HEMA LEC DISORDERS OF IRON AND HEME METABOLISM
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
Iron deficiency anemia
Anemia of Chronic inflammation
Sideroblastic anemias
Iron overload
Disorders of Heme and Iron metabolism (4)
Inadequate intake
Increased need
Impaired absorption
Chronic blood loss
Iron deficiency anemia common causes (4)
Stomach acid reducers
Medication that can inhibit iron absorption by decreasing gastric acidity
Functional iron deficiency
iron stores are adequate but the iron is not available to support normal erythropoiesis, what deficiency?
(iron is available but not utilizied)
1mg of iron
Approximately how much iron is lost from the body everyday?
Non-tropical sprue
Celiac disease
Tropical sprue
Bacteria
Occult blood
blood that cannot be seen in the stool but is positive on a fecal occult blood test
Chronic blood loss
Iron deficiency developed with repeated blood donations, chronic hemorrhage, or hemolysis
Paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria
Deficiency developed due to loss of iron in hemoglobin passed in the urine
Inadequate intake
most common cause of iron deficiency
Storage compartment
Transport compartment
Functional compartment
3 compartments of iron deficiency in order
Ferritin
Storage compartment of iron
Transferrin
Transport compartment of iron
Hemoglobin
Myoglobin
Cytochromes
Functional compartment of iron (3) (HMC)
Storage iron depletion
Stage 1 iron deficiency (asymptomatic)
Stage 1 of iron depletion
Hemoglobin: Normal
Serum iron: Normal
TIBC: Normal
Ferritin: Decreased
Which stage of iron depletion?
Transport iron depletion
Stage 2 iron depletion
Stage 2 of iron depletion
Hemoglobin: Normal
Serum iron: Decreased
TIBC: Increased
Ferritin: Decreased
Which stage of iron depletion?
Functional iron depletion
Stage 3 iron deficiency
Stage 3 of iron depletion
Hemoglobin: Decreased
Serum iron: Decreased
TIBC: Increased
Ferritin: Decreased
Which stage of iron depletion?
Total iron binding capacity
indirect measurement of transferrin
Frank anemia
symptomatic anemia, Stage 3, uses functional compartment mainly the Hb
Normal blood smear
Normal blood smear or iron deficiency anemia?
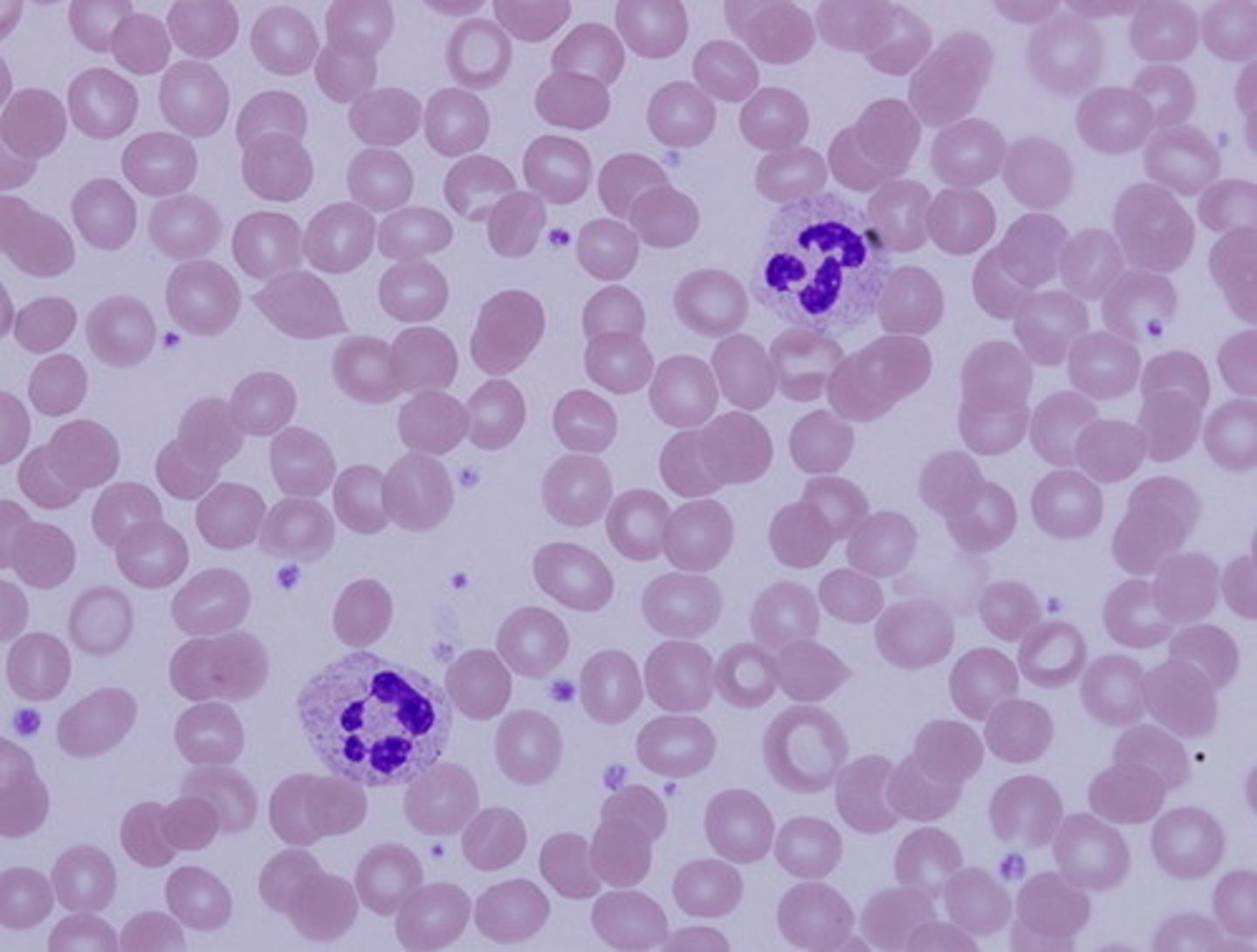
Central pallor enlarged
In iron deficiency anemia, the central pallor is ________________
Microcytic, hypochromic
Red blood cells of a person with IDA
Glossitis
Angular cheilosis
Koilonychia
Pagophagia
Symptoms of Iron deficiency anemia (4)
Glossitis
inflammation of tongue
Angular cheilosis
cracking of sides of lips
Koilonychia
spooning of fingernails
Pica
craving of non food items, severe IDA wherein mental is affected
Pagophagia
craving for ice
Menstruating women
IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
Epidemiology
Group of individuals especially at high risk for IDA.
Their monthly loss of blood increases their routine need for iron
1200mg of iron
IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
Epidemiology
If women of childbearing age do not receive proper iron supplementation, pregnancy and nursing can lead to a loss of nearly how much iron?
Iron supplementation
IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
Epidemiology
Even though breast milk is a better source of iron than cow's milk, it is not a consistent source.
Therefore, what is recommended for breastfed infants after 6 months of age?
Men and postmenopausal women
IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
Epidemiology
Iron deficiency is relatively rare in ____ and _____ because the body conserves iron so tenaciously, and these individuals lose only about 1 mg/day.
Necator americanus and Ancylostoma duodenale
IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
Epidemiology
The worm attaches to the intestinal wall and literally sucks blood from gastric vessels. What are these worms? (2)
Trichuris trichiura
Schistosoma mansoni
Schistosoma haematobium
IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
Epidemiology
Which parasites are the cause of heme iron lost from the body as a result of intestinal or urinary bleeding? (3)
Acidic environment
What kind of environment does iron like?
March hemoglobinuria
IRON DEFICIENCY ANEMIA
Epidemiology
Exercise induced hemoglobinuria, also called (?) develops when RBCs are hemolyzed by foot-pounding trauma and iron is lost as hemoglobin in the urine.
Screening
Diagnostic
Specialized
3 categories of testing in laboratory diagnosis:
No stainable iron
Bone marrow iron stain (Prussian blue reaction) in IDA
None
Sideroblasts in BM in IDA
Ferrous sulfate 3 times per day
If in stage 3 iron depletion (Iron deficiency anemia), what should you take and how many times per day?
65mg of elemental iron
1 tablet of ferrous sulfate contains how many milligrams?
Every morning when you wake up with an empty stomach
When should you take ferrous sulfate?
Anemia of chronic inflammation
most common anemia among hospitalized patients
Sideropenia
lack of iron in the blood
Sideropenia in the face of abundant iron stores
Central feature of anemia of chronic inflammation
Acute phase reactants
any substance that increases during inflammation
Hepcidin
Lactoferrin
Ferritin
3 APRs that are the culprits of ACI
Hepcidin
Prevents release of iron bound by ferritin - anemia of chronic disease.
a hormone produced by hepatocytes to regulate body iron levels, particularly absorption of iron in the intestine and release of iron from macrophages and hepatocytes.
Ferroportin
What does hepcidin degrade which exports iron from enterocytes into the blood, thus reducing the amount of iron absorbed into the blood from the intestine?
Lactoferrin
Prevents the phagocytized bacteria from using intracellular iron for their metabolic processes
Lactoferrin
Iron prefers (Lactoferrin/Transferrin)
9-11g/dL w/o reticulocytosis
Lab diagnosis for chronic inflammation. What is the Hb conc.?
Normocytic, normochromic
In ACI, red blood cells appears as ______ and _______
Leukocytosis and thrombocytosis
Indication of ACI
There are already iron present but iron is trapped in the cells
Transferrin will not be created in the liver if __________ and that's why TIBC is decreased in ACI
Treat first inflammation
Where to start when treating ACI?
Sideroblastic anemia
heme production is abnormal because iron and PPIX cannot combine
Microcytic, hypochromic
Appearance of red blood cells in sideroblastic anemias
Iron
In sideroblastic anemias, what is abundant in the BM?
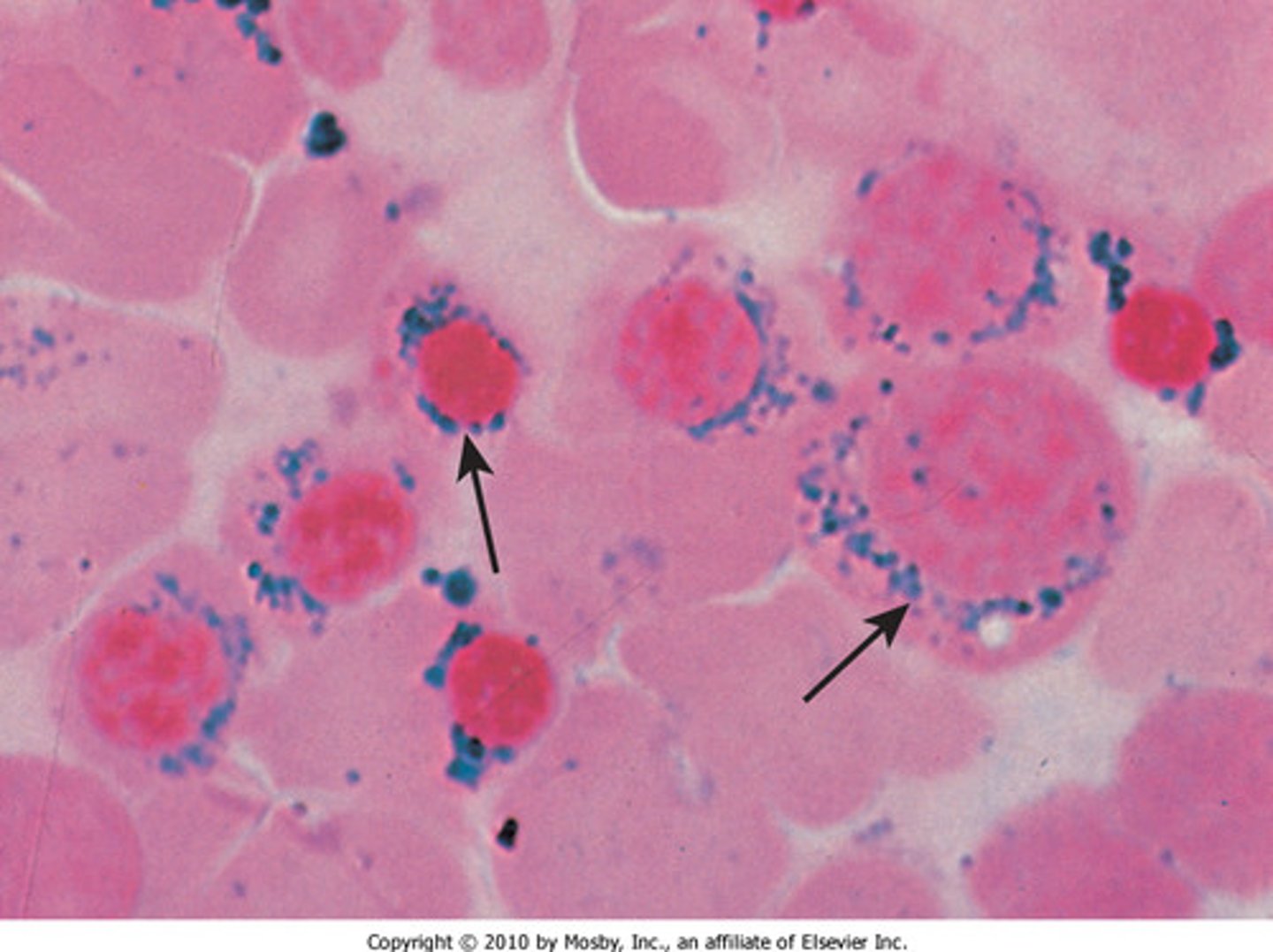
Prussian blue stain
shows normoblasts with iron deposits in the mitochondria
Ringed sideroblasts
Hallmark of sideroblastic anemia
X-linked and Autosomal mutation
Hereditary sideroblastic anemia (2)
Primary and secondary
Acquired sideroblastic anemia (2)
Refractory
Primary sideroblastic anemia is _________ which means cause is unknown
Secondary sideroblastic anemia
sideroblastic anemia caused by drugs and bone marrow toxins
Antitubercular drugs
Chloramphenicol
Alcohol
Lead
Chemotherapeutic agents
5 causes of secondary sideroblastic anemia (ACALC)
Lead poisoning
a cause of secondary anemia which affects CNS and hematologic systems
______ interferes with porphyrin synthesis
Paints
Lead poisoning is often due to expose to:
Porphobilinogen synthase
Ferrochelatase
2 enzymes inhibited by lead poisoning in porphyrin synthesis
Hypoplasia
Sideroblastic anemia leads to incomplete development of the BM, otherwise known as:
Basophilic stippling
Classic finding in sideroblastic anemia
pyrimidine 5'-nucleotidase
Lead inhibits _____, an enzyme involved in the breakdown of ribosomal ribonucleic acid (RNA) in reticulocytes.
Porphyrias
impaired production of heme, porphyrin accumulates
leads to accumulation of products which will be deposited in body tissues
Single enzyme deficiency
Porphyrias is either acquired through lead poisoning, or passed down by:
Photosensitivity
Porphyrias in skin leads to:
Fluorescence of developing teeth and bones
Porphyrias in children leads to:
Down
Down or normal
Up
Down
Up
No stainable iron
None
Iron deficiency anemia lab diagnosis
Serum ferritin: ?
Serum iron: ?
TIBC: ?
Transferrin sat: ?
FEP/ZPP: ?
BM iron: ?
Sideroblasts in BM: ?
Up or normal
Down
Down
Down or normal
Up
Up or normal
None/Very few
Anemia of Chronic Inflammation lab diagnosis
Serum ferritin: ?
Serum iron: ?
TIBC: ?
Transferrin sat: ?
FEP/ZPP: ?
BM iron: ?
Sideroblasts in BM: ?
Up
Up
Down or normal
Up
Up
Up
Up (ring)
Sideroblastic anemia lab diagnosis
Serum ferritin: ?
Serum iron: ?
TIBC: ?
Transferrin sat: ?
FEP/ZPP: ?
BM iron: ?
Sideroblasts in BM: ?
Congenital erythropoietic porphyria
Deficiency of uroporphyrinogen III synthase.
Erythropoietic protoporphyria
Ferrochelatase deficiency
Iron overload
Body's rate of iron acquisition exceeds the rate of loss
Transusion-related hemosiderosis
Acquired iron overload through repeated transfusions
Hemochromatosis
Hereditary iron overload through gene mutations
Skin
Liver
Pancreas
3 organs commonly affected by iron overload
Golden color
Deposition of hemosiderin in skin gives the skin what color?
Cirrhosis-induced jaundice
Deposition of hemosiderin in liver
Diabetes mellitus
Deposition of hemosiderin in pancreas
Bronzed diabetes
Iron overload
Pathogenesis
The traditional characterization
of hemochromatosis is "____"
Serum iron concertation/TIBC x 100
Transferrin saturation formula
Withdrawal of blood by phlebotomy
IRON OVERLOAD Treatment