Lec 6: Vestibulocochlear Nerve Cochlear Division/Nerve
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
the vestibular nerve and cochlear nerve are
2 Nerves in 1
what is vestibular nerve
Monitors head position and movement\
– Sensory Signals from Semicircular Canals and Vestibule
– Monitors head position and movement
what is Cochlear Nerve
Responds to sound stimulation
– From Cochlea
what is vestibular nerve receptors?
Hair cells in:
Semicircular Canals
Anterior
Posterior
Lateral
Vestibule
Utricle
Saccule
what is the receptors of cochlear nerve?
Hair cells of the Spiral Organ (Organ of Corti) – in the Cochlea
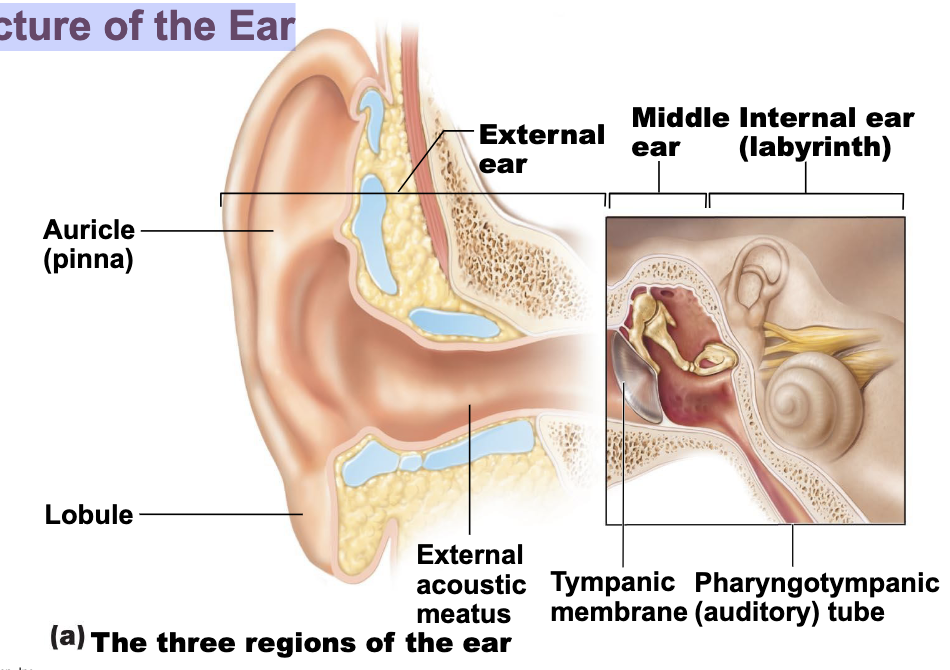
Structure of the Ear
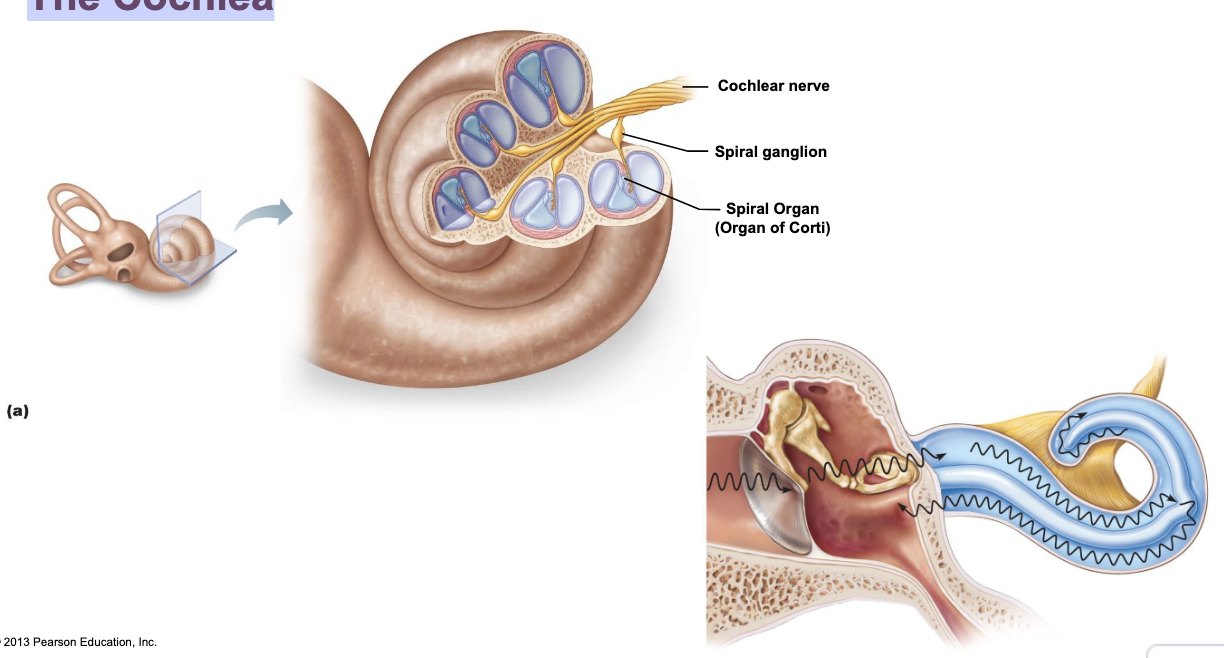
The Cochlea
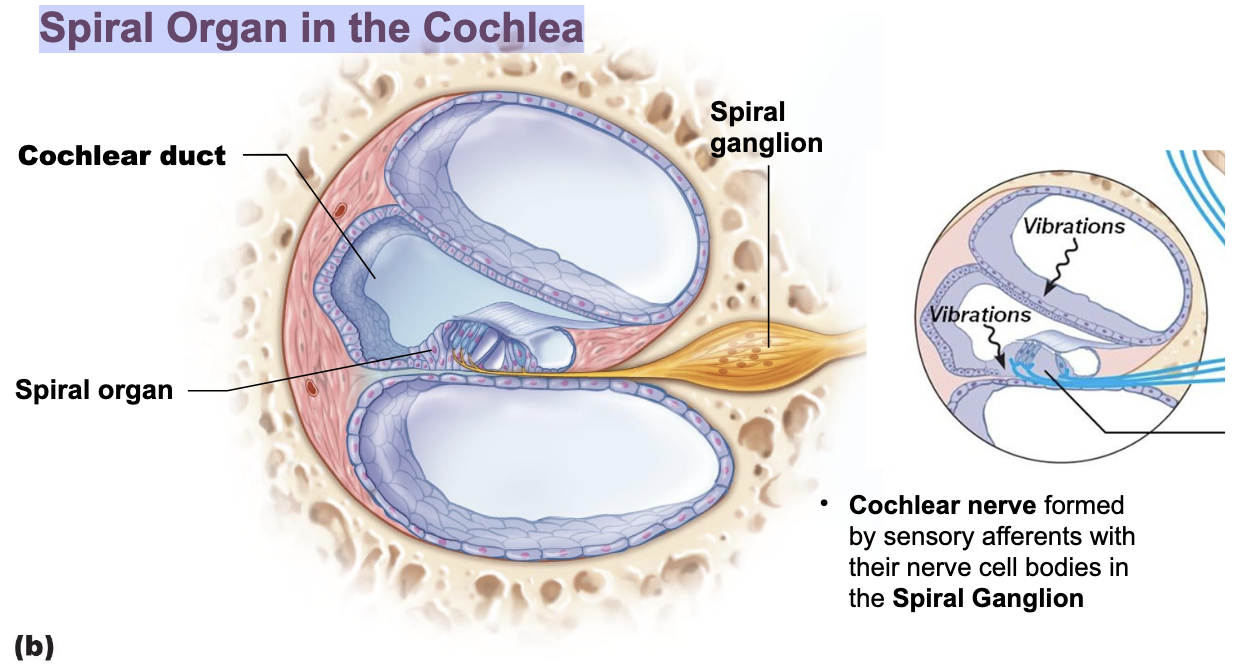
Cochlear nerve formed by sensory afferents with their nerve cell bodies in the Spiral Ganglion
Spiral Organ in the Cochlea
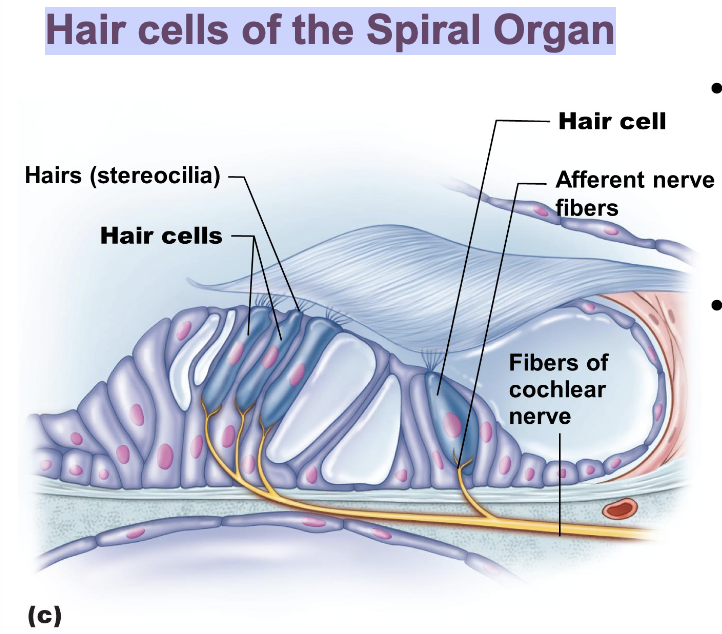
Hairs (stereocilia) bend and activate Hair Cell receptors
Sensory signals produced in the cochlear nerve
Hair cells of the Spiral Organ
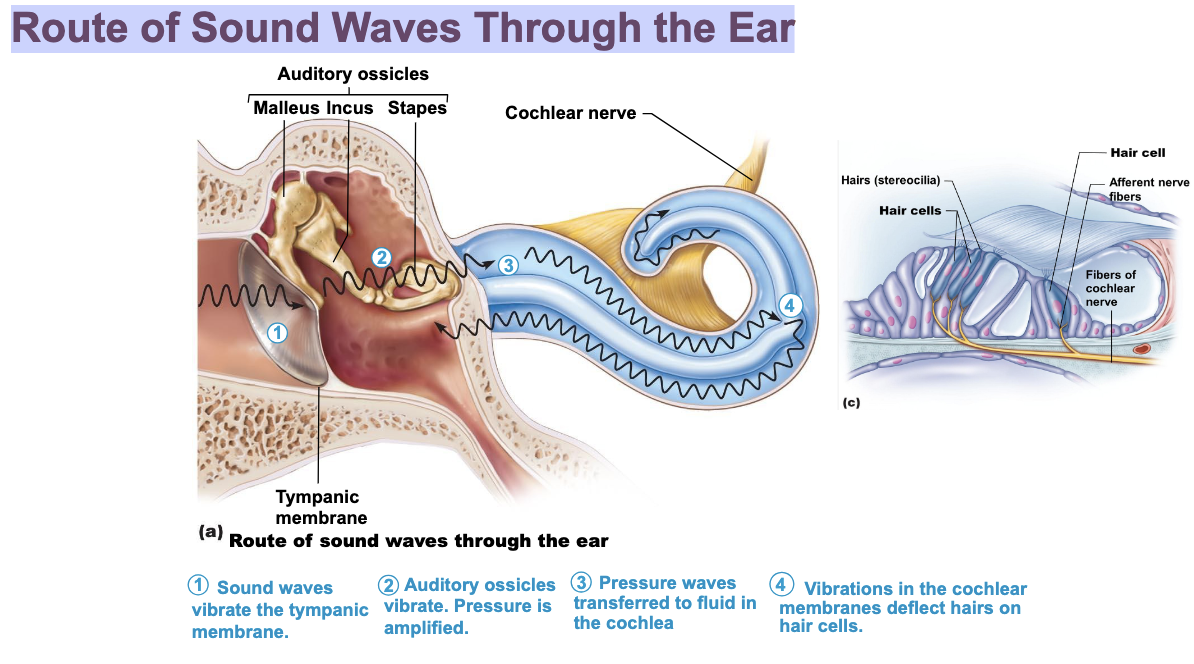
Route of Sound Waves Through the Ear
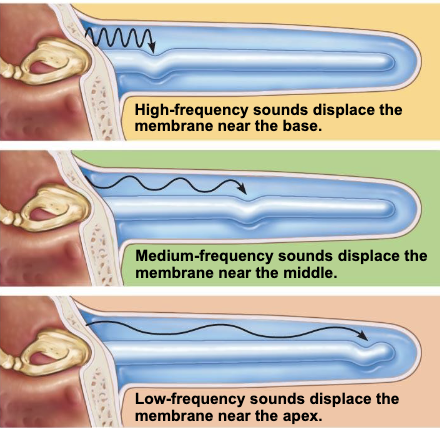
High Pitch Vs Low Pitch
__ (low frequency) sound waves are detected near the base/beginning of the cochlea
– __ detection declines with age
high pitch
(low frequency) sound waves are detected towards the end/apex of the cochlea
low pitch
Impulses from cochlea pass via __
spiral ganglion to cochlear nuclei of medulla
From spiral ganglion to cochlear nuclei of medulla, impulses sent
To superior olivary nucleus
Sound Localization
– Via lateral lemniscus to Inferior colliculus
Auditory Reflex Center
From there, impulses pass to __ of thalamus, then to primary auditory cortex
Auditory pathways decussate so that both cortices receive input from both ears
medial geniculate nucleus
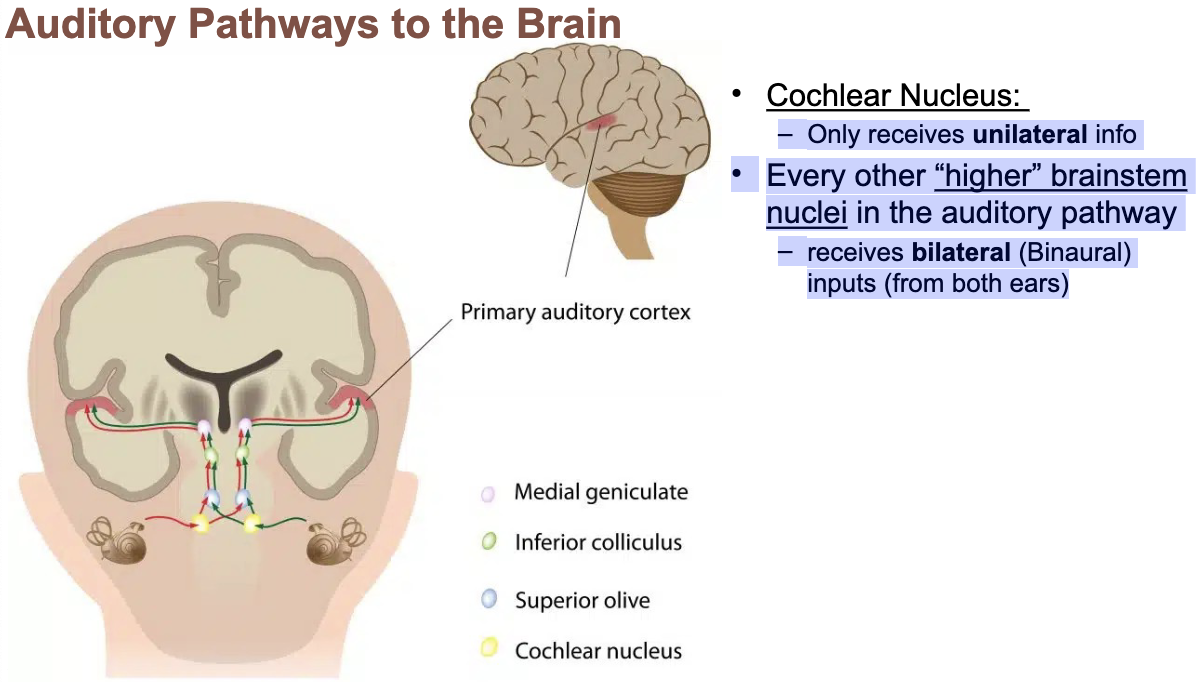
the most central site in which a lesion can produce deafness in the ipsilateral ear
receives a projection from only the ipsilateral ear
Only receives unilateral info
Every other “higher” brainstem nuclei in the auditory pathway
receives bilateral (Binaural) inputs (from both ears)
cochlear nucleus
lesions of the other higher auditory nuclei do not produce deafness
produce partial hearing loss that is more prominent contralaterally, because more second-order axons decussate
supplies the cochlear nuclei
• unilateral occlusion can produce deafness in one ear.
Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
what is Superior Olivary Nucleus?
integrates sound from both ears to precisely localize sound in three-dimensional space
When a sound comes from one side:
The ear closest to the sound receives a slightly louder stimulus than the ear further away
there is a delay in activating auditory neurons such that the cochlear nucleus nearer the source is activated first
Loss of hearing impairs the ability to localize sound in space
what is Inferior Colliculus?
• Sound location data becomes fully integrated by the inferior colliculus
• Produces the Startle Response
• Turns Head to Threatening/Interesting Sounds
• Also controls the Vestibuloocular Reflex (VOR
sends information to other brain areas to interpret sounds and to respond to them
Primary Auditory Cortex
Upon hearing a loud noise:
temporal lobe
parietal lobe
frontal lobe
what is temporal lobe?
identifies the sound
• Sorts through all your sound memories
what is parietal lobe
figures out how is was produced and where is came from
what is frontal lobe
produces a motor response
Upon hearing Spoken Language:
• Signals sent from Auditory cortex to Wernicke’s Area
• From Wernicke’s Area to Broca’s Area
• Broca’s Area to Primary Motor Cortex
• Spoken response produced