Principles of Modern Mathematics Final Exam (copy)
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Golden Ratio
A rectangle is golden or has the golden ratio or is called the golden rectangle if the length/width= 1+√5/2 ≈ 1.62
Irrational
They appear in architecture (greek temples), art (rectangles in paintings), product design (cereal boxes) and nature (shells).
Fibonacci Sequence
The infinite list of numbers {1,1,2,3,5,8,13…}
Rational, recursive sequence (to get to the next # you add the two previous numbers)
Found in nature (any flower with a distinct seed pattern)
Relationship Between Golden Ratio & Fib. Sequence
If you take #’s from the Fib. sequence and divide them by each other, you will get an answer closer to the golden ratio (1.62)
Regular n-gon
N-sided polygon with congruent sides and interior angles.
Two things must be true:
All polygons must have the same edge length.
The interior angles around any vertex must have measures that sum to 360.
Interior Angle Formula
(n-2) 180/n
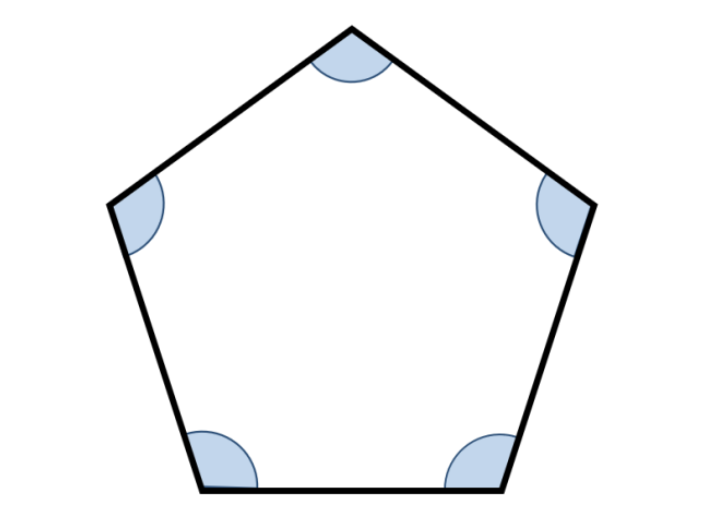
EX: Pentagon has 5 angles.
Interior angles around any vertex must sum to 360.
Using the formula: (5-2)180/n= 540/5
Interior Angle Measure= 108 degrees
Tessellations
A tiling of the plane with one or more repeated shapes that align edges to edges and vertices to vertices.
Start with a tessellation of the plane using r-polygons.
Modify the polygon by shrinking. or expanding side length.
Transform sides doing opposite moves.
What did Escher do?
M. C. Escher
He is one of the world’s most famous graphic artists.
Escher travels every year through Italy where he makes drawings and sketches that he later uses in his studio for his lithographs
He is most famous for his impossible drawings, such as Ascending and Descending and Relativity
In addition to his work as a graphic artist, he illustrates books, designs carpets, banknotes, stamps, murals, and intarsia panels
Symmetry
A movement of a shape that takes a shape to itself in such a way it is impossible to tell that the shape has moved.
Shapes with designs cannot be mirrored.
An r-gon with no design will have 2xN symmetries
Strip Pattern
An infinite length band with one or more designs repeated on it, and align on both the front and back.
These appear in sides of buildings, necklace chains, china, and wallpaper borders.
Fundamental region of a strip pattern
The minimal rectangular stamp needed to reproduce the strip pattern that has the full heigh of the strip by width.
Symmetry Code
P= permutation/translation
M= reflections across vert line, 1=no
M=reflections across hor line, A= glide reflection (reflection across horizontal line, translation=1/2 width of a fundamental region) ,1=no
2=180 rotation, 1=no rotations
Slope
A numerical measure of how fast a line is rising or falling as you move along it from left to right.
M= undefined if x(vertical) or y(horizontal)=0
M>0= rising M<0= falling
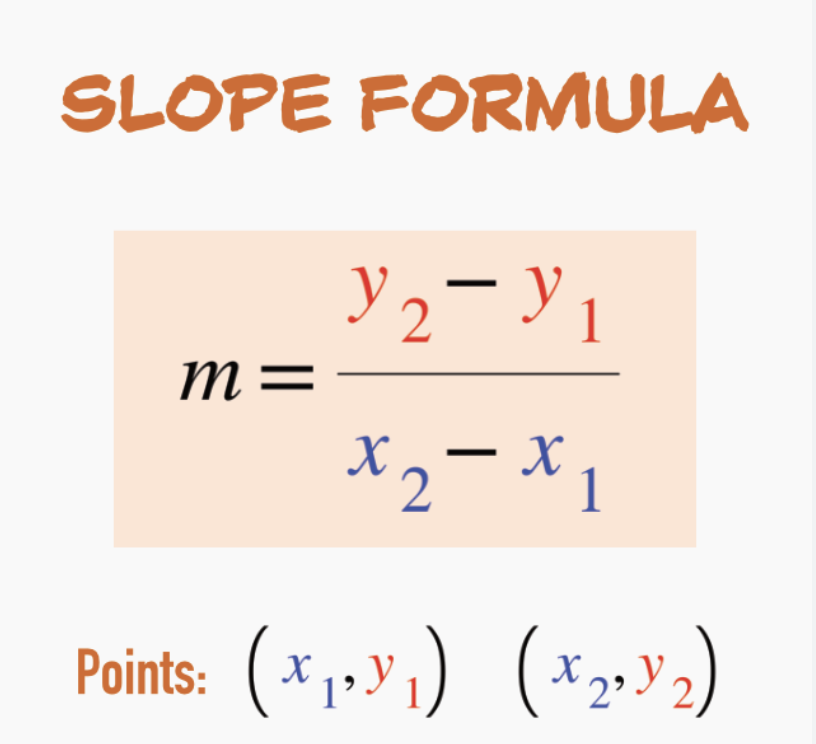
Point Slope
A line equation in which x1 and y1 are a point on a line, x and y are variables and m is the slope.
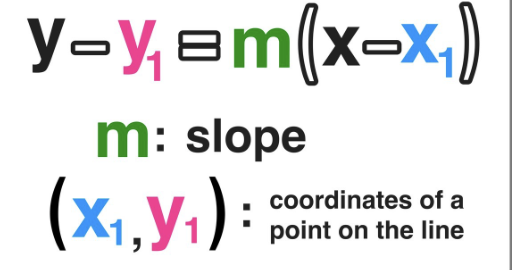
Slope Intercept
A line equation in which m is the slope and b is the point where the line intersects the y-axis.
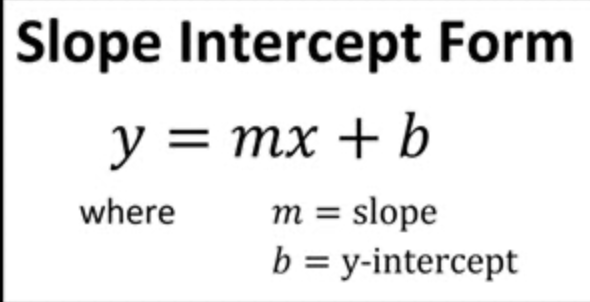
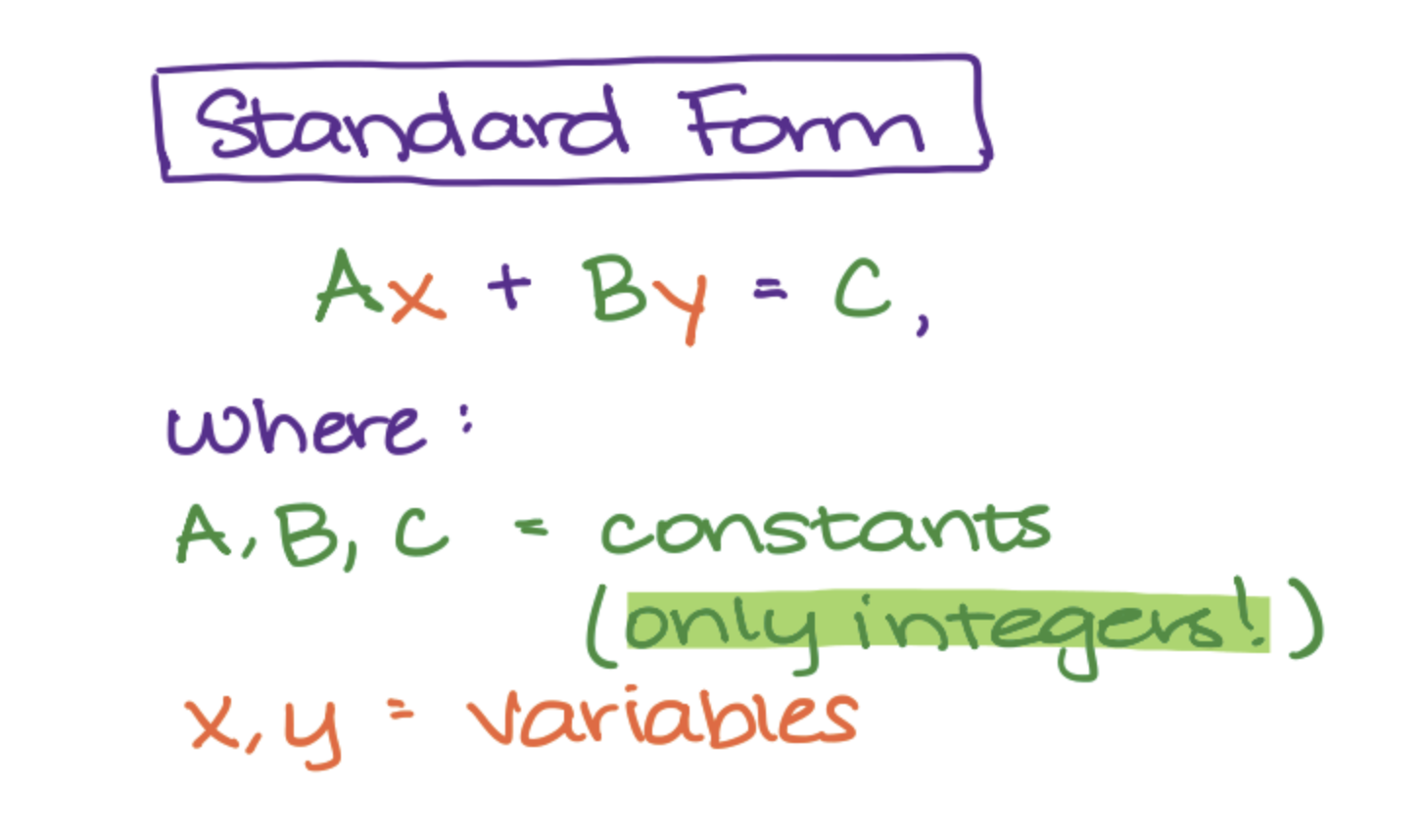
Standard Formula
A line equation in which a,b,c are constants and x and y are variables.