Mechanics III (Theory)
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Work and energy formula
W =Fs
What does W stand for? (Work formula)
Work/energy
What does F stand for? (Work formula)
Force
What does s stand for? (Work formula)
Distance
Unit of W
Joule (J)
Unit for energy
Joule (J)
Energy (definition)
The ability to do work
Forms of energy (10)
Kinetic. Potential. Internal. Electrical. Light. Heat. Chemical. Nuclear. Sound. Magnetic
Principle of conservation of energy (definition)
Energy cannot be created or destroyed only changed from one form to another
Why are kinetic and potential energy are subsets of these?
All forms of energy are subsets of these
Internal energy (Definition)
The sum of the kinetic and potential energy of the atoms/molecules in a substance
Why is internal energy important?
Useless and all useful forms of energy are slowly being turned into it.
Why is electrical energy important?
Easy to convert into other forms
Potential energy (Definition)
Energy an object has due to its position (height off the ground) or condition (squashed or stretched)
Potential energy formula
Ep = mgh
What does Ep stand for? (Potential energy formula)
Potential energy
What does g stand for? (Potential energy formula)
Acceleration due to gravity
What does h stand for? (Potential energy formula)
Depth
Kinetic energy formula
Ek = ½ mv2
What does Ek stand for? (Kinetic energy formula)
Kinetic energy
What does m stand for? (Kinetic energy formula)
Mass
What does v stand for? (Kinetic energy formula)
Velocity
Renewable energy (definition)
Those that will not run out. E.g. solar. Wind. Biomass. Geothermal. Hydroelectric. Waves. Tidals
Biomass (definition)
Energy gained from fast growing plants e.g. Elephant grass. Willow. Oilseed rape
Non-renewable energy (definition)
Those that will run out. E.g. fossil fuels. Turf. Nuclear
Light bulb converts what energy form into what?
Electrical. Light (+Heat)
Washing machine converts what energy form into what?
Electrical. Kinetic Heat and Light (+Sound)
Loudspeaker converts what energy form into what?
Electrical. Sound Kinetic and Light
Microphone converts what energy form into what?
Sound. Electrical Sound and Kinetic
Leaf converts what energy form into what?
Light. Chemical
Coal fire converts what energy form into what?
Chemical. Light Heat and Sound
Battery converts what energy form into what?
Chemical. Electricity
Battery charger converts what energy form into what?
Electrical. Chemical
Human converts what energy form into what?
Chemical. Kinetic Sound Heat Potential and Electrical
Petrol car converts what energy form into what?
Chemical. Kinetic Heat Light Sound and Potential
Advantages of Non-Renewable energy (3)
More reliable. Can be placed anywhere. Relatively cheap to build
Disadvantages of Non-Renewable sources of energy (2)
Causes global warming. More expensive to run
Advantages of Renewable sources of energy (2)
Doesn’t cause global warming. Cheaper to run
Disdvantages of Renewable sources of energy (3)
Not reliable e.g. wind doesn’t always blow. Cannot be placed everywhere. Expensive to build
Efficient use of energy at home (4)
Insulate attic. Insulate the walls. Double/triple glazed windows. Logging jacket around hot water cylinder.
Formula for power
P = W/t
What does P stand for? (Power formula)
Power
What does W stand for? (Power formula)
Work/energy
What does t stand for? (Power formula)
Time
Unit for power
Watt (W)
% Efficiency formula
Po/p / Pi/p x 100
What does Po/p stand for? (% Efficiency formula)
Power output
What does Pi/p stand for? (% Efficiency formula)
Power input
Examples of simple harmonic motion (4)
Atoms in a solid. Pistons in a petrol/diesel engine. Boat on a tide in a harbour. A weight on the end of a spring that’s pulled down.
Example of approximate simple harmonic motion
Pendulum
Why is a pendulum an example of approximate simple harmonic motion?
Because it moves in an arc while other examples of simple harmonic motion move in straight lines
Simple harmonic motion (definition)
An object is said to be in simple harmonic motion if its displacement from a fixed point is directly proportional to its acceleration which is always directed towards that point.
Formula for simple harmonic motion + derivation
a∝-s ∴ a = -(constant)s
Why is s negative in the simple harmonic motion formula?
s and a always point in opposite directions
What is a? (Formula for simple harmonic motion)
Acceleration (points towards fixed points)
What is s? (Formula for simple harmonic motion)
Displacement (measured from fixed point)
Hooke’s Law (definition)
The extension of a stretched spring is directly proportional to the force causing it, provided the elastic limit is not exceeded.
Formula for Hooke’s Law
F = -ks
What does F stand for? (Formula for Hooke’s Law)
(Restoring) Force
What does restoring force equal to?
Force of the weight on the spring
What does K stand for? (Formula for Hooke’s Law)
Spring constant
What does s stand for? (Formula for Hooke’s Law)
Extension
Big springs have a … K while small springs have a … K
Large. Spring
Prove that systems that obey Hooke’s Law execute simple harmonic motion
F = -Ks (Hooke’s Law) F=ma (Newton’s second law)
ma=-ks
a =-(k/m)s or a= -(k/m)s
If k and m are constant a= -(constant)s which is the definition of SHM (QED)
Periodic Time (Simple Harmonic Motion) Definition
The periodic time of a particle executing simple harmonic motion is the time interval between when a particle passes a particular point and when it passes the same point again, going in the same direction
Draw a diagram of one period
…
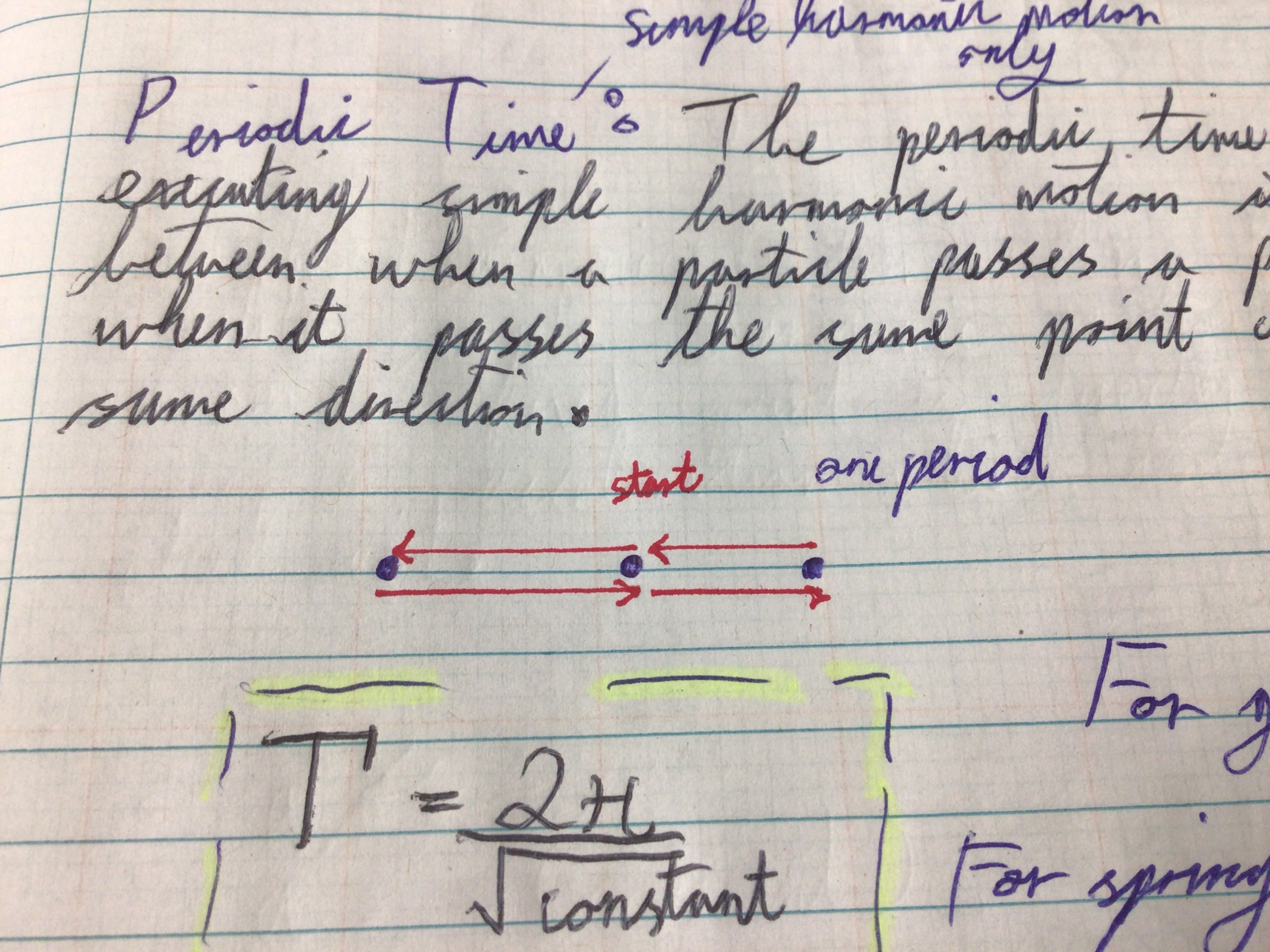
Formula for periodic time
T = 2π/√constant
Periodic time for general simple harmonic motion formula
T = 2π/√K
Periodic time for spring simple harmonic motion formula
T = 2π/√k/m
Periodic time for a pendulum simple harmonic motion formula
T = 2π/√g/l