Chapter 2: Molecular Representation
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
63 Terms
How many ways are there to represent molecules?
Many (Lewis structures, condensed structure, partially condensed structure, and molecular formula)
Which structure gives the most information?
Lewis structure
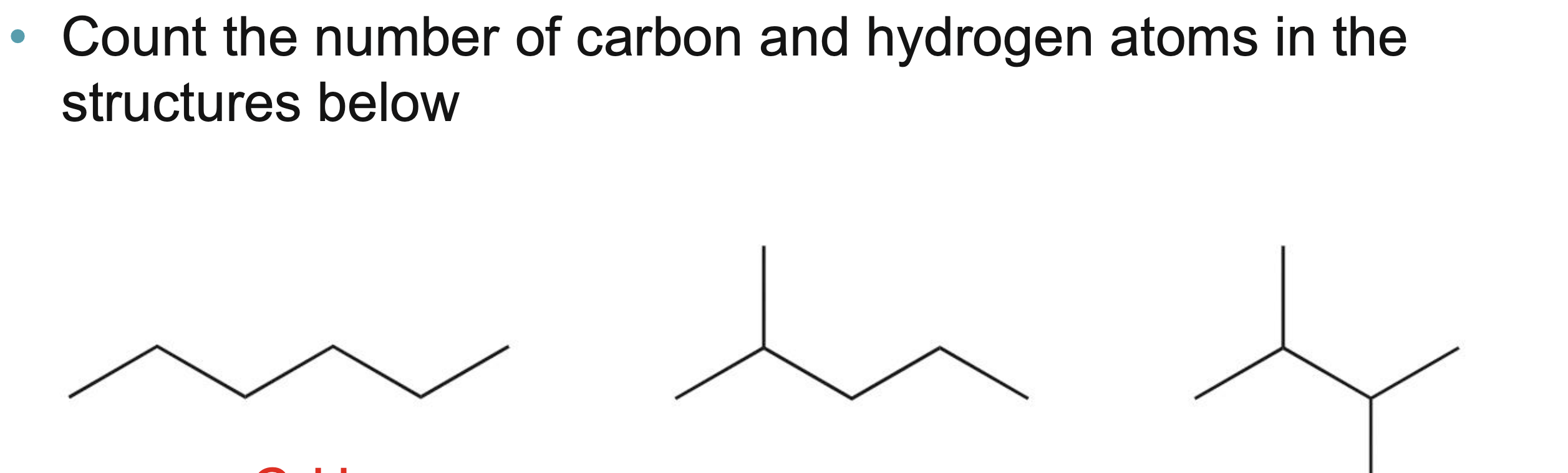
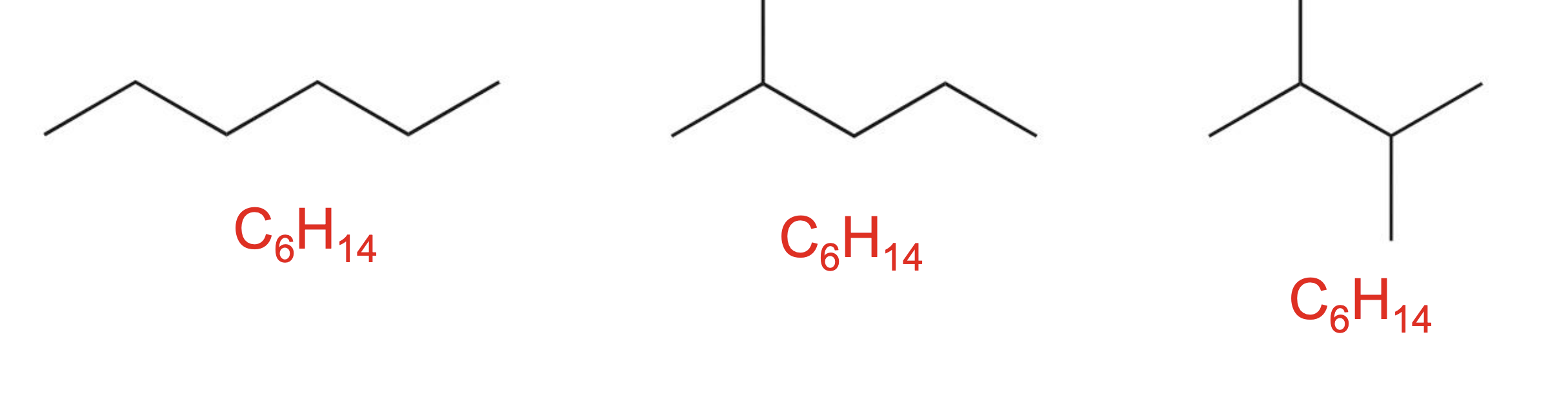
Count the number of carbon and hydrogen atoms in the structures below
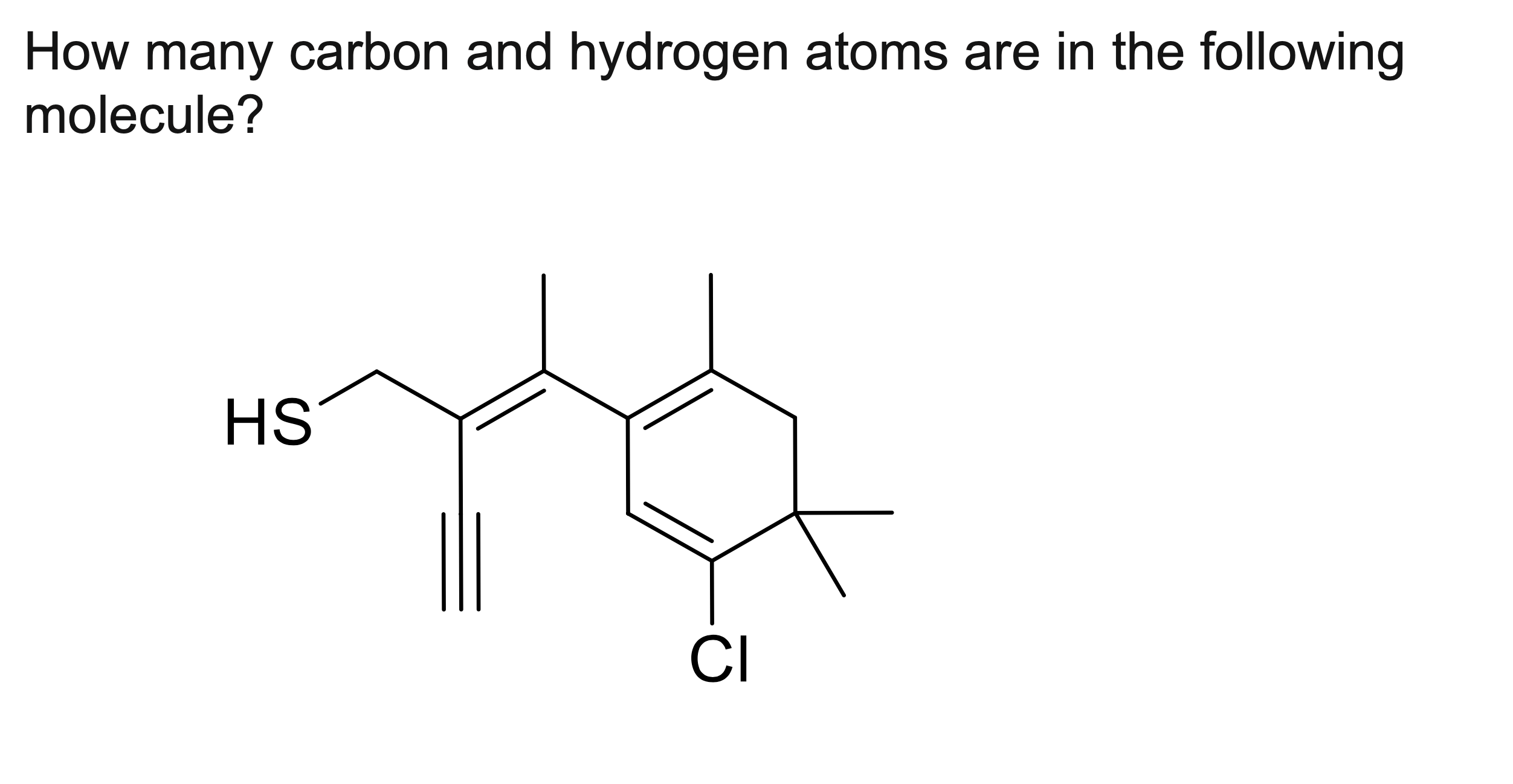
How many carbon and hydrogen atoms are in the following
molecule?
C₁₅H₂₃
Can single bonds rotate?
Yes so be aware of that
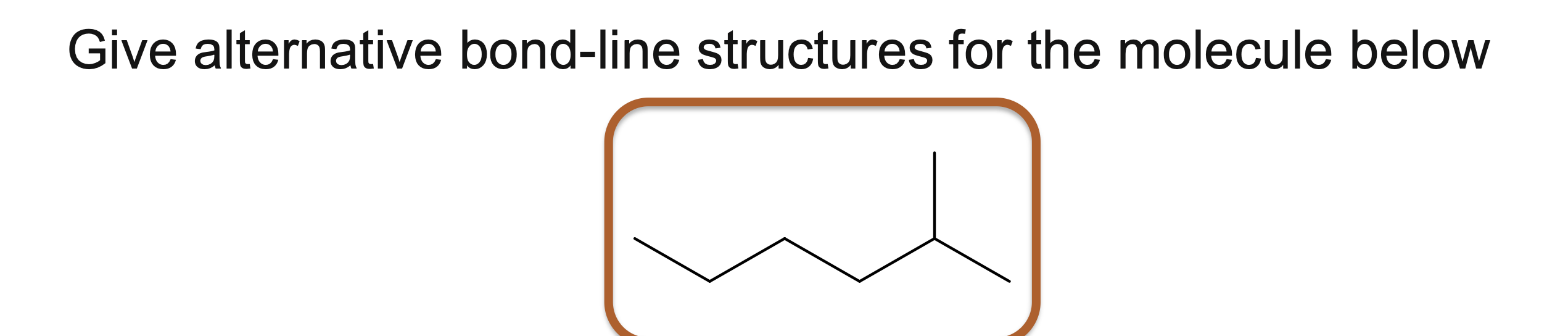
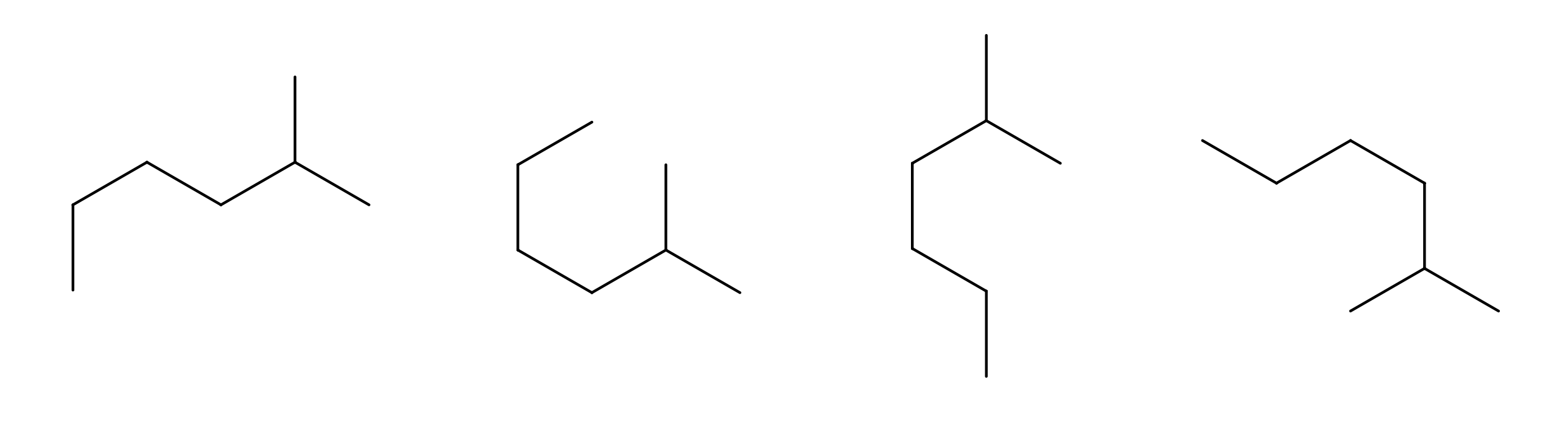
Give alternative bond-line structures for the molecule below
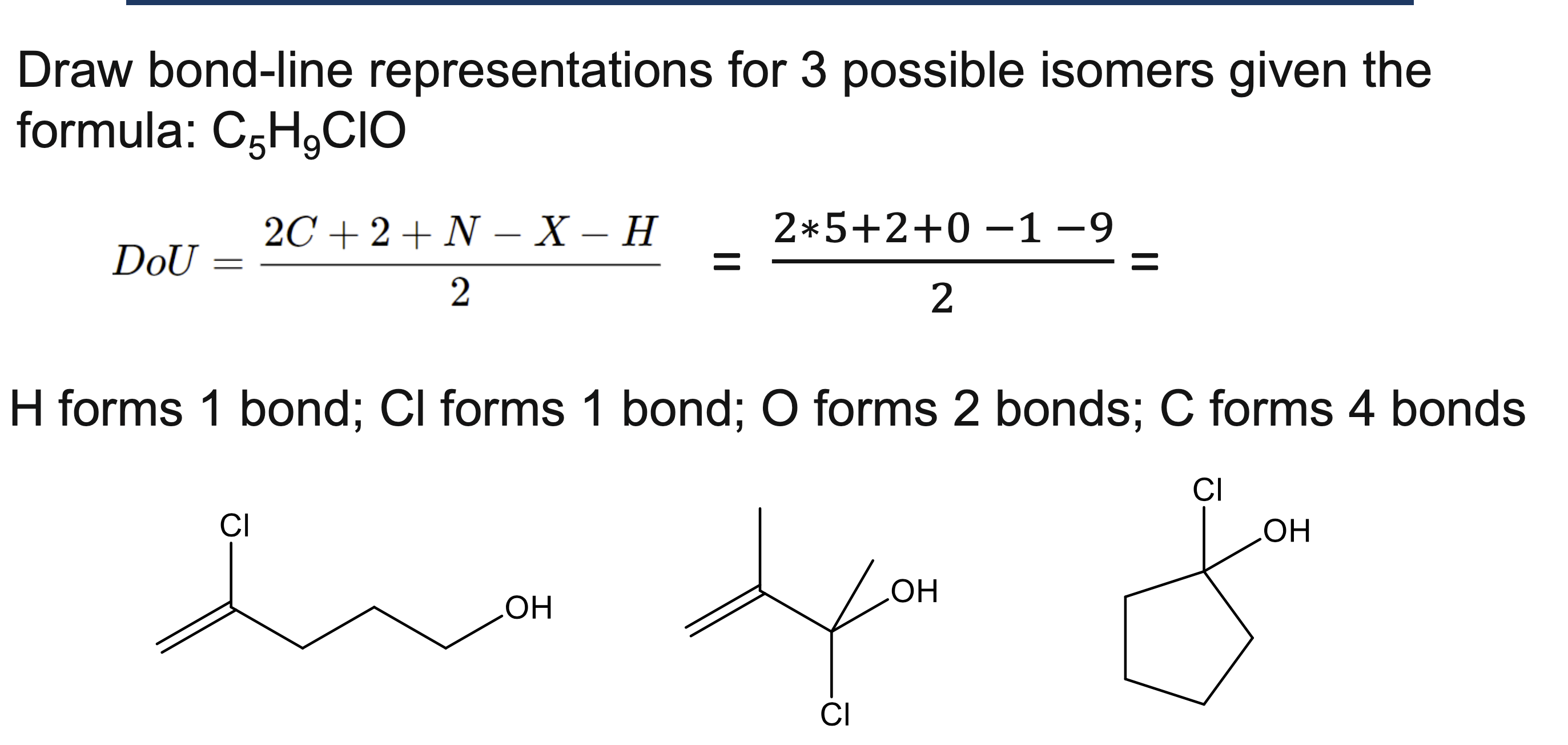
Draw bond-line representations for 3 possible isomers given the
formula: C5H9ClO
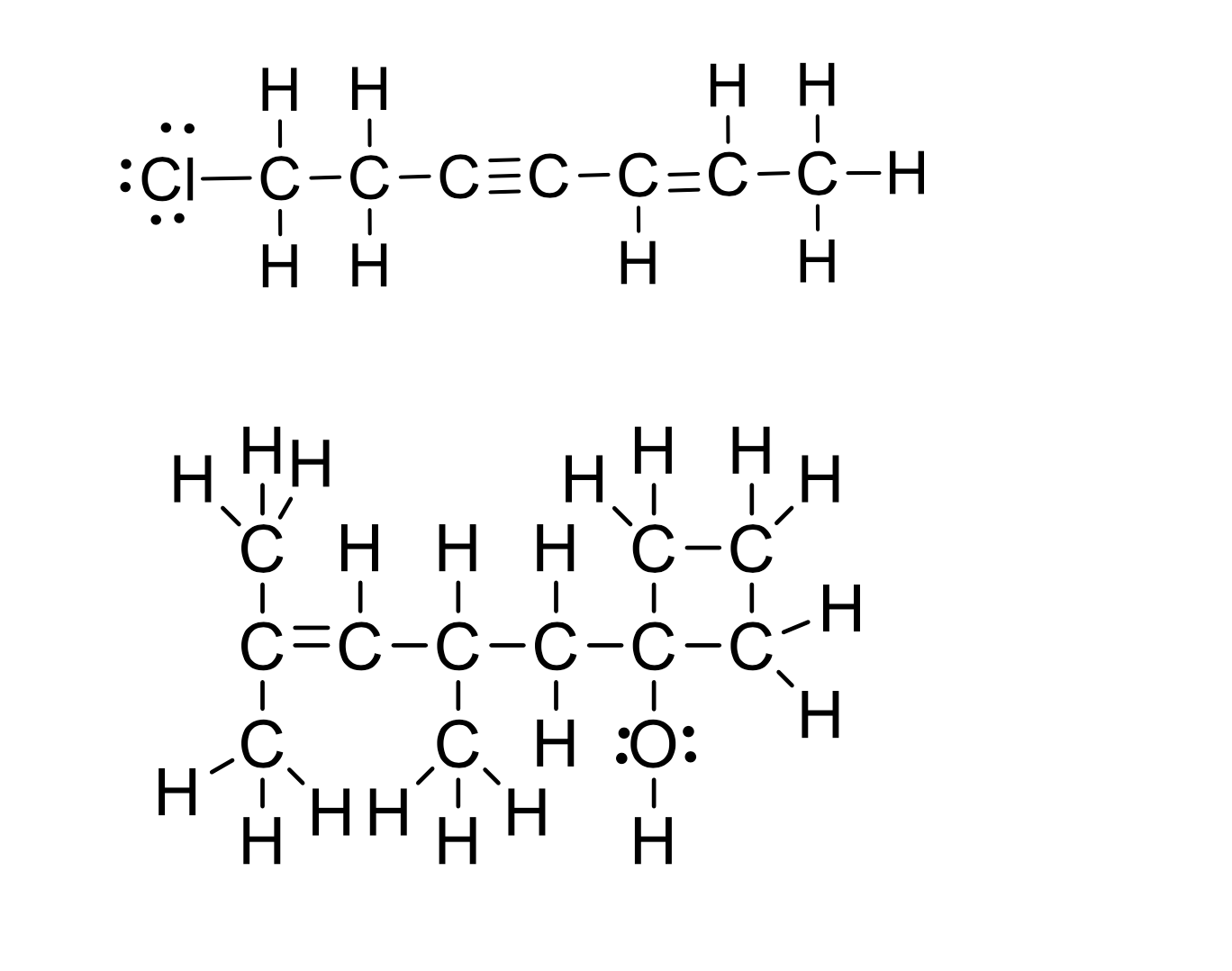
Draw bond-line representations for the following Lewis structures
What are functional groups?
When certain atoms are bonded together in specific arrangements, they undergo specific chemical reactions

Identify the functional group
alkyl halide

Identify the functional group
alkene

Identify the functional group
alkyne
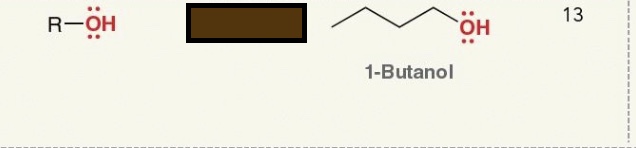
Identify the functional group
alcohol

Identify the functional group
ketone

Identify the functional group
aldehyde
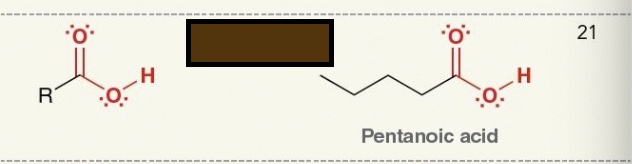
Identify thr fiunctional group
carboxylic acid
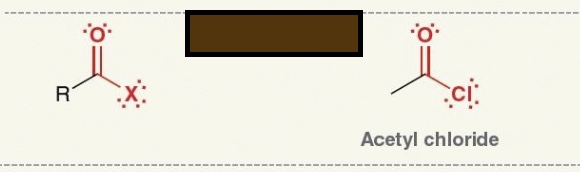
Identify the functional group
acyl halide

Identify the functional group
ether

Identify the functional group
thiol
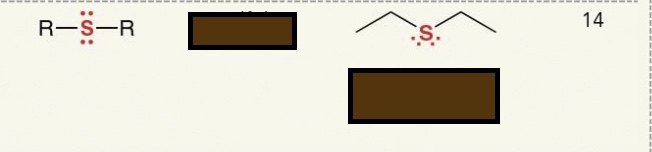
Identify the functional group
sulfide
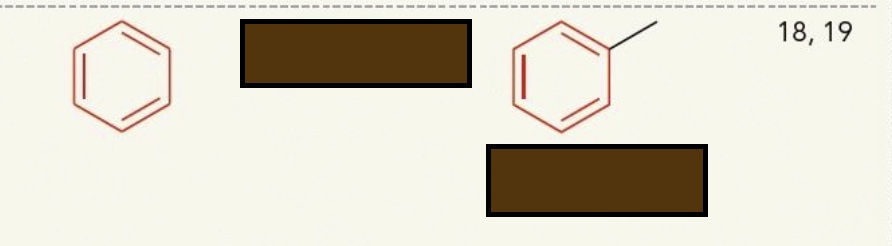
Identify the functional group
aromatic

Identify the functional group
anhydride
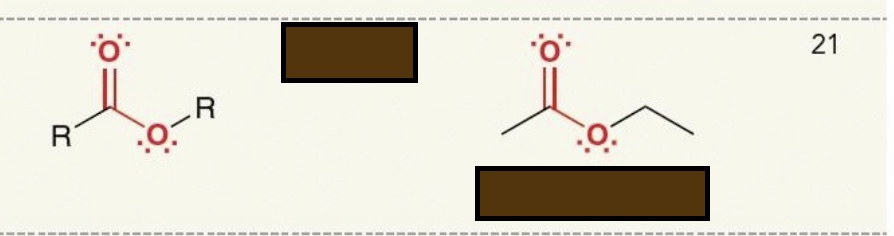
Identify the functional group
ester
Identify the functional group
amide

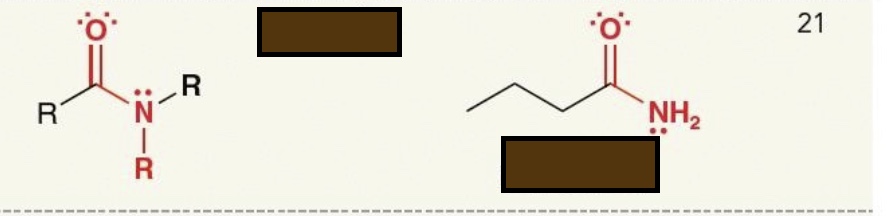
Identify the functional group
amine
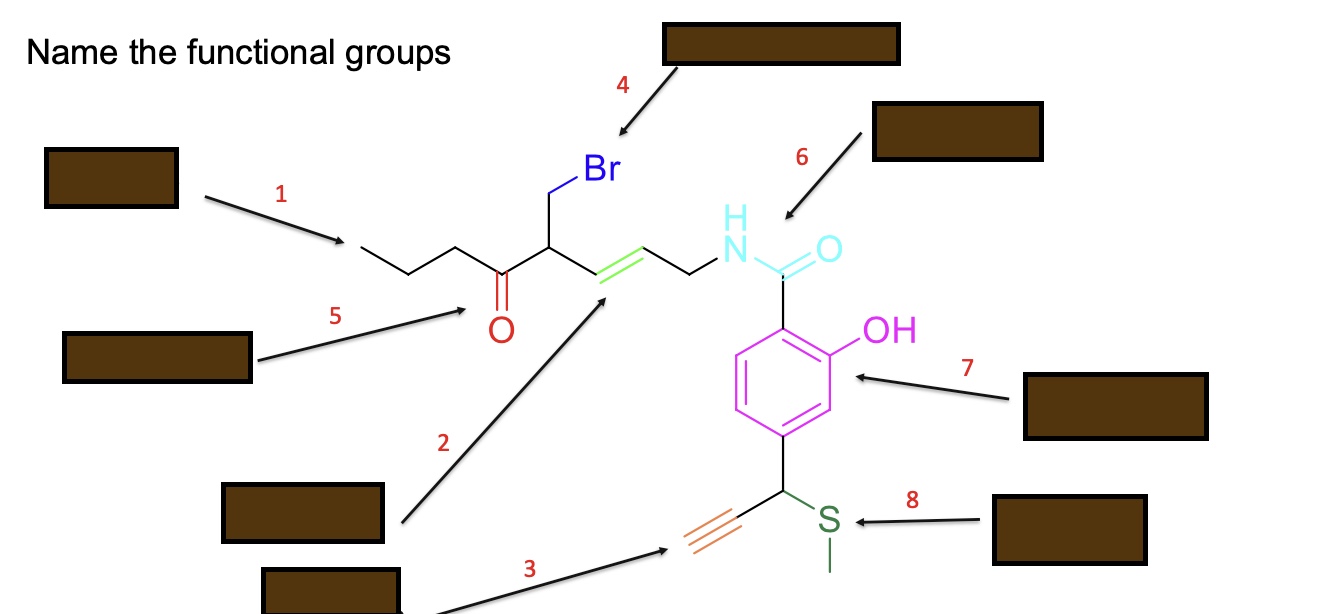
Name the functional groups
Alkane
Alkene
Alkyne
Alkyl halide
Ketone
Amide
Phenol
Sulfide
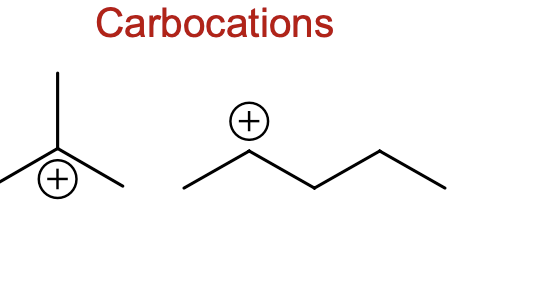
What are carbocations
a positive formal charge on carbon
What is a carboanion?
Is a negative formal charge on carbon
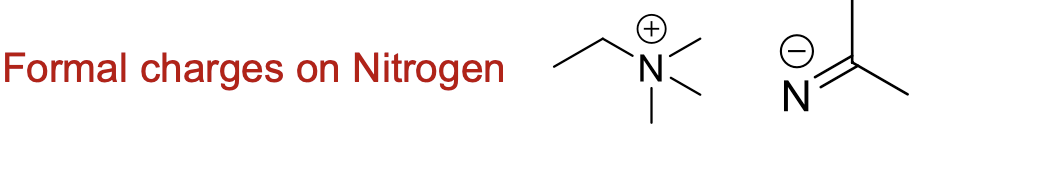
What does a formal charge on nitrogen look like?
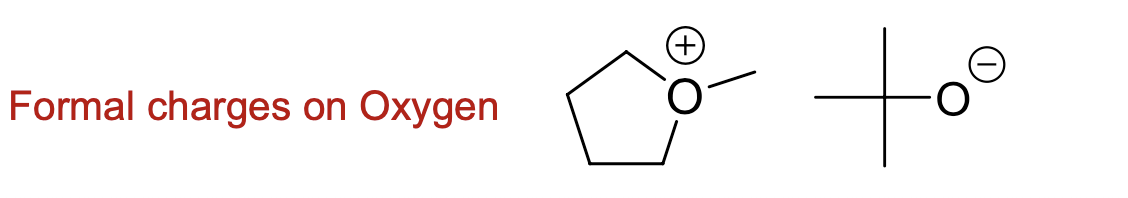
What does a formal charge on oxygen look like?
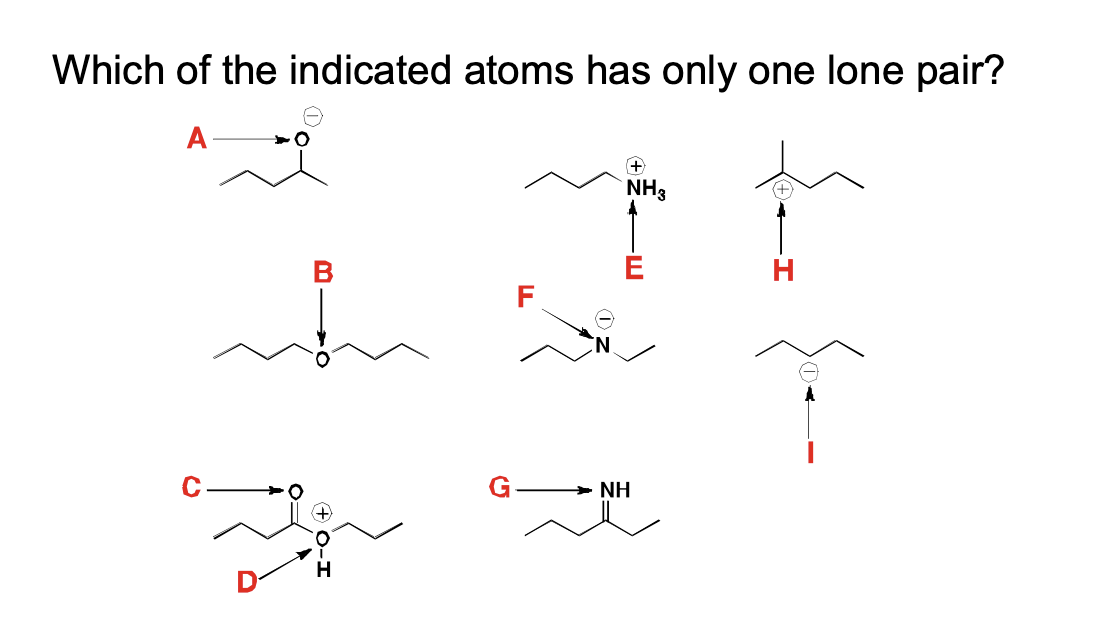
Which of the indicated atoms has only one lone pair?
D, I, G
How do we show a 3D molecule on a 2D piece of paper ?
dashed and solid wedges
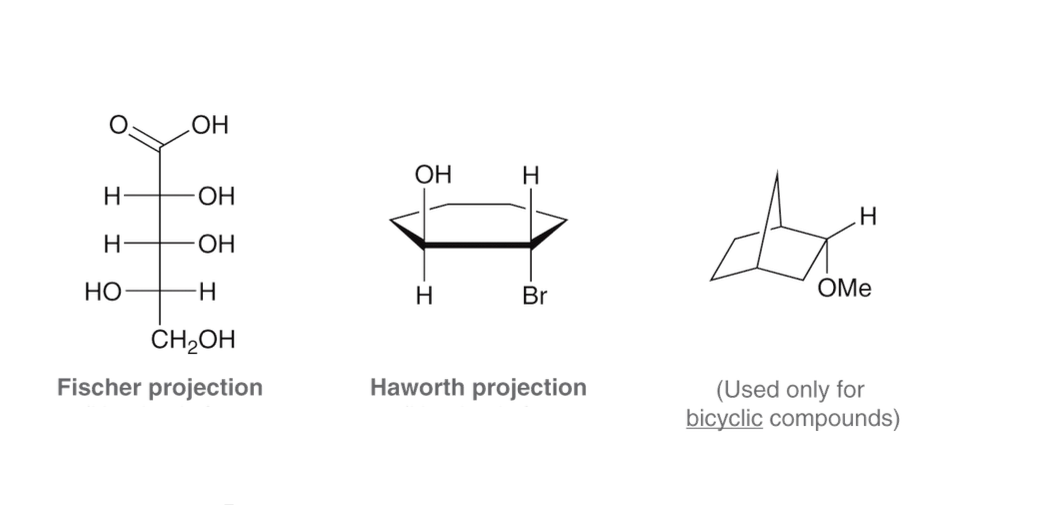
What are some of the ways to show 3D structures?
What is resonance?
when all carbons have un hybridized p orbitals
we used brackets to indicate both resonance contributors exist simultaneously
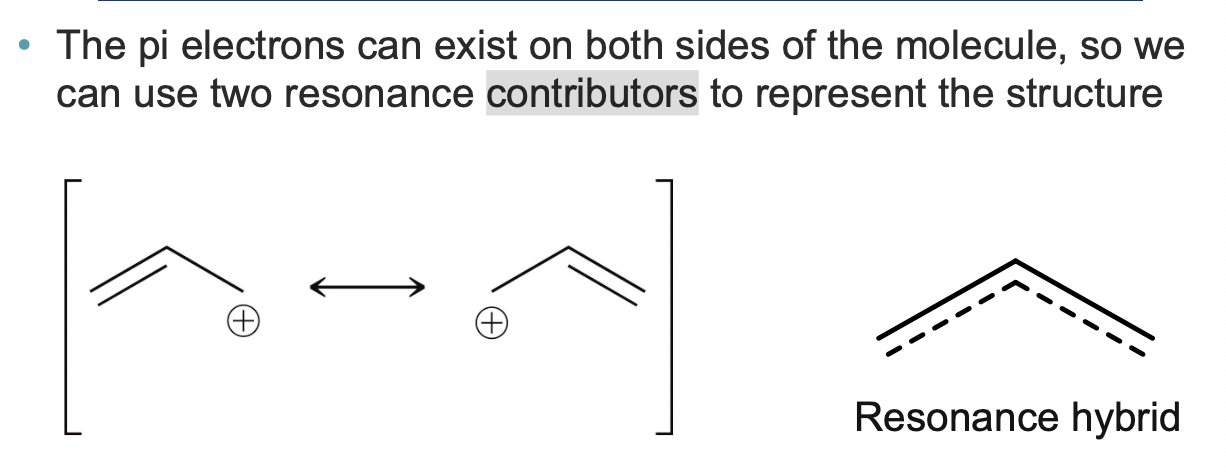
Does resonance make a molecule more or less stable?
MORE stable
Why does resonance make a molecule more stable?
Resonance increases stability by delocalizing electrons and charge.
Electron delocalization: electrons are spread over a larger area, reducing electron–electron repulsion and allowing interaction with multiple nuclei
Charge delocalization: charge is distributed over multiple atoms, making partial charges more stable than a single full charge
What do curved arrows represent in organic chemistry?
Curved arrows show the movement of electrons, usually electron pairs
The arrow starts where the electrons are currently located
The arrow ends where the electrons will be after the movement

What are the rules for using curved arrows to show resonance?
Avoid breaking a single bond, single bonds can break but not in resonance
Never exceed an octet for 2nd row elements (B, C, N, O, F)
2nd row elements (B, C, N, O, F) will rarely but sometimes have LESS than an octet
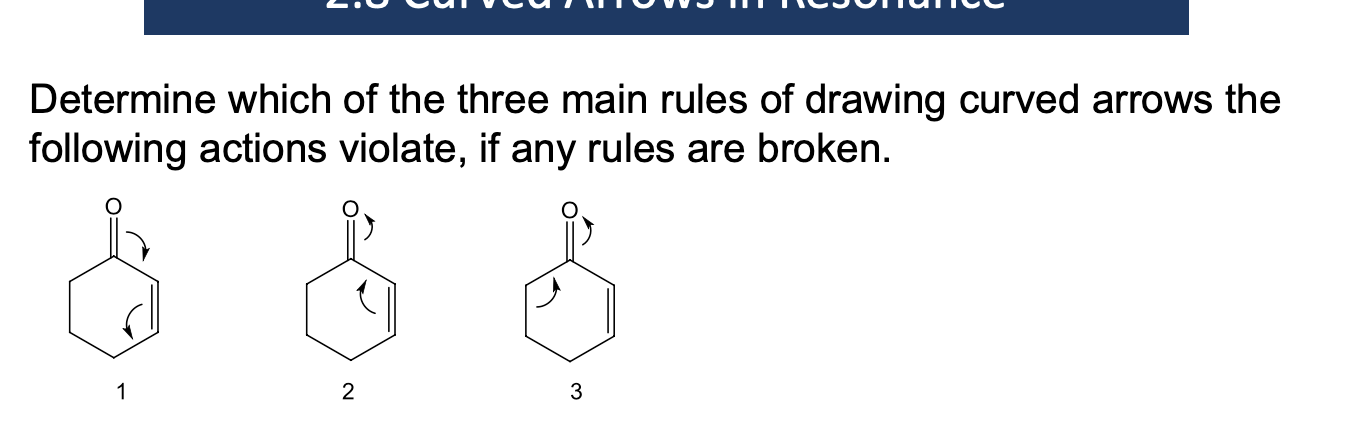
Determine which of the three main rules of drawing a curved arrows the following actions violate, if any rules are broken

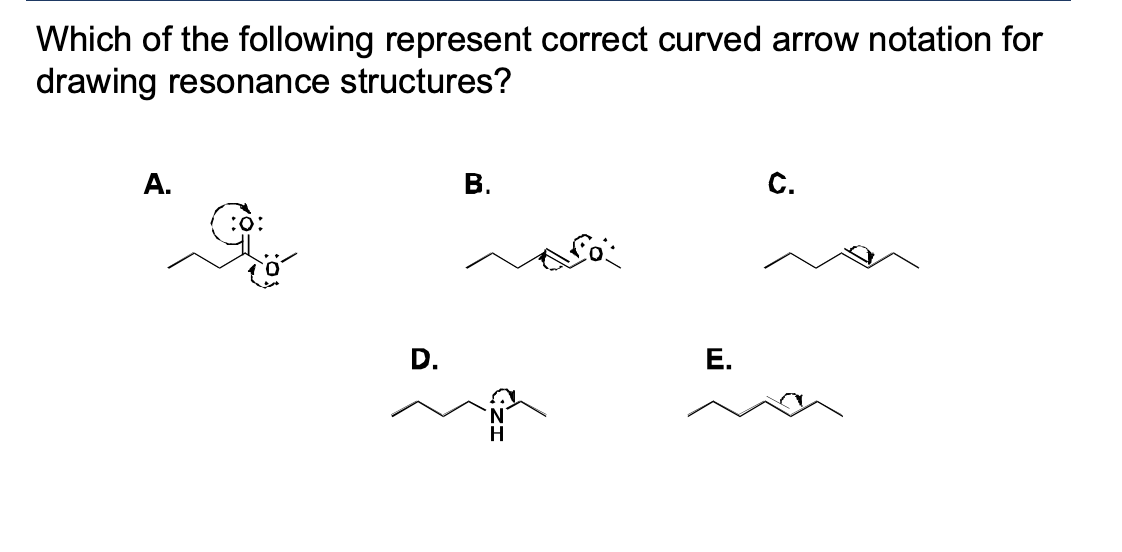
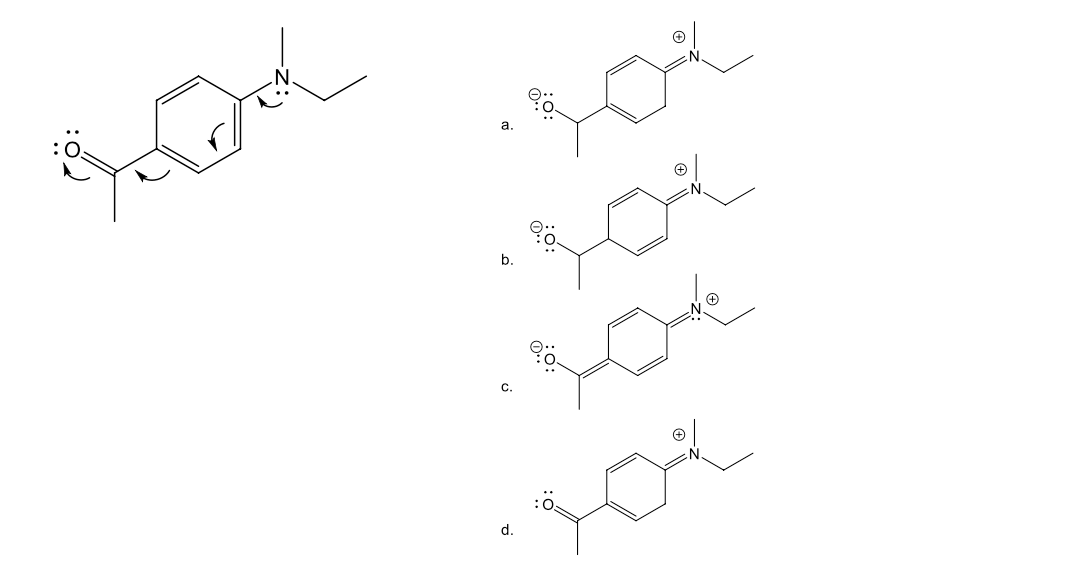
Which of the following represent correct curved arrow notation for drawing resonance structures?
A and B
There a 5 main bonding patterns in which resonance occurs, what are those 5 patterns?
Allylic lone pairs
Allylic positive charge
Lone pair of electrons adjacent to a positive charge
A pi bond between two atoms with different electronegativities
Conjugated pi bonds in a ring

What does vinyl mean?
directly bonded to C=C double bond
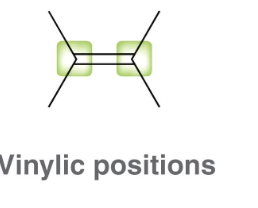
What does allyl mean?
one atom away from a C=C double bond
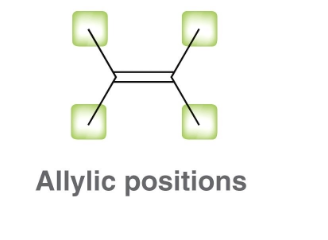
An example of vinyl and allyl in a compound


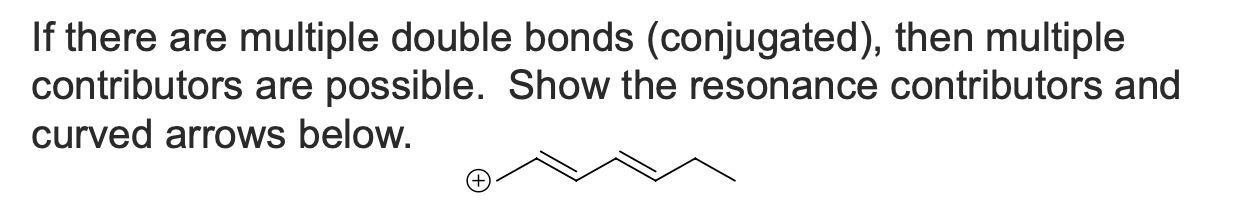
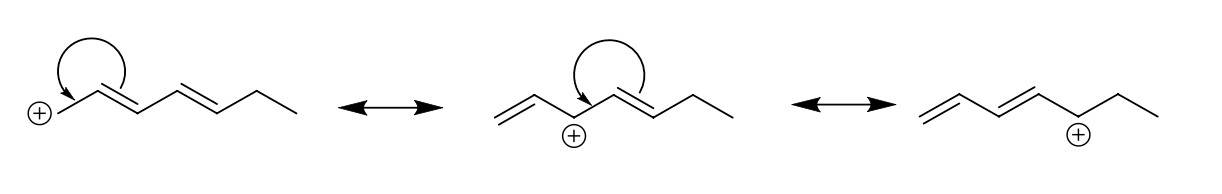
If there are multiple double bonds (conjugated), then multiple contributors are possible. Show the resonance contributors and curved arrows below
How many curved arrows are needed in common resonance patterns?
allylic lone pair = 2 arrows
allylic positive charge=1 arrow
lone pair next to + charge = 1 arrow
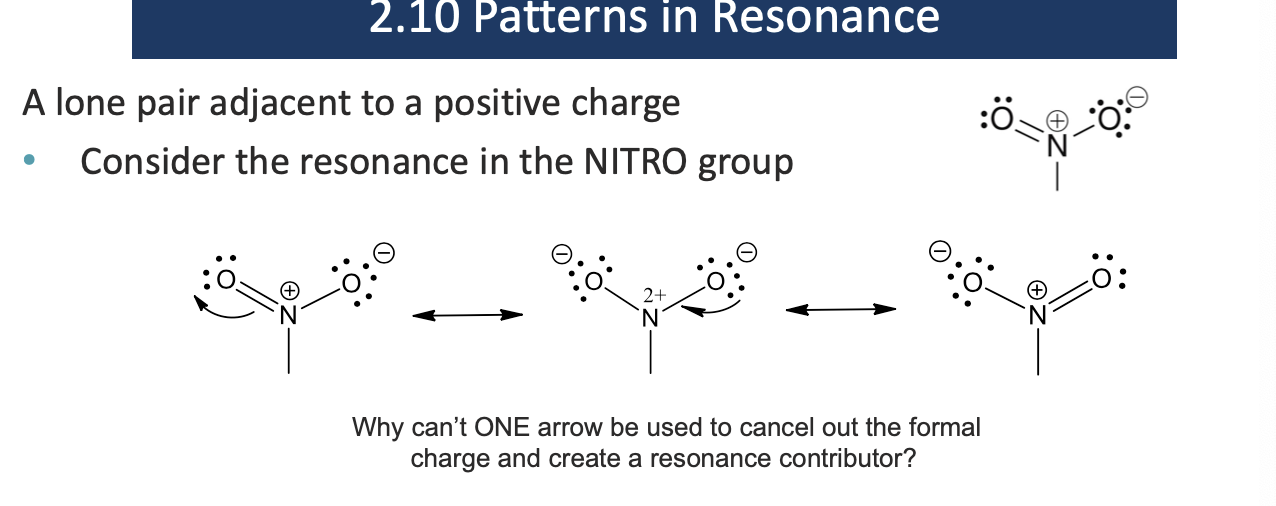
Nitro group = 2 arrows (to preserve octet)
Aromatic ring (benzene) = 3 arrows
Why can’t we use one curved arrow to remove the positive charge in the nitro group?
because one curved arrow would give nitrogen more than 8 electrons and violate the octet rule
What happens when a π bond in between atoms of different electronegativity?
The π electrons shift toward the more electronegative atom using one curved arrow, creating a resonance structure with:
a negative charge on the more electronegative atom
a positive charge on the less electronegative atom

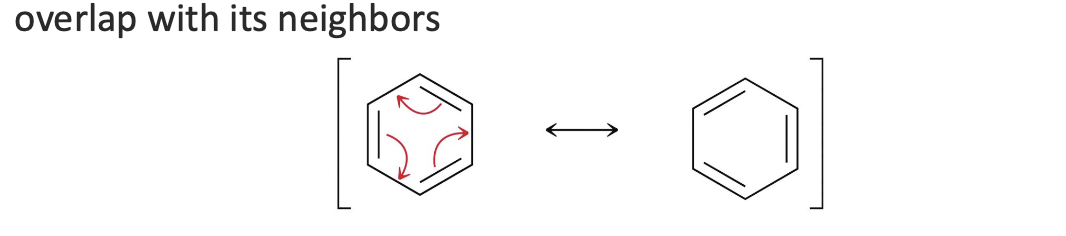
How do you draw resonance for conjugated π bonds in a ring?
Every atom must have a p orbital (sp2 or sp)
π electrons are delocalized around the ring
Move all π bonds together using three curved arrows
Arrows can go clockwise or counterclockwise

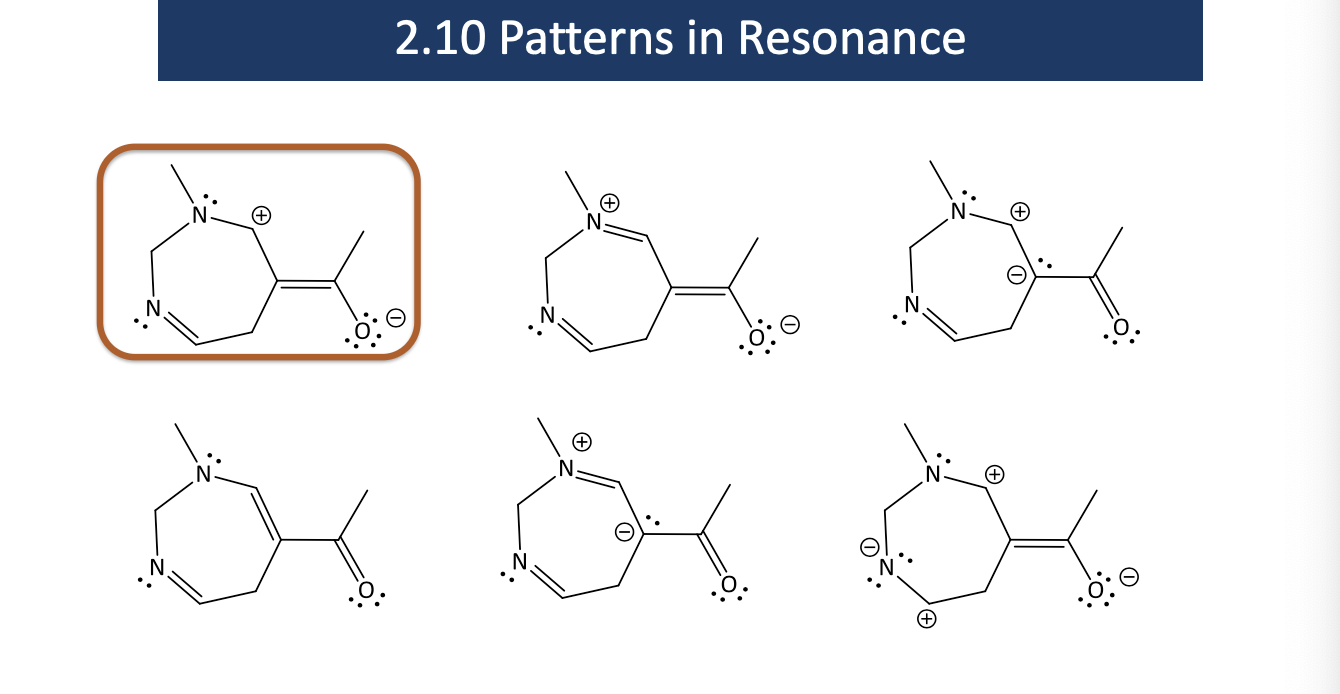
finish this answer
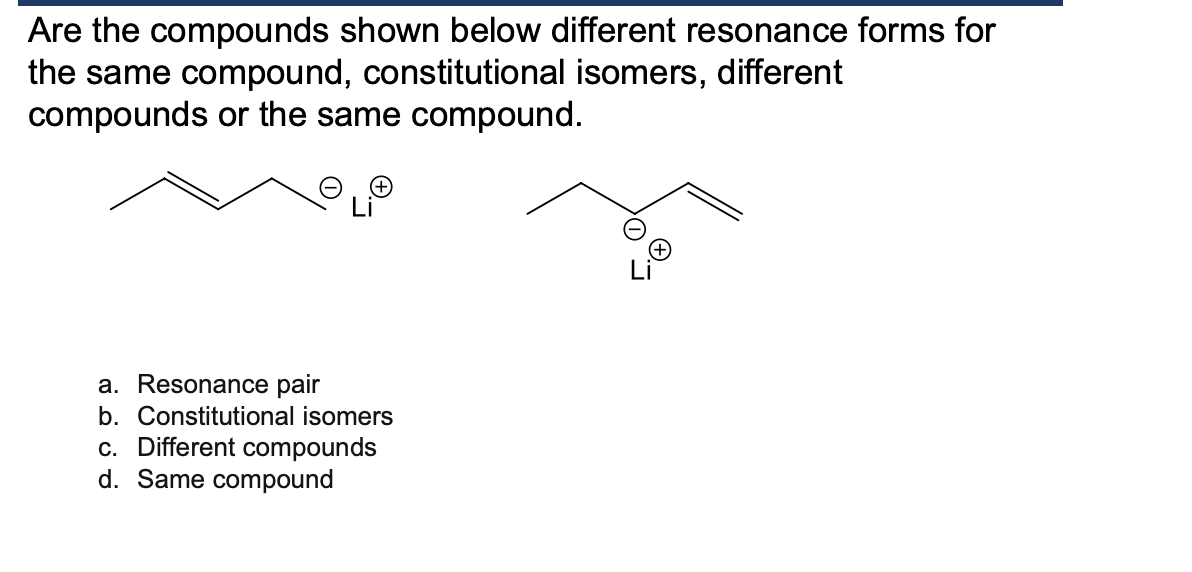
finish this answer
How is the stability of resonance contributors assessed?
Formal charge generally decreases stability, especially a +1 charge on an electronegative atom or -1 on a low electronegativity atom
Complete octet increases stability (more of a bigger factor than formal charge)
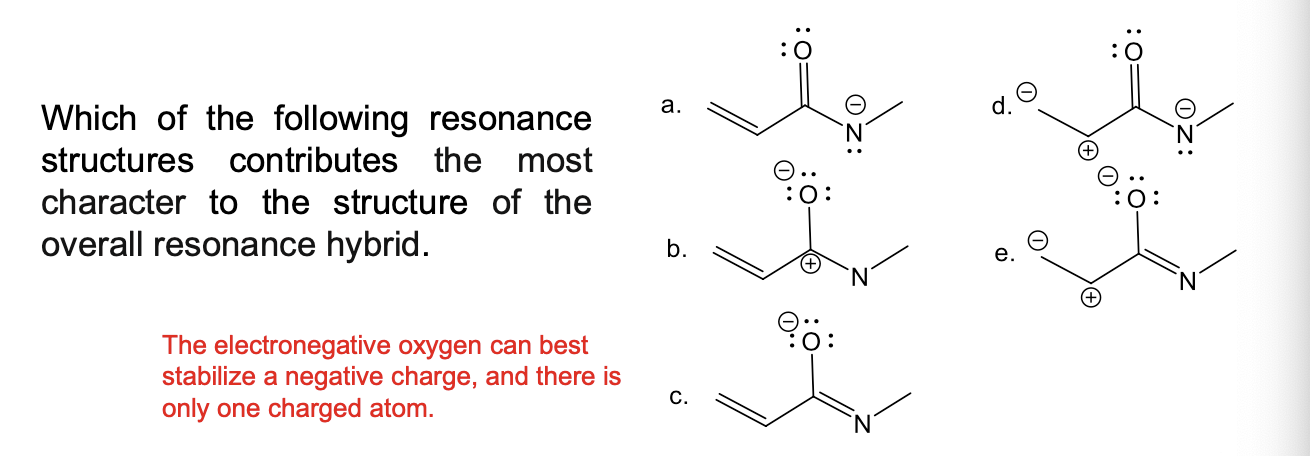
finish the answer
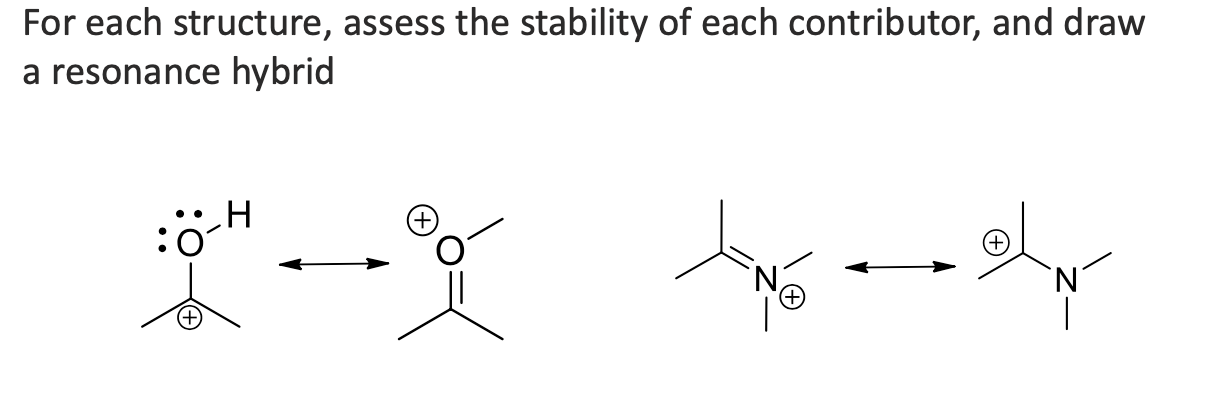
answer the question
What is localized electrons?
electrons are NOT in resonance
What are delocalized electrons?
electrons are in resonance
increases stability
How do we recognize electrons that are delocalized?
electrons must exist in an unhybridized p orbital that can overlap with p orbitals on neighboring atoms
To be delocalized, electrons must be on an sp or sp3 hybridized atom
What happens if a lone pair can participate in resonance?
The atom becomes sp2 hybridized to provide a p orbital for delocalization
so some atoms that would normally be sp3 will become sp2 hybridized
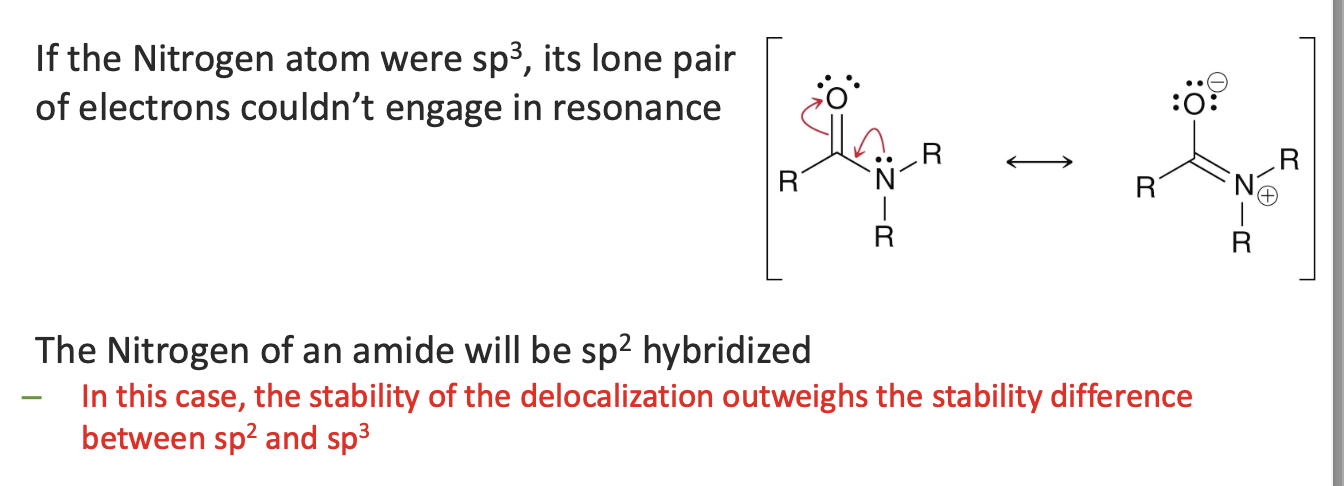
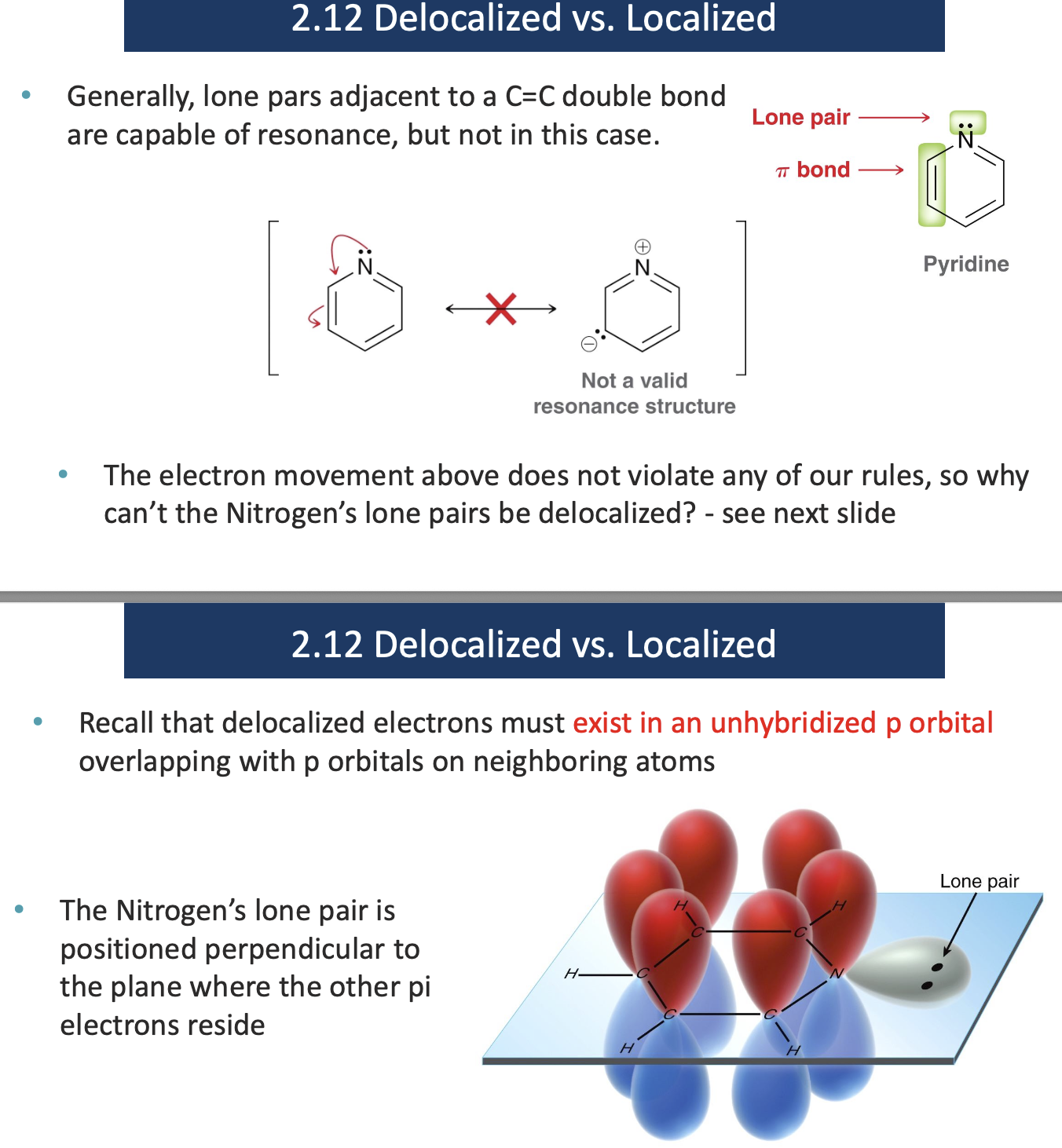
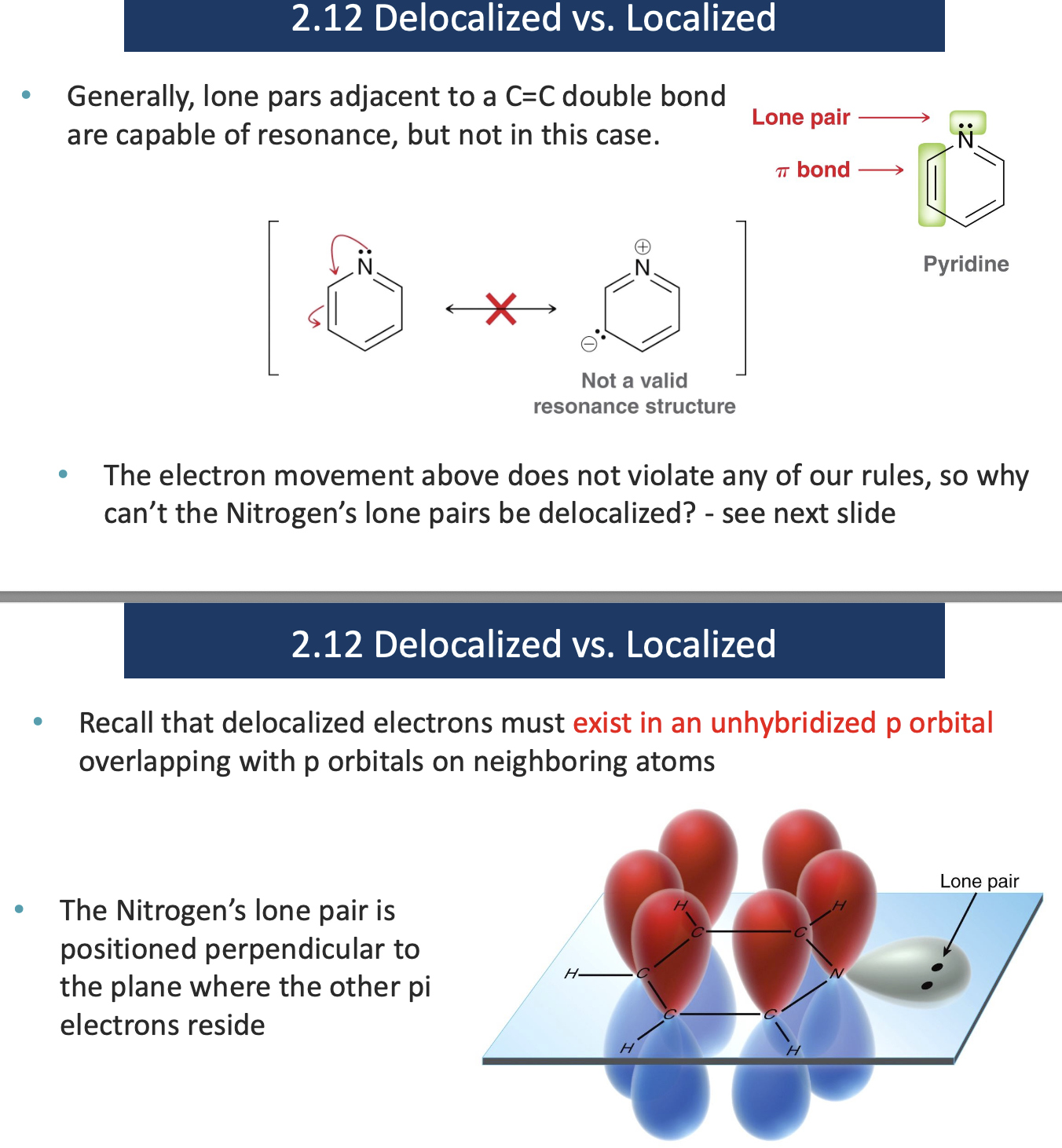

Identify which of the indicated lone pairs are localized.

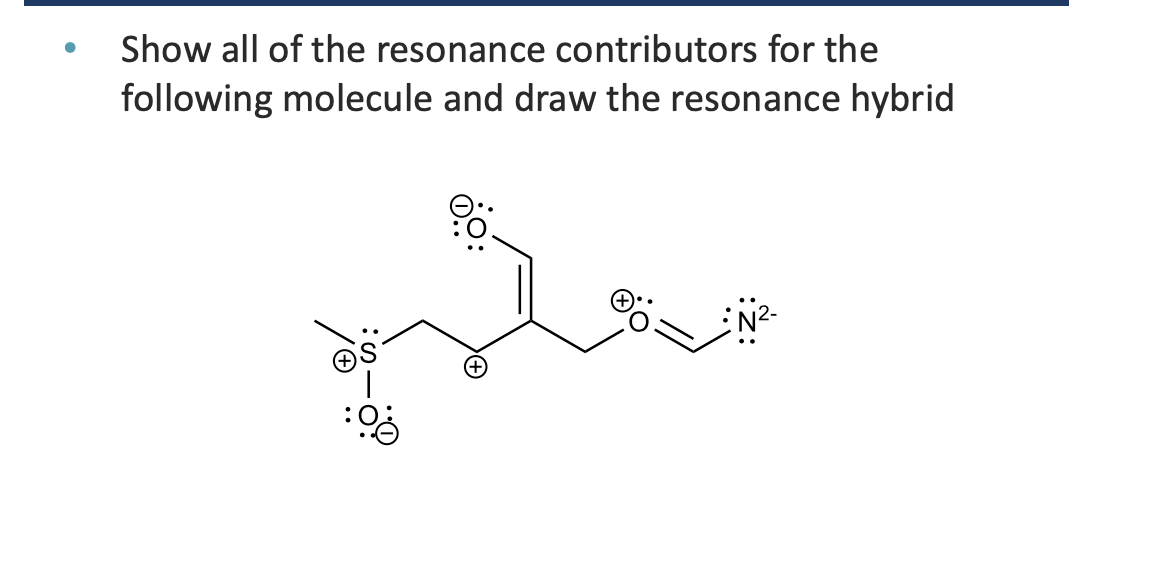
answer