AP Biology Semester 1
1/210
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
211 Terms
5 unifying characteristics of all cells
1. Cell membrane
2. DNA
3. Cytoplasm
4. Ribosomes
5. Same gene --> protein pathway
Surface Area : Volume ratio
Determines the efficiency at which cells can transport necessary materials and eliminate wastes
SA:V ratio (small cells)
High SA:V ratio --> higher efficiency in transport
(lots SA : less V)
SA:V ratio (large cells)
Low SA:V ratio --> lower efficiency in transport
(less SA : lots V)
Adaptations to increase SA:V ratio - located along all levels of biological organization
(lots of SA)
1. Branching (root systems, neurons, lungs)
2. Projections (ileum - small intestines, root hair)
3. Flattening (golgi app., chloroplasts, flatworms)
4. Folding (rough ER, mitochondria, small intestine)

Prokaryotic Cells: Evolution
1st to evolve (3.5 bya)
Prokaryotic Cells: Classification
Bacteria
Archeabacteria
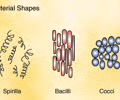
Prokaryotic Cells: Size and complexity
Small, simple internal network
Cell wall
Shape
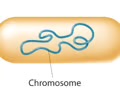
Prokaryotic Cells: DNA
Single circular chromosome (tightly packed into nucleoid, free in cytoplasm) (plasmids - ring of DNA, accessory gene)
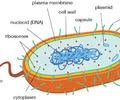
Prokaryotic Cells: Image
What does the Theory of Endosymbiosis explain?
The evolution of eukaryotic cells on a prokaryotic planet.
What is the relationship between two prokaryotic cells in the Theory of Endosymbiosis?
They live together and benefit one another.
What organelles in eukaryotes are thought to have originated from prokaryotic cells?
Mitochondria
Chloroplasts
What are some characteristics of mitochondria and chloroplasts?
They have their own DNA
Own ribosomes
Double membrane
Can reproduce on their own - semi-autonomous.
Eukaryotic Cells: Evolution
2nd to evolve (2.5 bya)
Eukaryotic Cells: Classification
Protista
Fungi
Plants
Animals
Eukaryotic Cells: Size and complexity
Large - can form multicellular organisms
Shape/function of each cell is unique
Eukaryotic Cells: DNA
Multiple, linear chromosomes
Nucleus - surrounded by nuclear envelope

Eukaryotic Cells: Image
Endomembrane Network - true membrane-bound organelles
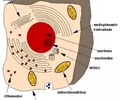
Compartmentalization - different locations for different reactions promotes organelle specificity and efficiency
Materials localized
Increased rate of reactions
Complexity for the cell itself & the cell's role in multicellular organisms
Metabolism
Obtain and use materials - ENERGY - chemical reaction
Homeostasis
Maintain a stable internal environment
heredity (DNA —> protein)
Store, use, copy, & transfer genetic info
METABOLISM: Chloroplasts
Perform photosynthesis - 6CO2 + 6H2O --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Generate glucose
Compartments increase SA

METABOLISM: Mitochondria
Perform cellular respiration - C6H12O6 + 6CO2 --> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
Generate ATP
Folding increase SA
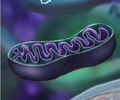
METABOLISM: Chloroplasts and mitochondria are evidence of endosymbiosis
1. Own DNA
2. Own ribosomes
3. Double membrane
4. Reproduce on own
METABOLISM: Chloroplasts and mitochondria are examples of
Compartmentalization - localized function (decrease V = increase rate of reaction)
Increased surface area - flattening & folding
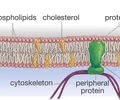
HOMEOSTASIS: Cell membrane
Plasma membrane - flexible membrane through which cells transport materials + communicate with other cells
HOMEOSTASIS: Cell wall
Rigid barrier - support & structure (plants, fungi, bacteria, & same protists)
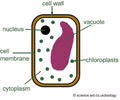
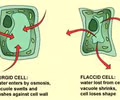
HOMEOSTASIS: Vacuole (membrane)
HOMEOSTASIS: Central vacuole (membrane)
Storage - water, pigment, starch, sugar
H2O maintains turgor pressure
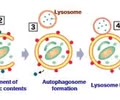
HOMEOSTASIS: Lysosome (membrane)
Waste breakdown - contains digestive enzymes - recycles old organelles and pathogens
HOMEOSTASIS: Cilia (surface projections)
Many short - move from place to place & move across a surface

HOMEOSTASIS: Flagella (surface projections)
Few long - moves from place to place

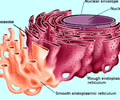
HOMEOSTASIS: Smooth
Lipid synthesis, detoxification, no ribosomes attached
HEREDITY
DNA to protein production pathway. Proteins, polypeptides regulate all cellular processes
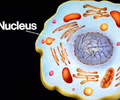
HEREDITY: Nucleus
Stores DNA in eukaryotic cells. Site of transcription (DNA --> mRNA)
HEREDITY: Ribosome
Uses mRNA code to build a polypeptide chain of amino acids. Can be free-floating or attached to rough endoplasmic reticulum.

HEREDITY: Rough ER
Polypeptide folding into 3-D shape.
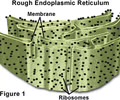
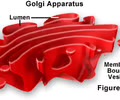
HEREDITY: Golgi apparatus
Packages and labels proteins for export to other cells
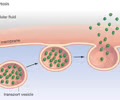
HEREDITY: Vesicle
Exports proteins via exocytosis
Binary fission
Bacteria reproduction

Mitosis
Asexual reproduction, growth, matinence, repair

Meiosis
Sexual reproduction from gametes like sperm & egg
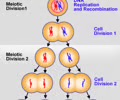
Centrioles
Only in eukaryotic animal cells. Organize chromosomes during cell division
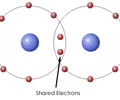
Covalent bonds – sharing a pair of valence electrons
Holds molecules together
Strongest
Holds the most potential energy, difficult to break
Solid line between atoms or two atoms together
Nonpolar covalent
No partially charged end
Nonpolar - Hydrophobic (water fearing)
EX: oils

Polar covalent
One atom in the bond is more electronegative - attracts electrons more than others
Polar - Hydrophilic (water loving)
Leads to hydrogen bonding

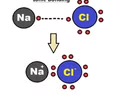
Ionic bonds - attraction between ions
Ions - atoms that have a charge based on the loss or gain of electrons
Not as strong as covalent bonds
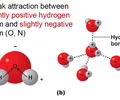
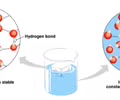
Hydrogen bonds – attraction between polar molecules and their partially charged ends
Reversible - form, break, and re-form
Weaker
These are the bonds that break when H2O boils
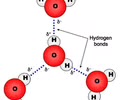
Results from polarity & lead to all properties of H2O
Polar molecule
Unsharing of a pair of valence electrons "sticky"
Cohesion
H-bonds form between 2 or more H2O molecules
Surface tension - caused by H-bonds
Adhesion
H2O forms H-bonds with another substance/surface
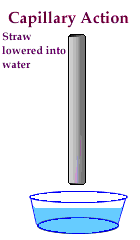
Capillary action
Movement of water up a narrow tube
Universal solvent
Dissolves other polar charged substance

Density of ice
Water is less dense when it is frozen
High specific heat
Resists change in temperature (homeostasis)
Moderate Earth's temperature
Moderate organisms temperature

High heat of vaporization
The amount of heat 1g of water must absorb to change from liquid to gas

Evaporative cooling
As water evaporates, the surface cools

Chemical equilibrium
The point at which reactions offset one another

H2O molecules image
Living systems are approximately __% water and __% biomolecules
71
29
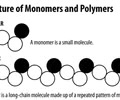
Monomer
One single subunit
EX: monosaccharides, fatty acids, amino acids, nucleotides

Polymer
Many subunits
EX: carbohydrates (polysaccharides), lipids, polypeptides/protein, nucleic acid (DNA/RNA)
Dehydration synthesis
Monomer --> polymer
- Removal of H2O to form a new covalent bond
- Coordinated by enzymes - proteins specifically shaped to catalyze reactions
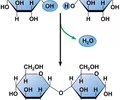
Hydrolysis
Polymer --> monomer
- H2O "added" to break the covalent bond between subunits in polymer
-Coordinated by specific enzymes

Macromolecules
Made of C, H, O, N
4 groups of macromolecules
1. Carbohydrates
2. Lipids
3. Proteins
4. Nucleic acids

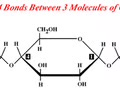
CARBOHYDRATES (polar): Atoms
CH2O
- Ratio 1:2:1
EX: Glucose (C6H12O6), Fructose (C5H10O5)
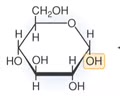
CARBOHYDRATES (polar): Monomer
Monosaccharide
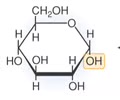
CARBOHYDRATES (polar): Polymer
Disaccharide
Polysaccharide

CARBOHYDRATES (polar): Functions
1. Energy supply - sugar used in cellular respiration to make ATP
2. Energy storage - short-term & accessible
3. Structure - cell wall in plants & fungi
CARBOHYDRATES (polar): Common structure image

CARBOHYDRATES (polar): Monosaccharide?
A simple sugar, such as glucose, which has the formula C6H12O6 and is used to make ATP.
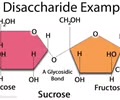
CARBOHYDRATES (polar): Disaccharide?
A carbohydrate formed from two monosaccharides, such as sucrose (table sugar) and maltose (two glucose monomers).
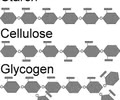
CARBOHYDRATES (polar): Polysaccharides?
Carbohydrates that consist of long chains of monosaccharides, such as starch and glycogen.
CARBOHYDRATES (polar): Starch?
A polysaccharide found in plants, consisting of a linear chain of glucose with a single point for hydrolysis.
CARBOHYDRATES (polar): Glycogen?
A polysaccharide found in animals, consisting of a branched chain of glucose with many points for hydrolysis, which increases the release of glucose.

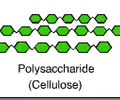
CARBOHYDRATES (polar): Cellulose?
A polysaccharide found in the cell wall of plants
Linear chain of glucose
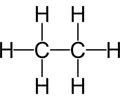
LIPIDS (nonpolar): Atoms
C H O
High amount of C-H
LIPIDS (nonpolar): Monomer
Fatty acids
LIPIDS (nonpolar): Polymer
Not true polymer - growth is finite

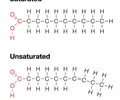
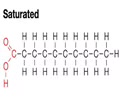
LIPIDS (nonpolar): Saturated fatty acid (animal)
- Each carbon is full of hydrogen
- Linear shape = allows fatty acids to pack tightly together
- Solid at room temp - high melting point
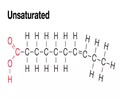
LIPIDS (nonpolar): Unsaturated fatty acid (plants)
- Have one or more C=C (double-bonded C)
- Double bond adds a bend to fatty acid - decreases tight packing (space between molecules)
- Liquid at room temp - low melting point
LIPIDS (nonpolar): Functions
1. Energy storage
2. Protection = warmth, waterproofing
3. Structure - cell membrane
4. Communication
LIPIDS (nonpolar): Triglyceride
Glycerol + 3 fatty acids (energy storage in C-H
LIPIDS (nonpolar): Phospholipid
- Cell membrane
- Fatty acid tails
- Combine saturated and unsaturated
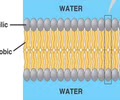
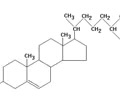
LIPIDS (nonpolar): Steroid
- Fatty acid folded into 4 rings
- Cholesterol
- Hormones (estrogen, testosterone, progesterone
PROTEINS: Atoms
C, H, O, N
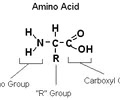
PROTEINS: Monomer
Amino acid
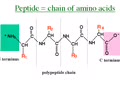
PROTEINS: Polymer
Polypeptide
PROTEINS: Functions
1. Enzymes - a catalyst in a chemical reaction
2. Structure
3. Carrier/transport
4. Cell communication - signals/receptors
5. Defense
6. Movement
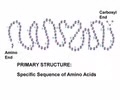
PROTEINS: Primary structure
- Found in ribosomes
- Linear polypeptide - chain of amino acids coded in DNA
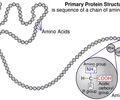
PROTEINS: Bonds in primary structure
- Covalent bonds - dehydration synthesis
- Peptide bonds between amino acid backbone (strongest)
PROTEINS: Secondary structure
Repeatedly coiled and folded polypeptide chains
- Found in RER
- Within a small section of polypeptide
- Local folding
- Beta pleated sheet or Alpha helix
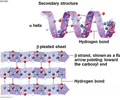
PROTEINS: Bonds in secondary structure
H-bonds between N-C-C backbones
PROTEINS: Tertiary structure
Overall structure of a polypeptide resulting from the interaction between side chains and amino acids
- Whole polypeptide folding
- Distant amino acids interact
- 3-D form
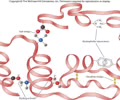
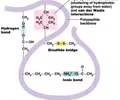
PROTEINS: Bond in tertiary structure
Bonds dependent on R group
- Covalent bond on disulfide bridge (S-S) (strong)
- Ionic bond - attraction between acidic (-) and basic (+) amino acids (weak)
- Hydrogen bonds ( OH---H)
PROTEINS: Quaternary structure
Overall structure that results from the aggregation of these polypeptide units
- Multiple polypeptides bind together
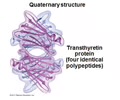
PROTEINS: Bonds in quaternary structure
Bonds vary

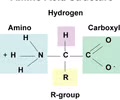
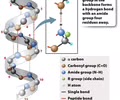
PROTEINS: Amino acid groups
Connected to the N-C-C backbone
1. Amino group
2. Carboxyl group
3. R group