Lecture 1: Intro to Radiology 2 (Basic of Radiographic Films)
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms

Terminology:
What is the correct term when referring to the films?
NOT called what?
Position:
Position is described in what 2 ways?
Conventional Radiographs
NOT X Ray
Position: (2)
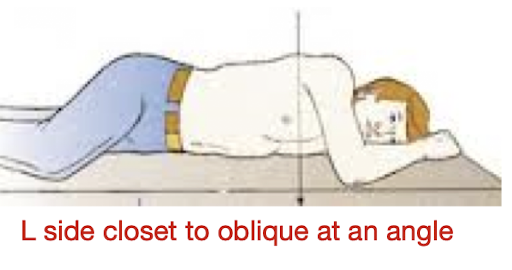
General body position
To describe the part closest to the image
Ex: L Ant Oblique Position
Terminology:
Projection:
What is it?
Ex:
Path of the X-Ray as it moves from tube through the patient
Ex: Post Ant Oblique Projection
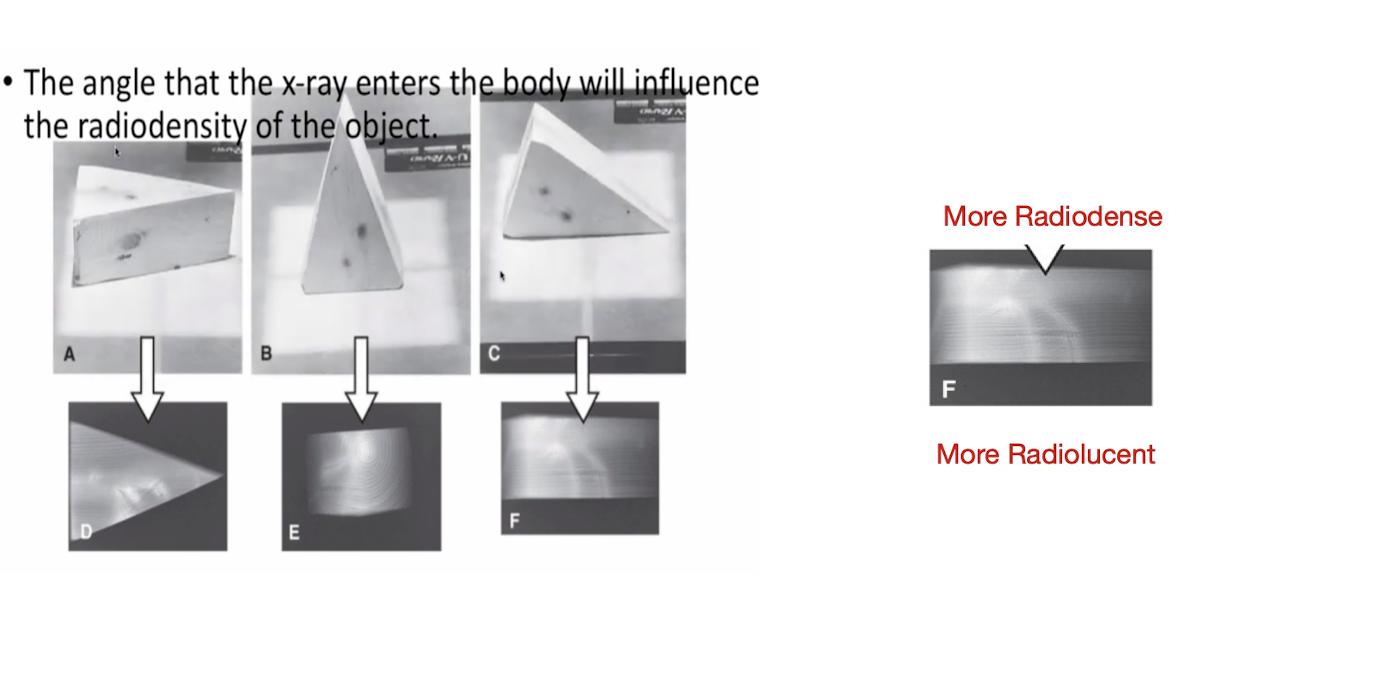
Angle of Projection:
The angle that the X-Ray enters the body will influence what?
Radiodensity of the Object
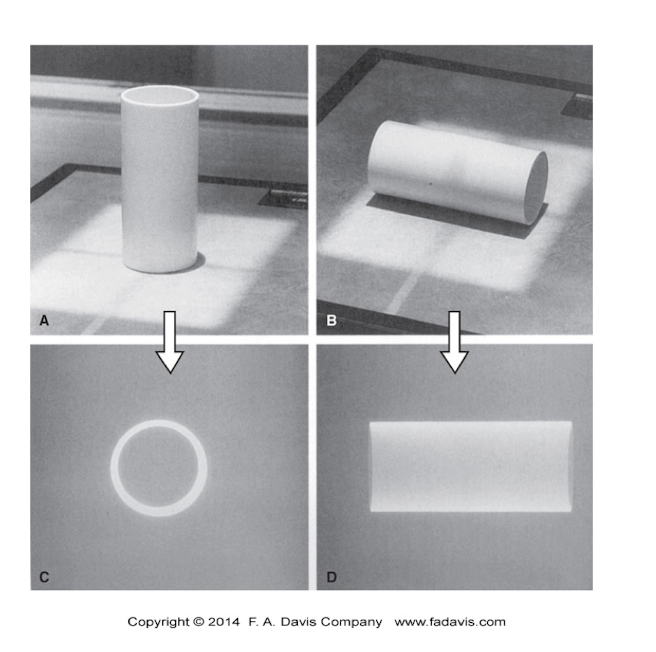
Curved Planes:
How to shoot Curved Planes compared to the image receptor?
How many planes is needed to view?
Shoot:
Perpendicular
Parallel
Need 2
One View is
NO VIEW
How many projections are needed see Right Angles?
In order to see an objects… (3)
T/F: Need to see three dimensions in your head when looking at a radiographic film
Need 2
Length
Width
Depth
True
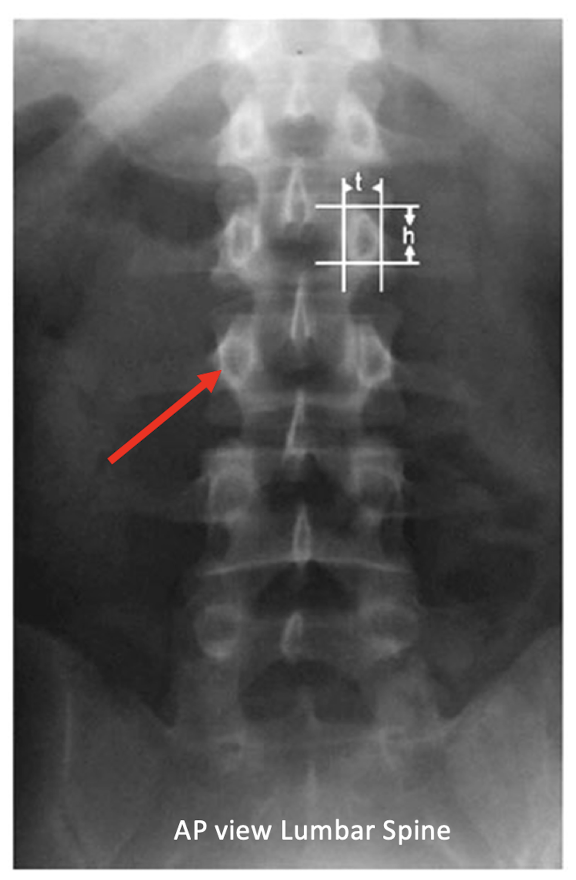
Projection:
What is the BEST view for looking at the spine?
AP
X Ray: Ant
Film: Post
Film Viewing:
Film is placed on the ___ with the patient is in ____ position.
True with what 2 views?
Box
Anatomical Position
True AP and PA
Film Viewing:
Hands and Feet:
Placed on the view box with toes and fingers pointing ___
Lateral Projections:
Placed on the view box as if seeing the image from the perspective of what?
Upward
X-Ray Beam
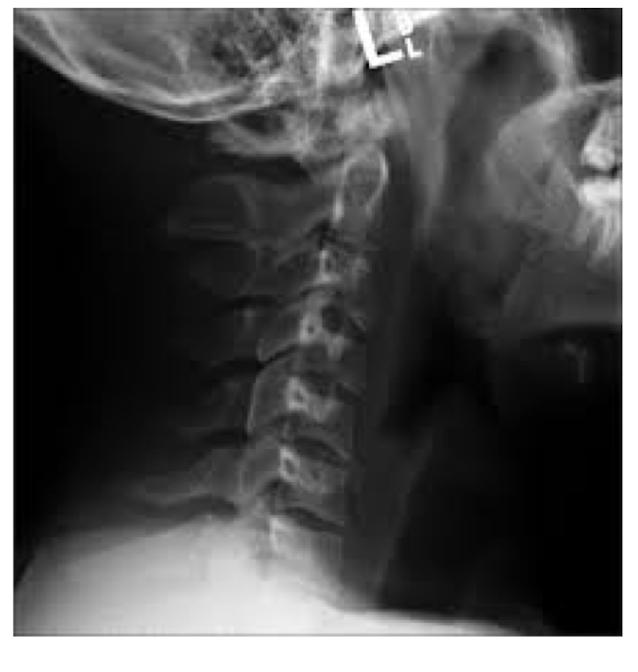
What view is this?
L Lateral View
Film on L
Patient facing R
Looking at it as if YOU are the machine and the receptor is behind them
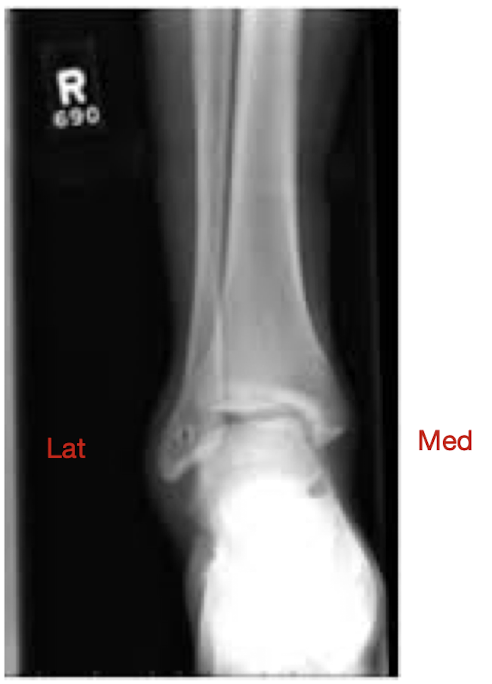
What view is this?
R AP View
Pt in Anatomical Position
Pt facing you
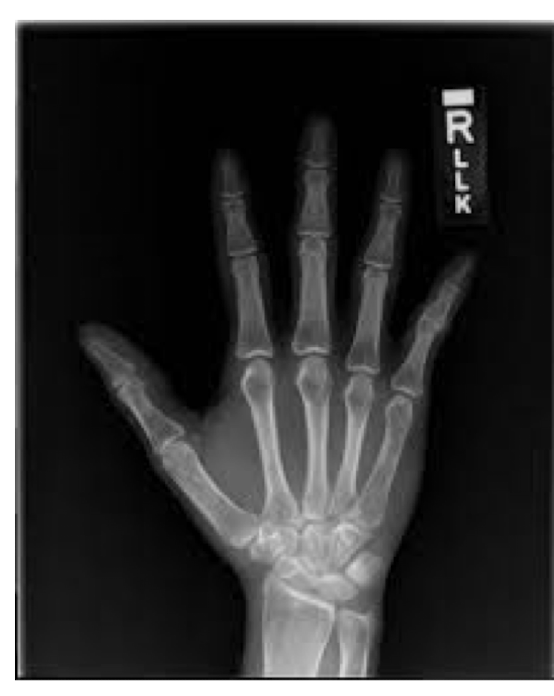
What view is this?
R Hand
Radiologic Evaluation:
What are the ABCS of Radiologic Analysis?
Search pattern helps account for what?
ABCS:
A: Alignment
B: Bone Density
C: Cartilage Spaces
S: Soft Tissue
Search Pattern
Structures needing visualization
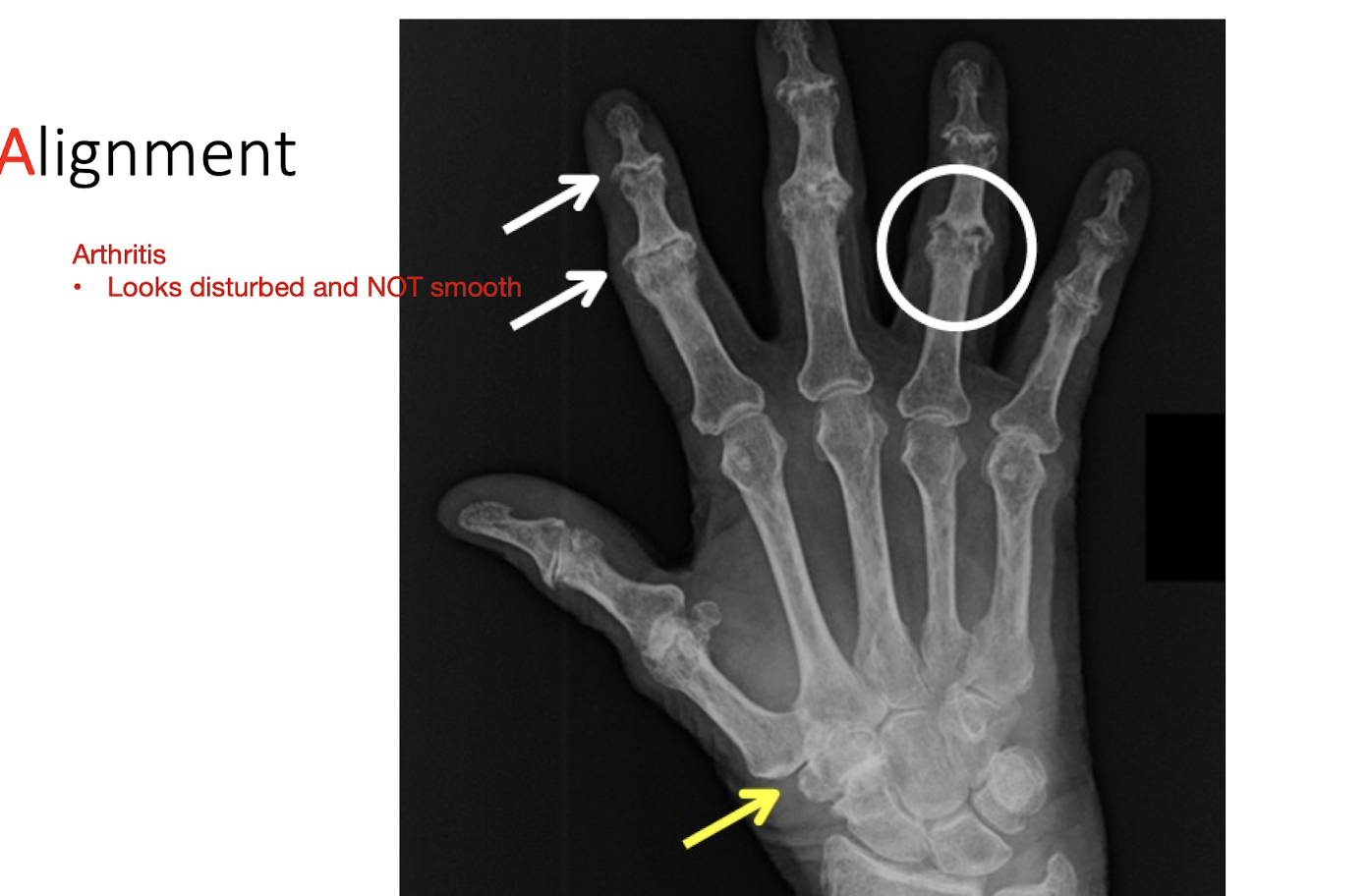
A = Alignment:
What to look for? (Pt 1 - 4)
Correct # of bones
Size of Bones
Bone abnormalities
Developmental Deformities

A = Alignment:
What to look for? (Pt 2 - 4)
Contour of Bones
Do edges look smooth?
External and Internal Abnormalities
Cortical Bone Outline
Breaks in Continuity
Sites of Muscle Attachment (Bone Spurs)
Past Surgical Sites
Bone Spurs
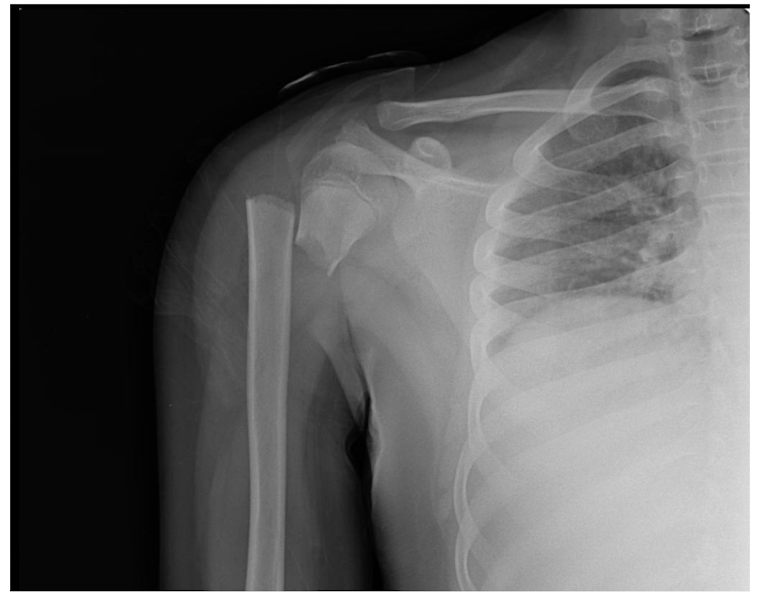
A = Alignment:
What to look for? (Pt 3 - 4)
Alignment of bones relative to adjacent bones
Fx
How this may disrupt jt articulations
Dislocation
Do joint articulations look normal
Subluxation
Partial dislocations
Signs of recent dislocations
B = Bone Density:
What to look for? (Pt 1 - 2)
Normal shades of gray
Compare to surrounding soft tissue and other bone
B = Bone Density:
What to look for? (Pt 2 - 2)
Look within bone itself
Contrast of cortical bone to medullary bone
Assess trabeculae of bone
Density Changes
Sclerotic Bone
May be normal or abnormal
Textural Abnormalities:
Assess the ___ for abnormalities
Trabeculae
Local Density Changes:
Sclerosis?
Normal or Abnormal?
Excessive Sclerosis?
Normal or Abnormal?
What is Reactive Sclerosis?
Sclerosis (Increased Bone Density)
Normal or Abnormal
Excessive Sclerosis:
May be Normal
Bone Healing
May be Abnormal
OC (hands and fingers)
Reactive Sclerosis:
Bodies way of surrounding an infection or tumor
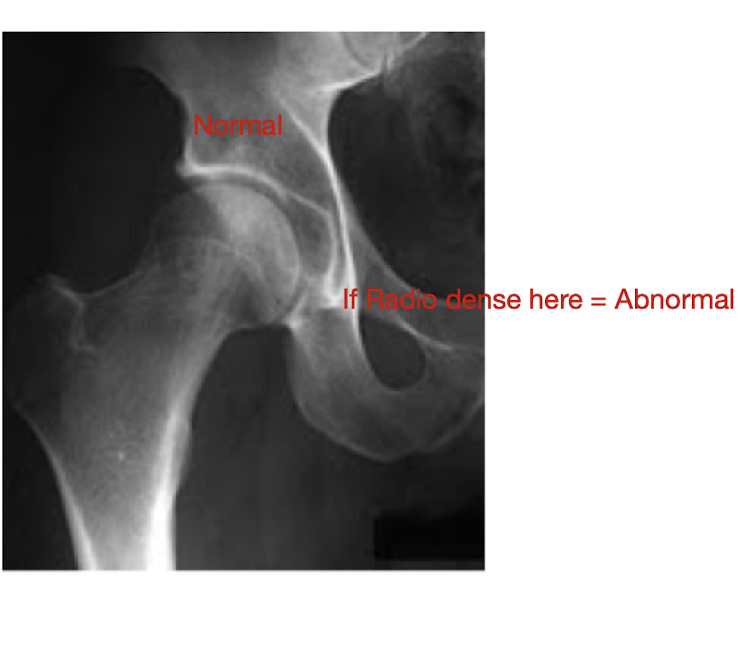
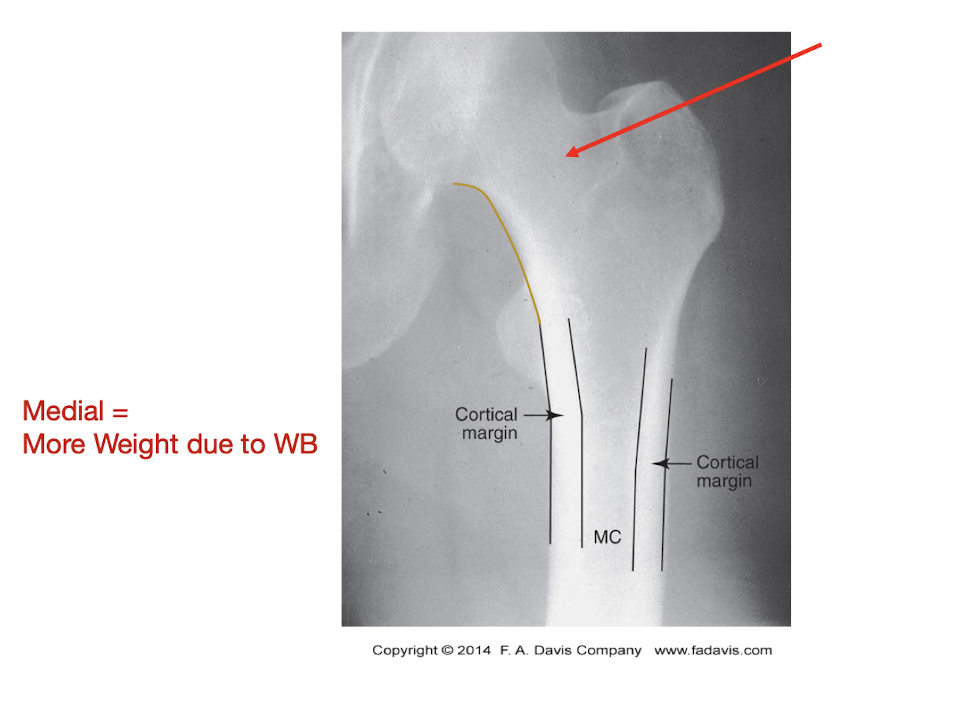
Local Density Changes:
Describe this Hip:
Normal Sclerosis:
Increased Bone Density
Response to WB
Wolf’s Law
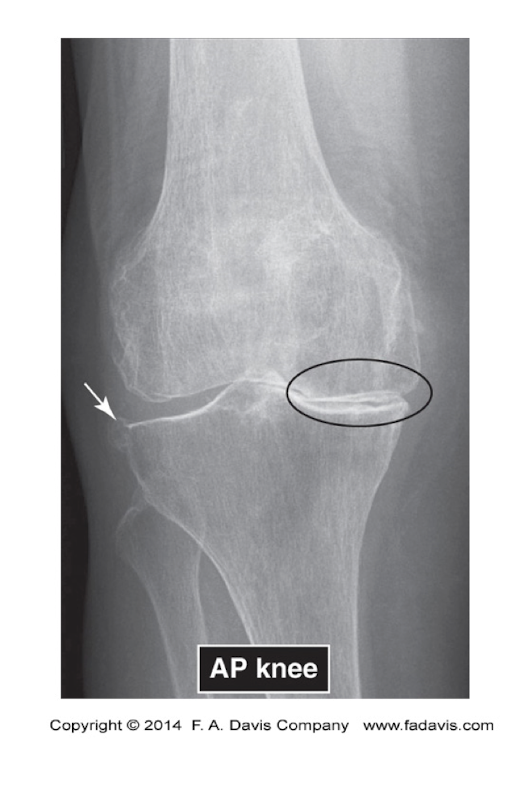
Knee OA Pic
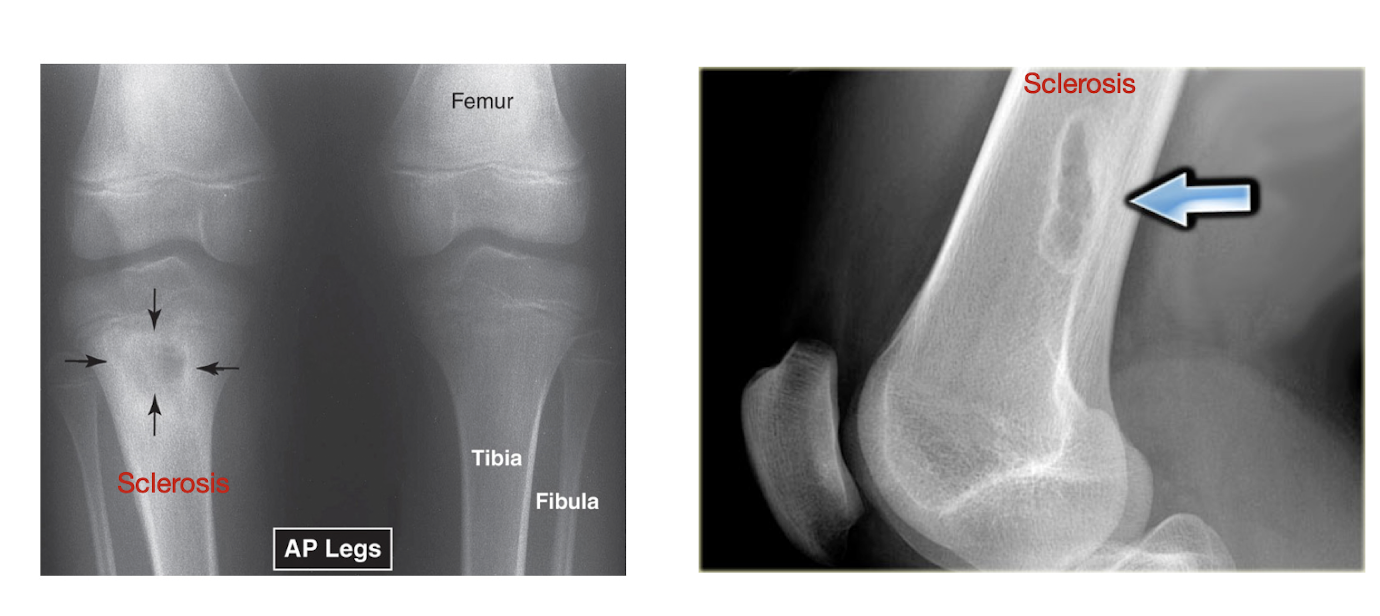
Excessive Sclerosis
C = Cartilage Spaces:
What does Cartilage Spaces explain?
What are the 2 main things that Subchondral Bone may show?
Why may show increased sclerosis?
Explains:
Joint Space width
Sunchondral Bone (Below the articular cartilage)
Erosions
Increased Sclerosis
Due to loss of articular cartilage new bone formation
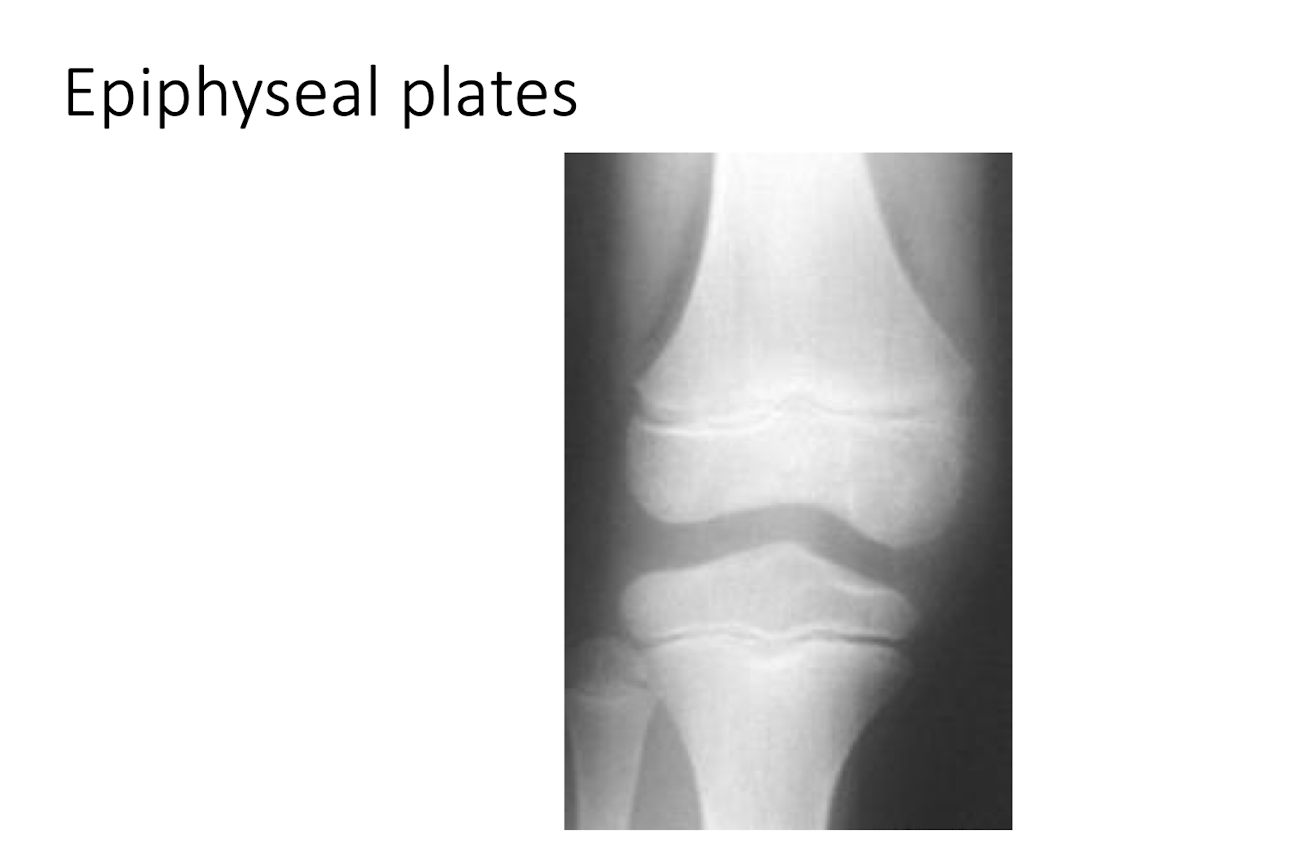
C = Cartilage Spaces:
What are the 3 main things that Epiphyseal Plates may show?
Disruption
Sclerotic Bone
Size of plate related to age of child
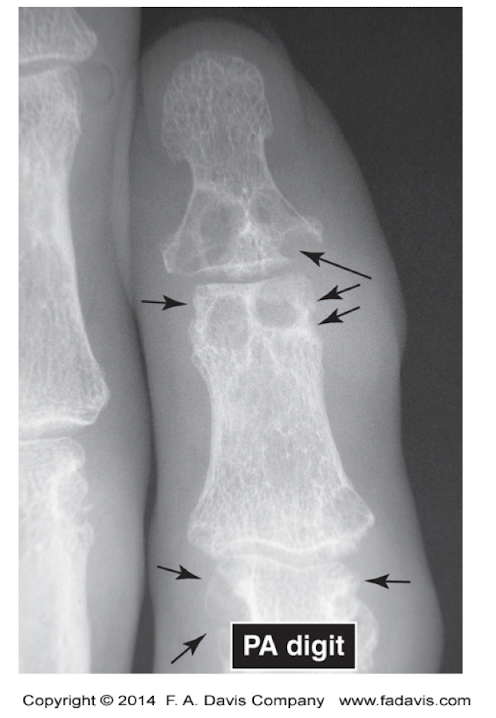
What does this show?
Gout
Increased Radiolucency
Subchondral bone erosions
Minimal Sclerosis
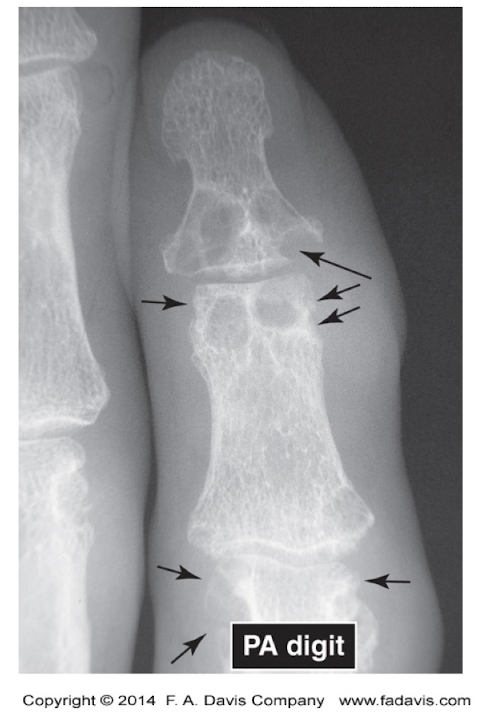
S = Soft Tissue:
What are the main things that can be seen when assessing Soft Tissue? (Pt 1 - 3)
Muscle
Gross Muscle Wasting
Swelling of Muscle and Soft Tissue
Fat Pads
Swelling or Displacement of a Fat Pad
Jt Capsule
If abnormal from swelling may see capsule
S = Soft Tissue:
What are the main things that can be seen when assessing Soft Tissue? (Pt 2 - 2)
Calficiations
Radiodense areas that should NOT be there
Foreign Bodies
Metal
Pacemakers