BIOL 1000 😐🔫
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:03 AM on 6/28/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
1
New cards
Evolution
Evolution is the unifying themes of biology and explain the history and diversity of life on this planet
2
New cards
Nature of science
The study of signs involves the process of making observations, for my hypothesis, is in conducting experiments, in an attempt to understand the principles of life
3
New cards
Biological systems
From communities of organisms to individual cells, all life is connected from the smallest atom to the largest ecosystem
4
New cards
Biology
Is the scientific study of life. Life is structured on a size scale ranging from the molecular to the Global. Biology scope stretches across the enormous diversity of life on earth.
5
New cards
Properties of life
6 properties
Living things are organized and made of cells.
Living things required/acquired materials and energy.
Living things maintain homeostasis. Living things respond to their environment.
Living things grow develop and reproduce.
Living things have adaptations and evolve.
Living things are organized and made of cells.
Living things required/acquired materials and energy.
Living things maintain homeostasis. Living things respond to their environment.
Living things grow develop and reproduce.
Living things have adaptations and evolve.
6
New cards
Defining life
All living things are comprised of the same chemical elements. I’ll be the same physical and chemical laws is nonliving elements. Unlike nonlife living things are complex and organized.
7
New cards
Cell
The smallest most basic unit of life. Cell→ tissue→organs→ organs systems→ one organisms
8
New cards
Life is organized
Life can be organizing a hierarchy of levels these levels of biological organization begin with Atoms, the basic unit of matter. Atoms combine to form small molecules which join to form larger molecules (macromolecules) within a cell, the smallest most basic unit of life.
9
New cards
Multicellular
Any living organisms are multicellular meaning they contain more than one cell. A multicellular organism similar cells made combine to form a tissue for example, the nerve and muscle tissues of animals. Tissues make up organs such as the brain or a leaf.
10
New cards
Biological organization
Levels of biological organization extend beyond the individual organism. Atom, molecule, organelle, so, tissue, Organ, organ system, organism, population, species, community, ecosystem, biomes in aquatic life systems, biosphere.
11
New cards
Atom
The basic unit of matter with specific properties and interactions.
12
New cards
Molecule
An integrated group of atoms with specific properties and interactions
13
New cards
Organelle
An integrated group of molecules that perform specific tasks for the cell in eukaryotes only
14
New cards
Cell
An integrated group of molecules and (in eukaryotes) organelles, the basic unit of life, that performs task at the ultimate direction of DNA. Living things are organized and made of cells. Three things all cells must have are: cell membrane, nuclear region with DNA, cytoplasm.
15
New cards
tissue
An integrated group of cells that perform a specific task for the Organ
16
New cards
Organ
An integrated group of tissues that perform a specific task for the organ system
17
New cards
Organ system
An integrated group of organs that perform a specific task for the organism
18
New cards
Organism
An integrated group of organ systems. An individual living thing.
19
New cards
Population
An integrated group of individuals of one species, all interacting with one another
20
New cards
Species
An integrated group of populations, integrated through their form, behavior and preferred living conditions, these are being a consequence of similar DNA and reproductive isolation from other species.
21
New cards
Community
An integrated group of all living organisms in an area, including many species and populations
22
New cards
Ecosystem
And integrate a group of all living organisms in an area plus the physical components that affect them.
23
New cards
Biomes and aquatic life systems
Integrated group of terrestrial ecosystems all existing within a particular region, and with a particular climate, an integrated group of marine or freshwater, ecosystems, all existing with any particular area of aquatic environment.
24
New cards
Biosphere
All of the Earth biomes, (terrestrial and aquatic)
25
New cards
Emergent properties
Each level of organization is more complex and has properties beyond proceeding level. Each new level of organization has emergent properties due to the interactions between different parts of the whole. Moving up the biological hierarchy, each level, acquire new emergent properties.
26
New cards
Unicellular
And unicellular organism has just a single cell with many complex organelles
27
New cards
Multicellular organism
A simple, multicellular organism, each cell has complex organelles.
28
New cards
Life has organized complexity
The organized and complex organs of the digestive system of this animal exhibit one of the properties of life
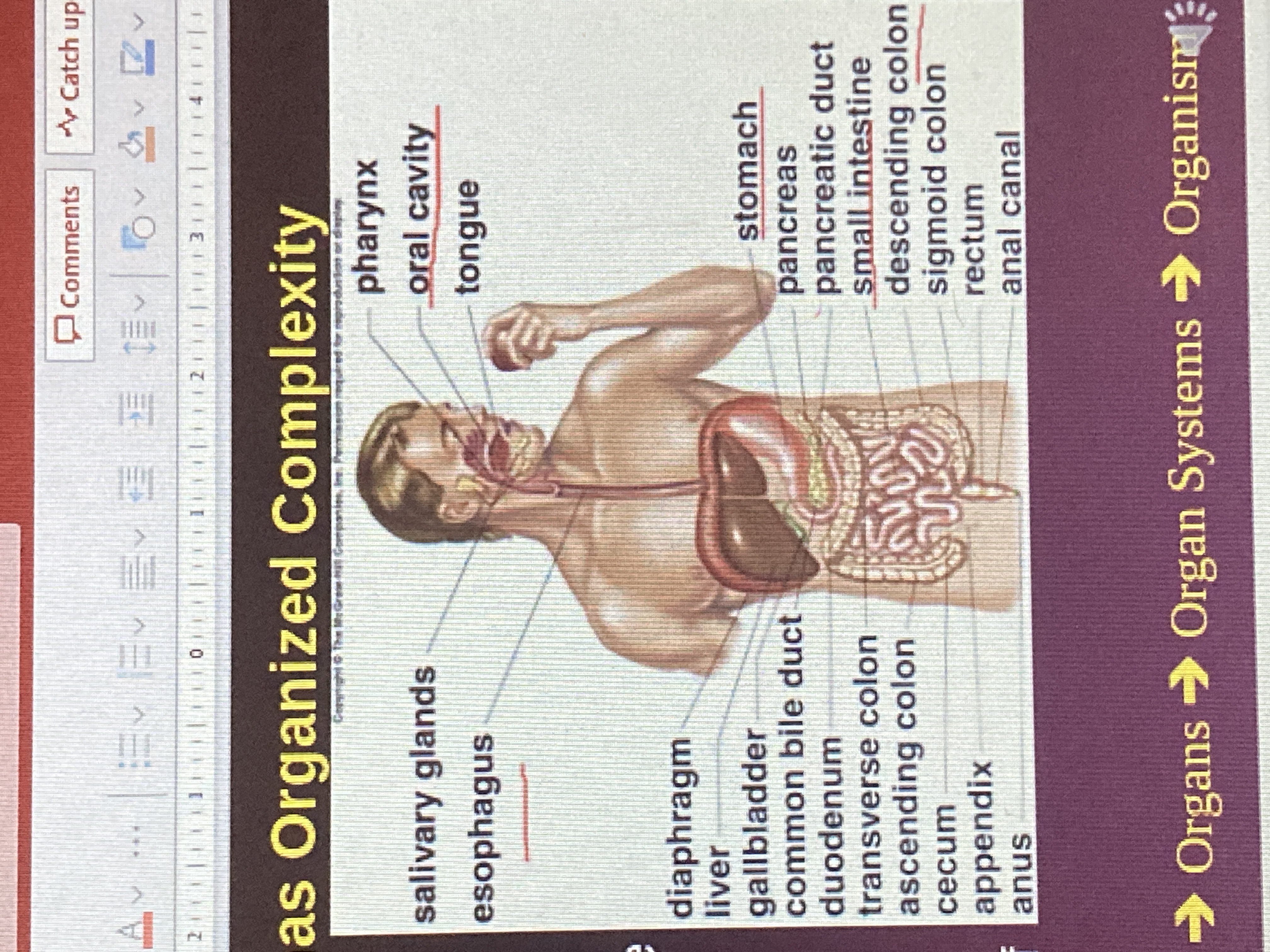
29
New cards
Life requires materials and energy
Energy is a capacity to do work work is usually some sort of form of movement. Examples of work are: mechanical movement, transportation of materials (into or out of cells, from one place to another), and chemical rearrangement. The Sun is the ultimate source of energy for nearly all life on the planet.
30
New cards
metabolism
Is the sum of all chemical reactions in a cell. Metabolism does work, uses energy and rearranges material like matter, atoms molecules, and provides the needs for the life of the cell. Metabolism in plants is photosynthesis; energy that comes from sunlight, materials come from simple chemicals, like carbon dioxide and water. Metabolism in animals is cellular respiration; both energy and materials come from food.
31
New cards
Energy flow and chemical cycling in ecosystems
The energy and chemical flow between organisms also defines how many ecosystem functions. Within an ecosystem, chemical cycling and energy flow begin when producer such as grass is taking solar energy, and inorganic nutrients to produce food by photosynthesis chemical cycling occurs as chemicals move from one population to another in a food chain until death and decomposition allows inorganic nutrients to return to the producers once again. Energy on the other hand, flows from the sun through plants and other members of the food chain as they feed on one another, the energy gradually dissipates and returned to the atmosphere is heat because energy does not cycle. Ecosystems could not stay in existence with our solar, energy and ability of photosynthetic organisms, to absorb it
32
New cards
Living organisms, maintain homeostasis
Homeostasis is the dynamic biological balance. For life to continue temperature in moisture level acidity in other physiological factors must remain within the tolerance range of the organism homeostasis is maintain by systems that monitor internal conditions, and make routine and necessary adjustments. Organisms have intricate feedback and control mechanisms that do not require any conscious activity.
33
New cards
Living things respond
In order to obtain materials in energy, avoid injuries and damage and maintain homeostasis living things must respond to the environment. Both the nonliving components: abiotic. In with the nonliving things: biotic. Both must absorb sunlight, find water, shelter, nutrients, etc. find an eat food avoid being eaten find meet with which to reproduce.
34
New cards
Growth, development and reproduction
Animals, multicellular organisms reproduction begins with the union of two cells called gametes (like sperm and egg) from different individuals. Reproduction produces a new individual living thing. From there it must grow and develop. When living organisms reproduce, their genes or genetic instructions are passed on to the next generation. All cells in multicellular organisms contain the same side of genes but only certain genes are turned on in each type of specialized cell. These differences are the result of mutations or inheritable changes in the genetic information. Mutation provides an important source of variation in the genetic information. Not all mutations are bad.
\
\
35
New cards
Biodiversity
All of the variations of life forms within a species, and among species. Evolution accounts for this combination of unity and diversity.
36
New cards
Evolution
Includes the way in which populations of organisms change over the course of many generations to become more suited to their environment. All living organisms have the capacity to evolve, in the process of evolution, constantly reshapes every species on the planet, potentially providing away for organisms to persist, despite a changing environment.
37
New cards
Natural selection
During the process of natural selection, some aspect of the environment, selects which traits are more apt to be passed on to the next generation. The selective agent can be an abiotic agent( part of the physical environment such as altitude), or can be a biotic agent (part of the living environment such as deer). Mutations feel natural selection, because mutation introduces variations among the members of a population. New characteristics and traits arise to the process of DNA change called modification.
38
New cards
Two Basic types of cells.
Prokaryotic: which are cells that have no organelles, they contain cell wall and cell membrane. Eukaryotic: which are cells that have organelles including the nucleus.
\
\
39
New cards
The diversity of life in three large groups
Bacteria, Archaea, and Eukarya. Both domain Bacteria and archaea may have evolved from the first common ancestor. Soon after life began. These two domains contain the prokaryotes. Would you like to membrane-bound found in the eukaryotes of domain Eukarya. Arteria organize their DNA differently than bacteria and their cell walls and memories are chemically more similar to eukaryotes than bacteria.
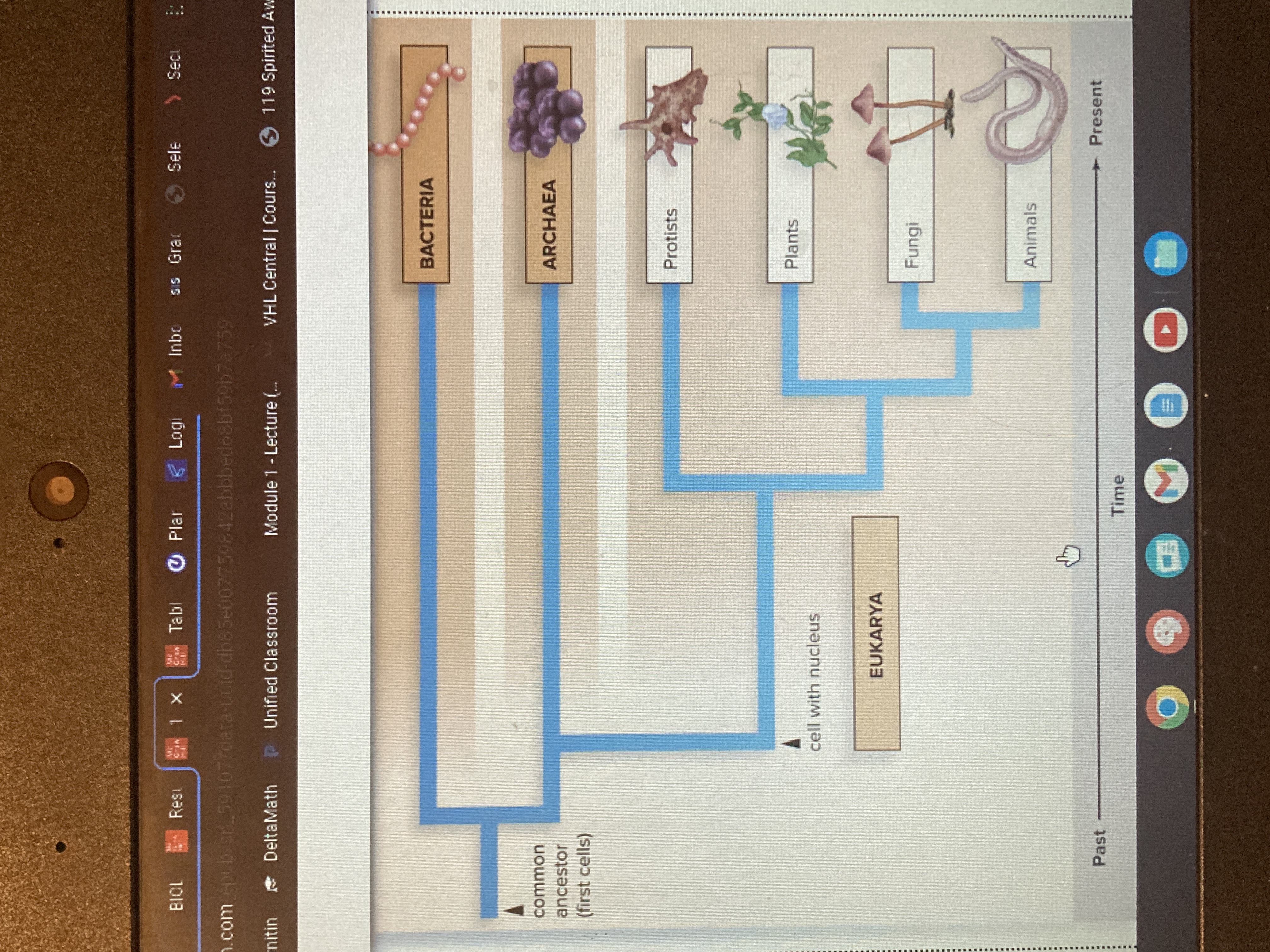
40
New cards
Taxonomy
Is the discipline of identifying and grouping organisms according to certain rules, taxonomy makes sense out of the bewildering variety of life on earth, and is meant to provide valuable insight into evolution.
41
New cards
Levels of taxonomy
From most inclusive is Domain, supergroup, kingdom, Phylum, class, order, family, genus, species. \*Supergroups only present in domain Eukarya. Species with one gene is share many specific characteristics and are the most closely related species placed in the same kingdom share only general characteristics with one another for example, all species in the genus Pisum look pretty much the same-that is like-pea plants- but species in the plant kingdom can be quite varied, as is evident when we compare grasses to trees.
42
New cards
Domain Archaea
Unicellular prokaryotes. Can live in extreme environments like: aquatic environments that lack oxygen or are too salty, too high or too acidic for most other organisms. Absorbs or chemo synthesizes food. Do you need chemical characteristics.
43
New cards
Domain Bacteria
Unicellular prokaryotes. Bacteria are variously adapted to living, almost anywhere in the water or soil in atmosphere, as well as on our skin and in our mouth and large intestine. Absorb photosynthesize or chemo synthesize food, prokaryotic cells are very shapes.
44
New cards
The Domain of Eukarya divided organisms into one of the four kingdoms
Both unicellular and multicellular. consist of:
K. Protista, K.Fungi, K. Plantae, K. Animalia
K. Protista, K.Fungi, K. Plantae, K. Animalia
45
New cards
Kingdom Protista
Comprised of a very diverse group of organisms range for a single cell forms to a few multicellular one some are photosynthesizers, and some must acquire their food. Common protist include algae, the Protozoans and the water mold.
46
New cards
Kingdom fungi
Among the fungi are familiar molds in mushrooms, that along with bacteria, help decompose dead organisms. Mostly multicellular filaments specialized complex cells. Absorbs food.
47
New cards
Kingdom Plantae
Multicellular photosynthetic organisms usually with specialized tissues. Example plants include azaleas, zinnias, and pines.
48
New cards
Kingdom Animalia
Multicellular organisms that must ingest and process their food and contain specialized tissues, containing complex, cells. Animals like aardvarks jellyfish, zebras, sponges, worms in six faces, frogs turtles, birds, and mammals.
49
New cards
Inductive reasoning
Occurs whenever a person uses creative thinking to combine isolated facts into a cohesive whole. Scientist use inductive reasoning to formulate a possible explanation
50
New cards
Deductive reasoning
To determine how to test a hypothesis, a scientist uses deductive reasoning. Deductive reasoning involves, “if, then” logic.
51
New cards
What is biology
The scientific study of life
52
New cards
Properties of life
Life needs and uses matter and energy.
Life maintains homeostasis.
Life has organized complexity.
Life grows, reproduces.
Life evolves.
Life responds to the environment/stimuli.
Life maintains homeostasis.
Life has organized complexity.
Life grows, reproduces.
Life evolves.
Life responds to the environment/stimuli.
53
New cards
Most of life properties are ______ because they arise from the interactions of the parts of the other system
Emergent properties
54
New cards
Which of these is most closely associated with ecosystems?
Energy flowing, chemical cycling
55
New cards
Which of these is most closely associated associated with evolution by natural selection?
Common ancestors, adaptations, changing Life forms overtime.
56
New cards
Scientific method
Observation, hypothesis, test
57
New cards
What is the simplest thing consider alive?
Cell
58
New cards
You belong to the kingdom Animalia. what are some characteristics common to all animals?
Eukaryotic. Multicellular with specialized tissue. Ingest food.
59
New cards
Adding more cells
Growth
60
New cards
Capacity to do work
Energy
61
New cards
Dynamic biological balance
Homeostasis
62
New cards
Producing a new living organism
Reproduction
63
New cards
In science, a hypothesis must be……
Falsifiable
64
New cards
What makes adaptation possible?
Natural selection
65
New cards
What allows scientists to think creatively about isolated facts and come up with a hypothesis?
inductive reasoning
66
New cards
What is a new disease called?
Emerging disease
67
New cards
Within domain eukaryote, there are six ______ that have been developed to explain evolutionarily relationships specifically among protist
Supergroups
68
New cards
CHAPTER 2
69
New cards
A scale used to describe the acidity or basicity of a solution
PH scale
70
New cards
______ are found in the atoms nucleus in a positively charged
Protons
71
New cards
________ are found in the atoms nucleus and do not have a charge
Neutrons
72
New cards
_______ Orbit around the atomic nucleus in shells
Electrons
73
New cards
Atoms of the same element that have different mass numbers are known as
Isotopes
74
New cards
Basic types of substances that cannot be broken down into other substances by ordinary chemical means. They have certain physical and chemical properties.
Elements
75
New cards
Chemical bonds formed by the attraction between polar molecules
Hydrogen bonds
76
New cards
Chemical bonds formed by the sharing of a pair of electrons between two atoms
Covalent bond
77
New cards
Chemical bonds formed from the complete transference of one or more electrons from one atom to the other, causing the atoms to be oppositely charged
Ionic bonds
78
New cards
How many electrons can the first shell hold maximum?
Two
79
New cards
How many electrons can the second and third shell hold maximum?
Eight
80
New cards
Substances form from two or more atoms bond together
Molecules
81
New cards
Substances formed from two or more different types of atoms, bonded together
Compounds
82
New cards
The smallest simplest most basic unit of matter that retains the properties of an element
atom
83
New cards
What are the parts of an atom?
Protons neutrons electrons
84
New cards
How to get atomic mass?
Add the number of protons and neutrons
85
New cards
How to get # of neutrons?
mass - #of protons
86
New cards
Electron valence shell
The number of electrons in an atoms outer shell
87
New cards
water has a high heat of evaporation due to which chemical property?
Hydrogen bonding
88
New cards
The main reason for putting a small amount of radioactive isotope in a sample to serve as a tracer is to…..
Detect molecular changes
89
New cards
The attraction between a hydrogen atom and an electronegative atom in another molecule results in a……
Hydrogen bond
90
New cards
Which property of water is due to the attraction between molecules of water
Cohesion
91
New cards
A hydrogen ion that has gained an electron and will have a negative charge is….
Hydroxide ion
92
New cards
Ionization
The disassociation of water into hydrogen ions and hydroxide ions.
93
New cards
Property of water that allows it to cling to other polar surfaces is called
Adhesion
94
New cards
Adding what to water will increase the concentration of H+
Acid
95
New cards
Anything that takes up space and has mass is called
Matter
96
New cards
What does atomic number represent
The sum of the protons and neutrons in the nucleus
97
New cards
True or false: the hydrogen bonding in water explains its high heat of evaporation. Which of the following is most directly responsible for water having a high heat capacity?
True. Hydrogen bonding.
98
New cards
Polar covalent bond
Bond in which electrons between atoms are unequally shared. Example H2O.
99
New cards
Non-polar covalent bonds
Bond in which electrons between atoms are equally shared example CH4 ( methane).
100
New cards
Which type of bond breaks when a DNA molecule unzips when DNA is being copied
Hydrogen bond