Unit 1 DNA structure
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
The ____ structure of DNA determine’s its ____
antiparallel complementary structure
function
Nucleotides are made up of
sugar
phosphate
nitrogenous base
Nucleotides can contain 1,2 or 3 Phosphates what are they in DNA versus RNA
DNA(deoxyribose)(lack a ‘OH)→ dNMPs, dNDPs, dNTPs
deoxy for d m for mono, di, trip
RNA(ribose) → NMPs, NDPs, NTPs
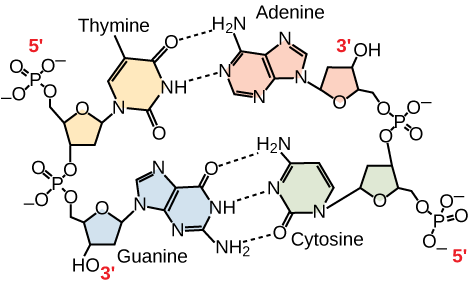
Purines versus pyrimidines
Purines are A and G
have 2 rings
Pyrimidines are T,C, U
1 ring like a pie
DNA primary structure
deoxyribonucleotides
Phosphodiester bonds (bw 3’ Oh and 5’ of next moleule) form the backbone of DNA
bw the 3’OH of the existing strand and the a-phosphate group of a dNTP
3’OH important bc it’s like the "anchor point" for adding new building blocks,
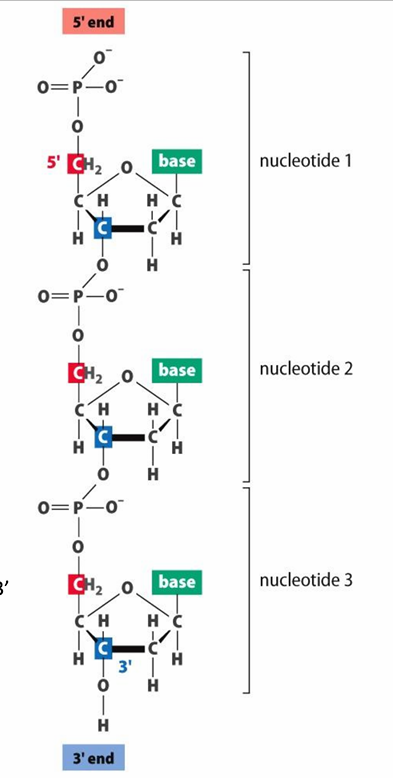
Draw the phosphodiester bond reaction
Show nucleotide’s 3’OH being attacked by a nucloeitde that has 3 P’s on it instead of 1
this forms a deoxyribonuclotide like the primary structure + PPi and H20
DNA secondary structure
double helix→ 2 strands
Has H bonds bw bases
Complementary pairing
Antiparallel strands → mechanism of replication (5’-3’ and 3’-5’)
What are the numeric facts about DNA secondary structure
each nucleotide pair ~ o.34 nm
10 nucleotide pairs per turn
2 nm in diamter
grooves bound by DNA binding proteins mostly bind the major groove
How is DNA structure different from RNA?
DNA has 2’ H RNA has 2’OH
RNA has U DNA has T → pyrimidine flavors different
Secondary structures are different
RNA has flexible stem loop strucs (less stable) versus DNA stiff double helix (very stable)
RNA has different base pairing
How does DNA’s secondary structure support its function
Function= it’s hereditary material, it stores and transmits genetic information
Info is on the inside
H bonds are a goldilocks bond
Weak enough to easily break apart and access info but strong enough to hold helix together and keep info stable/safe over long time
Information has redundancy
Damage to 1 strand can be repaired by looking at the other strand (double stranded nature)
Double code offers additional space for info storage (either strand could be coding)
What does PCR do
make copies of a specific segment of DNA
amplifies DNA
Why do PCR primers need to be complementary to the template DNA?
Answer:
Primers bind to the template strand so DNA polymerase can extend from the 3' end, allowing amplification of the target sequence.
Basically 1. heat seperates the double strand DNA into single strands 2. primers (short DNA seqs) bind to the specific segment to be copied 3. taq polymerase (dna poly) copies the DNA creating new but identical strands 4. the process repeats doubling DNA in each cycle
The coding (sense) or non template strand ..
has the same sequence as the primary RNA transcript
replace t’s with Us
goes from 5’-3’
to make mRNA take the strand and just switch T→U 5’--blah3’
Template (antisense) strand
has the complementary sequence to the primary RNA transcript
3’-5’ (bottom strand typically)
So if given the template strand and I need the mRNA the template strand will go from 3’-5’ so make the complemntary code and write it from 5’-3’ with Us
makes sense bc the complementary sequence would give you the top (coding) strand which has the same sequence as the mRNA but with Us
Nucleic acid synthesis proceeds in the ___ direction and requires a __. It is used in
5’-3’ direction
3’OH
Replicationm transcription, PCR, sanger sequencing
Show that double stranded nucleic acid structures are ANTIPARALLEL by drawing it
on onenote too