APES Energy Test
1/85
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
86 Terms
Energy
The ability to do work or make something move.
Work (Formula)
Work = Force × Distance.
Power (Formula)
Power = Energy / Time (Rate at which work is done).
Joule (J)
The basic metric unit of energy. (1 N · m).
Watt (W)
The unit of power. (1 Joule/second).
Kilowatt-hour (kWh)
A unit of energy (not power), used for household electricity bills. (1 kWh = 3,600,000 Joules).
British Thermal Unit (BTU)
The energy required to heat 1 lb of water by 1°F.
1st Law of Thermodynamics
Energy is conserved; it cannot be created or destroyed, only converted.
2nd Law of Thermodynamics
When energy changes form, some quality is lost (usually as waste heat); entropy increases.
1st Law Efficiency
Work Done / Energy Used.
2nd Law Efficiency
Minimum Energy Needed / Actual Energy Used (indicates potential for savings).
Cogeneration (Combined Heat and Power)
Using a fuel to generate electricity and using 'waste' heat for useful heating. Efficiency can reach 90%.
Typical efficiency of a Coal Power Plant
30-40%.
Typical efficiency of an Incandescent Light Bulb
5% (95% lost as heat).
EROEI
Energy Return on Energy Investment (Energy Obtained / Energy Invested).
Hard Path
Finding more fossil fuels and building larger power plants (Quantity over Quality).
Soft Path
Energy efficiency, conservation, and renewable sources.
Negawatt
A theoretical unit representing a watt of energy saved through conservation.
Coal formation
From ancient swamp vegetation (terrestrial plants) buried and compressed over millions of years.
Stages of Coal formation
Peat → Lignite → Sub-bituminous → Bituminous → Anthracite.
Primary pollutants from burning coal
CO₂, Sulfur Dioxide (SO₂), Nitrogen Oxides (NOₓ), Particulates (PM), Mercury, and Arsenic.
Methylmercury
Formed when mercury from coal enters aquatic ecosystems; highly toxic and bioaccumulates in fish.
Acid Mine Drainage
When water interacts with sulfur in coal mines to form sulfuric acid, leaching metals into groundwater.
Mountaintop Removal
A destructive mining technique where the top of a mountain is removed to access coal seams.
Centralia, PA case study
An underground coal mine fire that has been burning for 50+ years, resulting in town abandonment.
Formation of Oil and Natural Gas
From ancient marine microorganisms (phytoplankton) buried under ocean sediment.
Region with largest Oil Reserves
The Middle East (Venezuela, Saudi Arabia).
Country with largest Natural Gas Reserves
Russia.
Cleanest burning fossil fuel
Natural Gas (Methane); emits ~60% less CO₂ than coal.
Fracking (Hydraulic Fracturing)
Injecting water, sand, and chemicals at high pressure to crack rock and release trapped gas/oil.
Risks of Fracking
Groundwater contamination, induced earthquakes, and high water usage.
Tar Sands (Oil Sands)
Deposits of sand/clay containing Bitumen (thick, sticky heavy oil); major reserves in Alberta, Canada.
Keystone XL Pipeline
A controversial pipeline designed to transport Tar Sands oil from Canada to US refineries.
Hubbert Curve
A graph projecting the point of peak oil production followed by decline.
Methane Hydrates (Clathrates)
Methane trapped in ice crystals on the ocean floor; huge potential energy but risky to extract.
ANWR controversy
Debate over drilling for oil in the Arctic National Wildlife Refuge, a fragile ecosystem.
Major Oil Spills
Exxon Valdez (1989, Alaska) and Deepwater Horizon (2010, Gulf of Mexico).
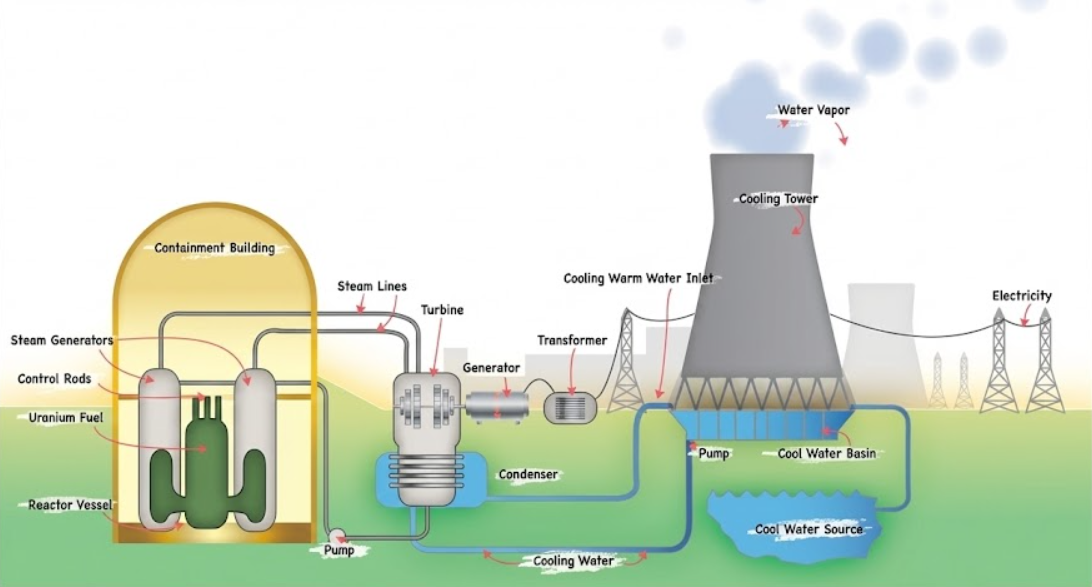
Nuclear reactor energy generation
Fission (splitting an atom).
Primary fuel for nuclear reactors
Uranium-235 (must be enriched).
Function of Control Rods
Absorb neutrons to slow down or stop the chain reaction.
Function of Containment Building
Concrete/steel shell designed to prevent radiation from escaping into the environment.
Output of a nuclear Cooling Tower
Water vapor (steam); NOT radioactive.
Breeder Reactor
A reactor that creates more fissile fuel (Plutonium-239) than it consumes.
Types of radiation emissions
Alpha (α, blocked by paper), Beta (β, blocked by foil), Gamma (γ, requires thick lead/concrete).
Half-Life
The time taken for 50% of a radioactive isotope to decay.
Safe radioactive waste consideration
10 Half-Lives.
Storage of High-Level Waste in the US
On-site at power plants (in pools or dry casks).
Yucca Mountain
The proposed permanent underground storage site for US nuclear waste (canceled/stalled).
Three Mile Island accident (1979)
Partial meltdown due to pump failure/human error; small release; stopped new US plant orders.
Chernobyl accident (1986)
Complete meltdown and explosion in Ukraine; massive radiation release.
Fukushima accident (2011)
Earthquake + tsunami disabled cooling pumps; three reactors melted down.
Passive Solar design
Building orientation and materials used to heat a home without pumps/fans.
Photovoltaic (PV) Cells
Silicon wafers that convert sunlight directly into electricity.
Active Solar
Using mechanical pumps/fans to circulate fluids heated by the sun.
Main drawback of Wind Energy
Intermittent (wind doesn't always blow), visual/noise pollution, bird/bat deaths.
Largest source of renewable electricity in the US
Biomass or Wind/Hydro depending on year.
Drawbacks of Hydroelectric Dams
Flood habitat upstream, disrupt fish migration, sediment buildup.
Geothermal Energy
Using heat from the Earth's interior; high efficiency, location-specific.
Hydrogen Fuel Cell
A device that combines Hydrogen (H₂) and Oxygen (O₂) to produce electricity and Water (H₂O).
OTEC
Ocean Thermal Energy Conversion; uses temperature difference between warm surface and cold deep water to generate power.
Baseload power
The minimum amount of power the grid needs 24/7, usually supplied by coal or nuclear.
Peaker Plants
Plants that turn on quickly to meet high demand, usually natural gas.
Smart Grid
A modernized grid with two-way communication between utility and consumer to manage demand efficiently.
Net Metering
A system where solar panel owners can sell excess electricity back to the grid.
Sector consuming the most energy in the US
Industrial (32%), Transportation (28%).
Percentage of US energy from non-renewable sources
~88% (roughly 81% fossil fuel + nuclear).
Nuclear power plant diagram (no term j an image to study)