Data recording, analysis and presentation
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Nominal level data
Data recorded in named categories
Ordinal level data
Data recorded as points along a scale with not necessarily equal gaps
Interval level data
Data recorded as points along a scale with equal gaps
Measures of central tendancy
Typical/ average score from a data set
Measures of dispersion
Variance/ spread of scores in a data set
Standard deviation
Square root of the variance
Variance
Average of the squared differences from the mean
Range
Subtracting the smallest from the biggest value and adding one to the total
Significance level
p<0.05
Chi- square test
nominal data + independent measures
Spearman’s Rho
ordinal or interval data + correlations
Types of reliability
Internal
consistency of results across a set
External
extent to which a test produces the same results with the same people in the same situation
Inter rater
researchers findings being similar
Test retest
checking that results are valid through retesting
Split half
comparing two halves of a test and seeing how well they correlate
Validity
Internal
if the processes in a study achieve the intended measures
Face
if the test if measuring what it is meant to
Construct
if the thing being measured actually exists
Concurrent
different measures of the thing result in the same circumstances at the same time
Criterion
a measure of a thing predicting the value of another measure of the same thing
Population
if the findings can be generalised to the entire population
Ecological
if the findings are generalisable to real life
Ethical considerations
Respect
informed consent
right to withdraw
confidentiality
Competence
psychologists must work within their own capabilities
Responsibility
protection of participants
debrief
Integrity
deception
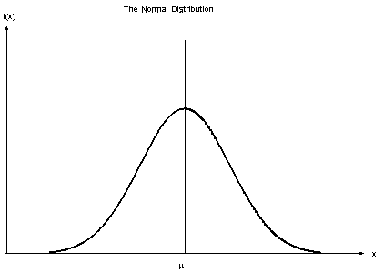
The median, mean and mode are…
all on the same point
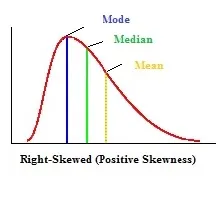
In a positive distirbution curve the order is…
Mode, median, mean
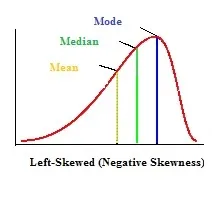
In a negative distirbution curve the order is…
Mean, median, mode
Criteria for using a parametric test
Data is interval or ratio + data must have a normal distribution + variences must be similar
WilcOxon Signed-Rank test
ordinal + repeated measures
BiNomial Sign test
nominal + repeated measures
Spearmans Rho
ordinal and interval + correlation
Type 1 error
incorrectly rejecting null hypothesis
Type 2 error
incrorrectly accepting null hypothesis
calc > crit so results are significant
Spearmans Rho
Chi Squared
calc < crit so results are significant
Mann- Whitney
Wilcoxon
Binomial