Exam 1: Cell Walls
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
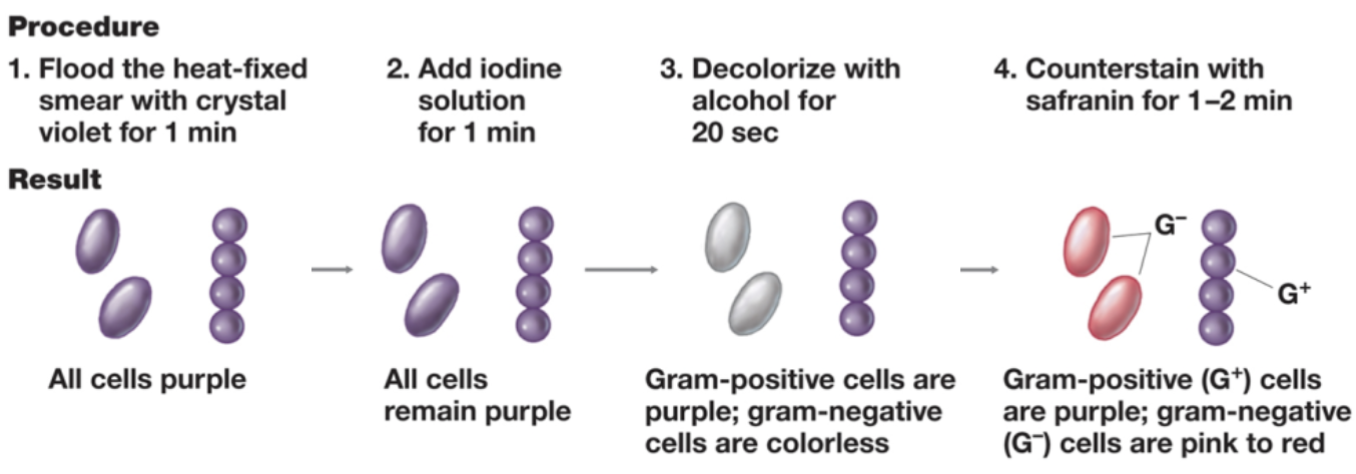
Christian Gram
Had a mixed culture.
Wanted to put them into groups → he developed a gram strain.
Differential strain.
Steps:
Heat-fix a smear of bacteria and expose to crystal violet for one minute.
Add iodine solution for one minute.
Iodine is a mordant.
Makes the solution sticky.
Decolorize with alcohol for 20-30 seconds.
Gram-positive cells keep the purple color.
Gram-negative cells lose the purple color.
Outer surface is membrane.
More susceptible to alcohol.
Counterstain with safranin for 1-2 minutes.
Attaches a red-pink color to gram-negative cells.
Also attached to gram-positive, but is out-competed by the purple.
Occurs because of the different membranes.
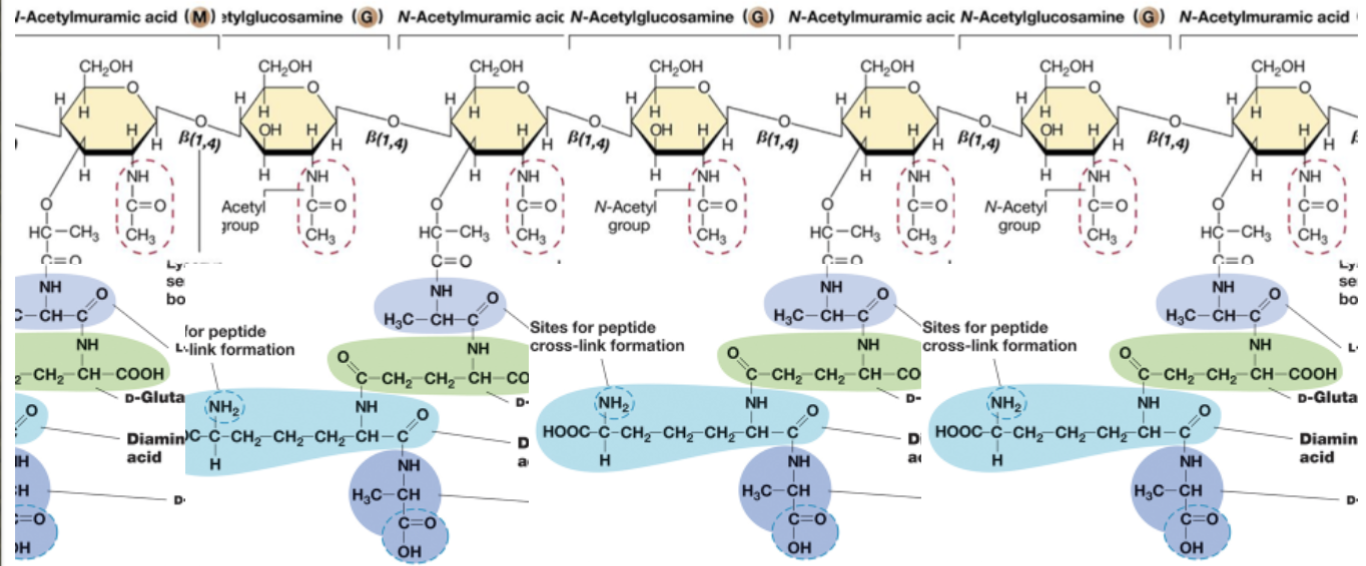
Peptidoglycan
Peptid → peptide.
Glycan → sugar.
Mesh-like polymer composed of identical subunits.
N-acetylglucosamine (NAG or G).
N-acetylmuramic acid (NAM or M).
NAM has peptides/amino acids attached.
Order goes NAM → NAG → NAM → NAG…
Linked by glycosidic bonds.
Several different amino acids.
Chains of linked peptidoglycan subunits are cross-linked by peptides.
Builds front to back, and then it layers.
By peptide bonds.
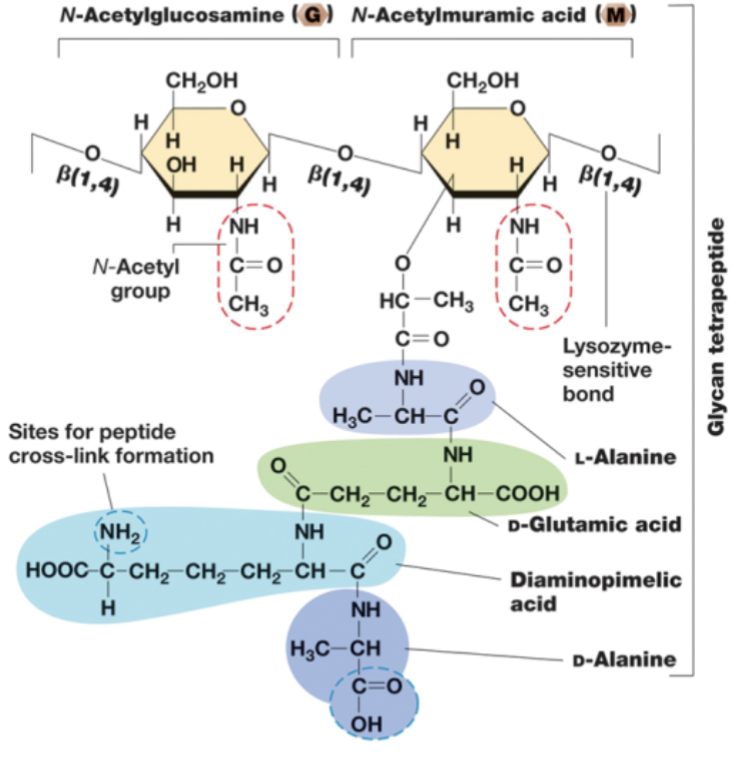
Peptidoglycan monomer
D-amino acids.
Peptidases recognize L-amino acids.
With peptidoglycan having D, it is resistant to peptidases.
D-glutamic acid.
D-alanine.
D is only found in peptidoglycan.
Meso-Diaminopimelic acid (DAP).
Found in gram-negative bacteria only.
L-Lysine.
Found in gram-positive peptidoglycan.
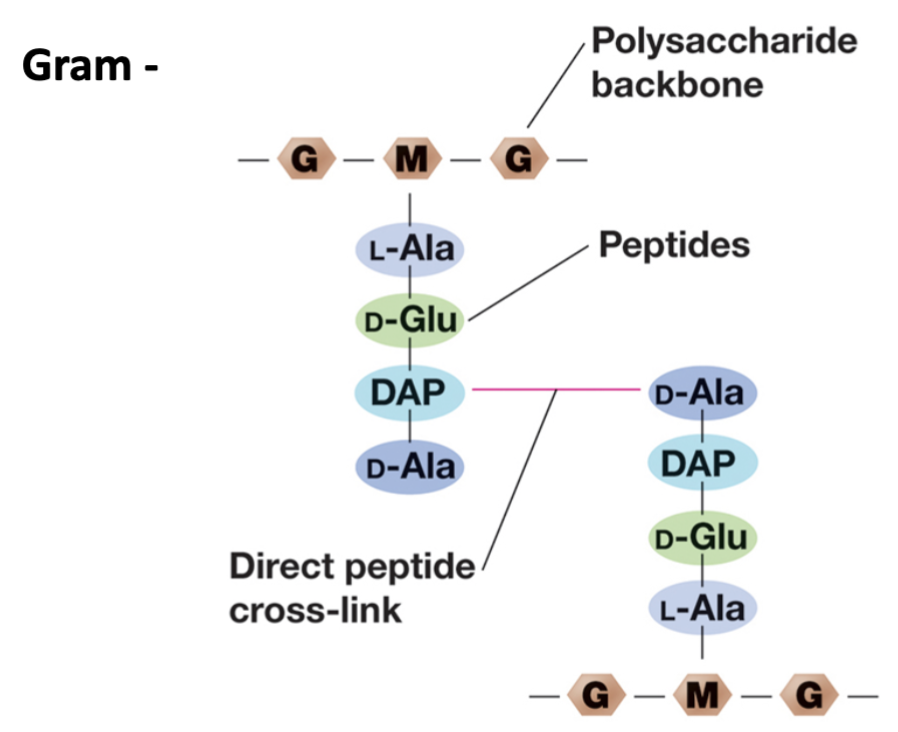
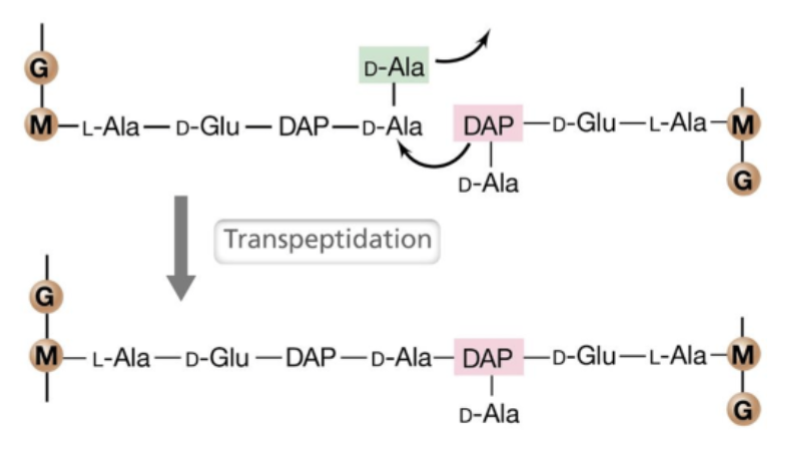
Gram negative peptidoglycan structure
D-alanine in one strand connects with DAP to link the peptides.
Covalently linked.
D-amino acids are unique.
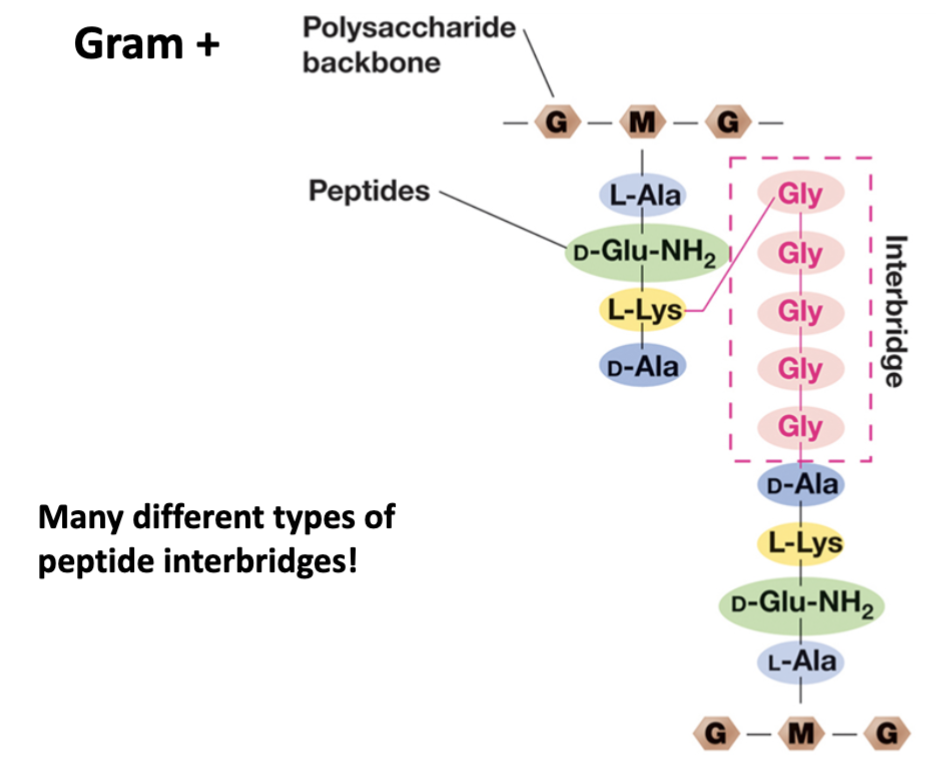
Gram positive peptidoglycan structure
Uses interbridge to attach peptides.
Five amino acids.
Uses the same five.
Links to L-Lysine.
Synthesis
Peptidoglycan precursor made in cytosol.
M-G pentapeptide.
Brought to membrane, interacts with bactoprenol.
Bactoprenol is stuck in the membrane because it has over 50+ carbons.
Bactoprenol flips it across the membrane → flippase.
From inside to outside.
Autolysins break existing bonds to allow for the peptides to enter.
Transglycosylase glues in backbone.
Transpeptidation
Chemical reaction that forms the peptide cross-links.
Penicillin binding protein (transpeptidase) connects peptides.
Antimicrobial target
Penicillin.
Binds to penicillin binding protein and inhibits it.
Cannot perform transpeptidation.
Make cell wall weak.
Works best with gram-positive interactions.
Vancomycin.
Treats resistance infections.
Last line of defense.
Bacitracin.
Triple antibiotic ointment.
Cycloserine.
Treats tuberculosis.
Fosfomycin.
Treats urinary tract infections.
Autolysins
Secreted by the cell in a small amount.
In order to grow, the bacterium needs to digest own peptidoglycan.
Autolysins digest peptidoglycan.
New material can then be added.
Gram positive bacteria review
Cell wall is on superficial surface.
On the outside.
Thick peptidoglycan.
Many layers.
Teichoic/lipoteichoic acids.
Lipoteichoic acid goes to membrane, teichoic does not.
Both extend off the surface.
Sortase: attaches secreted proteins covalently to the cell wall.
Attaches the teichoic acid to the cell wall.
Only in gram positive bacteria.
Gram negative bacteria review
Two membranes.
Outer.
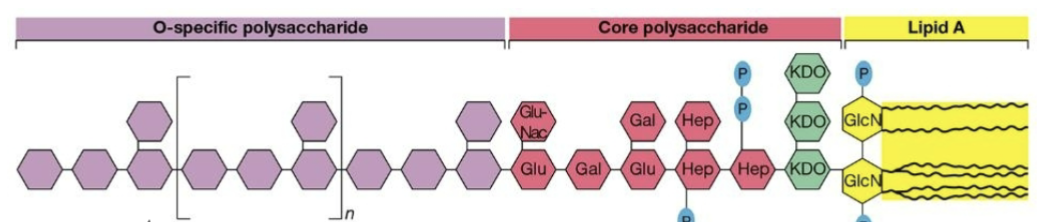
Has LPS.
The core polysaccharide is going to be the same in all strains of the species.
Lipid A is an attachment point.
Called an endotoxin because it is attached.
O-specific polysaccharide is variable.
Main focus.
Has porins.
Inner.
Cell wall is in the space between two layers.
Called the periplasm.
Has less layers of peptidoglycan.
Impact of cell wall and outer membrane
Support cell shape.
Protect from toxic substances.
The membranes for gram negative and positive will work differently.
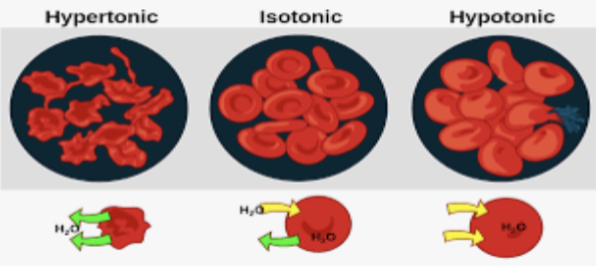
Osmotic protection:
Isotonic solution → happy cells.
Hypotonic solution → lysis; water moves in, more salt inside.
Hypertonic solution → plasmolysis; water leaves, more salt outside.
Contribute to pathogenicity.
LPS = endotoxin.
Considered a mitogen.
Non-specifically turns on immune cells.
Peptidoglycan.
Activates complement.
Immune system recognition.
Pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs).
Only found on microbes.
Recognized by pattern recognition receptors (PRRs).
Results in a number of defense responses.
Target for antimicrobials.
Sec secretion
One-step secretion process.
Something is secreted through one membrane.
Goes through the periplasm, then through the membrane.
Two-step secretion
Mainly with gram-negative bacteria.
Outer membrane and periplasm.
Most secreted proteins moves through the general secretory pathway (type 2).
Type 2: sec = secretes linear proteins (unfolded).
Type 5: tat = secretes folded proteins.
Autotransporter.
Some of the protein is used to create the opening for secretion.
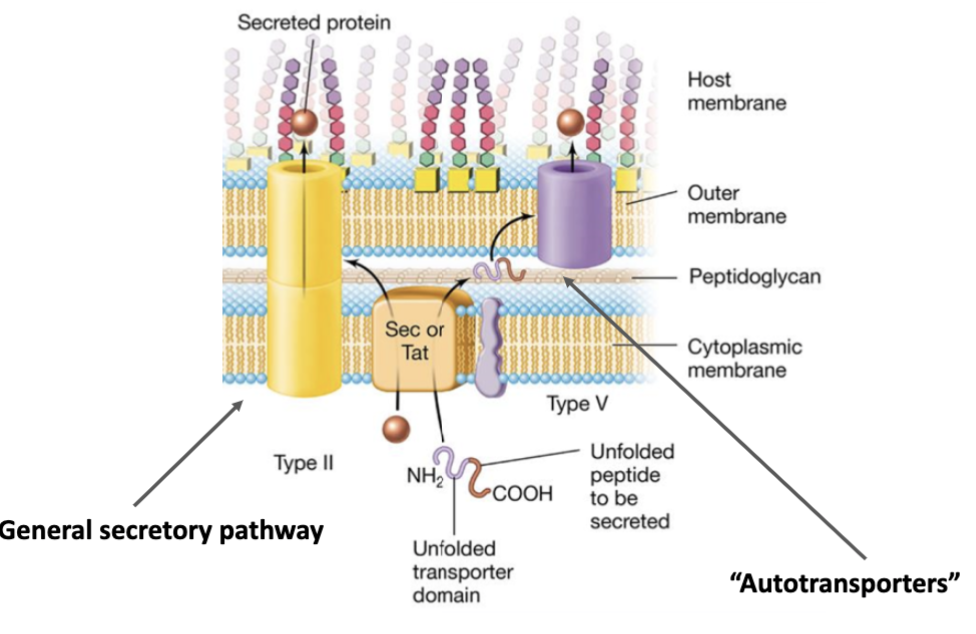
One-step secretion (across outer membrane)
Type 1:
Spans both membranes.
One-step system.
Type 3, 4, and 6:
Has needle-like structures.
Spans both membranes and host membrane.
Three membranes.
Type 3 is protein.
Type 4 is microbial DNA.
Type 6 has two forms:
Retracted vs. contracted.
Shoots the secretion through.
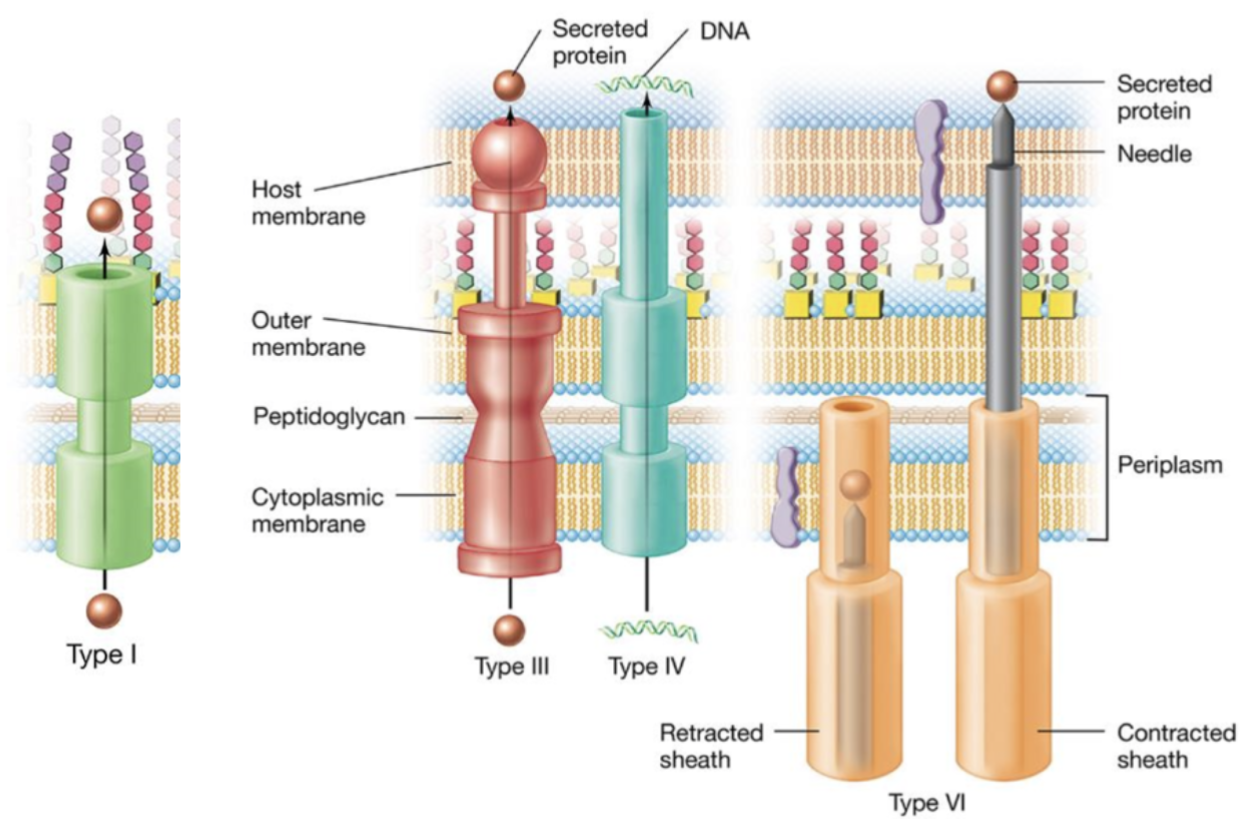
Archaeal cell walls
No peptidoglycan.
Different cell wall structures.
Pseudomurein.
Fake peptidoglycan.
Complex polysaccharides.
Protein, glycoprotein (S-layers).
Most have S-layers.
Psuedomurein vs. peptidoglycan:
NAG in peptidoglycan vs. N-acetyltalosaminuronic acid in psuedomurein.
Different linkages.
L-amino acids.
No D-amino acids in psuedomurein.
Fungal cell walls
Simpler.
Polysaccharides.
Chitin.
Cellulose.
Glucan.