BIOL 3410 Lab Practical 2
1/147
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
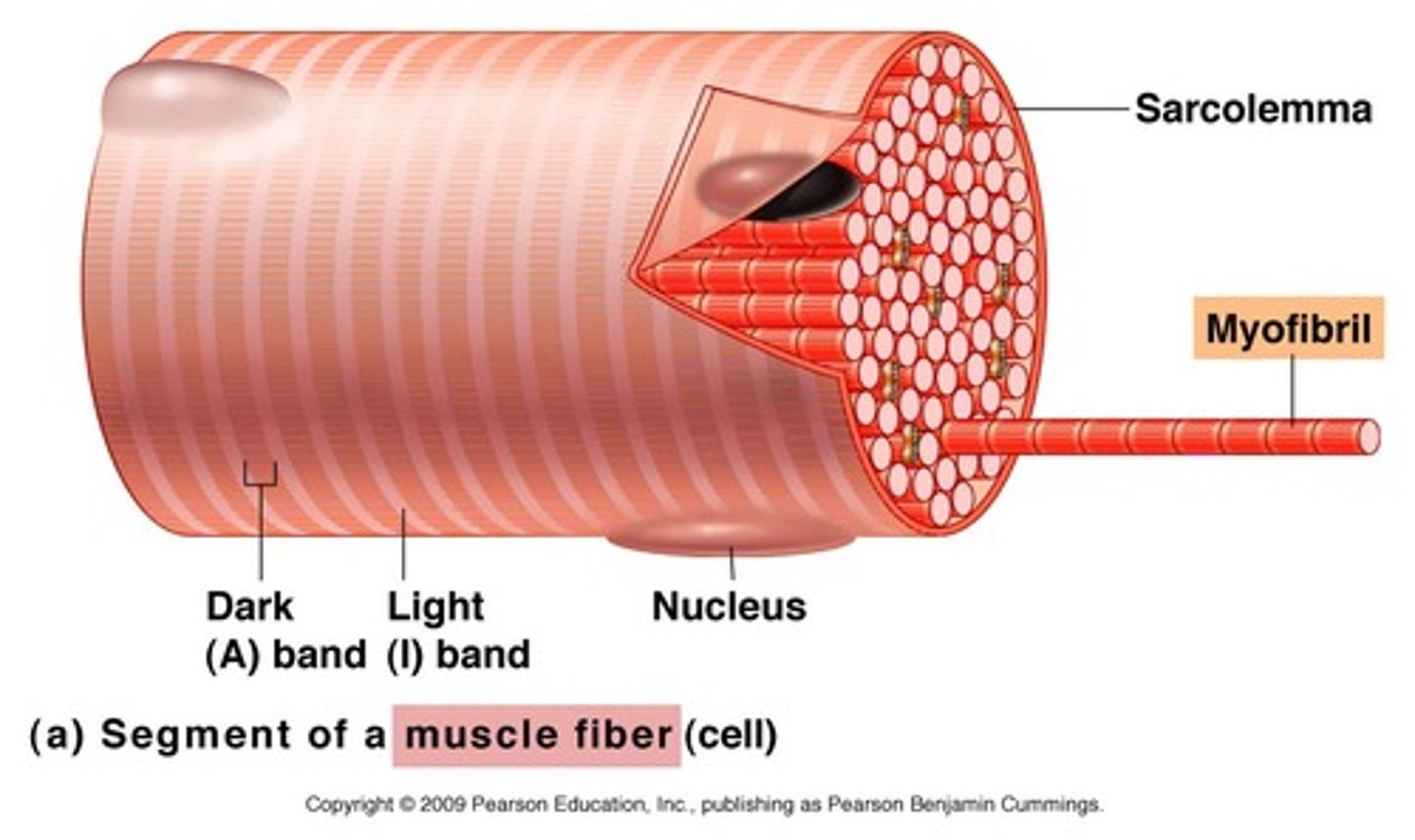
Myofibrils
Microscopic protein filaments that make up muscle cells.
Endomysium
Connective tissue surrounding a muscle fiber
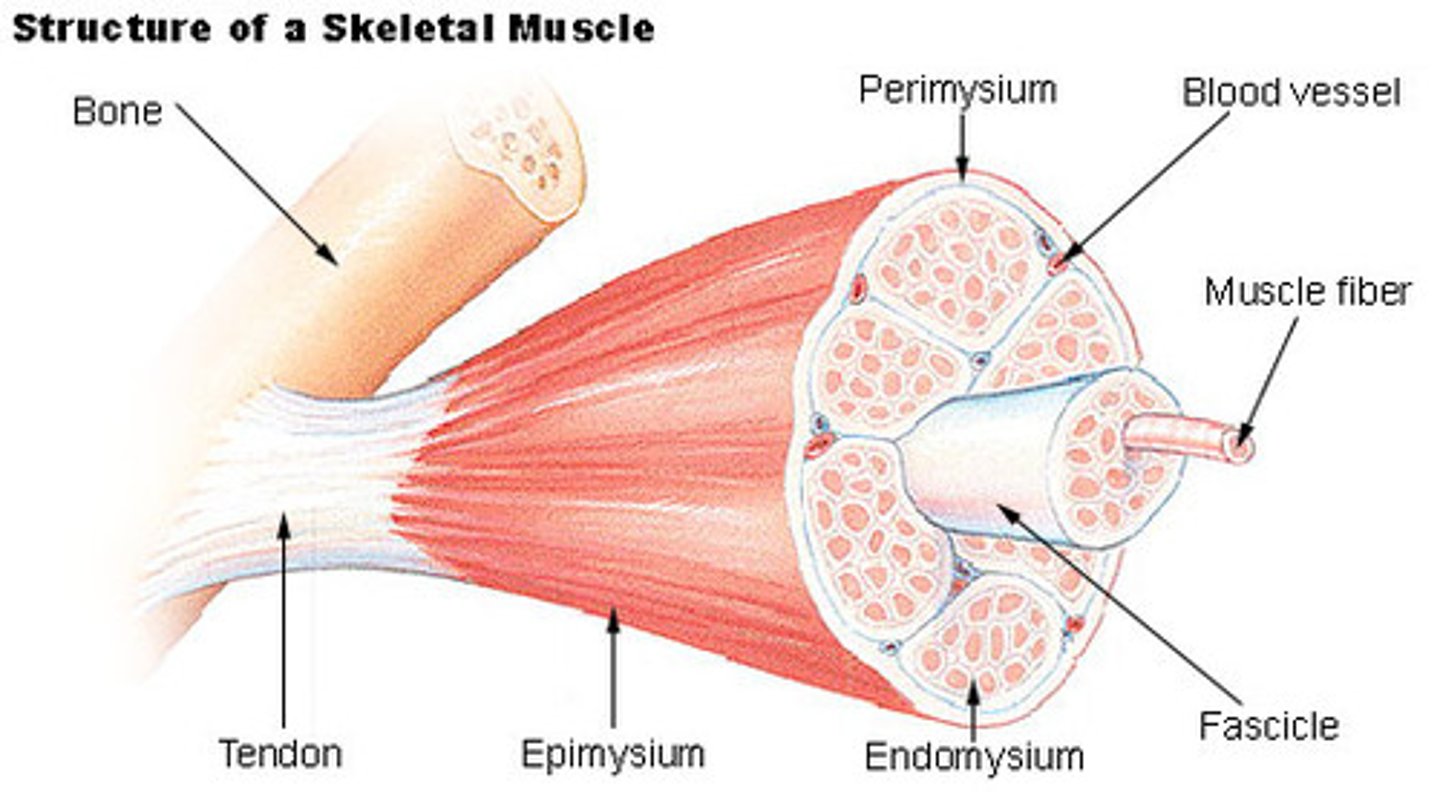
Epimysium
surrounds entire muscle
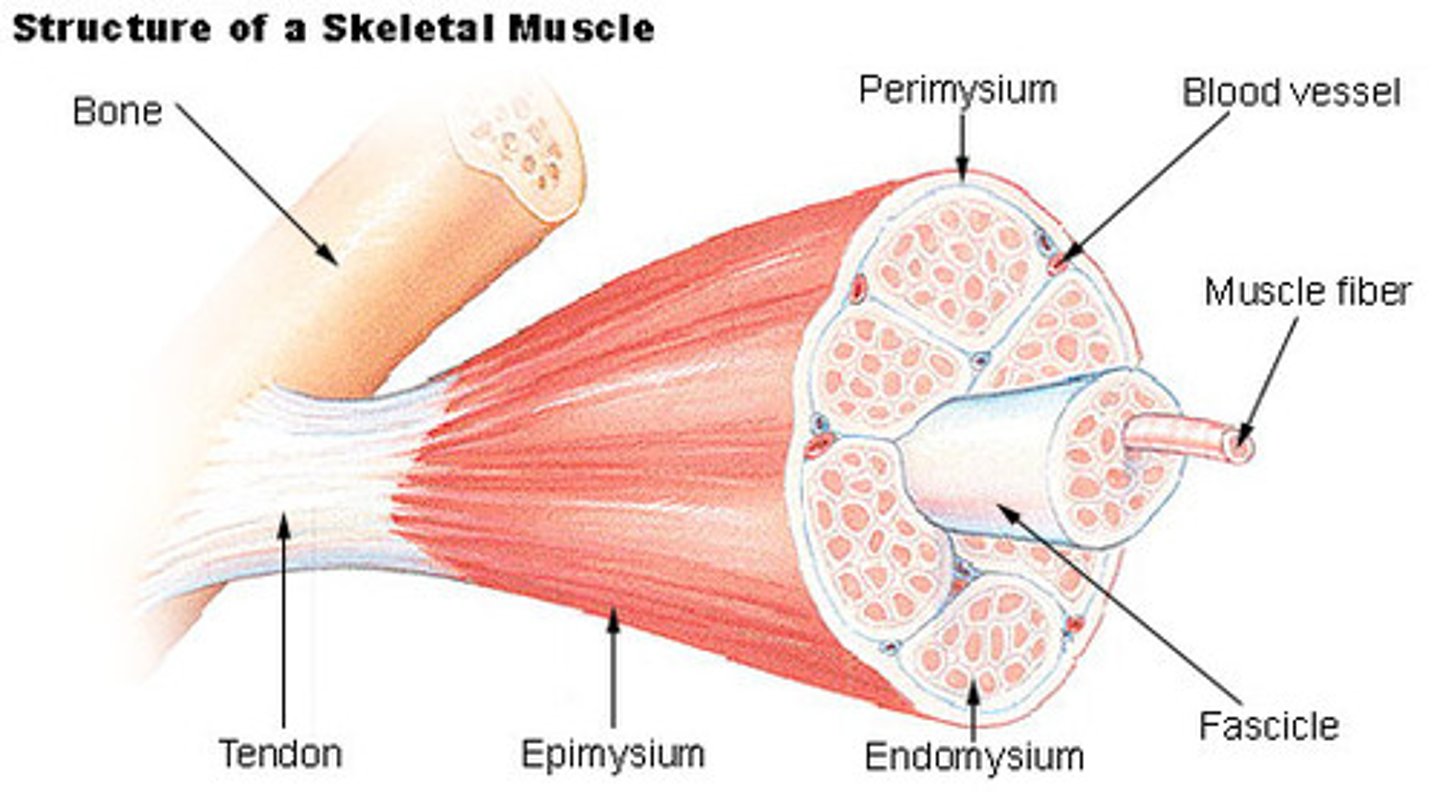
Perimysium
Connective tissue surrounding a fascicle
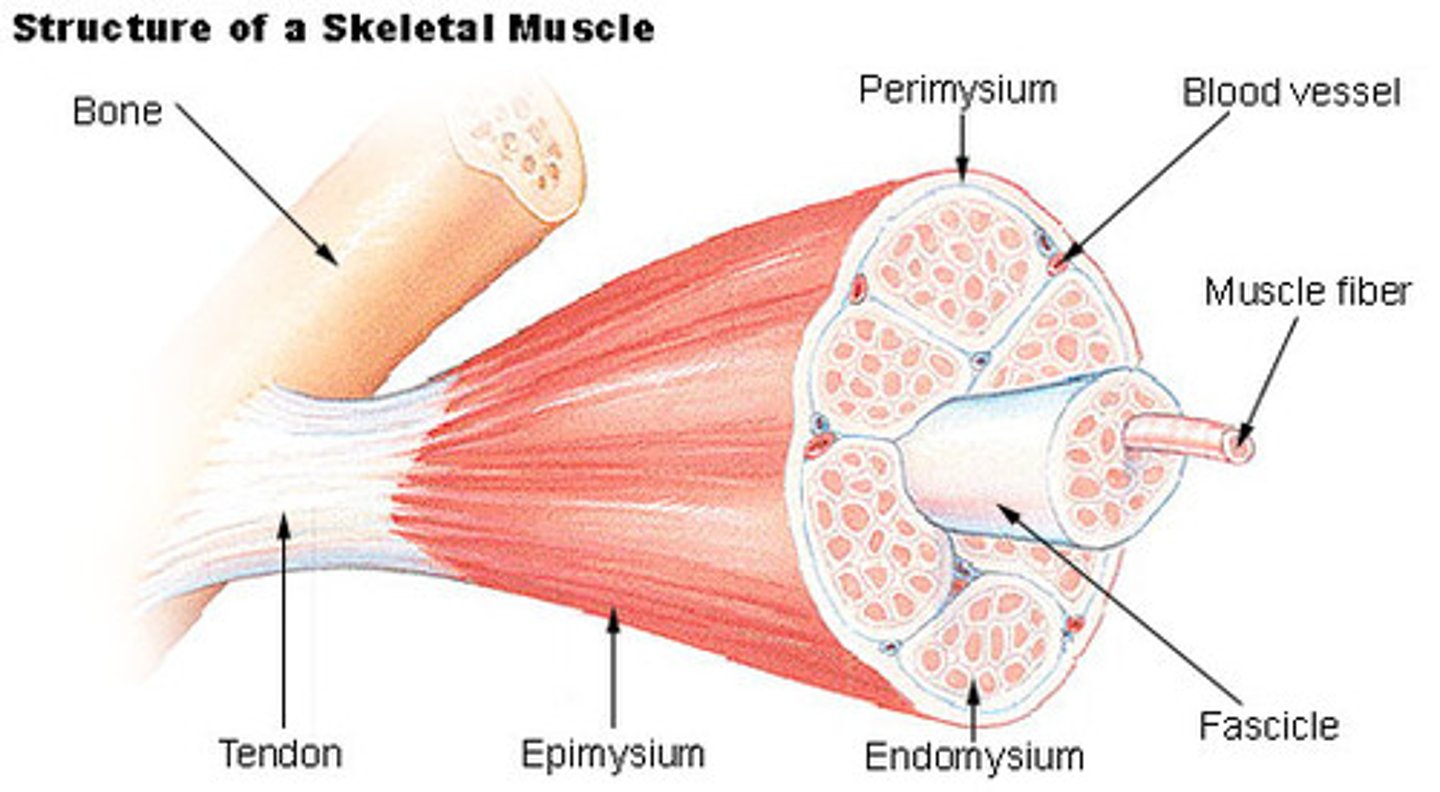
Insertion
the end that has attachment to movable bone
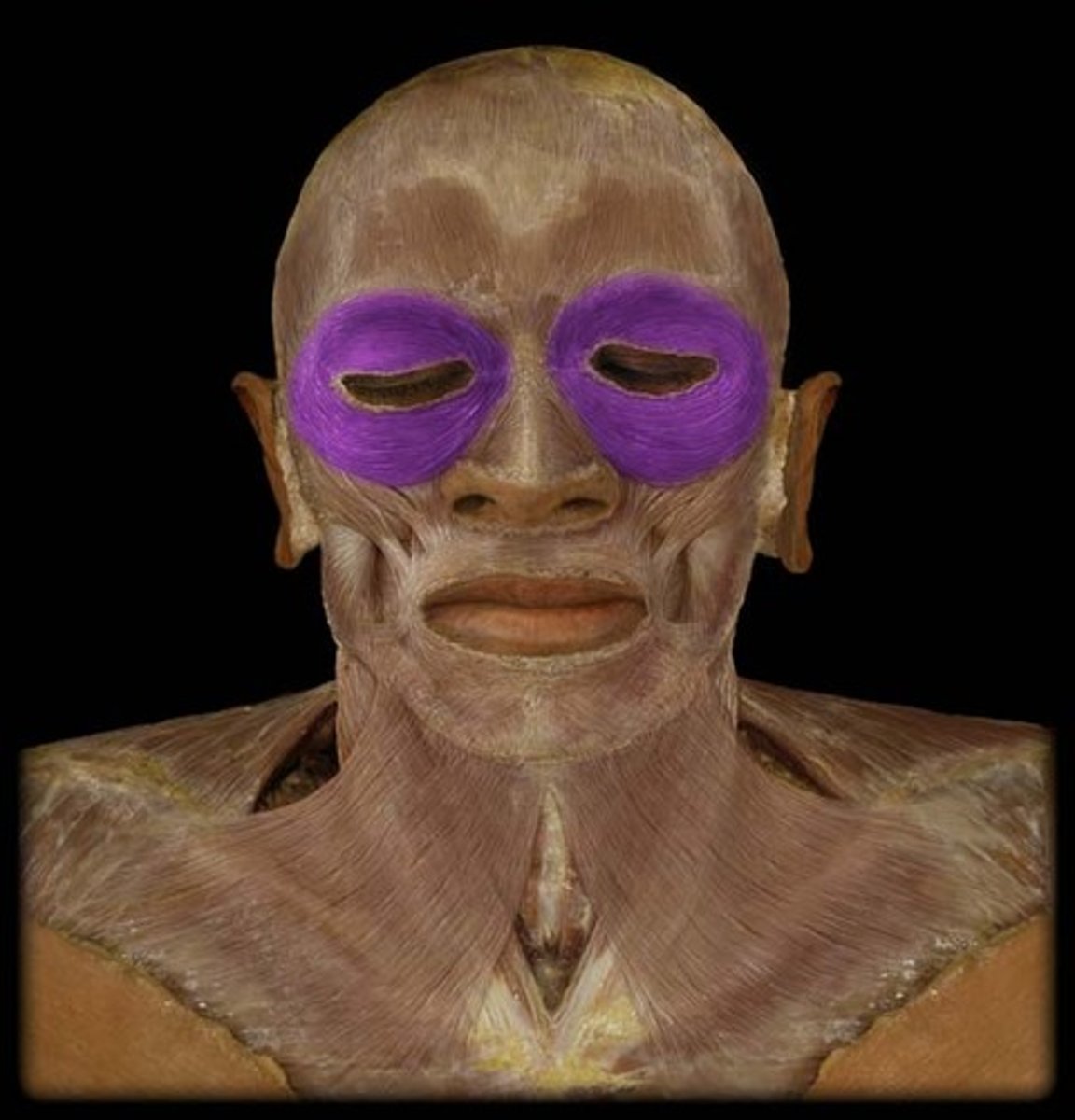
Orbicularis Oculi
Closes eyelids; used in blinking, winking, and squinting
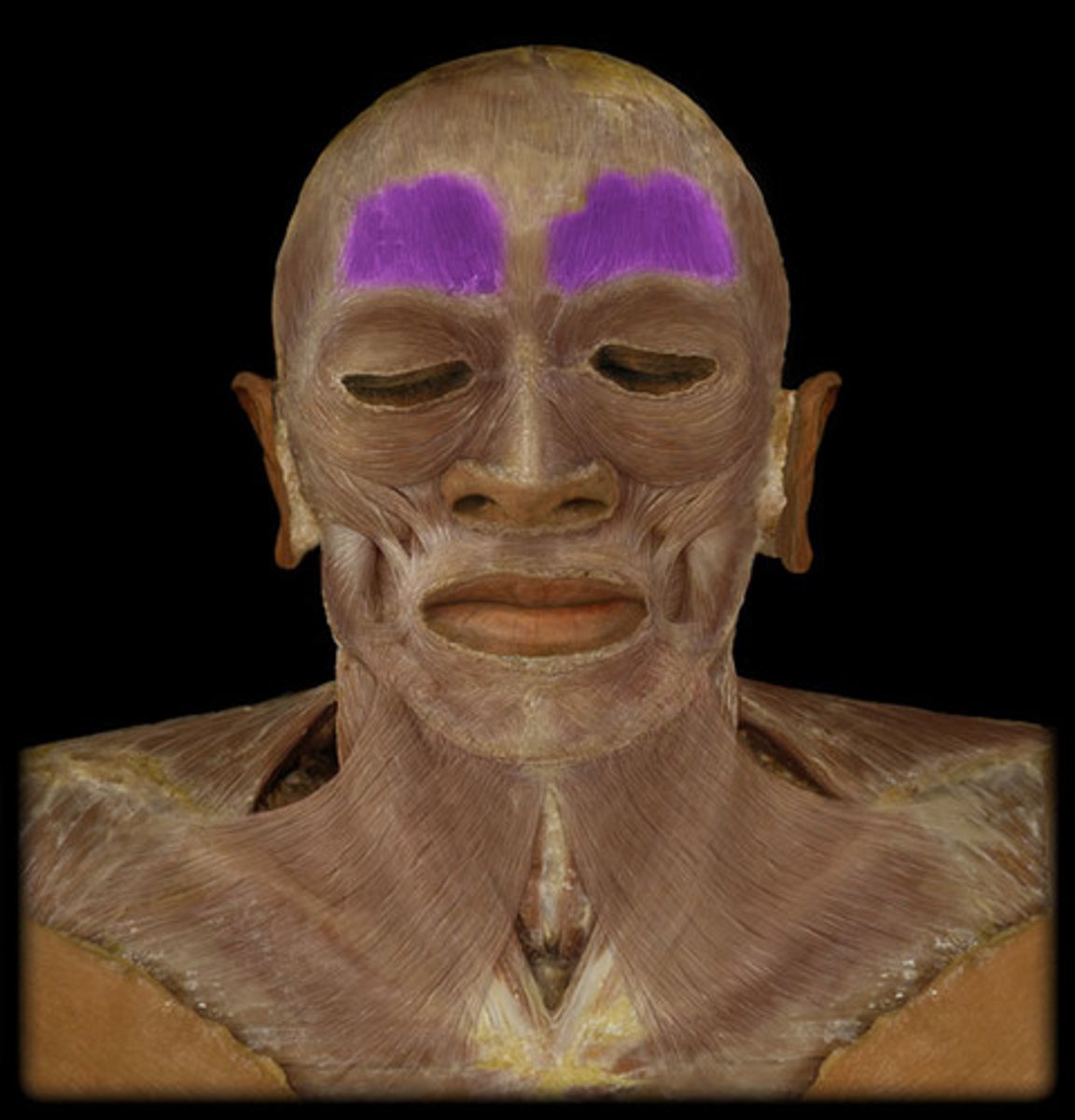
Frontalis
raises eyebrows, wrinkles forehead
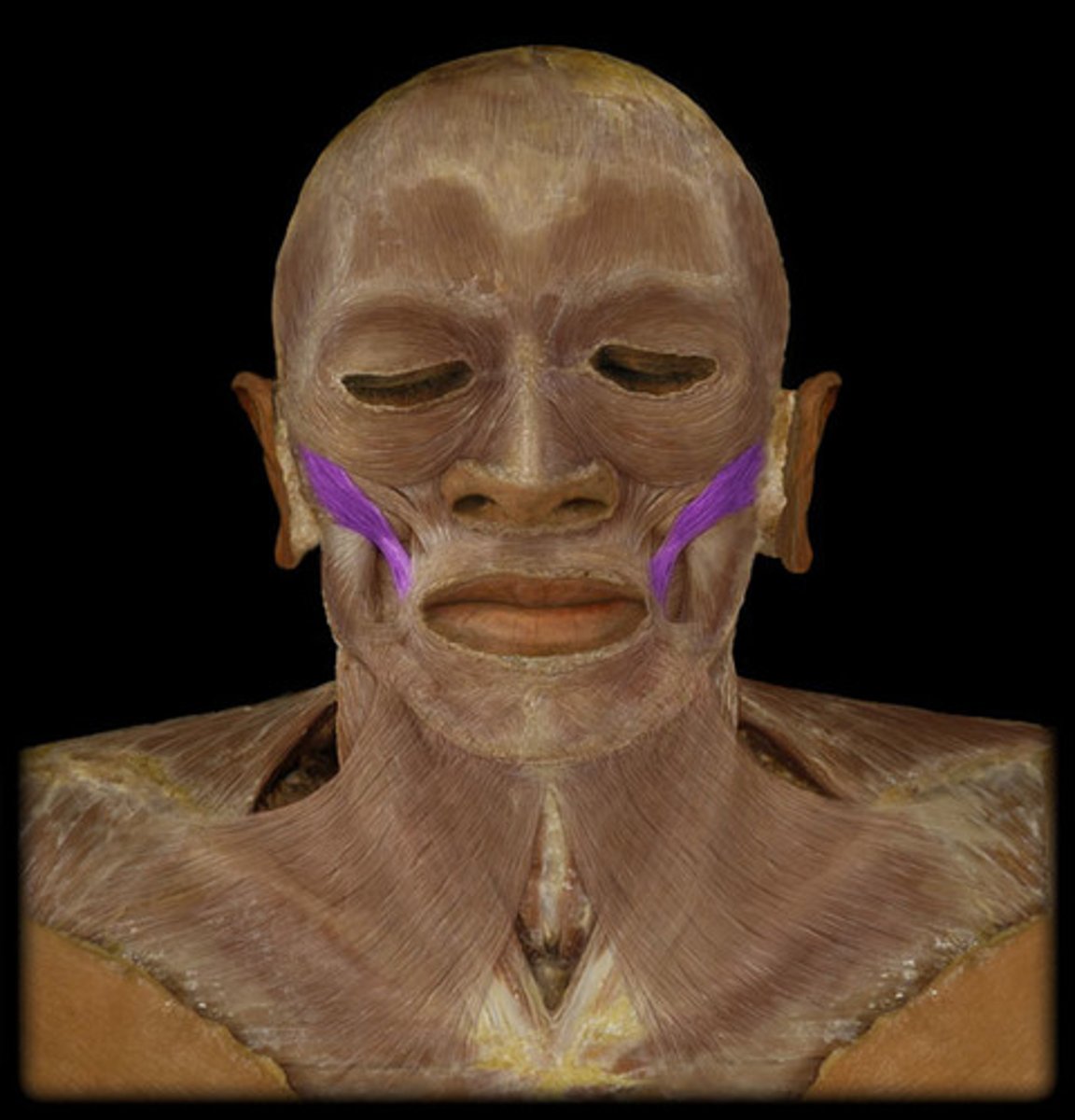
Zygomaticus Major
Muscles on both sides of the face that extend from the zygomatic bone to the angle of the mouth.
These muscles elevate the lip, pull the mouth upward and backward, as when you are laughing or smiling.
Zygomaticus Minor
retracts and elevates upper lip
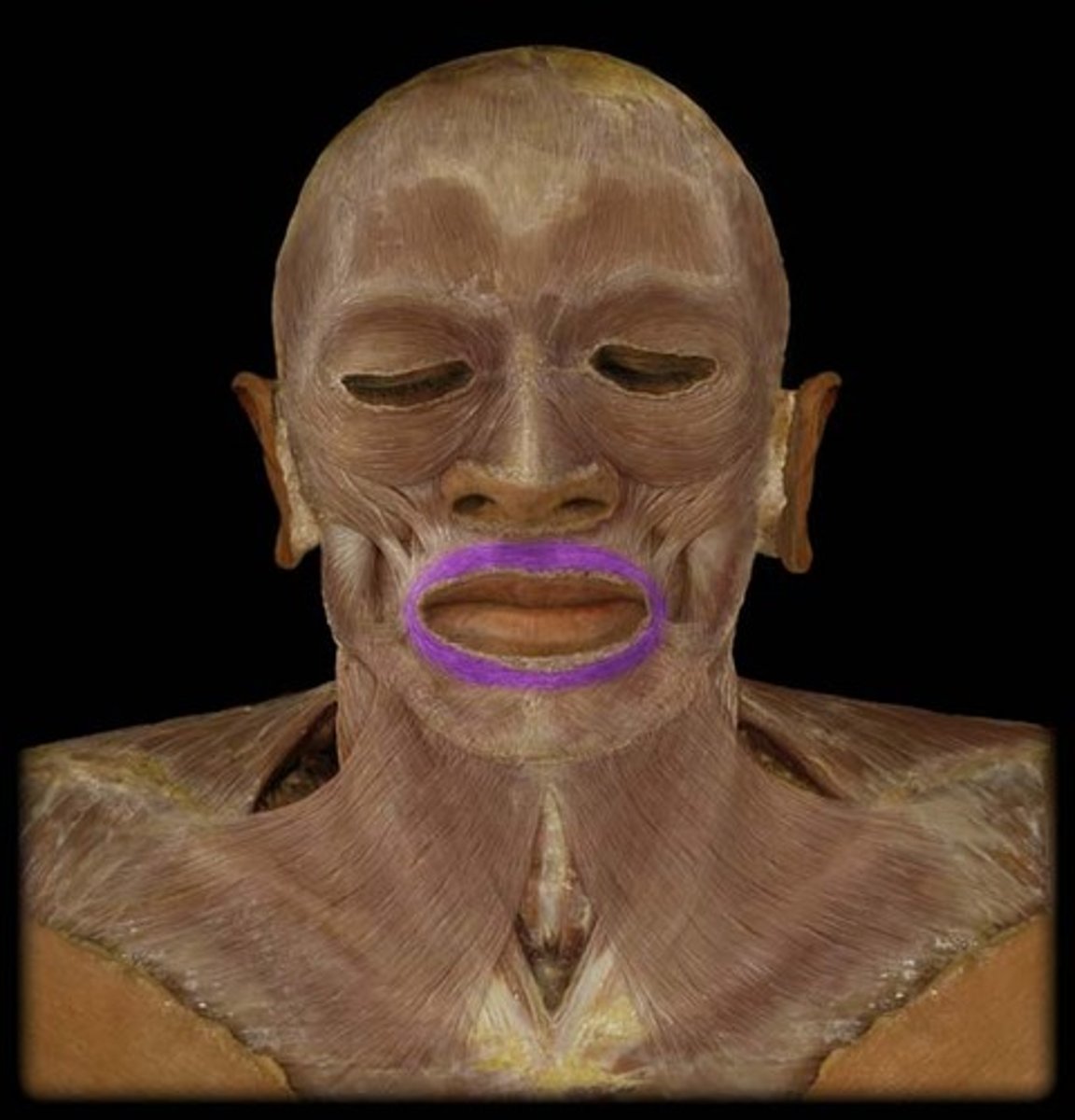
Orbicularis Oris
Closes and protrudes lips; used in whistling and forming many letters during speech; the "kissing muscle"
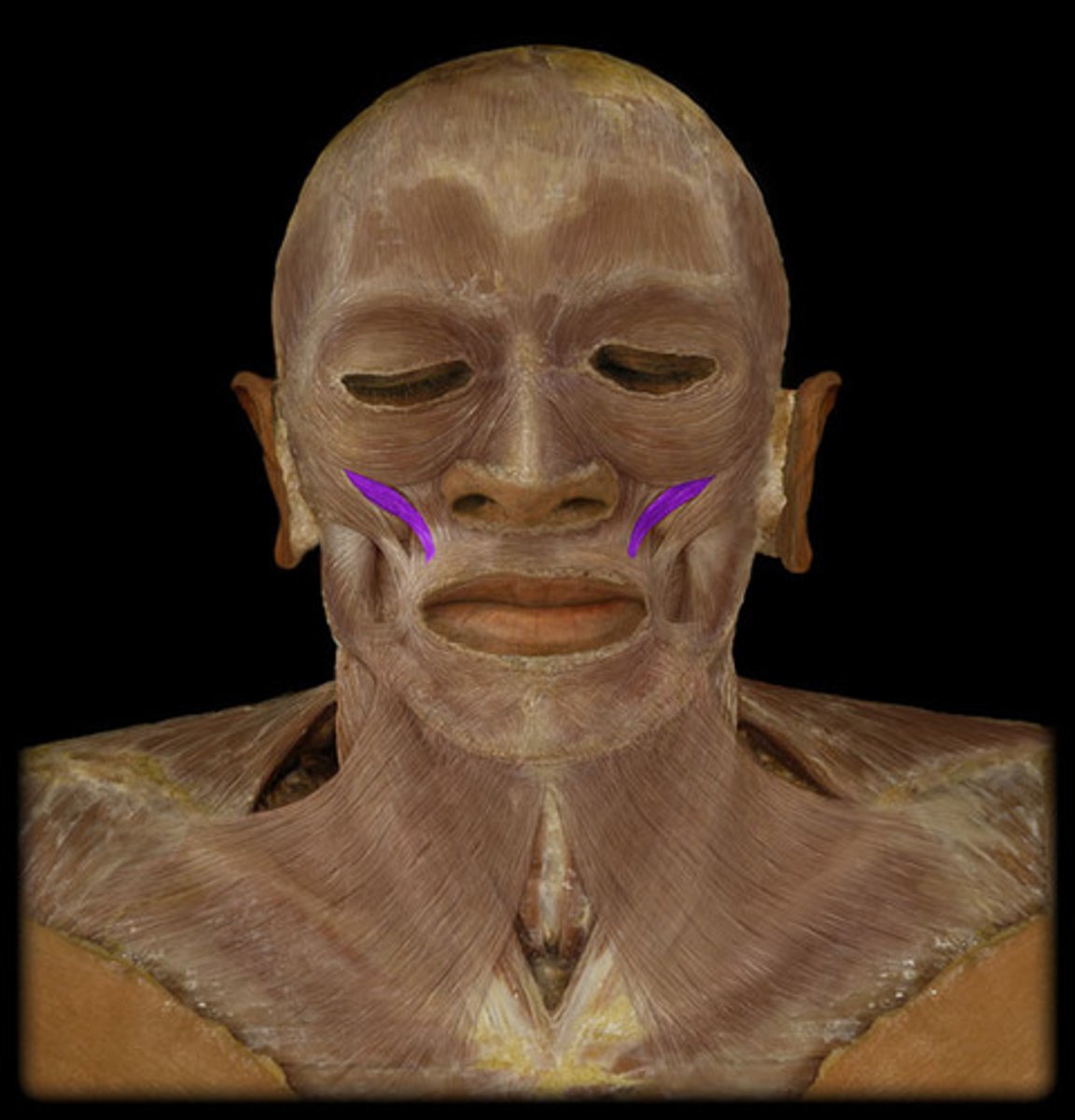
Risorius
Draws corner of mouth laterally
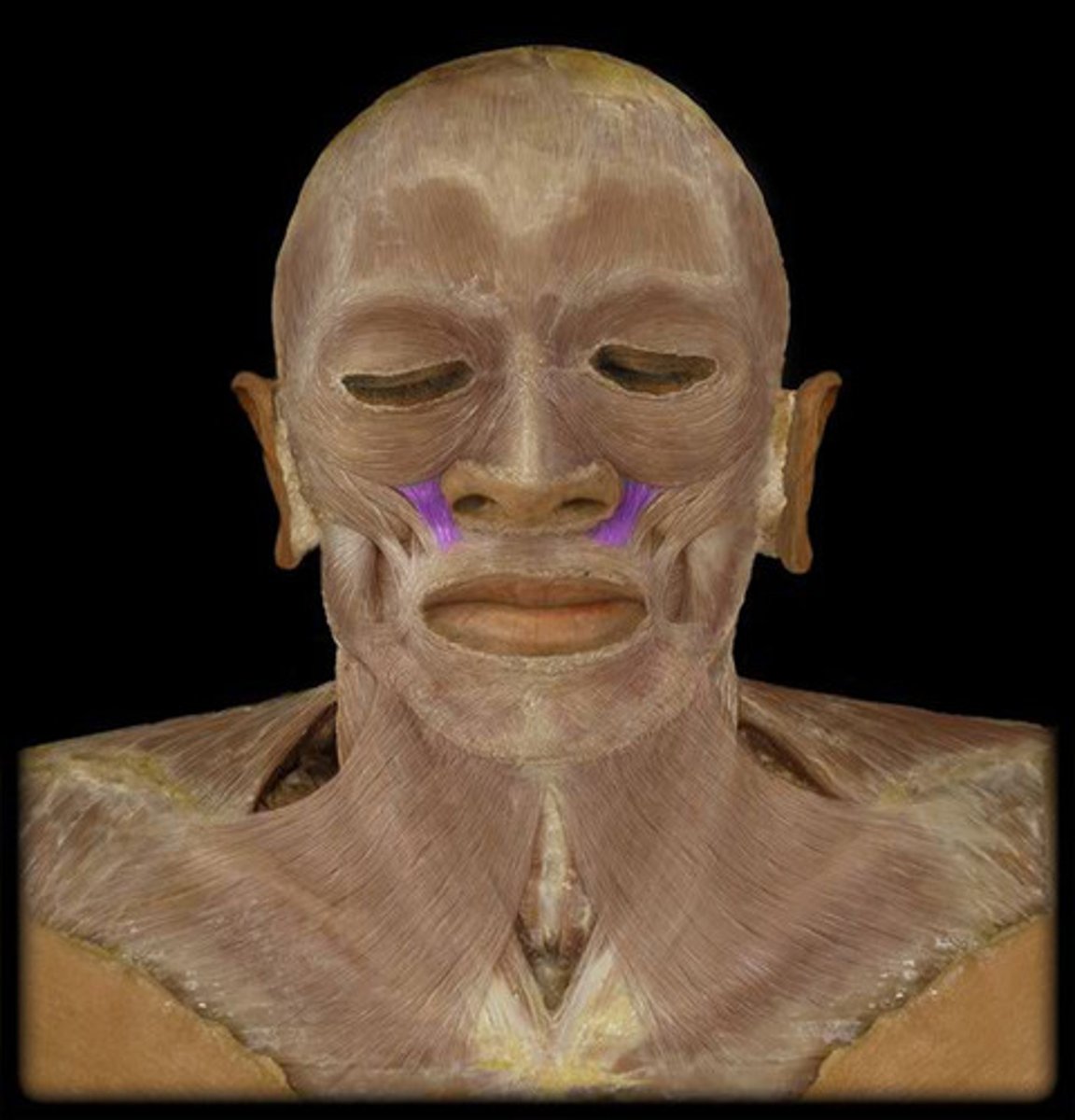
Levator Labii Superioris
elevates upper lip
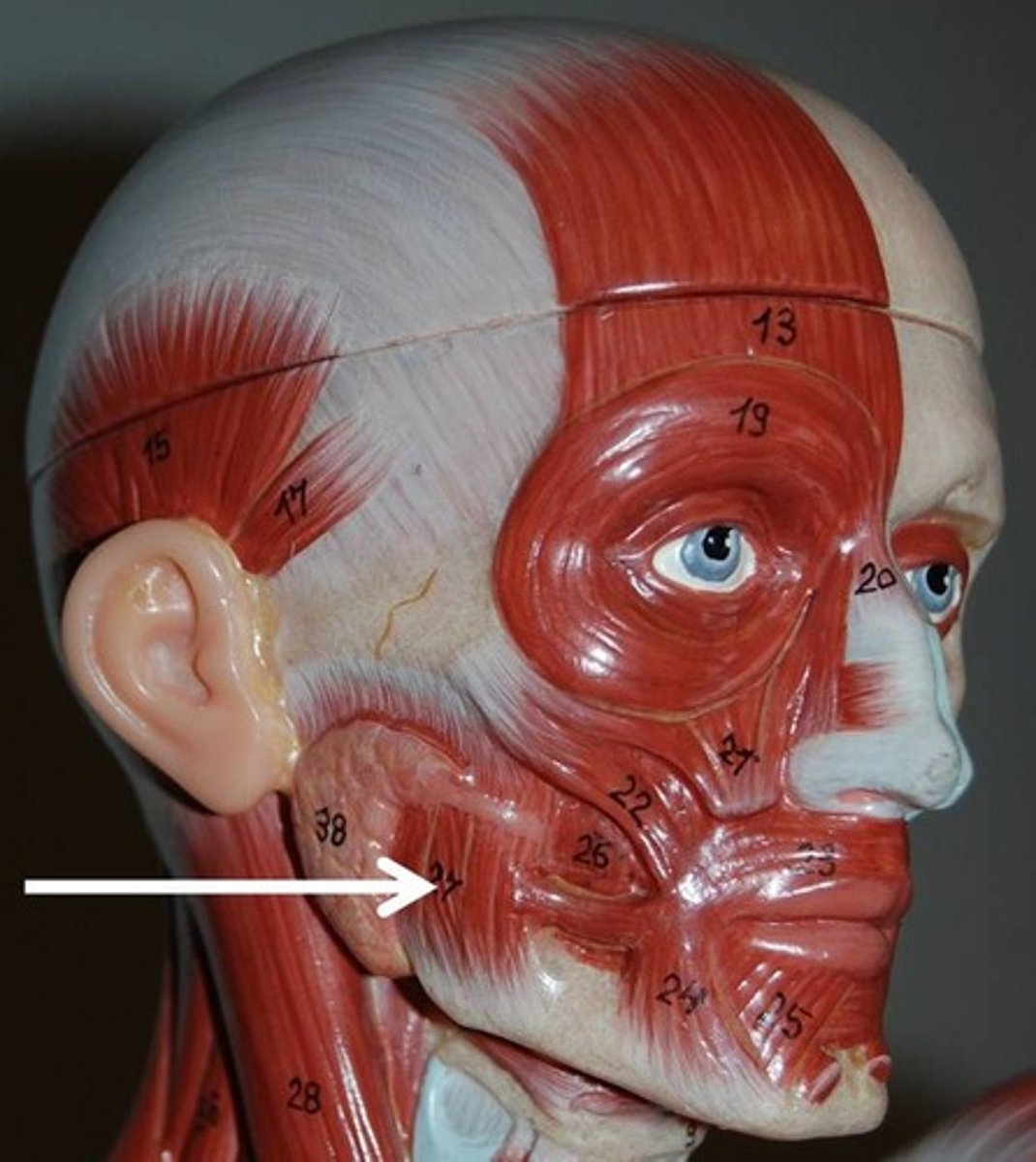
Masseter
elevates mandible and closes jaw
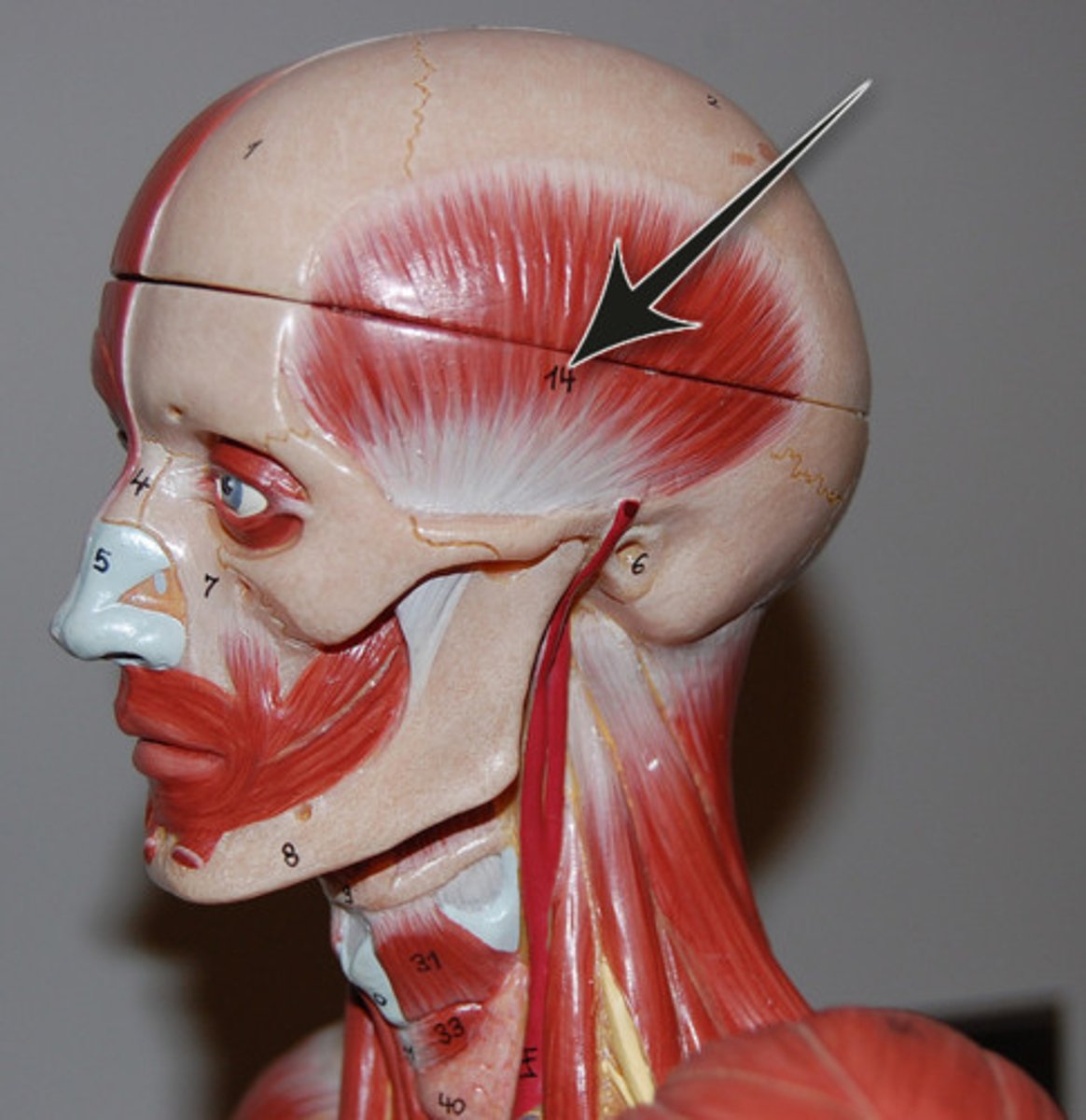
Temporalis
elevates and retracts mandible
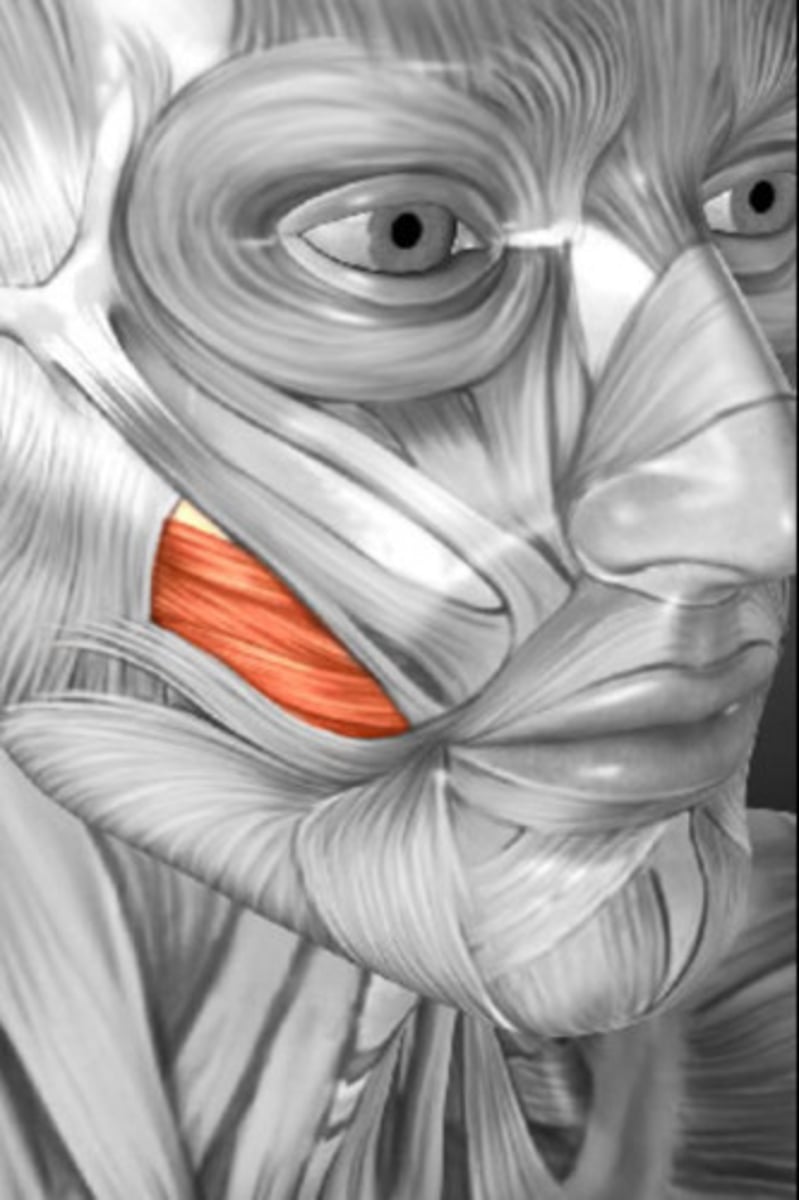
Buccinator
compresses cheek
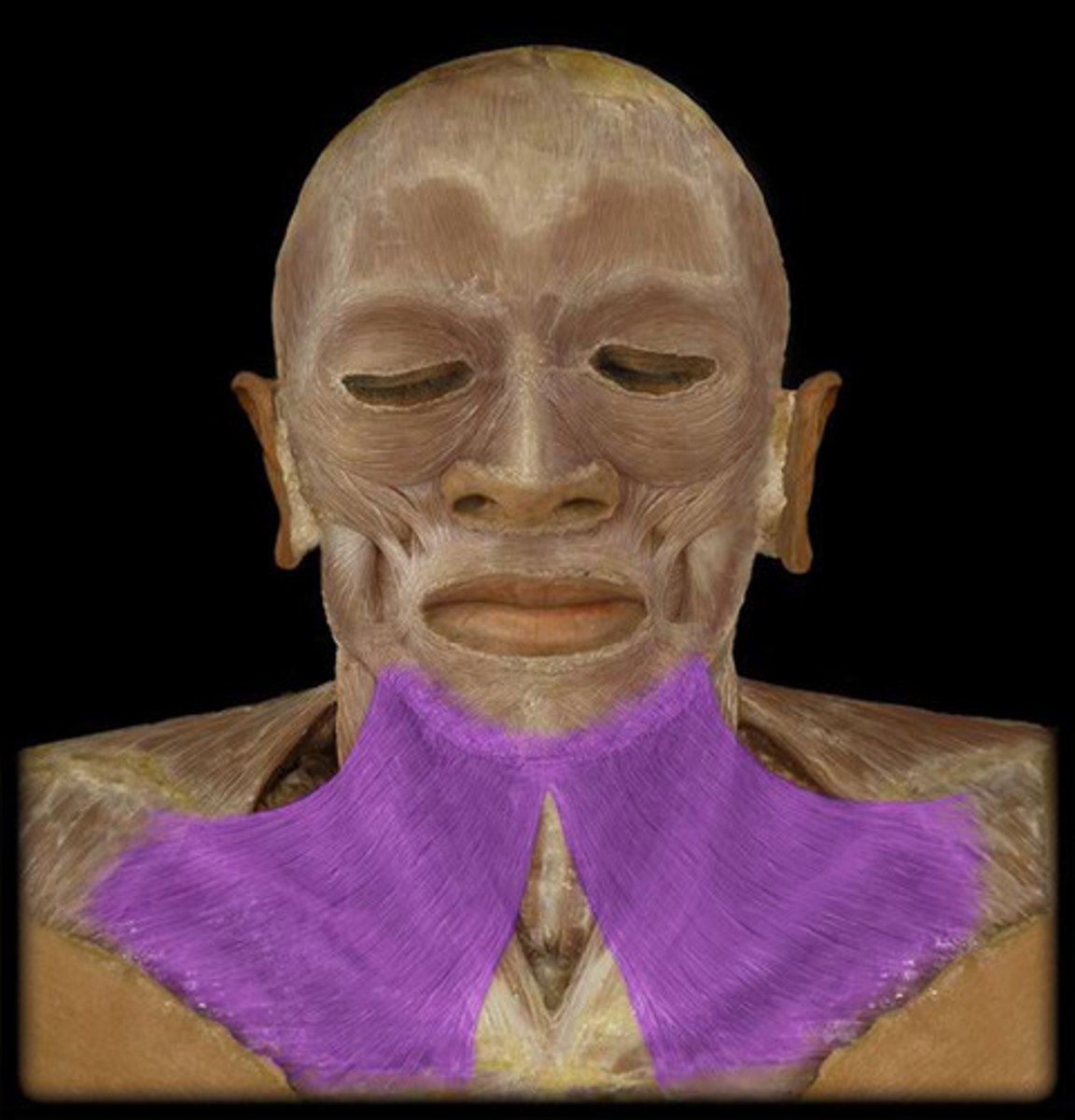
Platysma
Draws down the lower lip and angles of the mouth; tenses skin of the neck; helps depress mandible
Sternocleidomastoid
flexes neck; rotates head
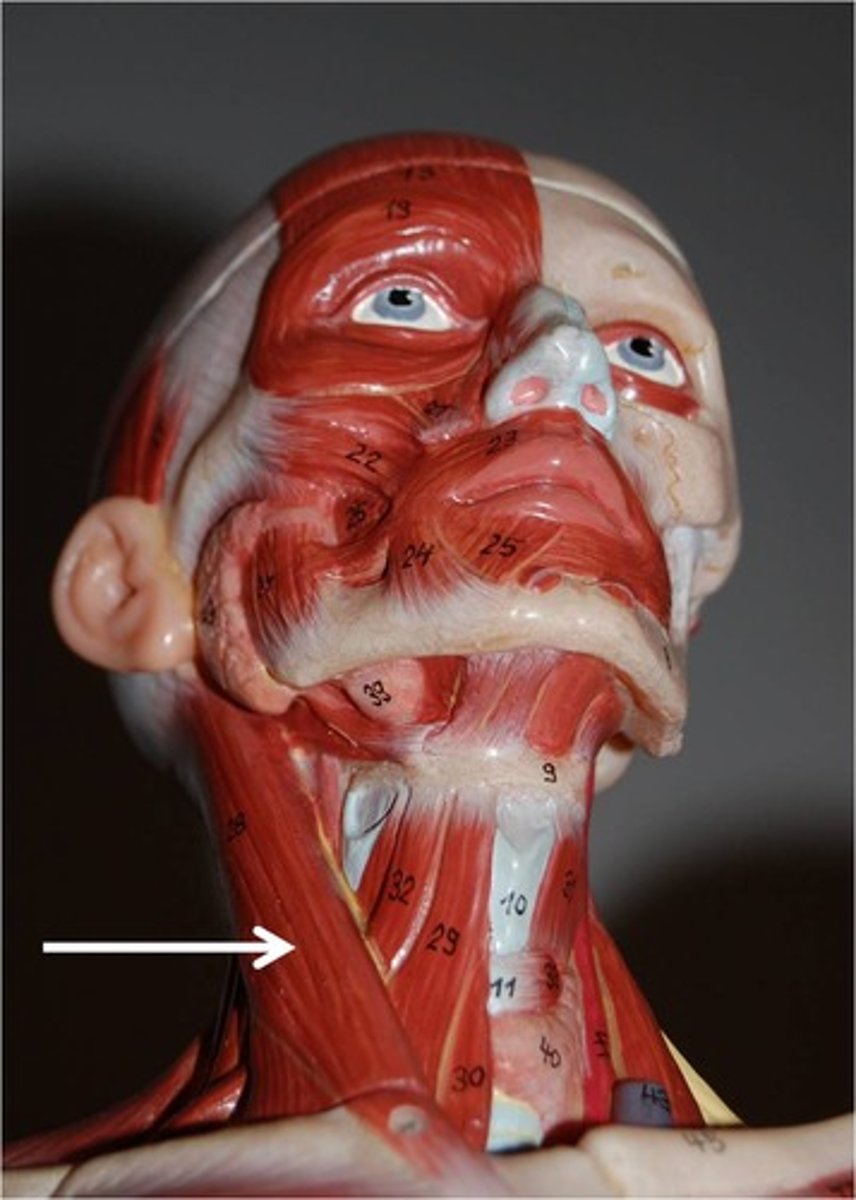
Levator Scapulae
Origin: Transverse processes of the C1-C4 vertebrae.
Insertion: Medial border of the scapula between spine and superior angle.
Action: elevates and adducts scapula, bends neck laterally
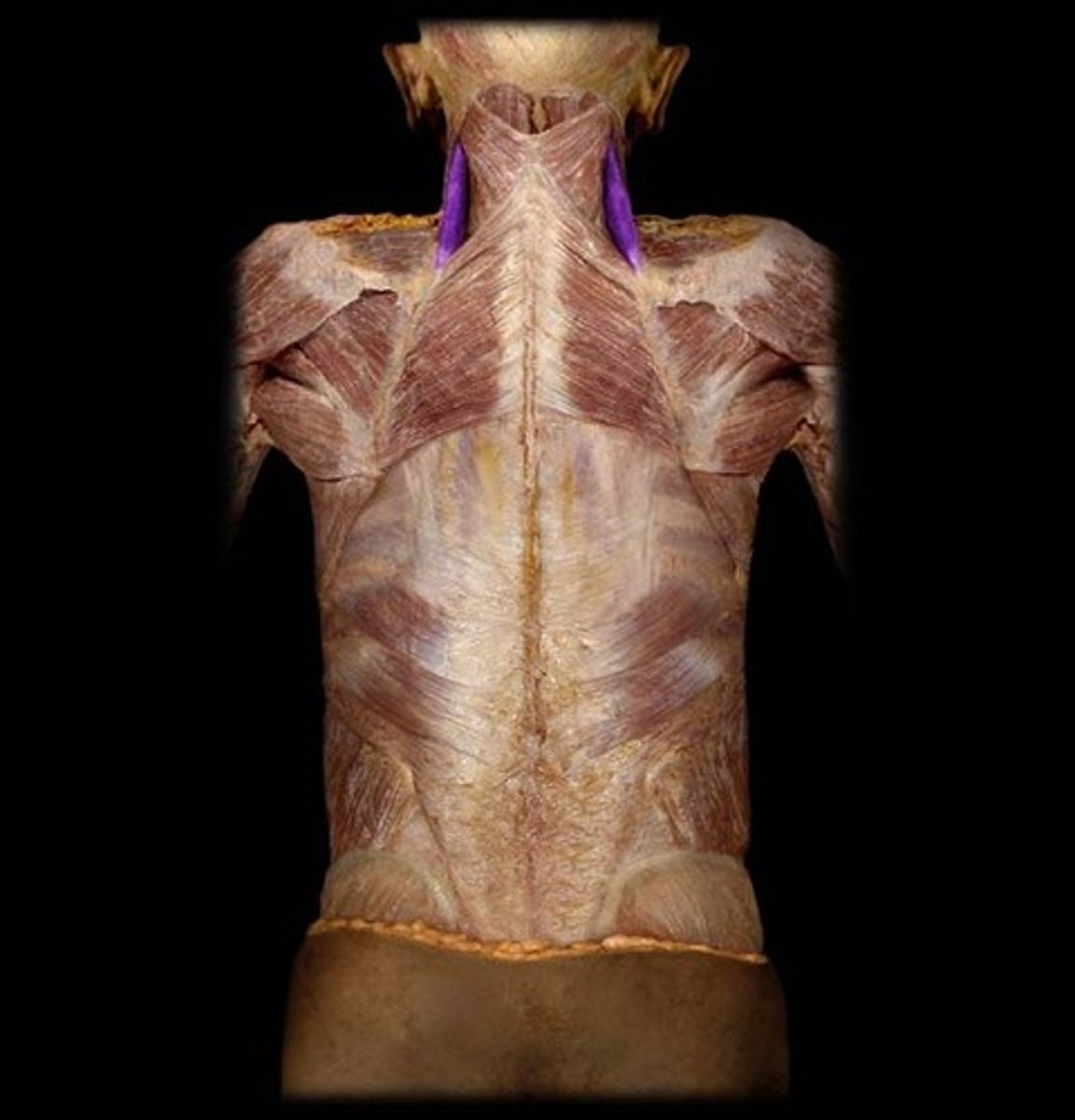
Scalenes
elevates first two ribs
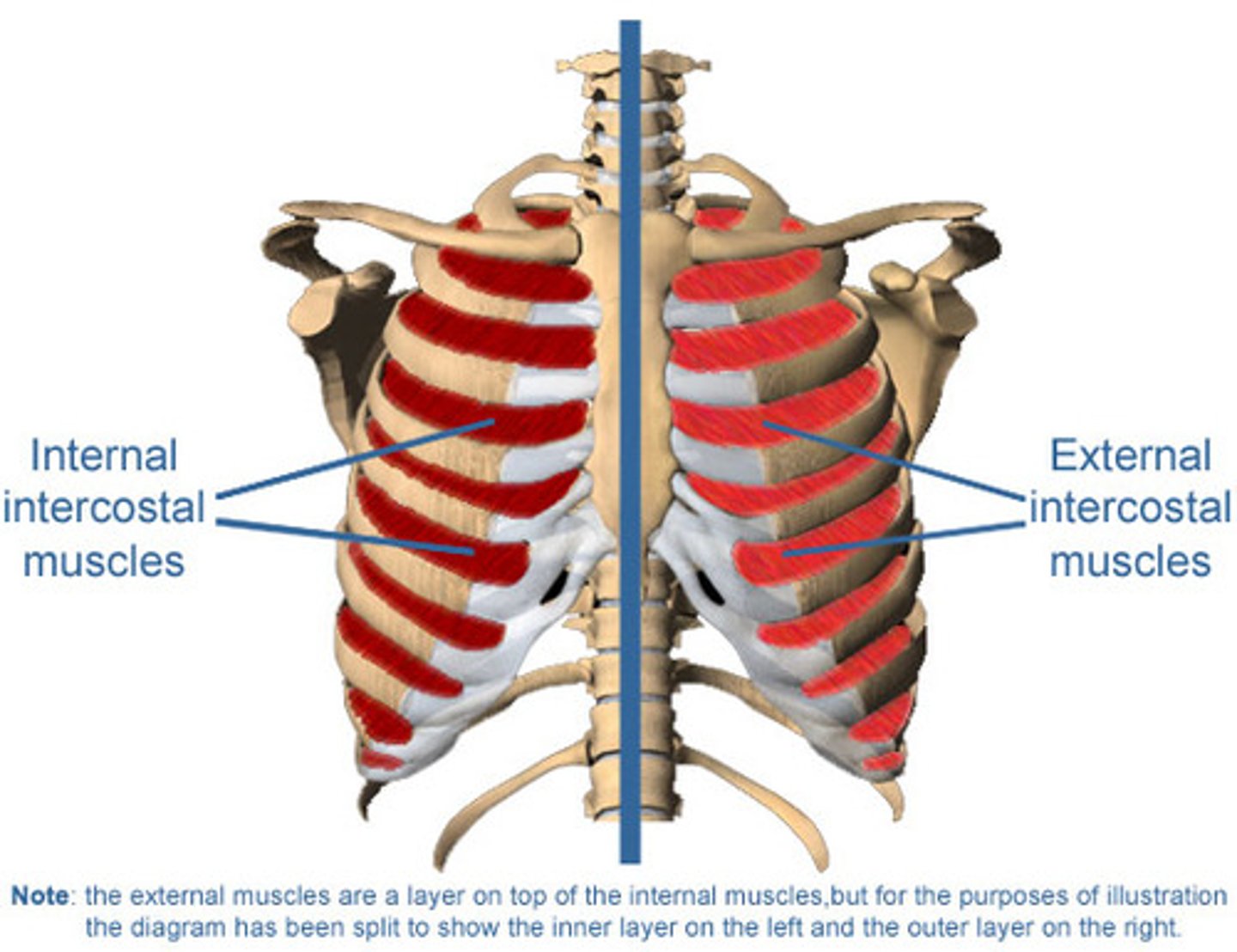
External / internal intercostals
expand and lower the ribs during breathing
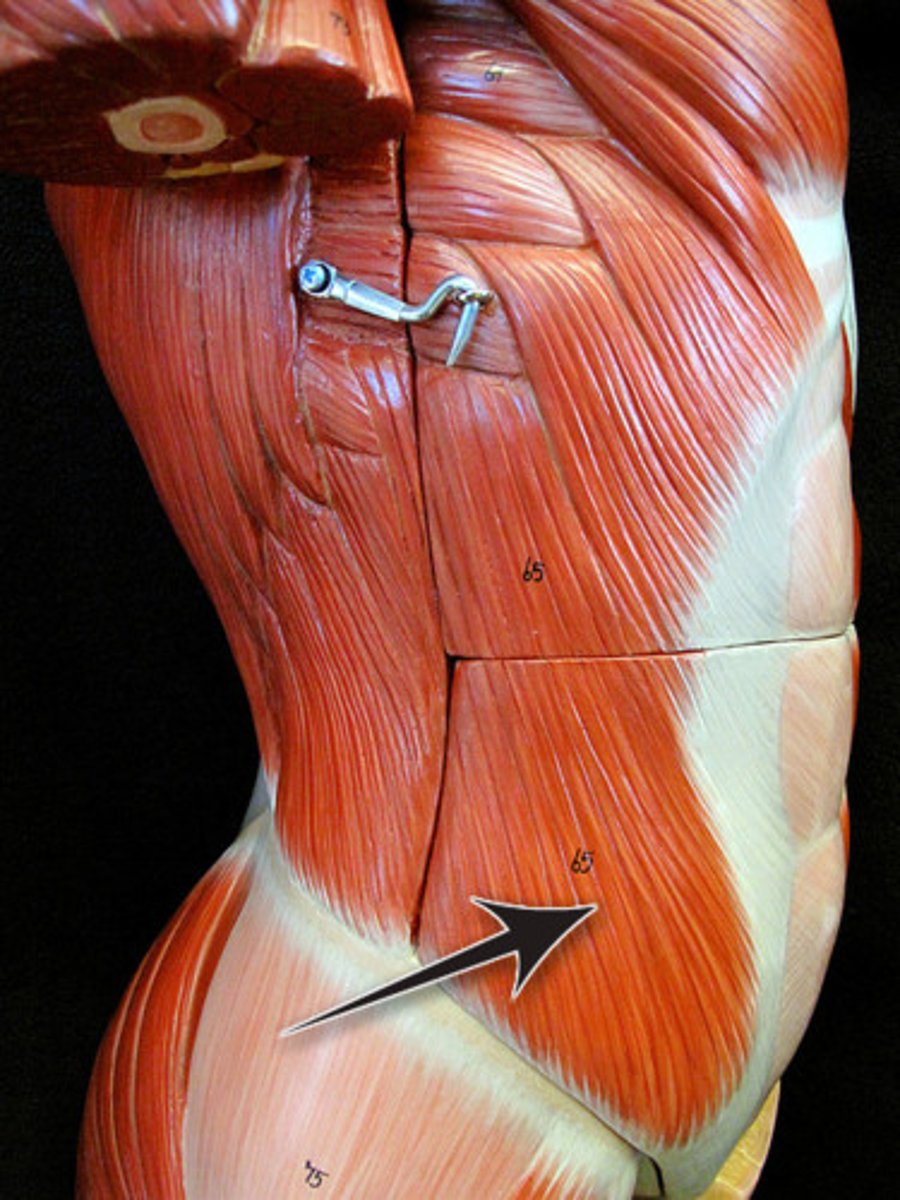
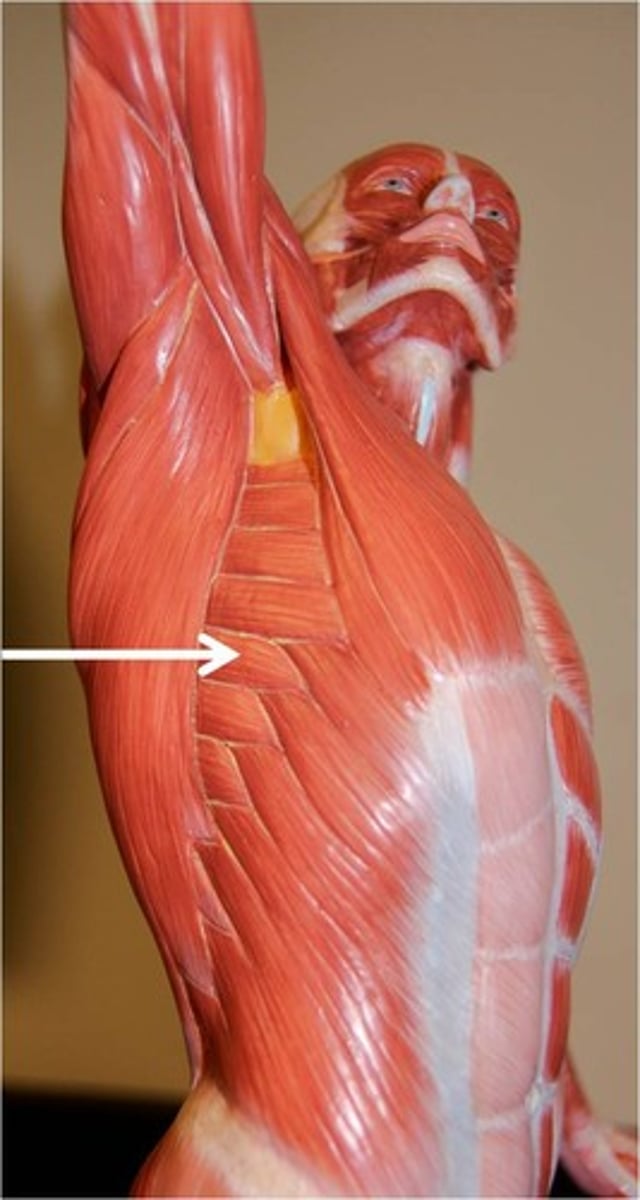
External Oblique
Origin: External surfaces of ribs 5-12
Insertion: Anterior iliac crest and abdominal aponeurosis to linea alba
Action: flexes torso (draws thorax downward), rotates torso, laterally flexes torso
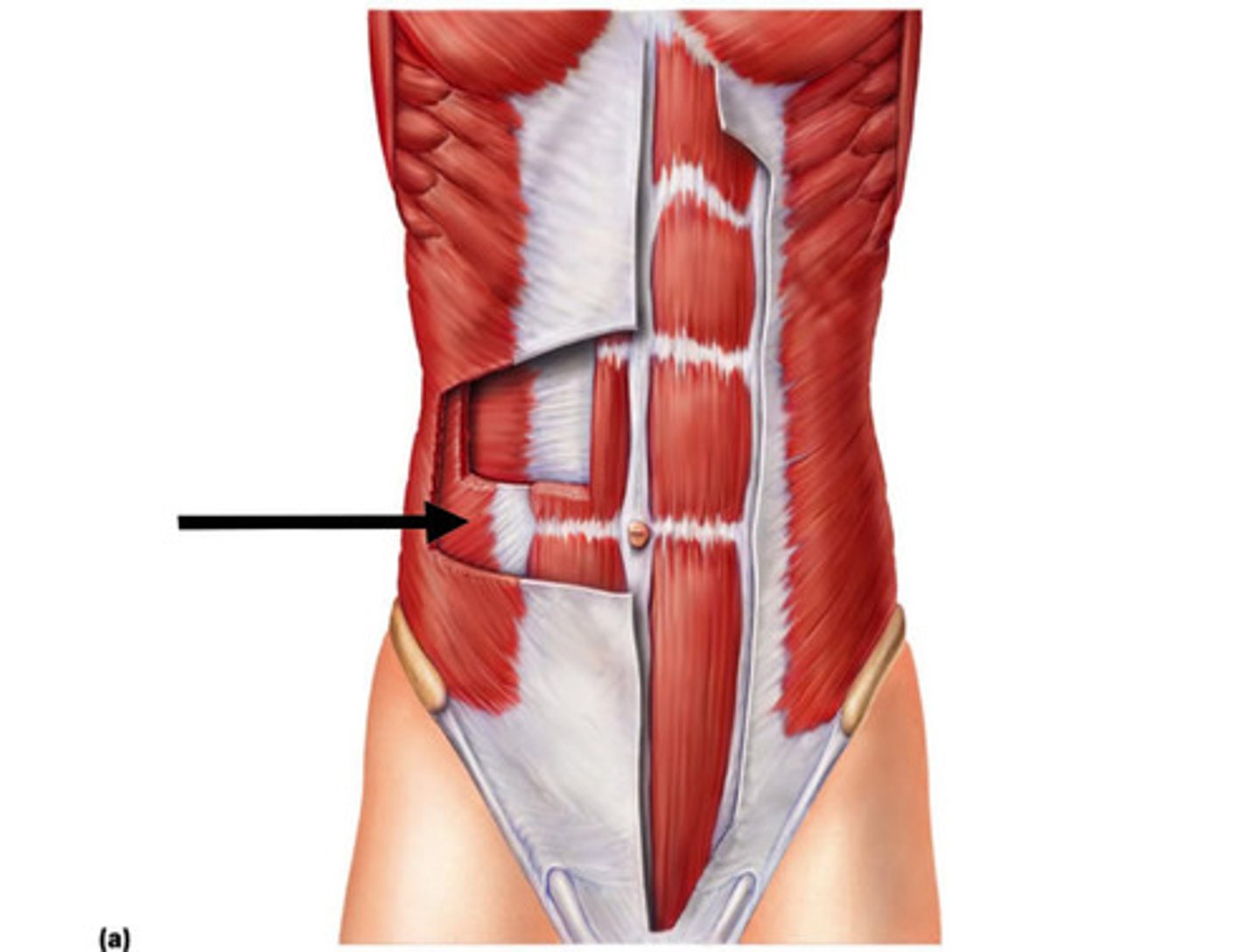
Internal Oblique
Origin: Anterior iliac crest, lateral half of inguinal ligament, and thoracolumbar fascia
Insertion: Costal cartilages of ribs 8-12; abdominal aponeurosis to linea alba
Action: flexes torso, rotates torso, laterally flexes torso
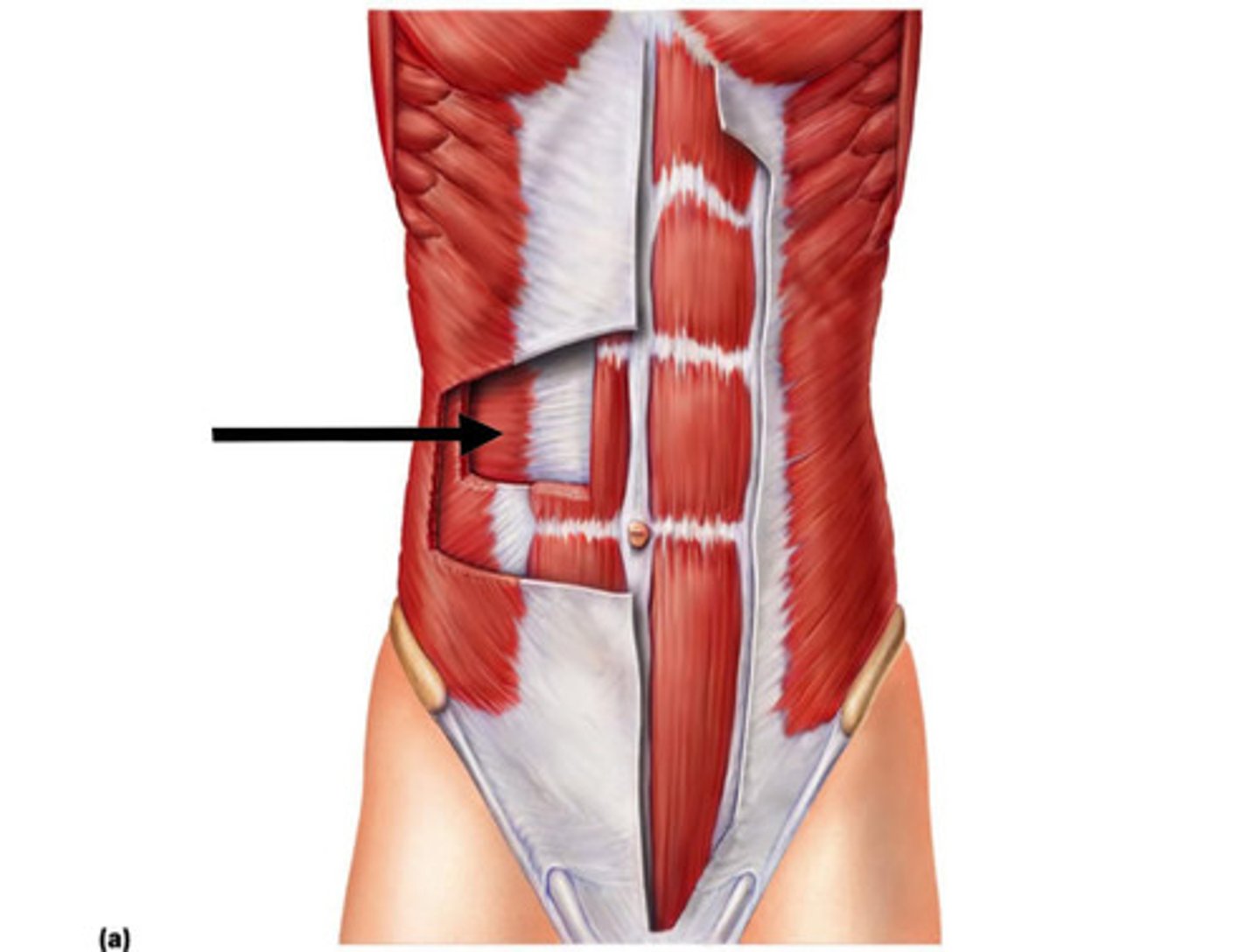
Transversus Abdominus
Origin: Anterior iliac crest, lateral half of inguinal ligament, thoracolumbar fascia and cartilages of ribs 6-12
Insertion: Abdominal aponeurosis to linea alba, xiphoid process and pubic symphysis
Action: compresses abdomen
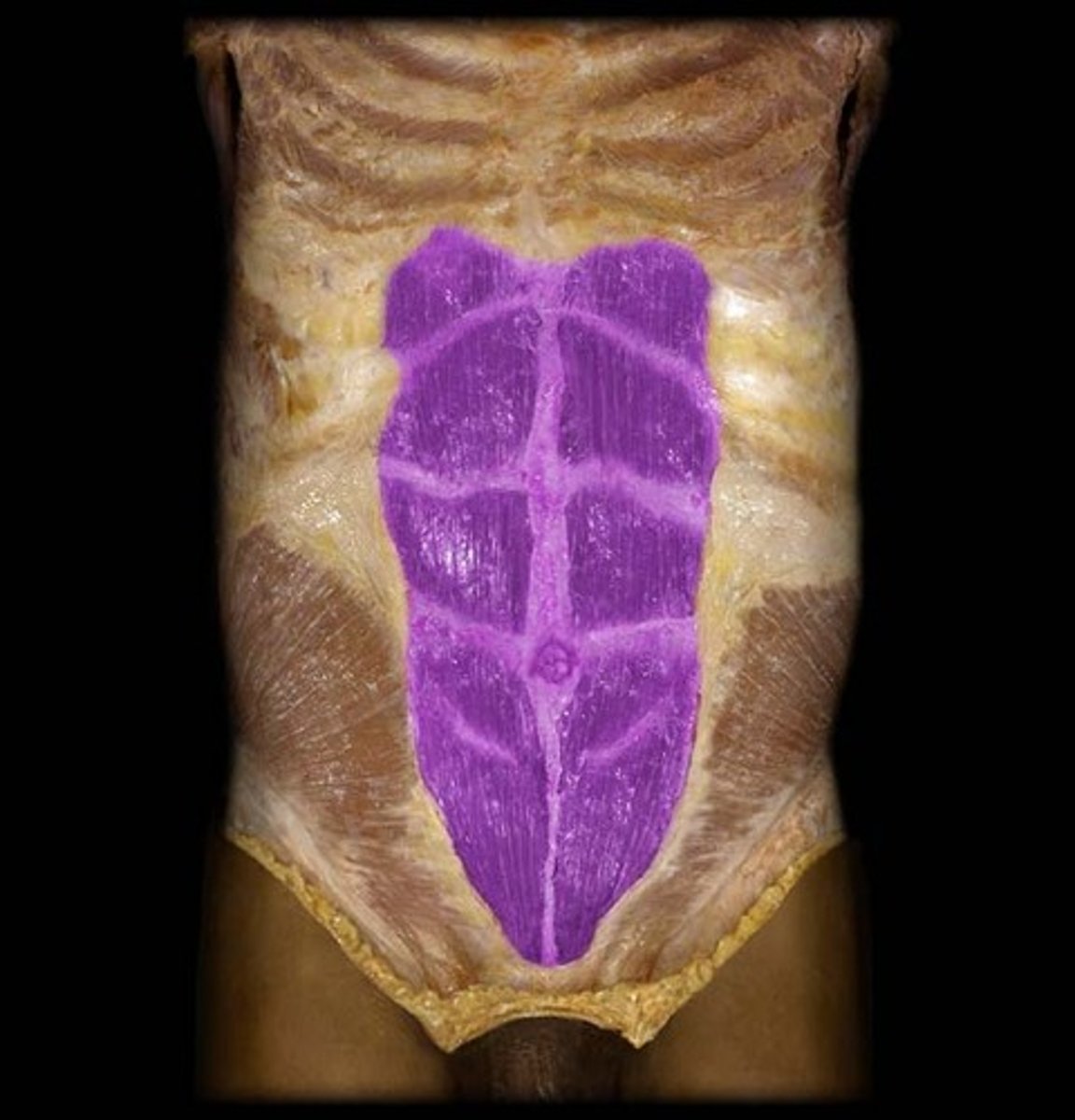
Rectus Abdominus
Origin: Pubic crest and symphysis pubis of the hip bone
Insertion: Costal cartilages of ribs 5-7; xiphoid process of sternum
Action: flexes vertebral column (torso)
Serratus Anterior
protracts scapula, assists in upward rotation of scapula
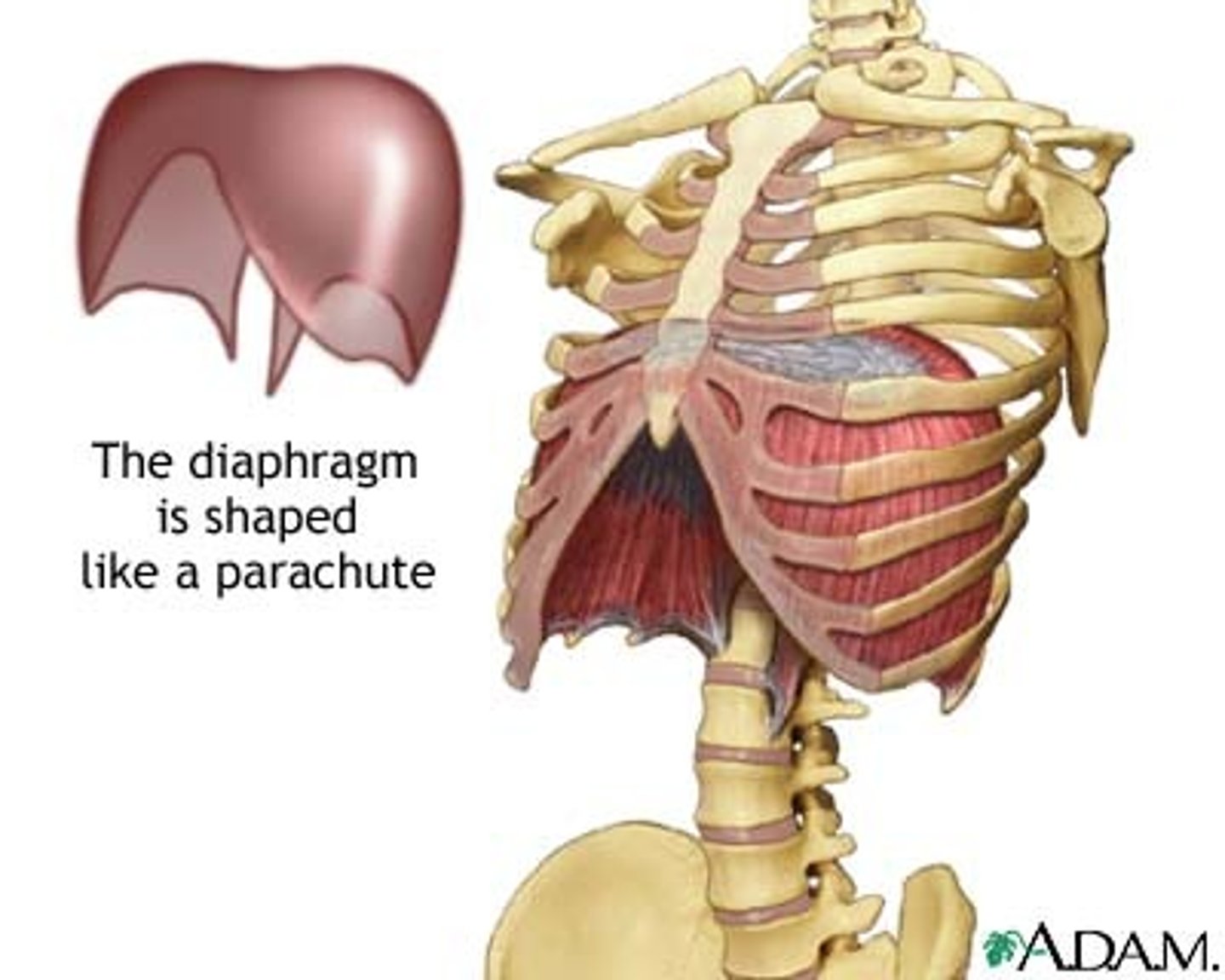
Diaphragm
Large, flat muscle at the bottom of the chest cavity that helps with breathing
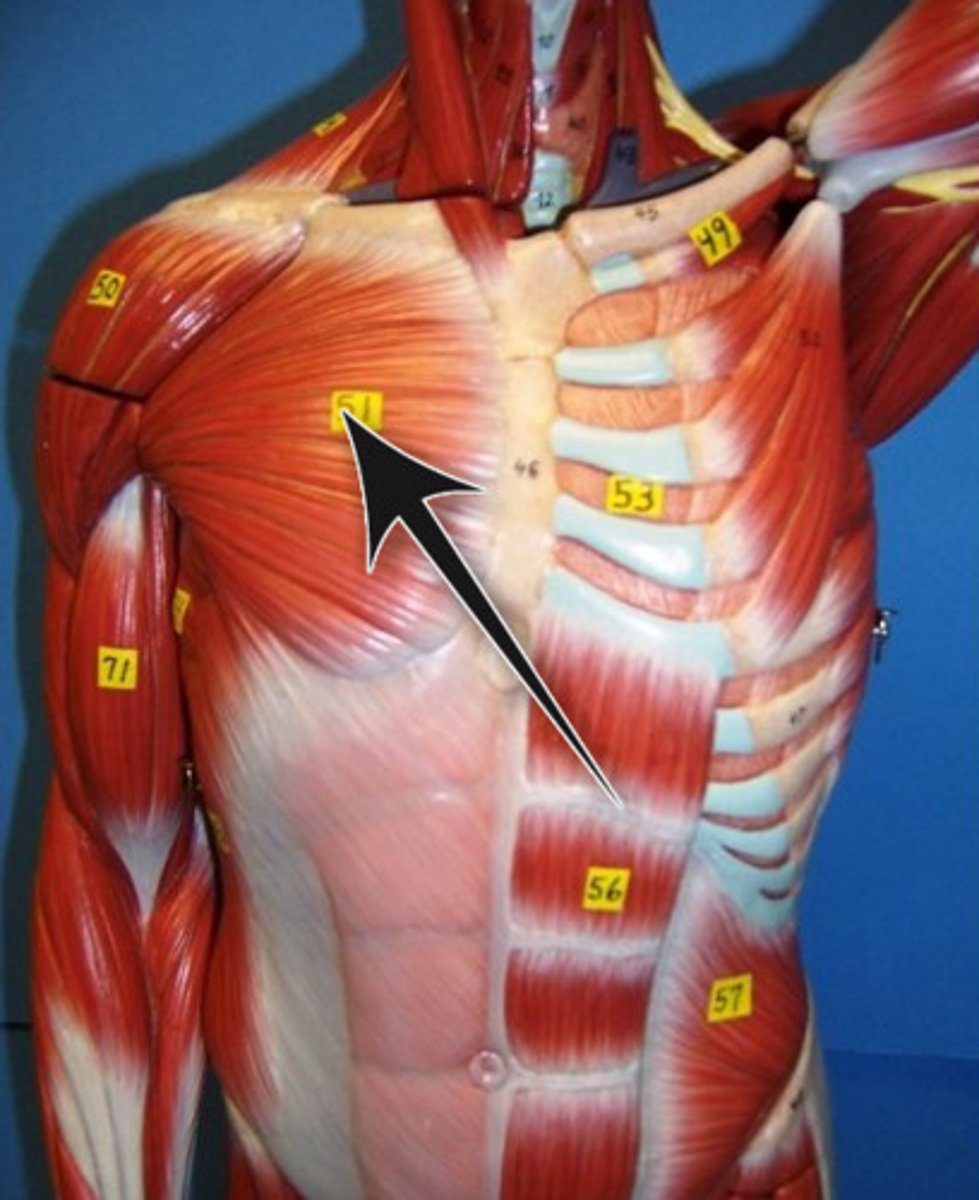
Pectoralis Major
Adducts and flexes humerus
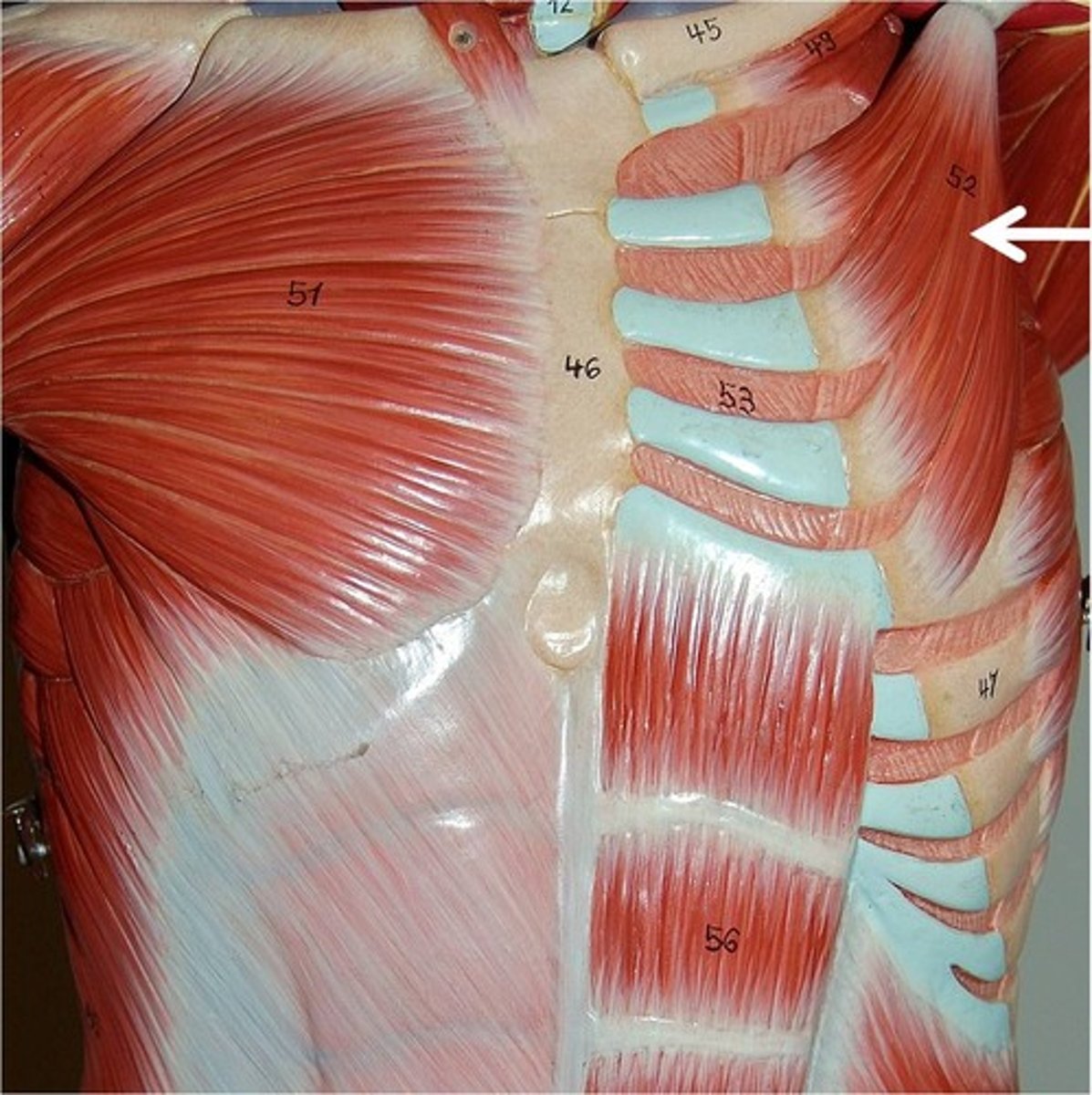
Pectoralis Minor
protracts and depresses scapula
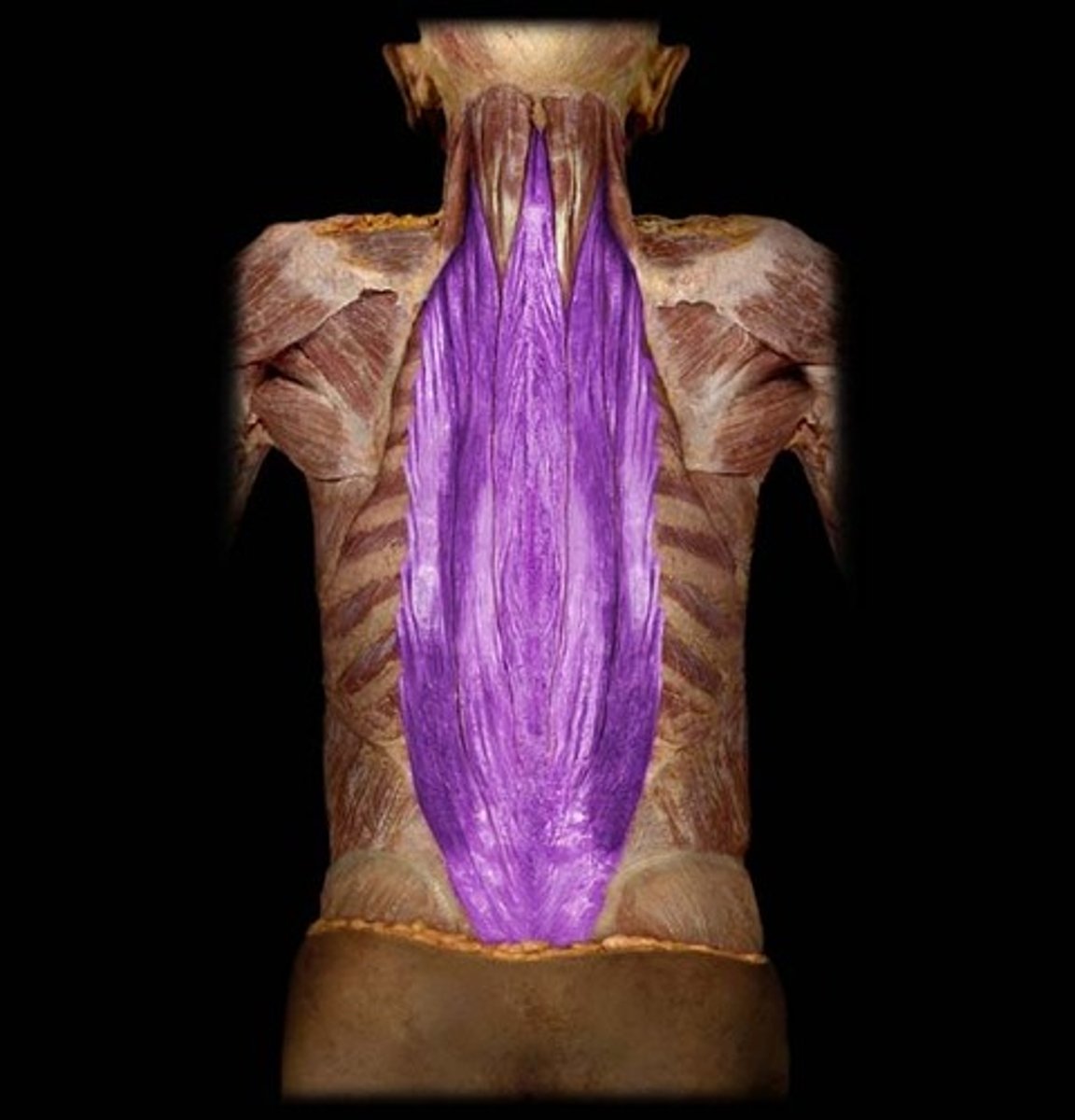
Erector Spinae Group
iliocostalis, longissimus, spinalis
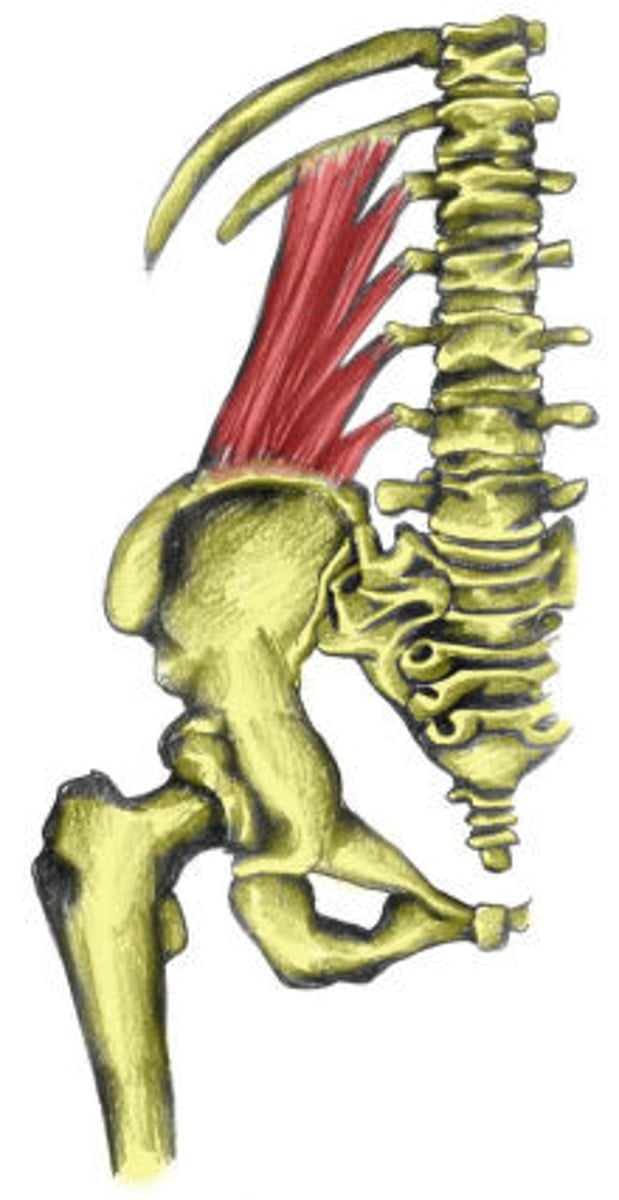
Quadratus Lumborum
Origin: Medial half of the posterior iliac crest and iliolumbar ligament
Insertion: Transverse processes of L1-L4 and medial half of 12th rib
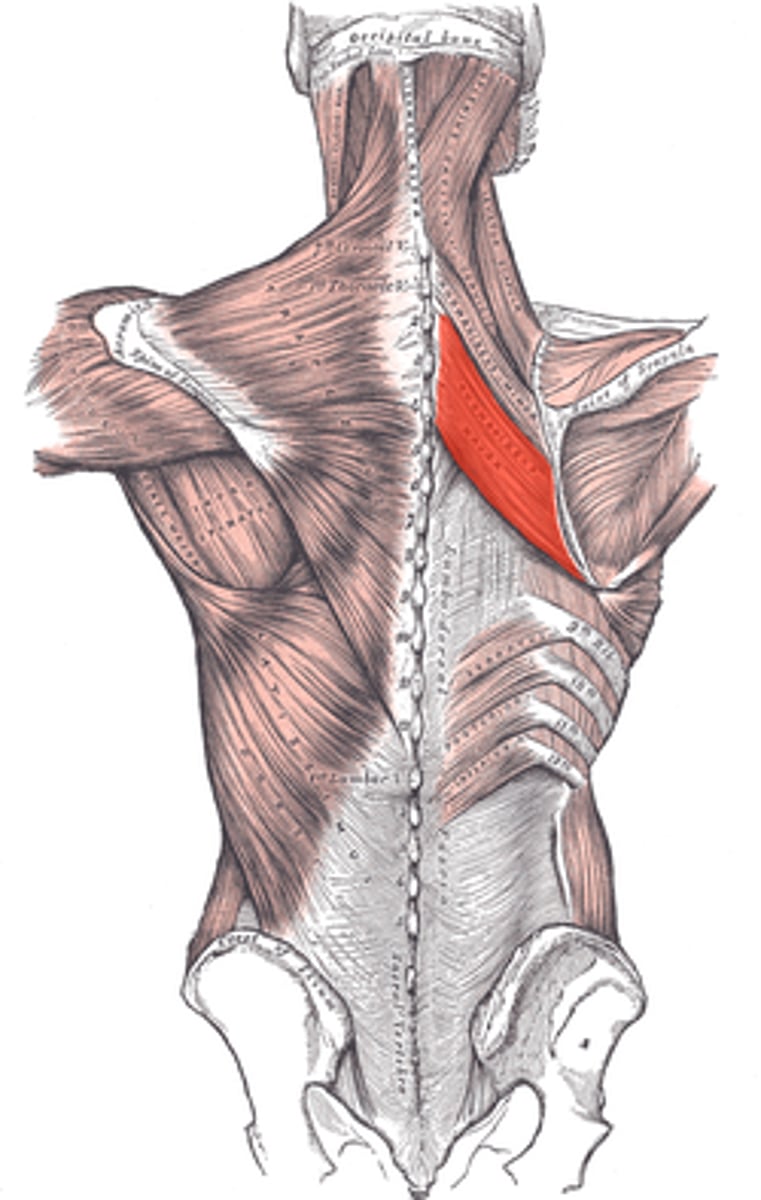
Rhomboid Major
Origin: Spinous process of T2-T5 vertabrae
Insertion: Medial border of scapula inferior to spina scapulae
Action: Retracts the medial border of scapula while it downwardly rotates the lateral angle. Elevates the medial border of scapula while it downwardly rotates the lateral angle
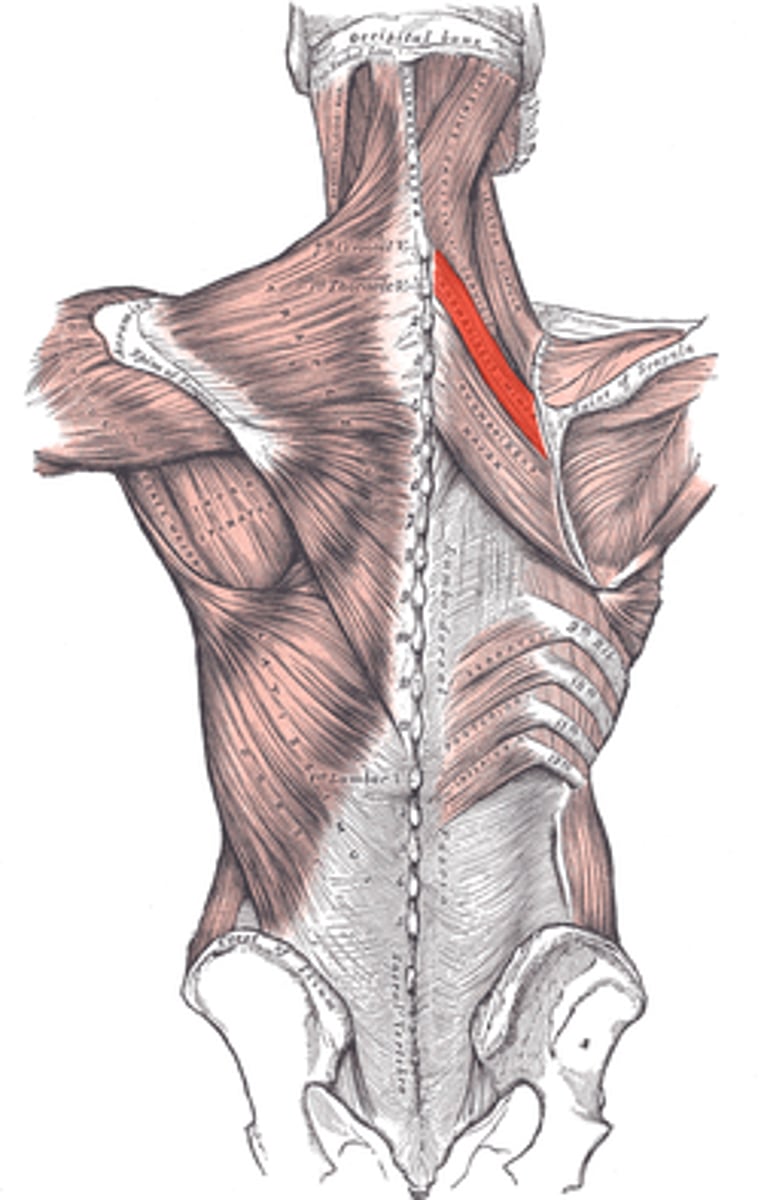
Rhomboid Minor
Origin: Spinous process of C7-T1 vertebrae
Insertion: Medial border of scapula superior to spina scapulae
Action: Retracts the medial border of scapula while it downwardly rotates the lateral angle. Elevates the medial border of scapula while it downwardly rotates the lateral angle
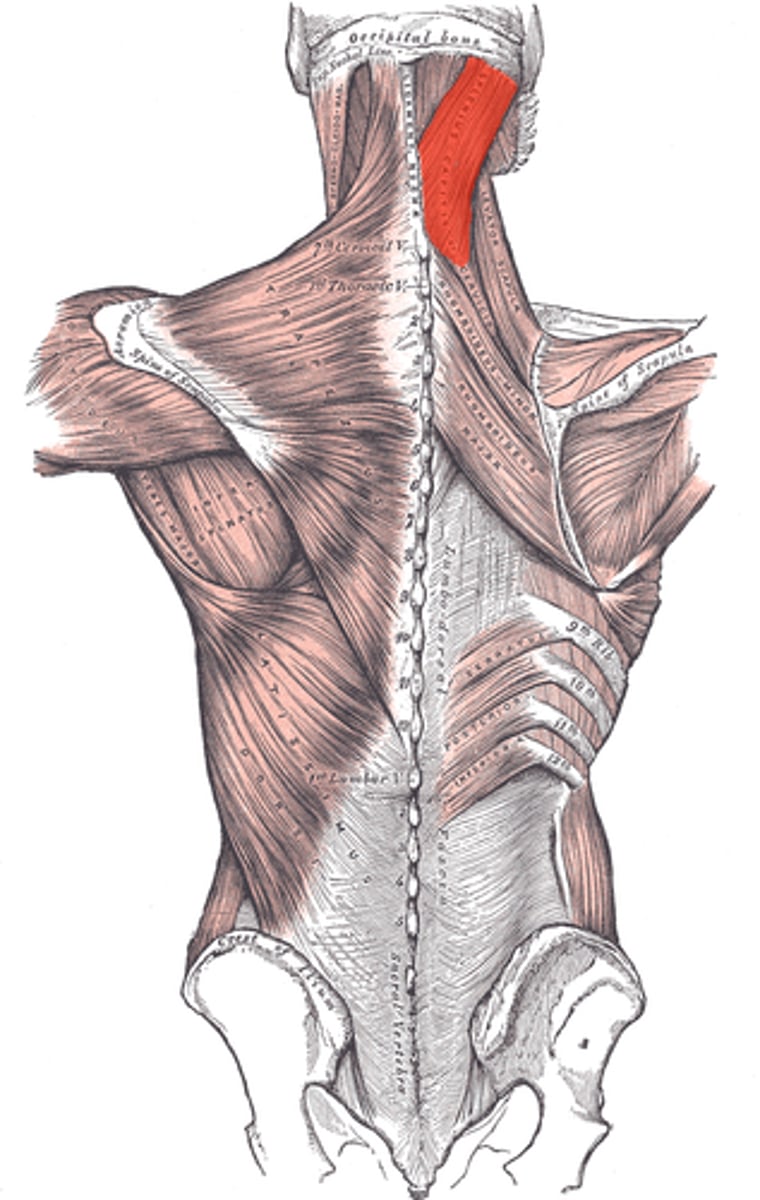
Splenius Capitis
Origin: Inferior half of ligamentum nuchae (C3-C6) and spinous processes of C7-T3
Insertion: Superior nuchal line of occipital bone and mastoid process of temporal bone
Action: Bilaterally extends head and neck. Unilaterally rotates head and neck to same side.
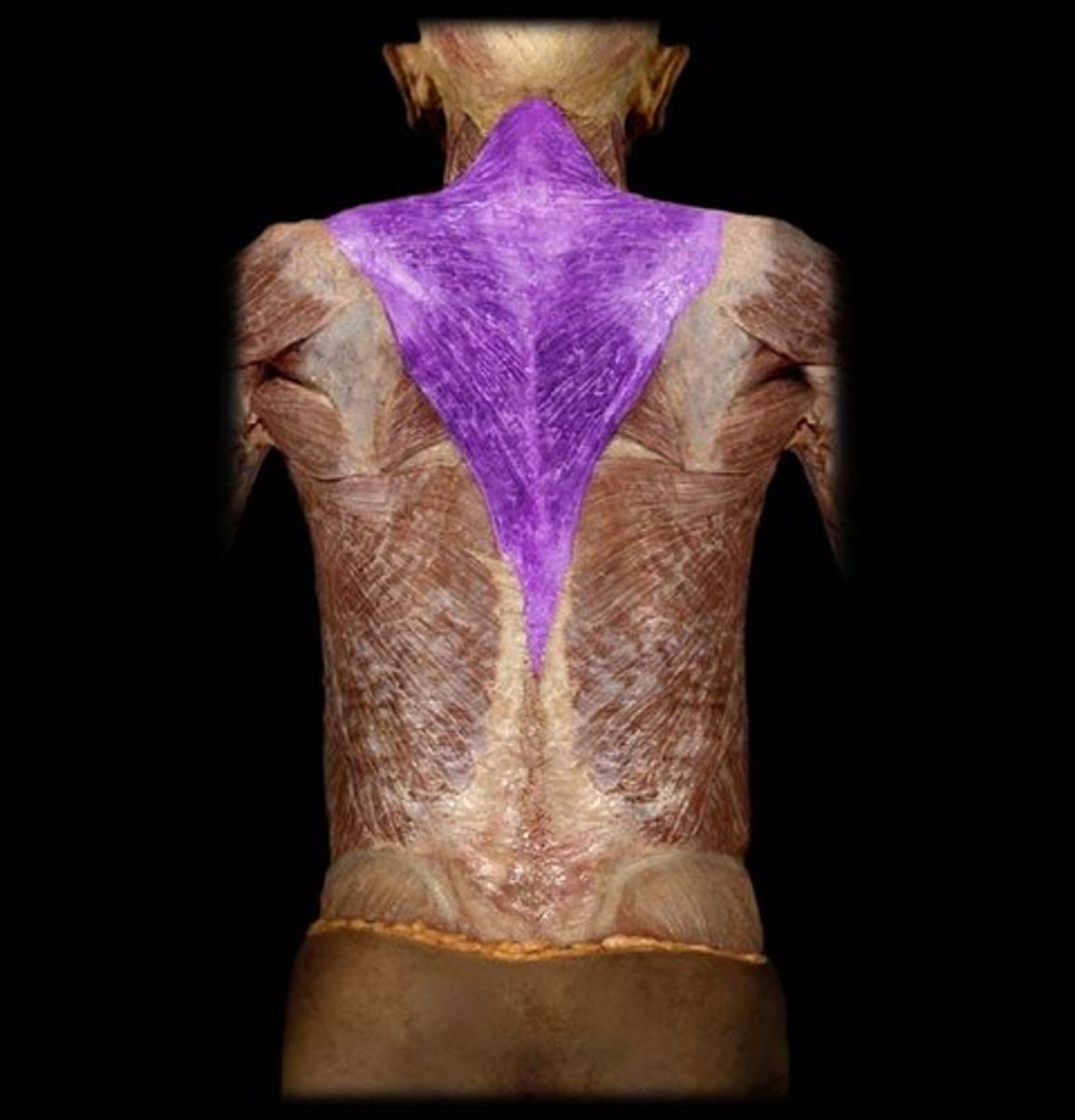
Trapezius
Origin: Medial superior nuchal line and external protuberance of occipital bone, ligamentum nuchae and spinous process of C7-T12.
Insertion: Lateral clavicle, acromion and spine of scapula.
Action: Upper fibers elevate and upwardly rotate scapula, extend neck
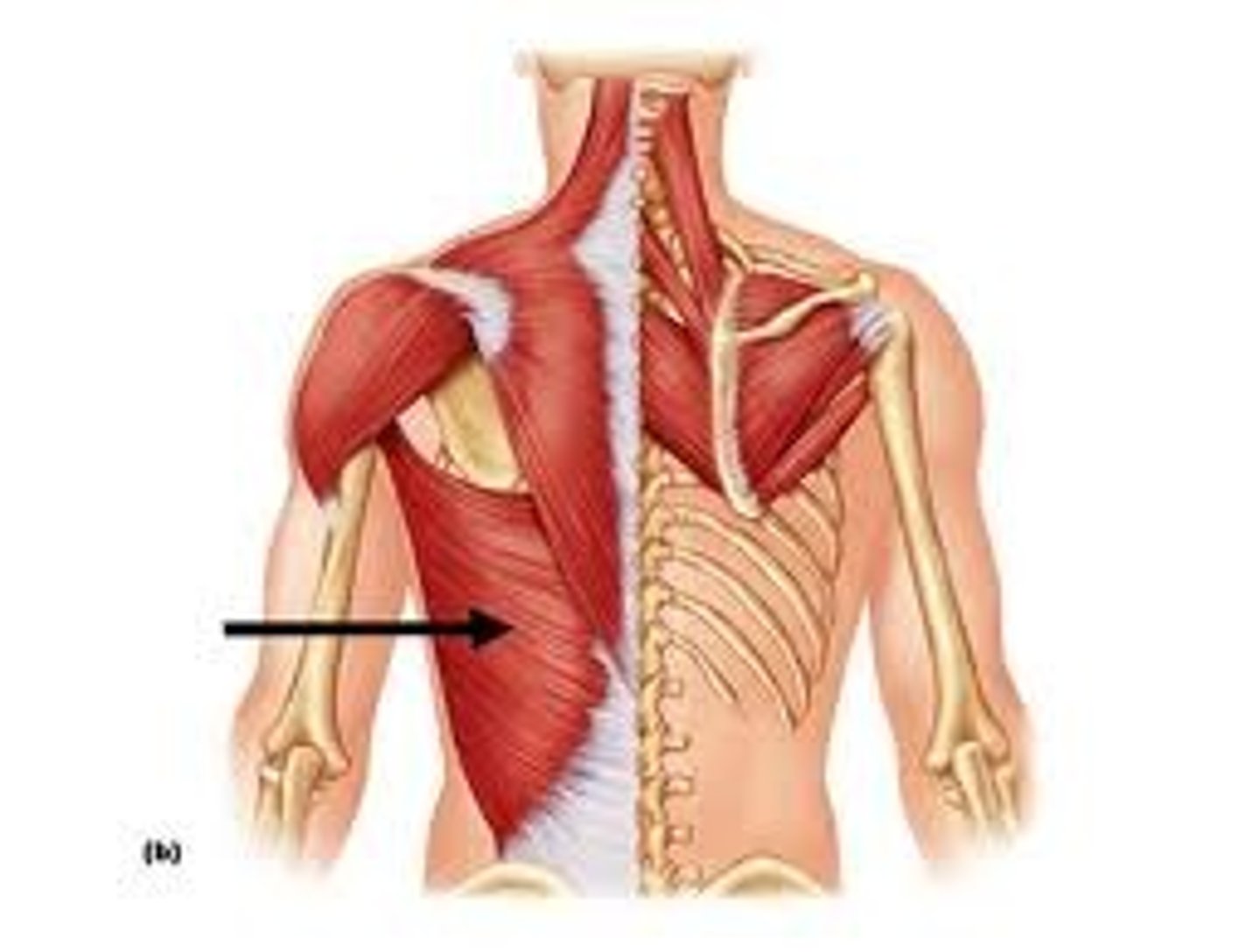
Latissimus Dorsi
Extends, adducts, and medially rotates the arm; draws the shoulder downward and backward
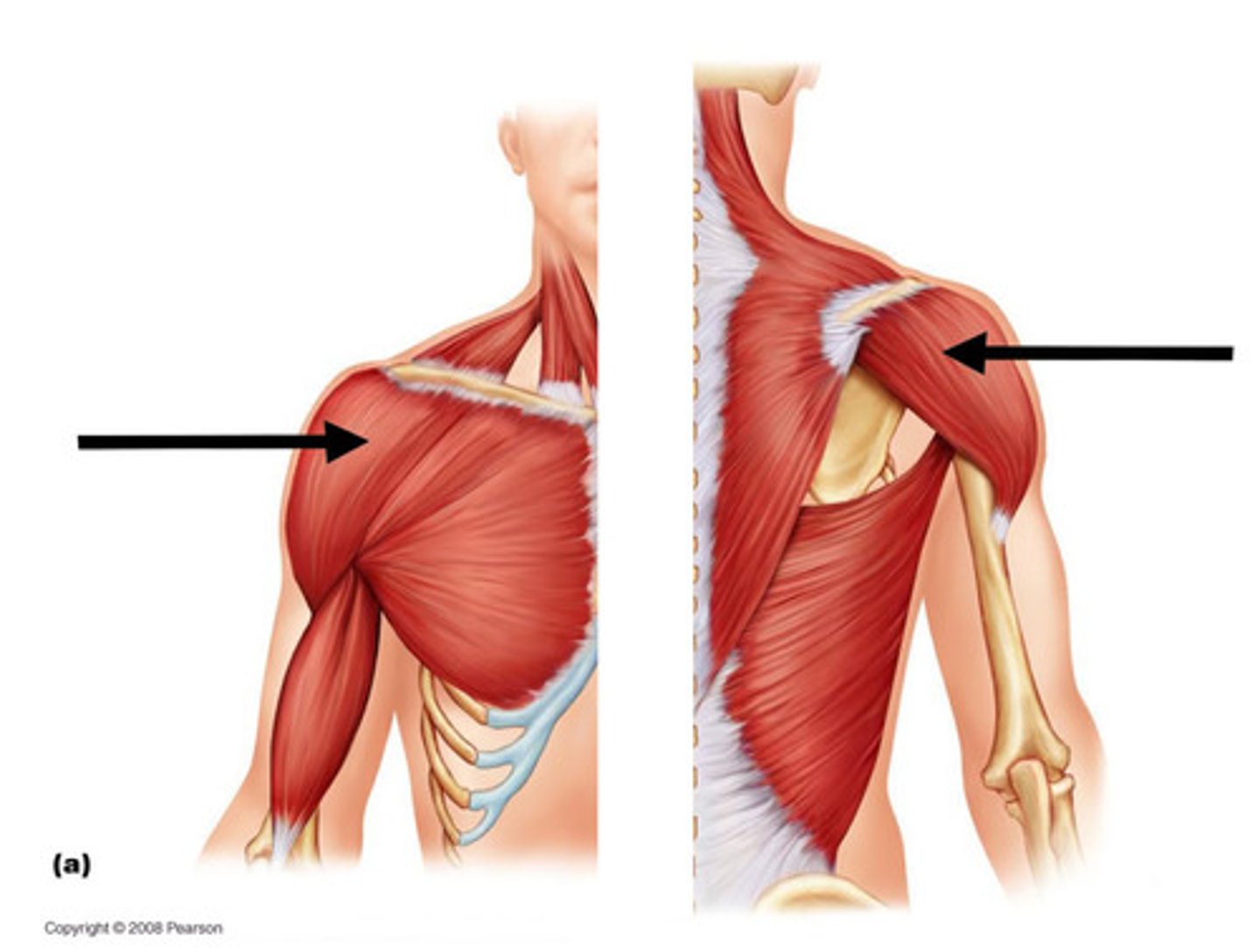
Deltoid
Origin:
a.Anterior (clavicular) head: anterior surface of the lateral clavicle.
b. Middle (acromial) head: acromion process and spine of the scapula.
Insertion: Deltoid tuberosity of the humerus.
Action: medially rotates the arm, abducts the arm
Supraspinatus
Origin: Supraspinous fossa of the scapula
Insertion: Superior aspect of the greater tubercle of the humerus
Action: abducts arm
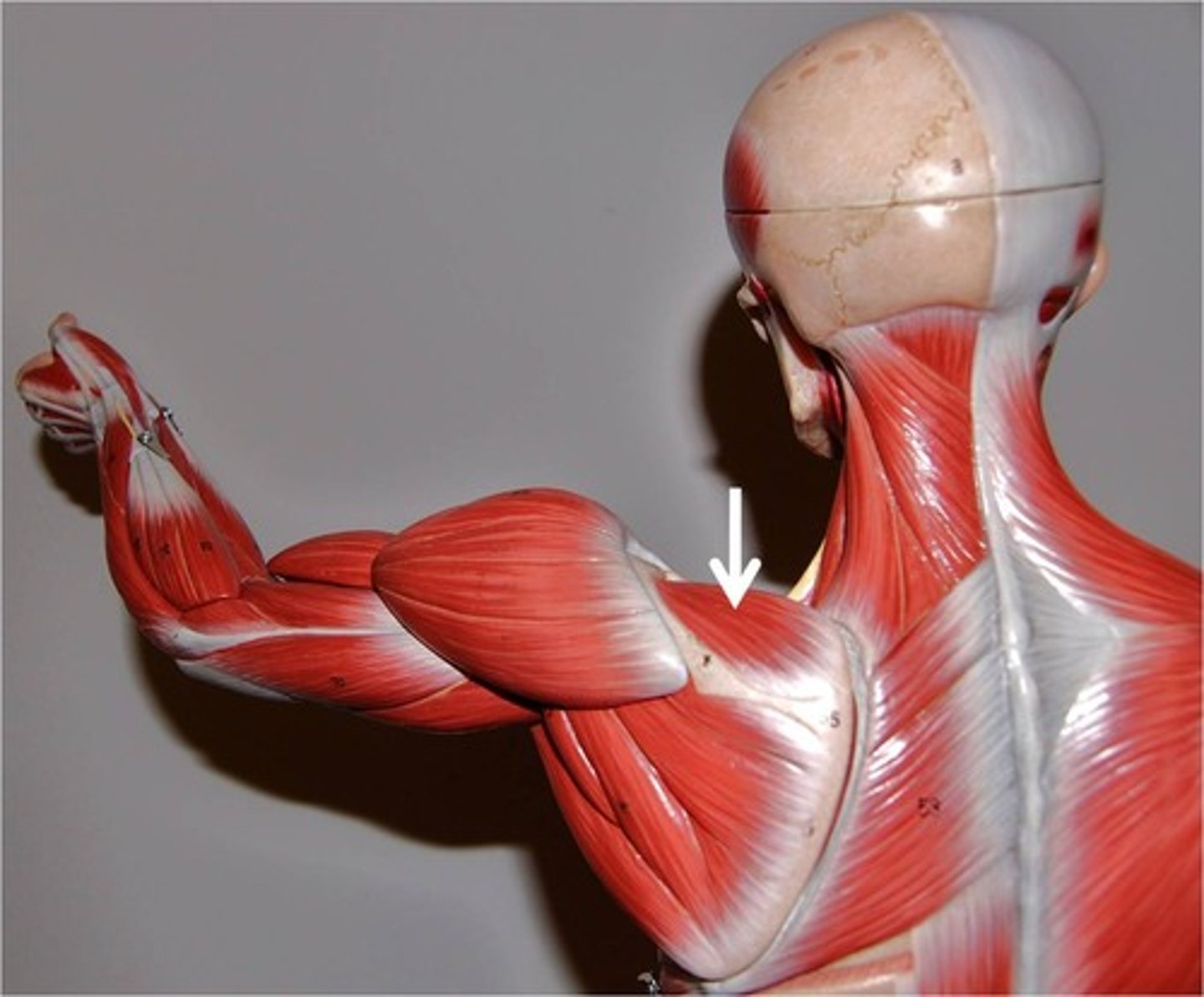
Infraspinatus
Origin: Infraspinous fossa of the scapula
Insertion: Middle part of the greater tubercle of the humerus
Action: rotates arm laterally
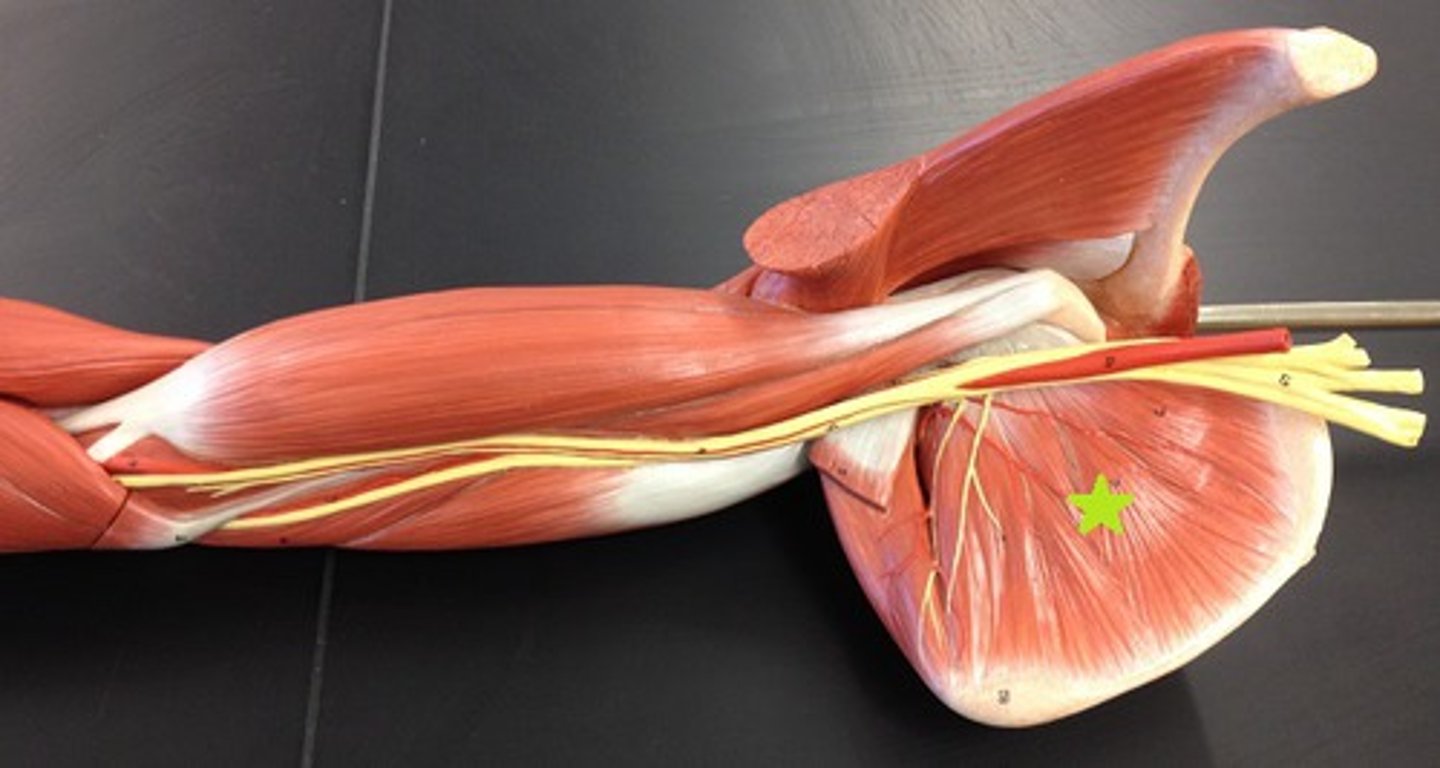
Subscapularis
Origin: Subscapular fossa of the scapula.
Insertion: Lesser tubercle of humerus.
Action: medially rotates arm
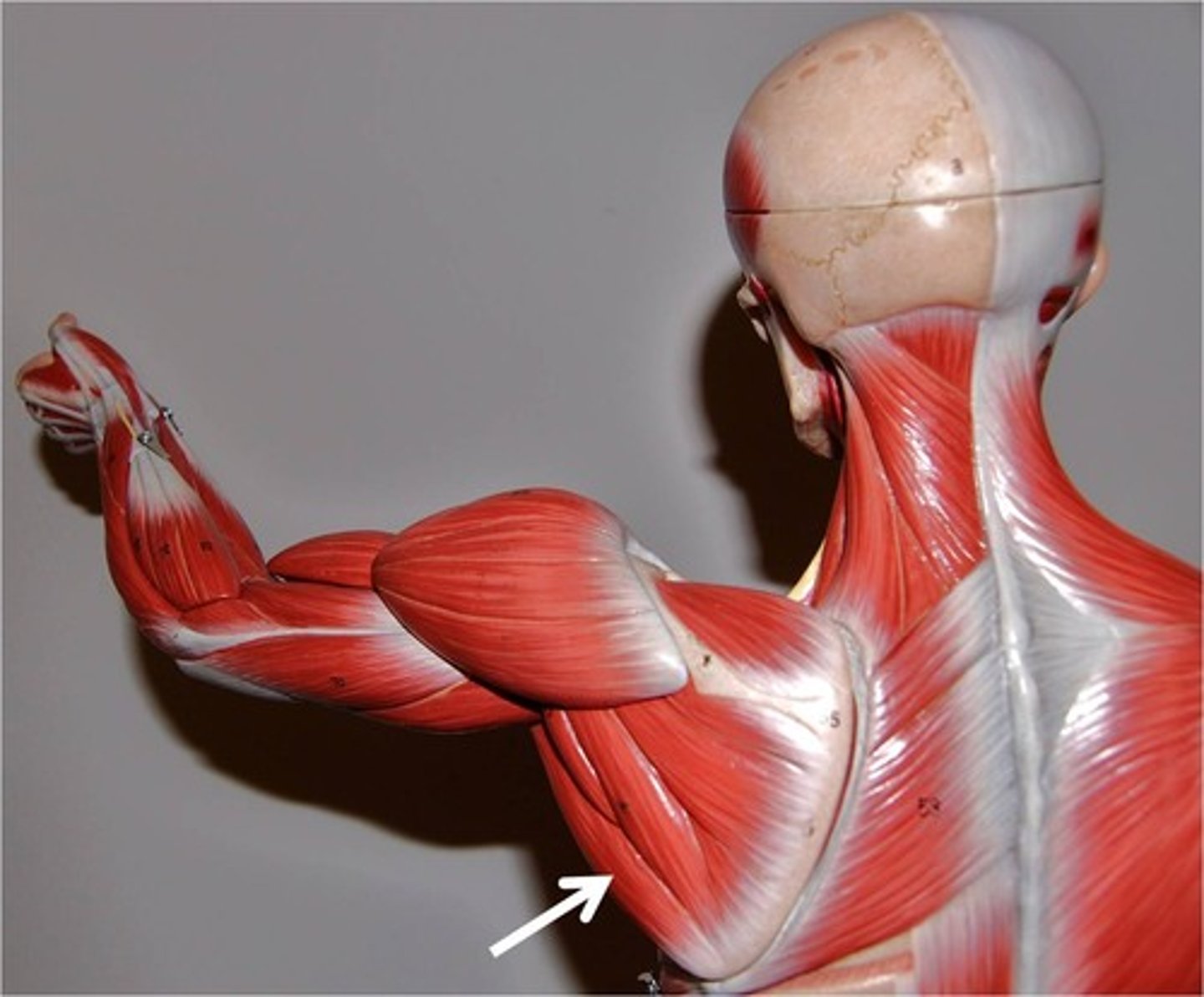
Teres Major
Origin: Lower lateral border and inferior angle of the scapula
Insertion: Medial lip of the intertubercular (bicipital) groove of the anterior humerus.
Action: extends, adducts, and medially rotates arm
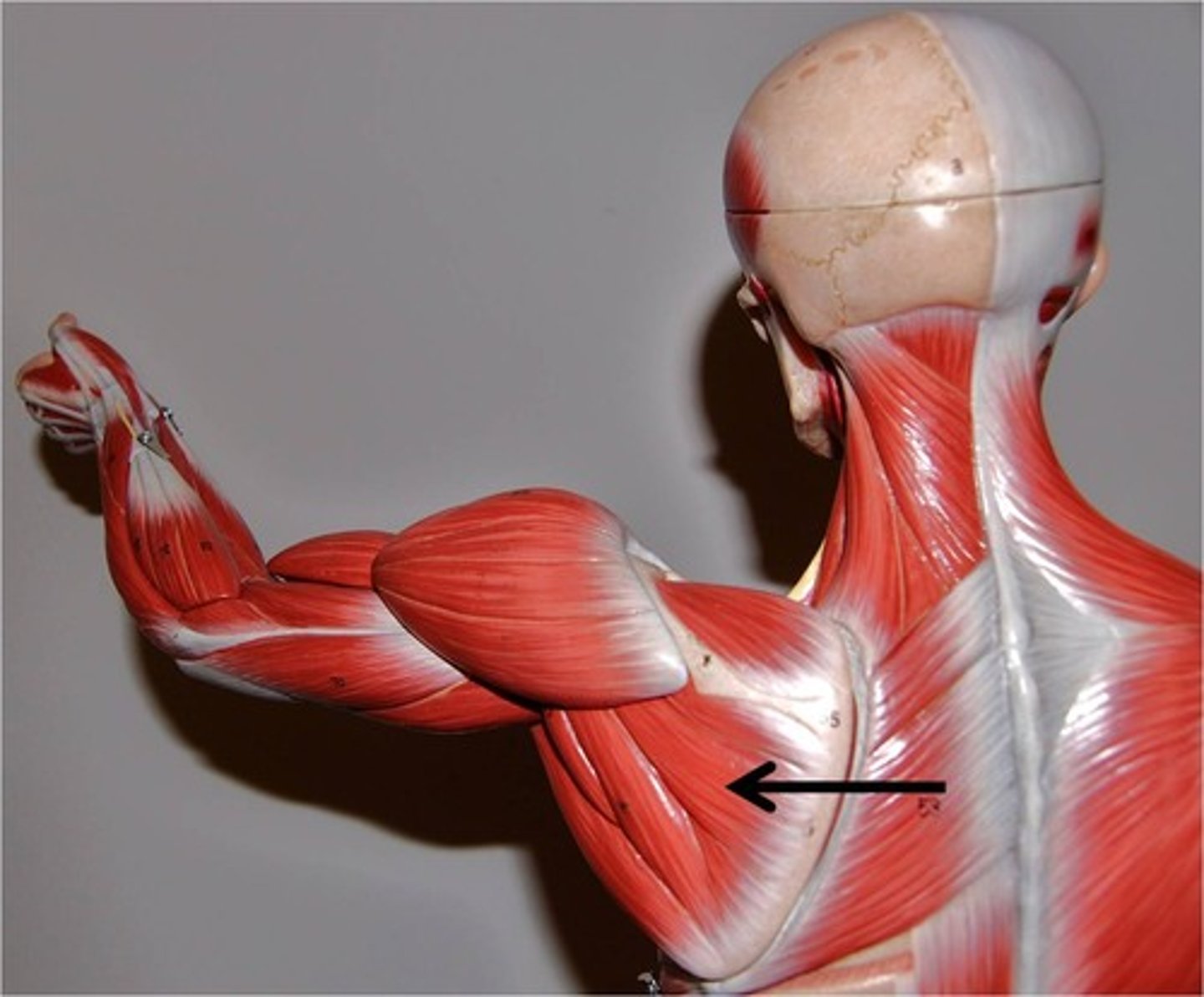
Teres Minor
Origin: Middle part of the lateral (axillary) border of the scapula.
Insertion: Inferior aspect of greater tubercle of humerus
Action: rotates arm laterally, stabilizes shoulder joint
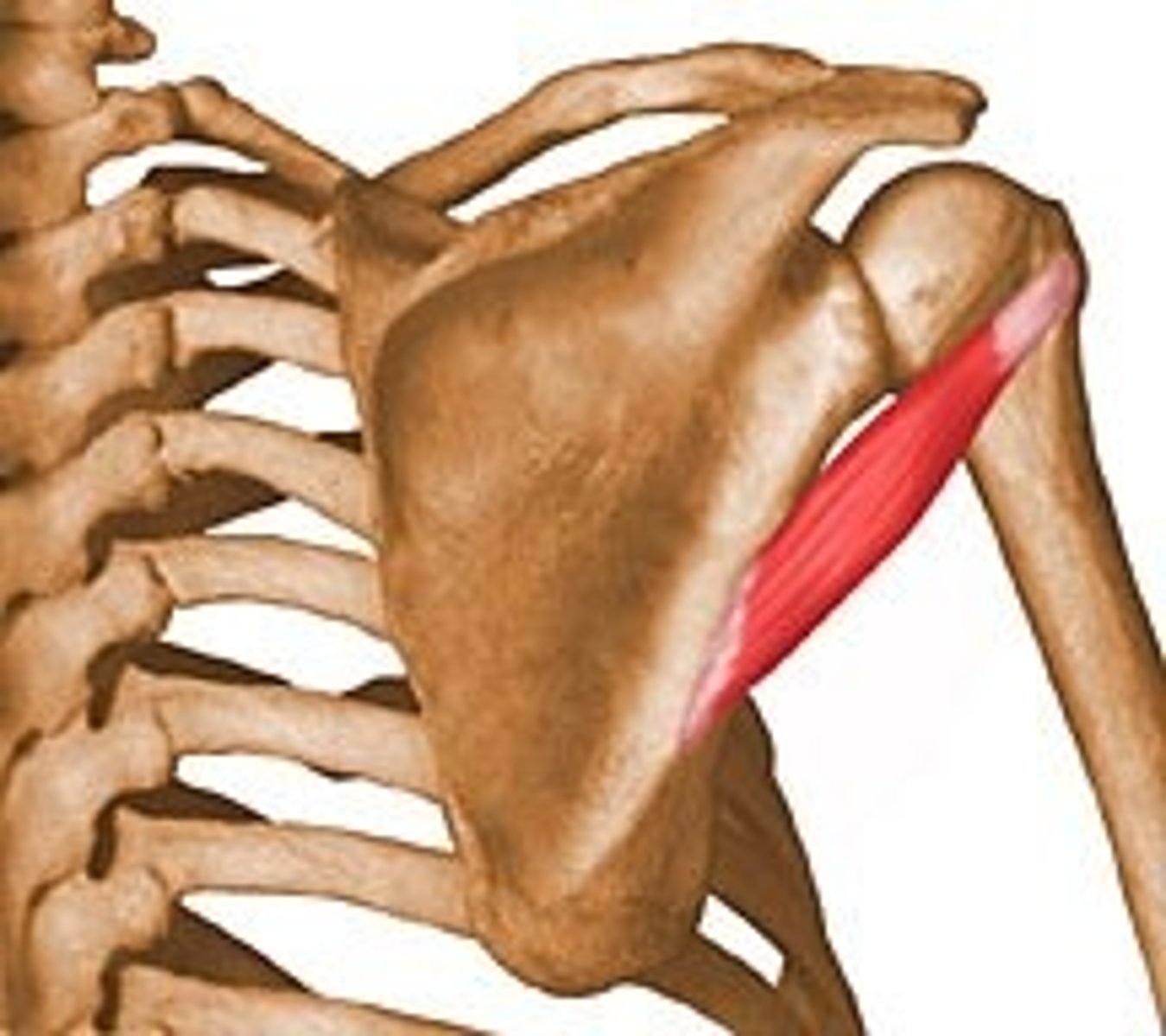
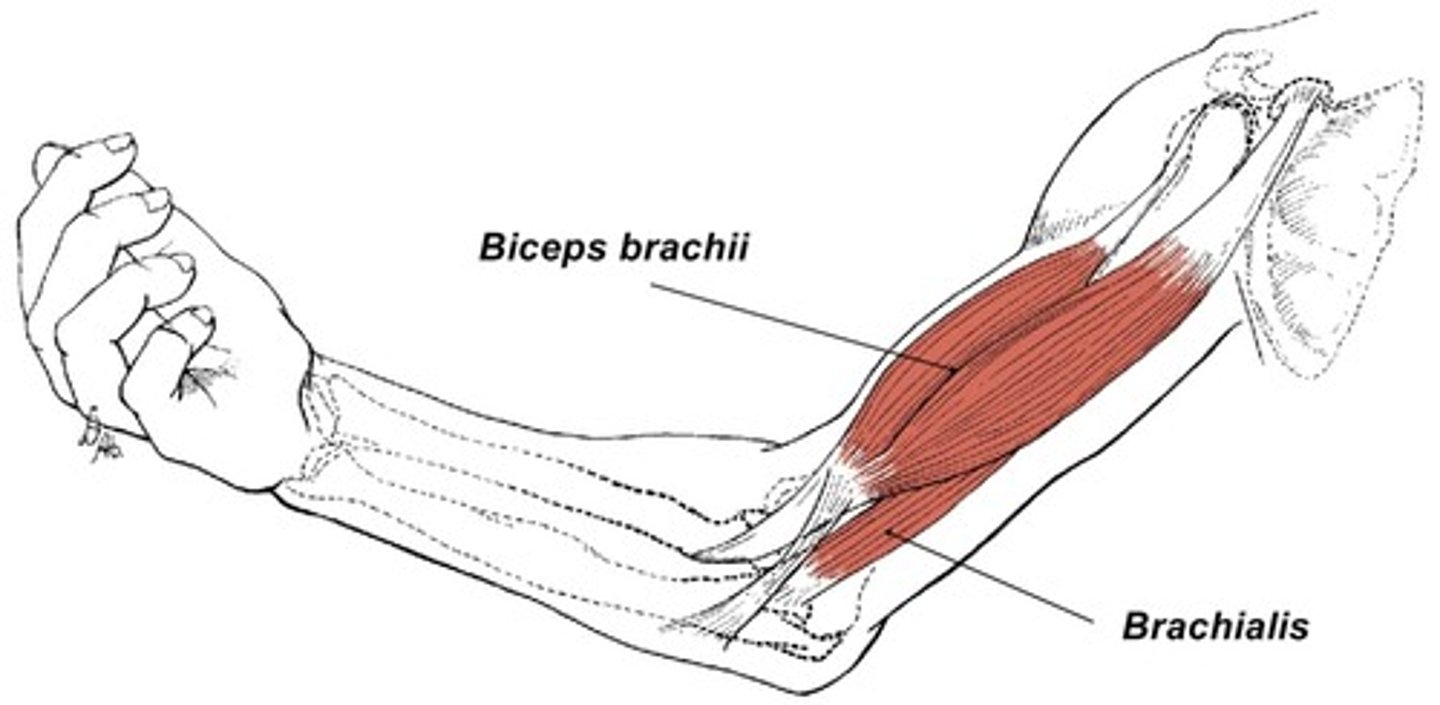
Biceps Brachii
Flexes and supinates forearm
Brachialis
flexes forearm
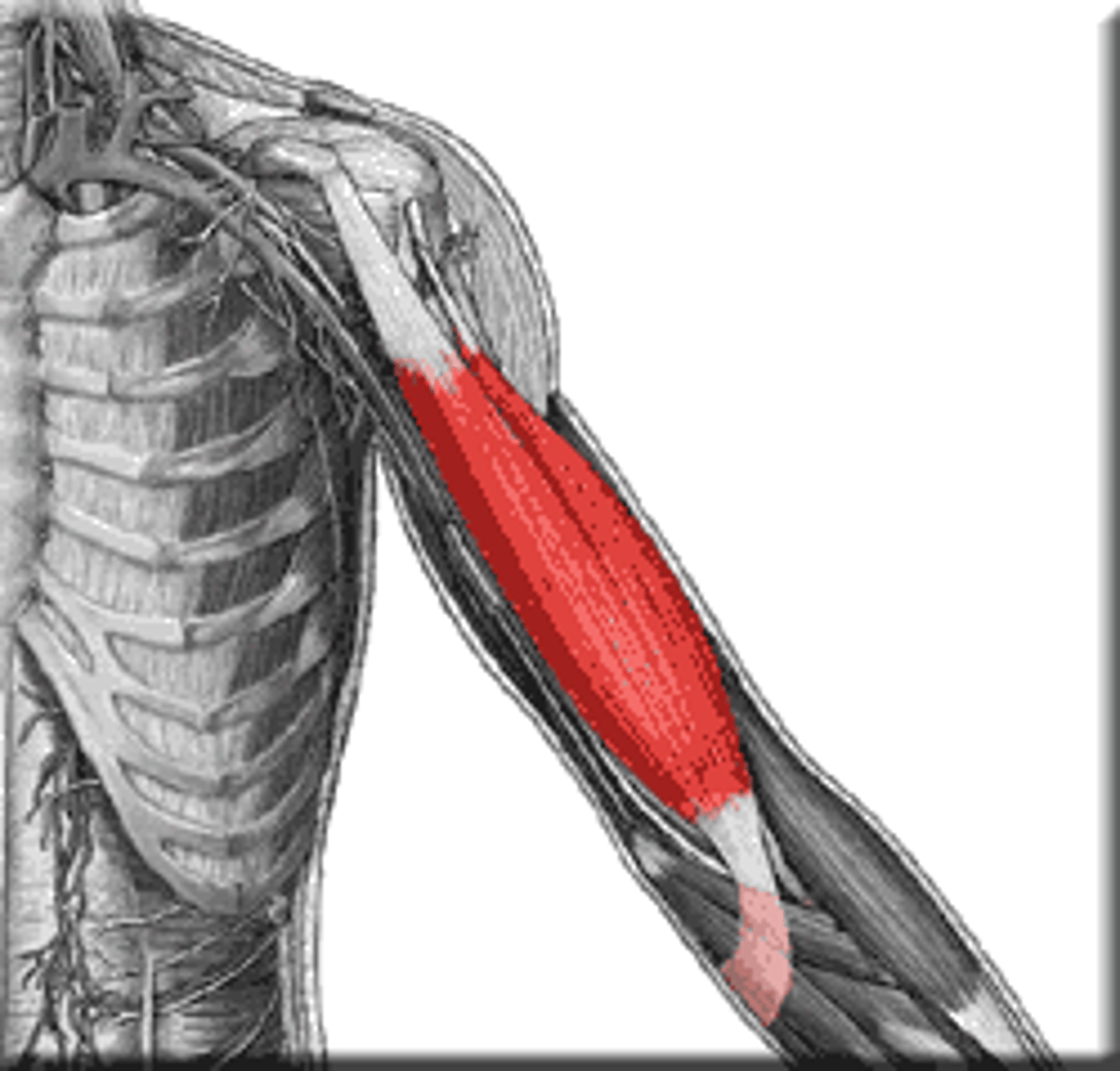
Triceps Brachii
extends forearm
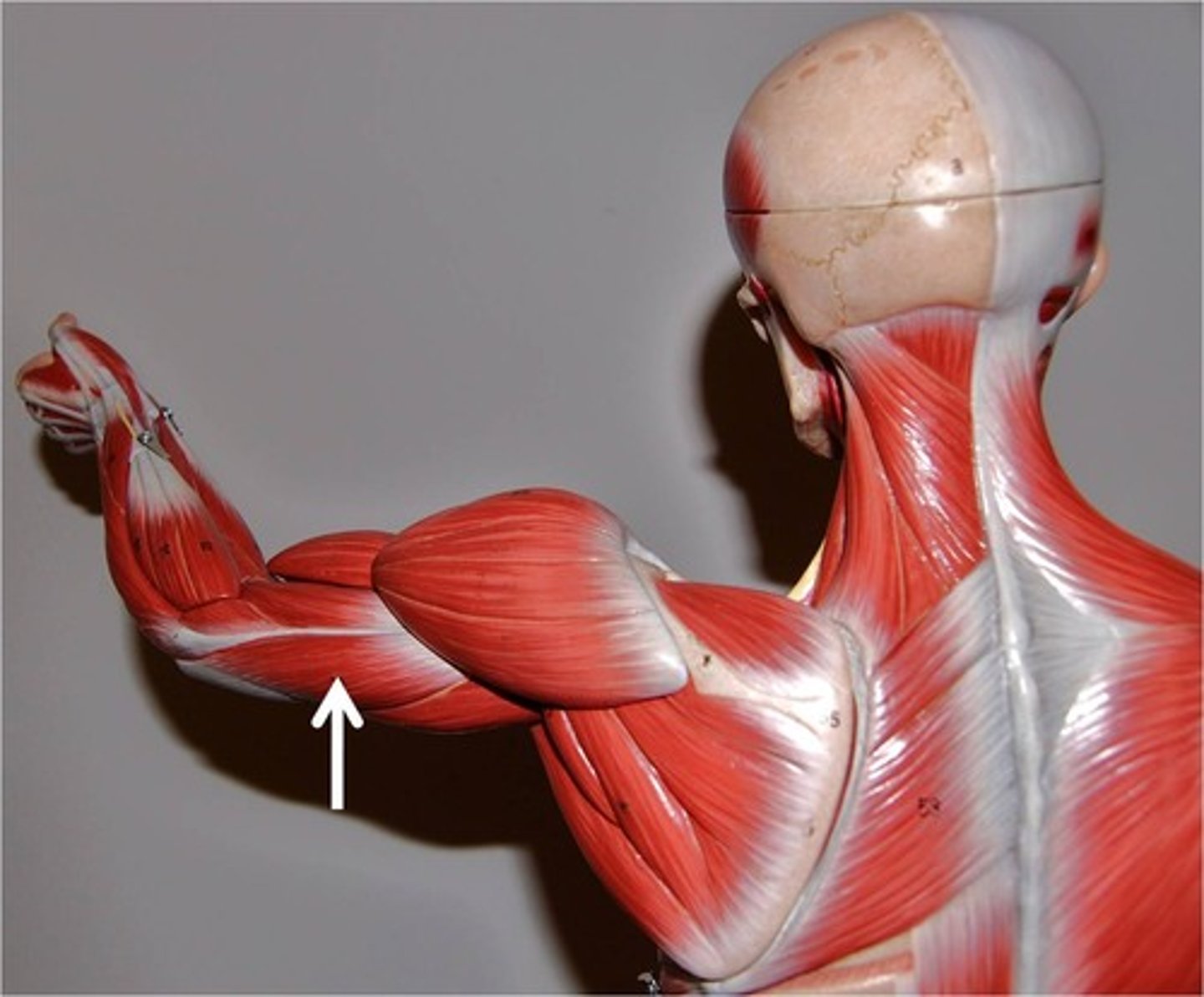
Brachioradialis
flexes forearm at elbow
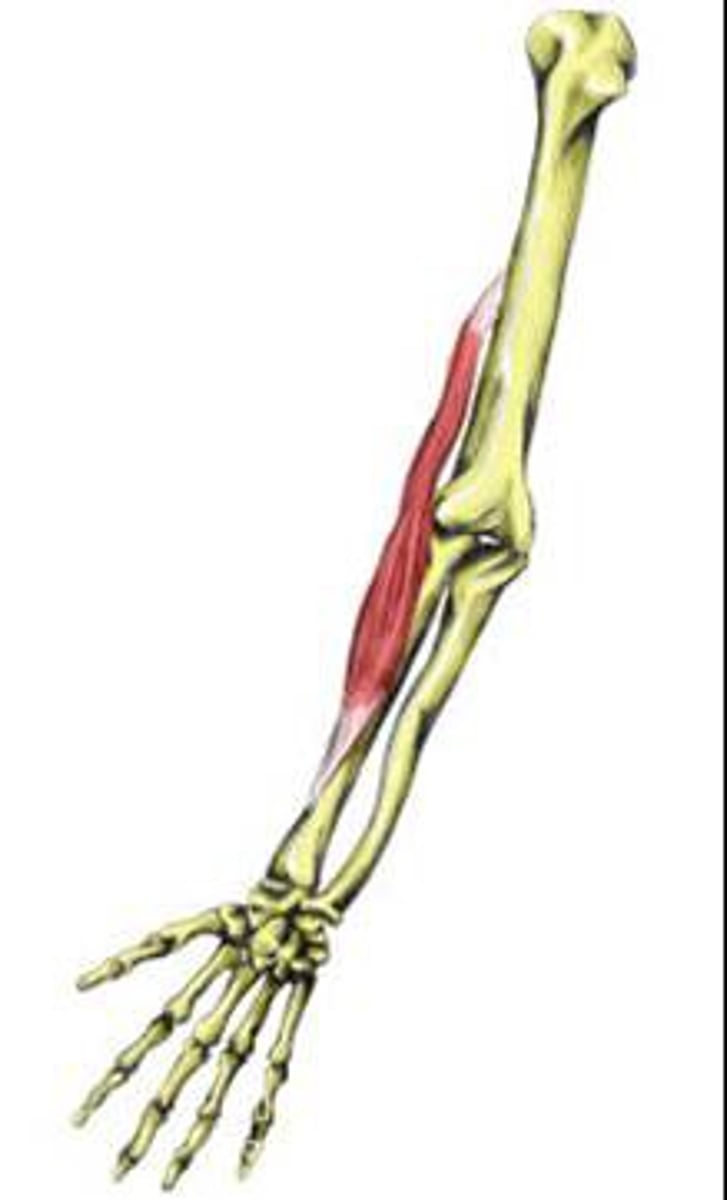
Supinator
supinates forearm
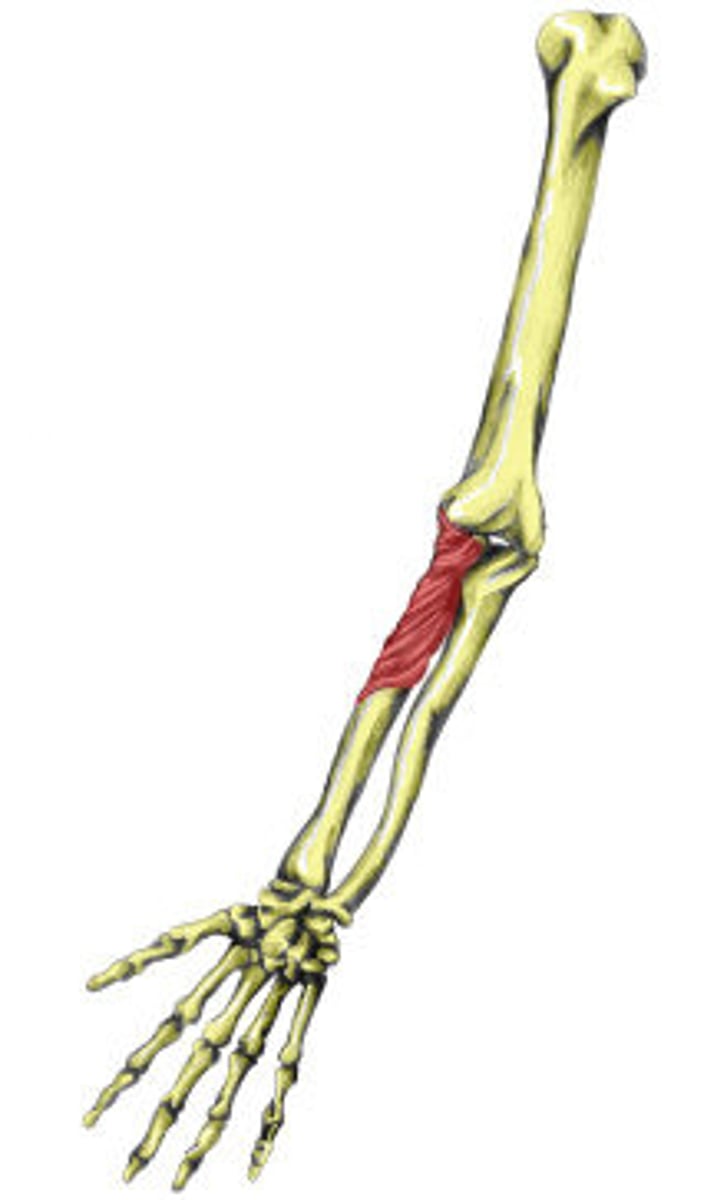
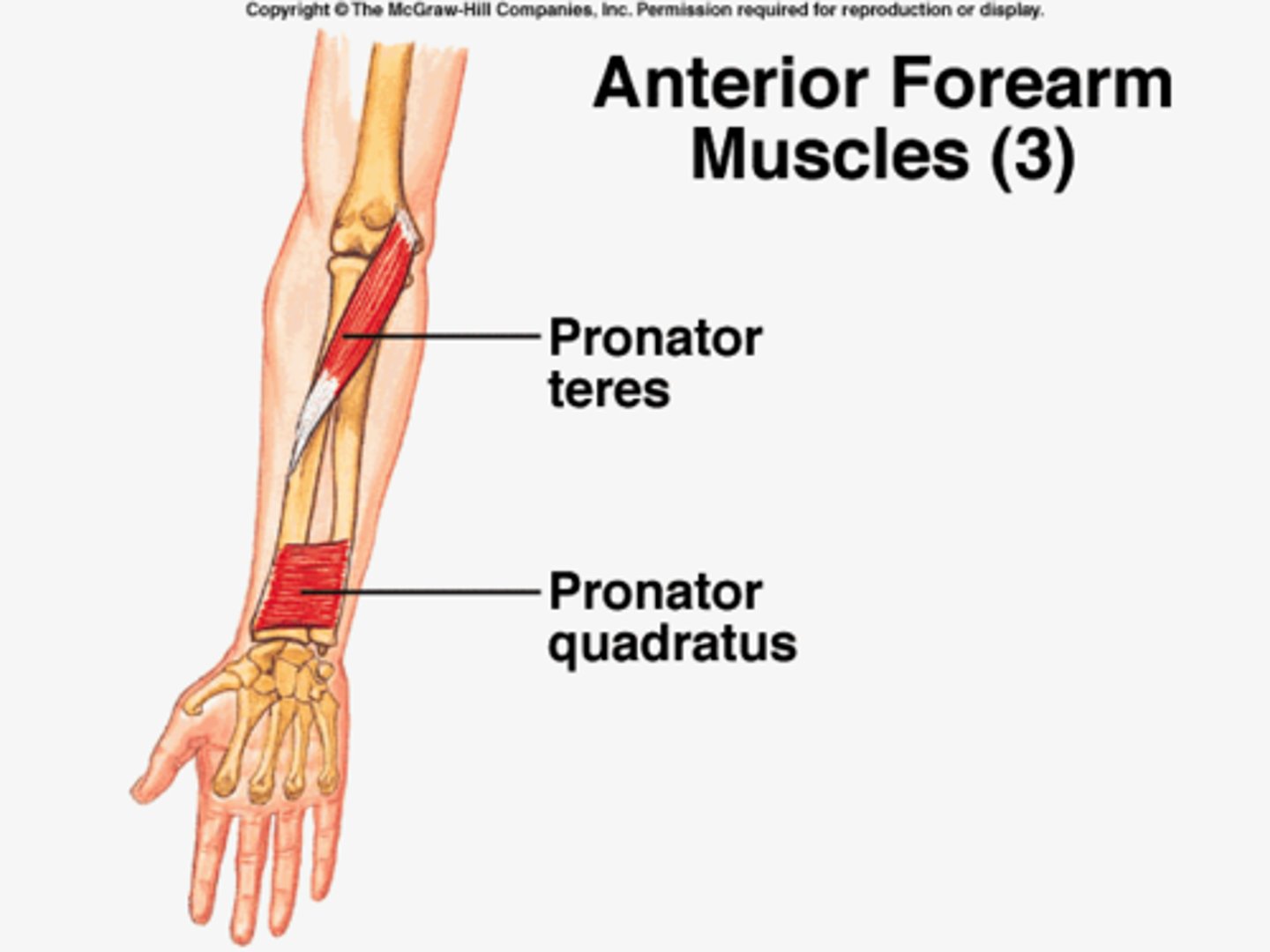
Pronator Teres
pronates forearm
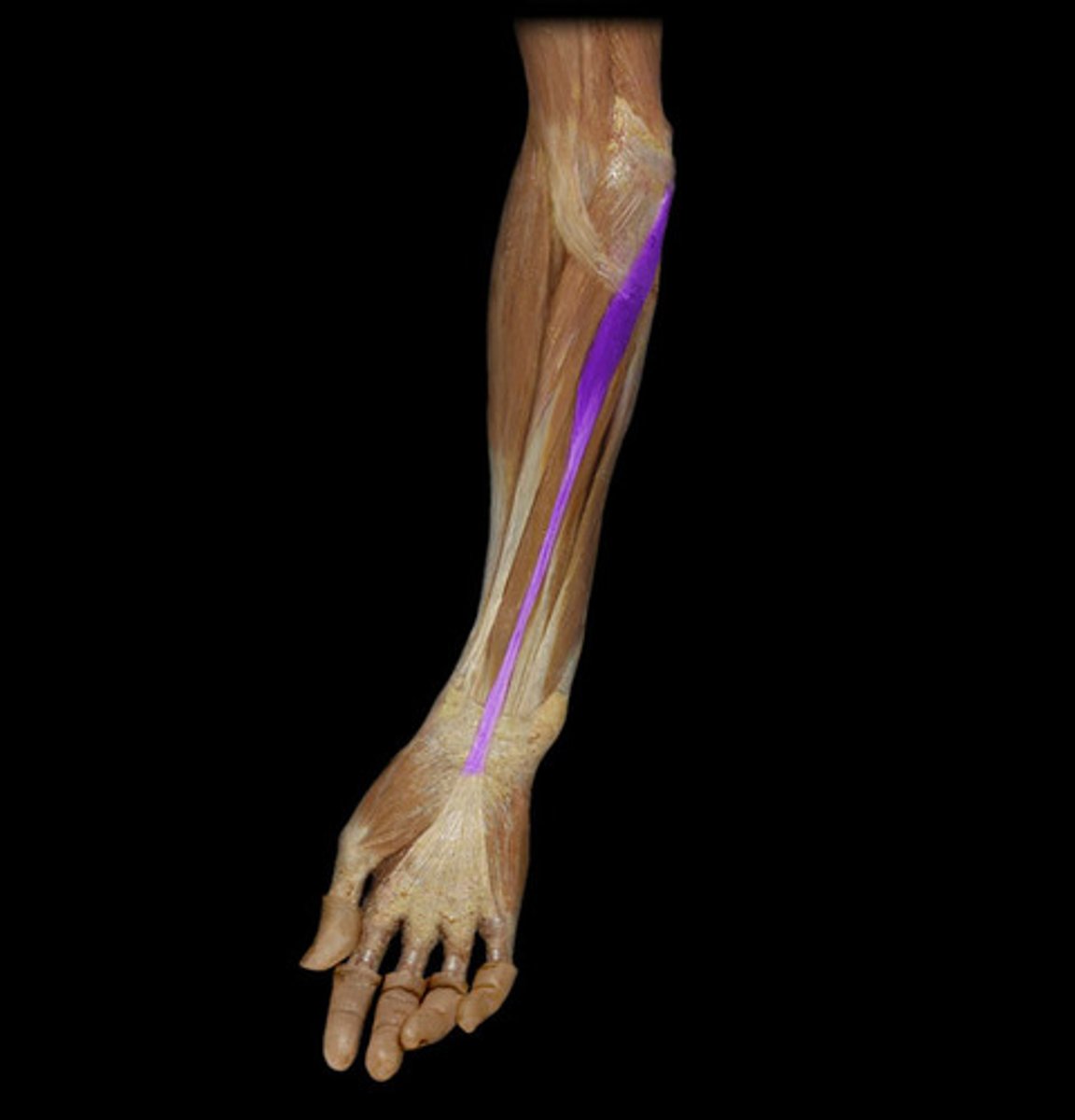
Palmaris Longus
flexes wrist
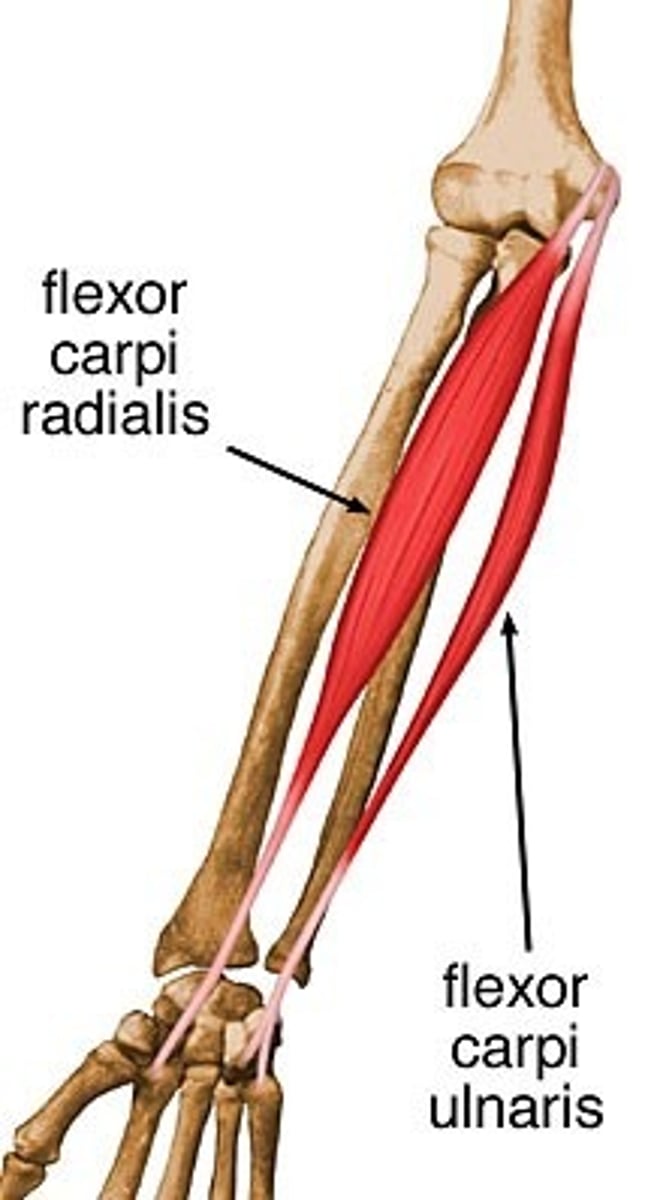
Flexor Carpi Radialis
flexes wrist and abducts hand
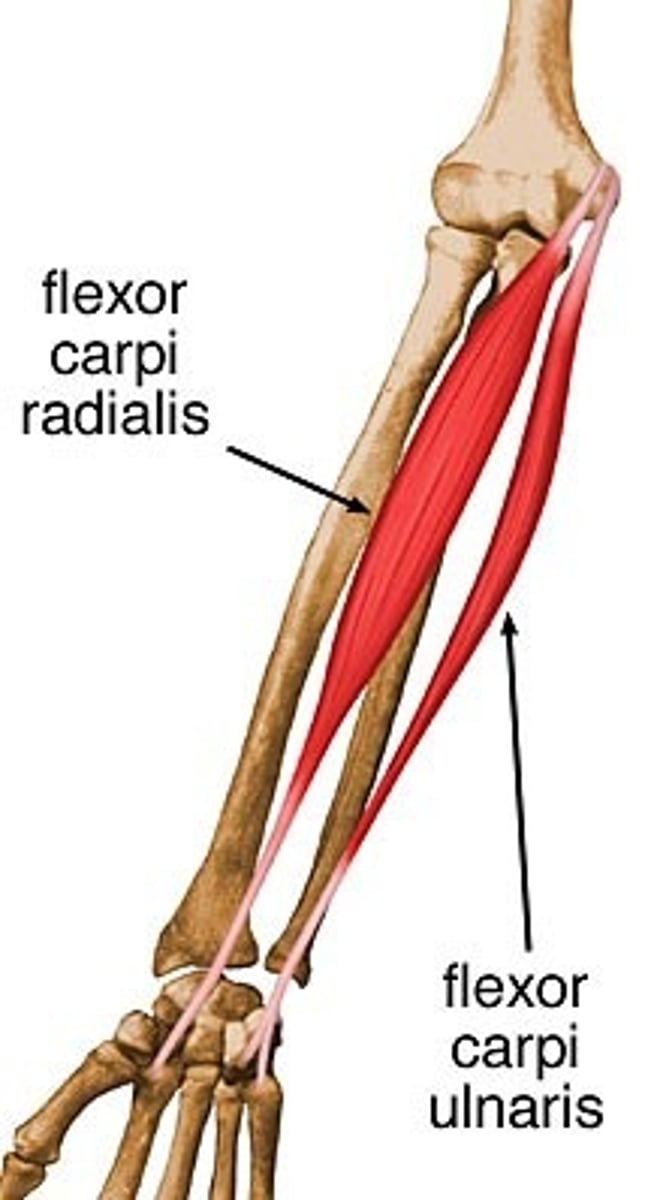
Flexor Carpi Ulnaris
Flexes and adducts hand at the wrist
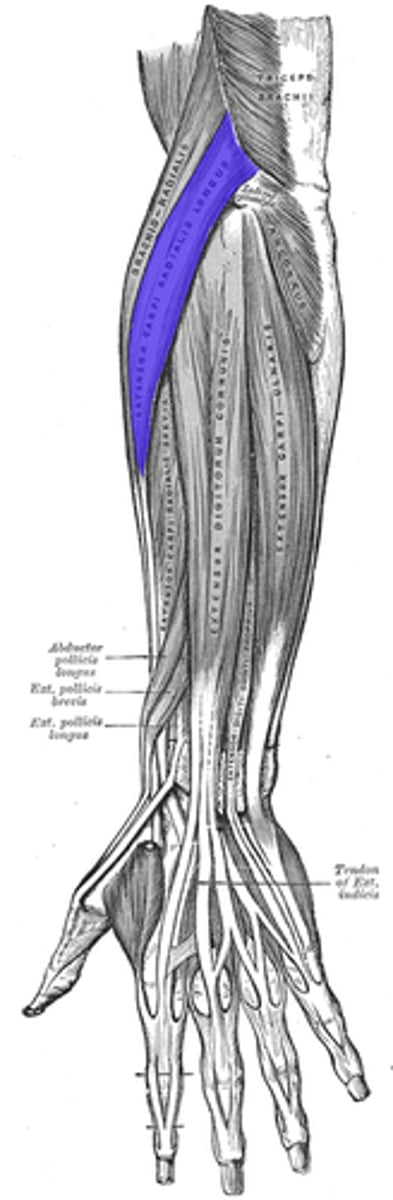
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
Extends wrist and abducts hand
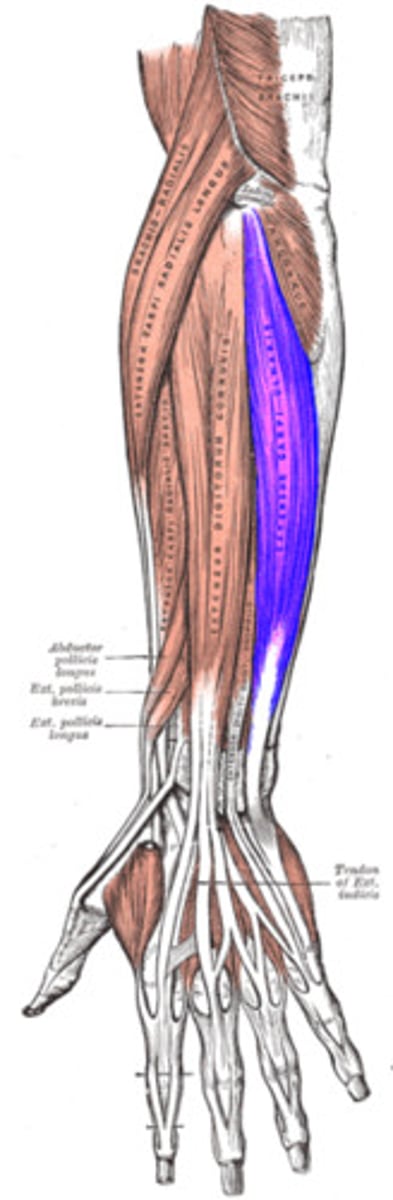
Extensor Carpi Ulnaris
extends and adducts wrist
Flexor Digitorum
flexes fingers
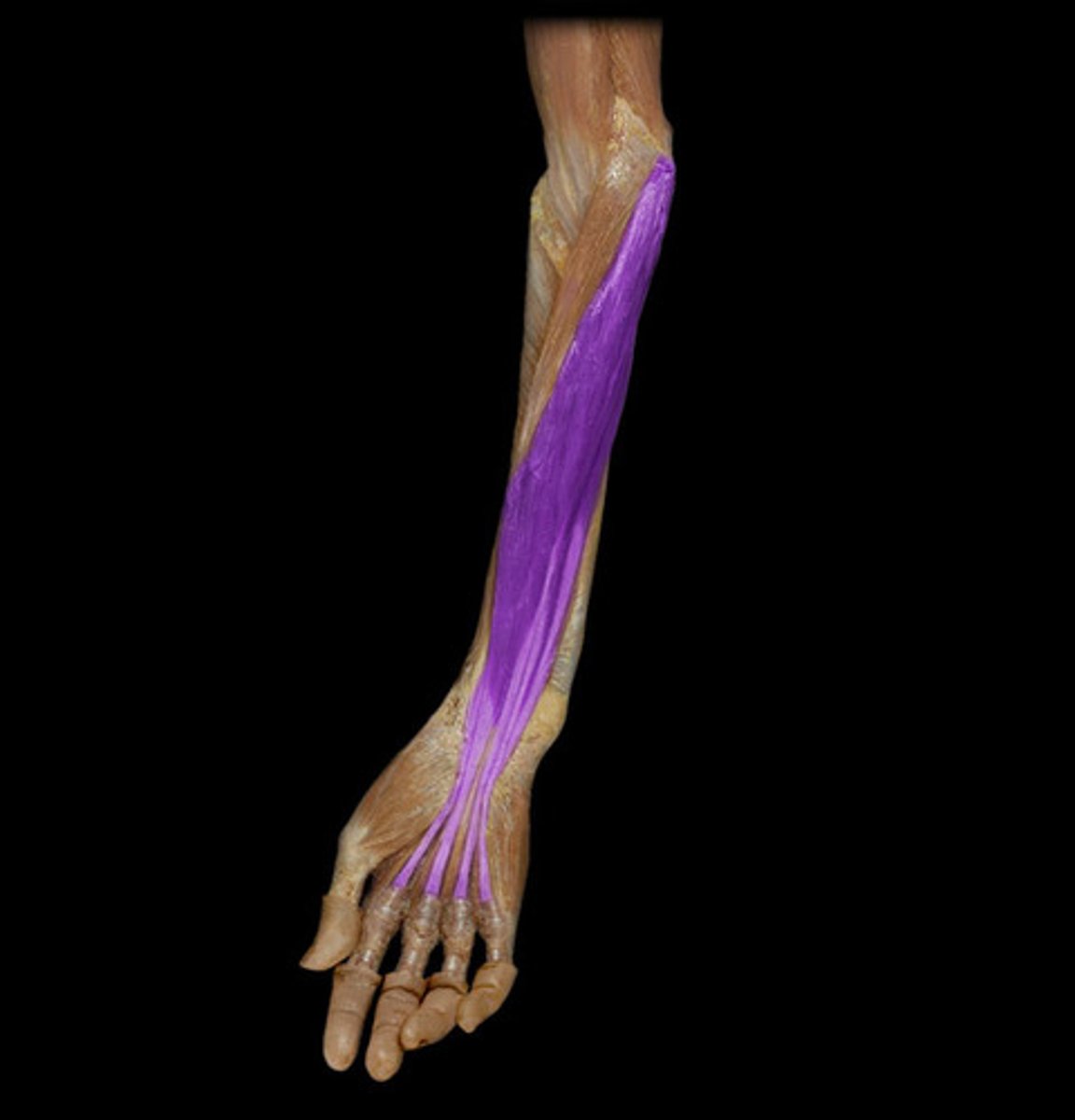
Extensor Digitorum
extends fingers
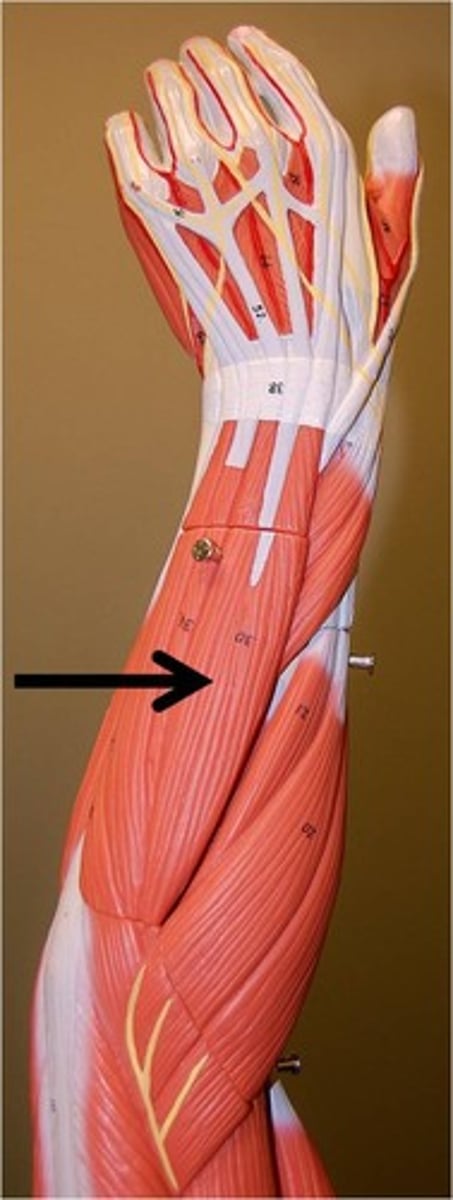
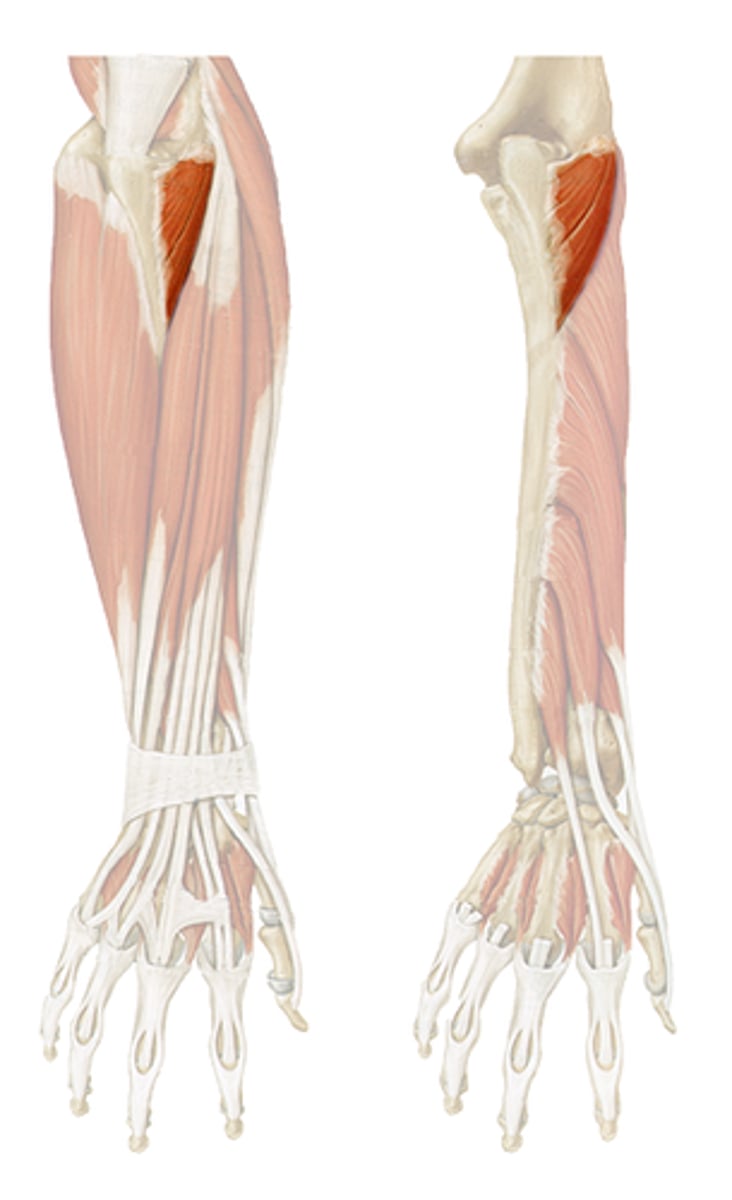
Anconeus
elbow
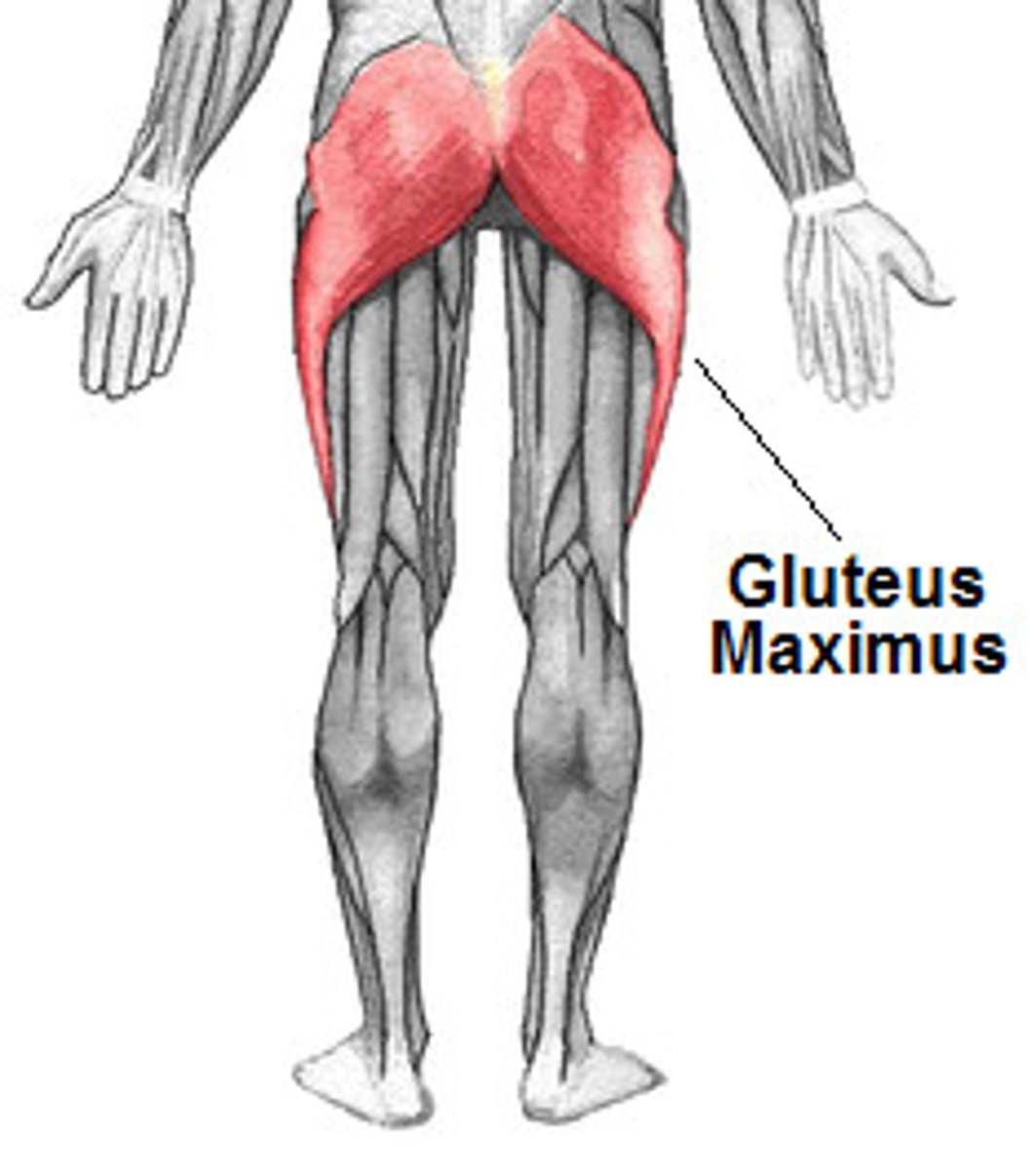
Gluteus Maximus
extends thigh
Rectus Femoris
Origin: Anterior inferior iliac spine and supracetabular groove of the ilium
Insertion: Tibial tuberosity (via patellar ligament)
Action: Flex the thigh and extend the leg
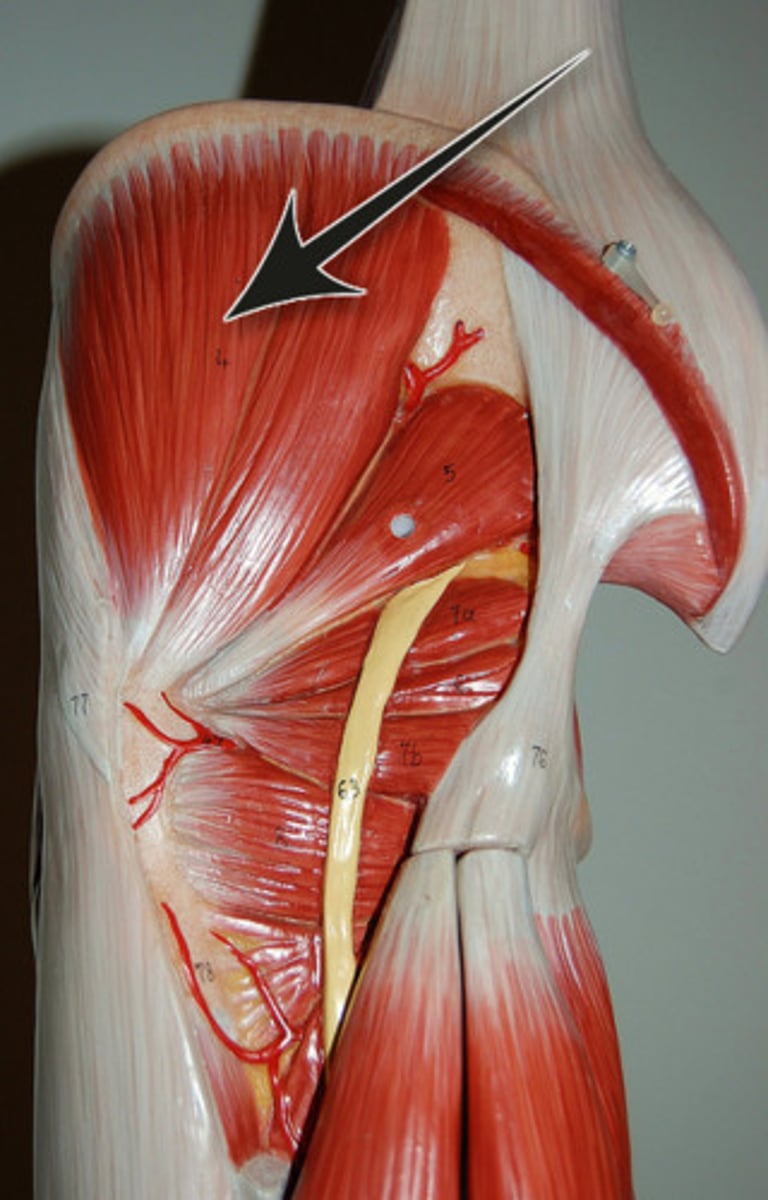
Gluteus Medius
abducts and medially rotates thigh
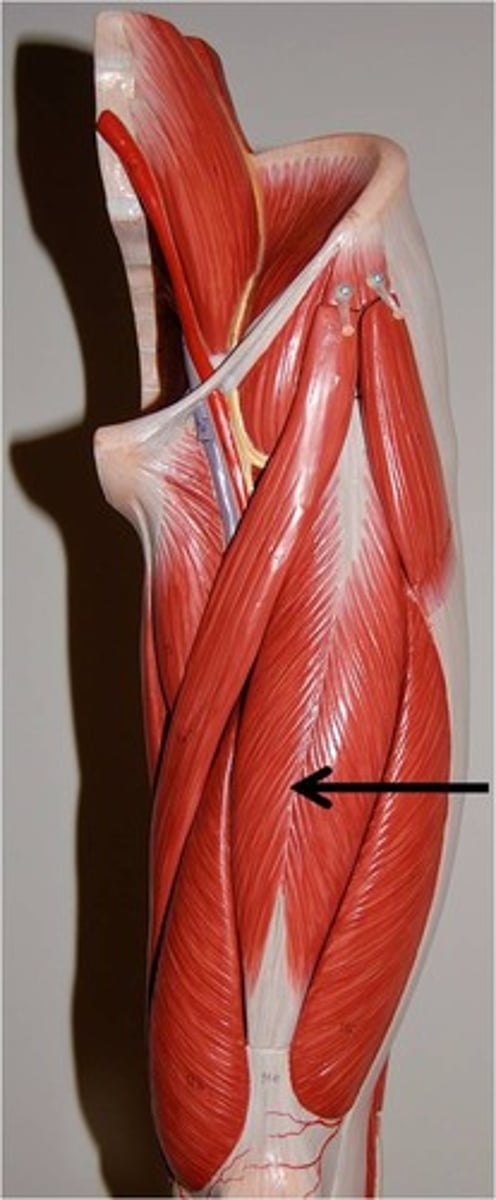
Vastus Lateralis
Origin: Greater trochanter of femur, intertrochanteric line, gluteal tuberosity and lateral aspect of linea aspera
Insertion: tibial tuberosity via the patellar ligament and also into the patella itself.
Action: Flex the thigh and extend the knee
Part of quadriceps femoris group
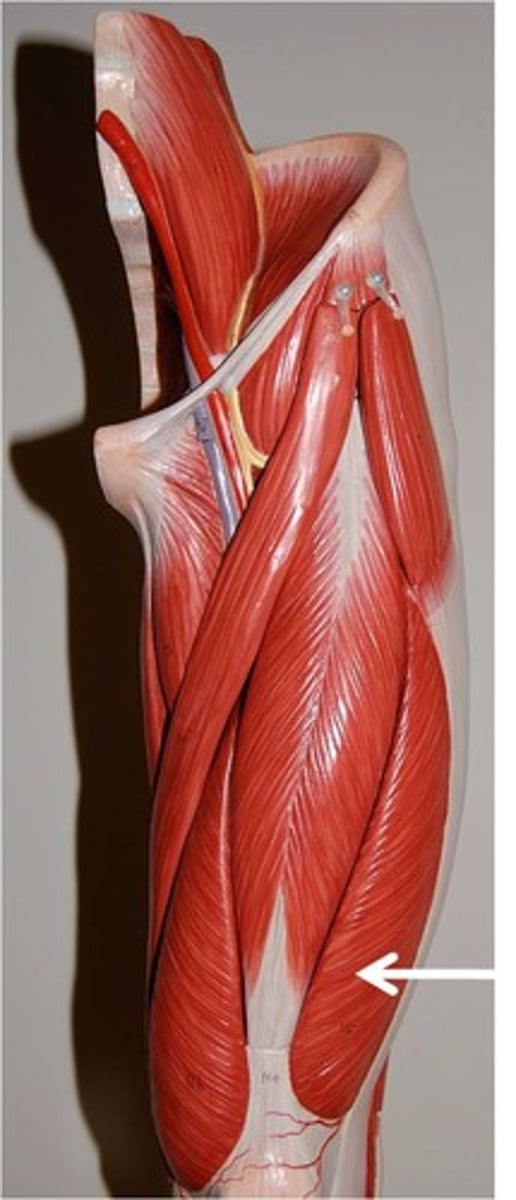
Tensor Fascia Latae
flexes and abducts thigh
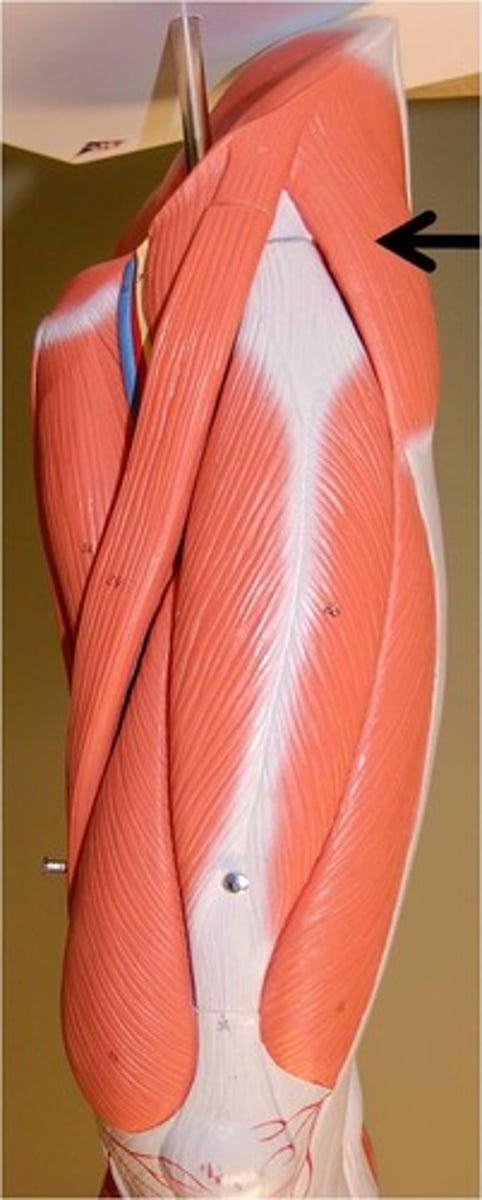
Vastus Intermedius
Origin: Anterior and lateral surface of the femoral shaft
Insertion: Tibial tuberosity (via patellar ligament) and the patella itself
Action: Flex the thigh and extend the leg
Part of quadriceps femoris group
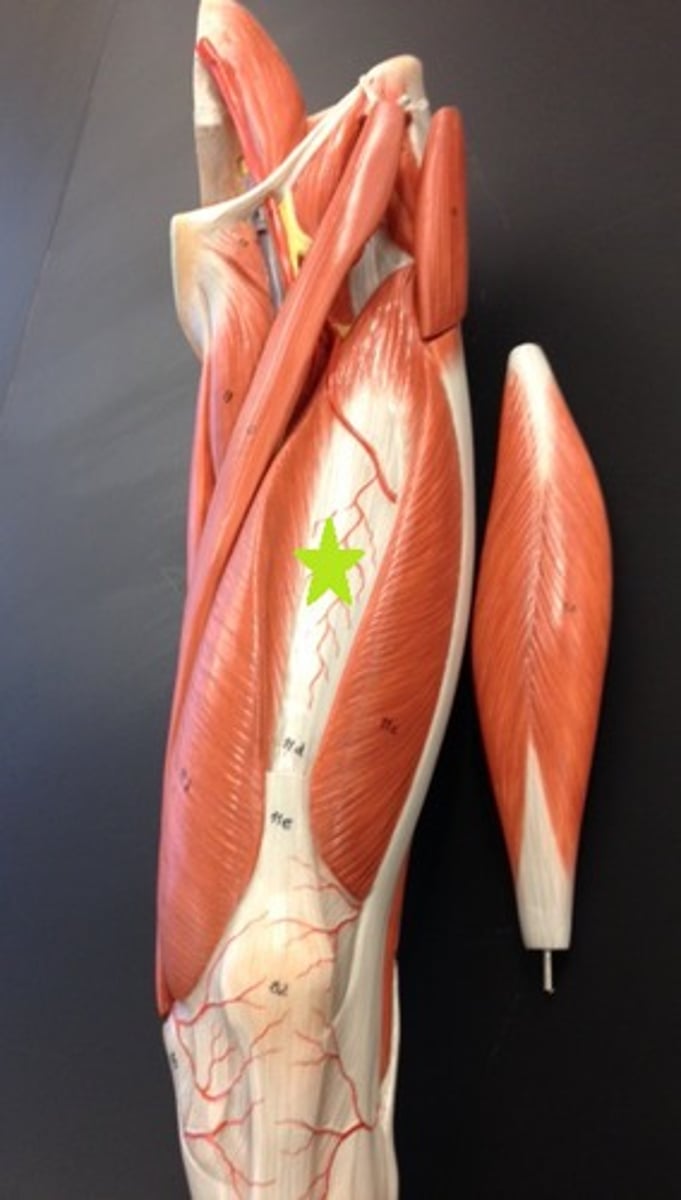
Adductor Brevis
adducts femur at hip
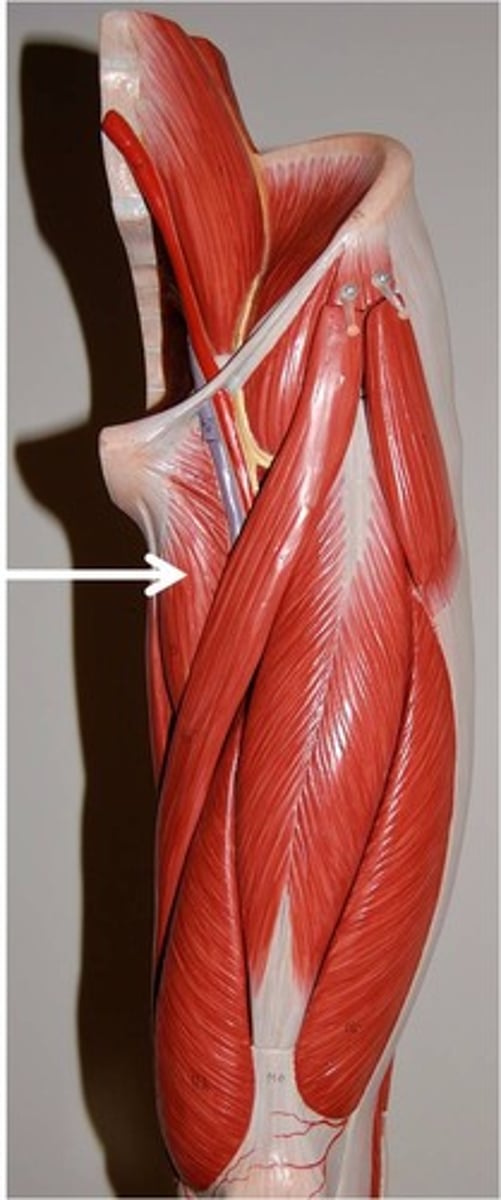
Vastus Medialis
Origin: Intertrochanteric line, spiral line and linea aspera, and the medial lip of linea aspera of femur
Insertion: Tibial tuberosity (via patellar ligament) and the patella itself
Action:Part of quadriceps femoris group, Flex the thigh and extend the knee
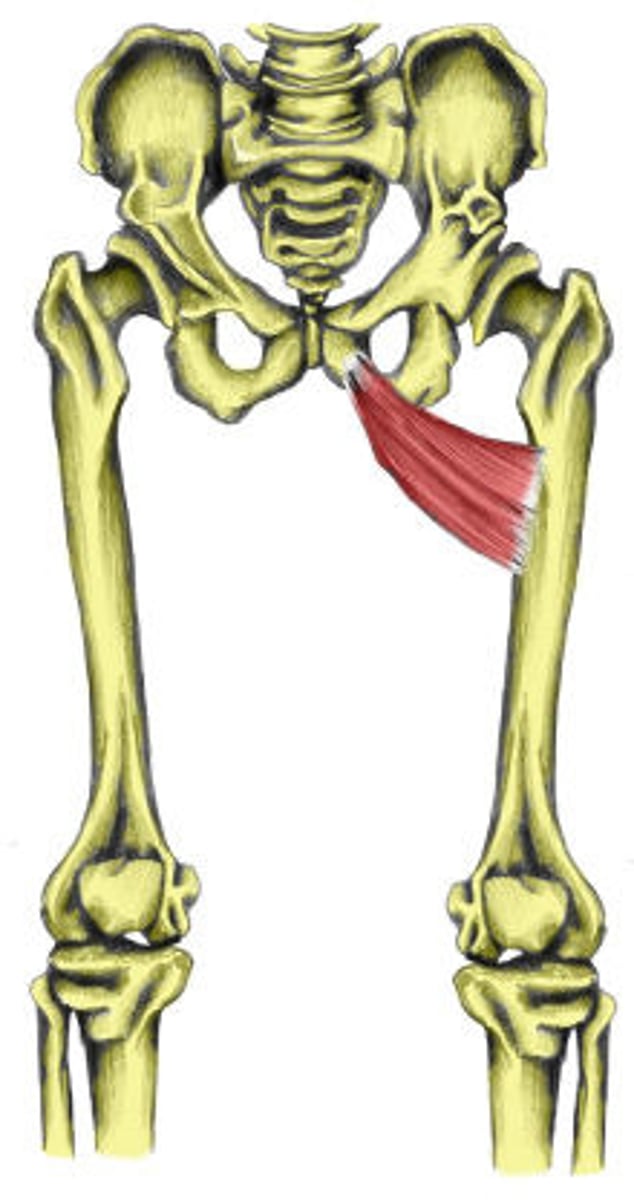
Adductor Longus
Origin: Superior aspect of pubis, below pubic tubercle
Insertion: Middle third of linea aspera of femur along medial lip
Action: Adducts the femur at the hip, flexes the thigh at the hip
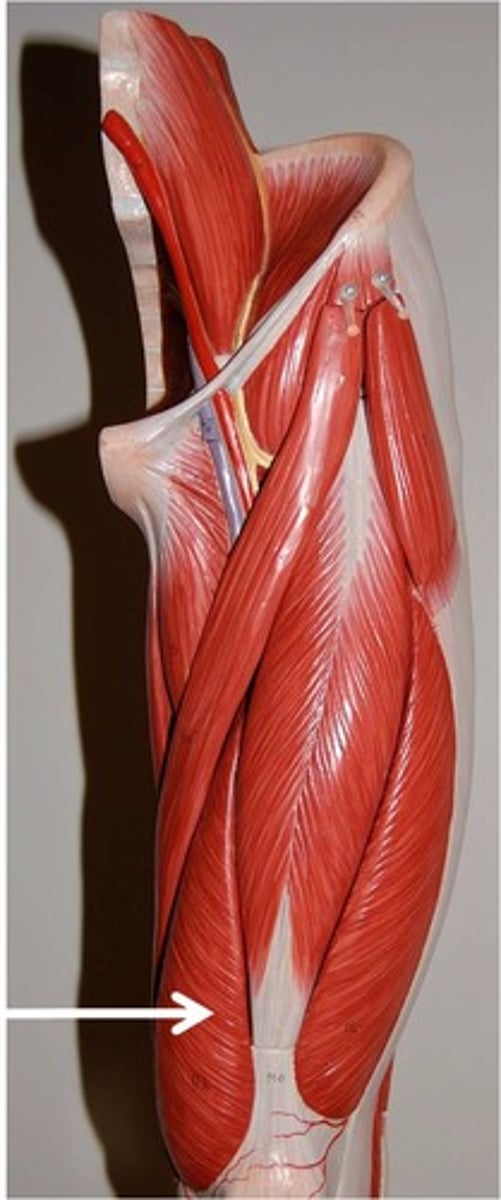
Biceps Femoris
extends thigh and flexes knee, part of the hamstring group
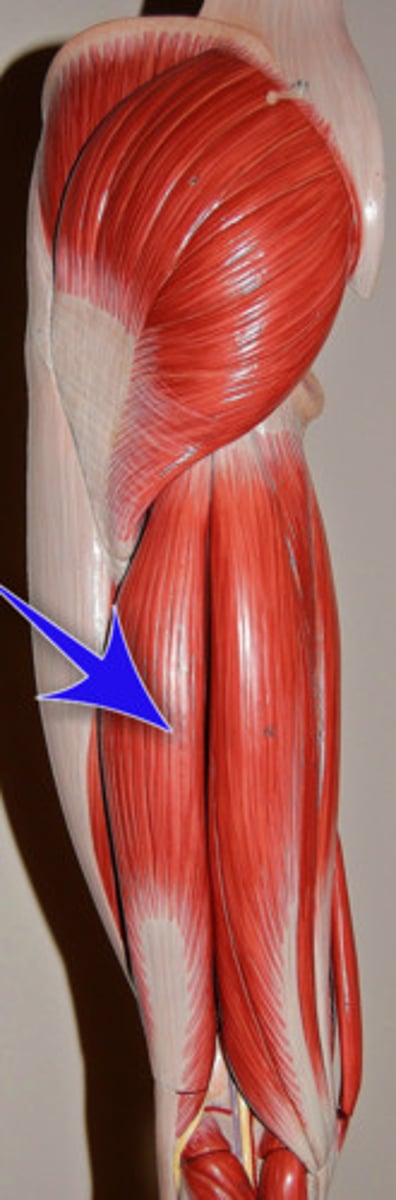
Adductor Magnus
Origin: Oblique head - inferior ramus of pubis & ischial ramus, Vertical head - ischial tuberosity.
Insertion: Oblique head - gluteal tuberosity, linea aspera and proximal supracondylar line of femur, Vertical head - adductor tubercle of femur
Action: Adducts the femur at the hip, Flexes thigh
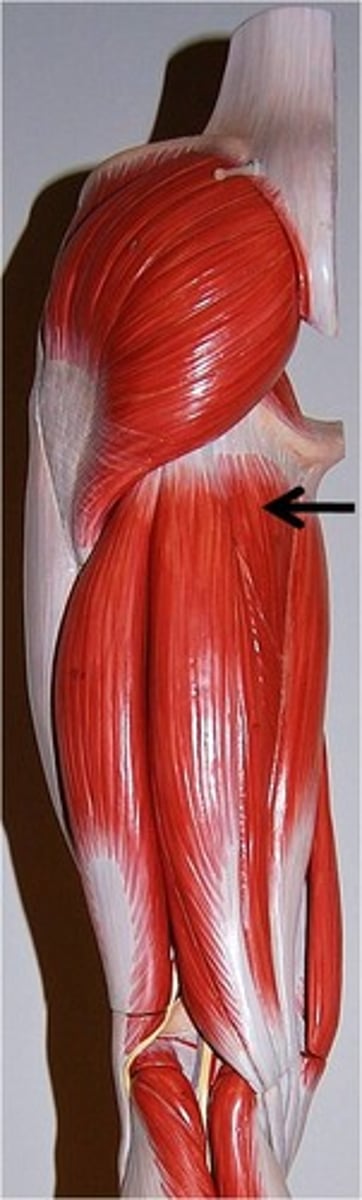
Semimembranosus
Flexes leg at the knee and extends thigh at the hip; belongs to the hamstring group
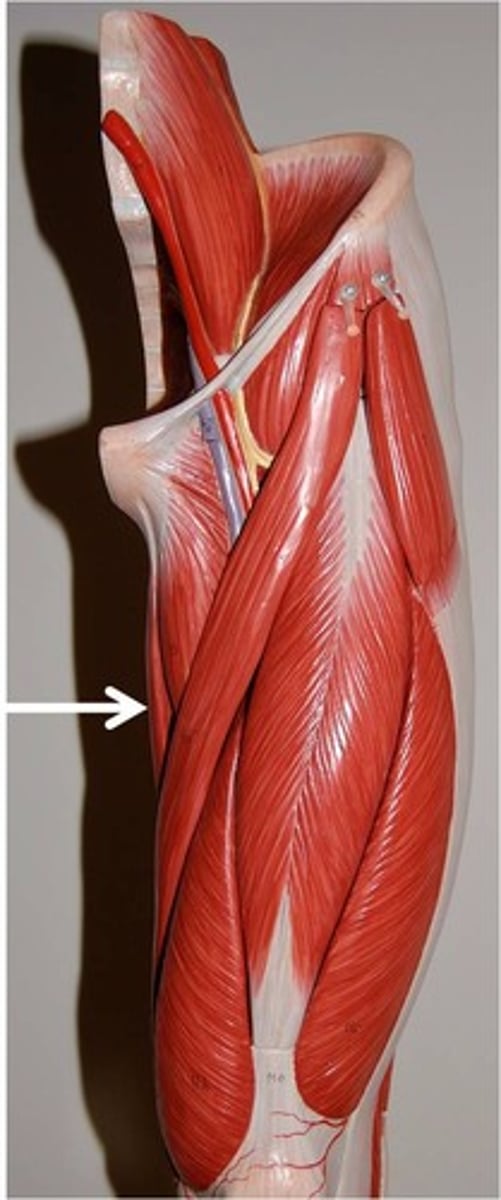
Gracilis
adducts thigh, flexes and medially rotates leg
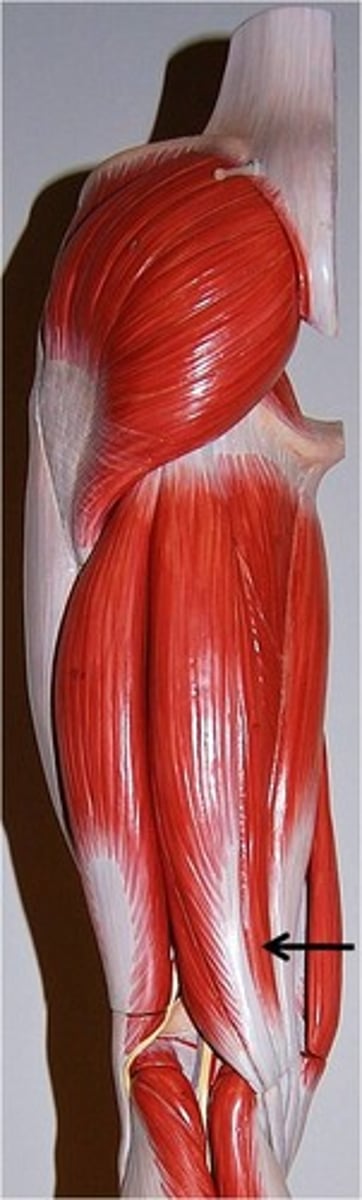
Semitendinosus
Flexes leg at the knee and extends thigh at the hip; belongs to the hamstring group
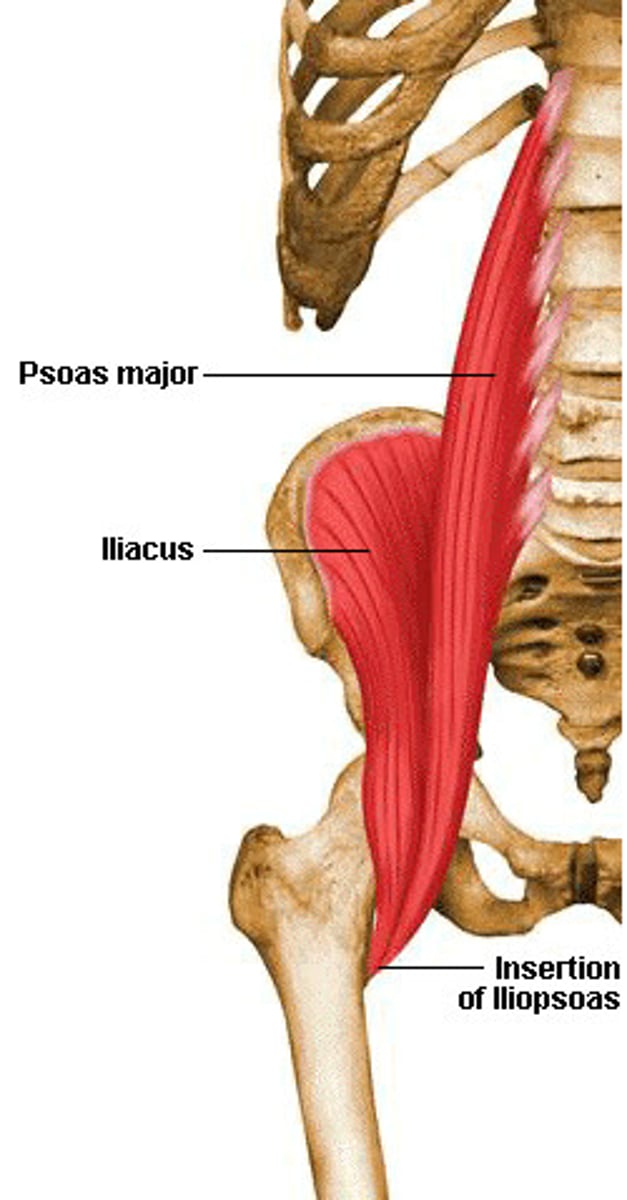
Iliopsoas (iliacus and psoas major)
Flex trunk at hip joint, flex thigh; lateral flexion of vertebral column (psoas)
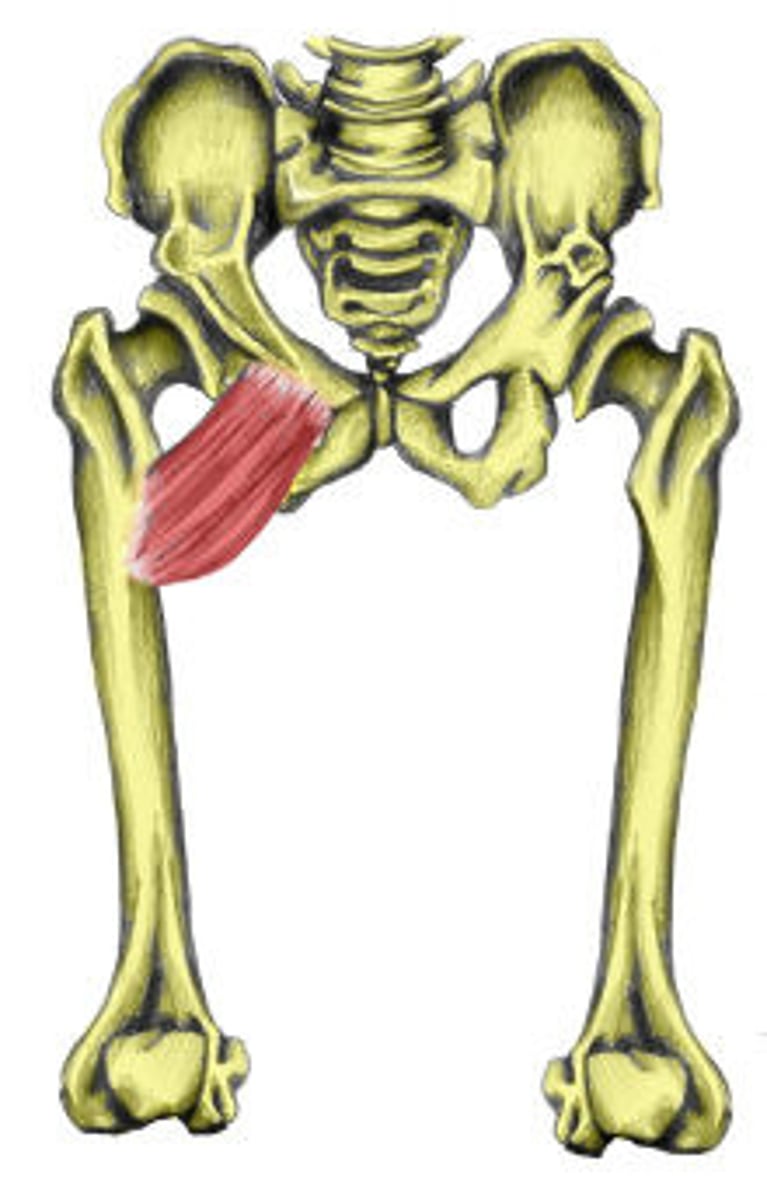
Pectineus
adducts, flexes, and medially rotates thigh
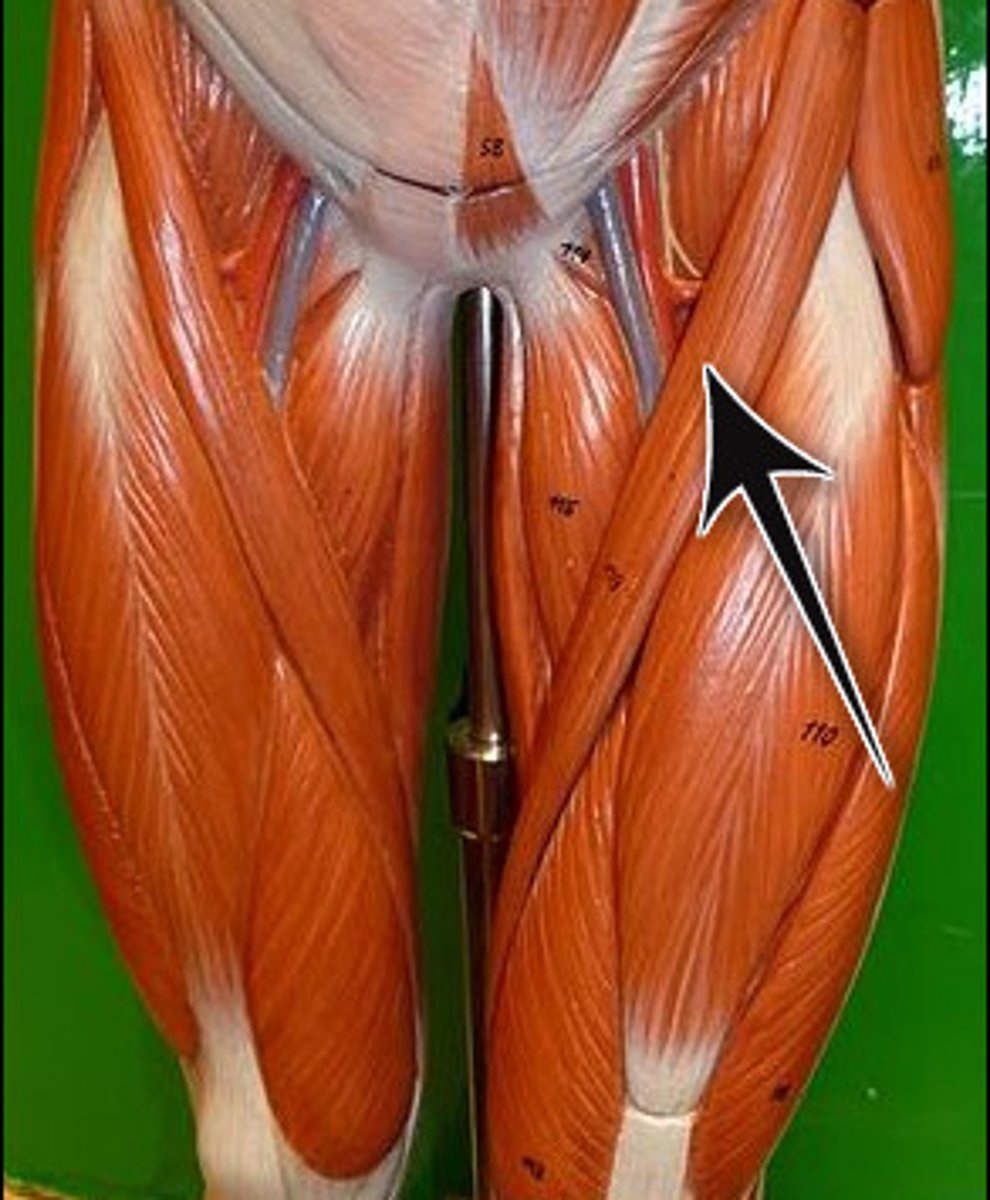
Sartorius
band-like muscle that extends from the anterior superior iliac spine to the medial side of the proximal tibia
This versatile muscle flexes the leg at the knee and flexes, abducts, and laterally rotates the leg at the hip.
This muscle allows us to sit cross-legged
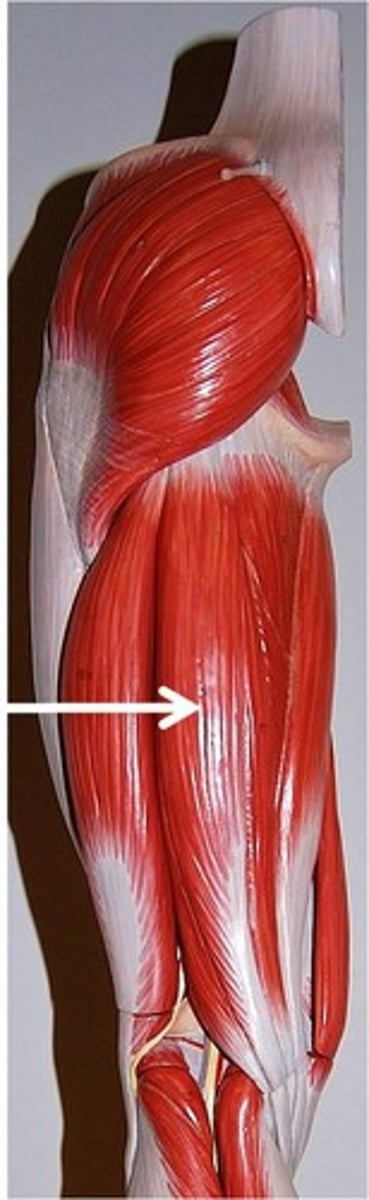
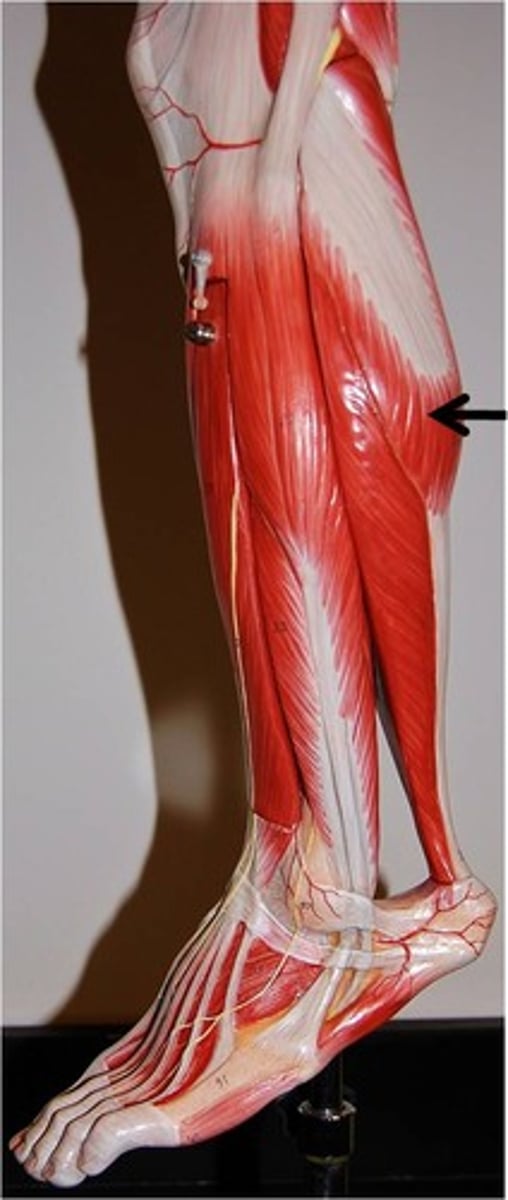
Gastrocnemius
plantar flexes foot
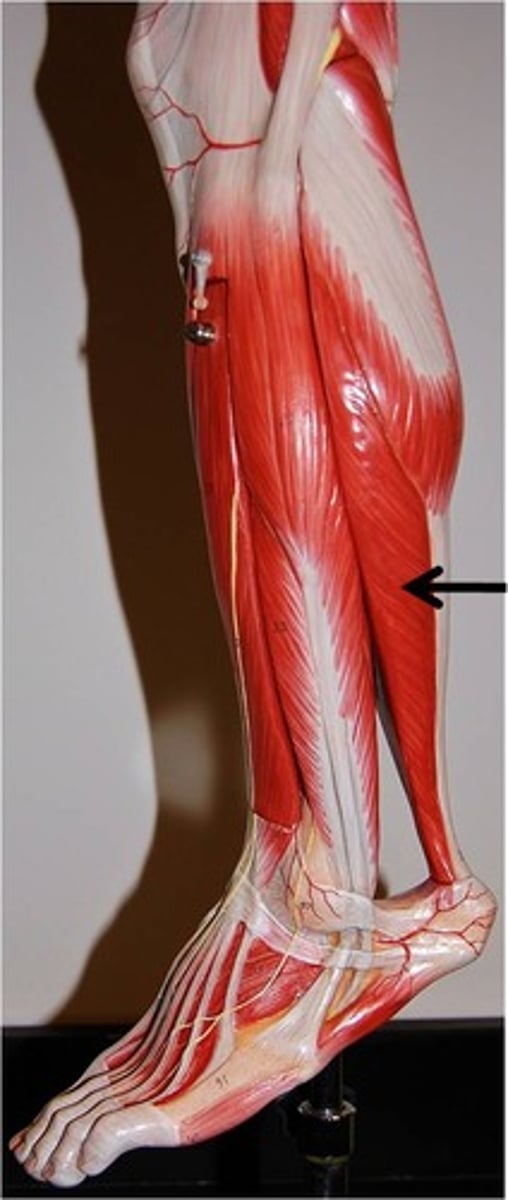
Soleus
plantar flexes foot
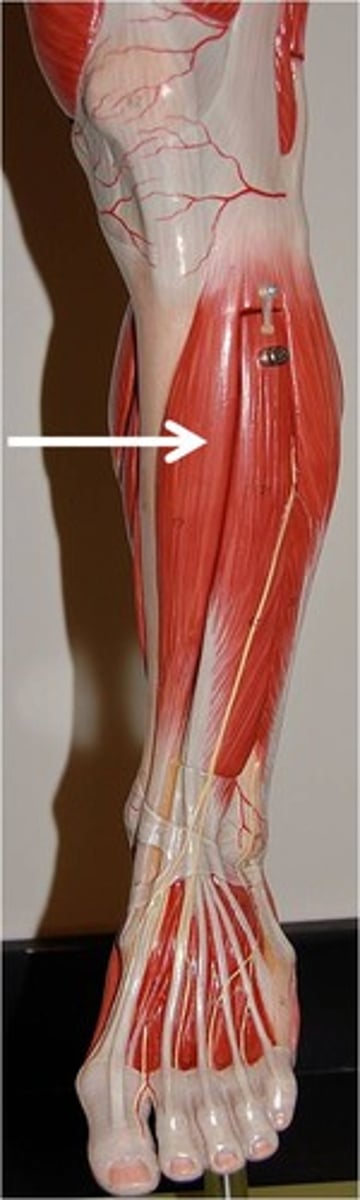
Tibialis Anterior
dorsiflexes and inverts foot
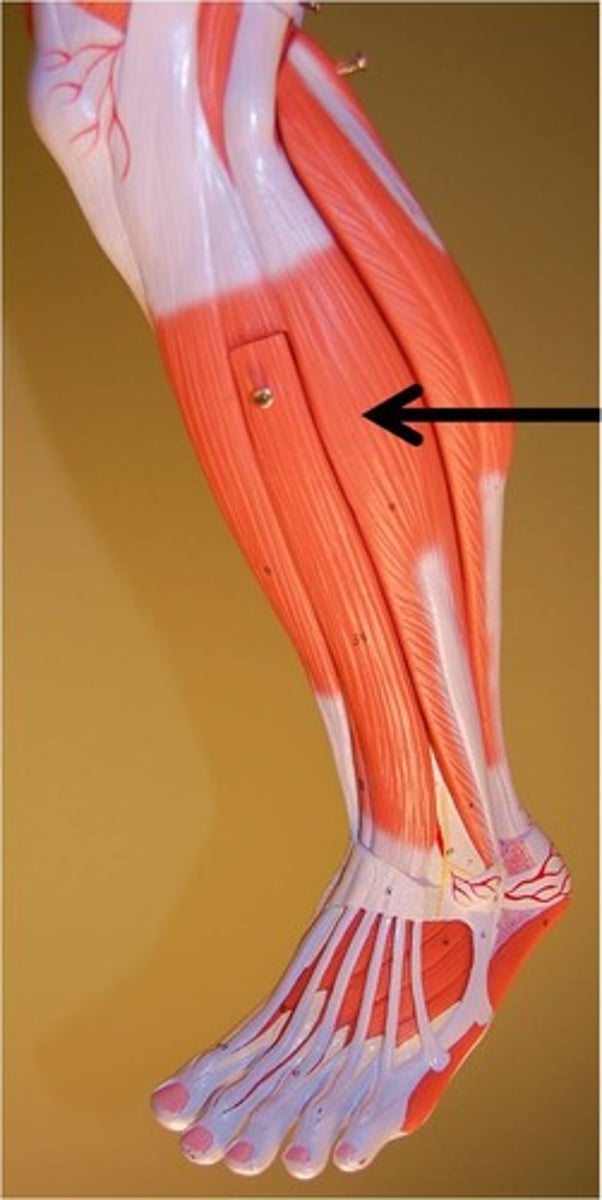
Fibularis Longus
plantar flexes and everts foot
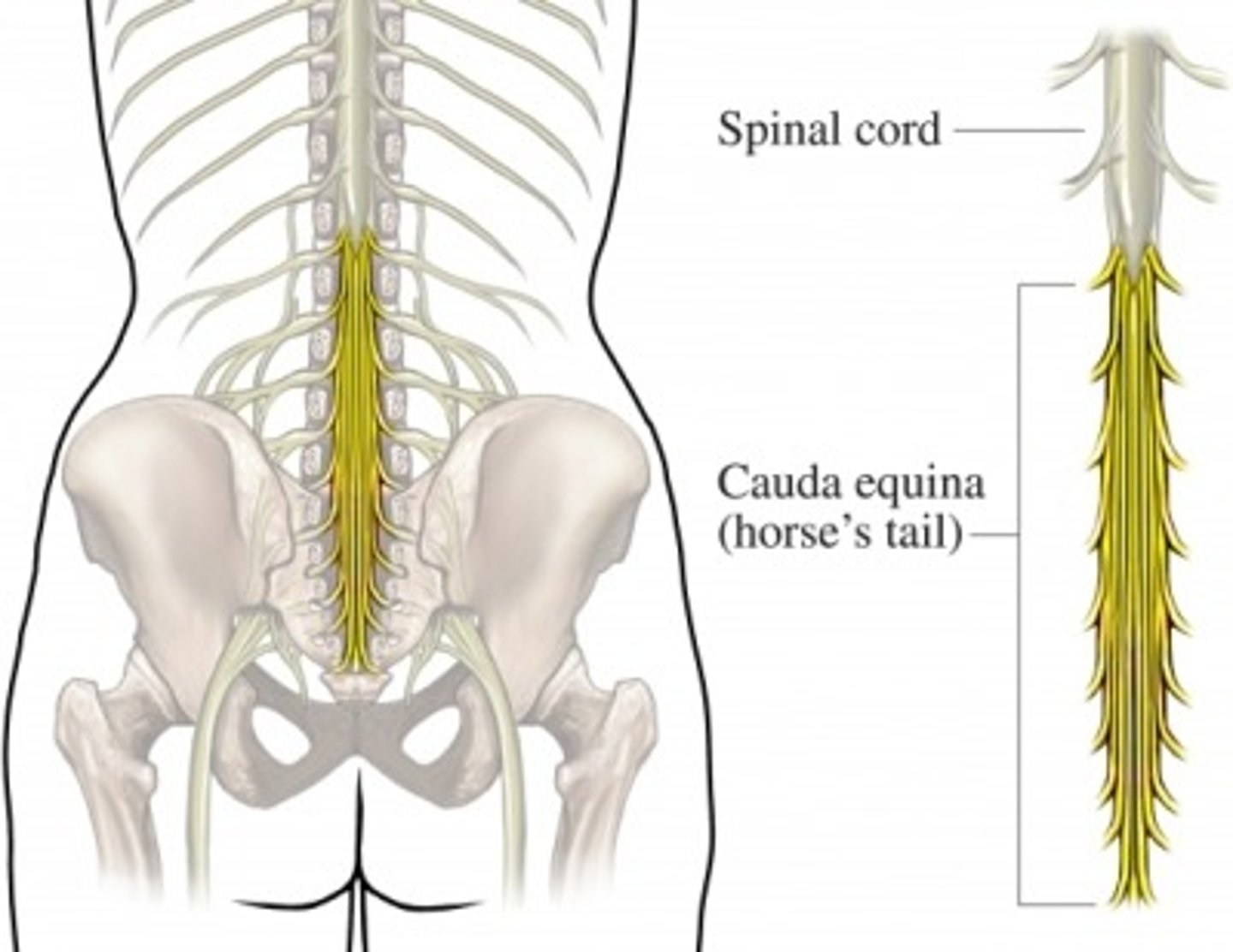
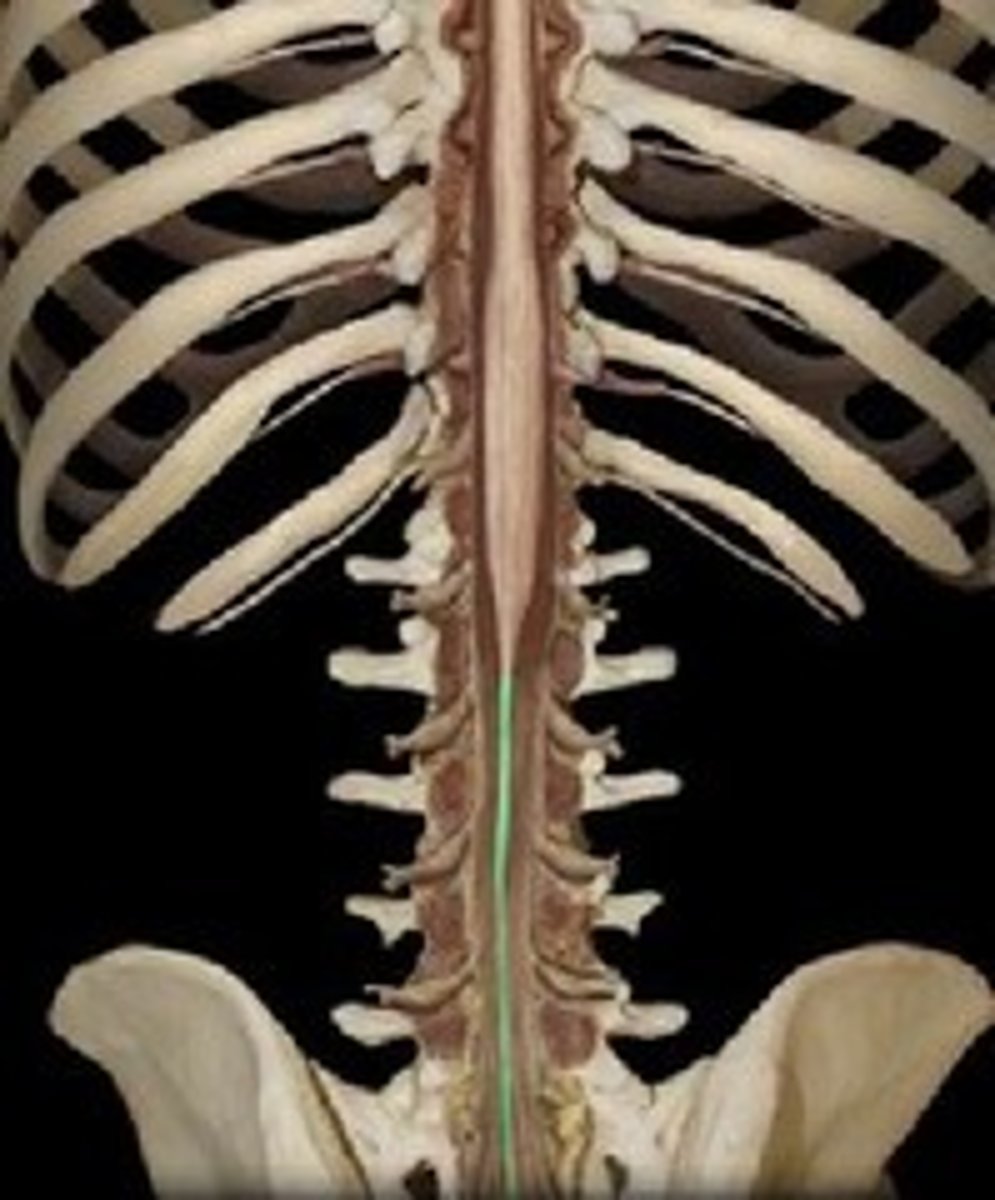
Spinal Cord
Nerves that run up and down the length of the back and transmit most messages between the body and brain
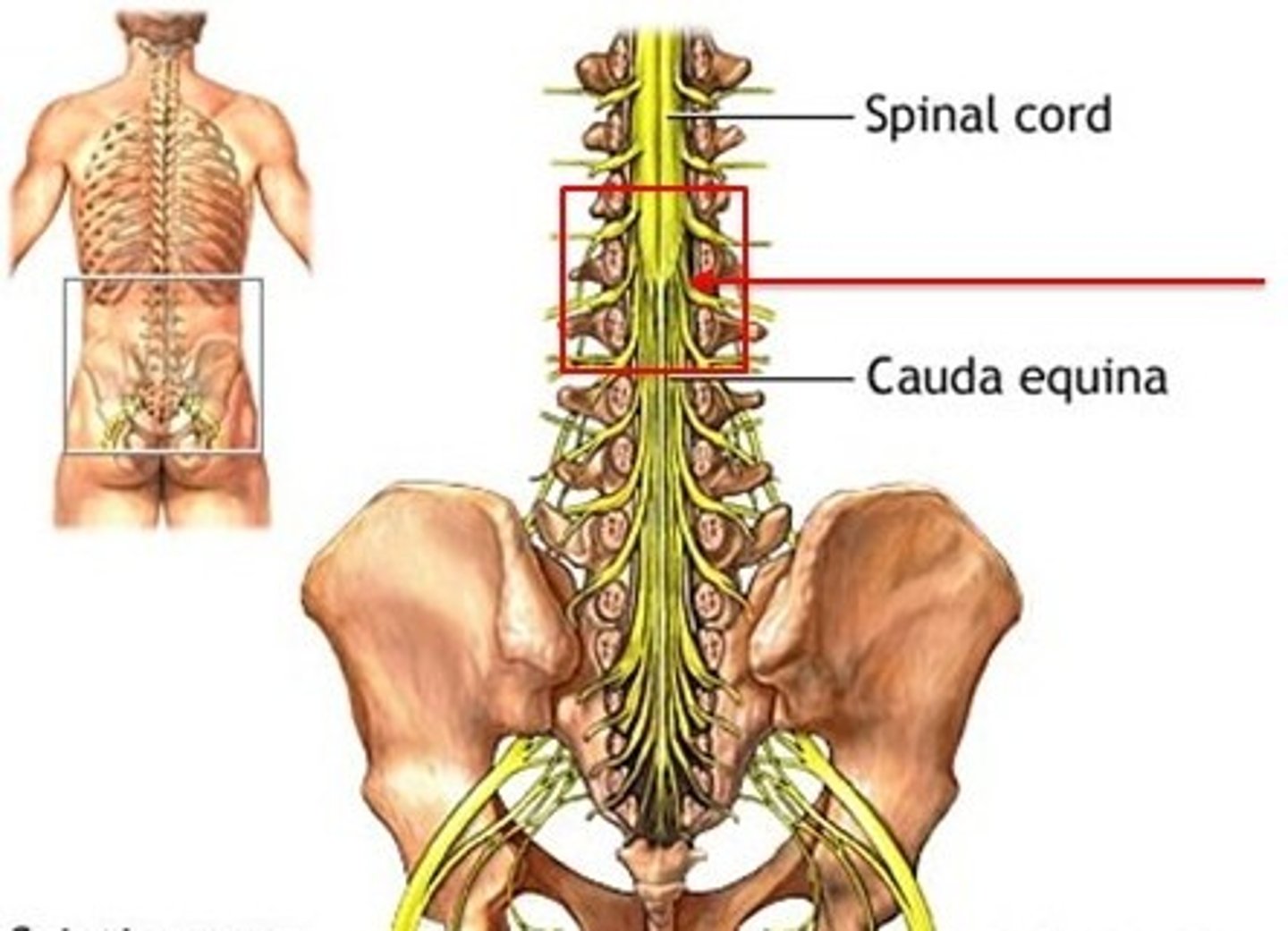
Conus medullaris
tapered end of spinal cord
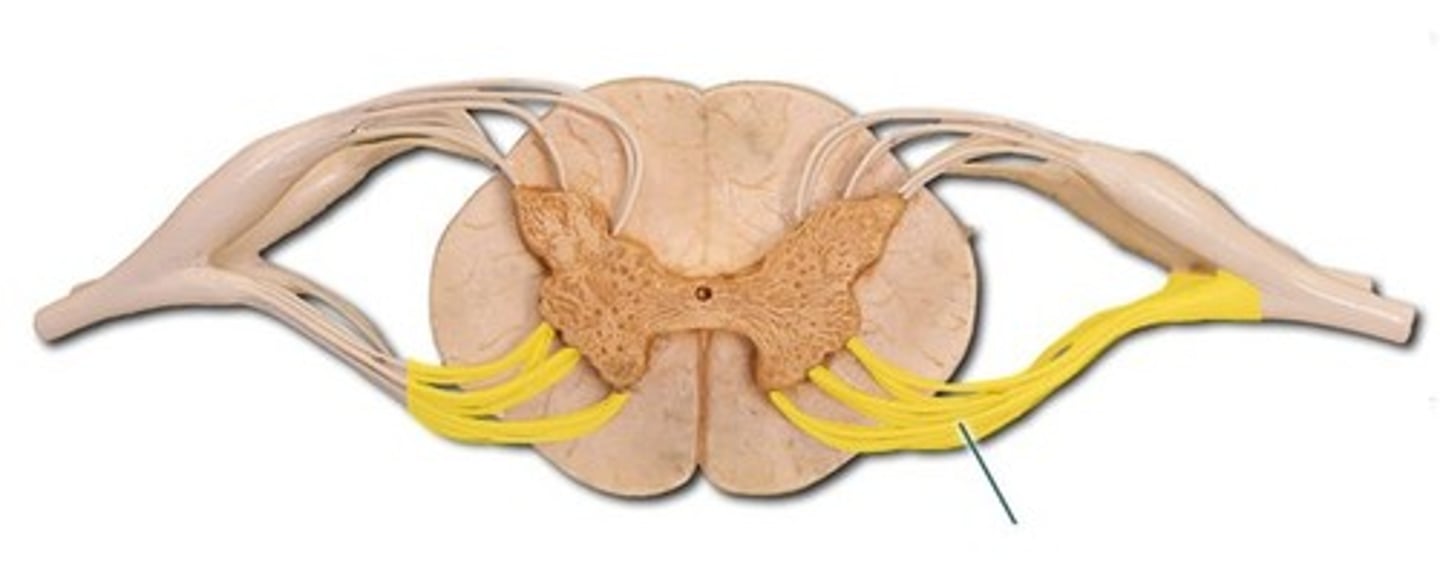
Dorsal Root
the sensory branch of each spinal nerve
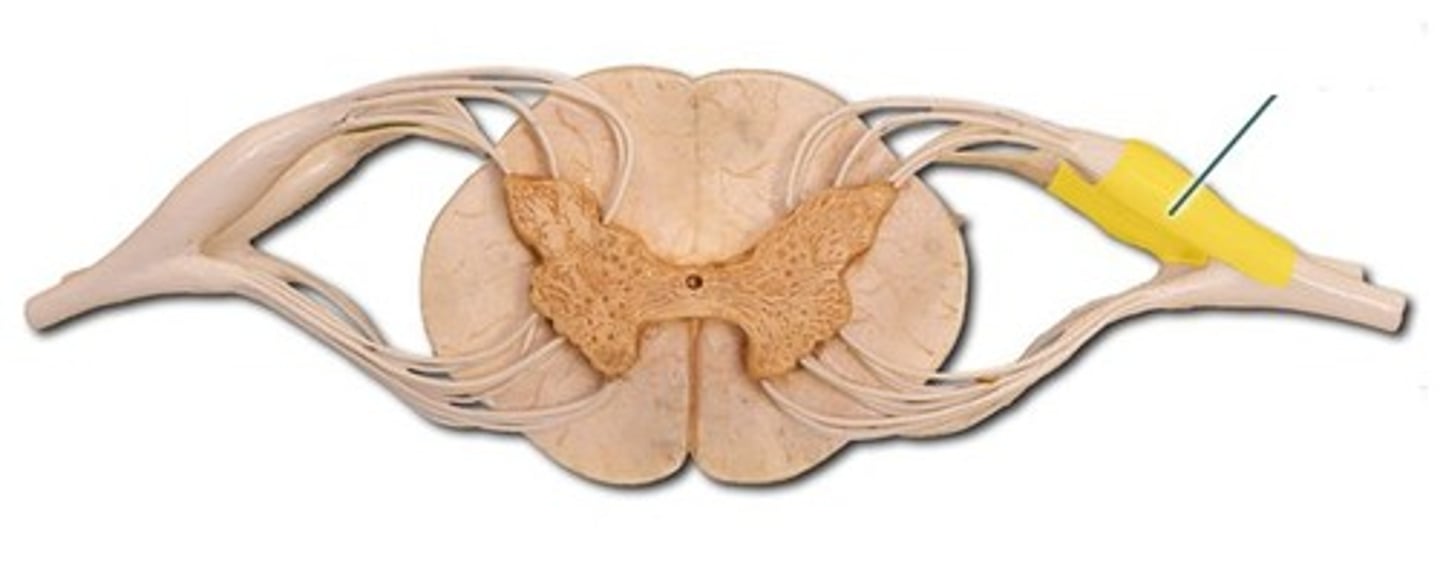
Ventral Root
the basal branch of each spinal nerve; carries motor neurons
Cauda Equina
collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord
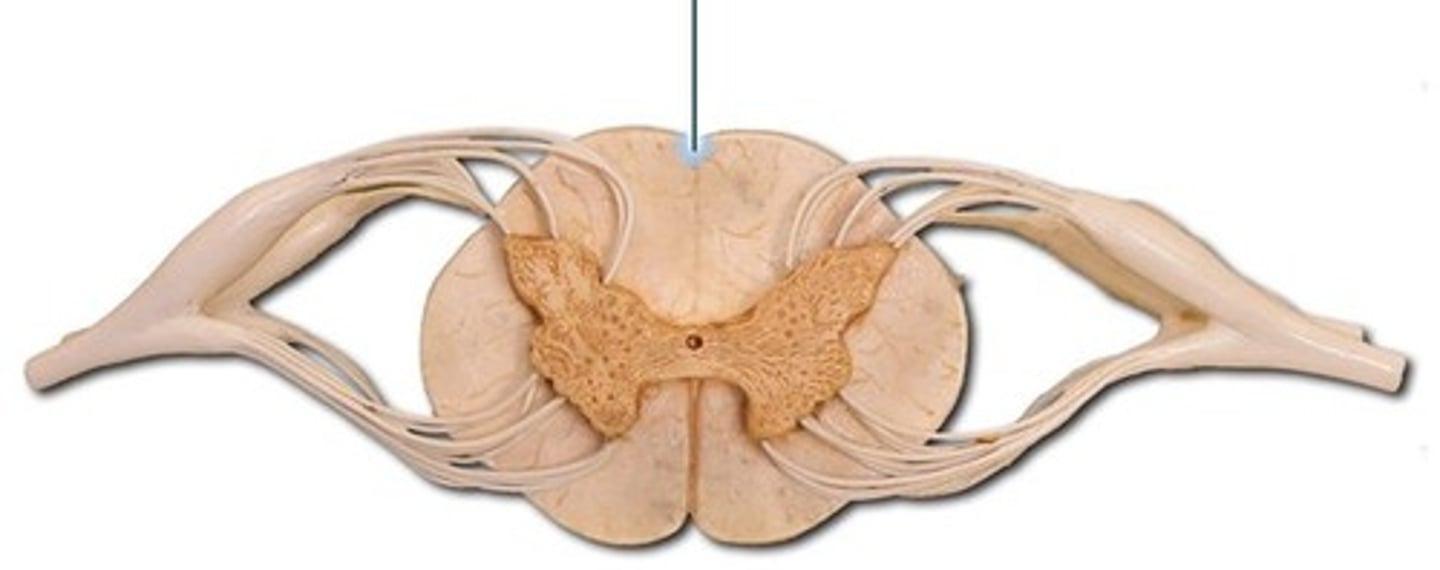
Posterior Median Sulcus
a shallow vertical groove dividing the spinal cord throughout its whole length in the midline posteriorly.
Filum Terminale
anchors spinal cord to coccyx
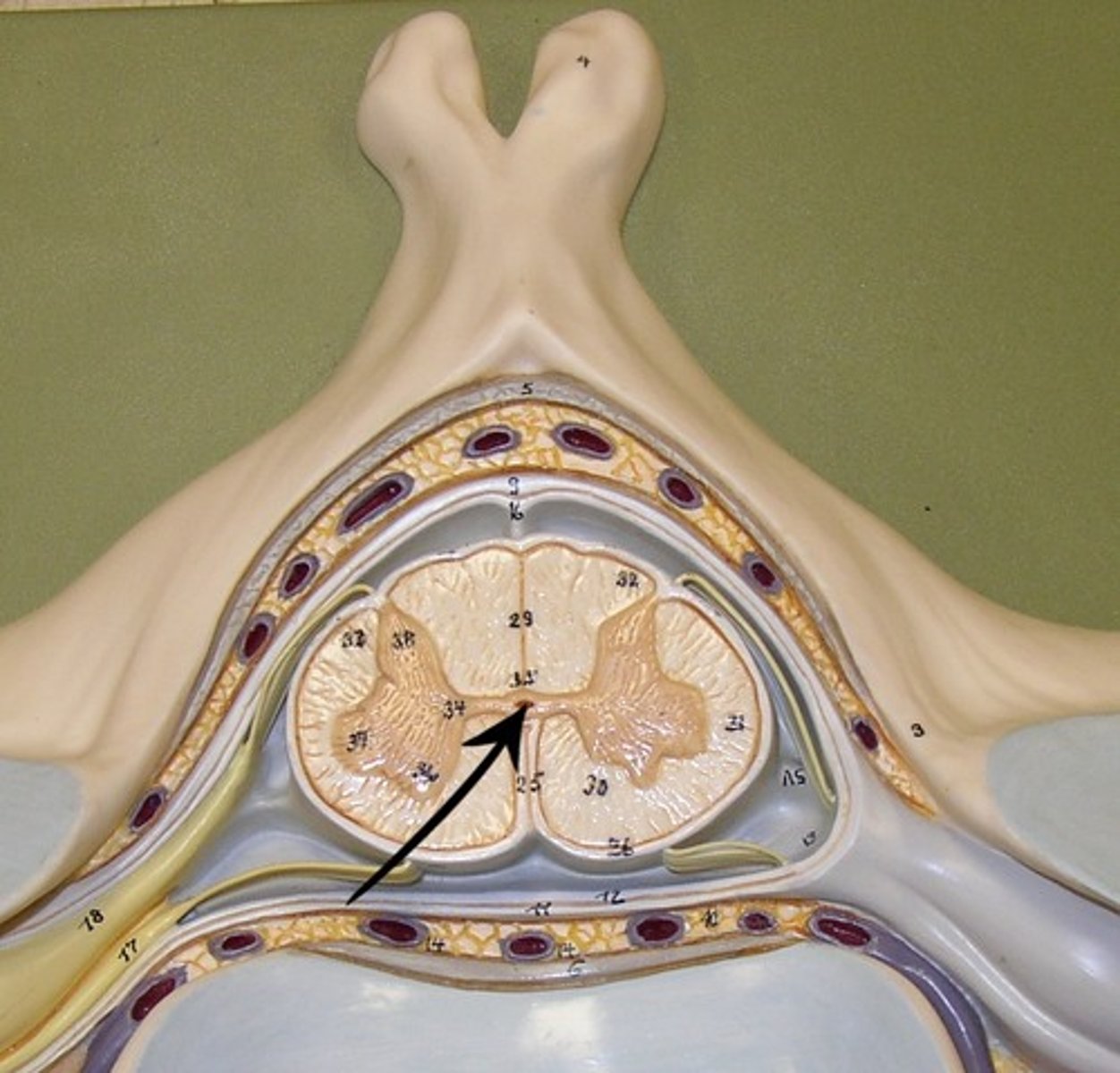
Central Canal
A tiny channel found within the spinal cord and inferior medulla oblongata
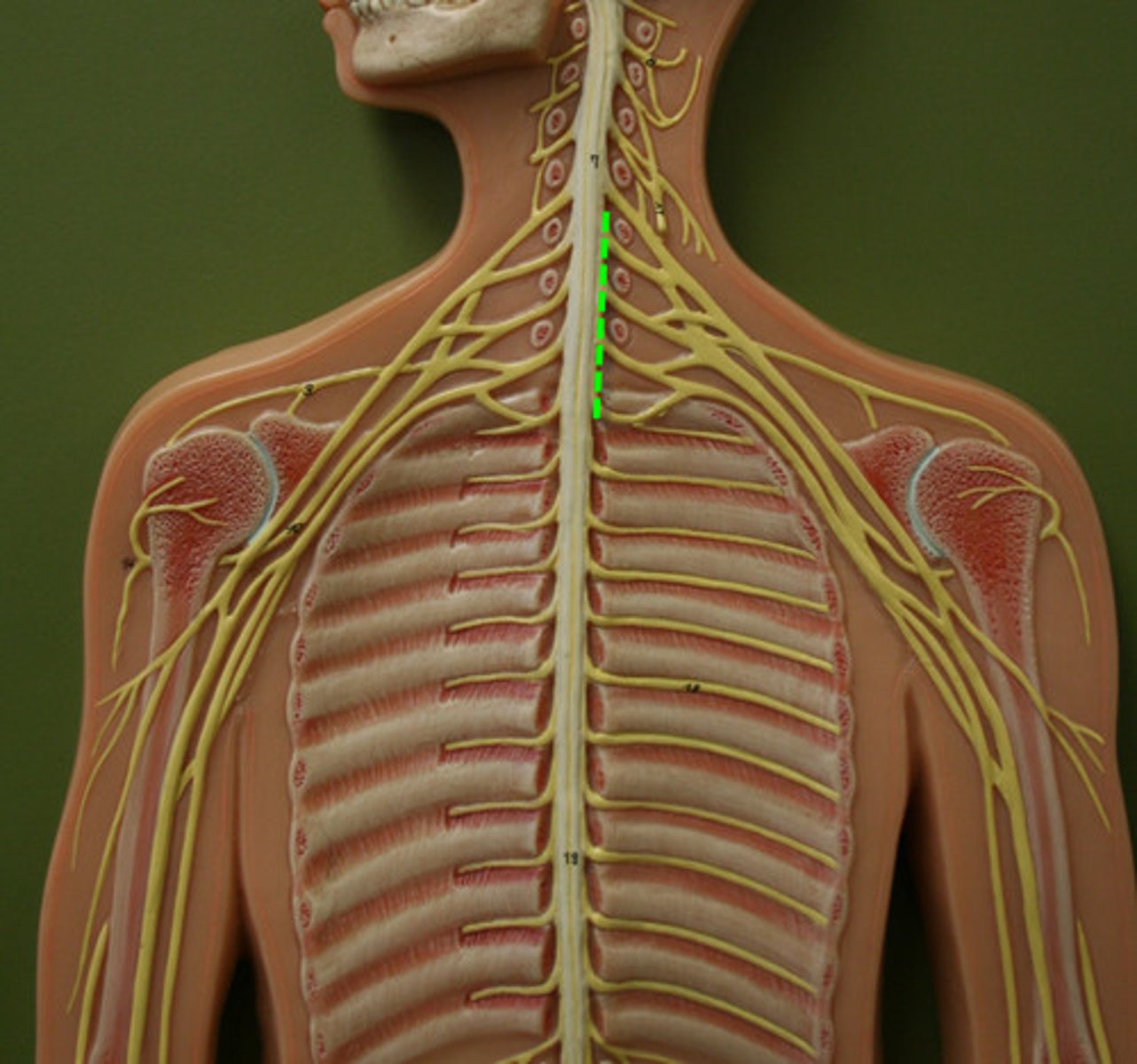
Cervical Plexus
C1-C5
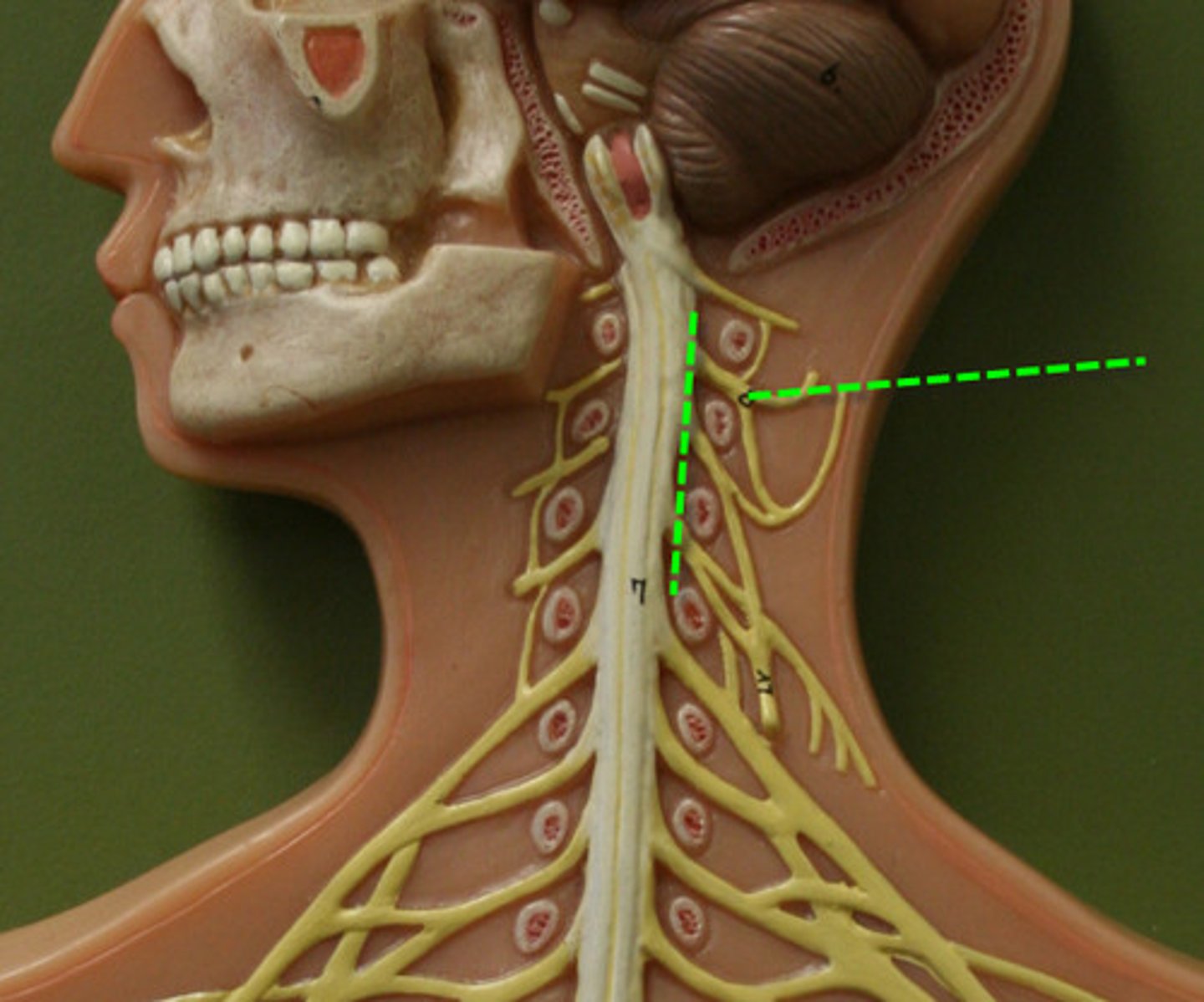
Brachial Plexus
C5-T1
Lumbar Plexus
L1-L4
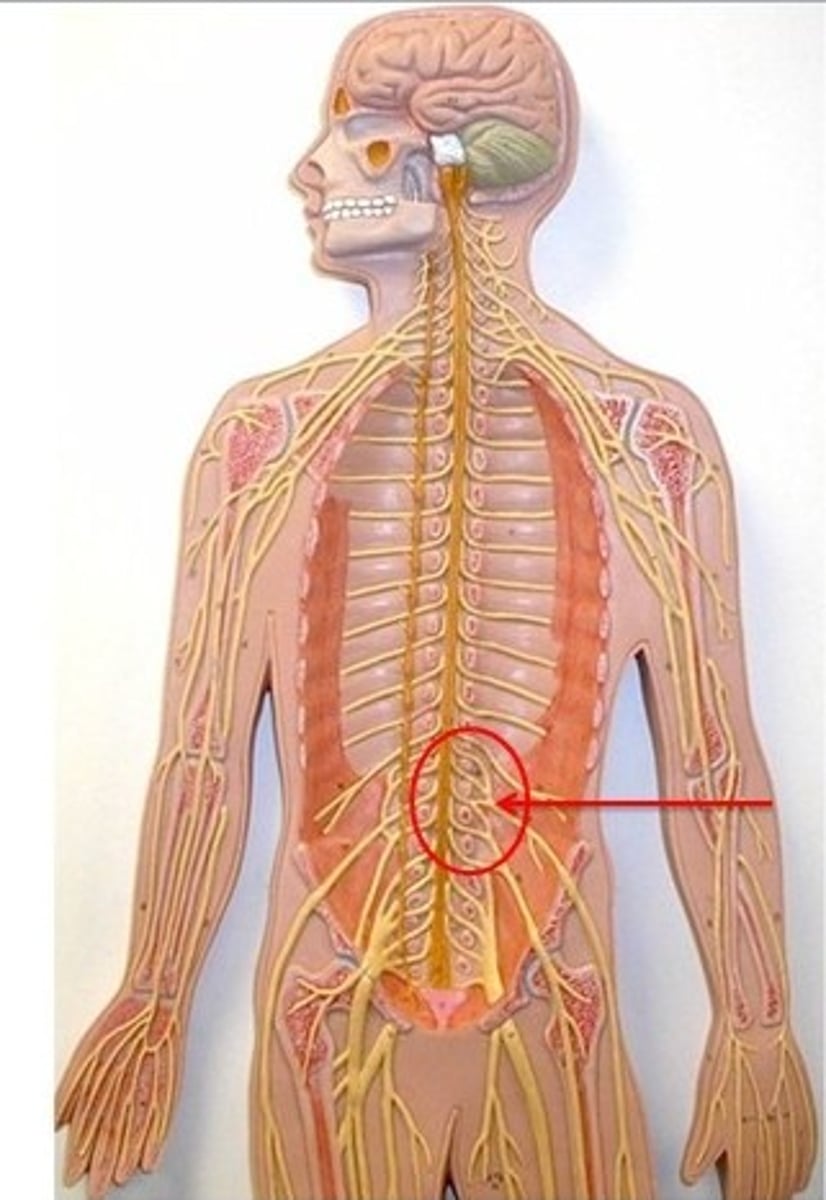
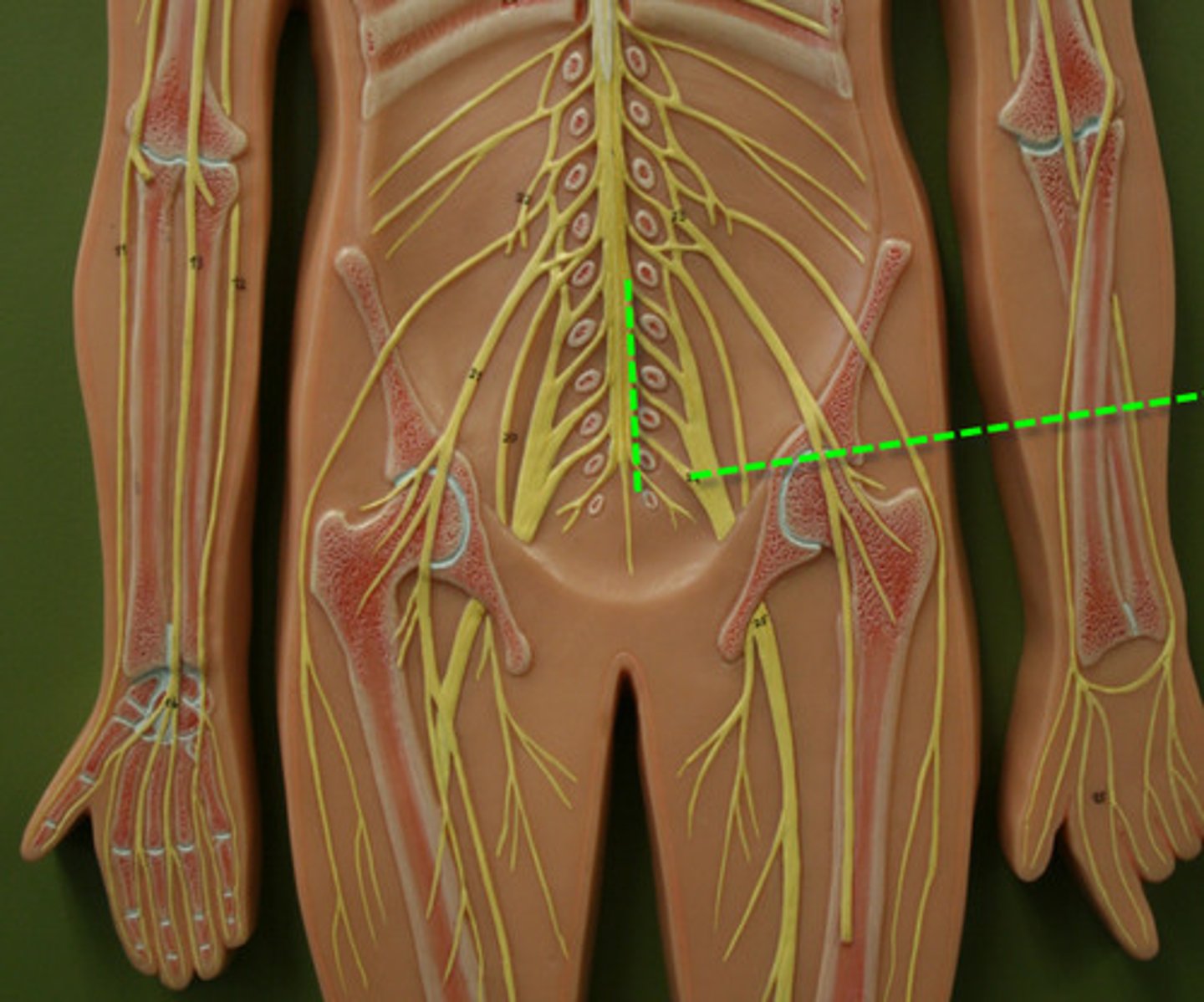
Sacral Plexus
L4-S4
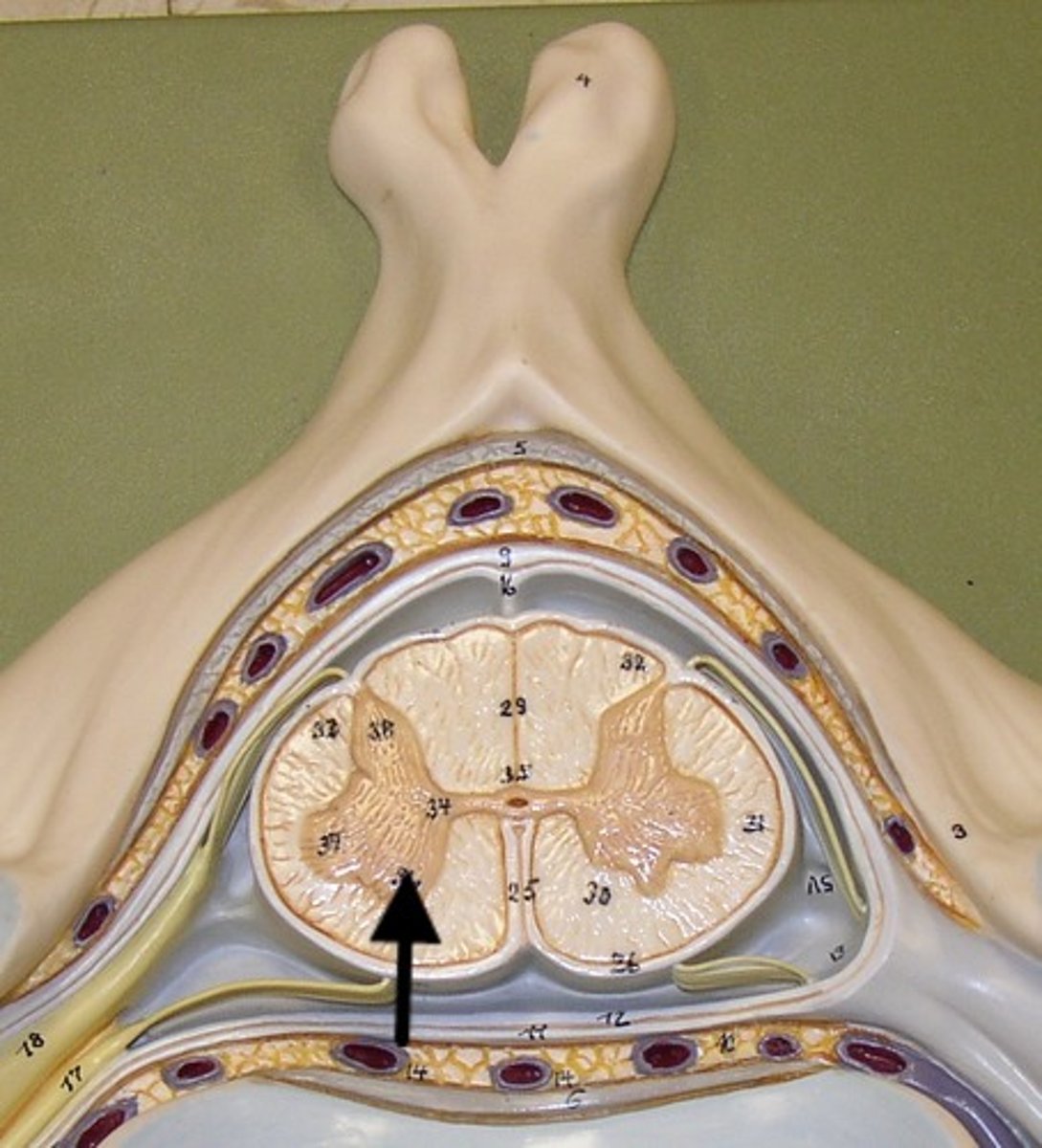
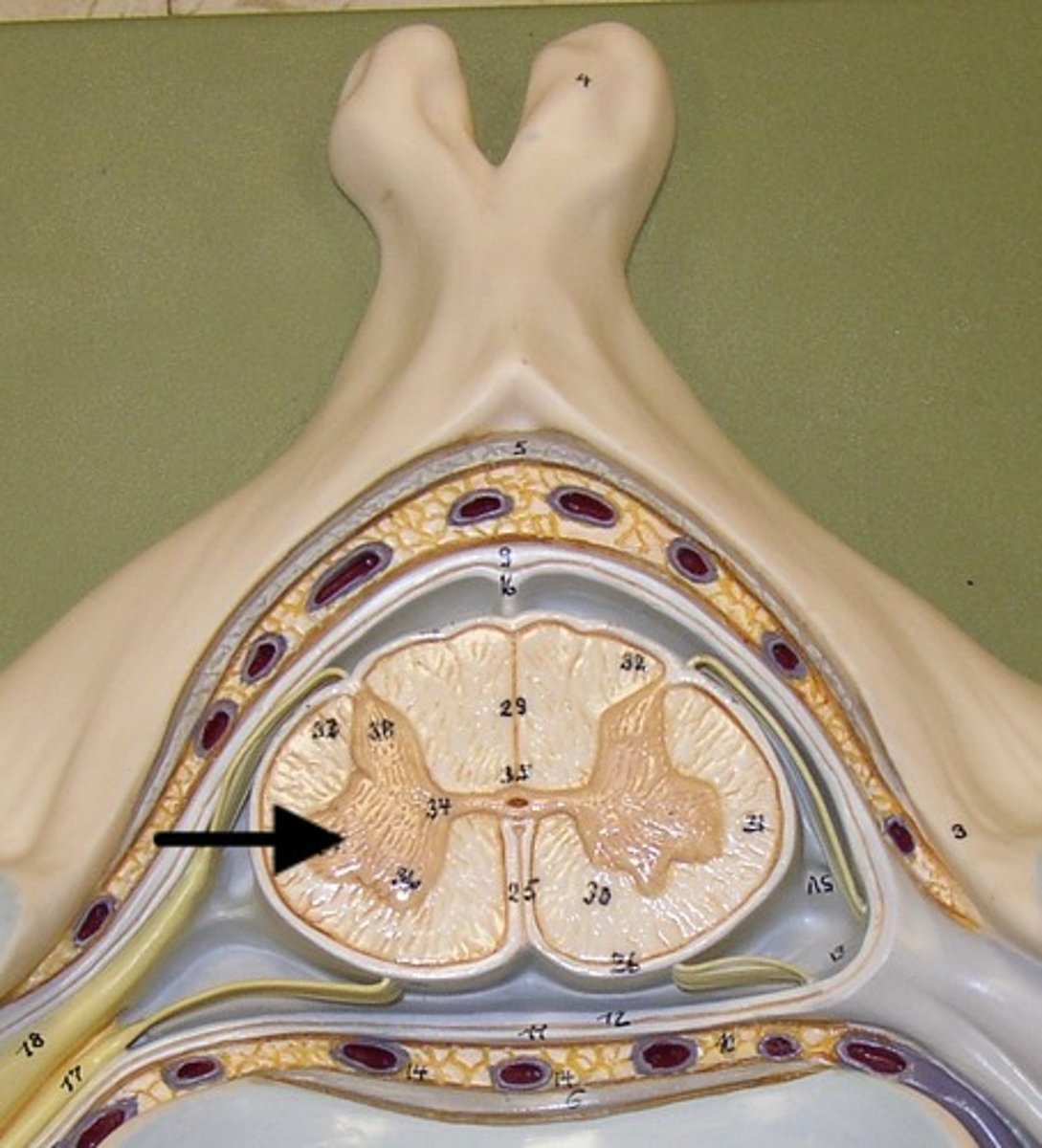
Dorsal Horn
Crescent shaped projection of gray matter within the spinal cord where sensory neurons enter the spinal cord
Ventral Horn
somatic motor neurons whose axons exit the cord via ventral roots
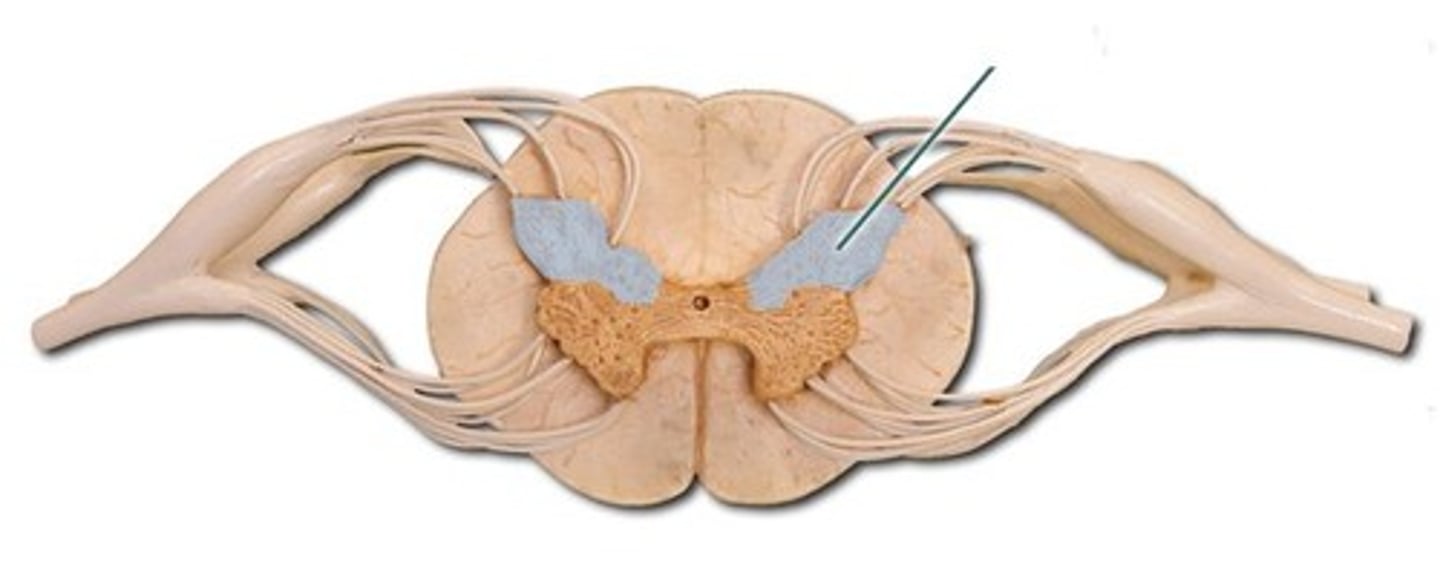
Lateral Horn
(only in thoracic and lumbar regions)
- sympathetic neurons
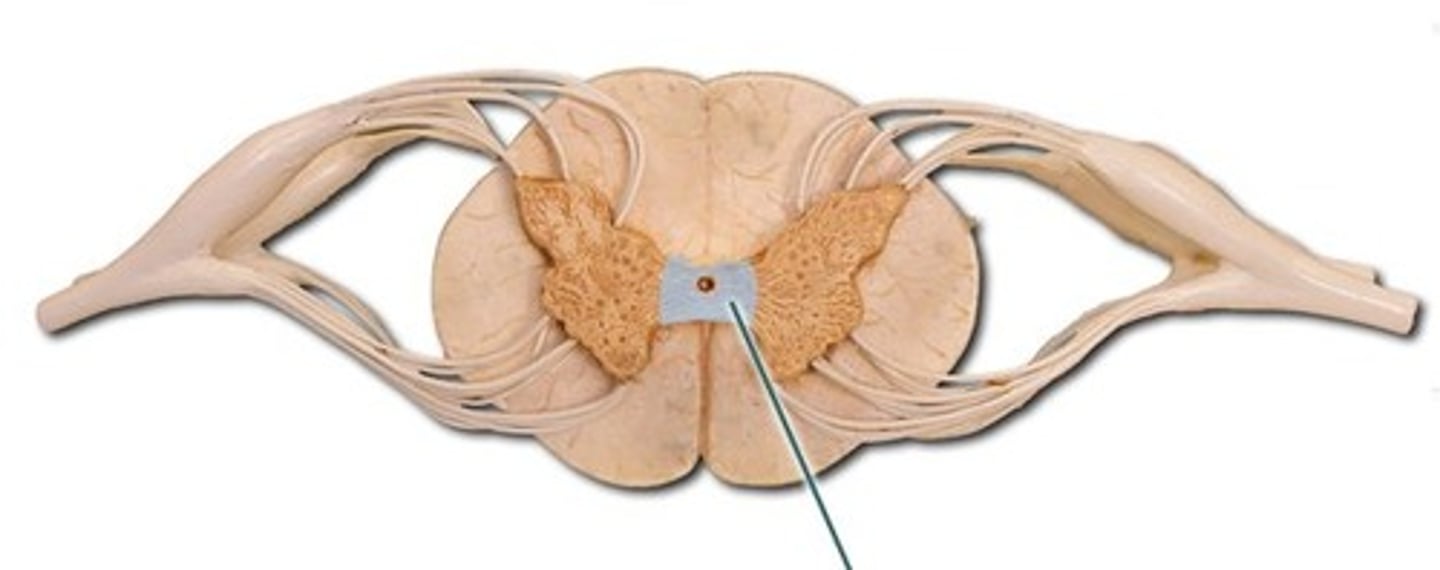
Gray Commissure
connects masses of gray matter; encloses central canal
Anterior Median Fissure
a groove along the anterior midline of the spinal cord that incompletely divides it into symmetrical halves
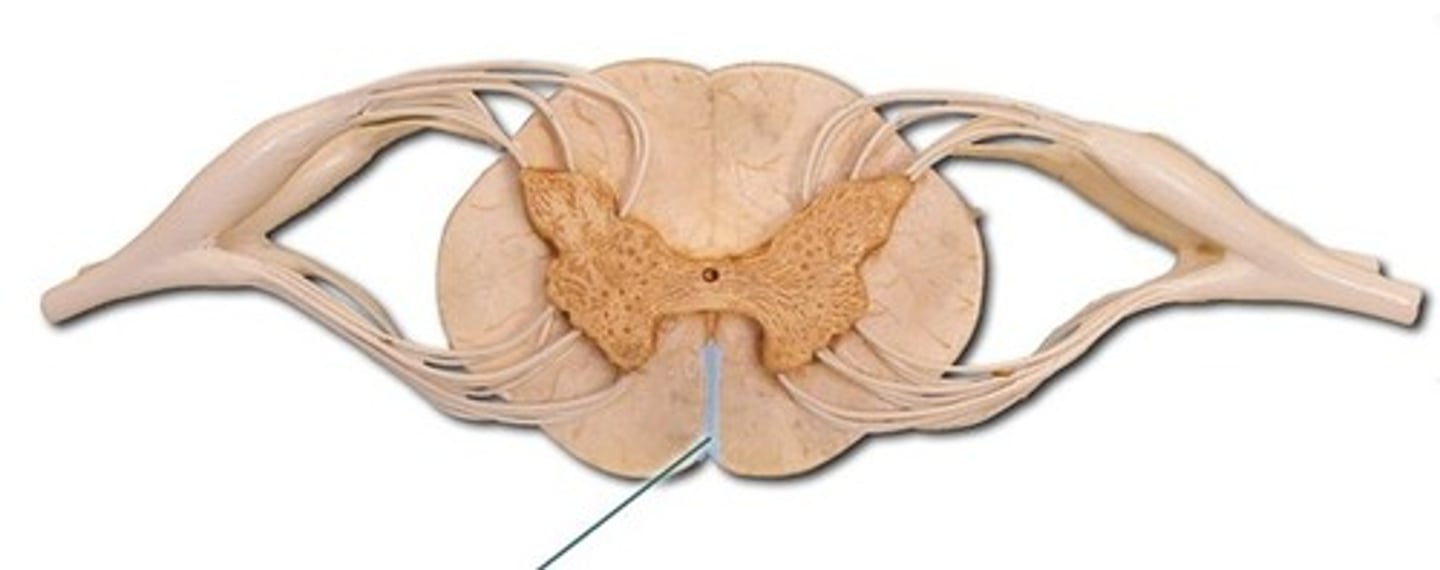
Dura Mater
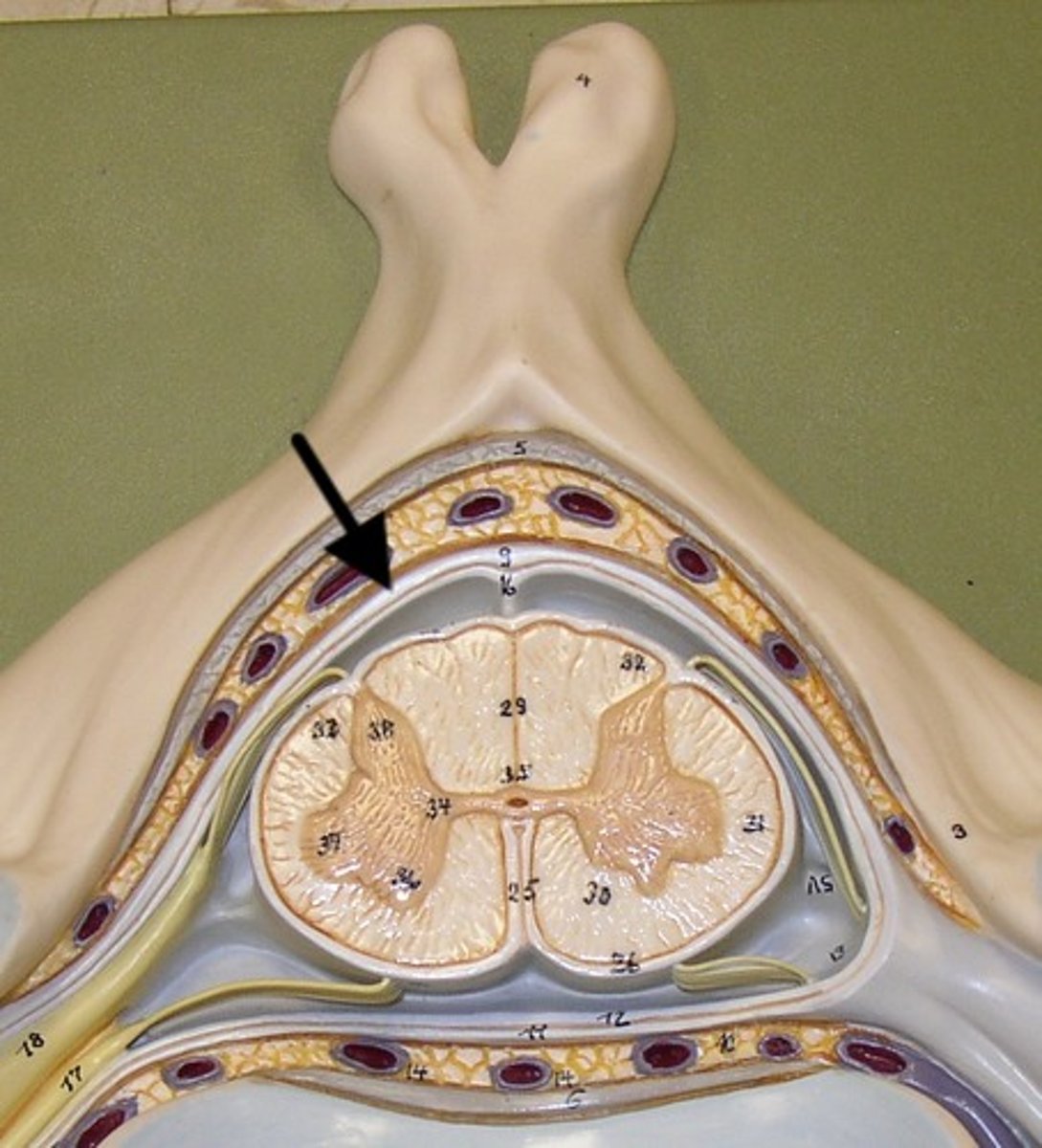
a thick fibrous layer and a strong protective sheath over the entire brain and spinal cord. It is anchored to the inner surface of the cranium and vertebral cavity
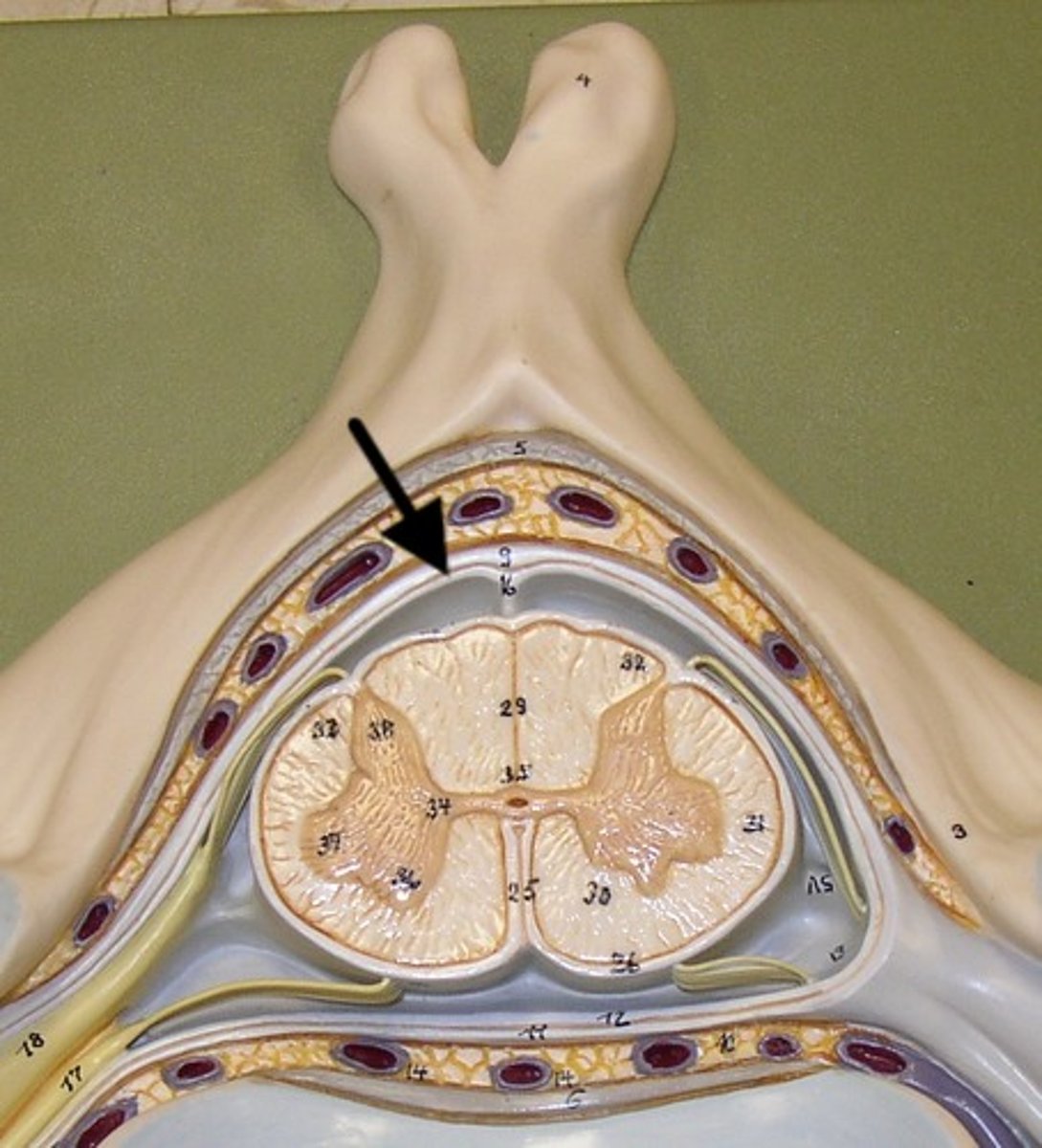
Arachnoid Mater
a membrane of thin fibrous tissue that forms a loose sac around the CNS
Cerebrum
Area of the brain responsible for all voluntary activities of the body
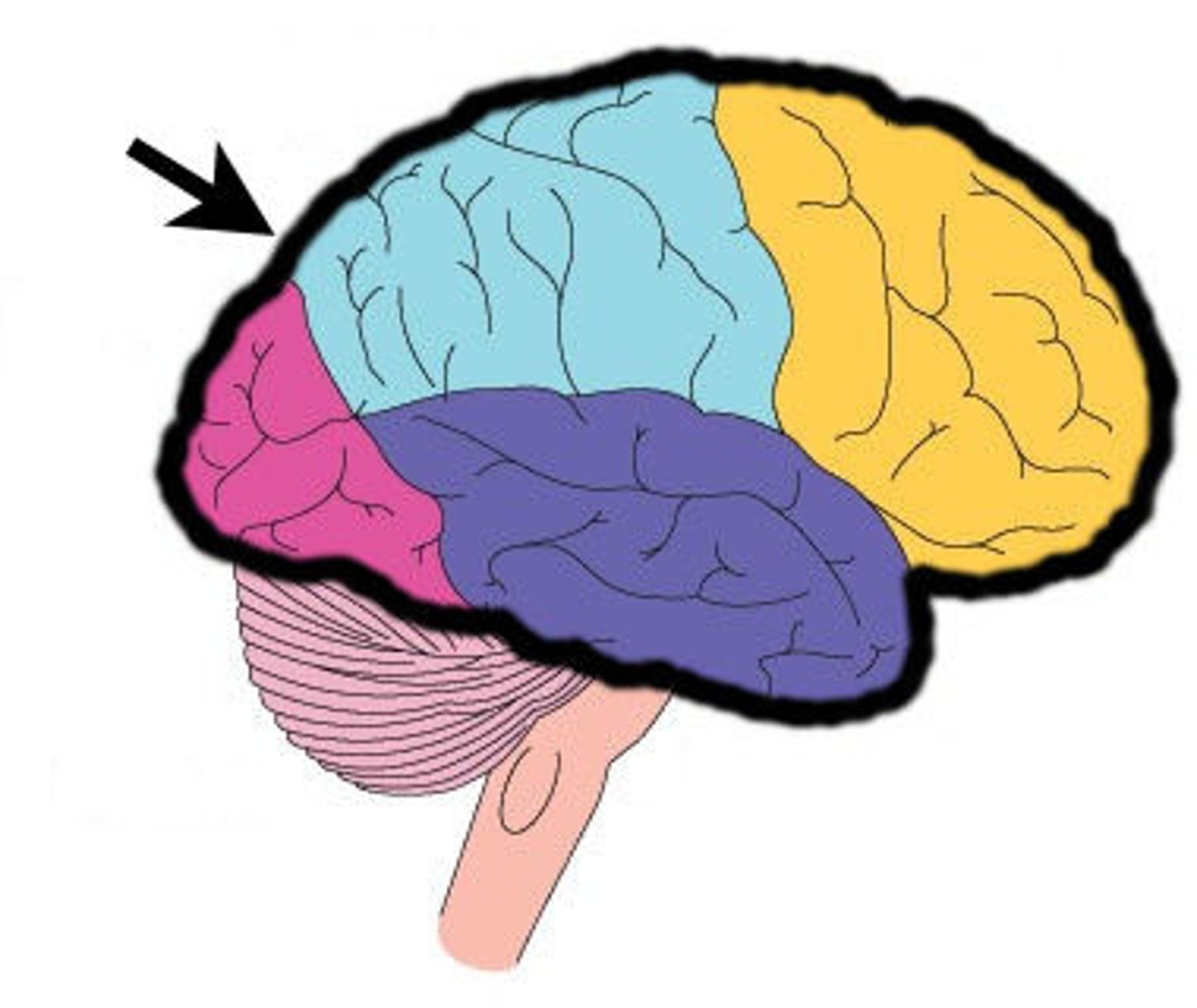
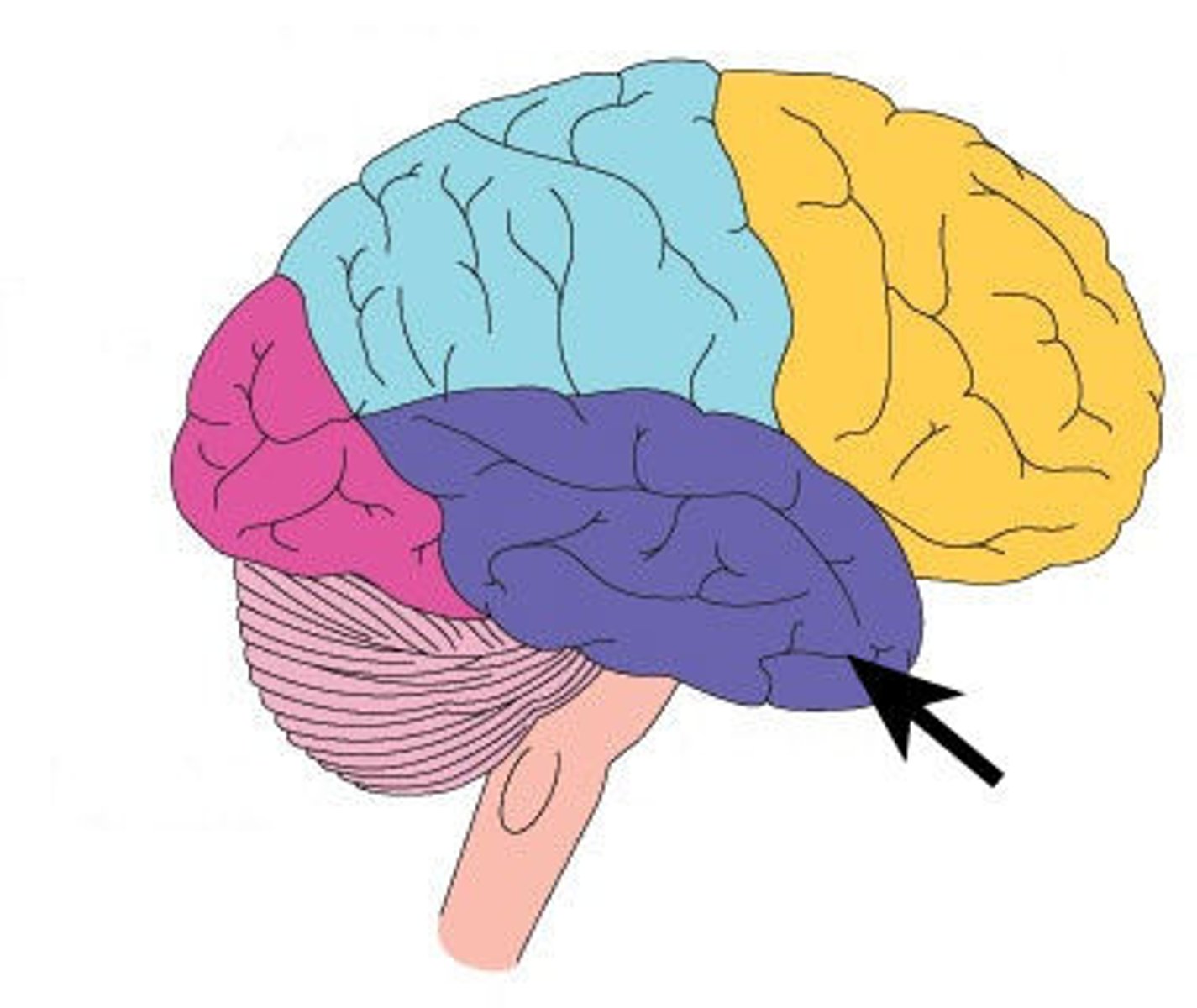
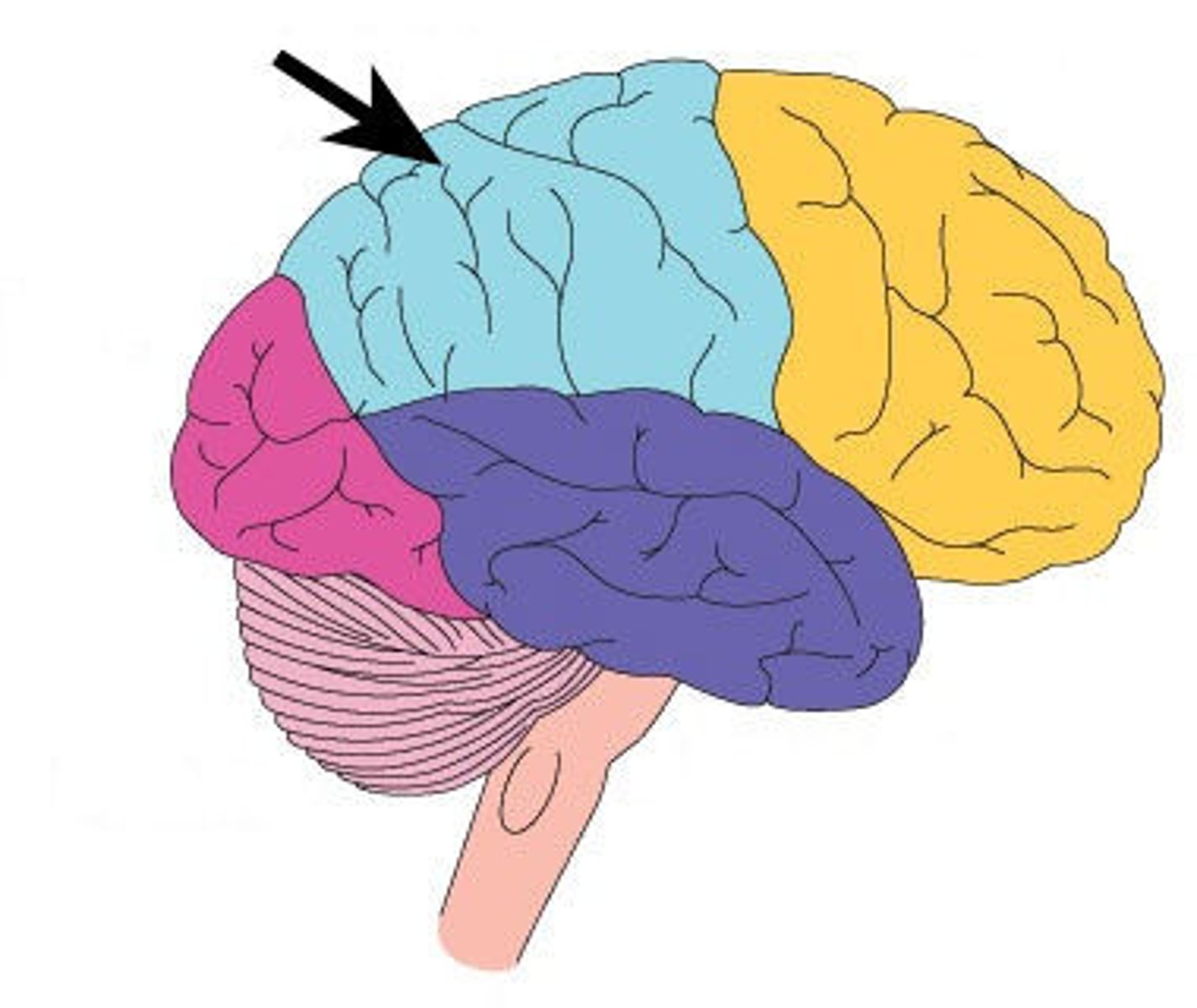
Frontal Lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that has specialized areas for movement, abstract thinking, planning, memory, and judgement
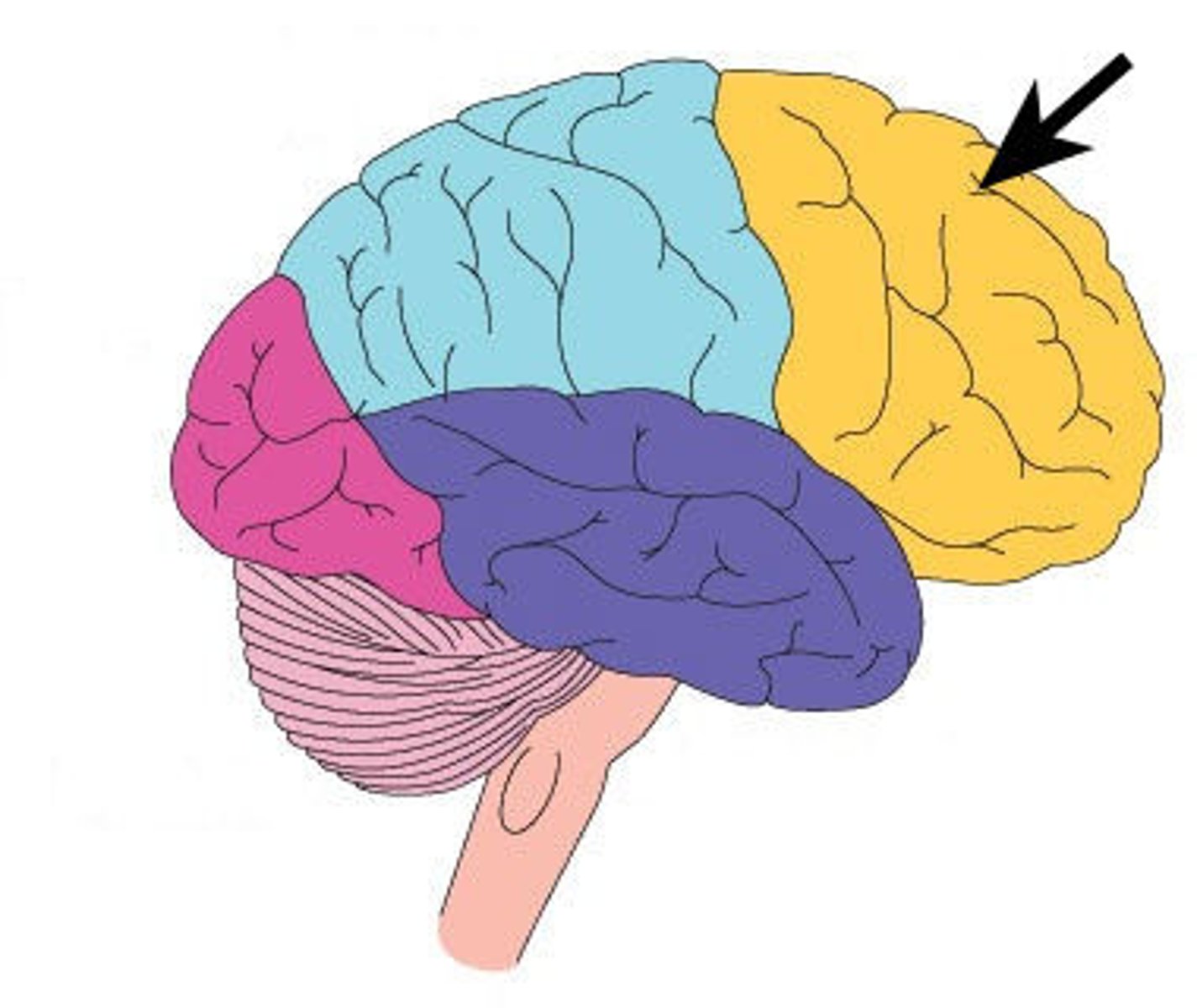
Parietal Lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex whose functions include processing information about touch, pressure, tickle, pain, itch, and vibration, as well as more general senses of the body such as proprioception and kinesthesia
Occipital Lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information
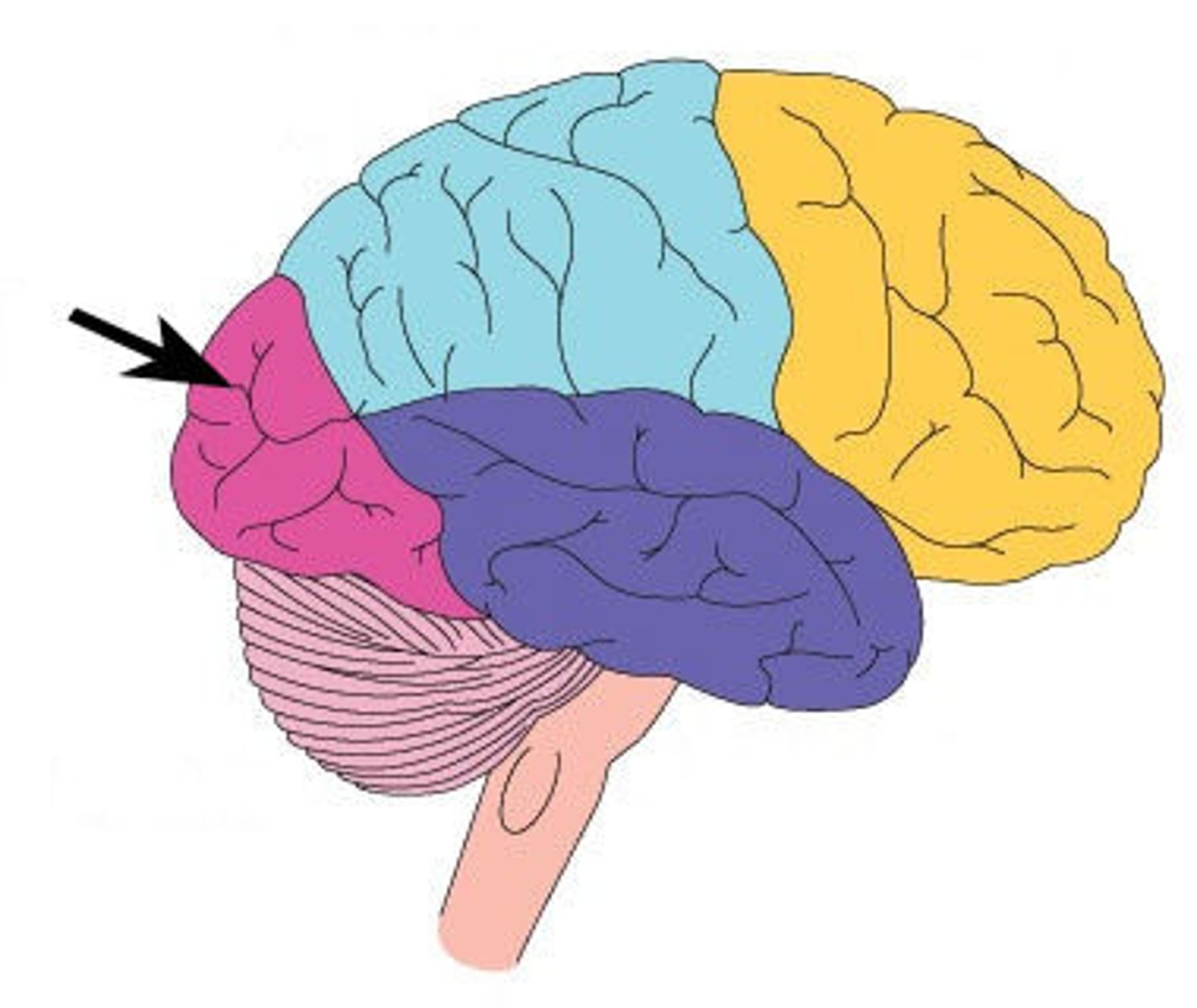
Temporal Lobe
A region of the cerebral cortex responsible for hearing and language.