DNA and RNA Structure
1/6
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
7 Terms
discovery of DNA
in the 1950s, Rosalind Franklin performed X-ray crystallography
of DNA
her work showed a pattern and was regular and repetitive
Edwin Chargaff analyzed DNA samples from different species
he found that A = T and C = G
then Watson and Crick combined these 2 findings to create a 3D double helix chain
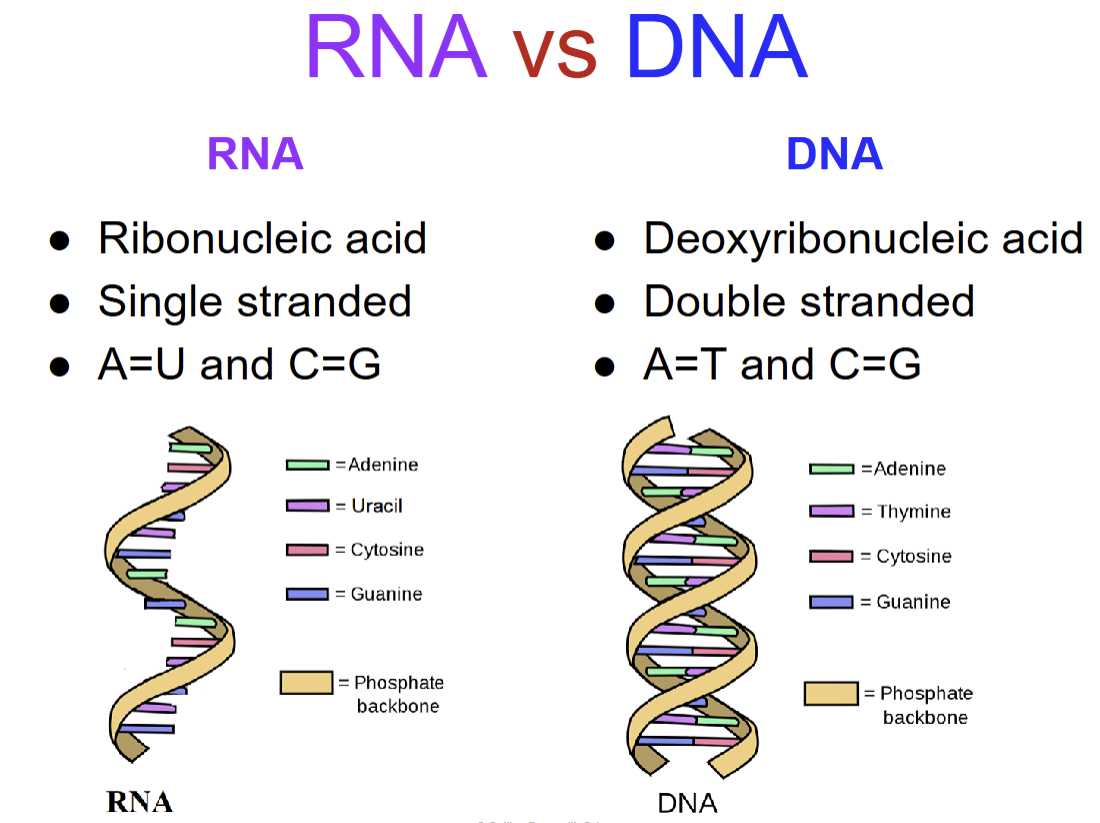
nucleotides
purines
double ring structure
(A, G)
pyrimidines
single ring structures
(C, U, T)
base pairs are held together by hydrogen bonds
A & T have 2 hydrogen bonds
C & G have 3 hydrogen bonds
dna structure
DNA is a double-stranded helix
backbone → sugar-phosphate
center → nucleotide pairing
DNA strands are antiparallel (two strands run in opposite directions)
one strand runs from 5’ to 3’, the other strand is upside down from 3’ to 5’
5’ → free phosphate group
3’ → free hydroxyl group
5' end → The strand's "start" has a free phosphate group attached to the 5th carbon of the sugar (deoxyribose).
3' end → The strand's "end" has a free hydroxyl group (-OH) attached to the 3rd carbon of the sugar.
function of DNA
DNA is the primary source for heritable information
generation information is stored and passed on through DNA
exception: RNA is the primary source of heritable information in some viruses
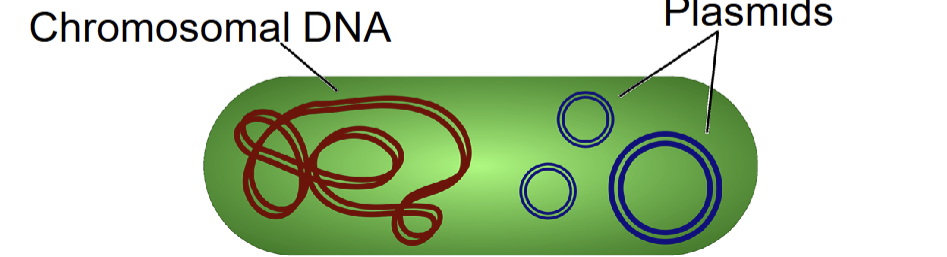
prokaryotic vs eukaryotic DNA
eukaryotic cells
DNA in the nucleus
linear chromosomes
prokaryotic cells
DNA is in the nucleoid region
chromosomes are circular
prokaryotes & (some eukaryotes) also contain plasmids
small, circular DNA molecules that are separate
from the chromosomes
plasmids
they replicate independently from the chromosomal DNA
often found in prokaryotes
carry genes that are useful to the prokaryote when it is in a certain environment, but are not required for survival
plasmids can be manipulated in labs
they can be removed from bacteria, then a favorable gene can be placed inside to form a recombinant plasmid DNA, to express something new
bacteria can exchange genes found on plasmids
with neighboring bacteria
once the DNA is exchanged, the bacteria can express the genes acquired
assists with the survival of prokaryotes
RNA vs. DNA