Physiology L37 - Renal
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
What is the most abundant substance in the body?
water
What function does water perform in the body?
solvent for all dissolved constituents in the body
What is total body water (TBW) comprised of?
-1/3 Extracellular fluid (ECF)
-2/3 Intracellular fluid (ICF)
What is ECF made up of?
-3/4 interstitial fluid
-1/4 plasma
What is the vital role of kidneys?
maintain the volume and composition of the body fluids constant despite wide variations in daily intake of water and solute via plasma purification (ensure ECF is pure)
What are the functions of the kidney?
regulate water and inorganic ion balance (osmolarity)
acid-base balance
eliminate metabolic waste products
eliminate foreign compounds
gluconeogenesis
secrete hormones
What happens to blood pressure when ECFV increases?
Increase in blood volume → increased blood pressure
Whan happens to blood pressure when ECFV decreases?
decrease in blood volume → decreased blood pressure
Can normal renal function be maintained when 1 kidney is removed?
Yes, because of …
-enhanced growth factor
-hypertrophy
-hyperplasia
-vasodilation
-hyperfiltration
What is the outer layer (cortex) of the kidney responsible for?
-site of glomerular filtration and convoluted tubules
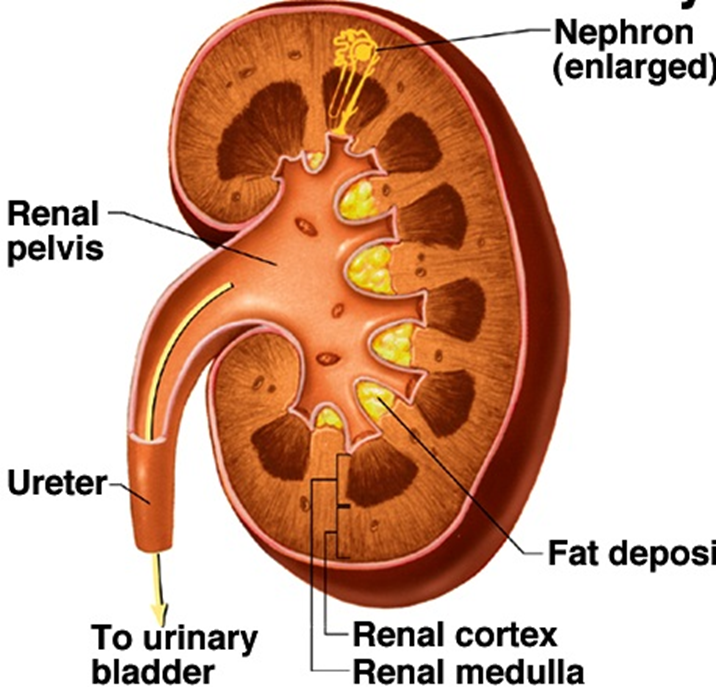
What is the inner part (medulla) of the kidney responsible for?
-location of longer loops of Henle
-drainage of collecting ducts into renal pelvis and ureter
How many nephrons in a kidney?
1 million (number assigned at birth)
What is a nephron?
the structural and function unit of a kidney
What is each nephron made of?
-glomerulus (a tuft of capillaries)
-renal tubule (forms cup chape around glomerulus called glomerular capsule (Bowman’s capsule)
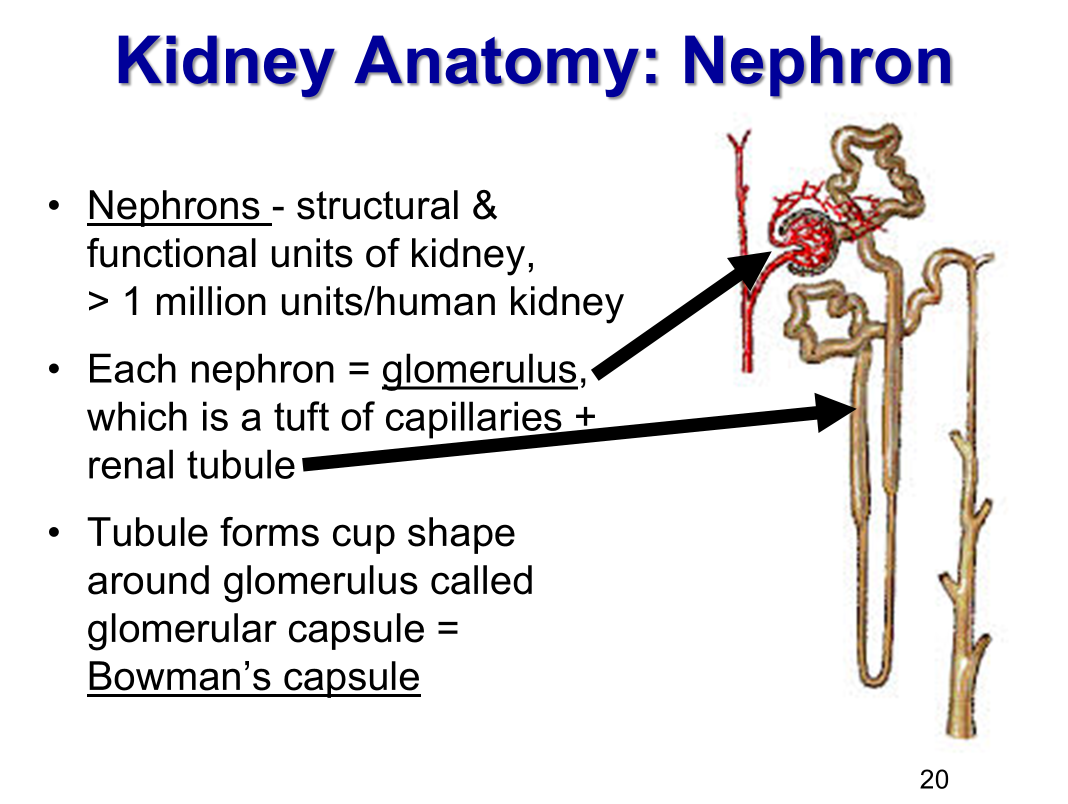
What are the two types of nephrons?
-Cortical nephrons
most nephrons are in this category
in short loops of Henle
-Juxtamedullary nephrons
in long loops of Henle
involves in concentration of urine
What 2 fluid filled spaces make up the renal corpuscle?
-vascular space
glomerular capillaries
contains plasma, RBCs, WBCs, proteins, electrolytes
-urinary space
Bowman’s space
contain ultrafiltrate of plasma
filtrate passes from vascular into tubule system
1st step in urine formation
What is the order of circulation for the kidney?
Afferent arteriole (smooth muscle; can contract and relax)
Glomerulus → capillaries
Efferent arteriole (smooth muscle; can contract and relax)
Peritubular capillaries
Vasa recta capillaries
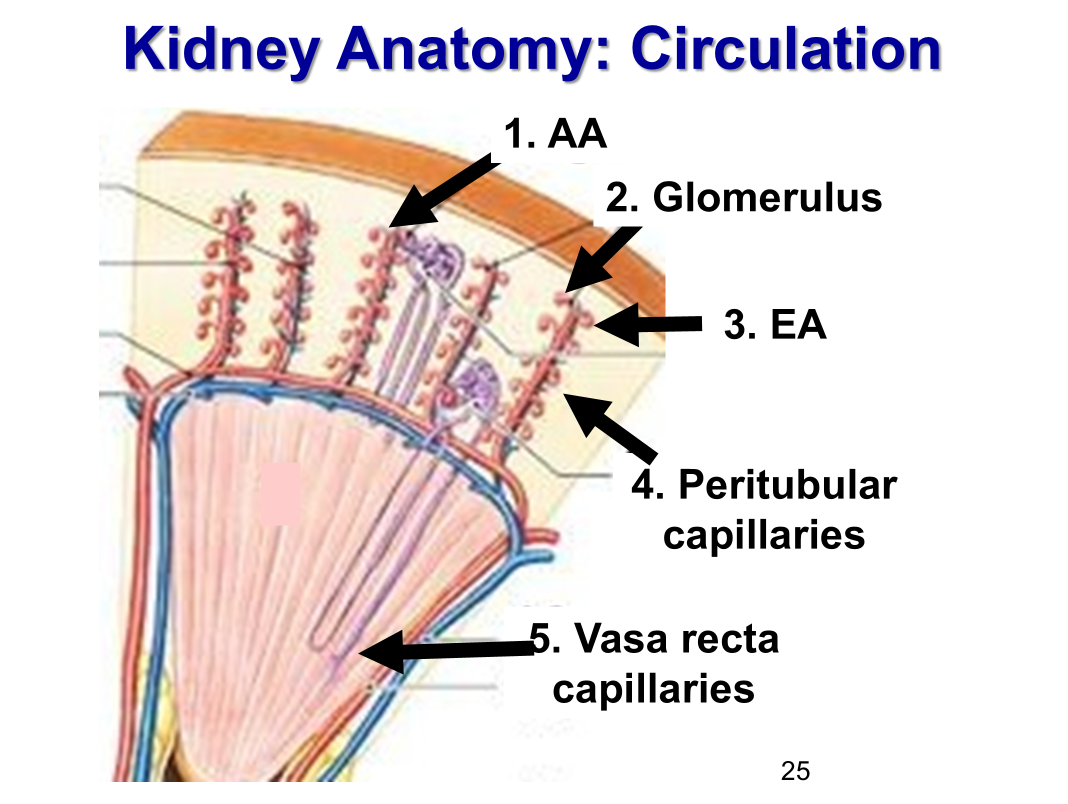
What are the functions of each capillary bed in renal circulation?
glomerular capillaries → ___________
peritubular capillaries → ____________
vasa recta capillaries → ____________
-glomerular capillaries → filtration
-peritubular capillaries → reabsorption, secretion
-vasa recta capillaries → concentrating
What is the result of only a few glomerular capillary being fed and drained by arterioles?
Allows glomerular capillary hydrostatic pressure to be very high, which forces fluid and solute out of blood into Bowman’s capsule by bulk flow
Most of filtrate is __________ by renal tubule cells and returned to blood through peritubular and vasa recta capillaries.
Most of filtrate is reabsorbed by renale tuble cells and returned to blood through peritubular and vasa recta capillaries
What are the three basic renal processes and where do they occur?
filtration: glomerular capillary lumen → Bowman’s space (bulk flow)
reabsorption: tubular lumen → pertitubular capillary plasma
secretion: peritubular plasma → interstitial space → tubular cell → tubular lumen
How do you calculate amount excreted in urine?
Amount filtered + Amount Secreted - Amount Reabsorbed
(F+S-R = E)
What does the Glomerular filtration barrier exclude?
-proteins
-blood cells
-large molecules
Which structure in the glomerular filtration barrier is primarily responsible for allowing large volumes of solute-rich fluid to pass while preventing cells from leaving the bloodstream?
Fenestrated capillaries in the glomerular capillary endothelium (allowing plasma to pass but blocking blood cells)
_______ pressure is generated by large molecules trapped (especially proteins) in solutions: “pulling” pressure”
Oncotic pressure is generated by large molecules trapped (especially proteins) in solutions: “pulling” pressure”
_______ pressure is exerted by liquids: “pushing pressure”
Hydrostatic pressure is exerted by liquids: “pushing pressure”
Starling Forces occur at the _____________ because _____________ due to hydrostatic pressure of heart pump, fluid filtered from blood through fenestra in glomerular capillaries & slit pores into Bowman’s space
Starling Forces occur at the glomerulus because there is no absorption of fluid into glomerular capillaries due to hydrostatic pressure of heart pump, fluid filtered from blood through fenestra in glomerular capillaries & slit pores into Bowman’s space
__________ and ______ are the two forces that determine NET flitration pressure across capillaries.
Hydrostatic pressure (P) and Oncotic force due to protein (π) are the two forces that determine NET filtration pressure across capillaries.
What two forces favor fluid flitration?
PGC
πBS (minimally)
What forces oppose fluid filtration?
PBS
πGC
What happens to rate of fluid filtered when PGC is decreased?
GFR decreases because PGC is the main force driving filtration
What is the significance of the net glomerular filtration pressure being positive?
Net glomerular filtration pressure = PGC – PBS - πGC
PGC has the highest pressure
positive pressure means filtration occurs continuously across the glomerulus