BIS 2C Lab Practical
1/277
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
278 Terms
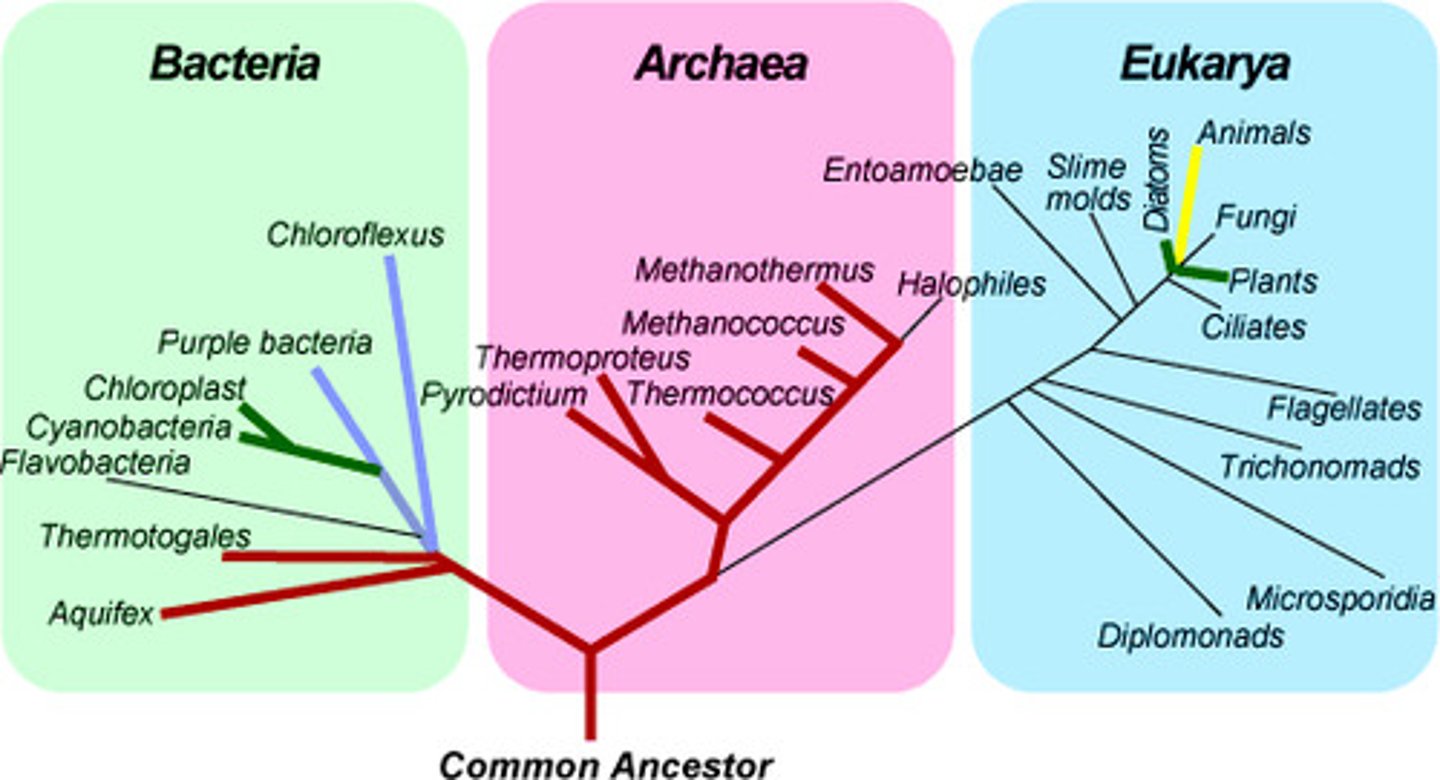
rooted phylogenetic tree
tree that has a root node; more rooted trees than unrooted statistically; specify evolutionary relationships with completeness
unrooted phylogenetic tree
tree that lacks root node; helpful because there are less unrooted trees than rooted ones statistically; does not entirely specify evolutionary relationships, but adds constraints
sister group
pair of taxa originating from same lineage split; most closely related; arise at same time

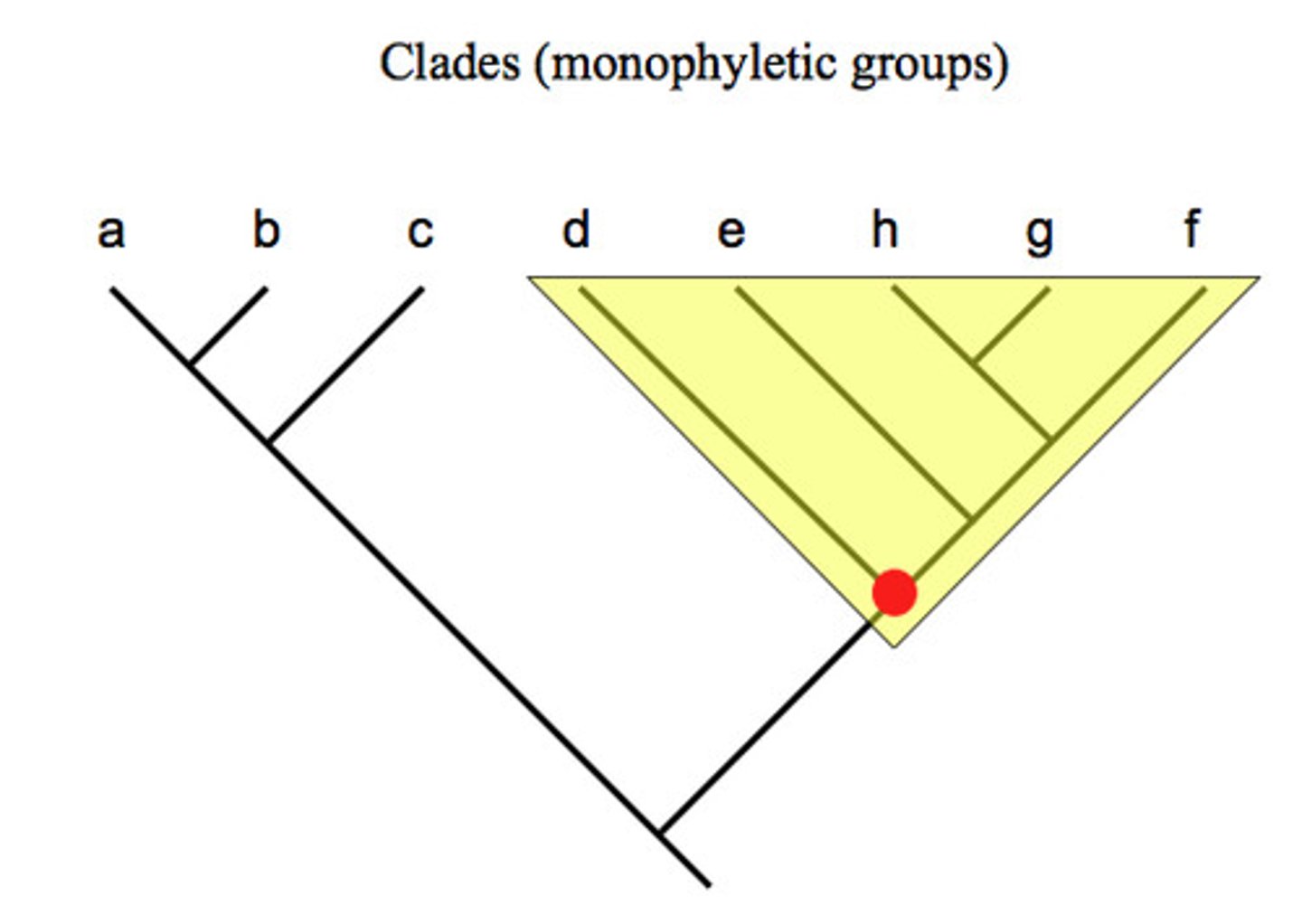
clade
synonym for monophyletic group
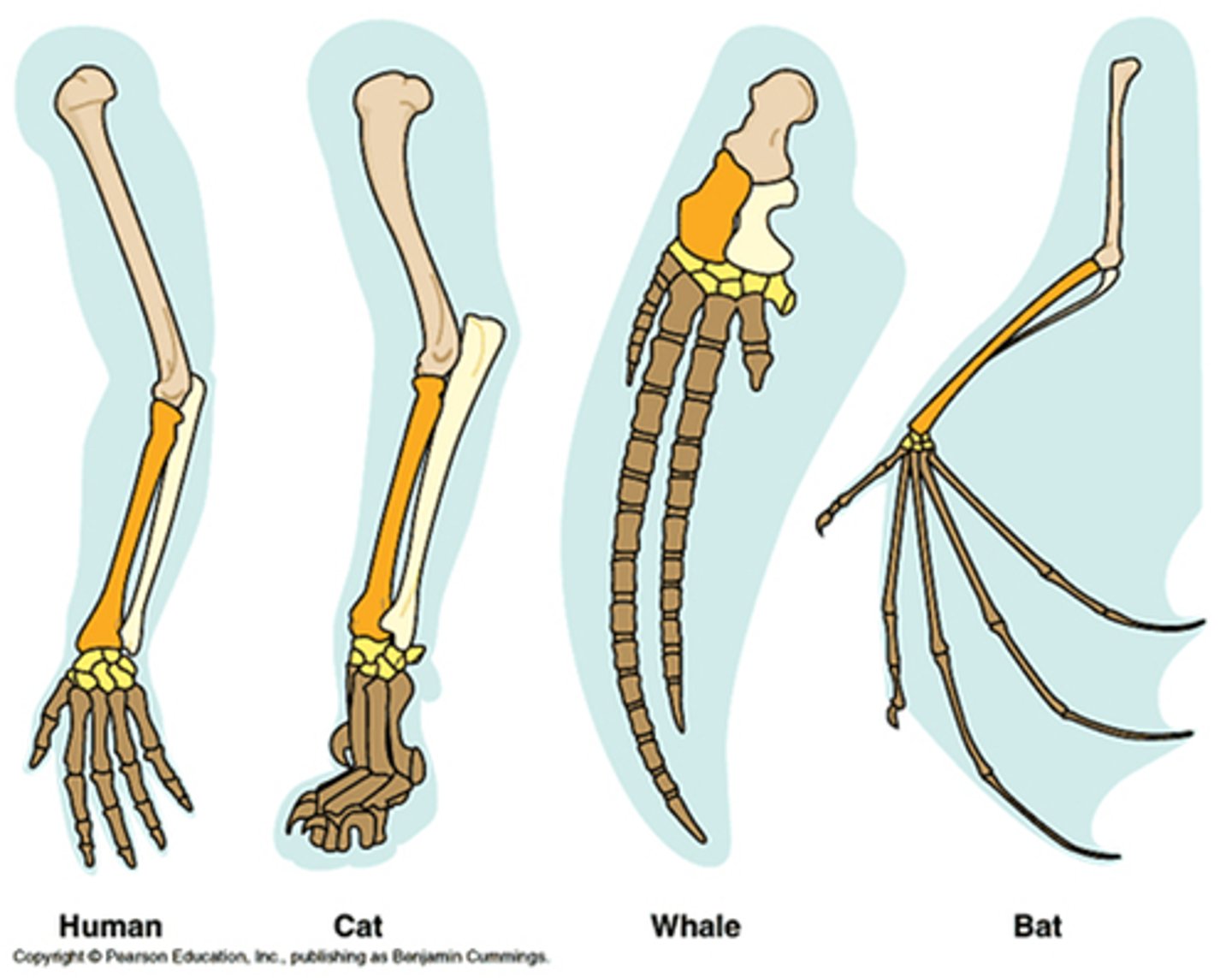
homology
Similarity in characteristics resulting from a shared ancestry.
homoplasy
similar characters caused by convergent evolution, not shared ancestry
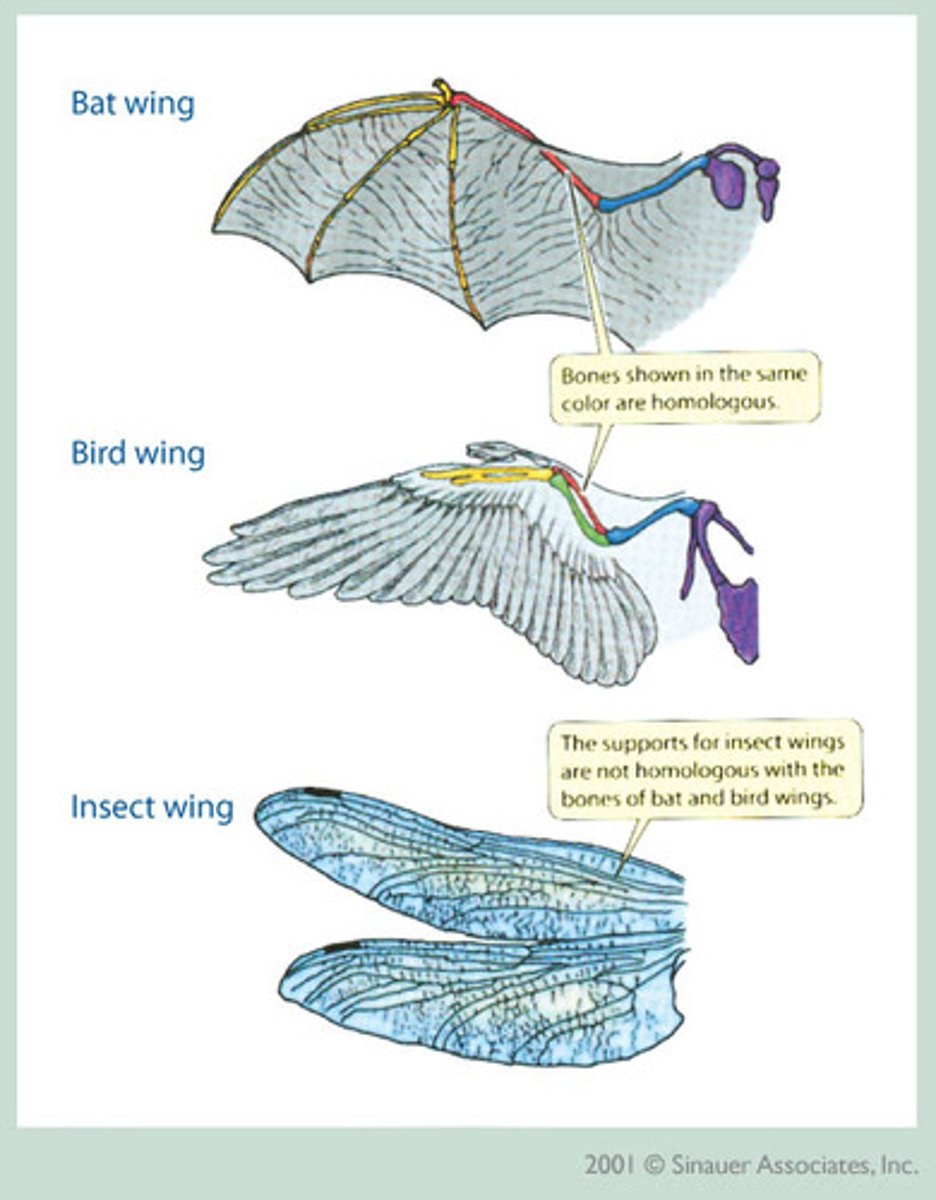
convergent evolution
Process by which unrelated organisms independently evolve similarities when adapting to similar environments
outgroup
at least one taxa that is as closely related as possible to ingroup species without actually being part of the ingroup; used as a reference and to help tree rooting
congruence
characters support hypothesized tree
conflict
characcters do not support hypothesized tree

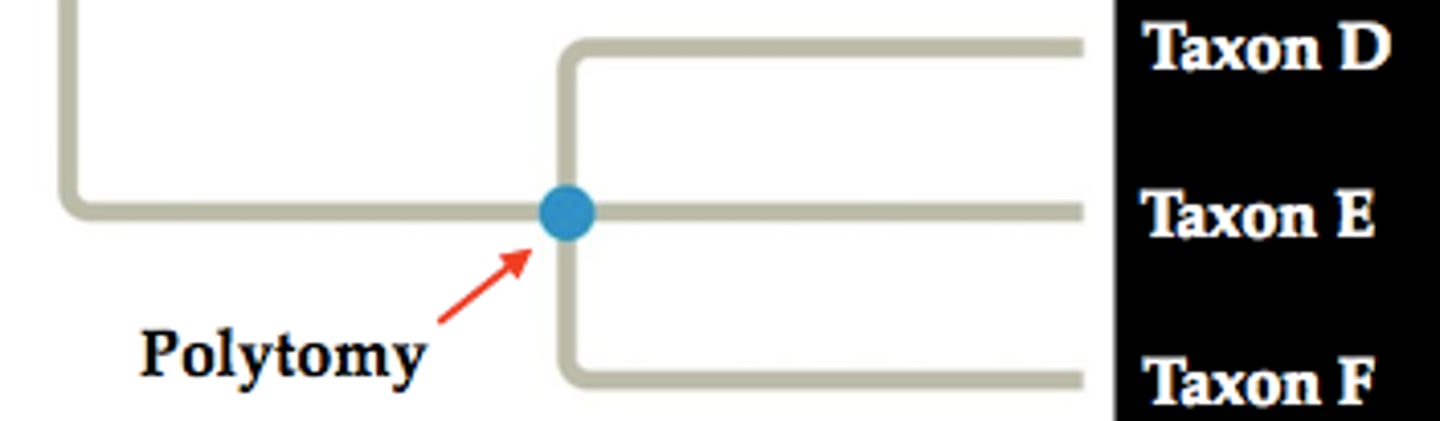
polytomy
a branch point from which more than two descendant groups emerge
soft = b/c missing data
hard = fast speciation, have data but unlikely to be resolved
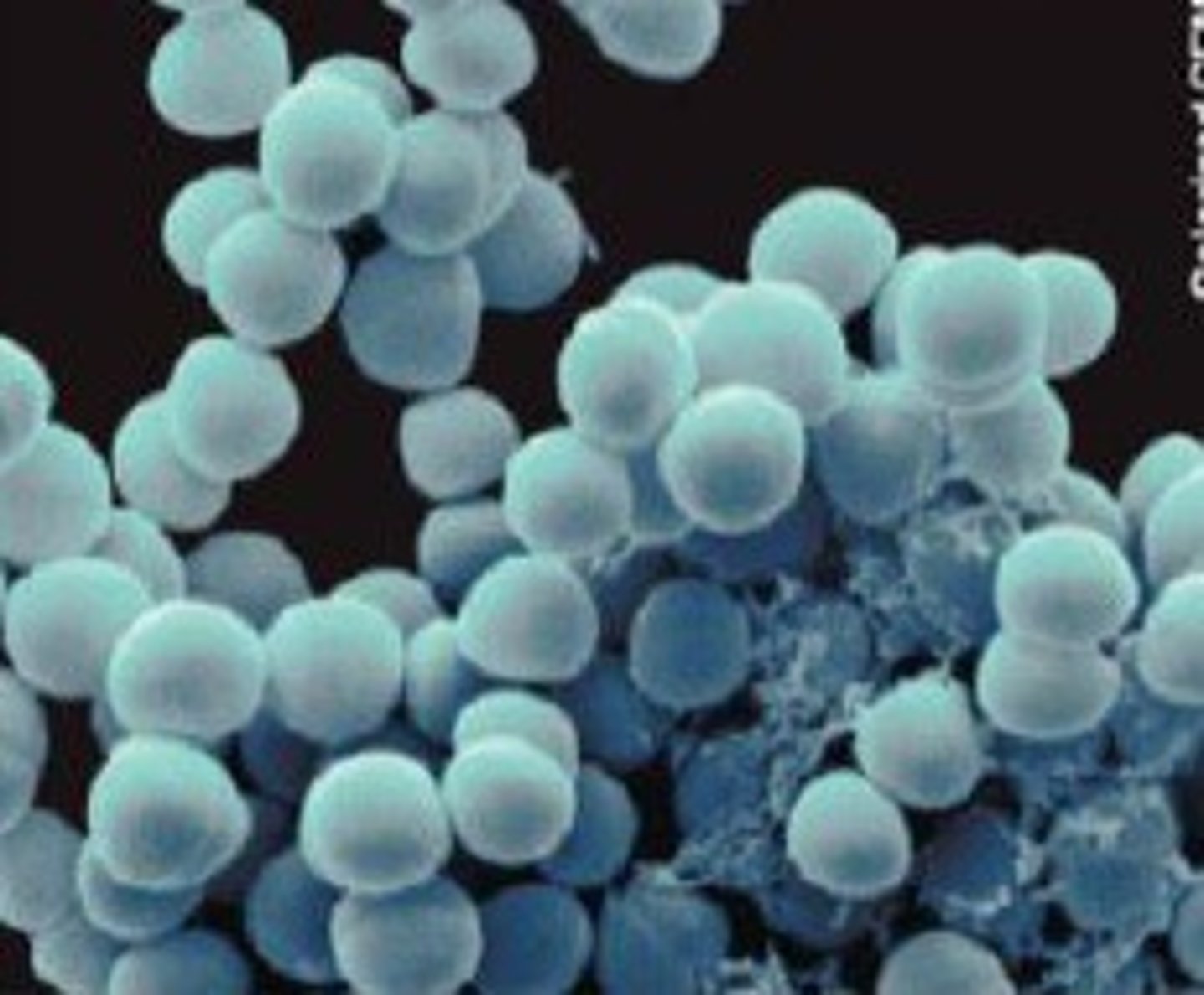
coccus
A spherical bacterium.
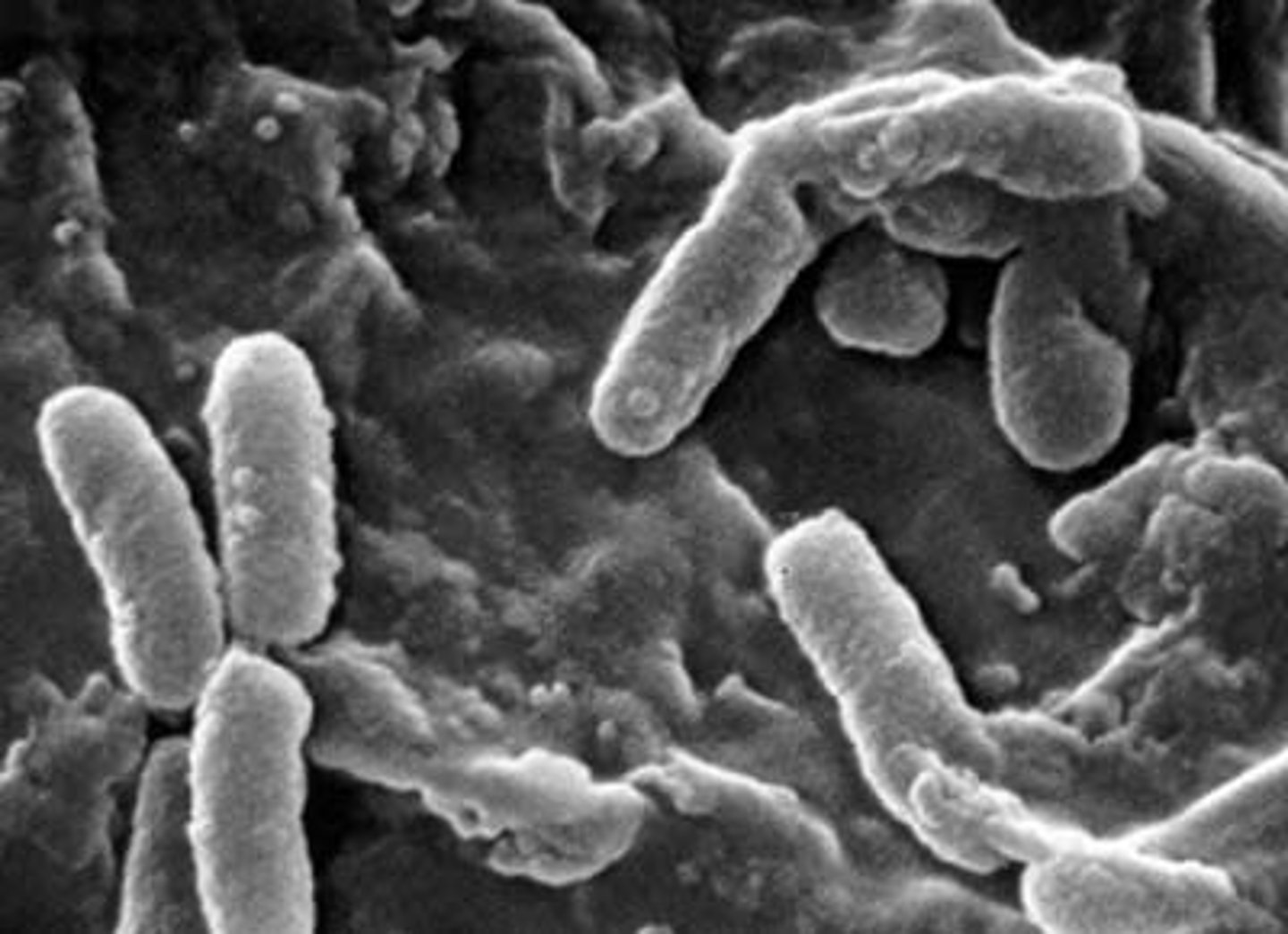
bacillus
rod-shaped bacterium
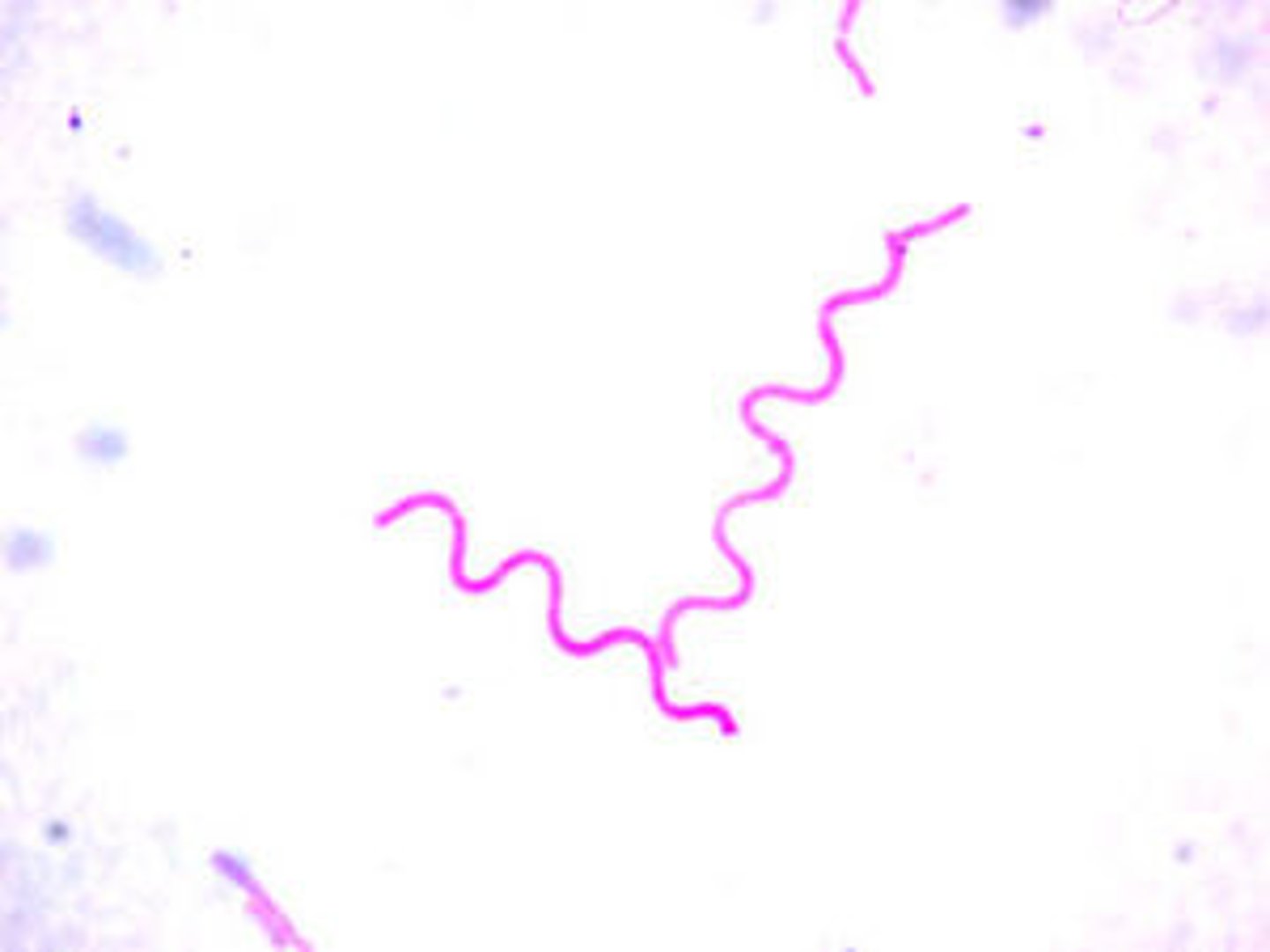
helical
elongate spiral bacterium
lateral gene transfer
unidirectional sharing of small portions of genomes between bacteria that product via binary fission. Can create big effects from small, non-sexual transfers.
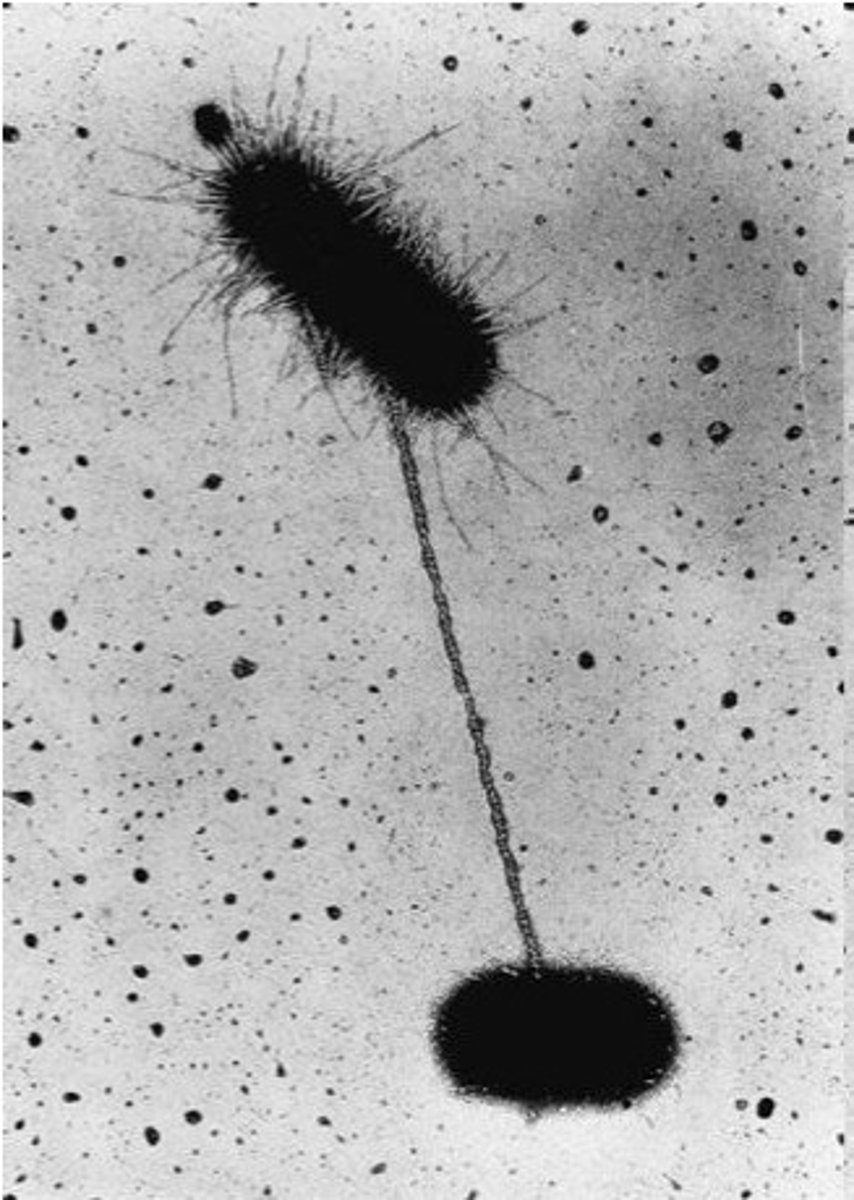
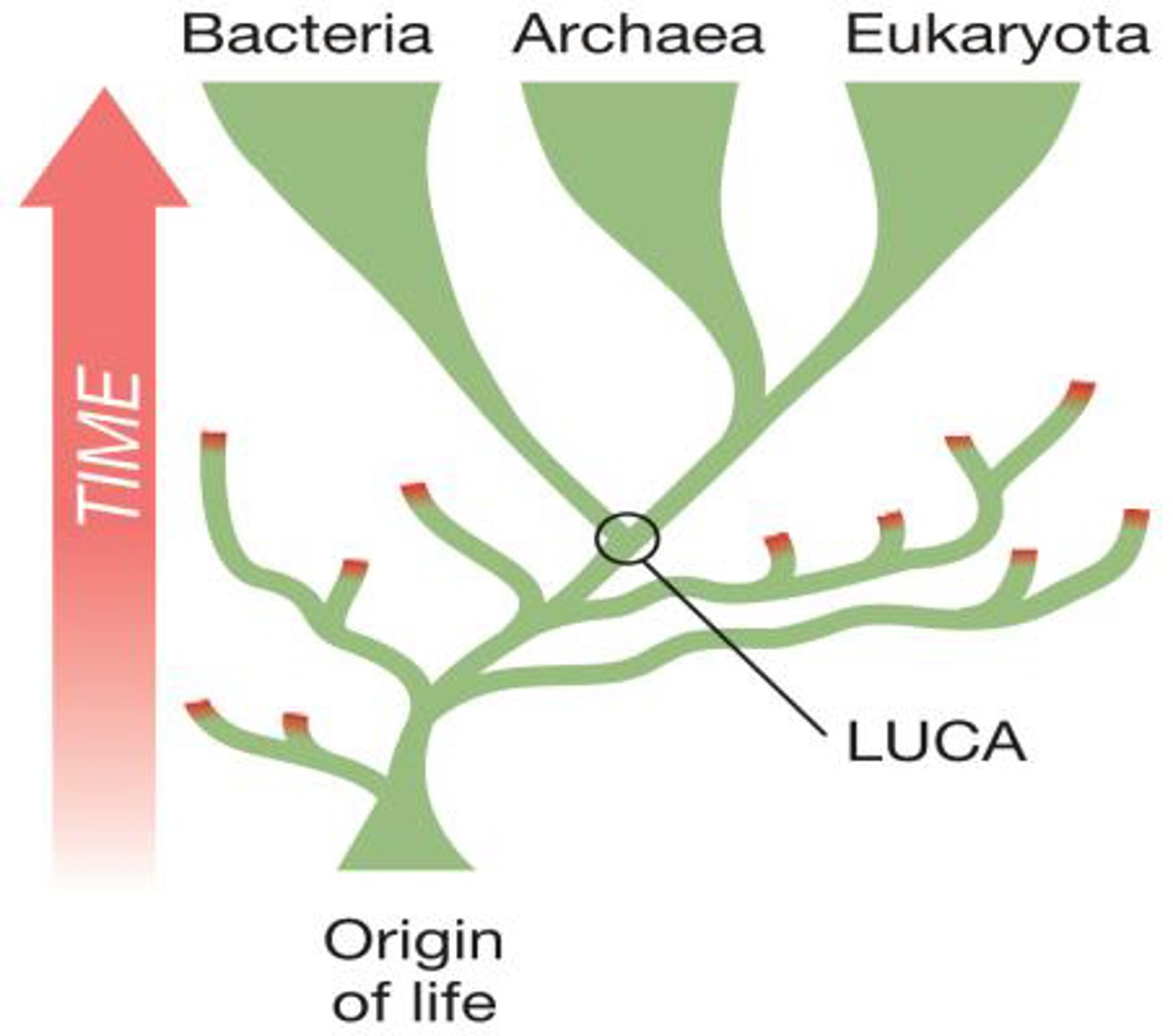
LUCA
Last Universal Common Ancestor. The shared ancestor that all life diverged from
microbiome
all of the microorganisms that live in a particular environment, such as a human body

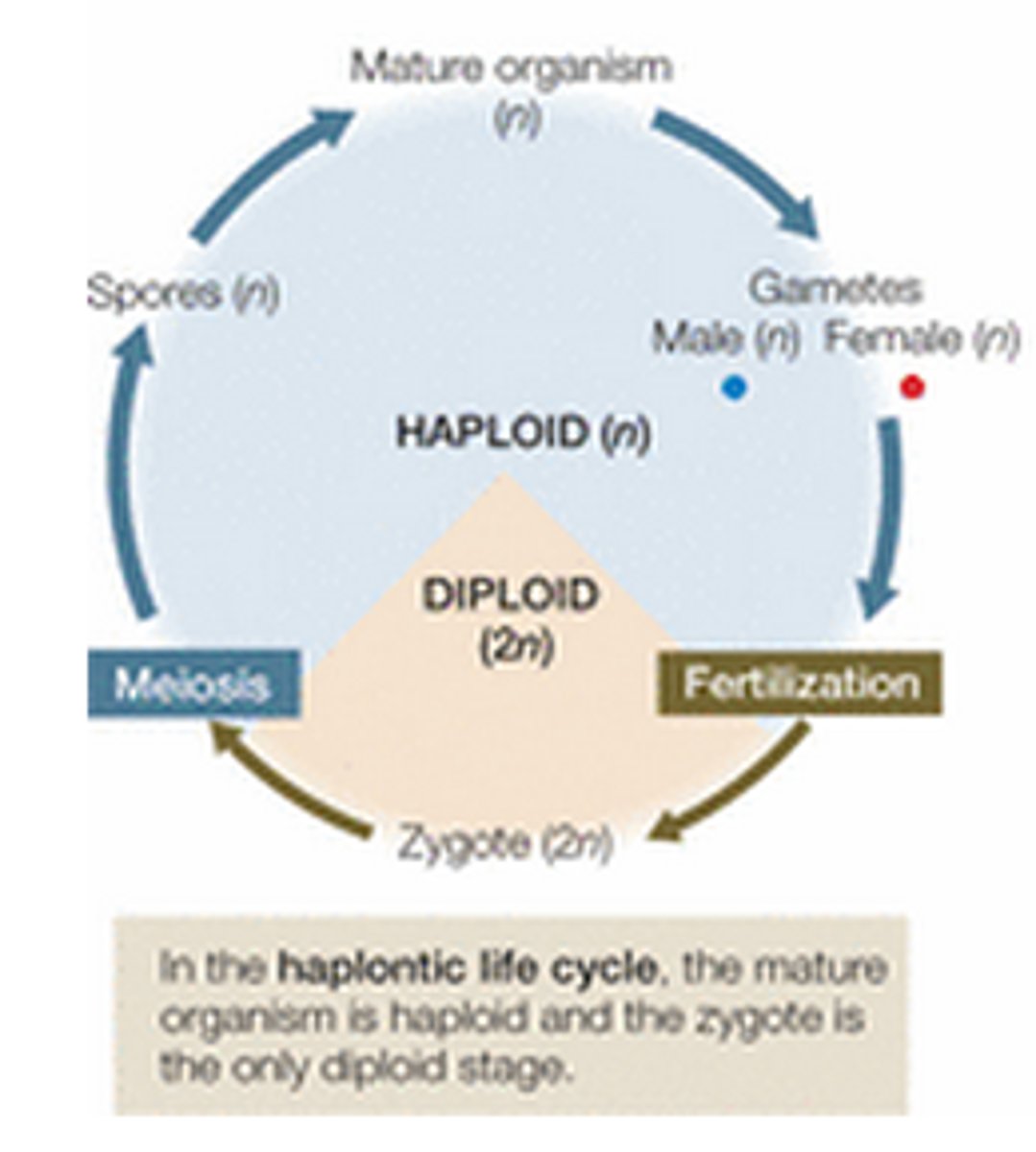
haplontic (n)
describes a life cycle in which the haploid stage is the dominant stage
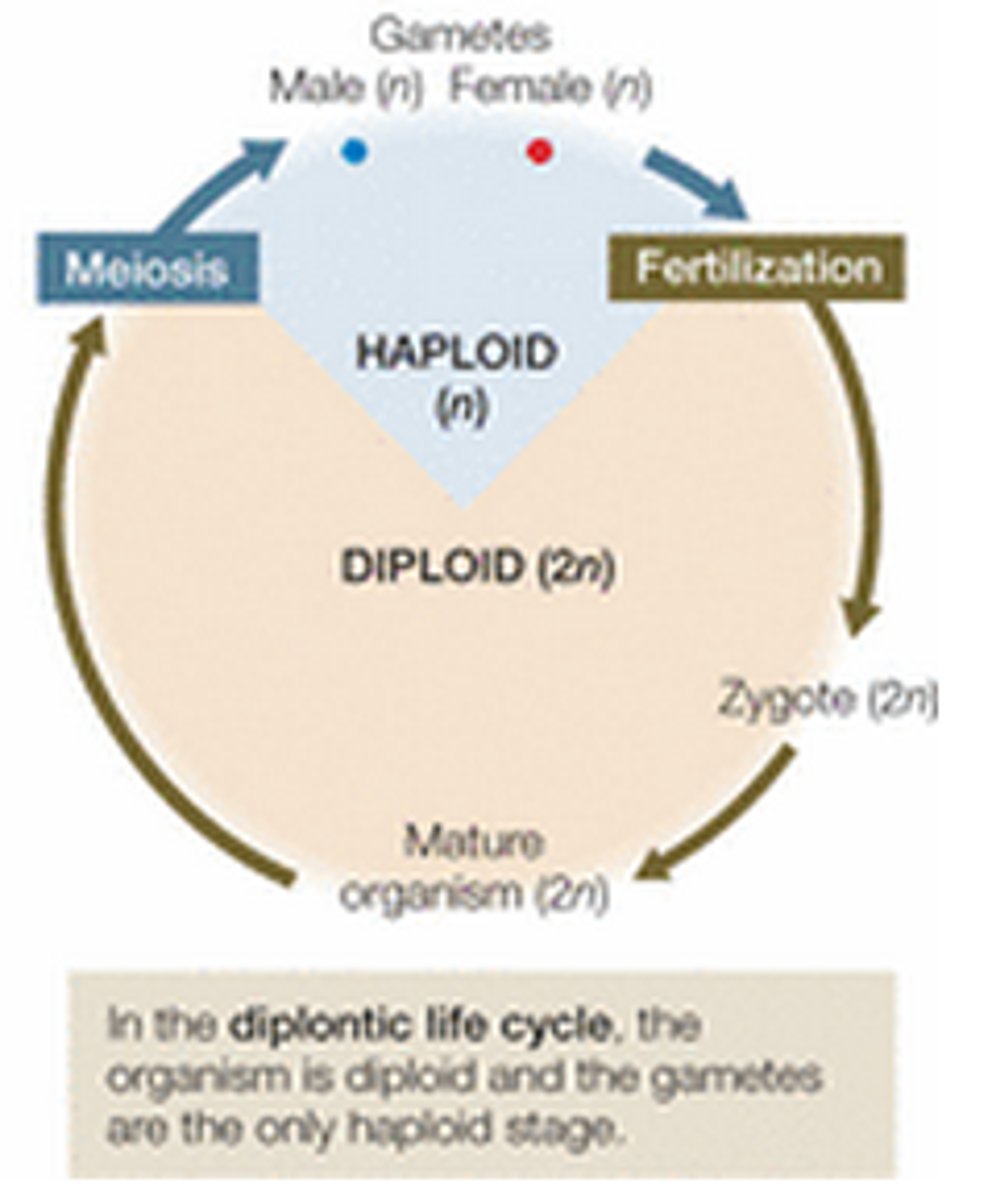
diplontic (2n)
describes a life cycle in which the diploid stage is the dominant stage
alternation of generations
the alternation between the haploid gametophyte and the diploid sporophyte in a plant's life cycle
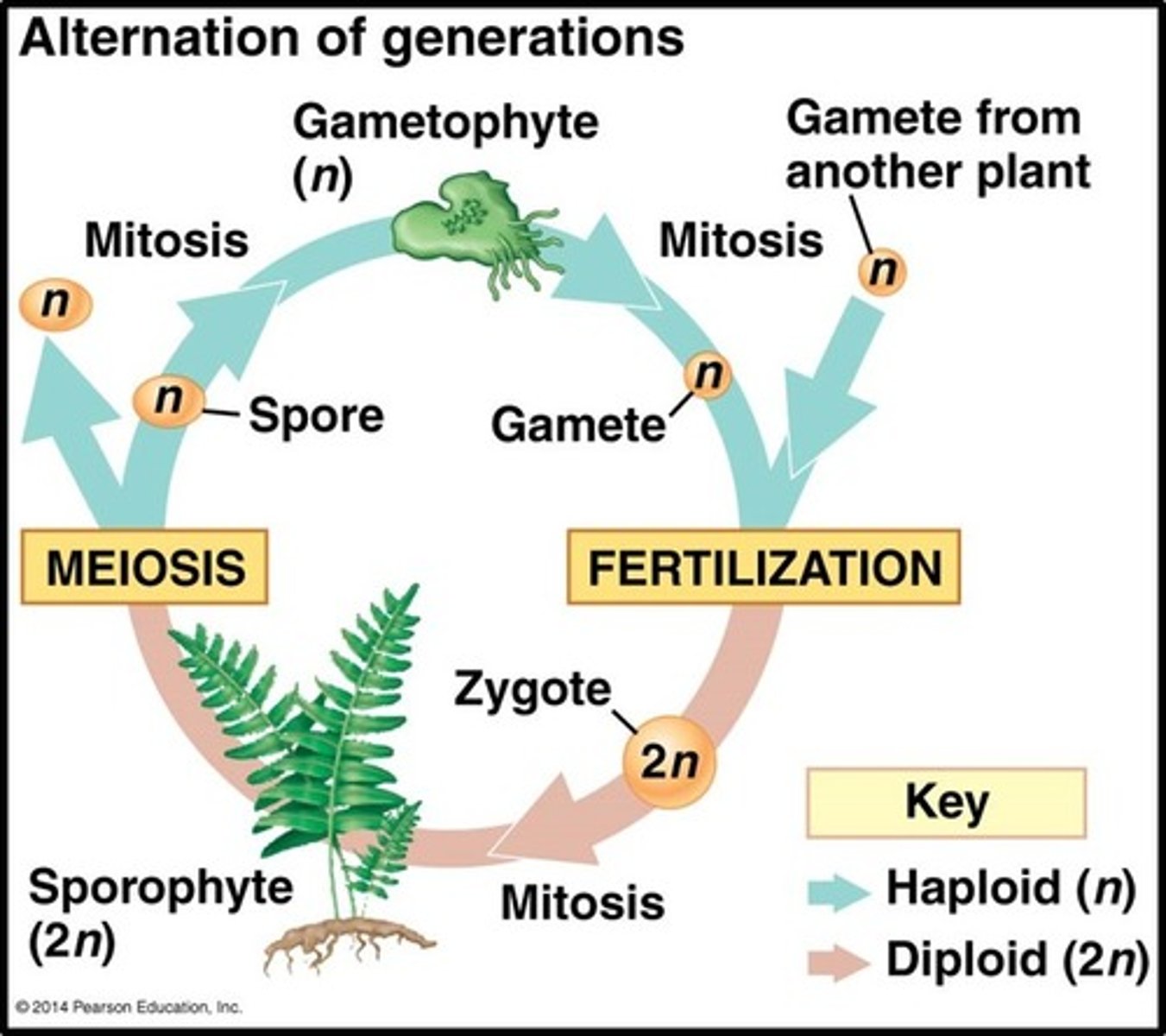
gametophyte
Haploid, or gamete-producing, phase of an organism
sporophyte
Diploid, or spore-producing, phase of an organism

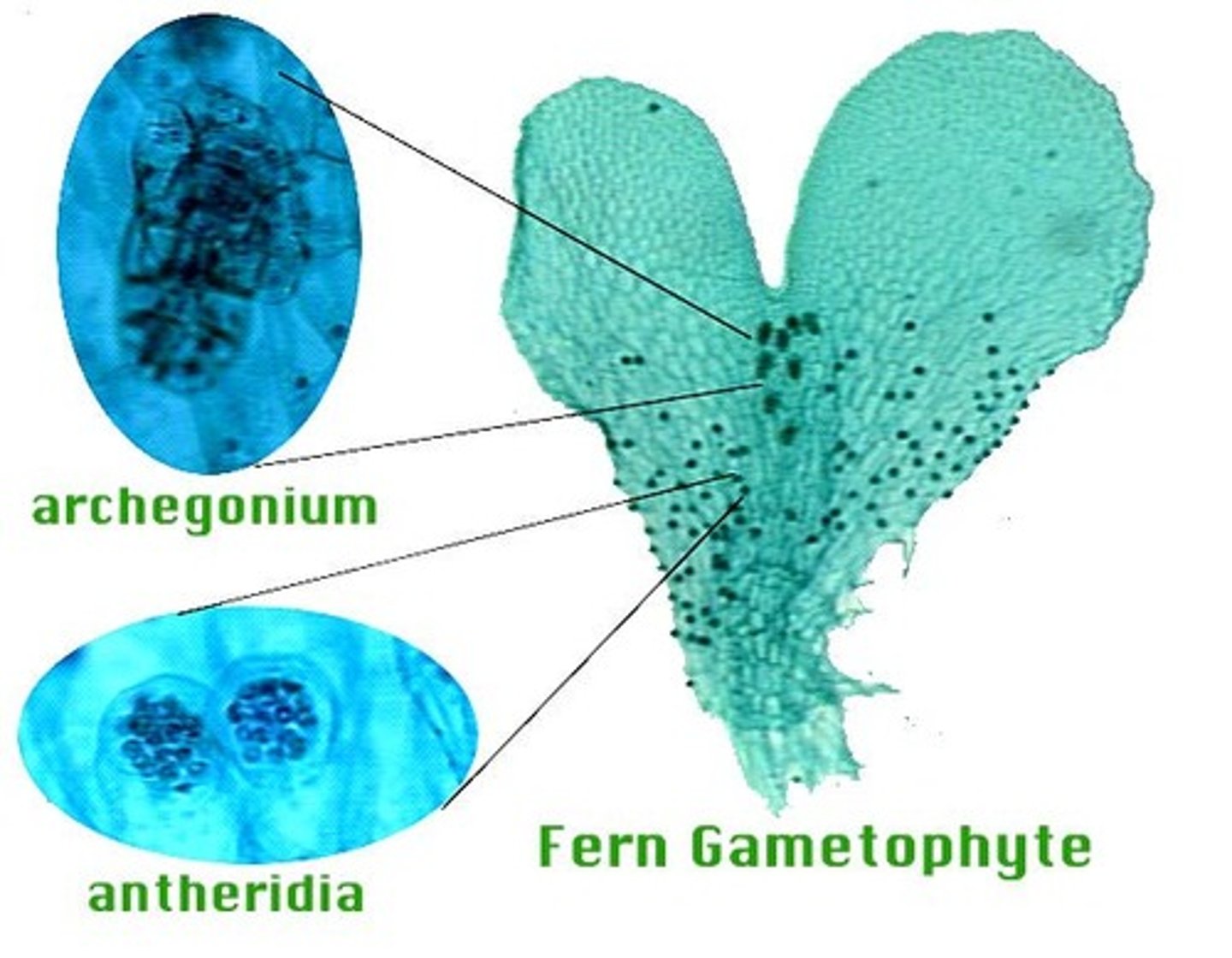
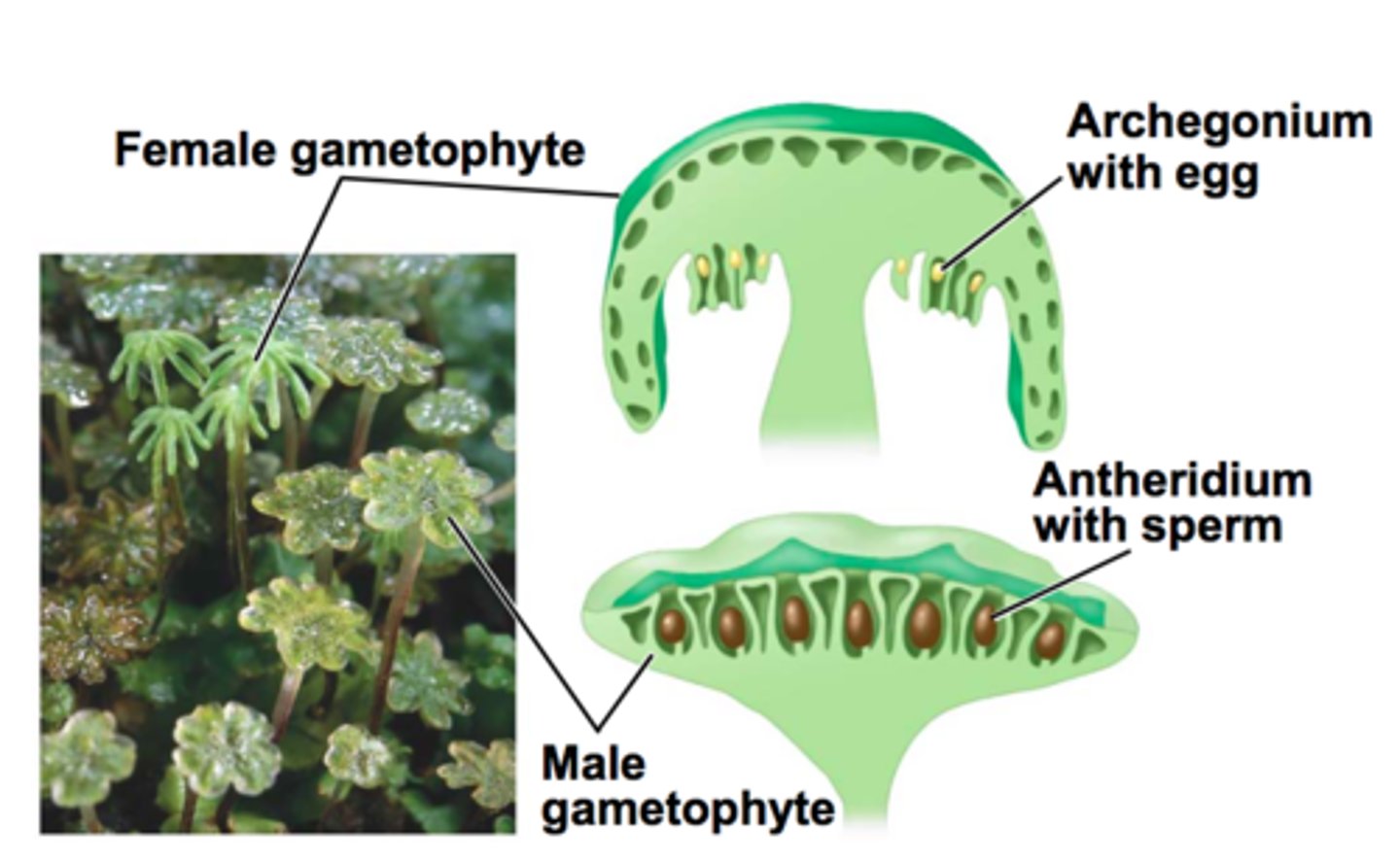
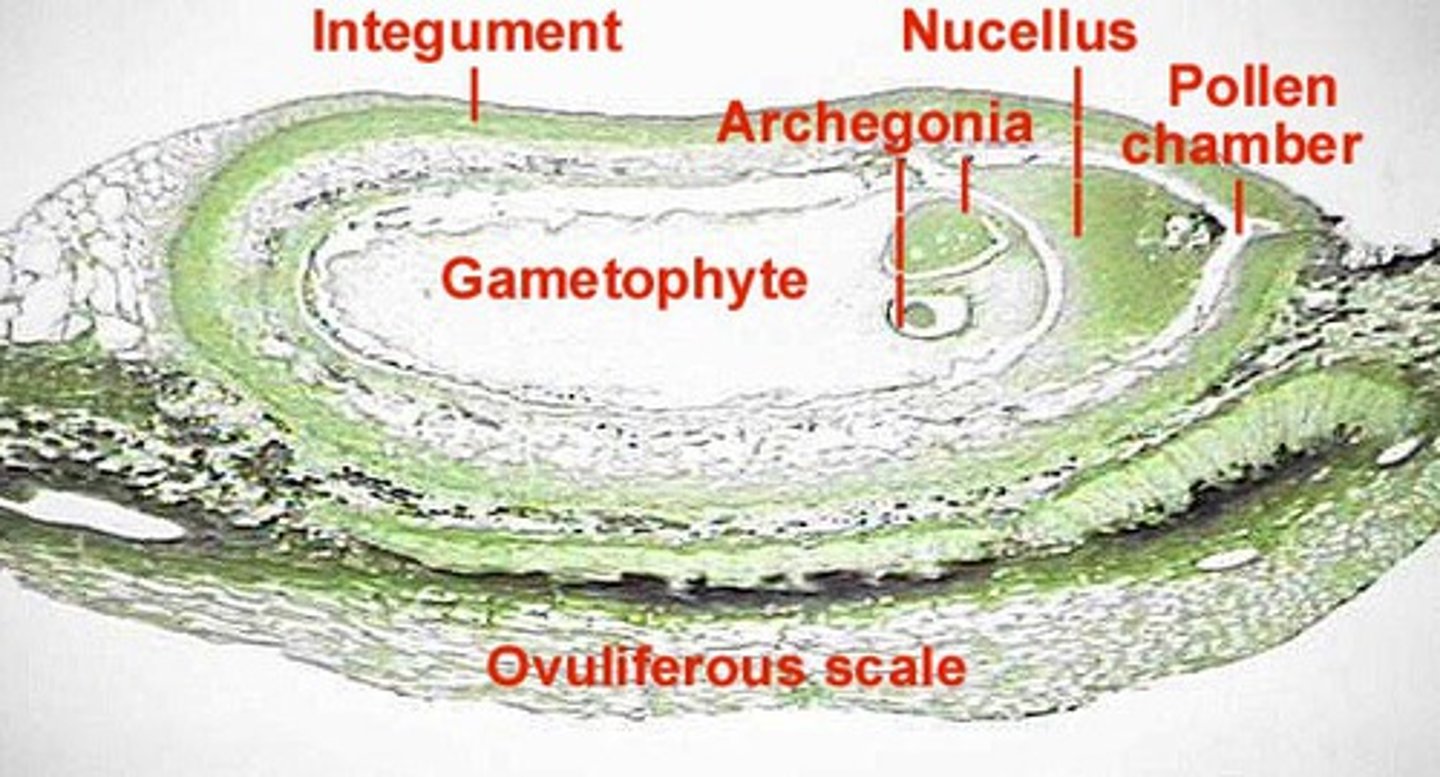
archegonia
female gametangia

antheridia
male gametangia

gametangia
A reproductive organ that houses and protects the gametes of a plant
sporangium
spore capsule in which haploid spores are produced by meiosis
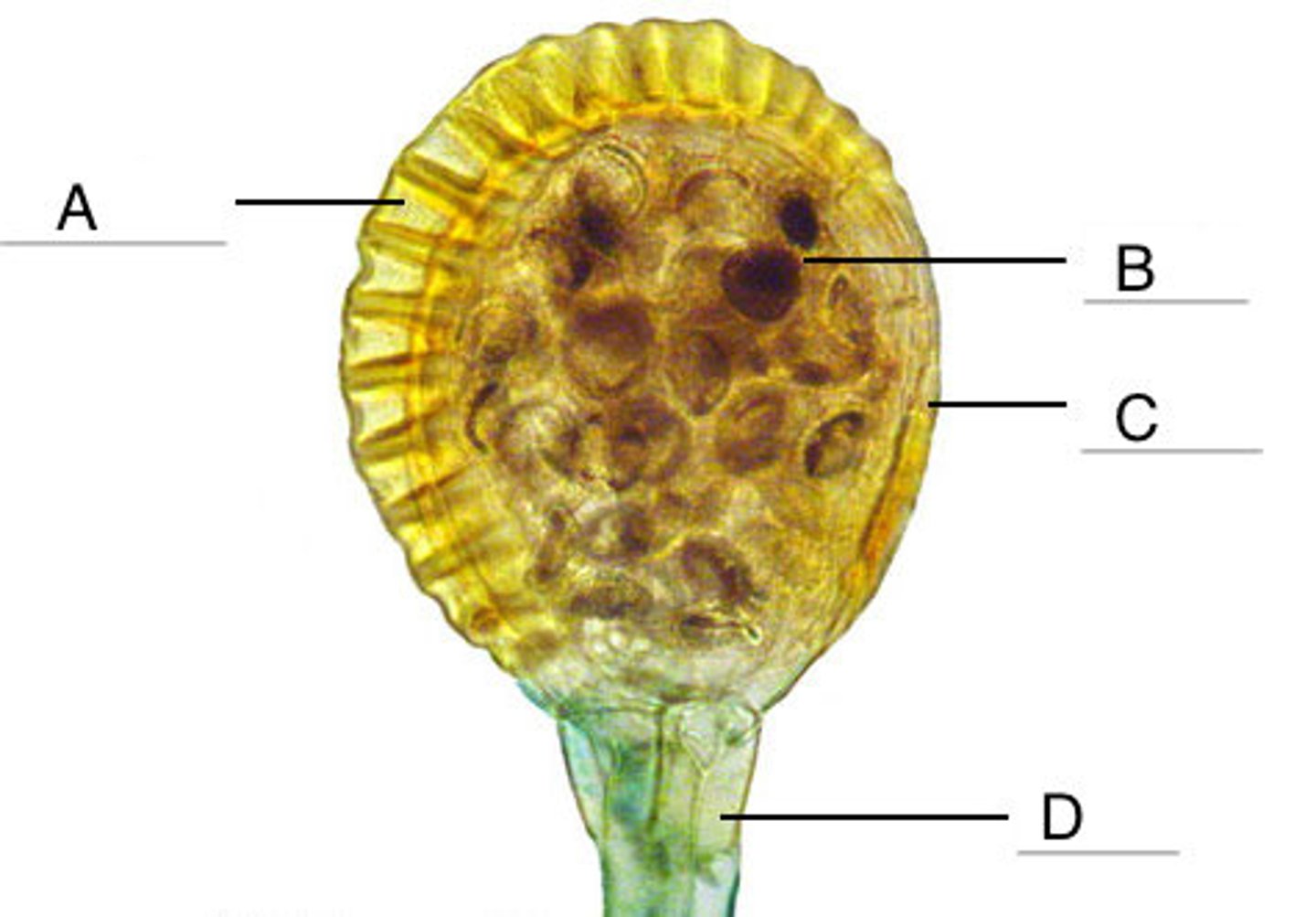
spore
A reproductive cell with a hard, protective coating sporopollenin. Haploid
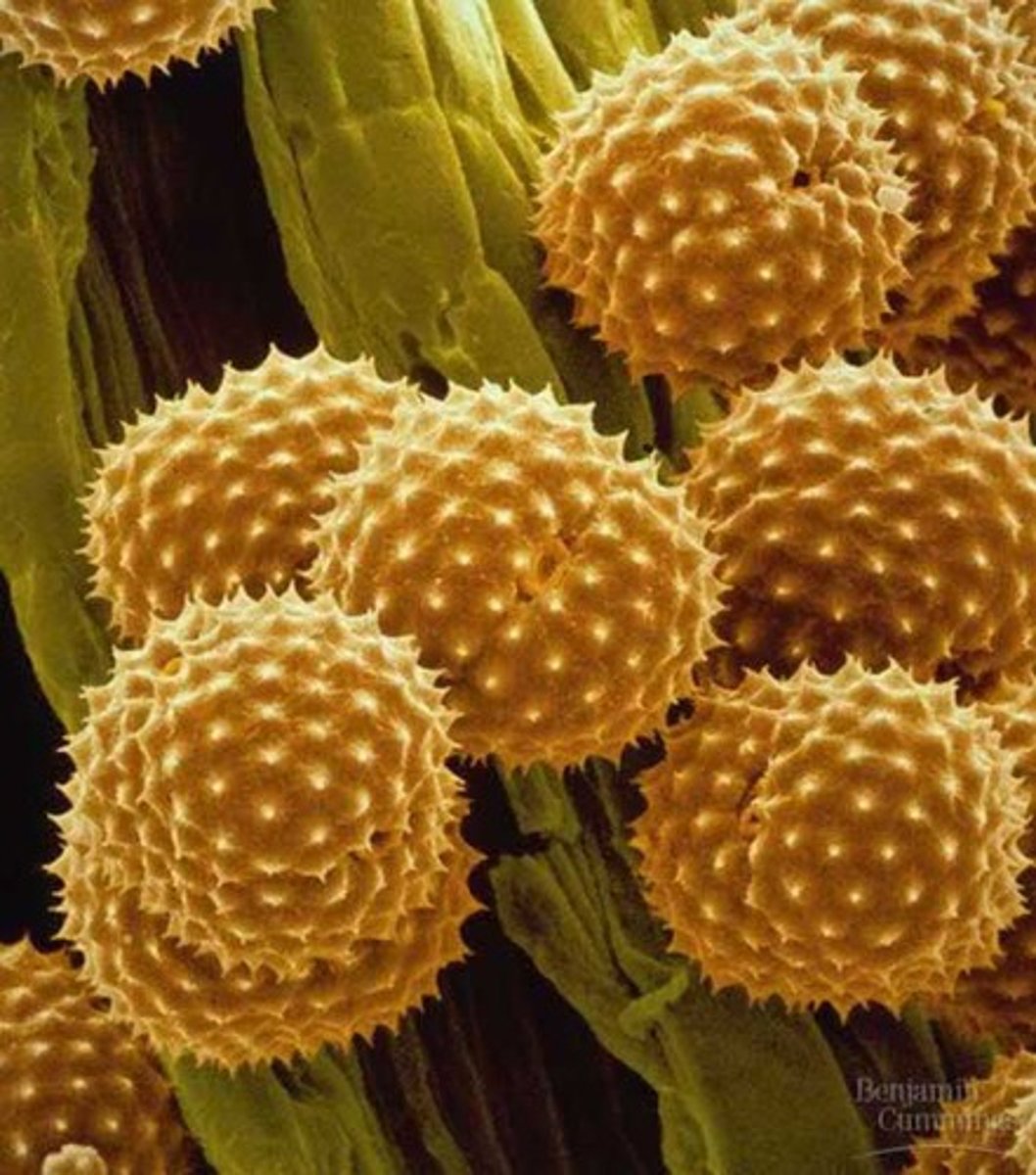
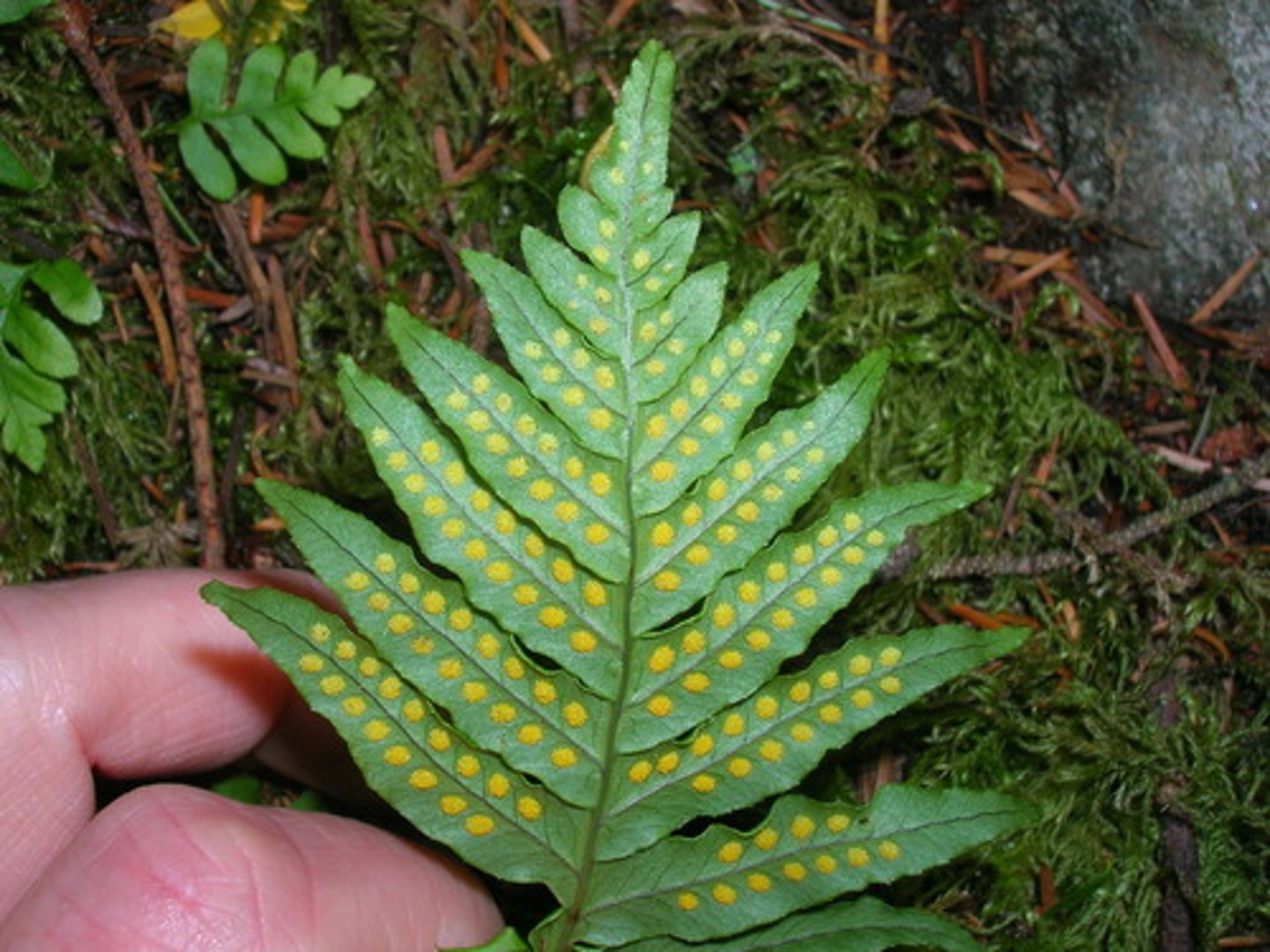
sori
raised spots located on the underside of sporophyte ferns, clusters of sporangia

vascular tissue
Plant tissue consisting of cells joined into tubes that transport water and nutrients throughout the plant body.
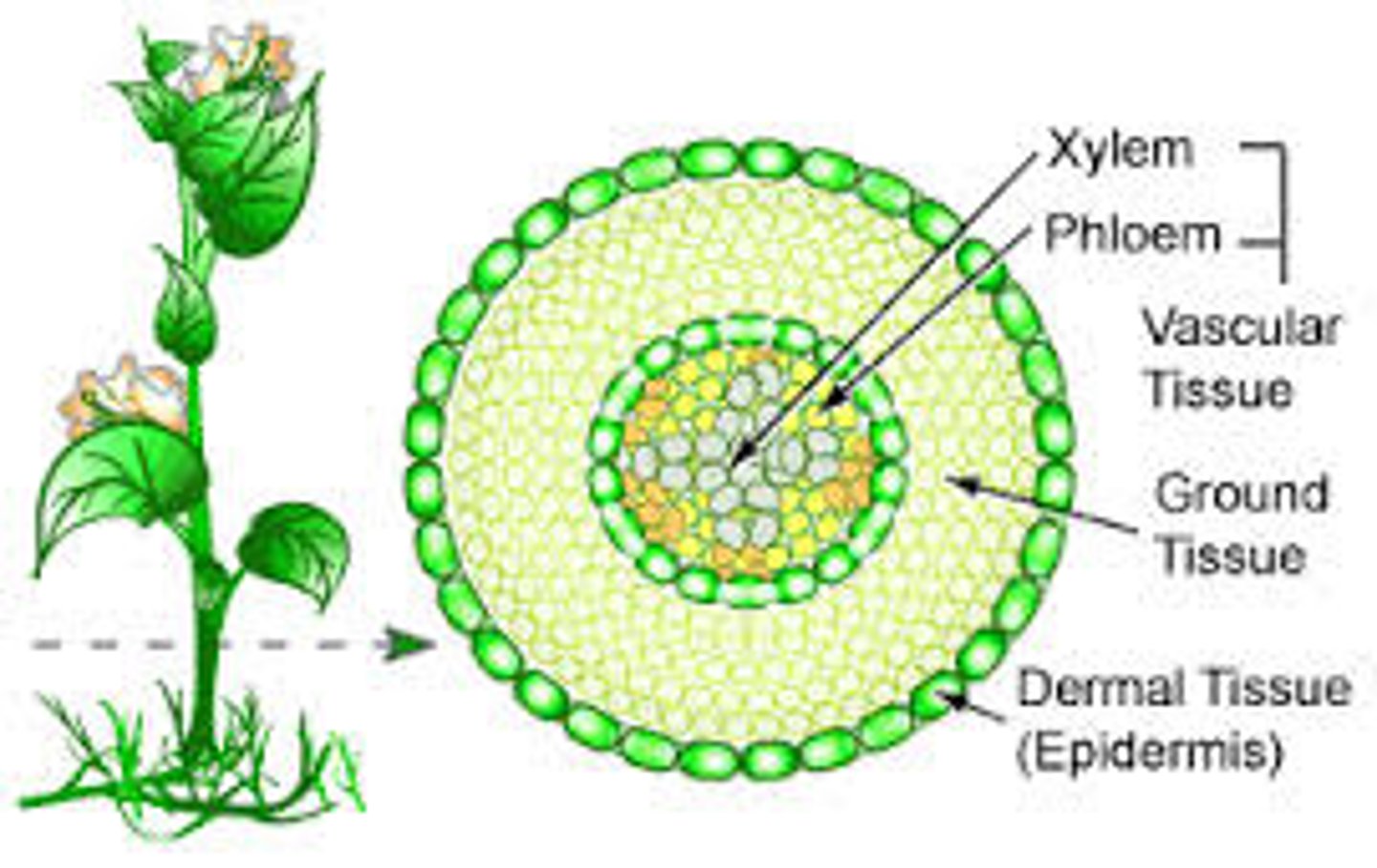
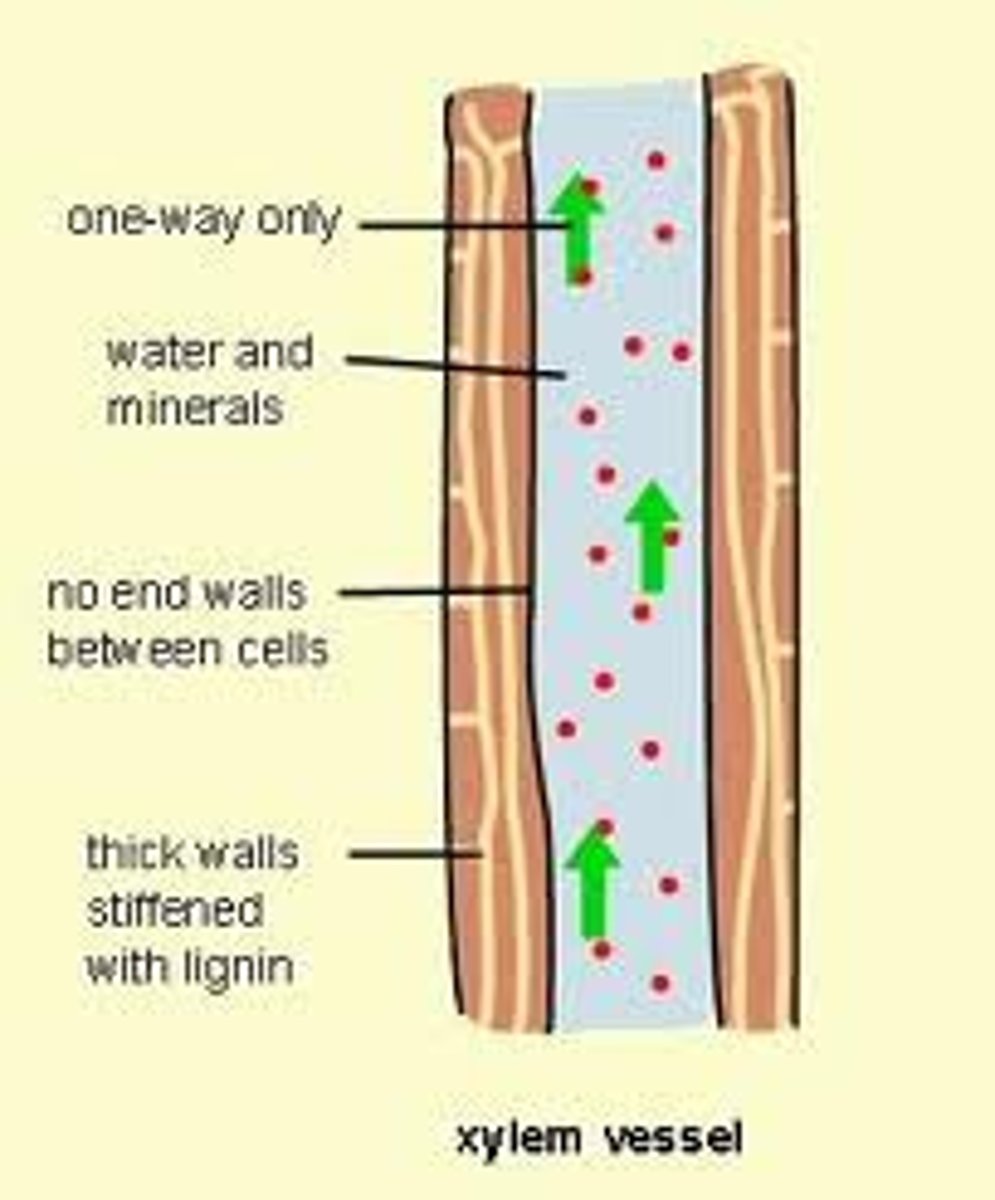
xylem
vascular tissue that carries water upward from the roots to every part of a plant. In a tree, makes up wood
pholem
the vascular tissue in plants that conducts sugars and other metabolic products downward from the leaves. Becomes bark in trees

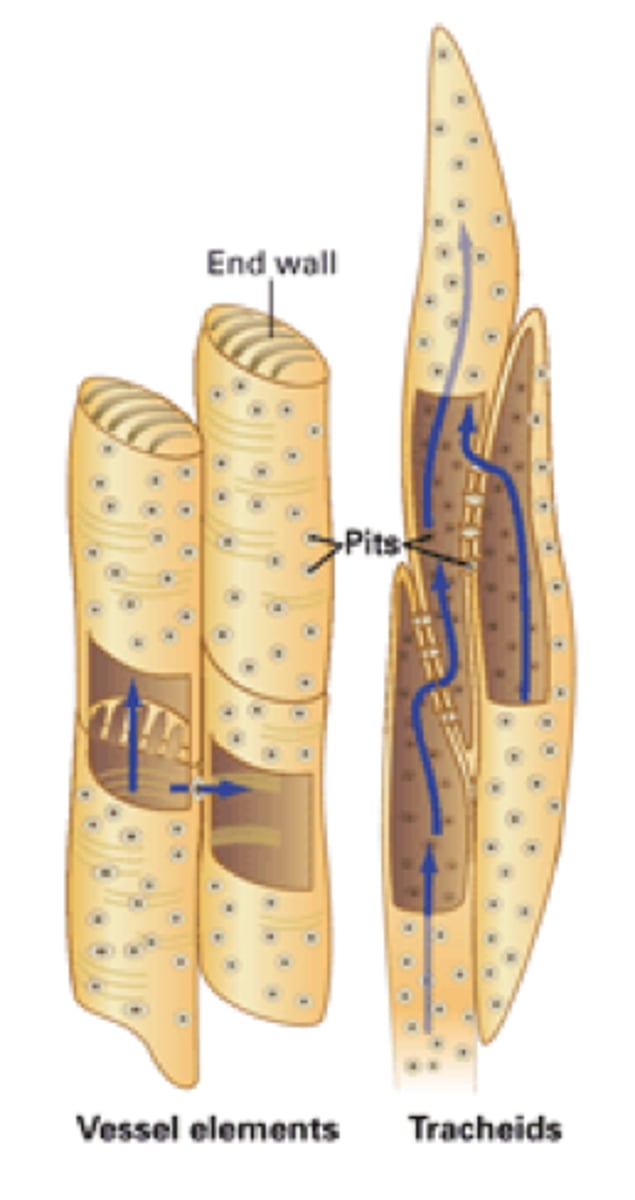
tracheid vessel element
water-conducting cells of the xylem
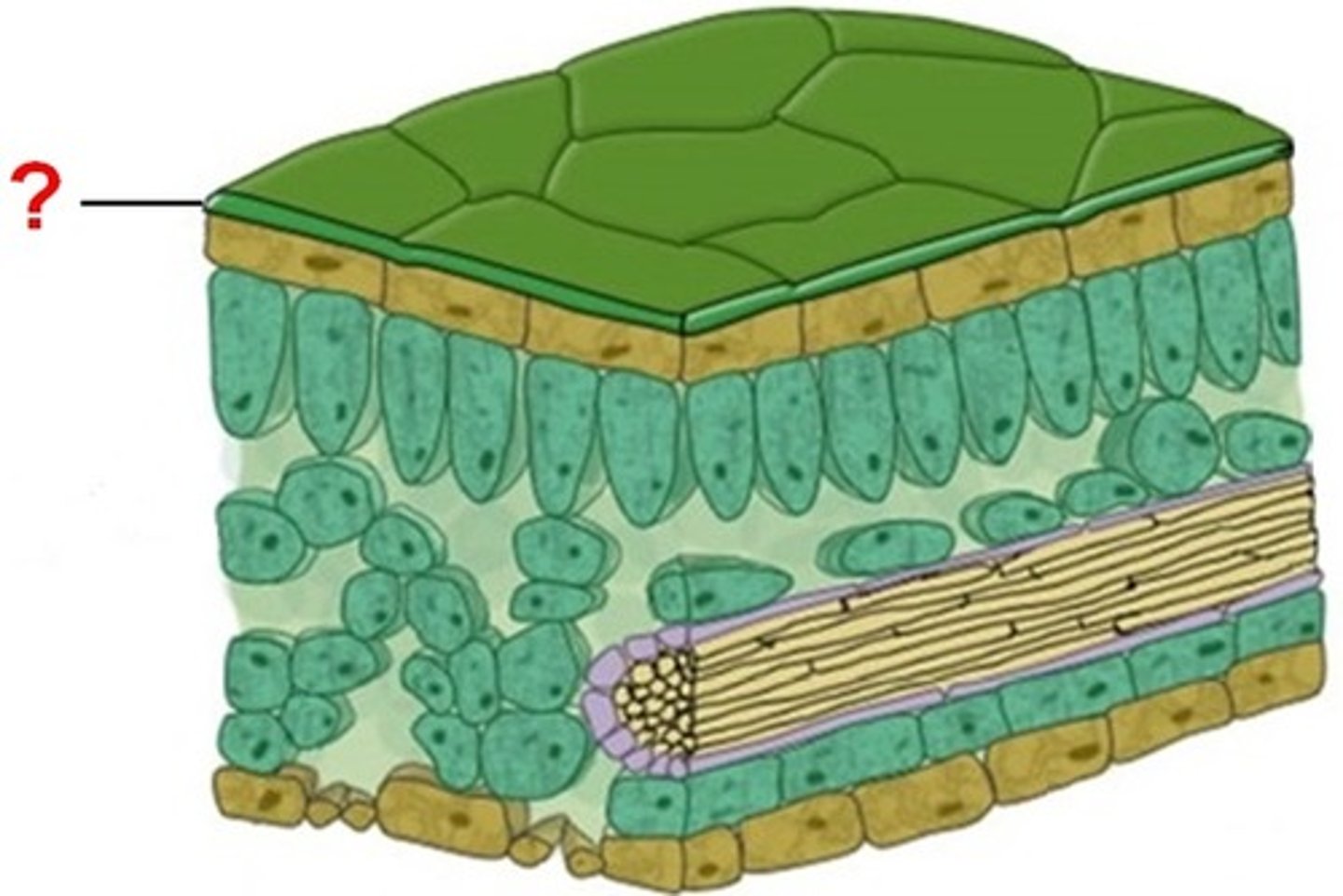
waxy cuticle
Forms a waterproof layer to stop water loss due to photosynthesis/evaporation
dominance
A characteristic in which an allele that expresses its phenotype even in the presence of a recessive allele. either sporophyte or gametophyte usually mostly expressed

independence
sporophyte and gametophyte do not depend on one another to survive. Seen in ferns

stem
supporting structure that connects roots and leaves and carries water and nutrients between them. indeterminate growth

leaf
the main organ of photosynthesis and transpiration in higher plants. determinate growth, all consistent with one another in a plant

root
An organ in vascular plants that anchors the plant and enables it to absorb water and minerals from the soil.
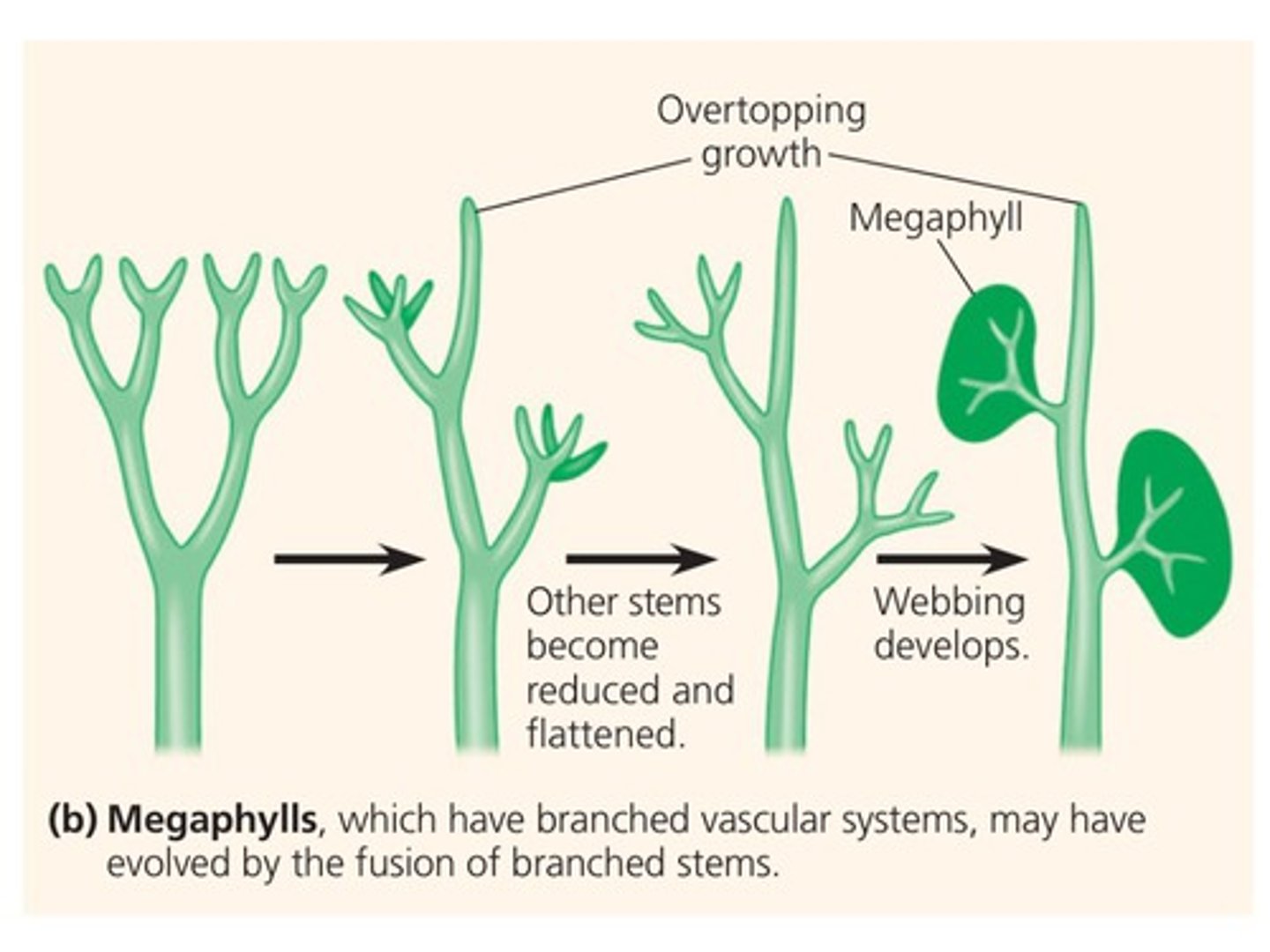
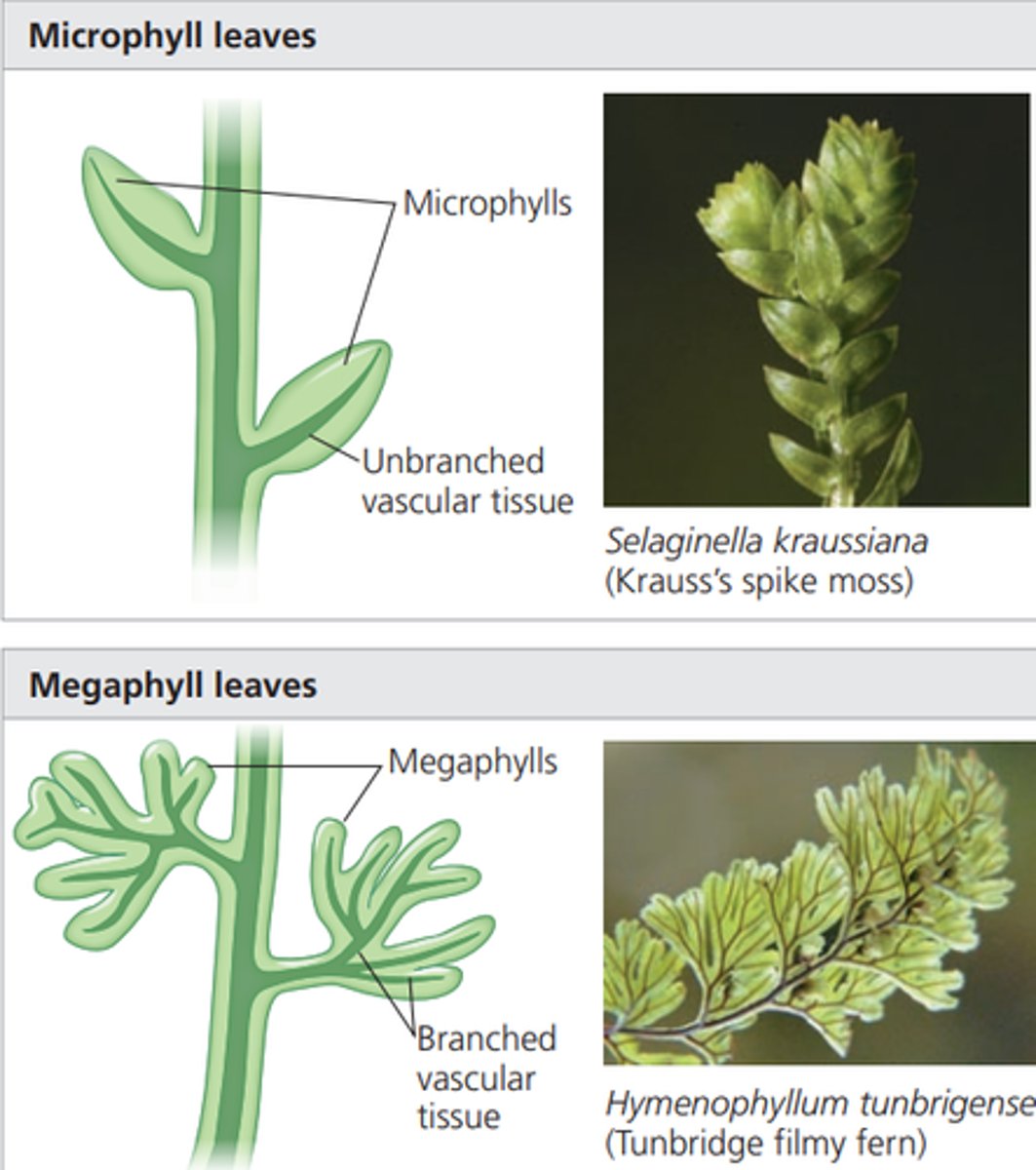
megaphyll
A leaf with a highly branched vascular system, characteristic of the vast majority of vascular plants. Overtopping, planation (flattening), webbing.
microphyll
A small, usually spine-shaped leaf supported by a single strand of vascular tissue, found only in lycophytes.
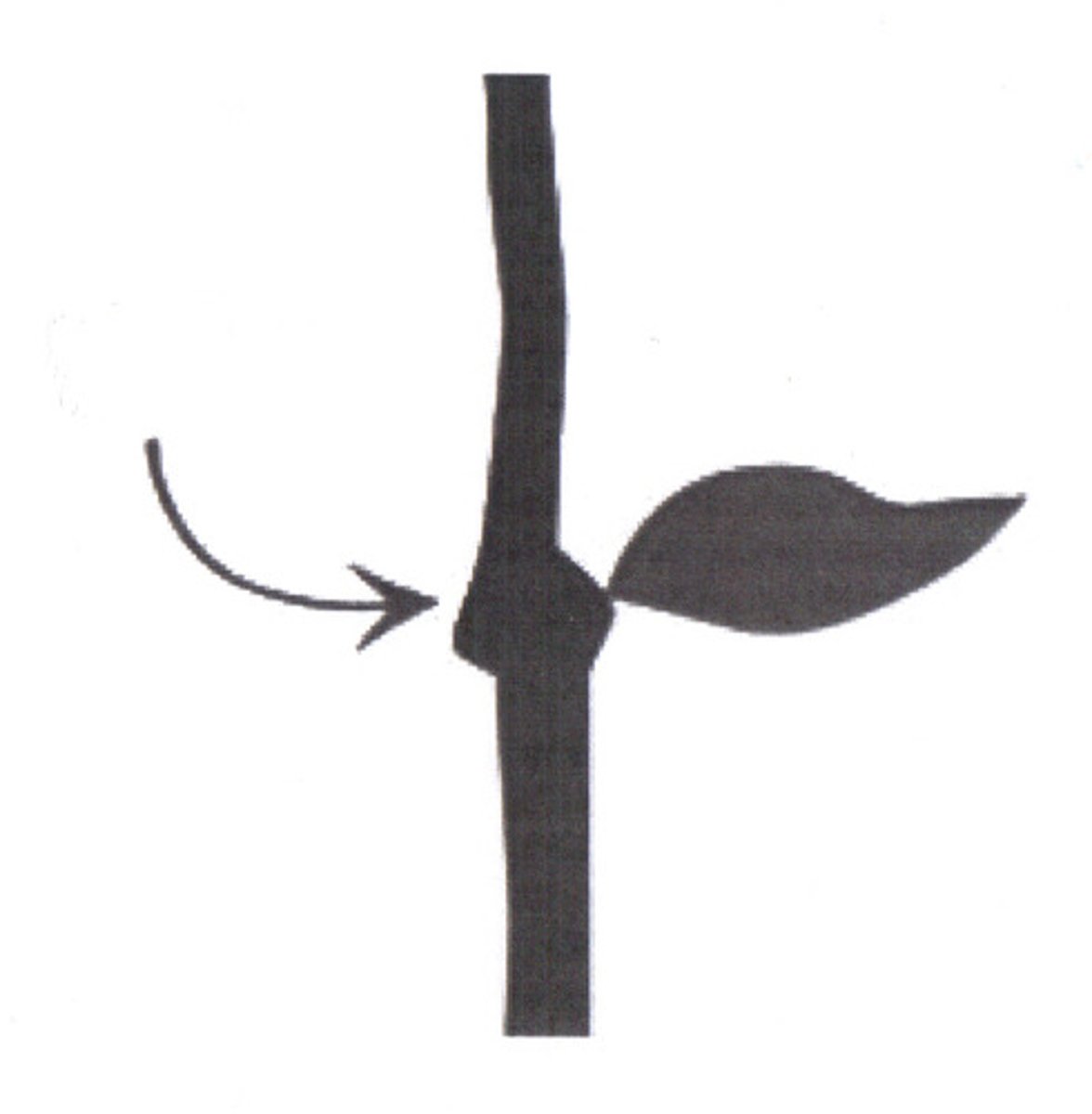
nodes
where leaves grow from
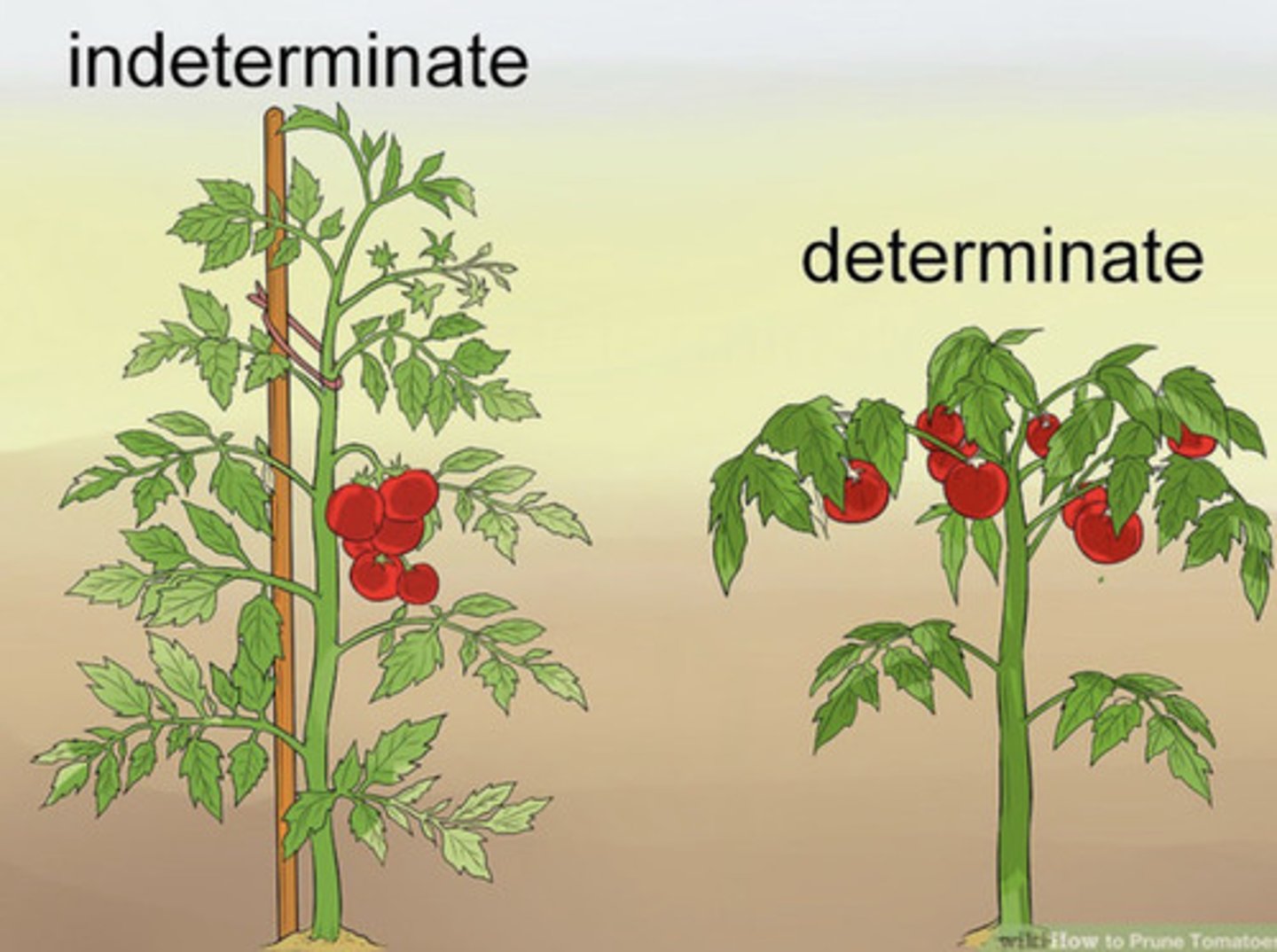
determinate growth
some plant organs cease to grow at a certain size

indeterminate growth
A type of growth characteristic of plants, in which the organism continues to grow as long as it lives.
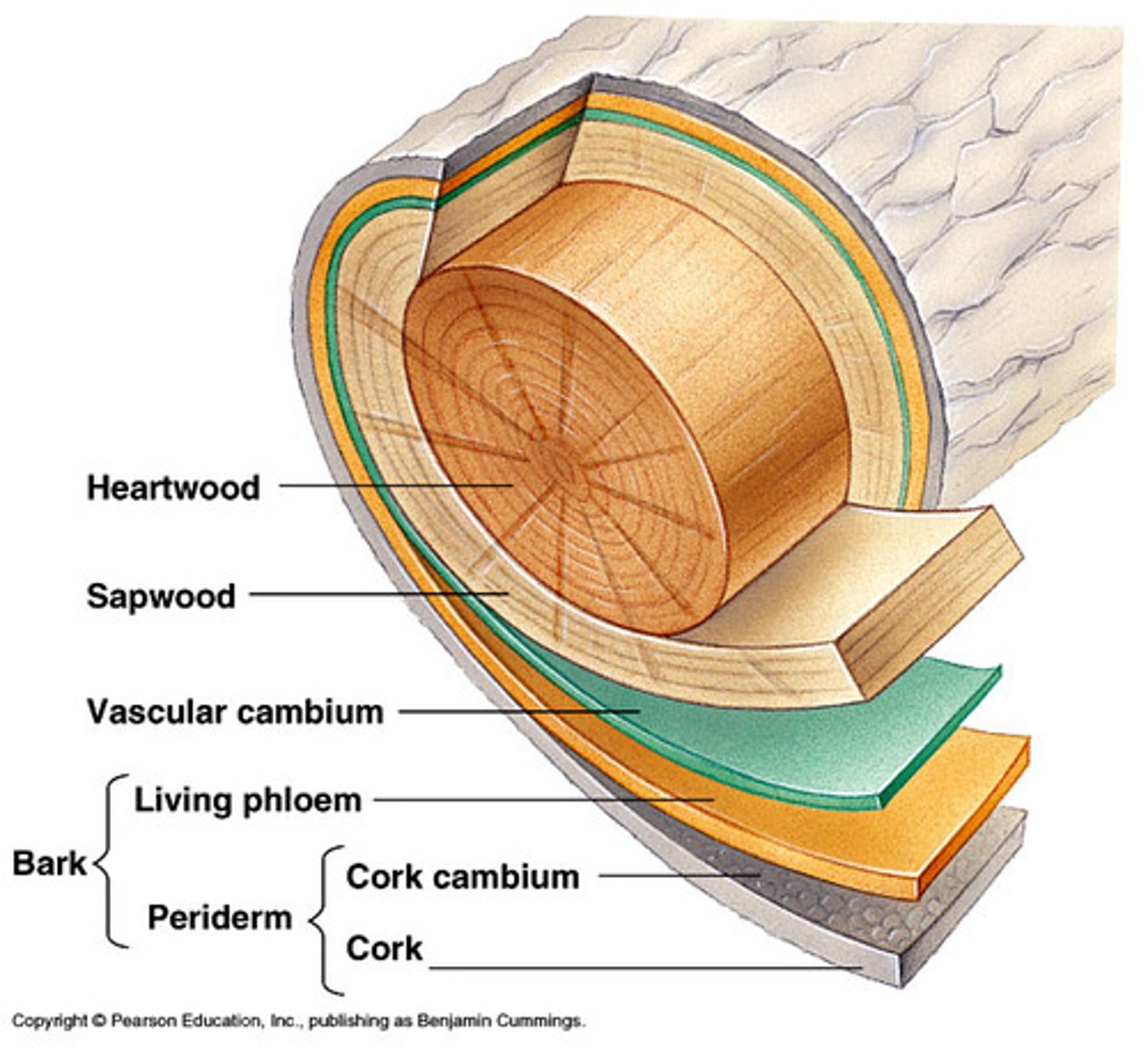
bifacial vascular cambium
A way to produce more vascular tissue and thicker stems; it is a type of meristem that continues to divide and produce new vascular cells and tissues on two sides
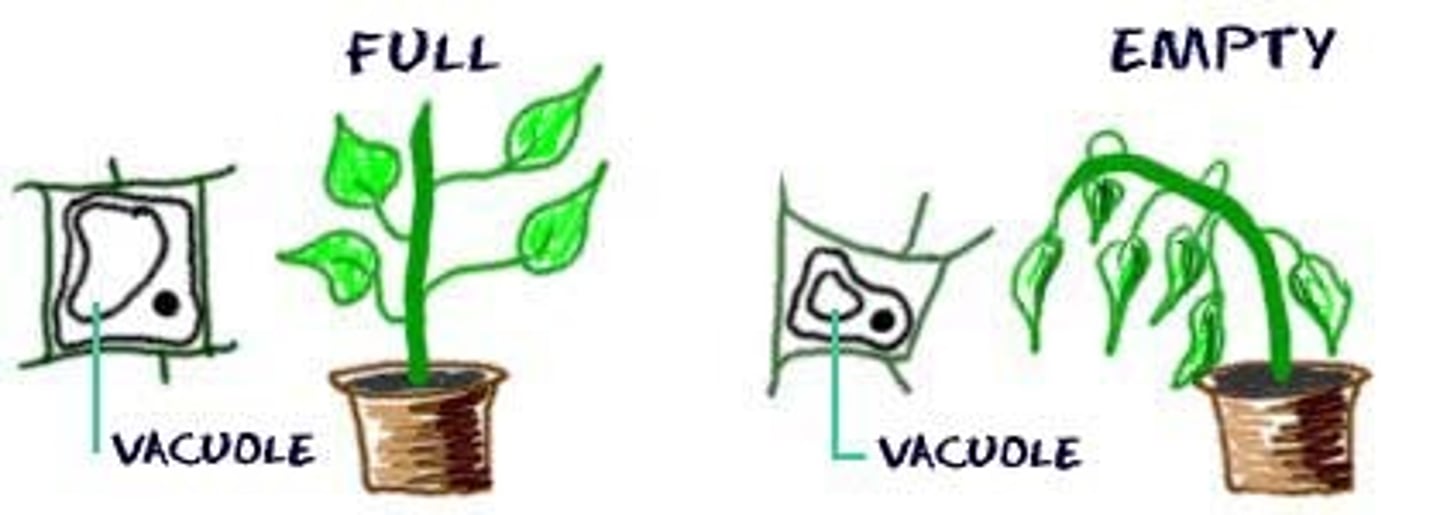
turgor pressure
The pressure that water molecules exert against the cell wall
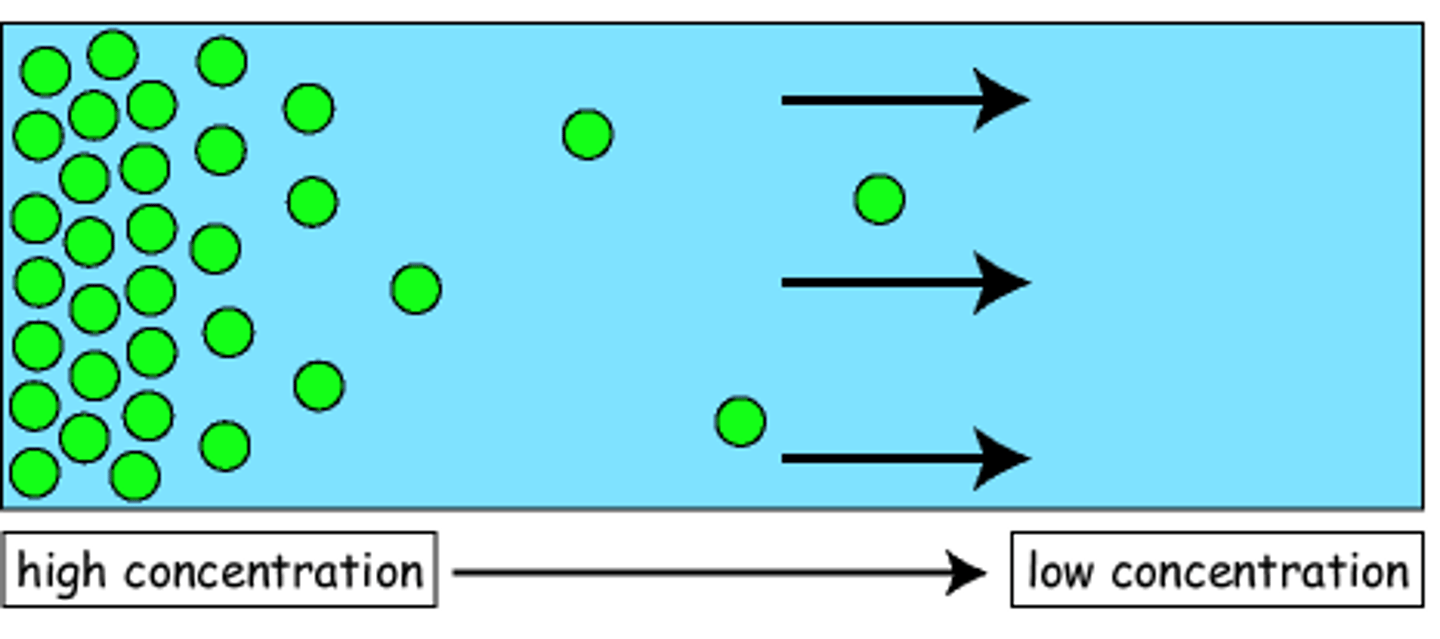
diffusion (osmosis)
Movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration.
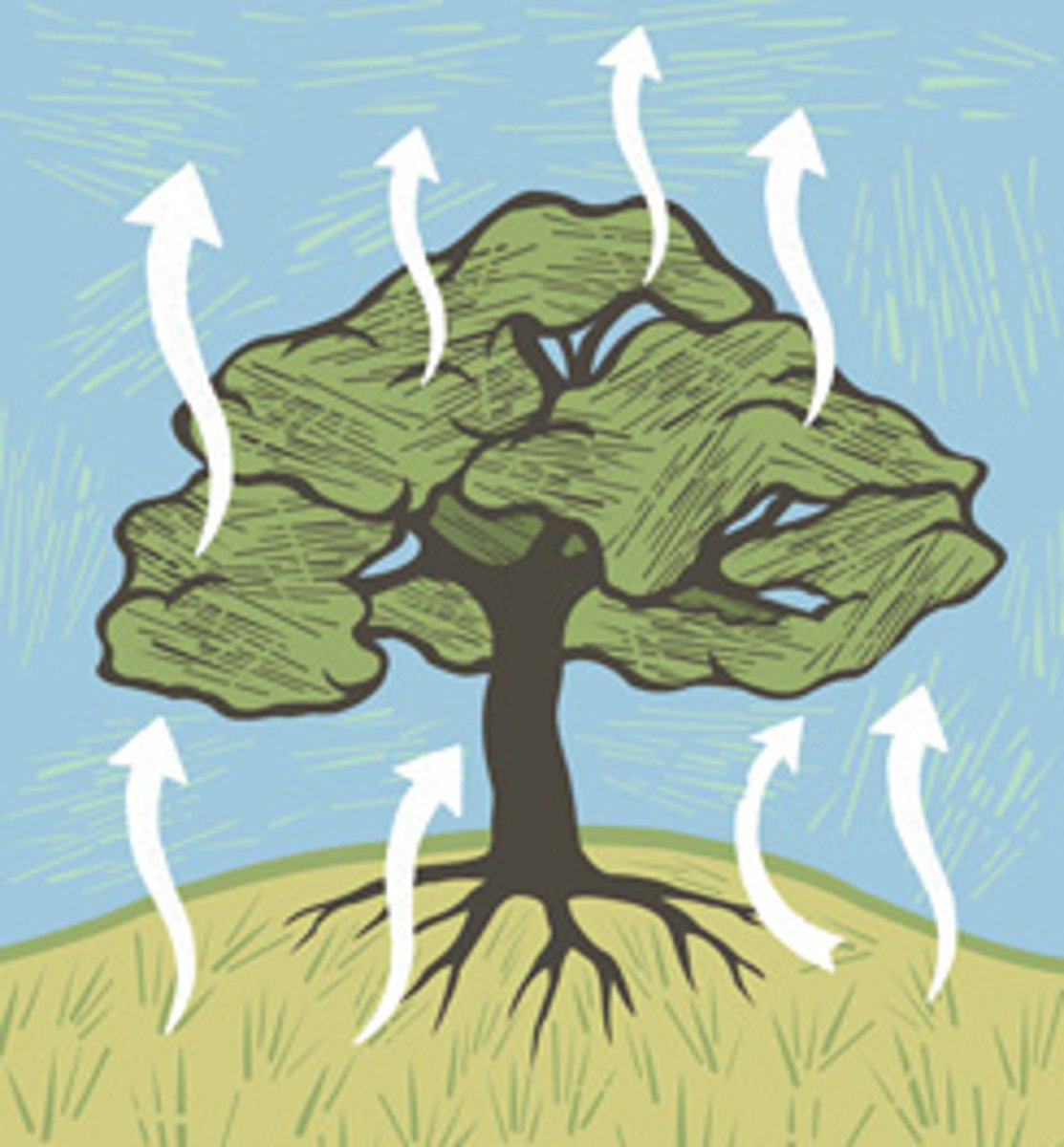
evapotranspiration
water evaporates from leaves, causing soil water to be pulled into xylem and carried up to all parts of plant

sporophyll
A modified leaf that bears sporangia and hence is specialized for reproduction.
strobilus
compact cluster of spore-bearing structures in some seedless vascular plant sporophytes. CONE!
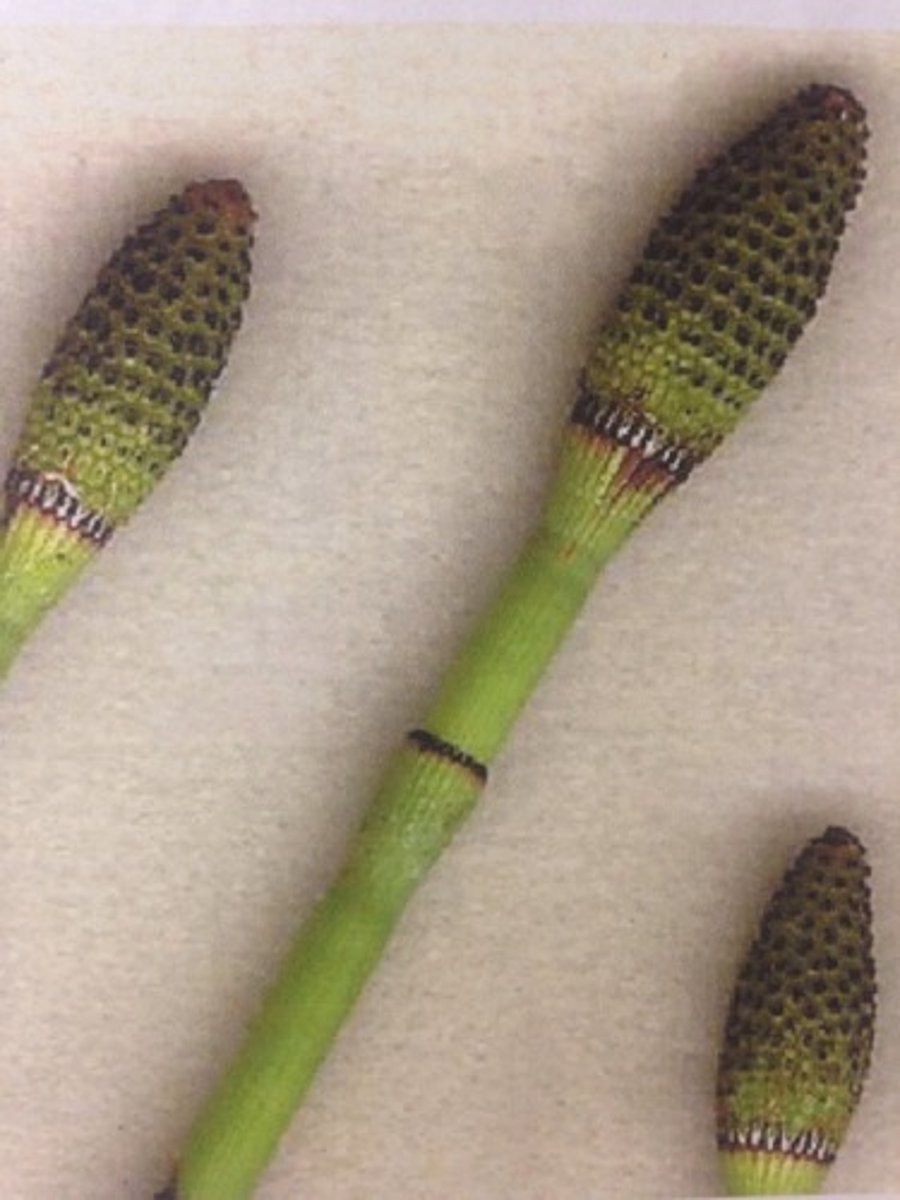

homospory
production of a single type of spore

heterospory
production of two different types of spores

nutritive tissue
in seed plants: tissue surrounding egg in archegonia that nouishes seed
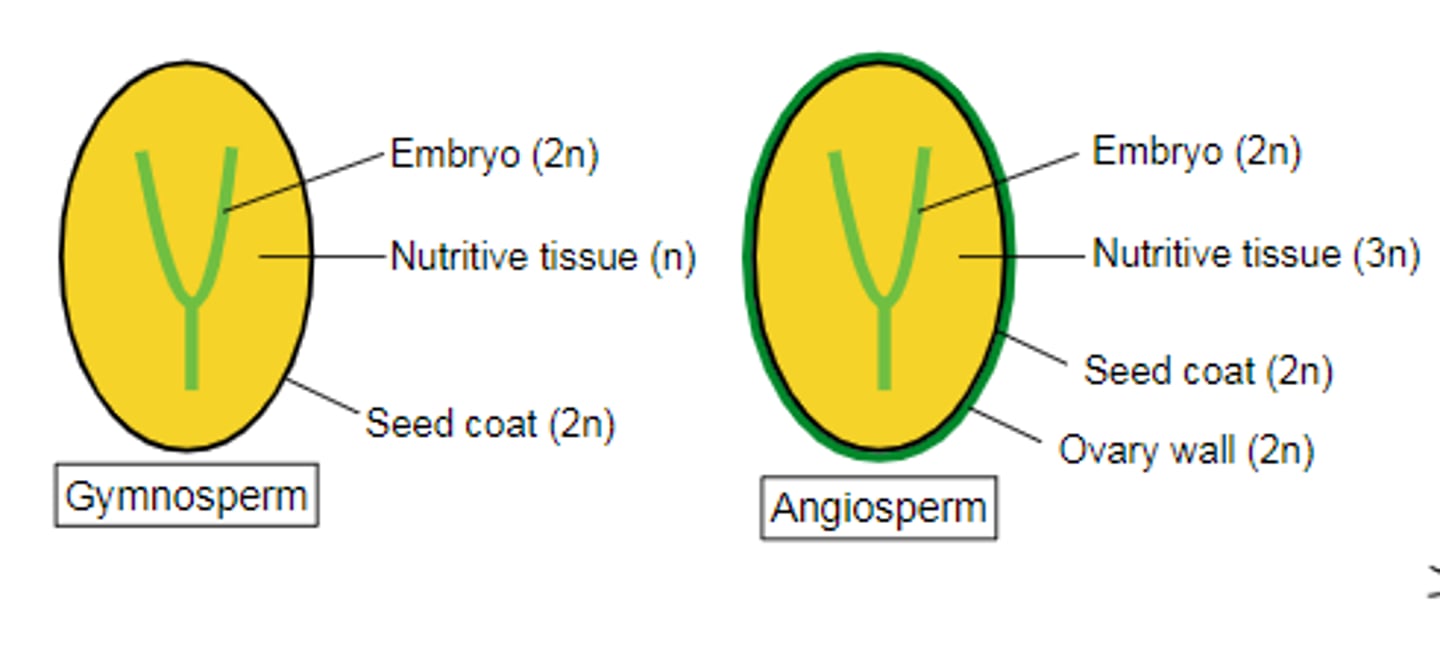
endosperm
In angiosperms, a nutrient-rich tissue formed by the union of a sperm with two polar nuclei during double fertilization. Provides nourishment to the developing embryo in angiosperm seeds. TRIPLOID
seed integument
part of ovule. Tissue layers surrounding megasporangium
seed coat
A tough outer covering of a seed, formed from the outer coat of an ovule (integuments)

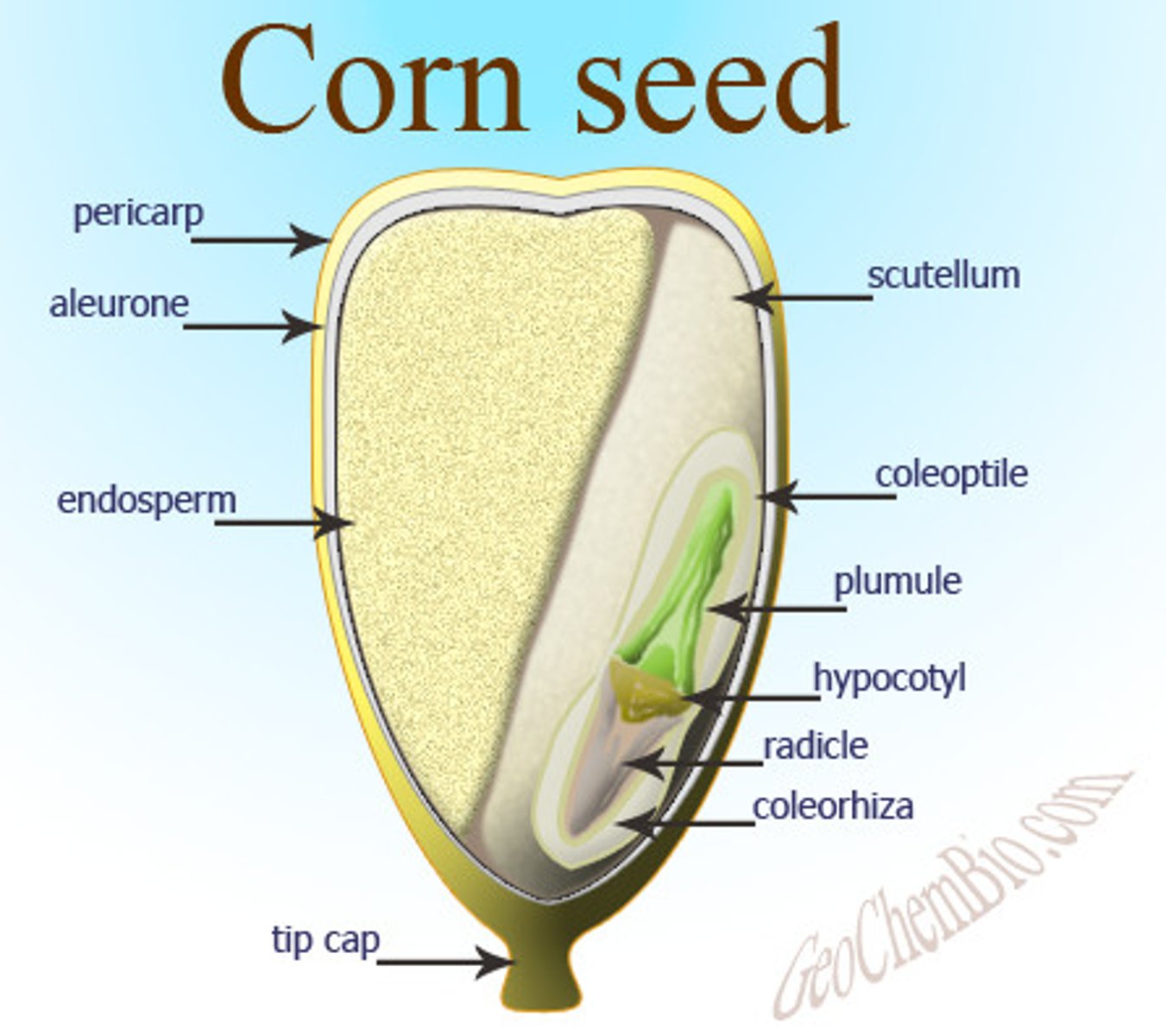
plant embryo
the early, undeveloped stage of a new plant
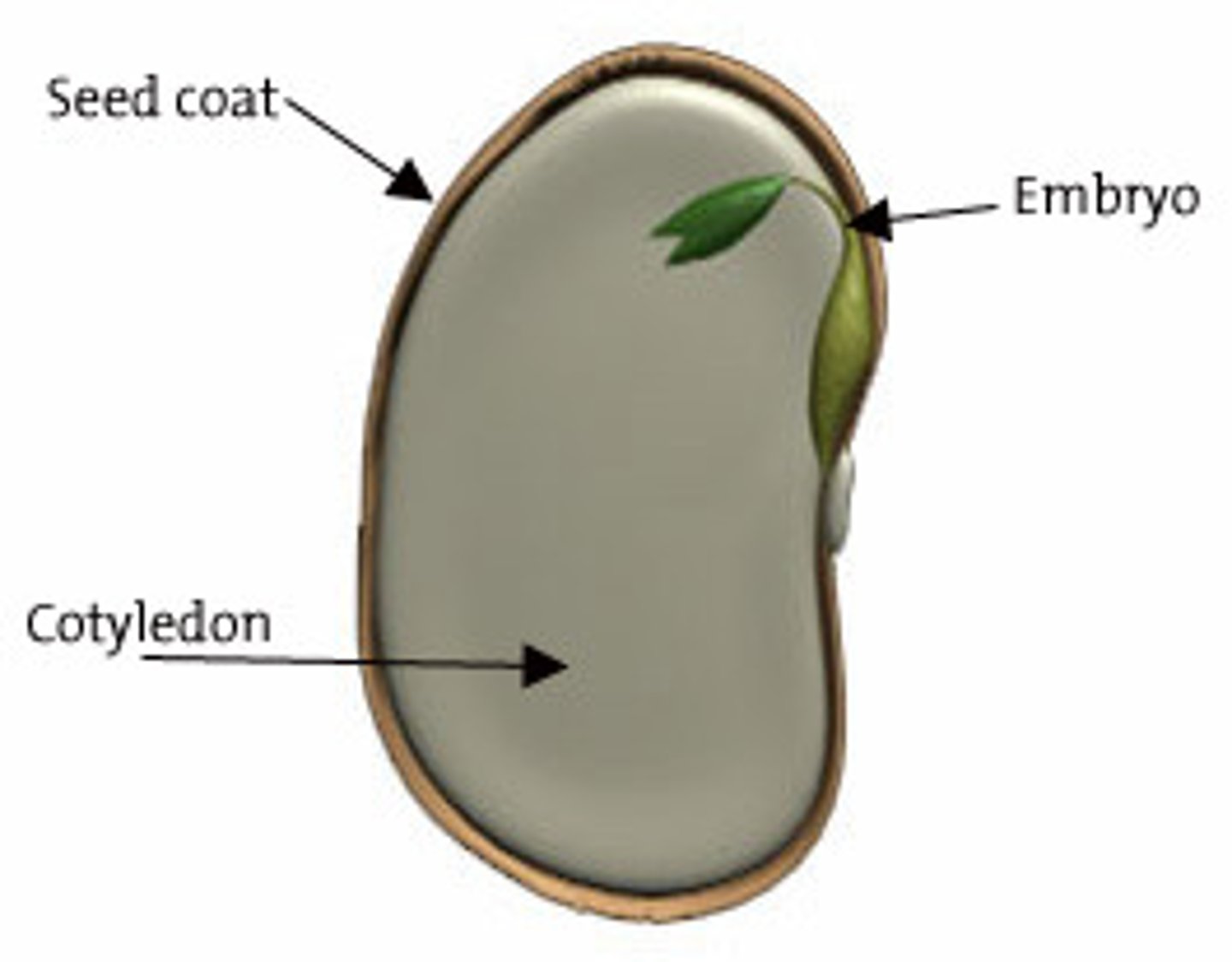
cotyledon
first leaf or first pair of leaves produced by the embryo of a seed plant

monosulcate
having one long furrow; typically describes type of pollen
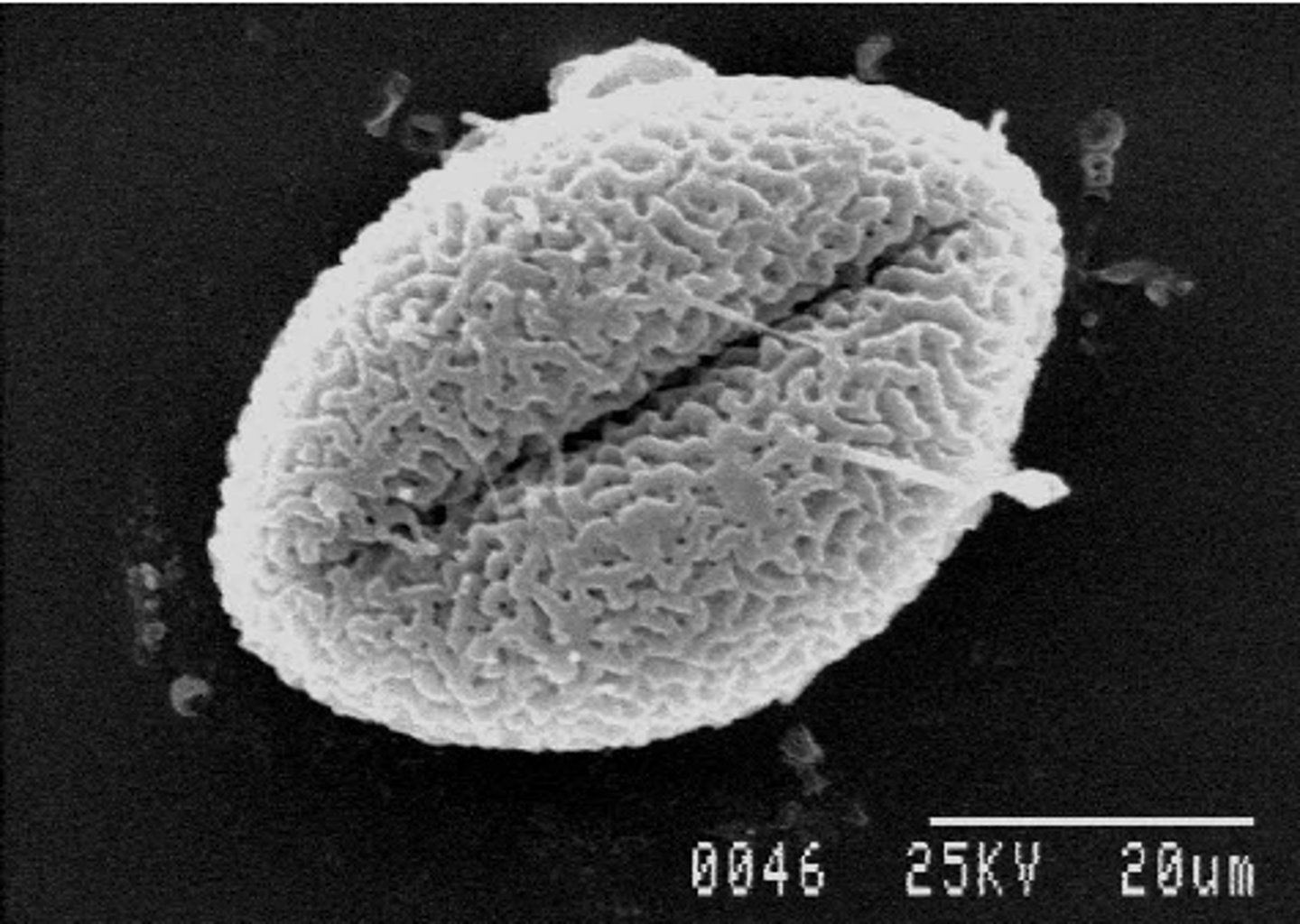
tricolpate
having three pores; typically describes type of pollen

petal
A modified leaf of a flowering plant; petals are the often colorful parts of a flower that advertise it to insects and other pollinators.
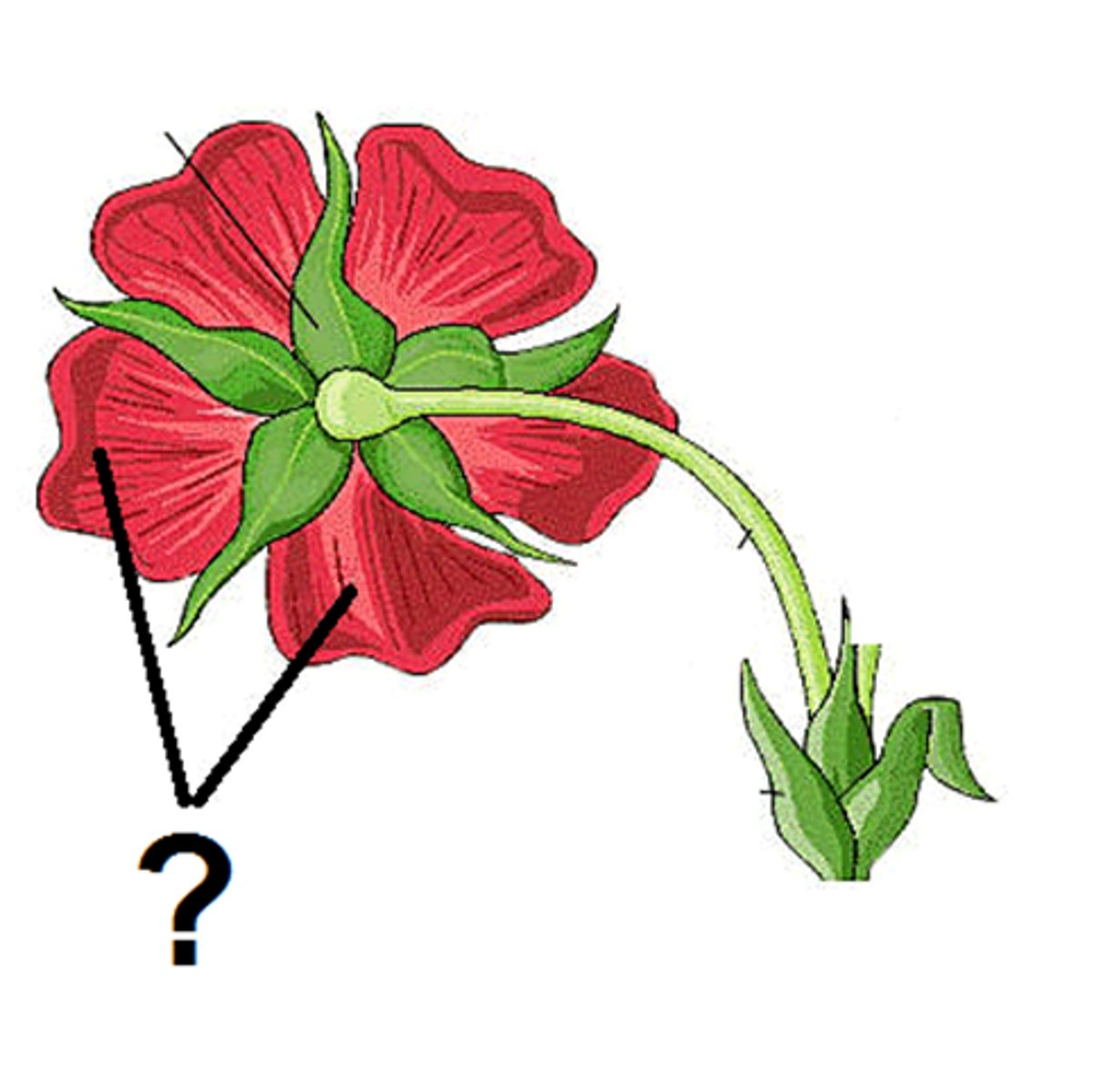
stamen
the male reproductive organ of a flower
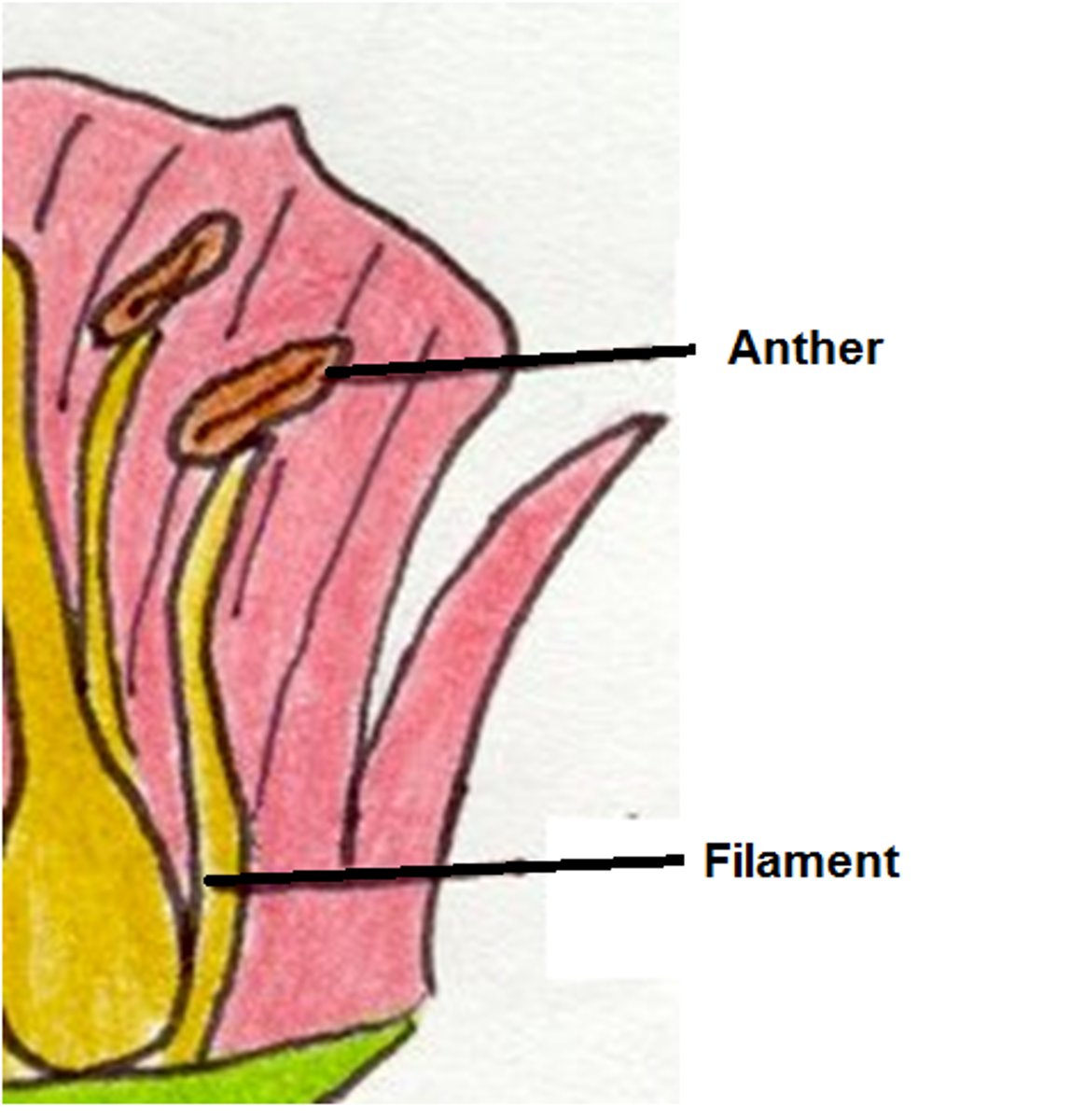
anther
the part of a stamen that contains the pollen.
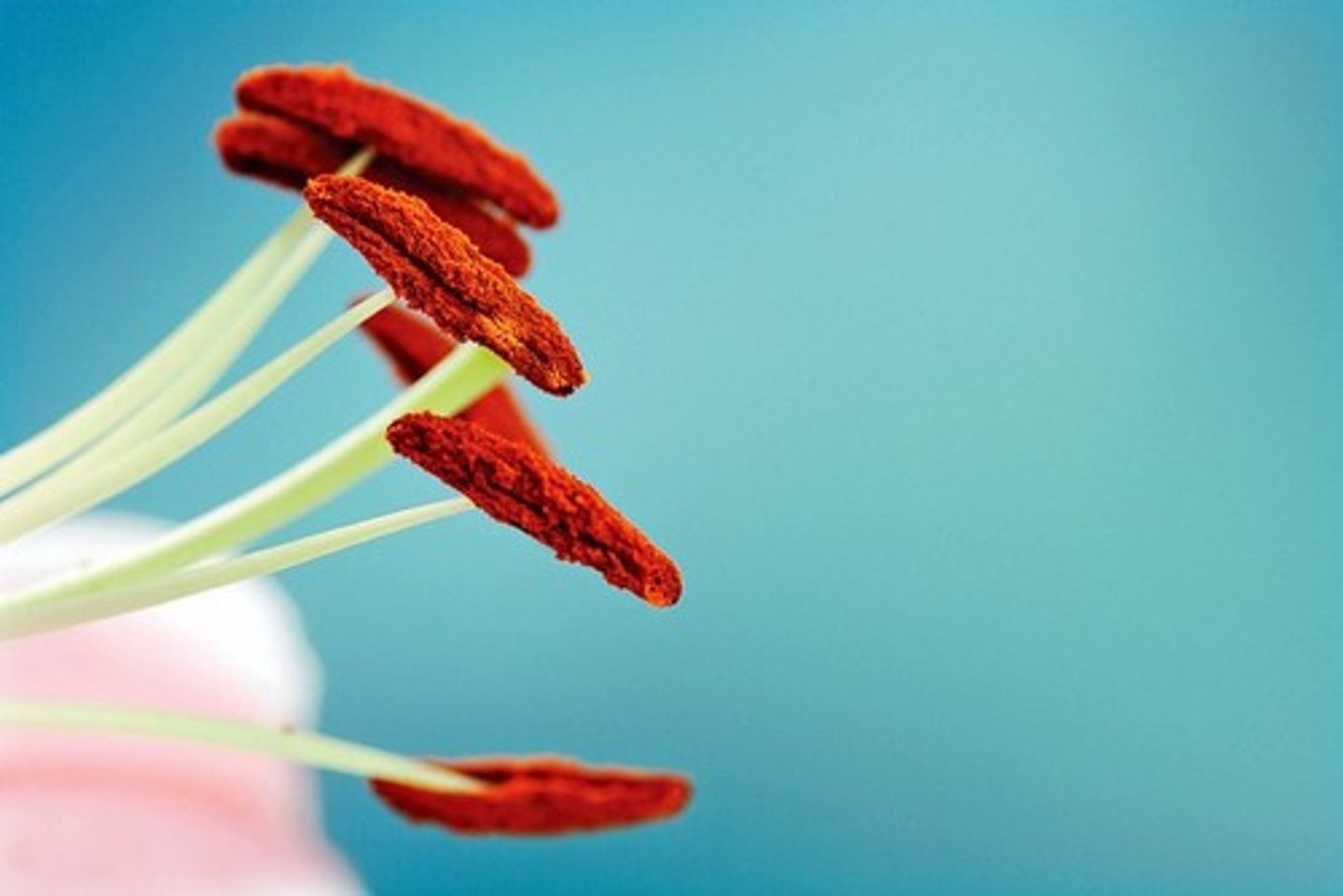

filament
Supports the anther

pistill
female reproductive organ of a flower

stigma - plant
sticky portion at the top of the style where pollen grains frequently land
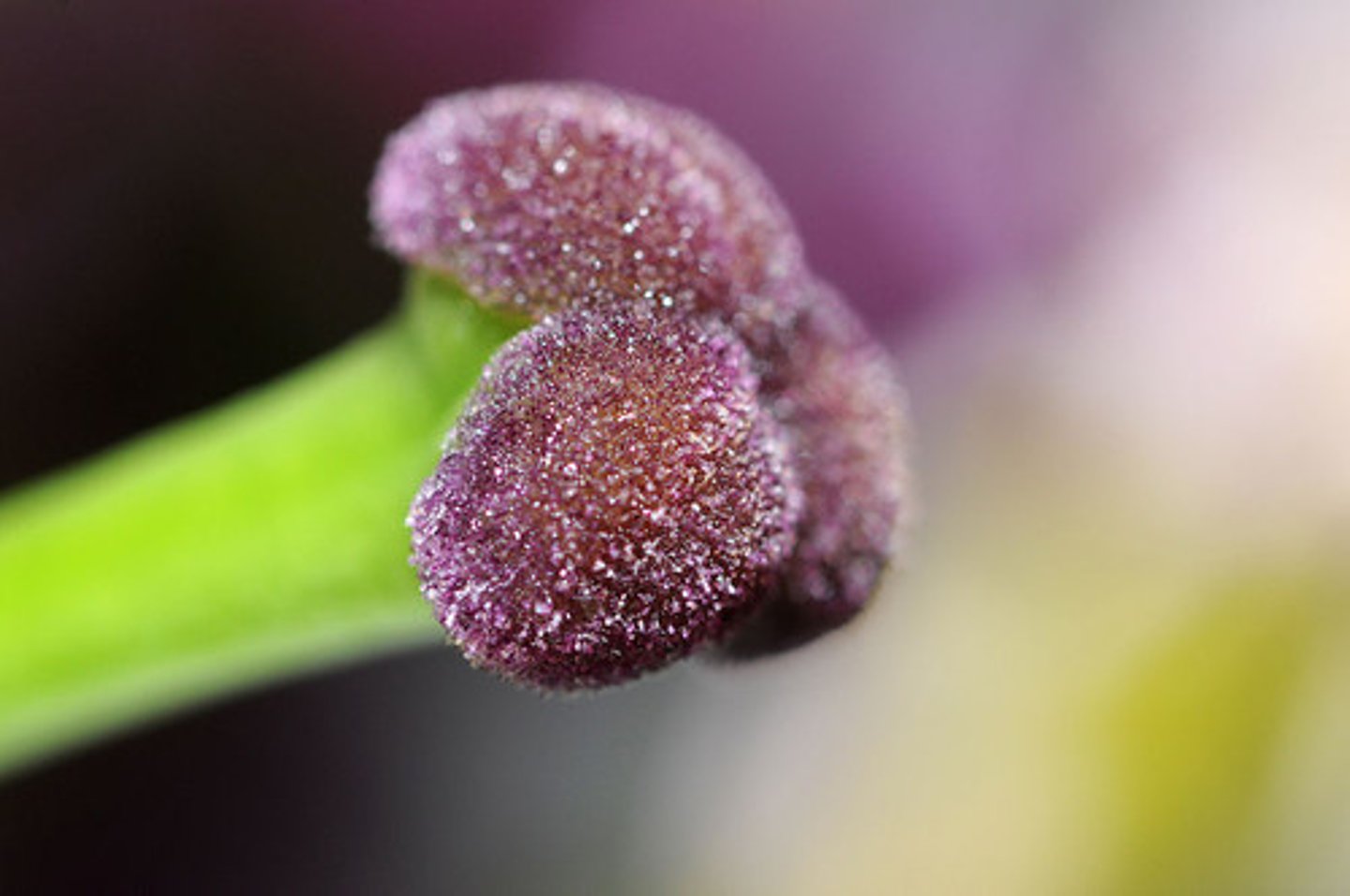

style
The stalk of a flower's carpel, with the ovary at the base and the stigma at the top.
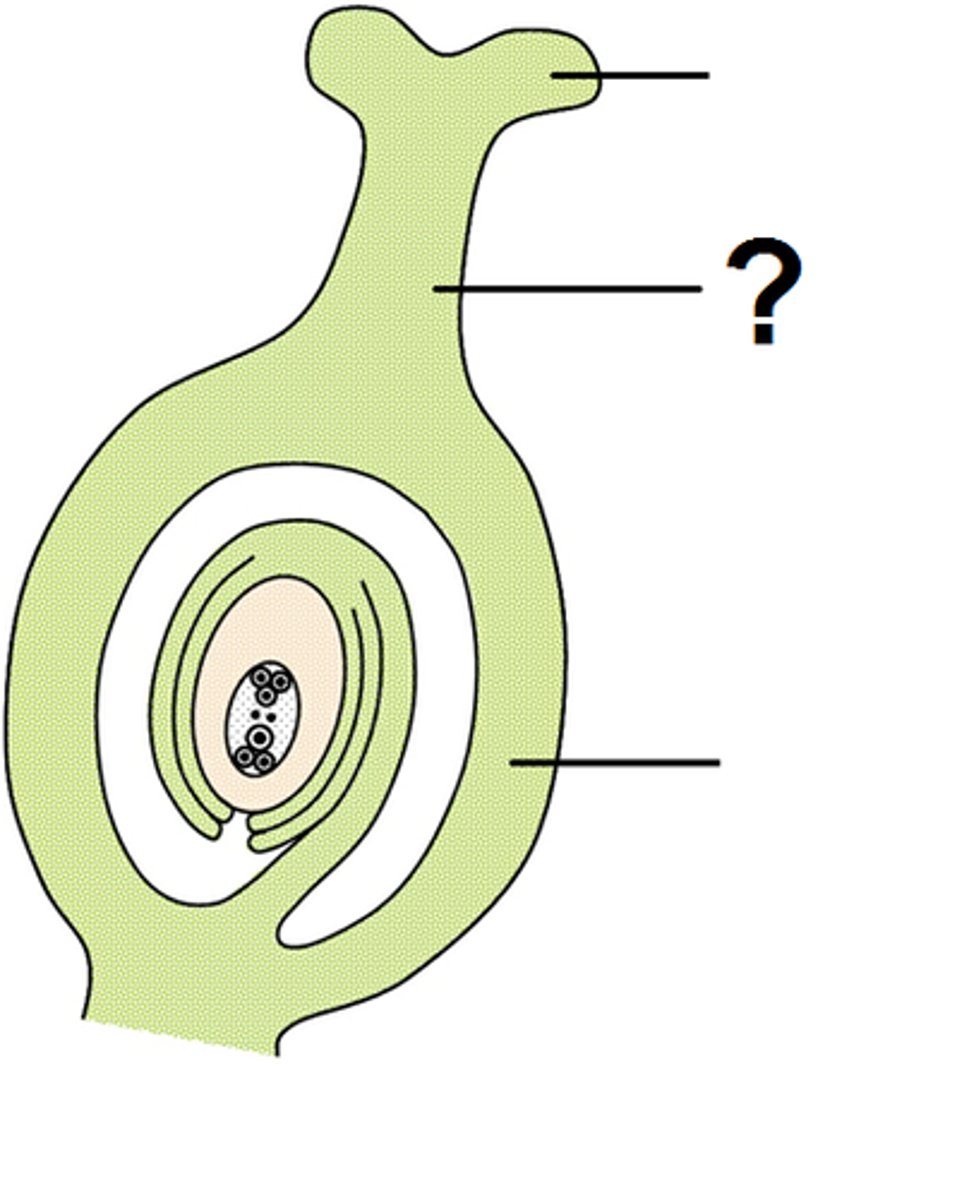
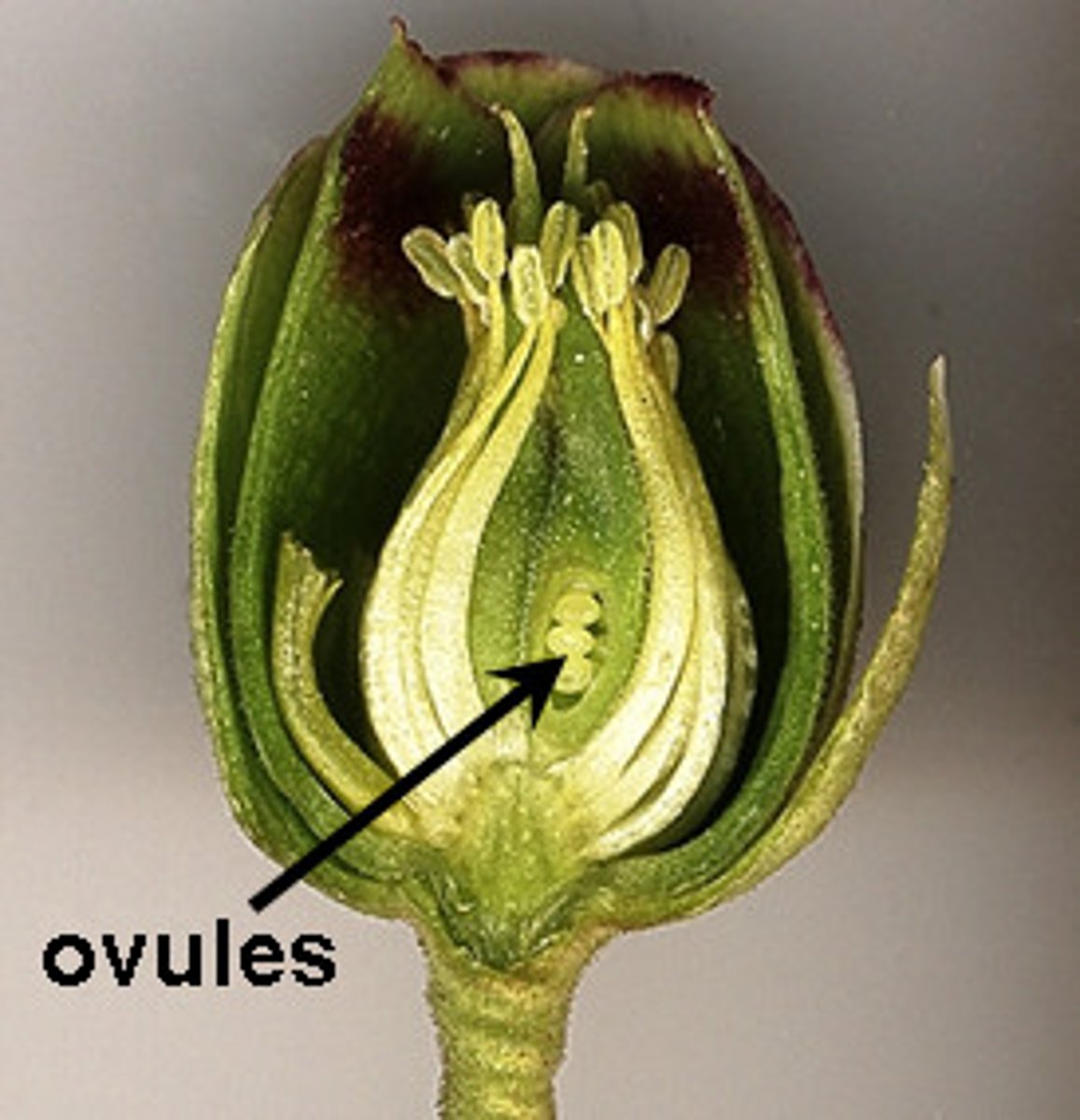
ovary
In flowers, the portion of a carpel in which the egg-containing ovules develop. Ovary usually results in fruit
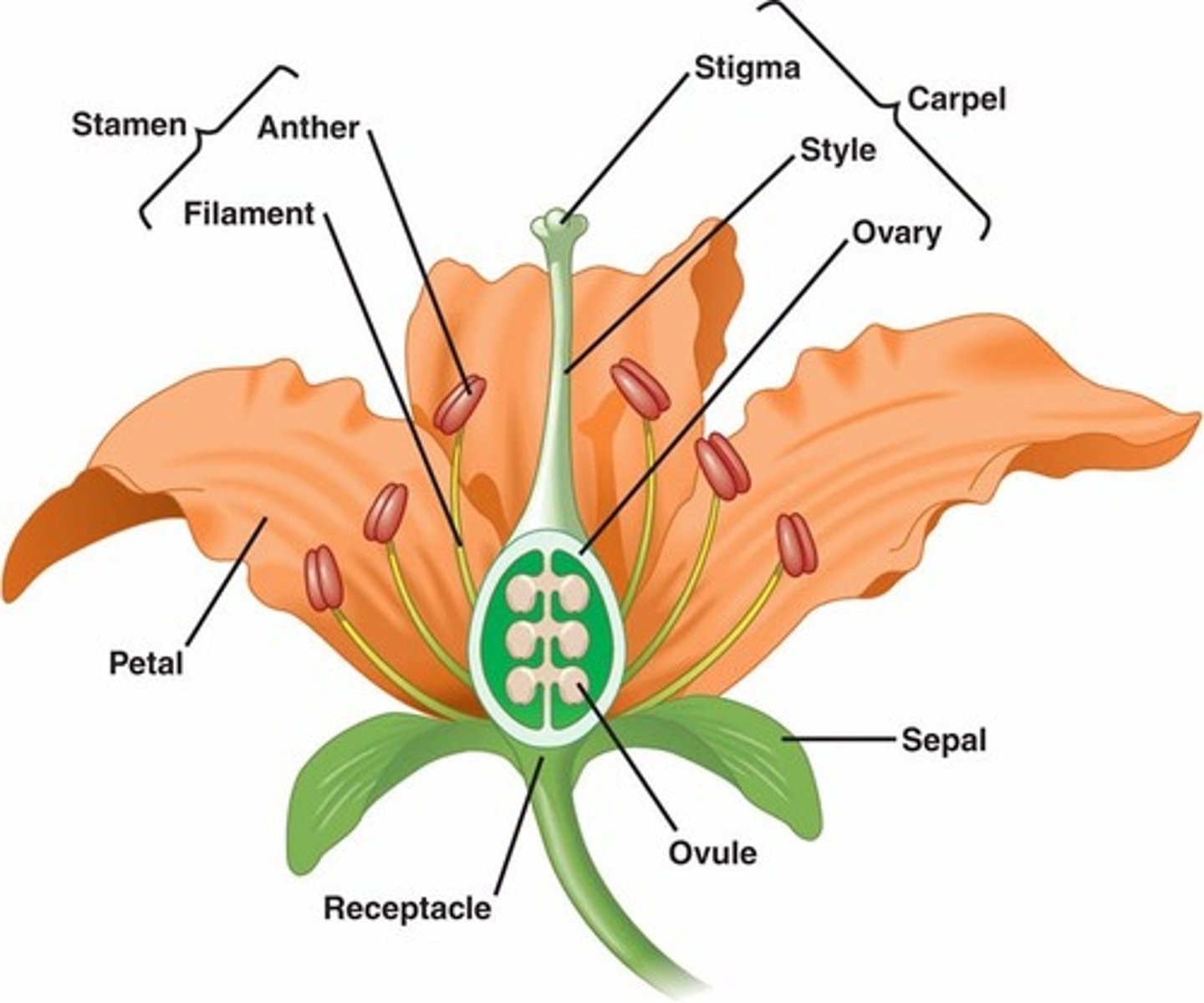
ovule
A structure that develops within the ovary of a seed plant and contains the female gametophyte.

trichome
hairlike projections that extend from a plant's epidermis; help reduce water evaporation and may provide protection from herbivores

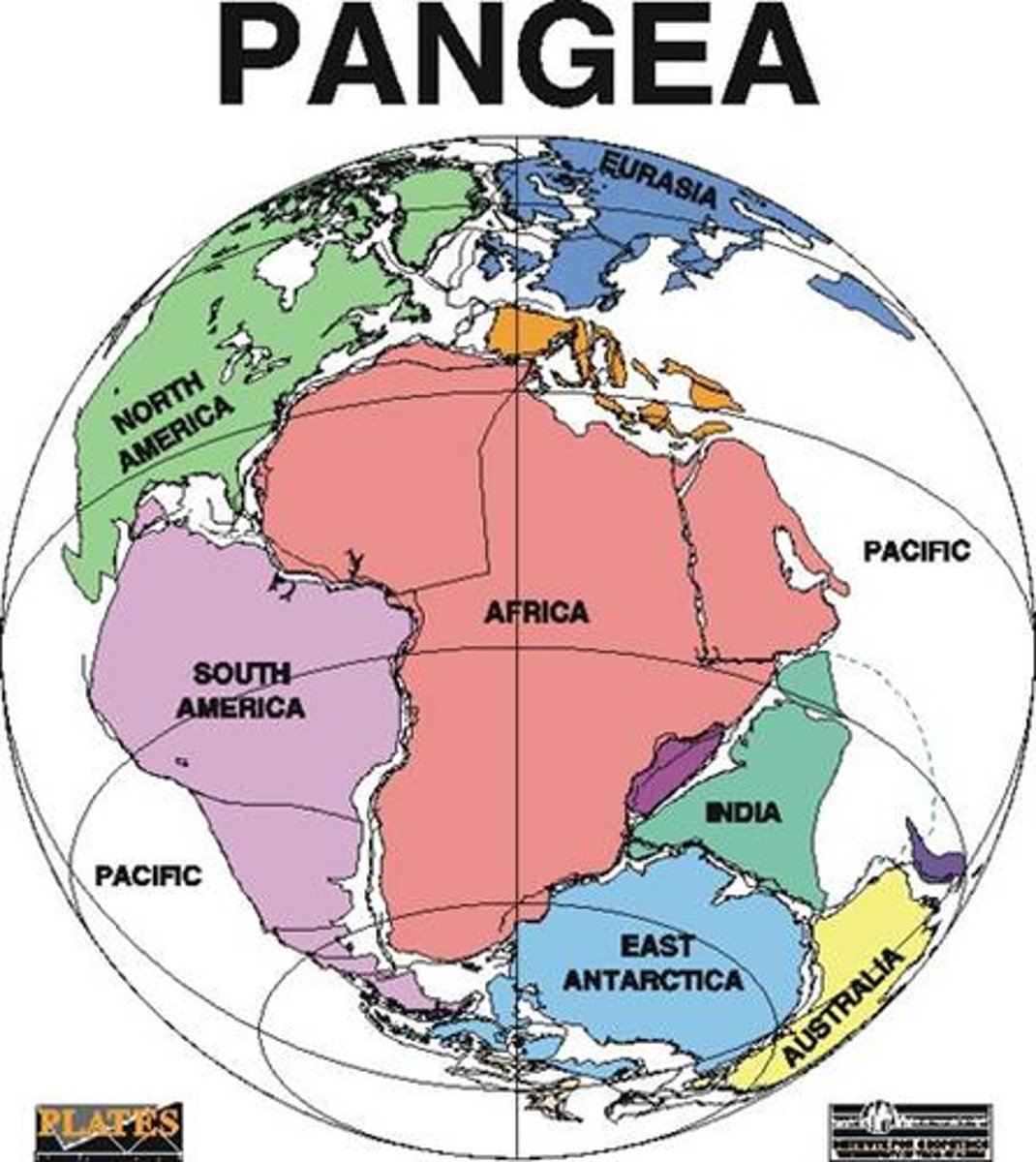
pangaea
The name of the single landmass that broke apart 200 million years ago and gave rise to today's continents
hyphae
The branching, threadlike tubes that make up the bodies of multicellular fungi
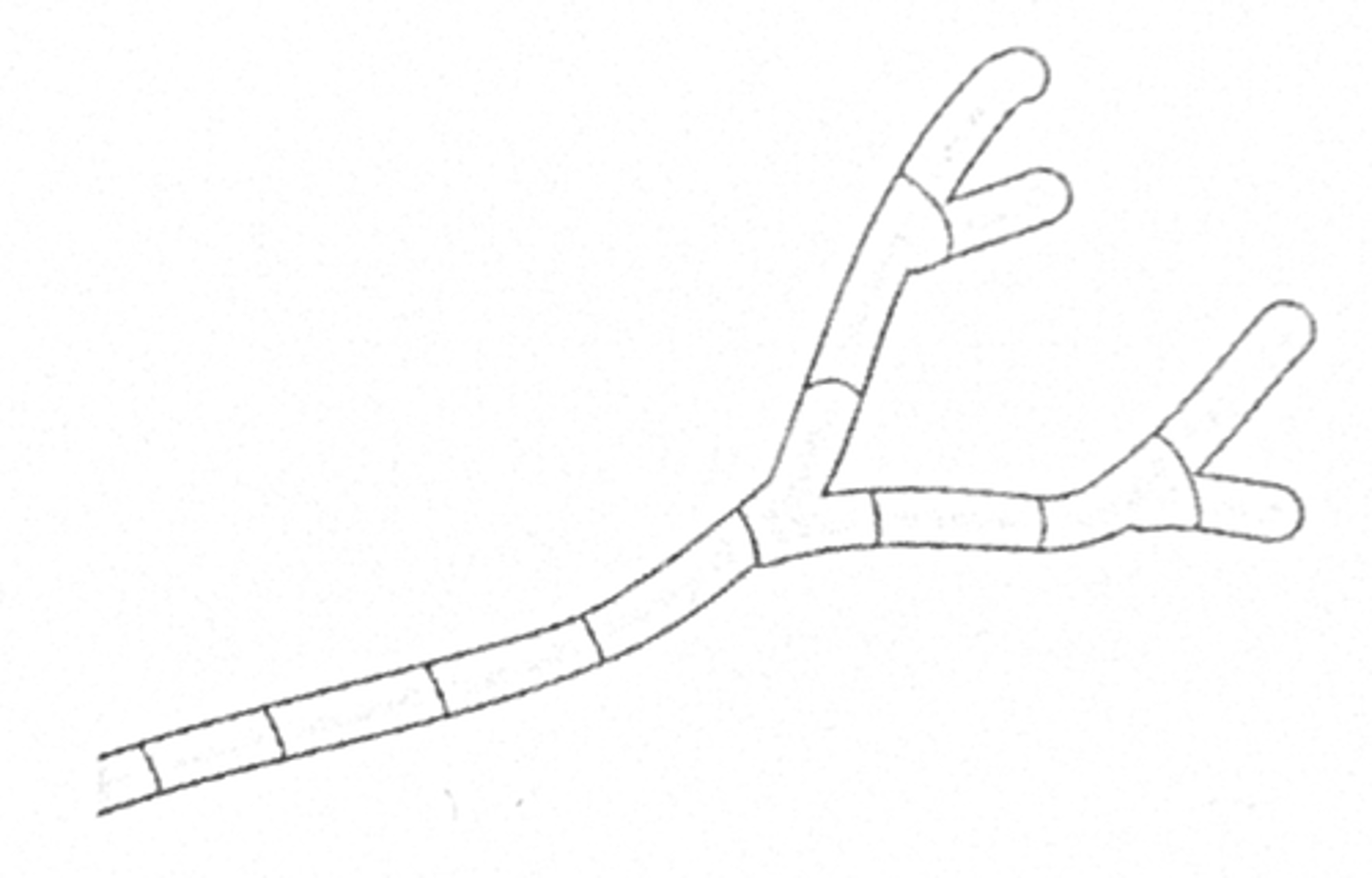
mycelium
densely branched network of the hyphae of a fungus

fruiting body
The reproductive structure of a fungus that contains many hyphae and produces spores

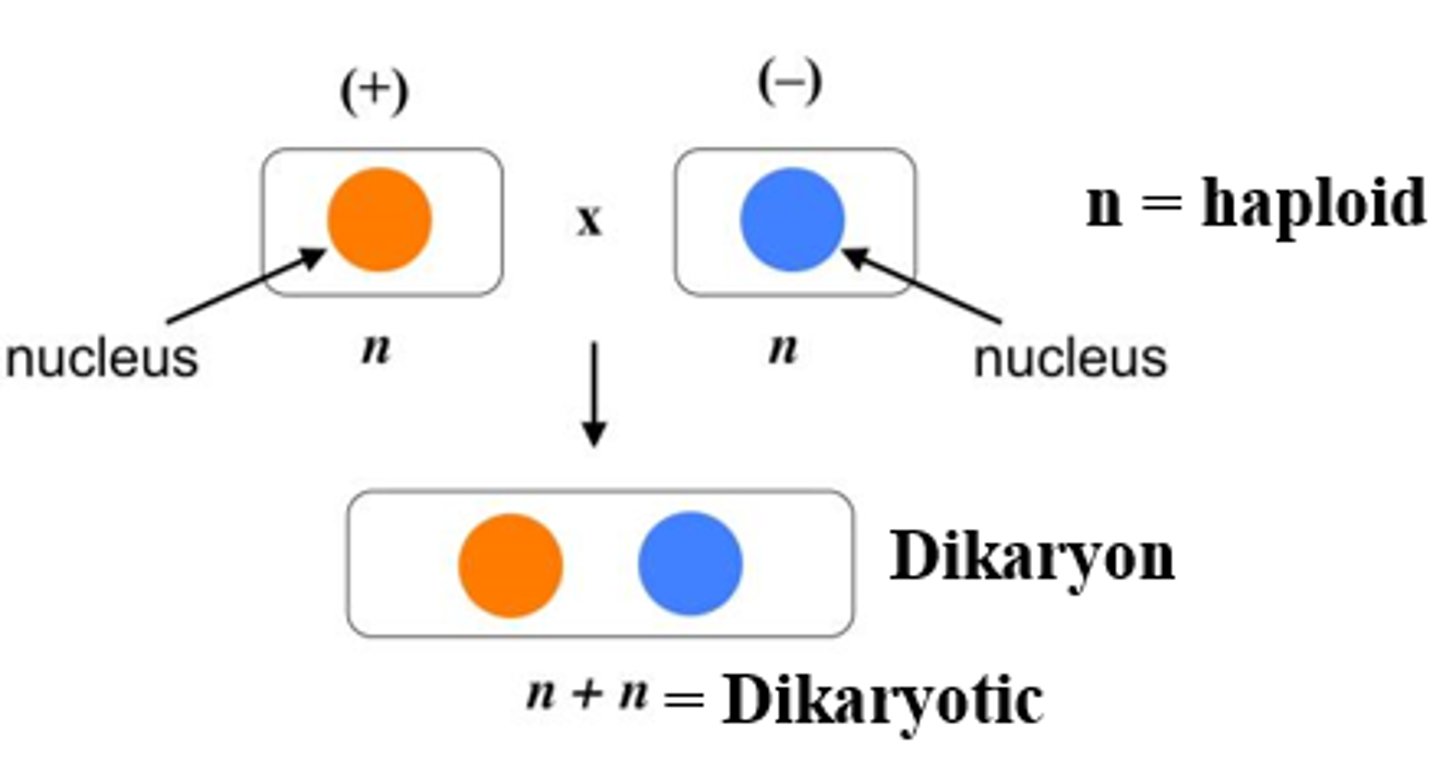
dikaryon
hyphae with cells having 2 different nuclei in each cell.
septate
hyphae with cross walls
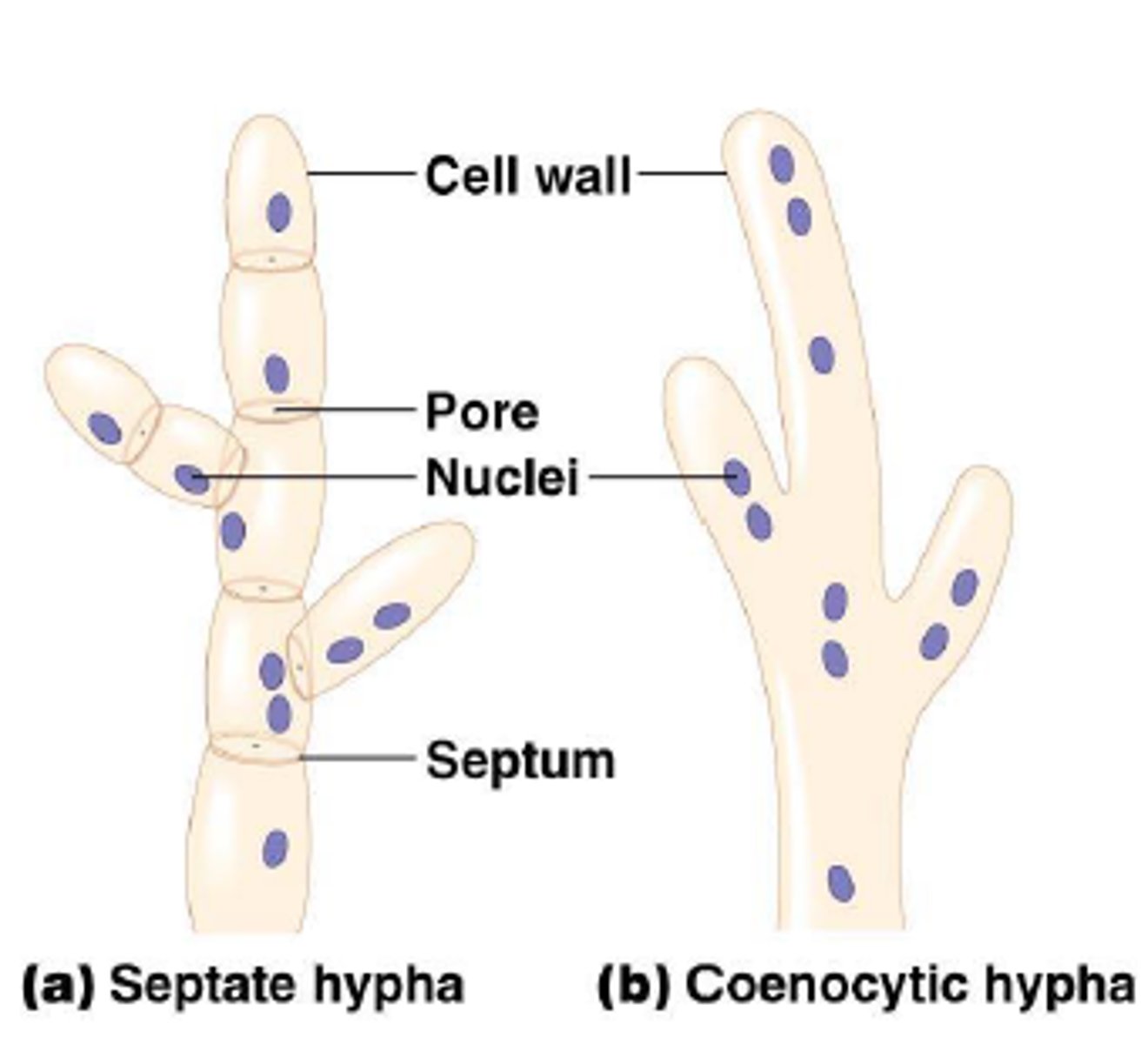
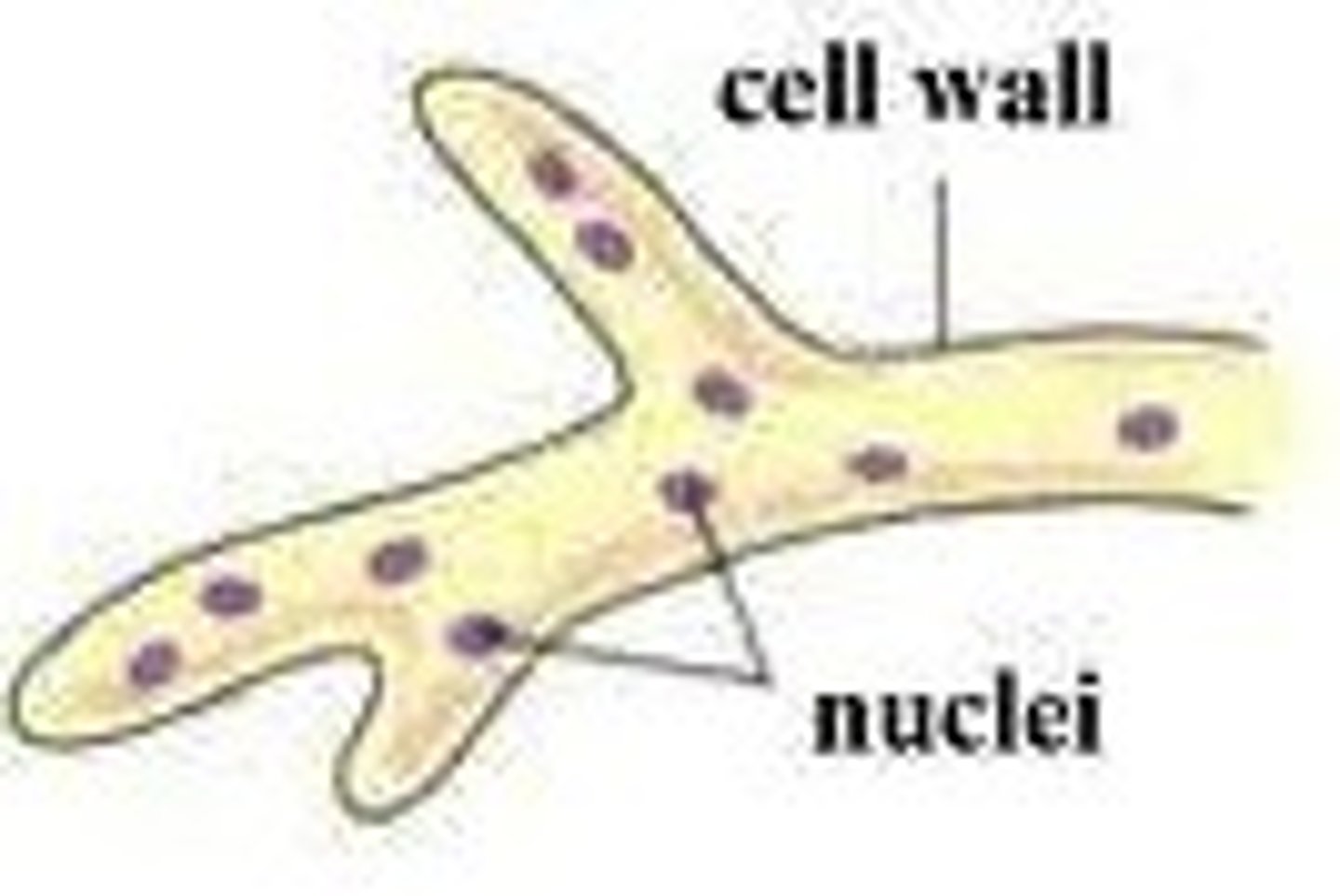
aseptate
hyphae that have no cross-walls and are multinucleate
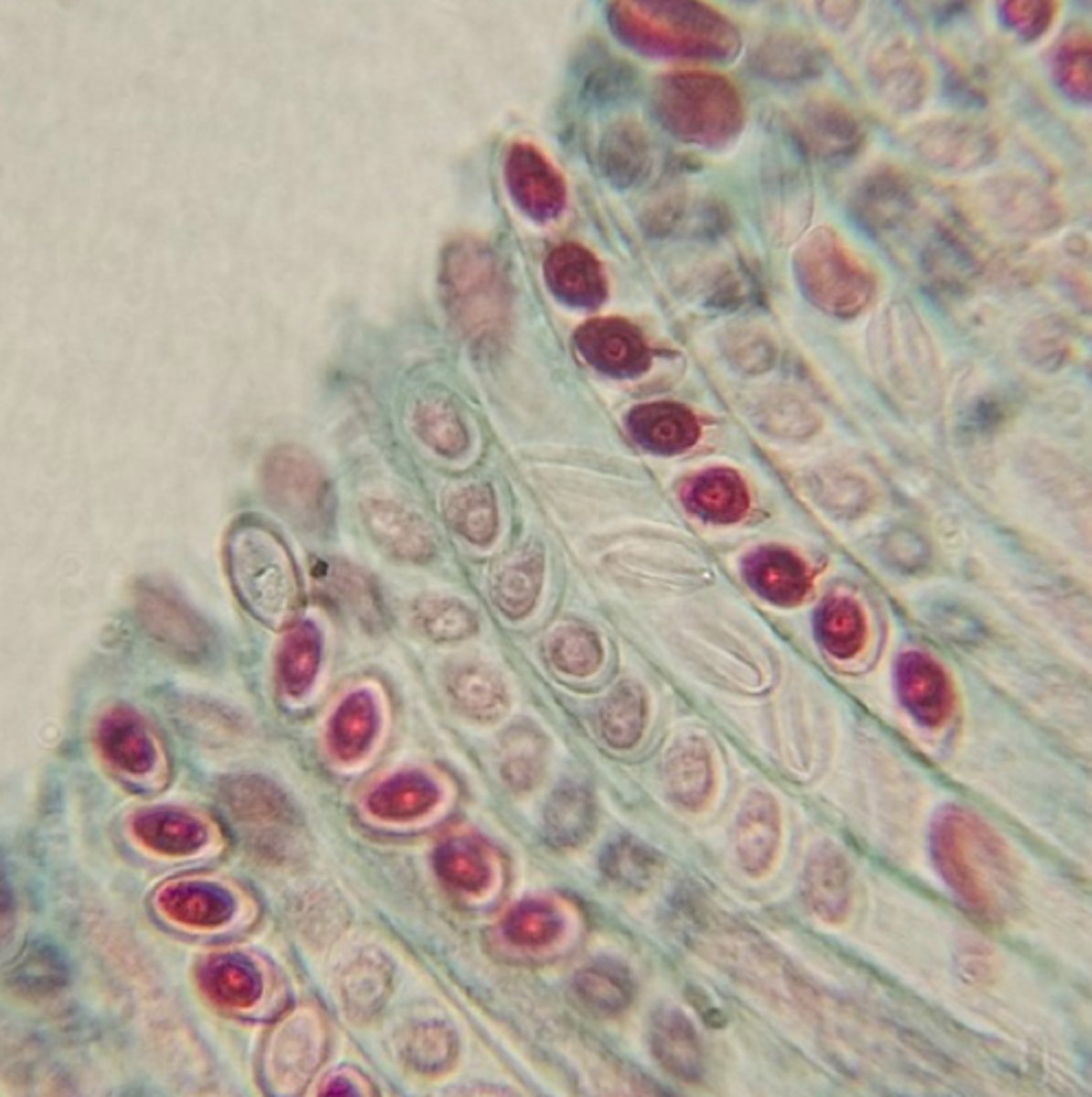
ascus
vertical, sac-like strucures containing 8 ascospores. Characteristic of ascomycota
ascocarp
fruiting body of ascomycetes made of several asci
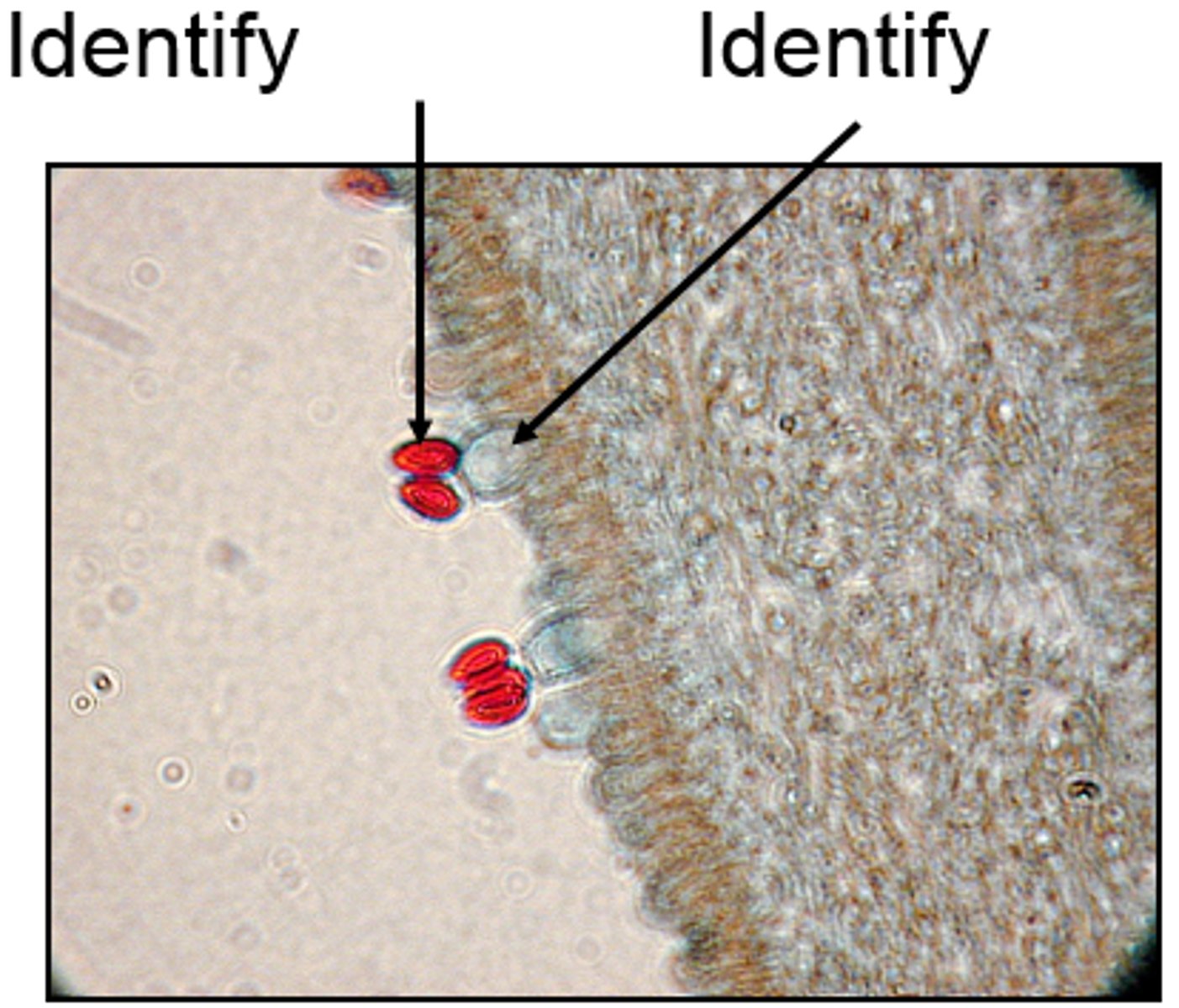
basidium
Club-shaped, reproductive structure in which club fungi produce 4 external basidiospores. Characteristic of basidiomycota
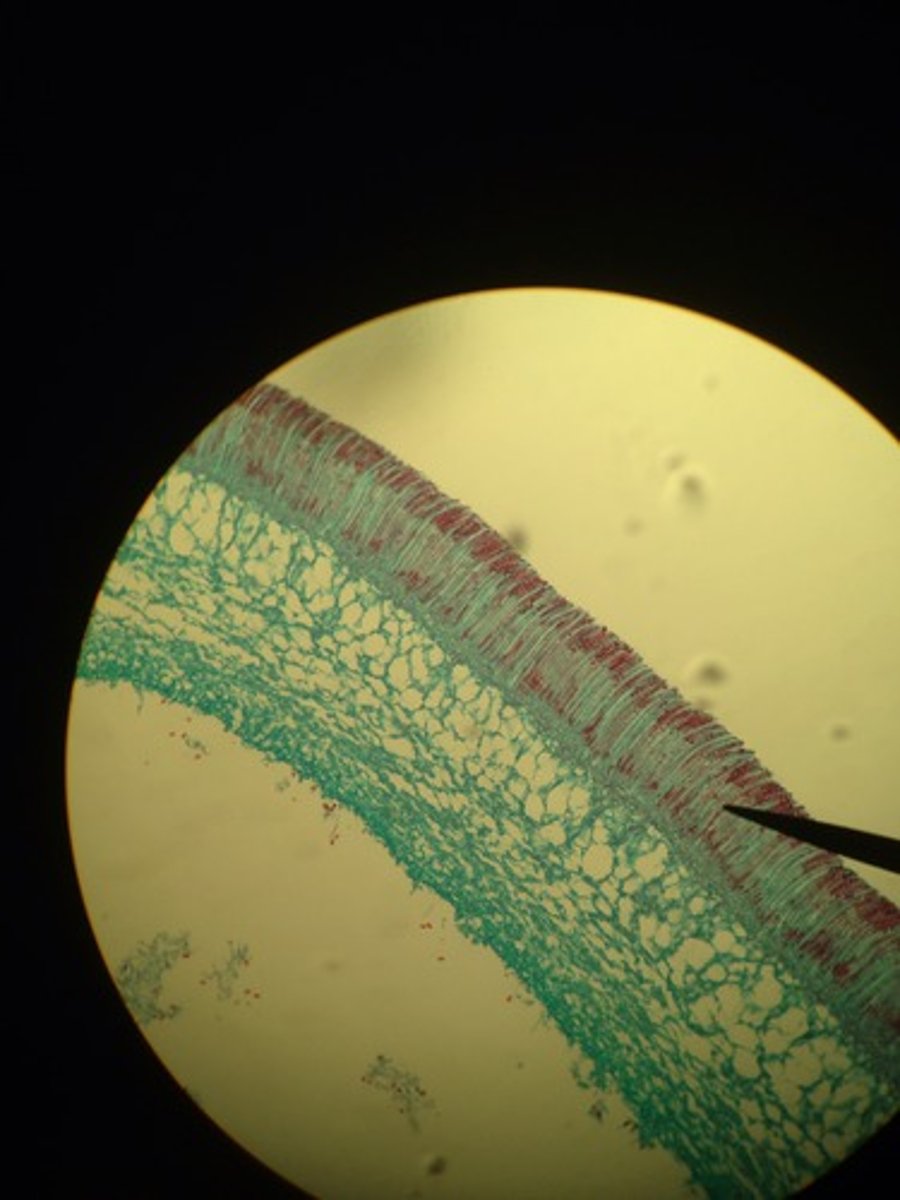
basiocarp
Fruiting body of basidiomycota. Made of a stalk called the stripe and a flattened cap with gills called Basidia underneath.
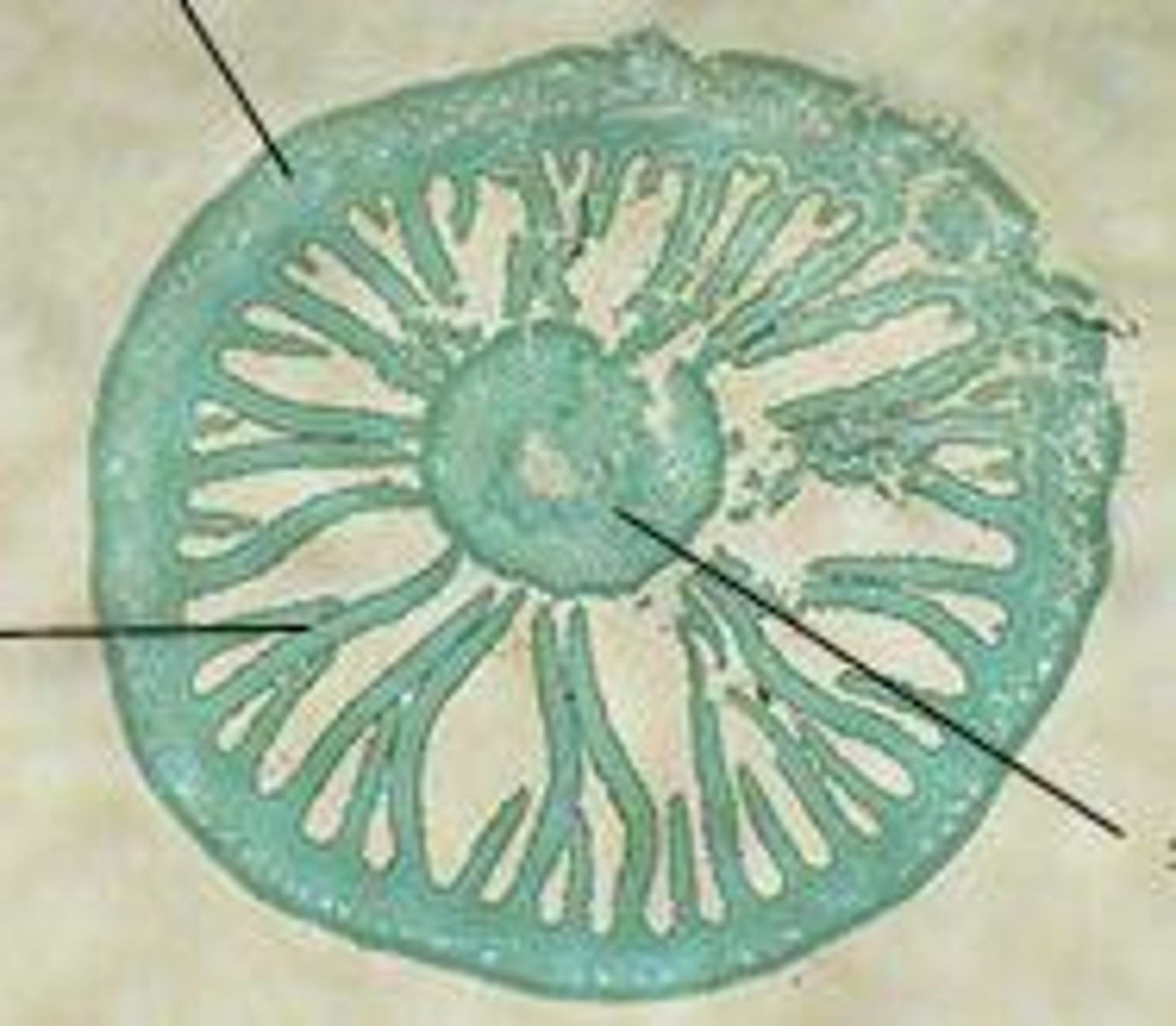
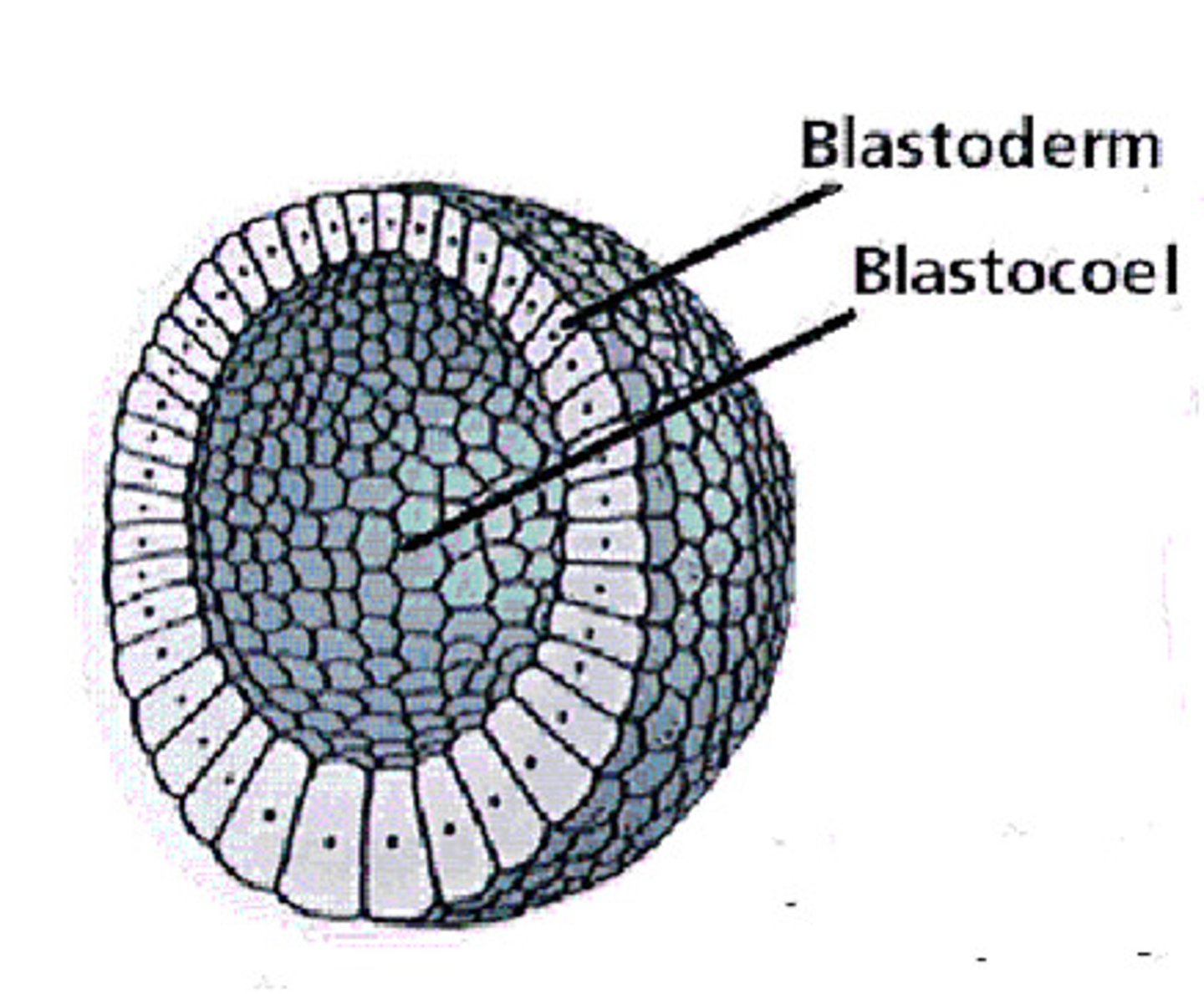
blastula
hollow ball of cells
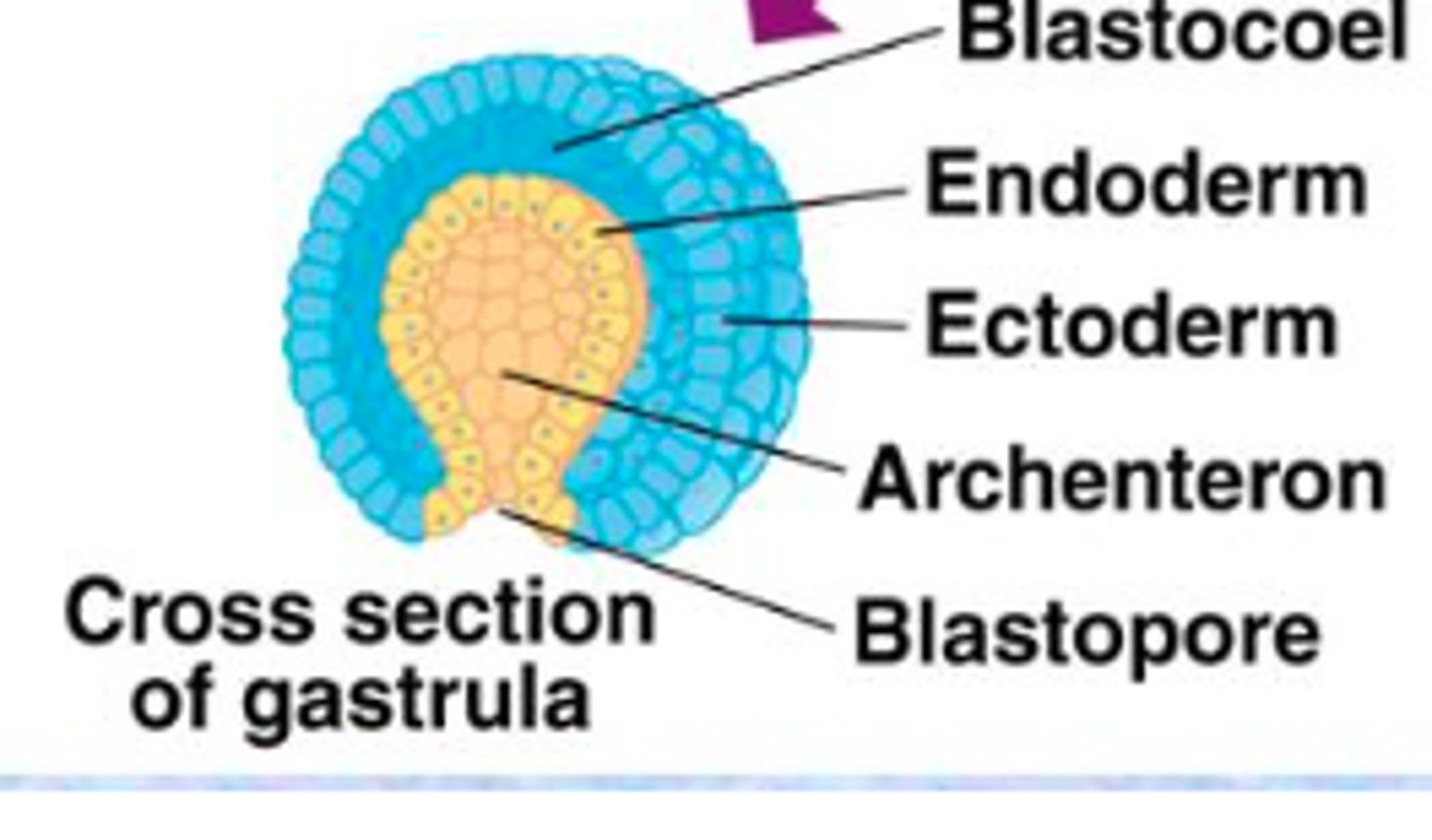
gastrula
In animal development, a series of cell and tissue movements in which the blastula-stage embryo folds inward, producing a three-layered embryo, the gastrula.
ectoderm
outermost germ layer; produces sense organs, nerves, and outer layer of skin
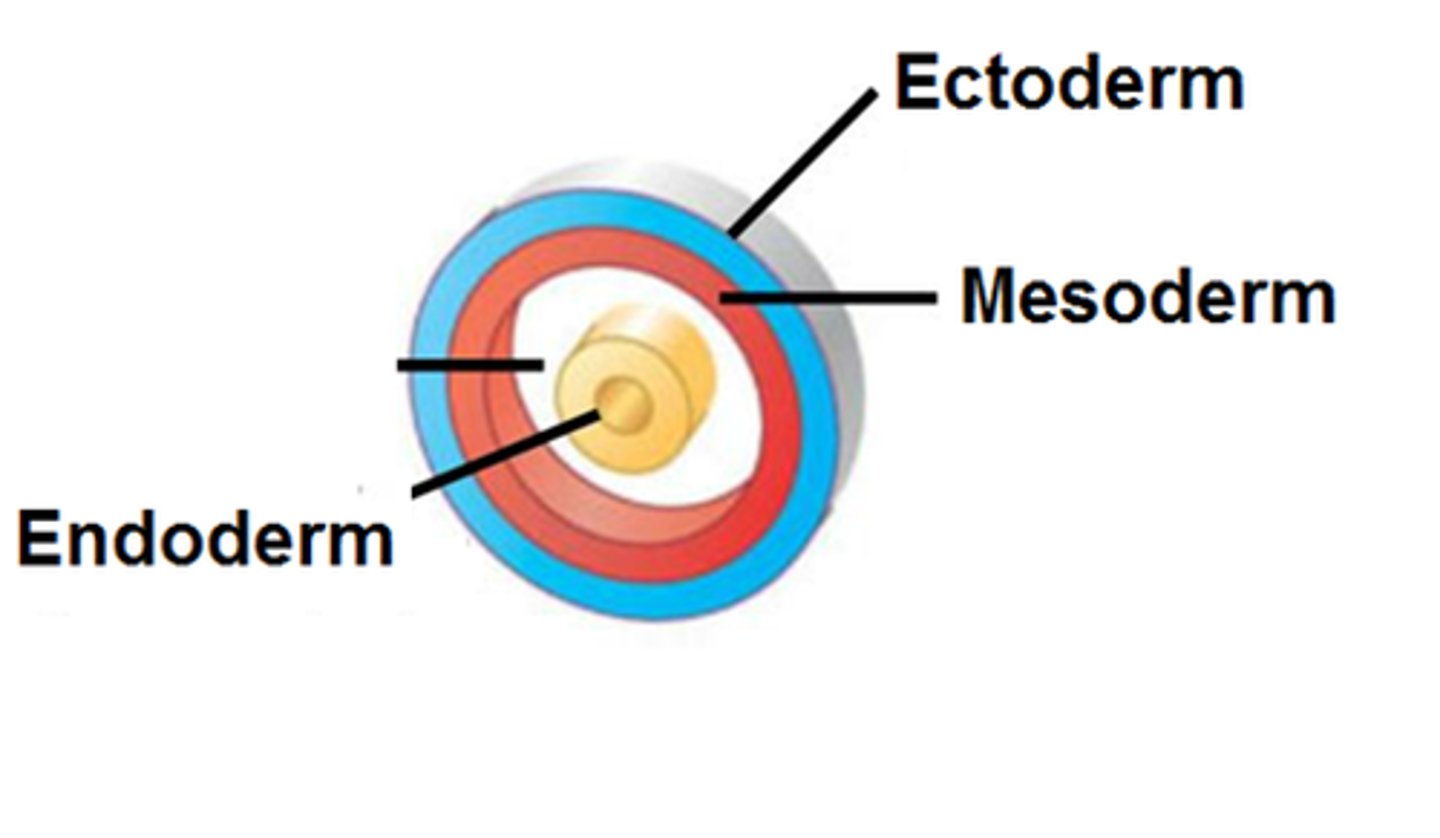
endoderm
the inner germ layer that develops into the lining of the digestive and respiratory systems
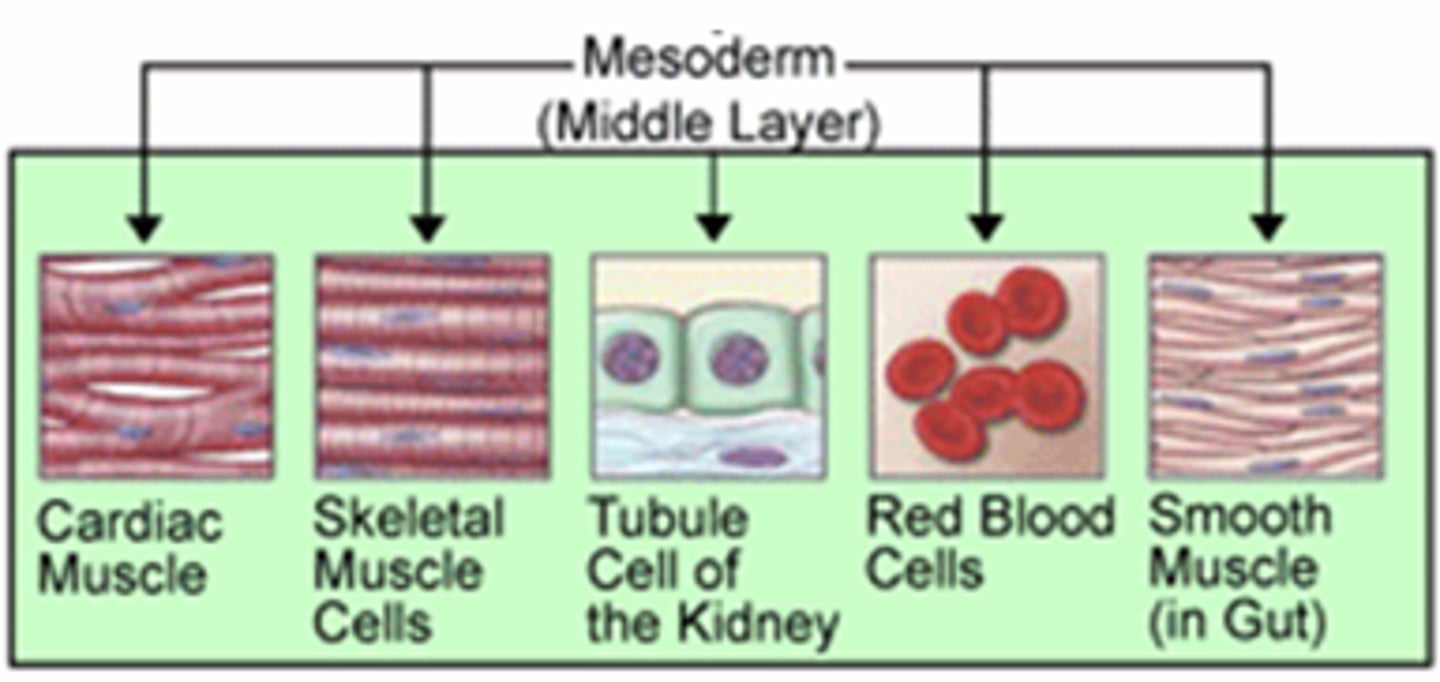
mesoderm
middle germ layer; develops into muscles, and much of the circulatory, reproductive, skeletal, and excretory systems
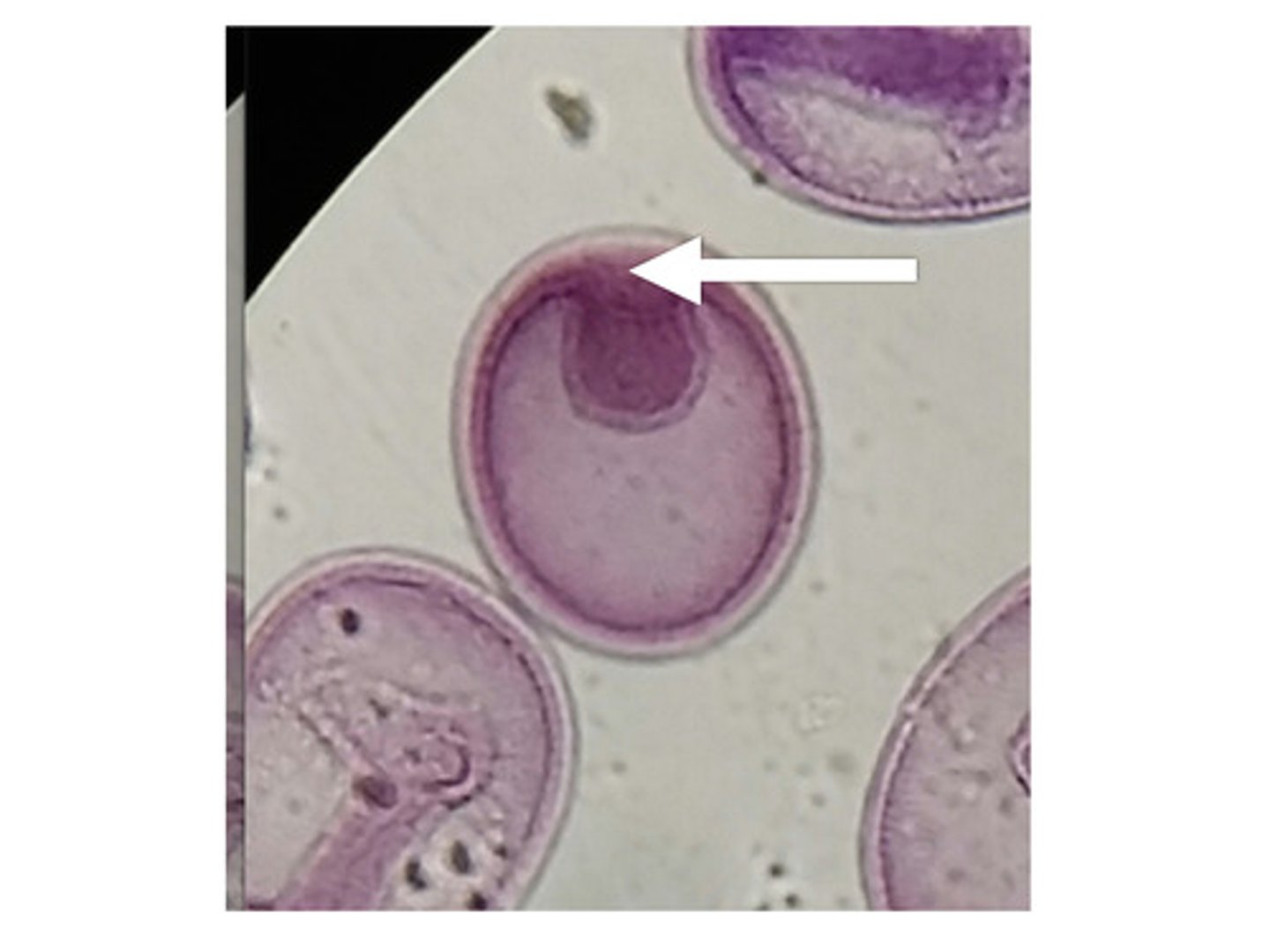
blastopore
the opening of the central cavity of an embryo in the early stage of development.
complete gut
two openings, a mouth an and anus. One-way
incomplete gut
gut has a single opening rather than a separate mouth and anus. Blind, two-way gut.

acoelomate
an animal that lacks a coelom, or body cavity
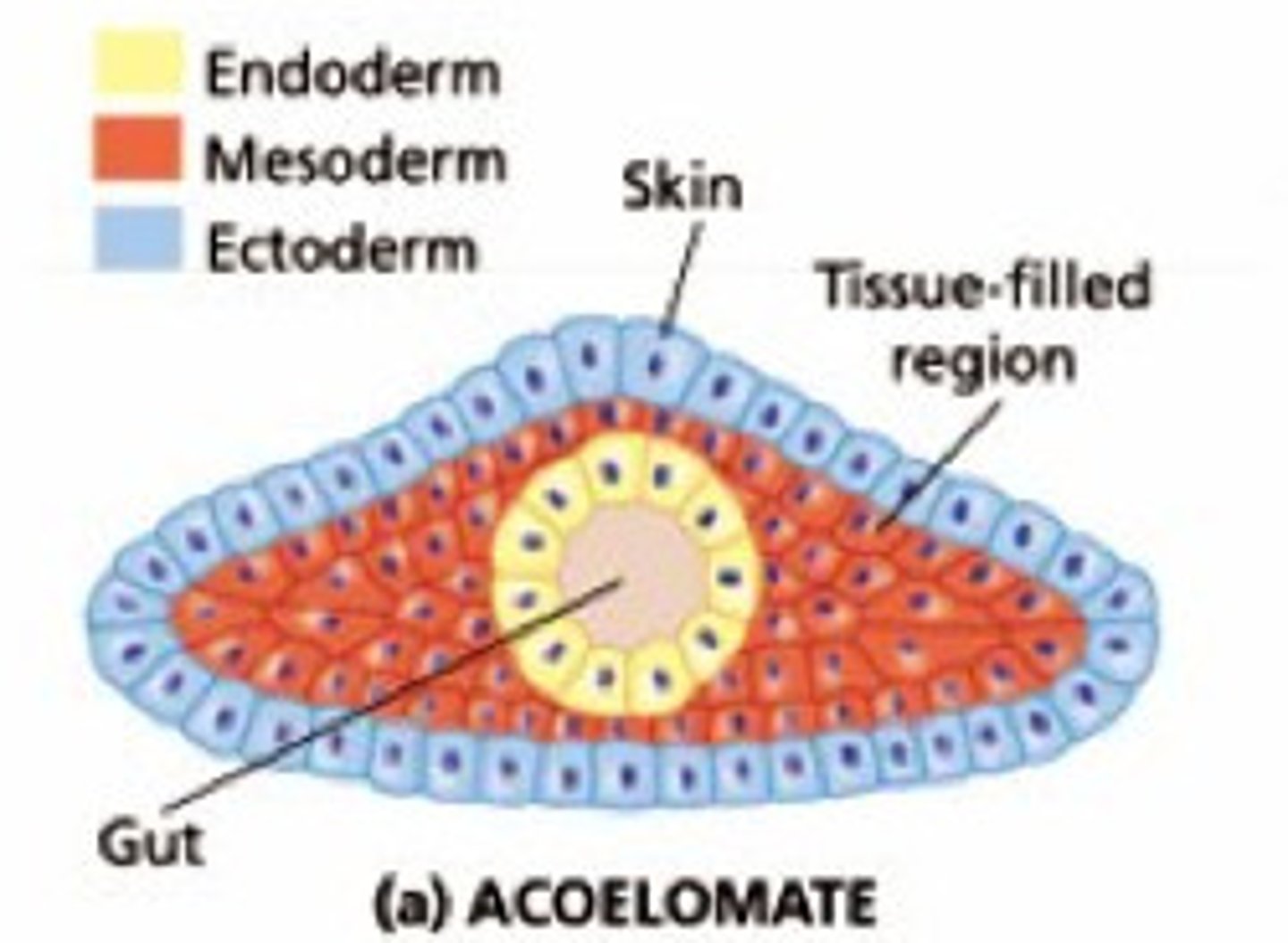
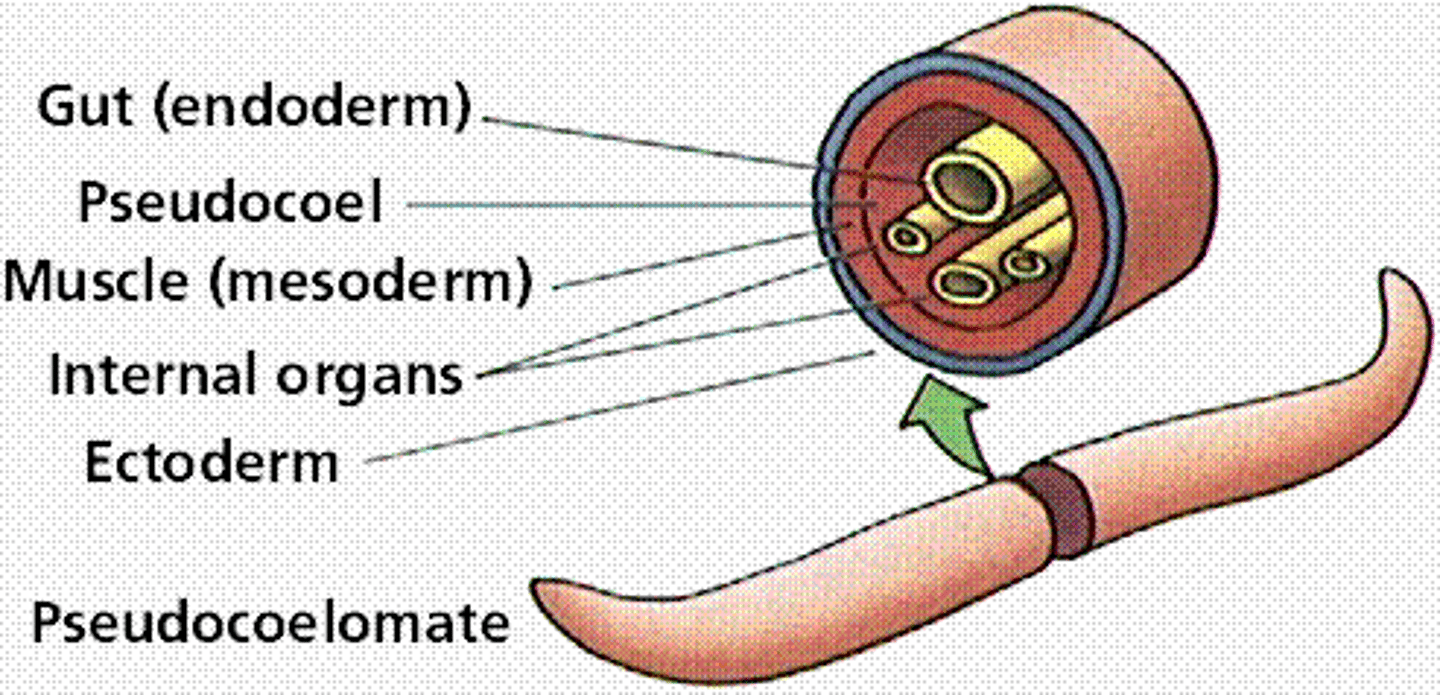
pseudocoelomate
An animal whose body cavity is not completely lined by mesoderm
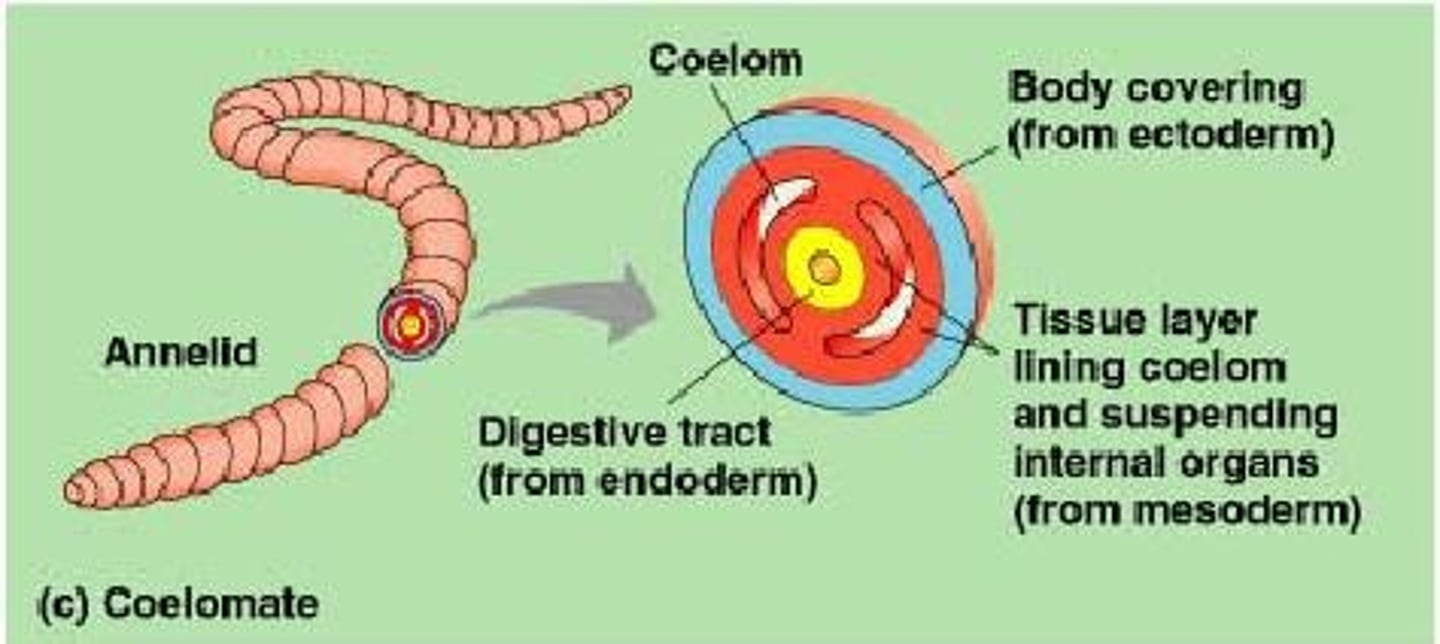
coelomate
An animal that possesses a true coelom (a body cavity lined by tissue completely derived from mesoderm).
radial symmetry
The quality of having many lines of symmetry that all pass through a central point.

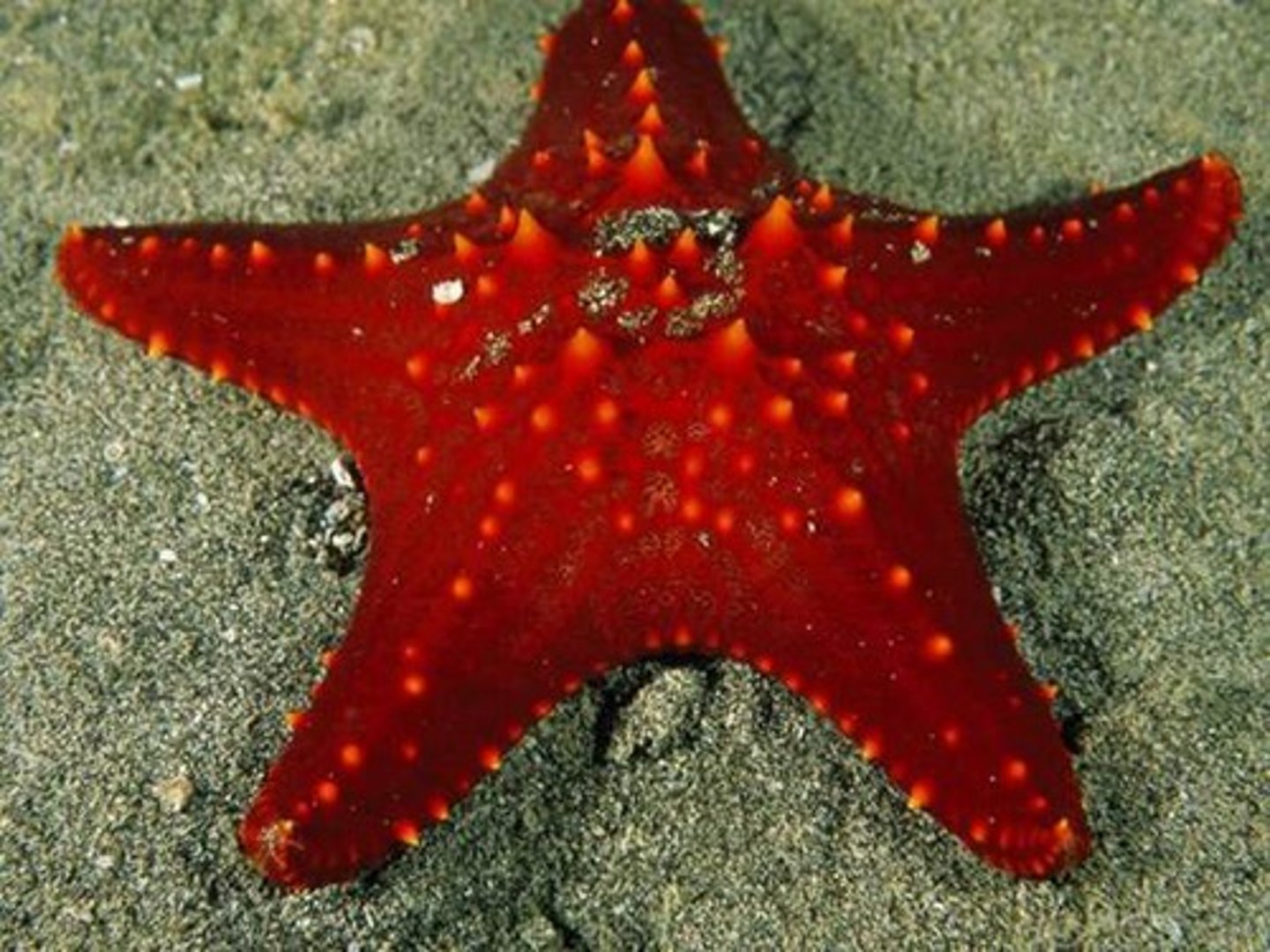
pentaradial symmetry
circular body plan that can be divided into 5 equal parts

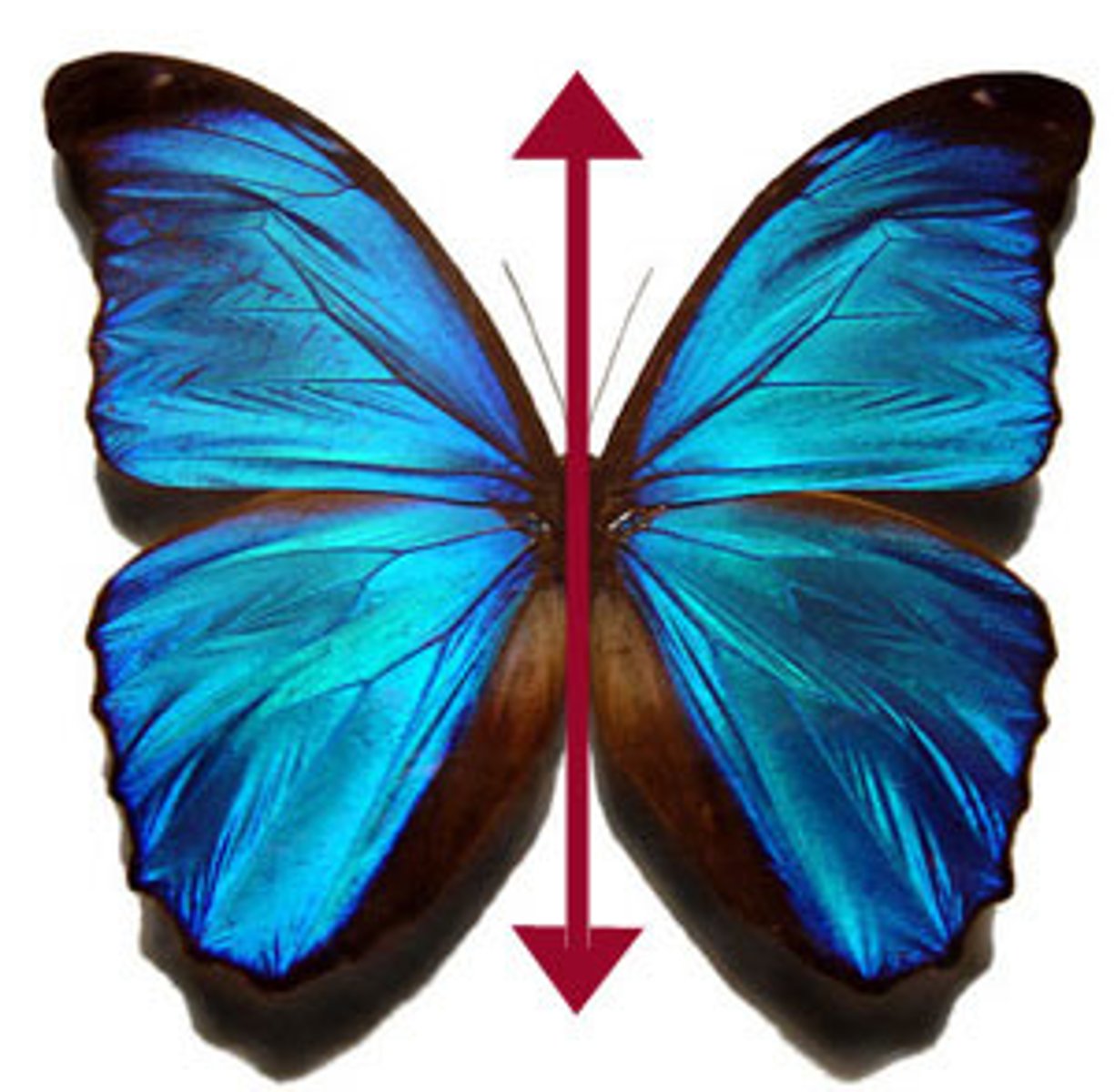
bilateral symmetry
Body plan in which only a single, imaginary line can divide the body into two equal halves.

asymmetrical
no symmetry
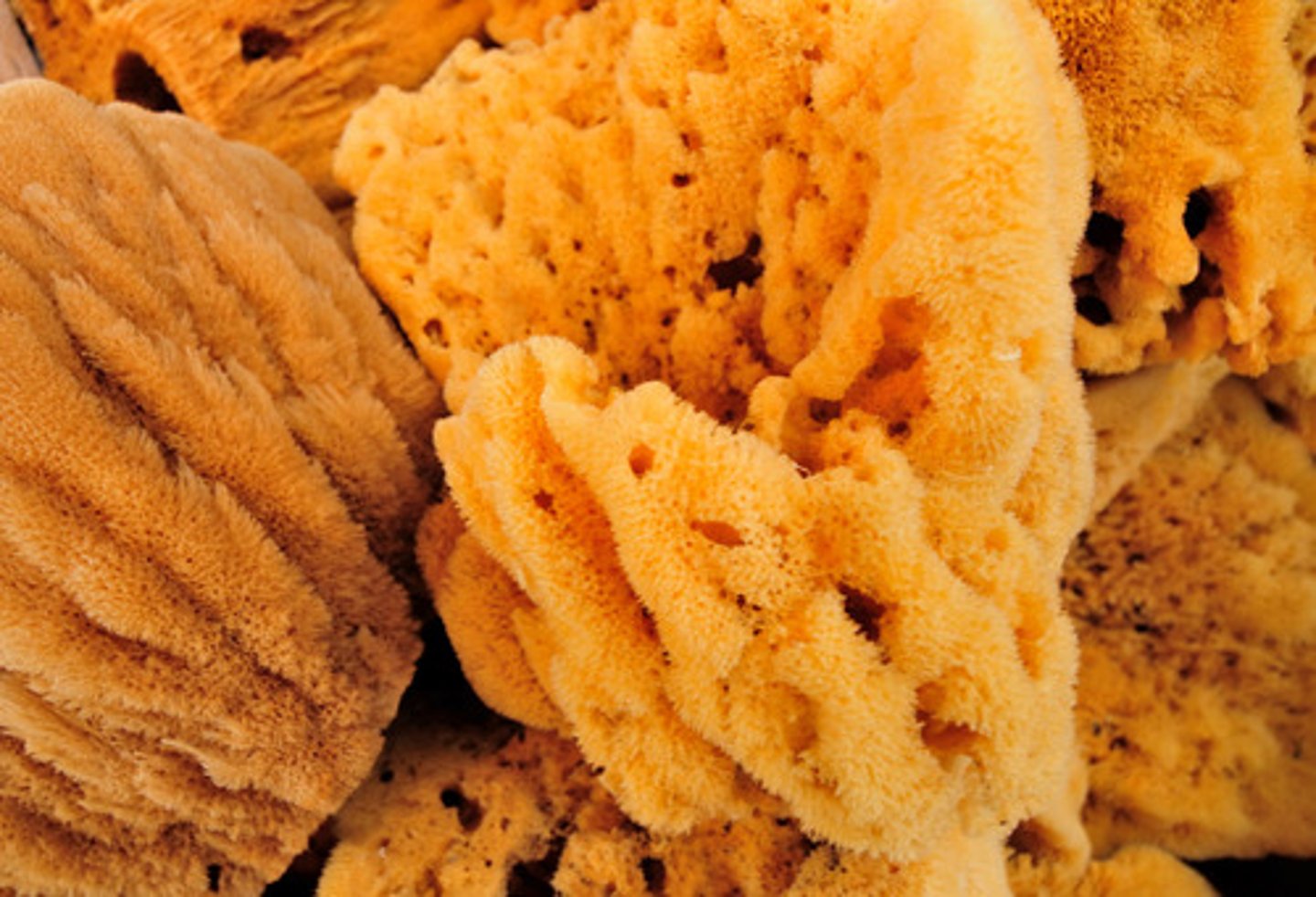

spicule
a needle of silica or calcium carbonate in the skeleton of some sponges. Morphology can be characteristic of species

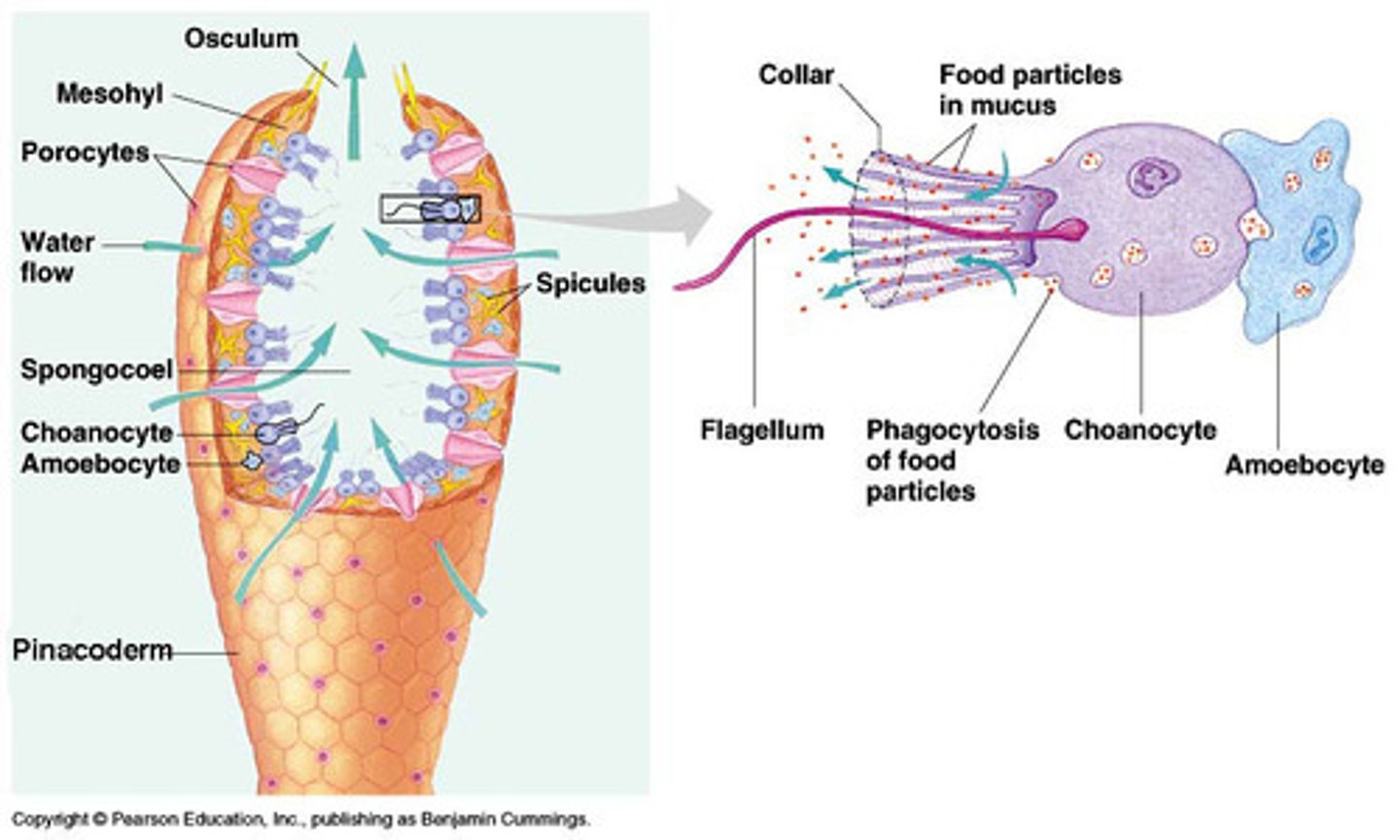
choanocytes (collar cells)
a flagellated cell with a collar of protoplasm at the base of the flagellum, numbers of which line the internal chambers of sponges.
cnidocytes
Special stinging structures on cnidarians that look like small harpoons.
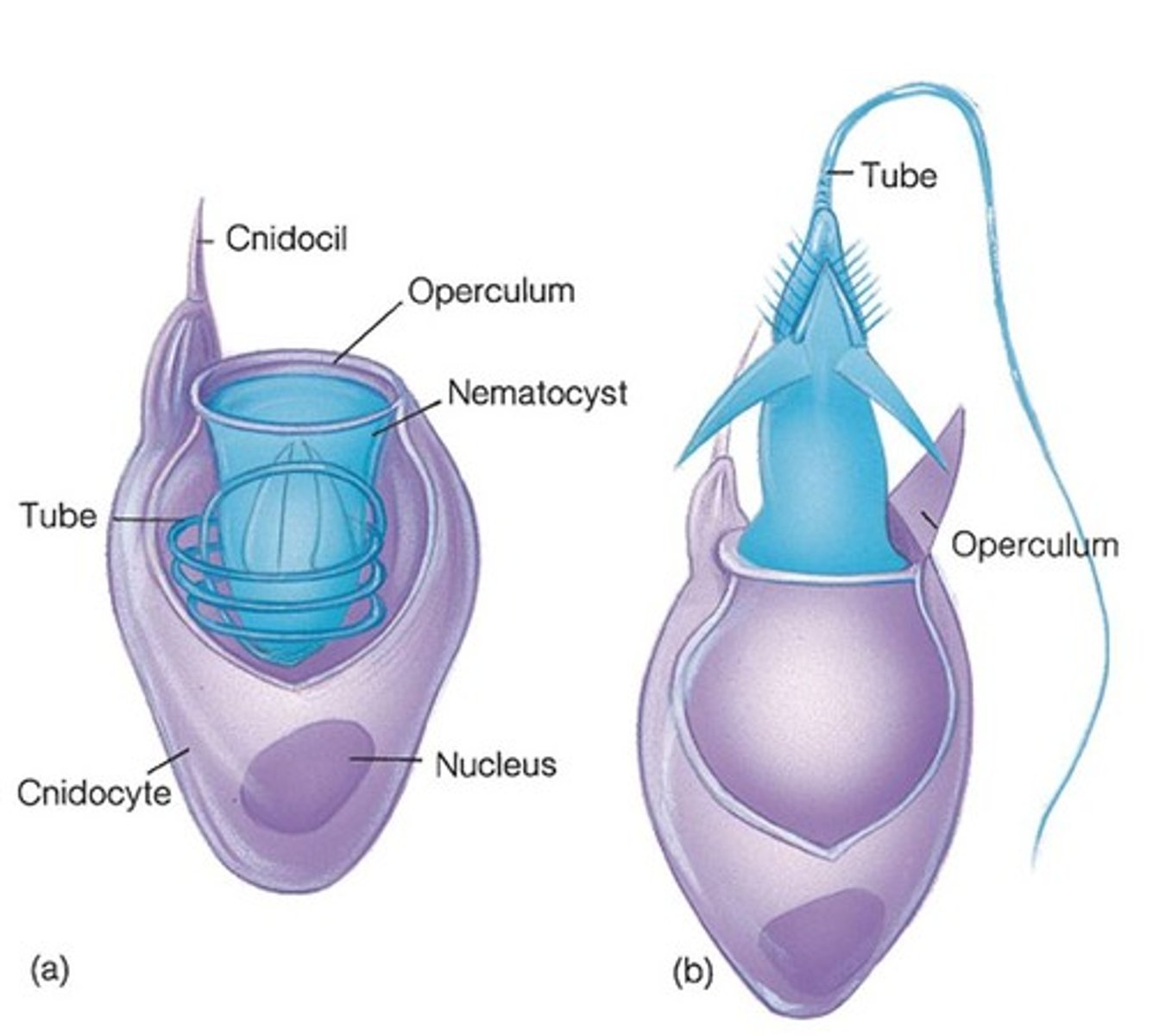
nematocysts
specialized organelles within cnidocytes that eject a stinging thread
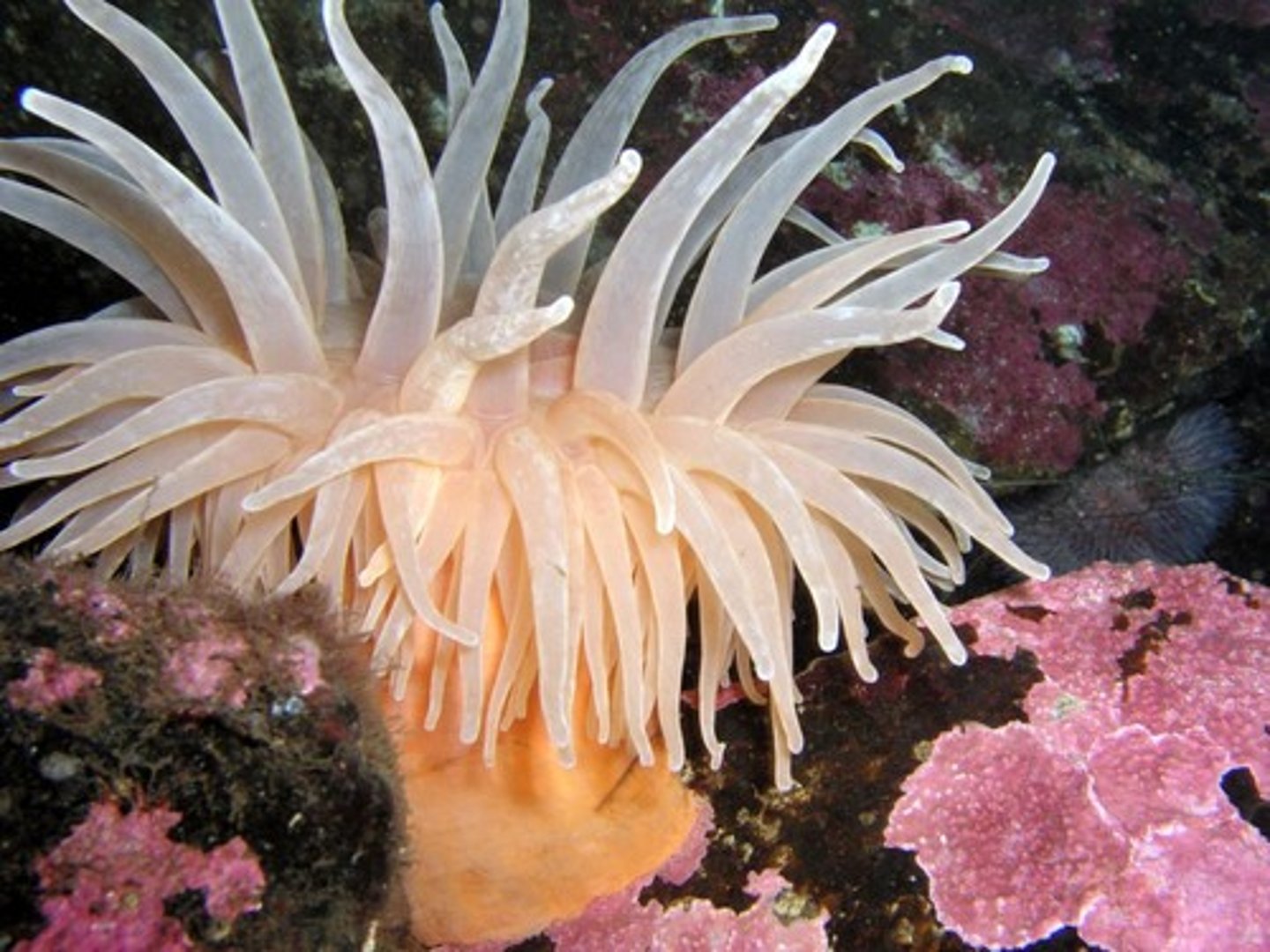

polyp
The sessile, tubular form of a cnidarian with a mouth and tentacles at one end and a basal disk at the other
