Cell and Tissue Functions
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
what is connective tissue used for?
these cells are used for binding, support, protection, insulation, and transportation (usually blood)
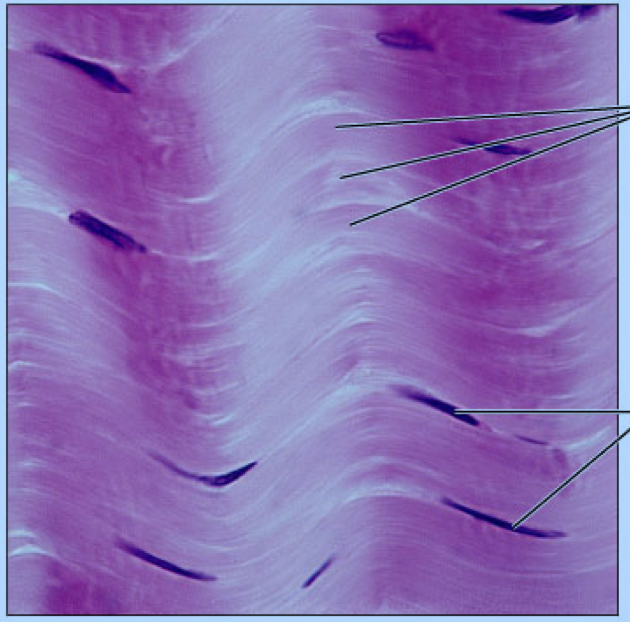
dense regular
Connective tissue proper, Fibers that grow in one direction, found in tendons and ligaments, attaches muscles to bones or other muscles, withstands high stress
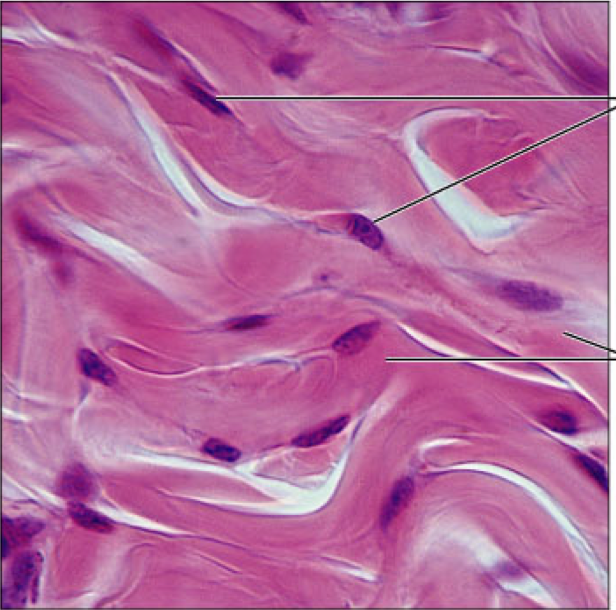
dense irregular
Connective tissue proper, Fibers in random directions, found in the dermis, fibrous capsules of organs, can withstand tension in multiple directions, structural strength
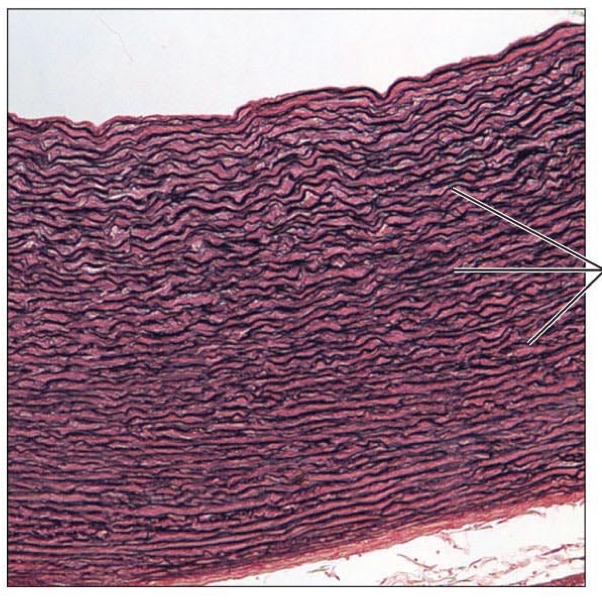
elastic
connective tissue proper, Dense elastic fibers, allows for stretching, maintains flow through arteries, found in arteries and bronchial tubes
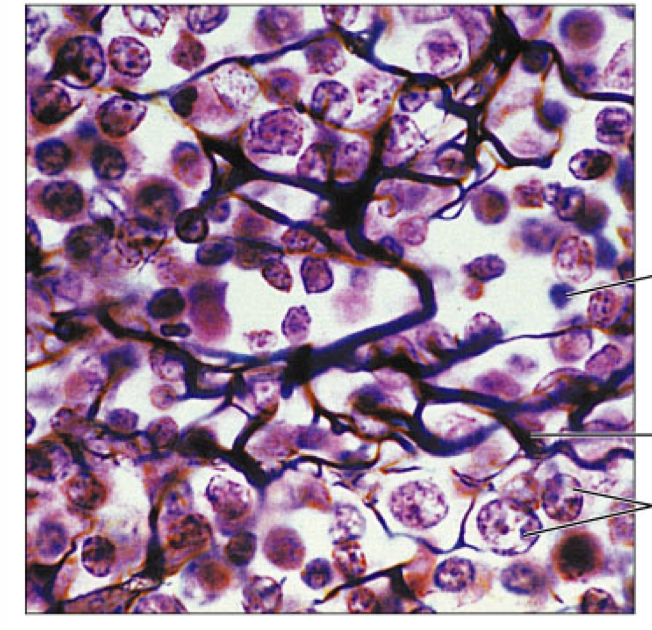
reticular
Connective tissue proper, loose, network of reticular fibers, form soft internal skeleton for support of other cell types inside organs, found in lymph nodes, bone marrow, and spleen
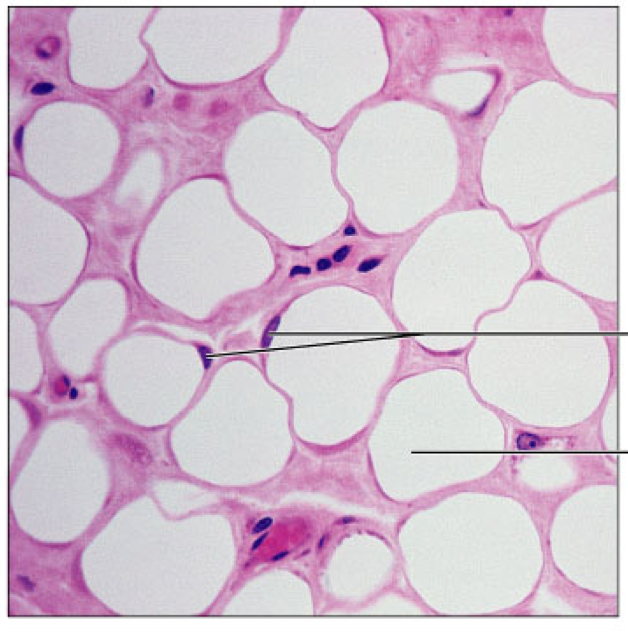
adipose
connective tissue proper, loose, matrix of fat cells, energy storage, insulation, support and protection of organs, found under skin, in abdomen, and breasts
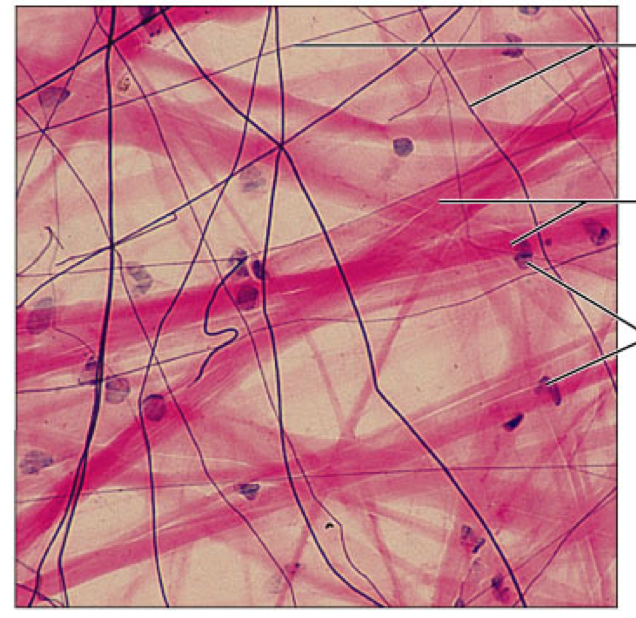
areolar
connective tissue proper, loose, matrix of all 3 fiber types, wraps and cushions organs, packages organs, surrounds capillaries
What are epithelial cells used for?
used for providing cover for organs and protection, can secrete or absorb
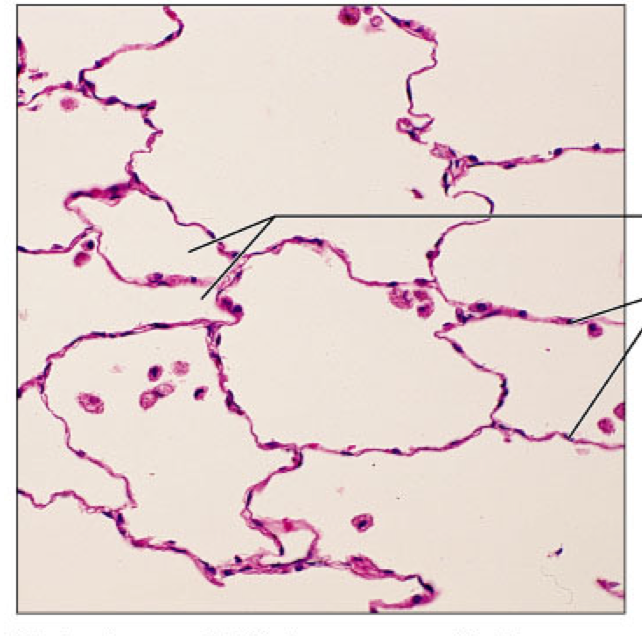
simple squamous
epithelial, single layer of flattened cells, allows for diffusion and filtration, used for secretion, found in kidneys, lungs, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels, ventral body cavity
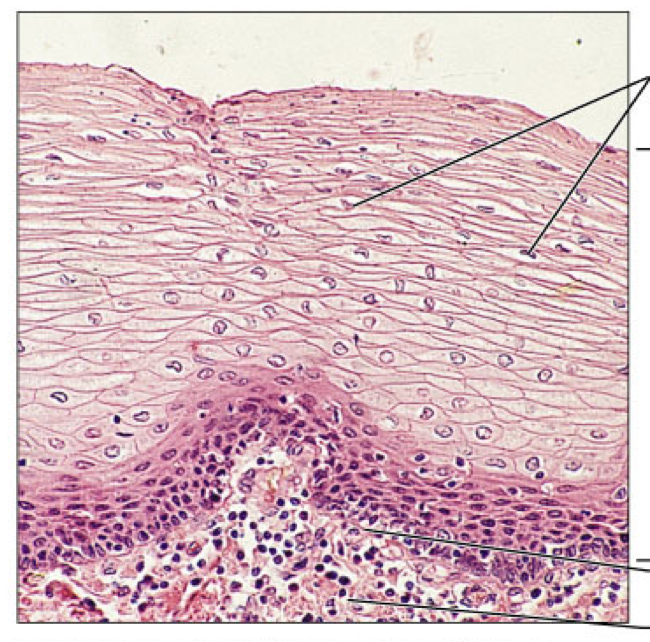
stratified squamous
epithelial, thick membrane of several cell layers of fat cells (squamous), used for protection, makes up lining of mouth, esophagus, vagina, and keratinized version forms epidermis
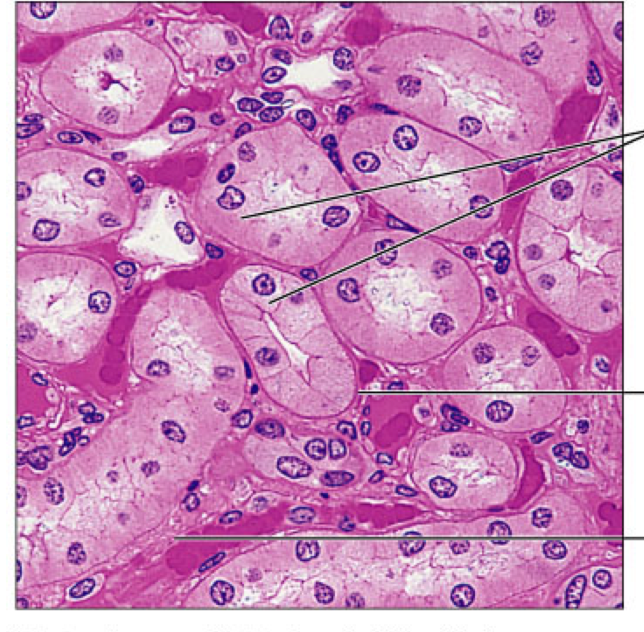
simple cuboidal
epithelial, single layer of cubelike cells, used for secretion and absorption, found kidney tubules, small glands, and ovary surface
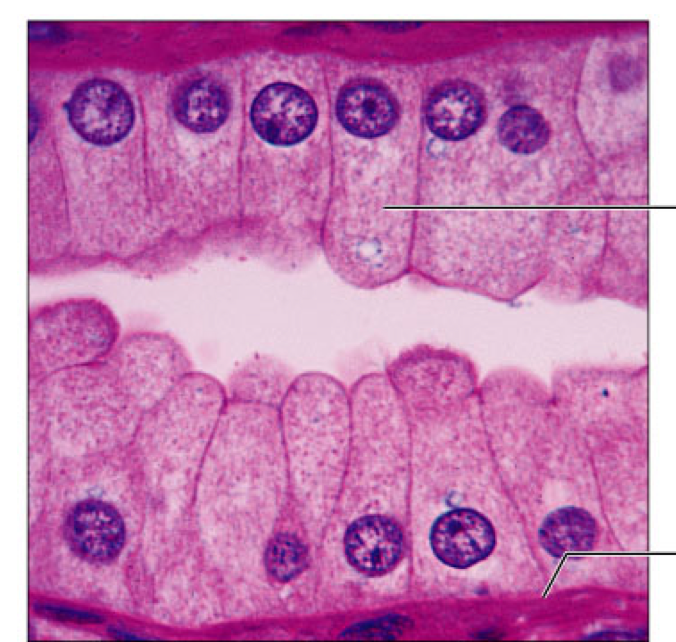
simple columnar
epithelial, Single layer of tall cells, used in absorption, secretion, ciliated type propels mucus, found in digestive tract, excretory ducts, small bronchi, and uterus
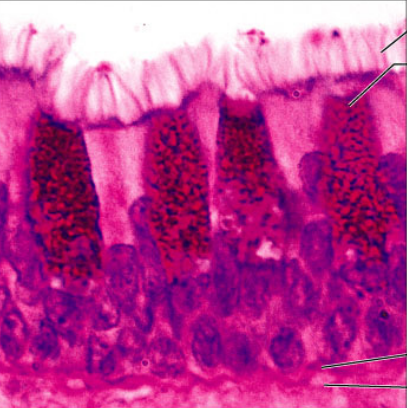
Pseudostratified Ciliated Columnar
epithelial, single layer of cells with differing heights, used in secretion and propulsion of mucus, found in sperm ducts, ducts of large glands, trachea, upper respiratory tract
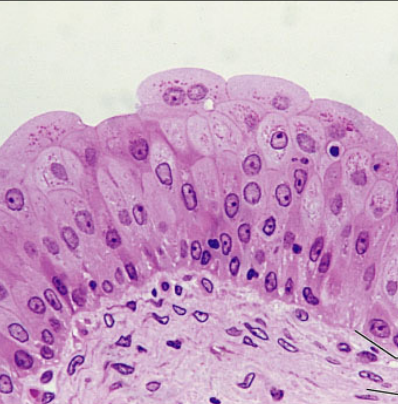
Transitional
epithelial, Resembles both stratified squamous and stratified cuboidal, used for stretching, found in uterus, bladder, and part of the urethra
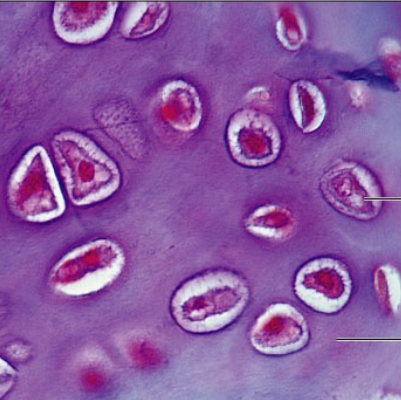
hyaline cartilage
connective tissue, amorphous but firm matrix, supports and reenforces, cushions, resists compressive stress, found in embryonic skeleton, end of long bones in join cavities, costal cartilage of ribs, cartilage of nose, trachea and larynx
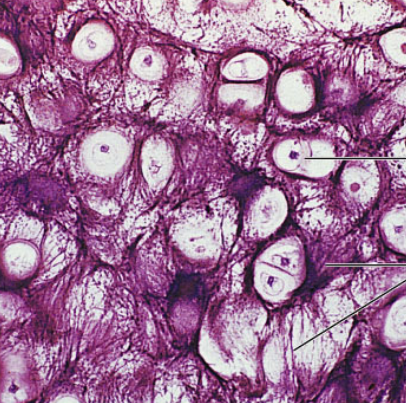
elastic cartilage
connective tissue, similar to hyaline cartilage, maintains shape of structure while allowing great flexibility, found in external ear (pinna) and epiglottis
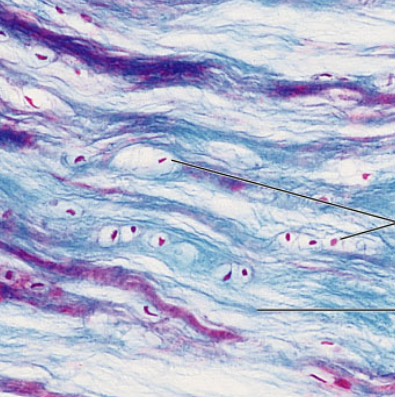
Fibrocartilage
connective tissue, Matrix similar to but less firm than hyaline cartilage, used for tensile strength with the ability to absorb compressive shock, found in intervertebral discs, pubic symphysis, discs of knee joint