Chapter 3.6 - Chromosomes
1/67
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
68 Terms
heterochromatin
darker chromatin
euchromatin
lighter chromatin
histones and DNA
chromatin is made up of _____ and _____
p arm
the short arm of the chromosome
q arm
long arm of the chromosome
centromere
the largest constriction of the chromosome and where spindle fibers attach
heterochromatin
darkly staining, contains mostly repetitive DNA
euchromatin
contains more protein encoding genes
telomeres
chromosome tips composed of many repeats of TTAGGG and shorten with each cell division
subtelomeres
the chromosome region between the chromatin and telomeres
8,000 - 300,000 bases
the subtelomeres consist of _____ - _______ bases
500
subtelomeres includes at least ___ protein-encoding genes
subtelomeres
in this region there is a 6-base repeat similar to telomeres
multigene families
genes that are related in structure
pseudogenes
genes that have become inactive over time
subtelomeres
multigene families and psuedogenes are in what region of the chromosome?
False
True or False: Every chromosome has the centromere in the same place
telocentric
centromere position is at the tip
acrocentric
centromere position is close to the end
submetacentric
centromere position is displaced from the center
metacentric
centromere position is at the midpoint
True
True or False: chromosomes differ in size
satellite chromosome
there is a secondary constriction near the tip of the chromosome with a satellite structure attached at the end
46 chromosomes; 23 diploid chromosomes
a normal karyotype has…
diploid
two sets of each chromosome
haploid
one set of each chromosome
number of chromosomes or missing pieces of chromosomes
chromosome abnormalities can happen due to … (2)
polyploidy
addition of whole sets of chromosomes
17%; 3%
___% of all spontaneous abortions and ____% of all stillbirths and newborn deaths show polyploidy
triploid
three copies of each chromosome; produced by two sperm fertilizing one egg or a haploid sperm fertilizing a diploid egg
aneuploidy
cells with extra or missing chromosomes; gametes produced with one extra chromosome and another with one missing chromosome
nondisjunction
common cause of aneuploidy
Down Syndrome
Trisomy 21
Trisomy 21
most common trisomy
down syndrome
distinctive facial and physical problems, many medical problems (treatable), varying degrees of developmental disabilities, link with one form of Alzheimers disease, may also be produced by a translocation
True
True or False: maternal age is a risk factor for having a child with Down syndrome
edwards syndrome
trisomy 18
trisomy 18
most due to nondisjunction in meiosis II in oocyte and do not survive
trisomy 18
2nd most common trisomy
trisomy 18
80% of people with this trisomy are female
edwards syndrome
characterized by small head, malformed ears, widely spaced, eyes, clenched hands, heart abnormalities, and kidney malformations
patau syndrome
trisomy 13
patau syndrome
very rare and generally do not survive 6 months; medical and physical abnormalities (facial malformation and eye fusion)
aneuploidy
trisomy and monosomy are associated with what?
turners syndrome
only one copy of x chromosome; 1 in 2,500 female births; 99% of affected fetuses die in utero; absence of Y leads to development as a female; phenotypes include short statue, webbing at back of neck, incomplete sexual development (infertile), and hearing impairment
not in every cell
turners syndrome is mosaic meaning it is…
45
people with turners syndrome have ___ chromosomes
47
people with triplo-X aneuploidy have ___ chromosomes
triplo-X aneuploidy
1 in 1,000 female births; extra copy of every x-linked gene, few modest effects on phenotype include tallness, menstrual irregularities, and slight impact on intelligence; x inactivation of two X chromosomes occurs and the cells have 2 barr bodies
klinefelters syndrome
1 in 1,000 male births; extra copy of each x-linked gene; phenotypes include incomplete sexual development, rudimentary testes and prostate, long limbs, large hands and feet, some breast tissue development; some cases are not diagnosed until fertility problems arise or remain undiagnosed
47
people with Klinefelter syndrome have ___ chromosomes
XXYY sendrome
mistaken for Kleinfelters; associated with ADHD, OCD, learning disabilities, and infertile; treated with testosterone
XYY/Jacobs syndrome
1 in 1,000 male births, extra y chromosome, 96% phenotypically normal, modest phenotypic differences may include: tall, acne problems, minor speech and reading disabilities
47
people with XYY or Jacobs syndrome have ___ chromosomes
deletions
chromosomal ______ result in missing copies of genes; usually bad as it can allow recessive allele to dominate
duplication
chromosomal ______ result in extra copies of genes; unequal crossing over
True
True or False: larger regions of deletion or duplication increase the likelihood that there will be an associated phenotype
translocation
nonhomologous chromosomes exchange segments
derivative chromosomes
an abnormal chromosome formed from a rearrangement, such as a translocation or insertion, involving parts of two or more chromosomes or multiple aberrations within a single chromosome
robertsonian and reciprocal
what are the two types of translocation?
robertsonian translocation
where two nonhomologous acrocentric chromosomes break at the centromere and long arms fuse; the short arms are often lost
reciprocal translocation
two nonhomologous chromosomes exchange a portion of their chromosome arms; some individuals carry a translocation but are not missing any genetic material unless a translocation breakpoint interrupts a gene
inversion
these chromosomes have a region flipped in orientation; 5-10% of these cause health problems probably due to disruption of genes at the breakpoints; these may impact meiotic segregation
paracentric
inverted region does NOT include centromere
pericentric
inverted region includes centromere
isochromosomes
chromosomes with identical arms; form when centromeres divide along the incorrect plane during meiosis
ring chromosomes
chromosomes shaped like a ring; occur in 1 in 25,000 conceptions; may arise when telomeres are lost and sticky chromosome ends fuse; have phenotypes associated with the loss or addition of genetic material
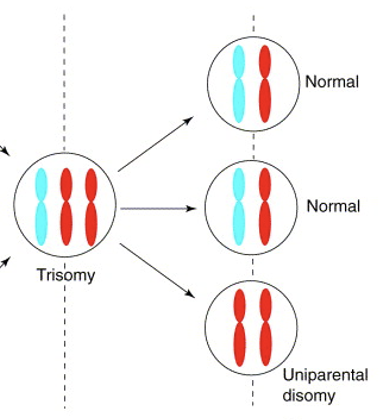
uniparental disomy
inheritance of two chromosomes or chromosome parts from the same parent