The Ottomans Empire
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
The Ottomans
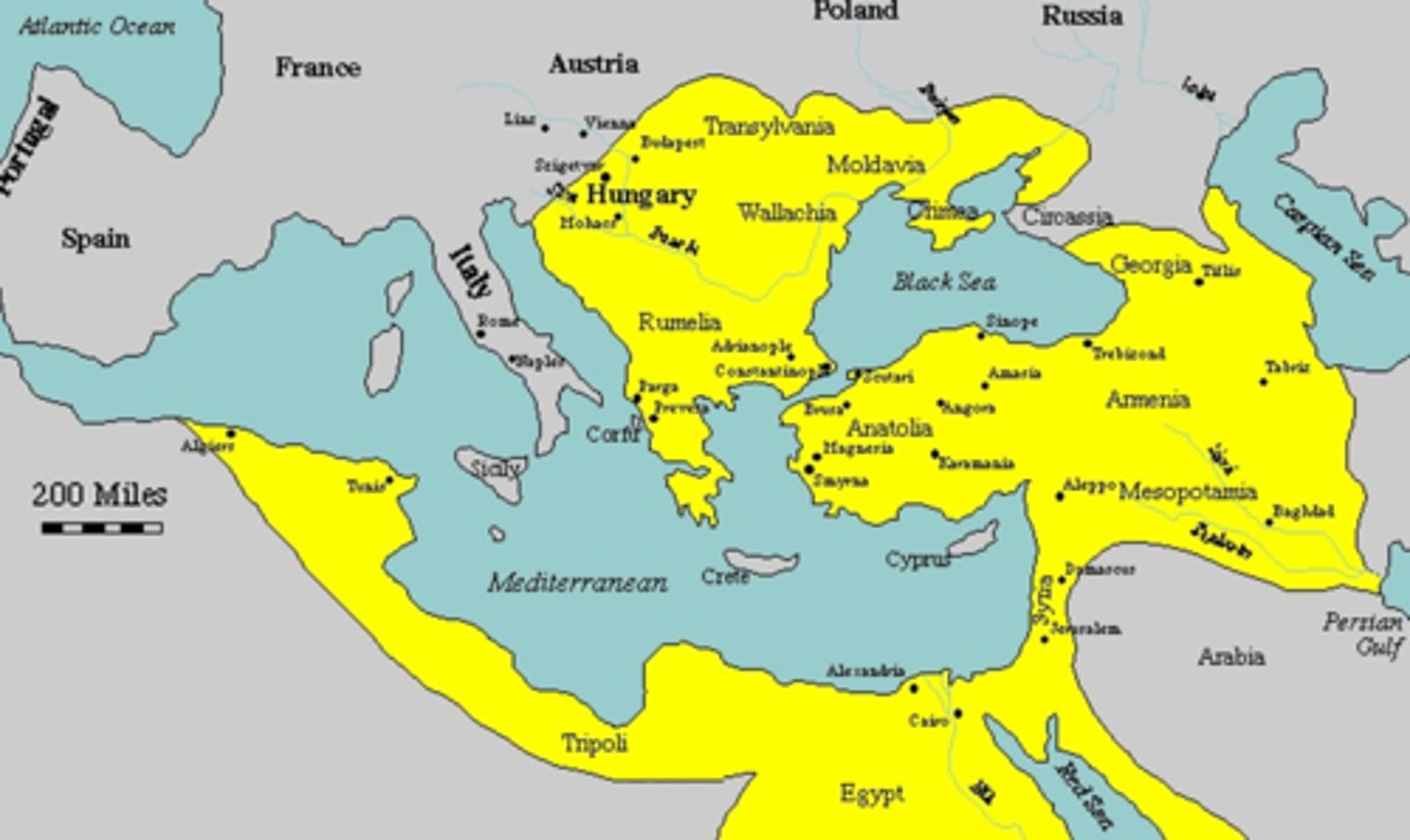
Powerful and militaristic Sunni Muslim Empire that lasted 1300-1922CE. Conquered the Anatolian Peninsula (Turkey Today) in early 1300's and Great City of Constantinople in 1453 CE
The Byzantine Empire
Christian empire, many Romans fled there after Rome fell in 476 CE. Lived mainly in/near the great Walled city of Constantinople, their capital.

Ghazi
warrior for Islam who belonged to a military society with a strict code of conduct.

infidels
ones who don't believe in Islam.
Sultan
name for Ottoman leader, name means overlord or "one with power".

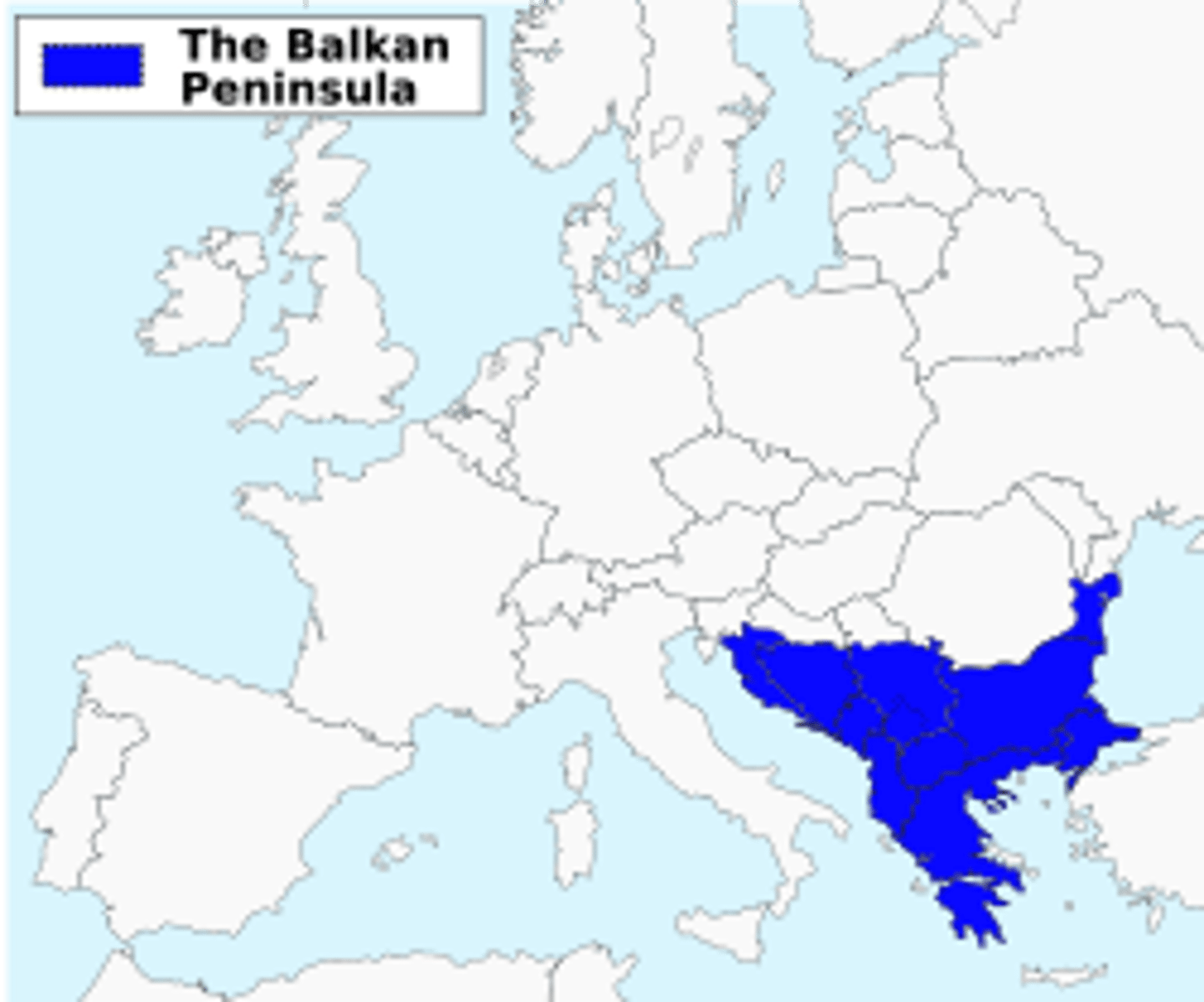
Balkans
a large peninsula in southeastern Europe where many Christians were conquered and enslaved by Ottomans , Greece and Constantinople are on it
Mehmed II
Conquered city of Constantinople (now Istanbul) in 1453 CE

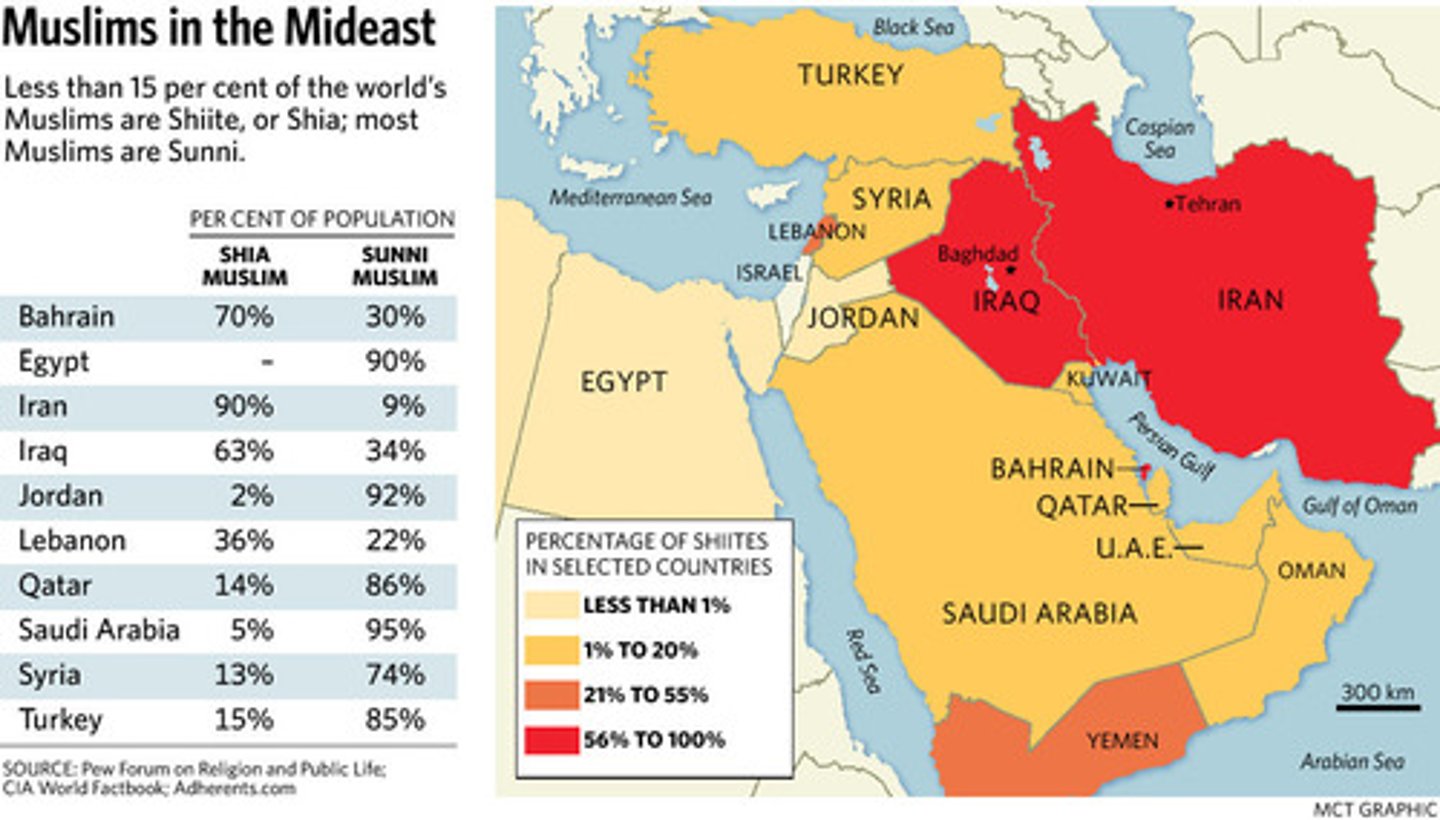
Shia Islam
follows the "bloodline" or family lines of Muhammad after his death. Shia followers follow the son in law of Muhammad, Ali. Many Shi'a resided in Safavid Empire, today Iran.
Sunni Islam
85% of Muslims today in the world are Sunni Sect of Islam. They wanted to follow the elected Iman's or leaders after Muhammad's death.
Janissaries
"Private" army to the Sultan, of Christian slaves origin taken from Balkans then raised Islamic. They were armed with gunpowder firearms, worked in government
Side Note: Why would a sultan want his own private army? The Ottomans had a trained army of Muslim Warriors? So why have a slave army loyal only to the Sultan? Think?
Millet System
Christian or Jewish religious community/town under Ottoman Empire. Could run own religious schools and courts but did have to pay a higher tax (Jiyza tax) than Muslims
Anatolia Peninsula
Where the nation of Turkey resides today. Peninsula south of Black Sea
1300 CE - 1922 CE
Ottoman Empire begins and ends
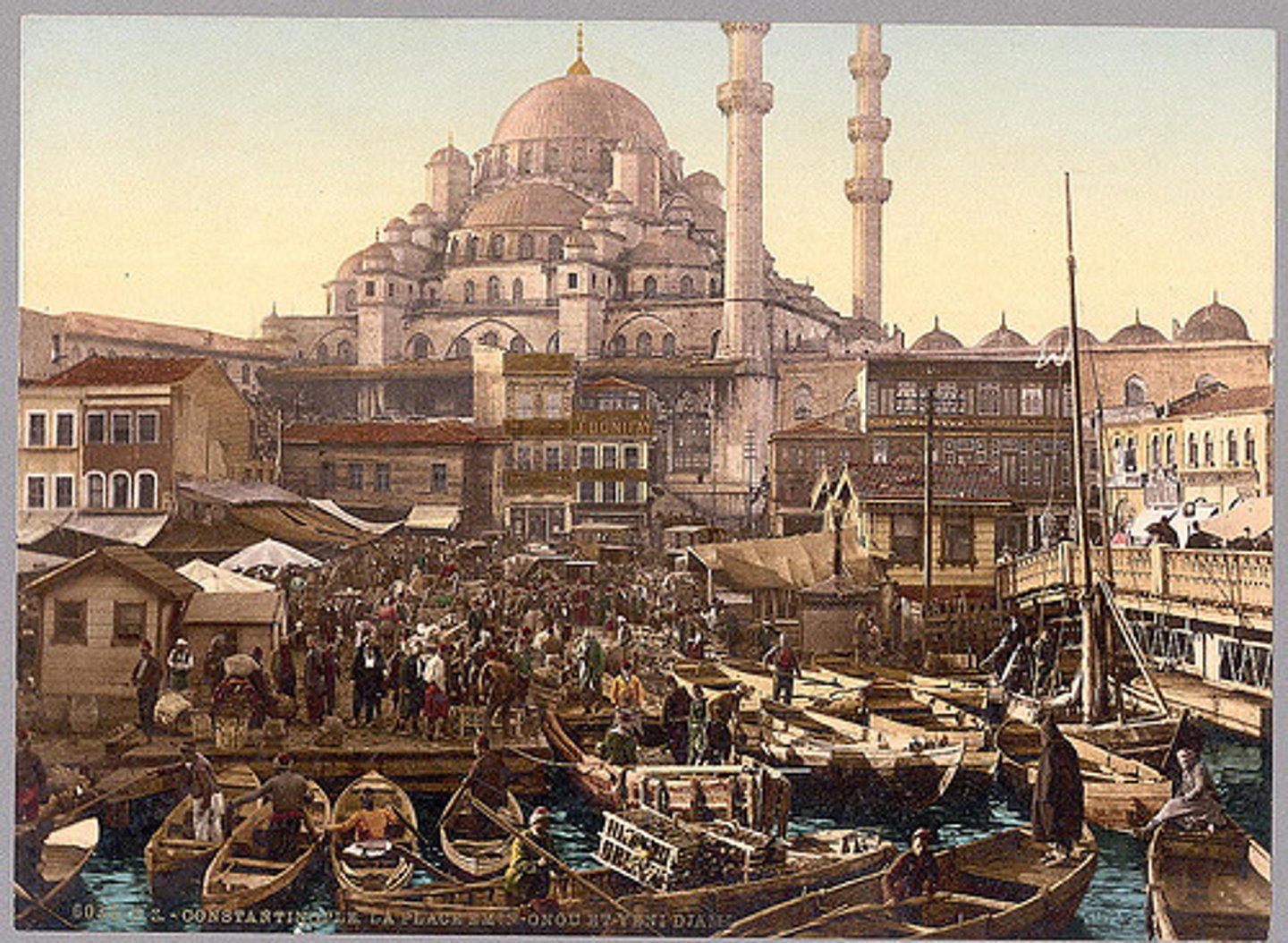
Constantinople
wealthy trading city of Byzantine Empire where east (Asia) Meets West (Europe)

Turks
People of the Ottoman Empire nomadic warriors from Altai mountains/central Asia/West Mongolia

Bureaucracy
A system of managing government through departments run by appointed "government officials"
Vizier
a high government official in in Muslim countries

Diplomacy
Negotiation or interactions between nations. When you talk instead a fight. Send a "diplomat" to negotiate.
Jiyza tax
tax on non muslims
individual merit
People getting rewarded for their hard work, intelligence not who parents/relatives are (nepotism)

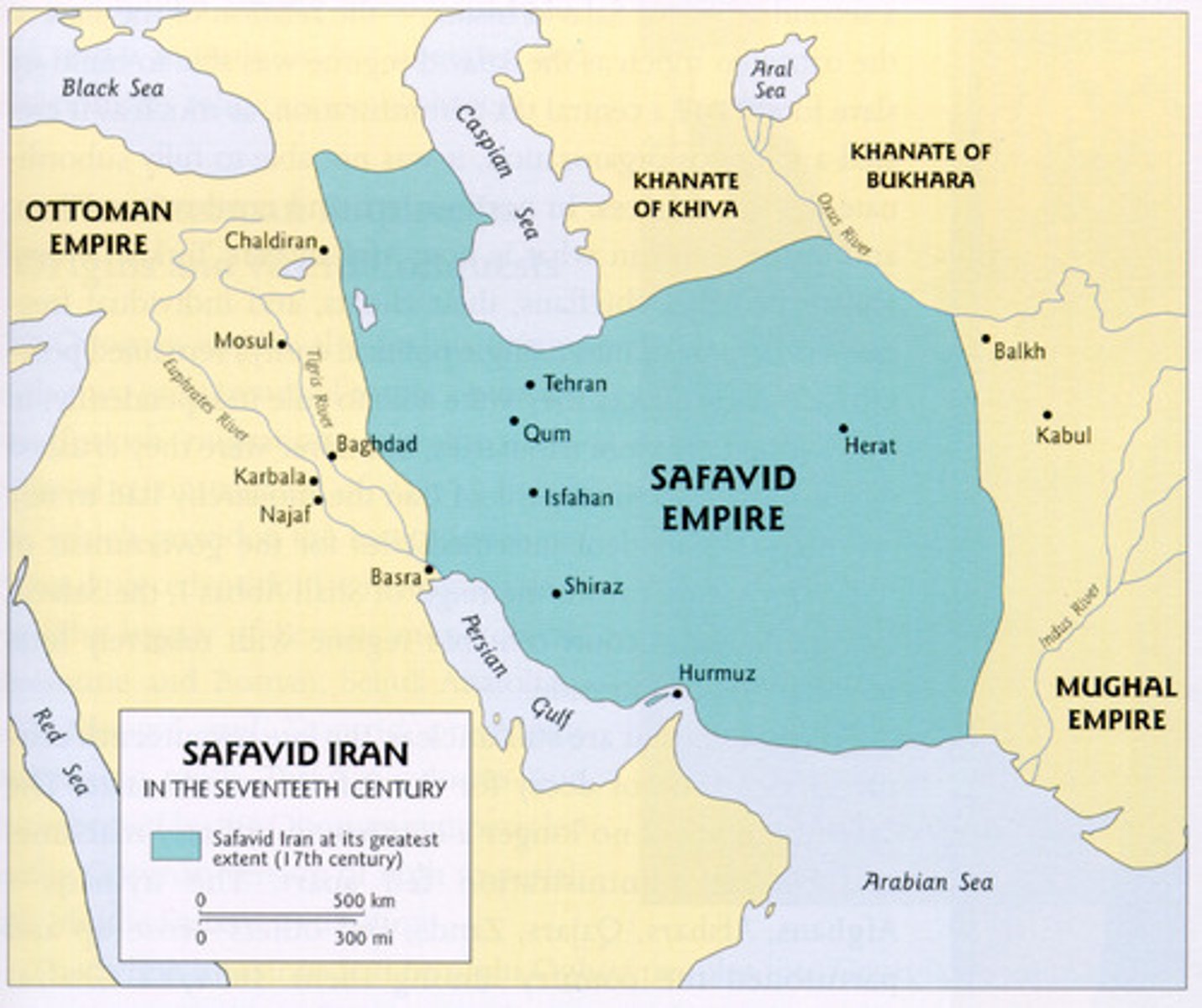
Safavid Empire
Iranian kingdom (1502-1722) established by Ismail Safavi, who declared Iran a Shia state.
sect
a subgroup of a major religious group
(Sunni/Shia) (Protestant/Catholic)
Jeruselum
City in Israel today, if fell to European Christian during the Crusades in 1099 CE

Arabs
ethno-linguistic group whose first language is Arabic. Lives throughout North Africa and the Middle East
Zakat Tax
Tax for Muslims. Like a sales tax on goods and trade items and also on land
622 CE
Founding of Islam in Saudi Arabia

476 CE
Fall of Rome/Beginning of Middle Ages

1500 CE
Modern Times Begins
1453 CE
Date: Ottomans capture and conquer Constantinople. Renames the city of Istanbul

Social Mobility (Ottoman)
Slaves able to rise to high govt. positions like Vizier. Also slaves were paid if in Janissary army. Greater Social mobility attainable in Ottomans vs. not attainable under EU Feudalism
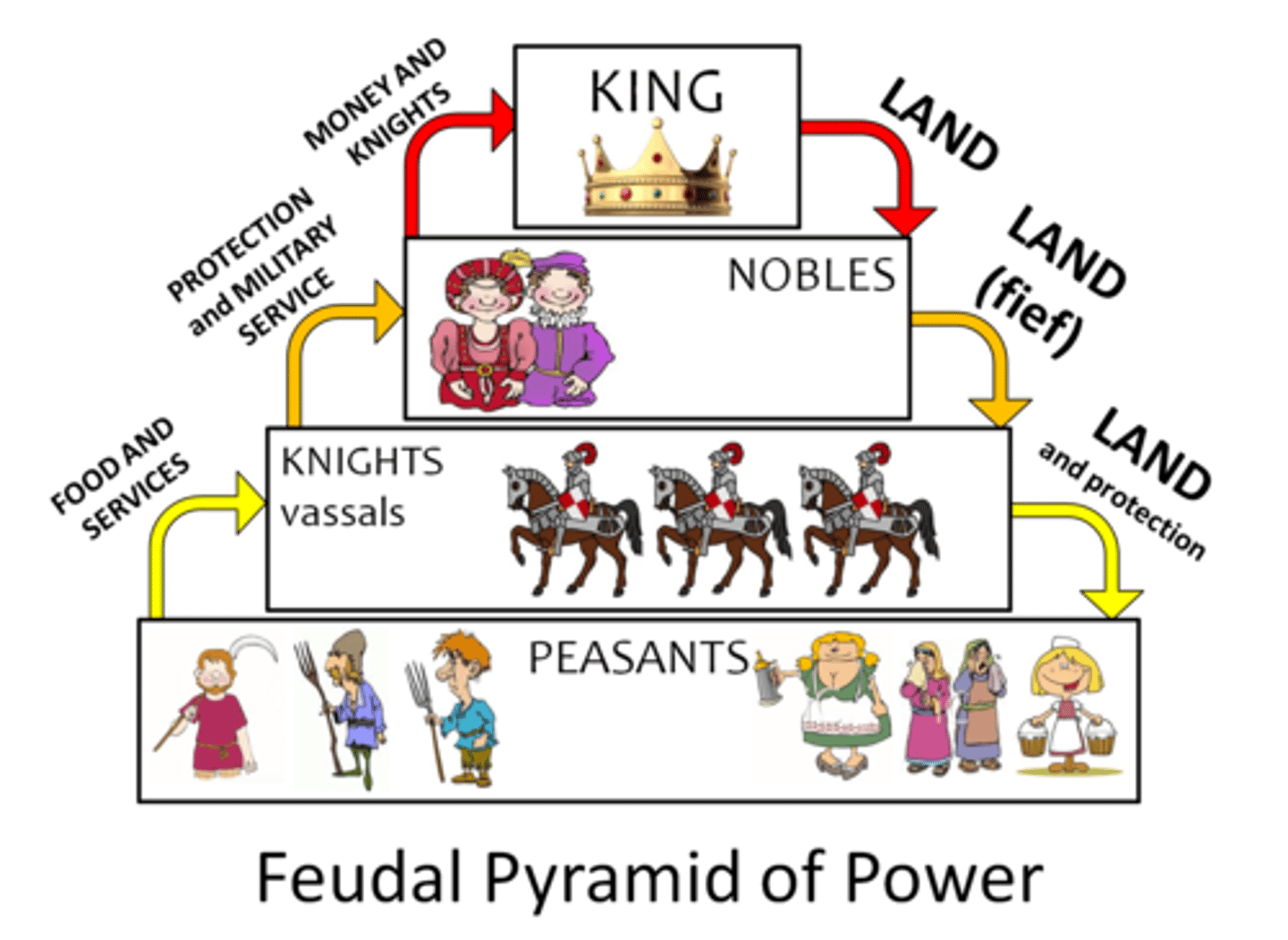
Feudalism
A EU political and social system based on mutual agreements between King & nobles/knights/peasants and serfs.
Peasant's farmed the land for free, but were given protection and some food to survive.
Caliph
A supreme religious leader in a Muslim government
devshirme
The practice of recruiting Christian boys to serve in the Ottoman government and military, often converting them to Islam and training them as soldiers or administrators.
treaty of karlowatz
A peace treaty signed in 1699 between the Ottoman Empire and the Holy League, ending the Great Turkish War and resulting in significant territorial losses for the Ottomans.