Lecture 9 -- Equine Forelimb Anatomy
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
What is another name for proximal interphalangeal joint?
Pastern joint
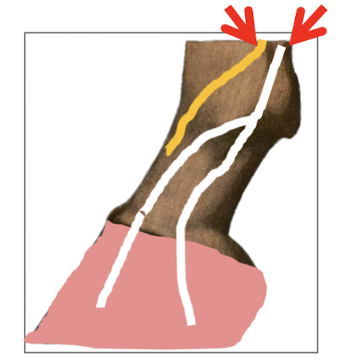
Where do the collateral ligaments of the proximal Interphalangeal Joint run?
Collateral ligament x2 pairs
1. Runs from the Proximal Phalanx (P1) to the Middle Phalanx (P2)
2. Proximal Phalanx (P1) to navicular bone
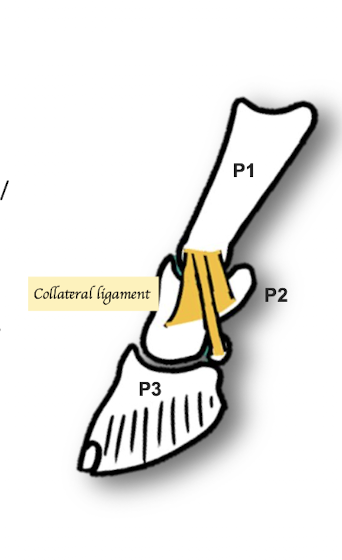
What structures make up the Distal Interphalangeal Joint (DIP)?
Middle Phalanx (MP), Distal Phalanx (DP) and navicular bone
What is another name for distal interphalangeal joint?
Coffin joint
What are the ligaments of distal sesamoid?
Collateral ligaments
Middle phalanx to Distal phalanx
Impar ligaments
Navicular bone to Distal phalanx
Where is the Navicular / podotrochlear bursa located?
Between the Navicular and Deep Digital Flexor Tendon (DDFT)
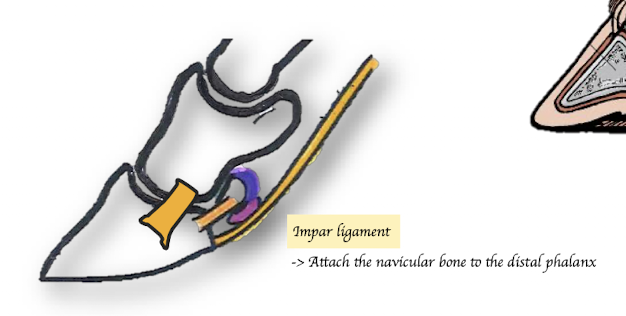
Different from dogs and cats, what ligament is absent in horses in their distal interphalangeal joint?
No dorsal elastic ligament in horses
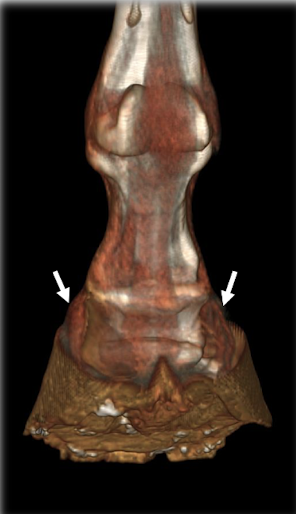
What bones are shown in the picture?
Lateral / Ungual Cartilage
Where are the ungual cartilages located? What are the function of ungual cartilages?
Located at the lateral + medial aspect of the palmar processes of distal phalanx
Function: Shock absorption
Are ungual cartilages able to be visualise in radiograph?
Normally not → Cartilage not visible (Slightly darker than bone) → BUT Mineralise as age (Able to identify in radiograph) = Sidebone
Where does the Common digital extensor (CDE) insert?
Crosses the dorsal aspect of the carpus and inserts on PP, MP & DP
Different from dogs, where does the Lateral digital extensor (LDE) insert?
Inserts on the Proximal Phalanx (P1)
P.S. In dogs, lateral digital extensor inserts into 4th and 5th digits
How does the function of the extensor carpi ulnaris differ between horses and dogs?
Horses:
Acts as flexion of carpus joint
Dogs
Acts as extension of carpus joint
How does the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon in horses differ from dogs?
Horses:
Lie on top of the superficial digital flexor tendon (SDFT) on the caudal aspect of the forelimb
Dogs:
Beside the extensor carpi ulnaris
How do the deep digital flexor tendon and the superficial digital flexor tendon interact?
In horses:
SDFT + DDFT pass through carpal tunnel → SDFT splits to allow the DDFT pass through it → SDFT inserts into MP, while DDFT inserts into DP
In dogs:
SDFT and DDFT runs parallel over the phalanges
What are the accessory check ligaments?
Superior check ligament
Locate above the carpus
Originates proximal to carpal canal
Fuses with SDFT
Inferior check ligament
Locate below the carpus
Originates from fibrocartilage plate on palmar aspect of carpus
Fuses with DDFT
If we perform an ultrasound examination of the proximal metacarpus in horses, which structures can we visualize?
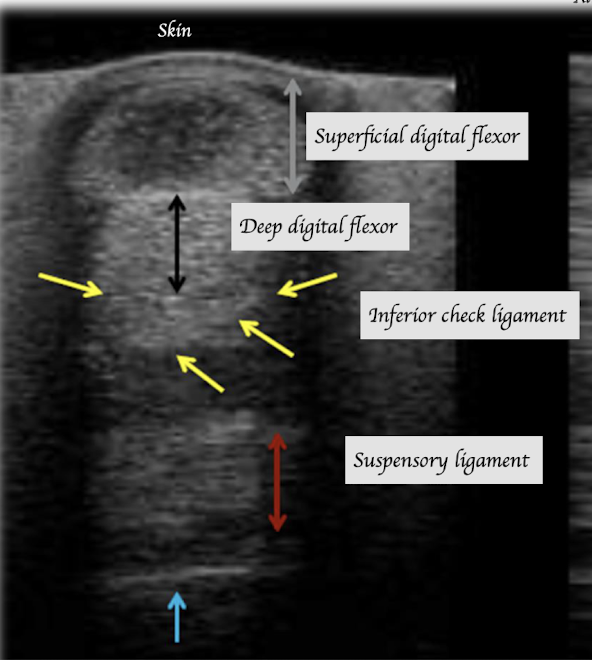
If we perform an ultrasound examination of the distal end of metacarpus in horses, which structures can we visualize?
NO inferior check ligament
What is scutum? Where is the intersesamoidean ligament located in relation to the scutum?
Cartilage shield
Located on top of the intersesamodiean ligament, which sits between the proximal sesamoid bones
Allow smooth passage for DDFT and SDFT
What structure holds the Deep Digital Flexor Tendon (DDFT) and Superficial Digital Flexor Tendon (SDFT) against the bones in the digital region?
Annular ligaments
List out all the annular ligaments in digital region
Proximal annular ligament
Attach around the metacarpo-phalangeal joint
Proximal phalanx annular ligament
Attach at the proximal phalanx
Distal annular ligament
Attach around the distal interphalangeal joint
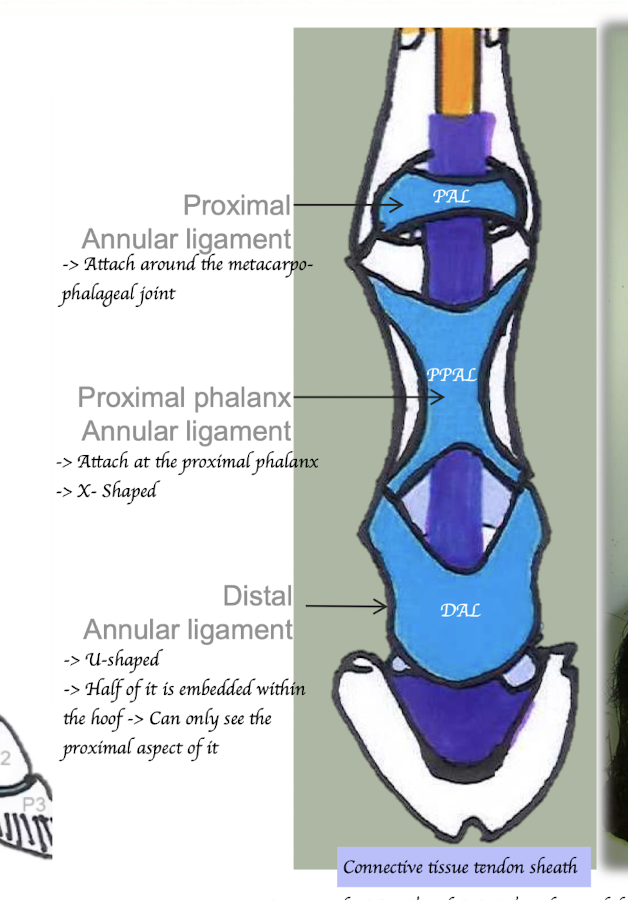
What structure is shared by the SDFT and DDFT and extends distally from the annular ligament?
Tendon sheath
Order of fetlock structures from palmar/plantar to dorsal:
Intersesamoidean ligament → Scutum → DDFT → SDFT → Annular ligament → Tendon sheath
What is the stay apparatus?
Mechanism for passive weight bearing → Horses can stand for extended period of time without using energy
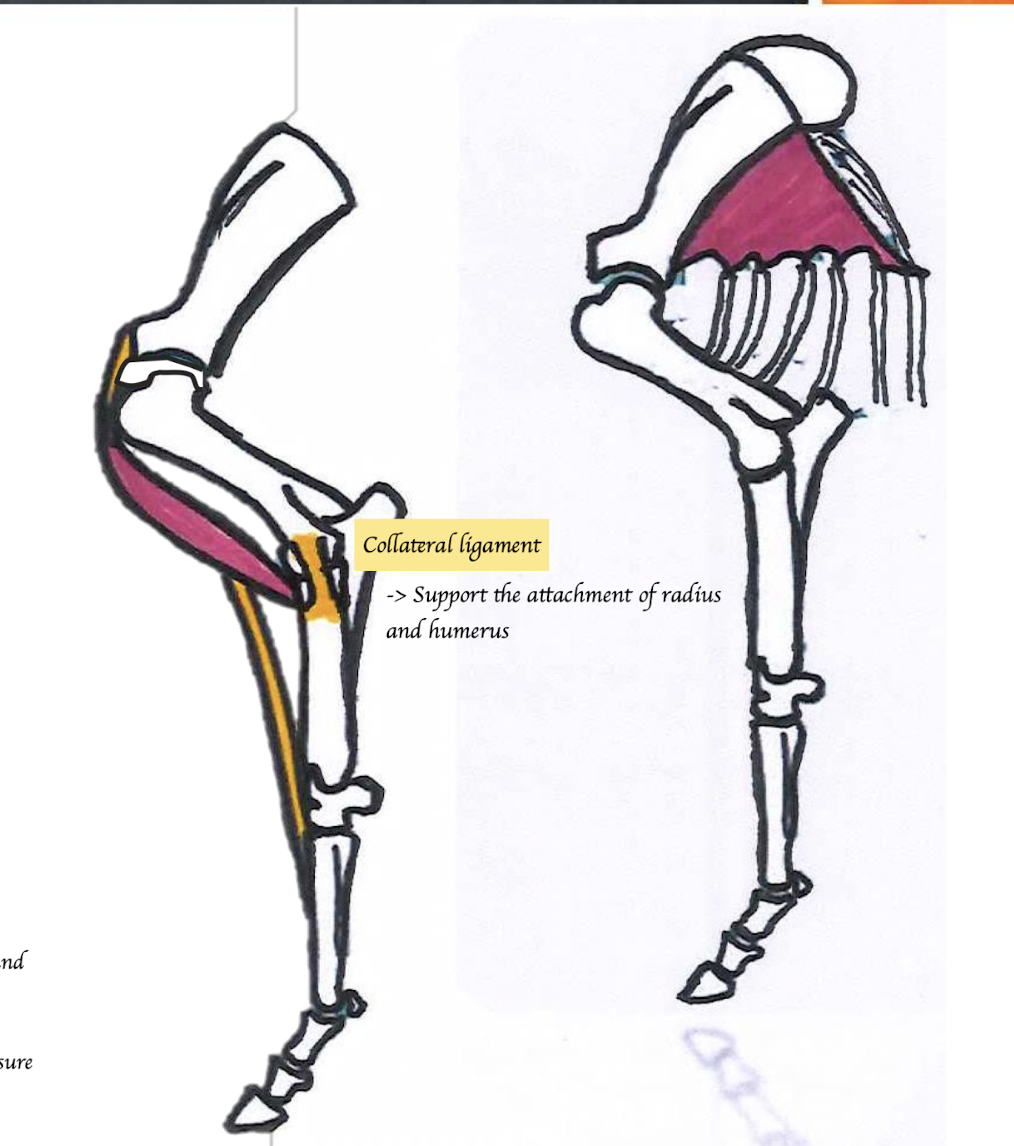
Which structure cooperates in maintaining extension and preventing flexion in the stay apparatus?
Shoulder:
Biceps brachii tendon
Elbow:
Collateral ligament (between humerus and radius and ulna) → Support the attachment of radius and humerus
Carpus:
Lacertus fibrosus
Connect the biceps to the extensor carpi radialis
If one joint is extended, the other joint atomically become extended e.g. shoulder joint is extended, it pulls the carpal joint to be extended
Which structure works to prevent hyperextension of the forelimbs in the stay apparatus?
Carpus
SDFT
Check ligament
Palmar fibrocartilage joint reinforcement
Retinaculum
MCP joint:
Suspensory ligament
Proximal sesamoids
Distal sesamoidean ligament
Common digital extensor
MCP, PIP and DIP joint:
DDFT, SDFT
Check ligament
Annular ligaments
Describe the arterial supply in horses.
Similar to dog
Subclavian artery → Axillary artery → Brachial artery → Median artery
Is the nerve supply of horses similar to dogs?
Same beaches as dog
Same motor function as dog
BUT different sensory areas
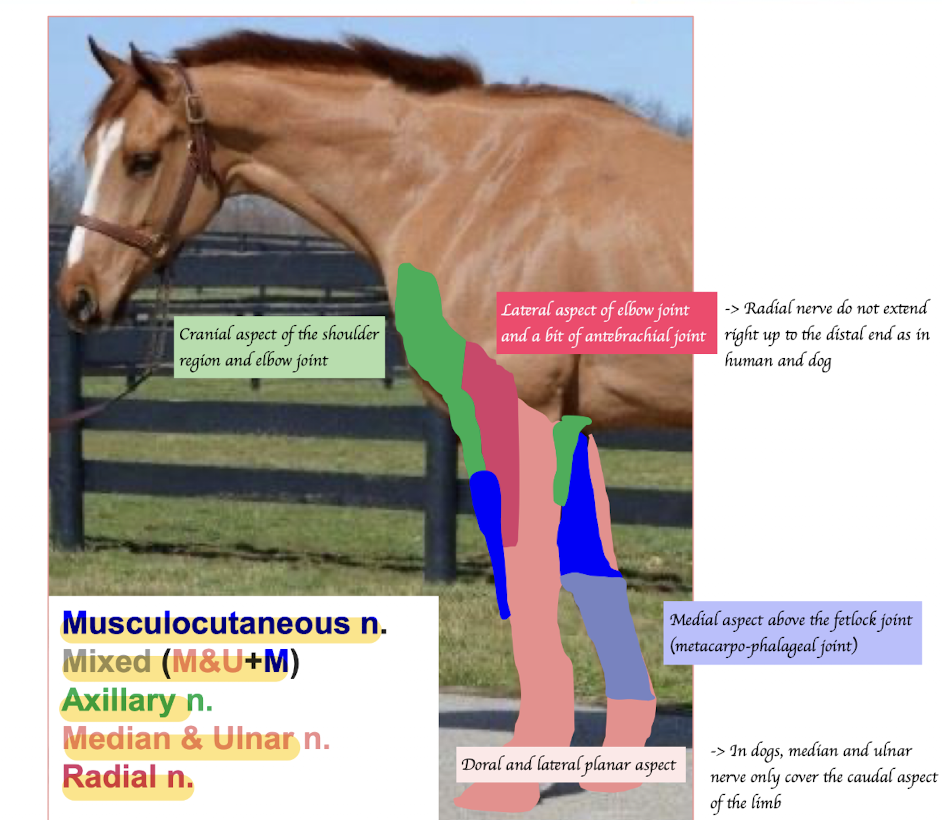
The brachial plexus in horses has the same motor functions but supplies different sensory areas. Describe which regions are innervated by which nerves.
Musculocutaneous nerve: Medial aspect of antebrachium
Axillary nerve: Cranial aspect of the shoulder region and lateral aspect of elbow joint
Medial and ulnar nerve: Palmar aspect of carpus, metacarpus and digits
Radial: Lateral aspect of elbow joint + a bit of antebrachial joint
Median and ulnar nerves combine with musculocutaneous nerve → Supply the pastern and foot + medial aspect of metacarpal
Which two major branches that the median and ulnar nerves that branches off? What are their functions?
Medial and ulnar nerves combines then branches off as …
Palmar metacarpal nerve (Yellow)
Paired (Medial and lateral)
Runs between MC3 and splint bones (MC2 + MC4)
Emerges at the distal end of splint bone
Supply the dorsal aspect of P1
Palmar nerves
Paired (Medial and lateral)
Runs between suspensory ligament and SDFT/DDFT → Cross abaxial aspect of the two proximal sesamoids → Become palmar digital nerves → Divides into dorsal and palmar branches of palmar digital nerves → Supplies hoof components
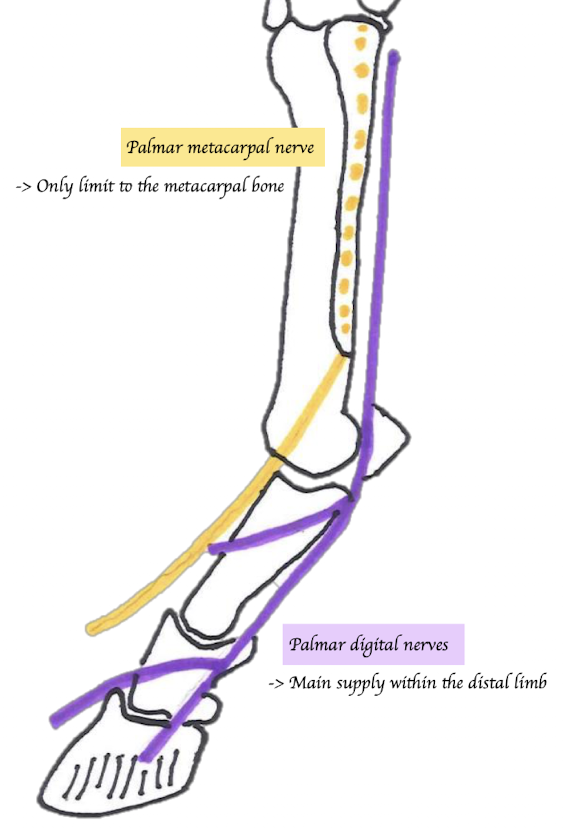
What structures does the palmar nerve usually accompany?
The palmar nerve usually runs with the palmar artery and palmar vein, forming the neurovascular bundle
List the three major types of nerve blocks of the hoof.
Palmar metacarpal nerve block = 4 point block
Abaxial sesamoid nerve block
Palmar digital nerve block
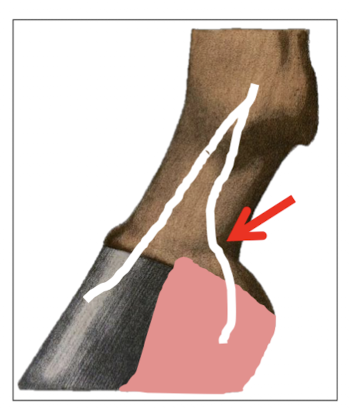
Describe the palmar digital nerve block in detail.
Aim to block the palmar branch of the palmar digital nerves
= Caudal ½ foot
Locations:
1cm above coronary band
2 points of injections (Medial and lateral injection)
Medial palmar branch of palmar digital nerve
Lateral palmar branch of palmar digital nerve
Check for function of distal phalanx, navicular bone and distal sesamoid
Describe the abaxial sesamoid nerve block in detail.
Aim to block the palmar digital nerve before it branching off dorsal and palmar branches
= Block the entire foot (Includes the dorsal branches of the palmar digital arteries)
2 points of injections
Medial and lateral palmar digital nerves
Location:
Right beside the abaxial aspect of sesamoids = Around the fetlock joint
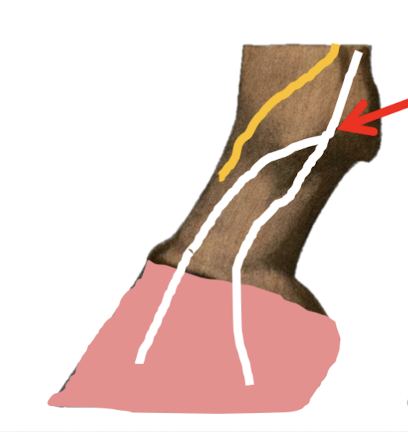
Describe the palmar metacarpal nerve block = 4 point nerve block in detail.
Aim to block and palmar metacarpal nerve and the palmar digital nerve
= Block the entire digit (P1, P2 and P3)
4 points of injections
Medial palmar metacarpal nerve
Lateral palmar metacarpal nerve
Medial palmar nerve
Lateral palmar nerve
Location:
Distal end of the two splint bones (Named button)