruvate
net gain of 2 ATP and NADH
Transitional steps of pyruvate
pyruvate → Acetyl CoA
yields 1 NADH and 1 CO2
using transport protein from cytosol to mitochrondrion
structure of mitochondria
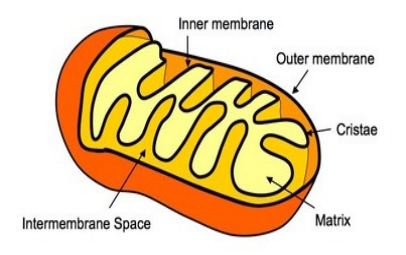
Citric acid cycle
electrons carry into mitochondria Acetyl CoA starts krebs cycle and makes carbon dioxide and ATP
Oxidative phosphorylation
electron transport chain and chemiosmosis
makes 32 ATP
occurs in inner membrane + matrix
fermentation
2 glucose → 2 pyruvate 2 acetaldehyde → 2 ethanol
anaerobic respiration in anaerobic bacteria
glucose → 2 pyruvate → 2 lactate
What is Bromothymol Blue
a pH indicator that changes color based on a solution's acidity
yellow = acidic
blue = basic
green = neutral
photosynthesis formula
CO2 + H2O — sunlight → C6H12O6 + O2
What are autotrophs
organisms that made their own energy
What are heterotrophs
organisms that cannot make its own food, dependent on producers
BUT both are dependent on the sun, however not directly for heterotrophs
Chloroplast structure
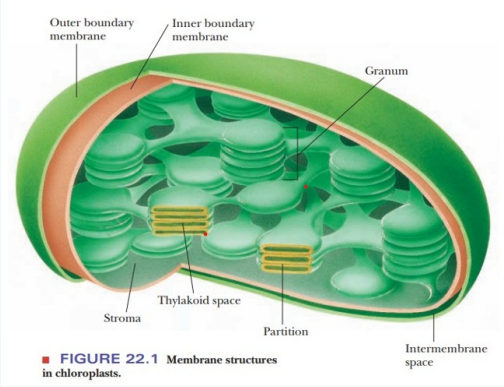
Light reaction
depends on light
transforms light to ATP and NADPH
occurs in granum
Dark reaction/calvin cycle
independent of light
uses ATP and NADPH to make glucose
in stroma
Dark reaction steps
carbon fixation
reduction
regeneration
in granum/thylakoid
What is chromatography
technique used for separation of molecules
molecules will be separated based on their size, shape, molecular weight, affinity to the solvent, affinity to the solid phase, affinity to the solvent to the solid phase
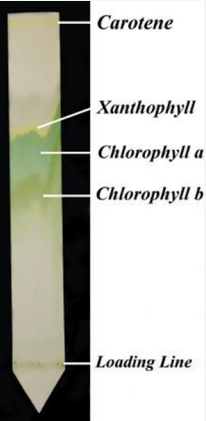
What is spectrophotometry
the wavelengths a substance absorbs is its absorption spectrum
Cell cycle
mitotic phase: pro,meta,ana,telaphase
first growth phase: growth and normal metabolic roles
synthesis phase: dna replication
second growth phase: growth and preparation for mitosis
Which parts of the cell cycle is interphase?
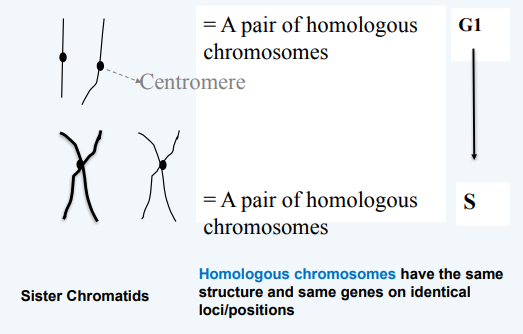
G1, S, G2
Chromosome Structure