1.1.1 Architecture of the CPU
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
What is the purpose of the Central Processing Unit (CPU)?
The CPU executes instructions in order to run programs.
What does the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) do?
Performs arithmetic calculations, logical operations and shift operations.
What are examples of the arithmetic calculations the ALU does?
Addition, Subtraction, Multiplication and Division
What are examples of the logical operations the ALU carries out?
AND, OR, NOT
What does the Control Unit (CU) do?
The control unit organises the execution of instructions, including managing the other components in the processor.
What tasks if the CU responsible for?
Ensures the execution of instructions in the correct sequence
Decodes every instruction that the processor will execute
Sends and receives control signals to and from other components
Checks that signals have been delivered successfully
Makes sure that data goes to the correct place at the correct time
The control unit also contains the ______. This is a tiny component that controls the rate at which instructions are __________ in the processor.
clock, executed
What is cache?
A small, fast memory device located on the CPU that stores frequently used data and instructions.
What are registers?
A very fast memory location within the CPU used in the execution of instructions.
What are the five special-purpose registers?
Current Instruction Register (CIR), Memory Address Register (MAR), Memory Data Register (MDR), Program Counter (PC) and Accumulator (ACC)
What is the function of the Current Instruction Register (CIR)?
Holds the current instruction that the processor is executing.
What is the function of the Memory Address Register (MAR)?
Temporarily stores the address of the data to be fetched from or the address where the data is to be stored.
What is the function of the Memory Data Register (MDR)?
Temporarily holds the data that is read from or written to the main memory.
What is the function of the Program Counter (PC)?
Stores the address of the next instruction to be fetched from memory.
The Program Counter _________ during each _____-______ cycle.
increments, fetch, execute
What is the function of the Accumulator (ACC)?
Stores the results of calculations or operations carried out by the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU). Also temporarily holds data being processed.
Give the stages of the fetch-decode-execute cycle.
The address of the next instruction is transferred from the Program Counter to the MAR.
The instruction is fetched from memory and copied into the MDR.
The Program Counter is incremented.
The instruction is decoded by the CU.
The decoded instruction is then executed by the CPU or ALU.
The process repeats.
What happens in the ‘fetch’ stage of the fetch-decode-execute cycle?
Each instruction is fetched from memory (in order), and put into the appropriate registers. The control unit can then access the instruction for the next stages.
What happens in the ‘decode’ stage of the fetch-decode-execute cycle?
The instructions (which are received in binary) need to be decoded before they can be run. This is the process the control unit uses to work out what the other components need to do.
What happens in the ‘execute’ stage of the fetch-decode-execute cycle?
The control unit will tell the other components what they need to do in order for the instruction to work.
What is Von Neumann architecture?
A system where instructions and data share the same memory and bus.
What does the Von Neumann architecture consist of?
a processor
a memory unit that can communicate directly with the processor
connections for input and output devices
secondary storage for saving/backing up data
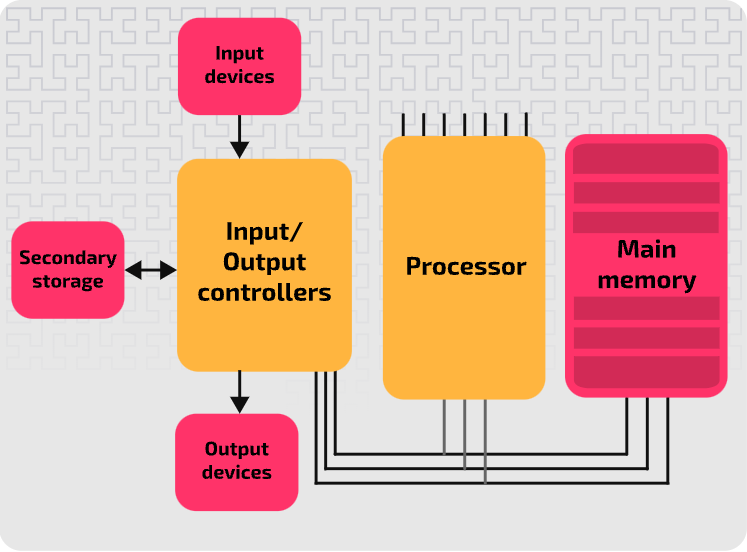
The processor can access the ____________ and _____ in the _____ memory as required to _______ the program. It does this by using dedicated connections called _______.
instructions, data, main, execute, buses
What is an address bus used to do?
An address bus is used to identify the addressed location.
What is a data bus used to do?
A data bus is used to transfer the contents to/from that location.
What is the control bus used to do?
The control bus is used to synchronise and control operations.
The _____ address and data buses are used in the process of ________ instructions and ____ between _____ ________ and the ___________.
same, transferring, data, main memory, processor
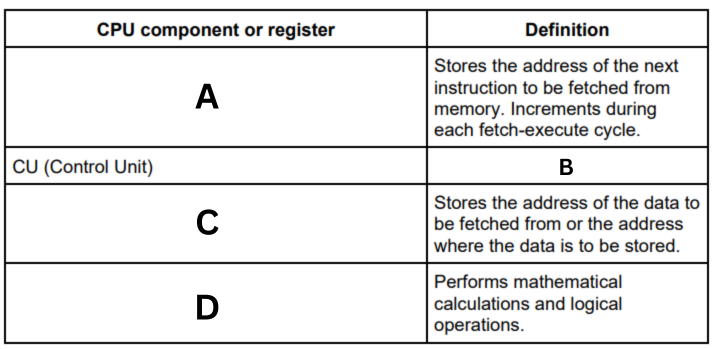
Complete the table by writing the missing definition or name of each of the common CPU components and registers. (A)
Program Counter (PC)
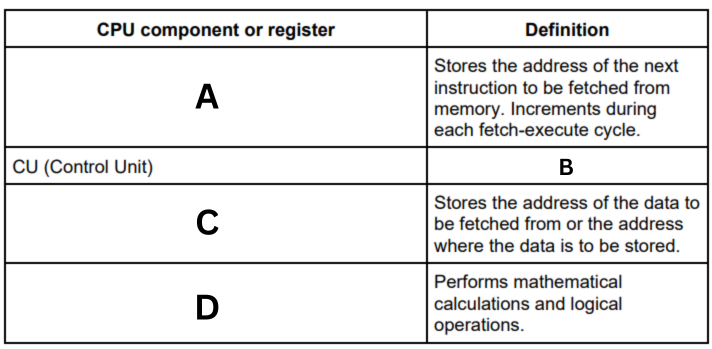
Complete the table by writing the missing definition or name of each of the common CPU components and registers. (B)
The control unit organises the execution of instructions, including managing the other components in the processor.
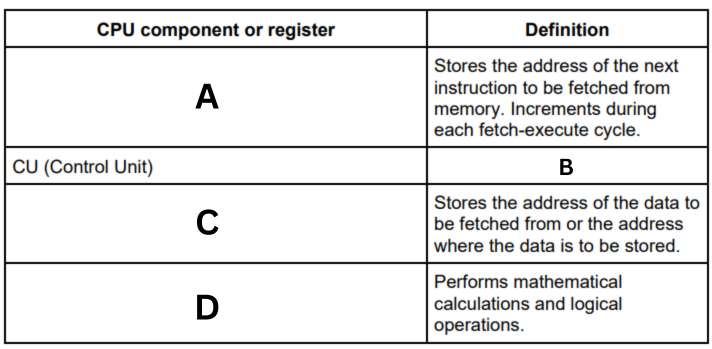
Complete the table by writing the missing definition or name of each of the common CPU components and registers. (C)
Memory Address Register (MAR)
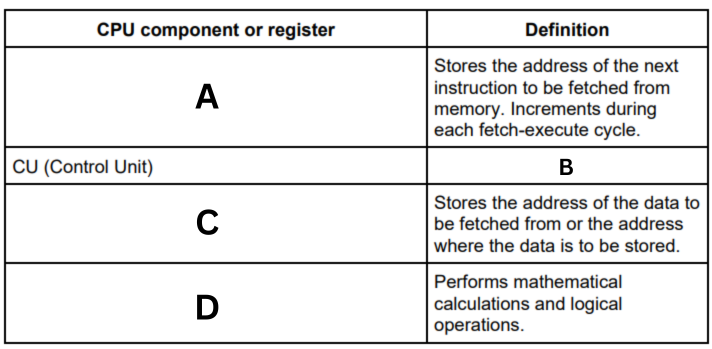
Complete the table by writing the missing definition or name of each of the common CPU components and registers. (D)
Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU)
Identify the first two events that take place during the fetch-execute cycle.
An instruction is fetched from memory
The instruction is then decoded