principles of inheritance
1/89
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Well known Indian breed of cow found in Punjab
Sahiwal
7 year of experiment was done between
1856-1863
Mendel took into consideration____ characters
14
Mendel took into consideration____ pair of contrasting characters
7
dominant seed shape
round
Dominant seed colour
yellow
dominant pod shape
inflated
dominant pod colour
green
dominant flower position
axial
dominant flower colour
violet
dominant plant height
tall
Contain information that is required to express a particular trait in an organism
gene
reginald c punnet was
british geneticist
organism showing dominant character is crossed with recessive parent is called
test cross
Characters are controlled by discrete units called factors
Factors occur in pairs.
In a dissimilar pair of factors one member of the pair dominates(dominant) the other (recessive)
law of dominance
Law is based on the fact that the alleles do not show any blending and that both the characters are recovered as such in the F2 generation, though one of these is not seen at the F1 stage
law of segregation
Exception to law of inheritance
Incomplete dominance ,co dominance
dog flower or snapdragon or antirrhinum sp
incomplete dominance
less efficient enzyme
dominant trait
non functional enzyme
recessive trait
no enzyme at all
recessive trait
multiple alleles can be found while studying
population
starch synthesis in pea shows ______ type of dominance
complete dominance
starch grain size in pea shows _____ type of dominance
incomplete dominance
dominance is not a/an_______ feature
autonomous
_____ depends on the gene product and production o a particular phenotype from this product
dominance
no of genotypes obtained in F2 generation of dihybrid cross
9
no of phenotypes obtained in F2 generation of dihybrid cross
4
scientist who rediscovered mendel’s work
hugo de vries, von tschermak, correns
scientist who concluded that behaviour of chromosomes is parallel to behaviour of genes
walter sutton and theodore boveri
independent pair segregate independently
chromosomes
one pair segregates independently of another pair
gene
who united the knowledge of chromosomal segregation with Mendelian principles and called it chromosomal theory of inheritance
sutton
experimental verification of chromosomal theory of inheritance was done by
thomas hunt morgan
morgan carried out several ____ crosses on fruit flies
dihybrid cross
law of dominance and law of segregation was given after
monohybrid cross
law of independent assortment was given after
dihybrid cross
exception to law of independent assortment
linkage
closely linked in fruit flies
body colour and eye colour
loosely linked characters in fruit flies
eye colour and wing size
ex of polygenic inheritance
skin colour
ex of pleiotropy
phenylketonuria
this disease manifests itself phenotypically -mental retardation, hair reduction, skin pigmentation
phenylketonuria
x chromosomes discovered by
henking
sex determination in insects
XO type
ex of XO sex determination
grasshopper
male heterogamety is seen in
insects and mammals
female heterogamety seen in
birds
in bees sperm and egg develops into
queen or worker
in bees Unfertilised egg develops into
male / drone
in bees males develop by the process of
parthenogenesis
_____ are commonly observed in cancer cells
chromosomal aberrations
change in single base pair of DNA results in
point mutation
deletion or insertion of base pair of DNA causes
frameshift mutation

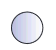
what does this symbol mean?
male
what does this symbol mean?
female

what does this symbol mean?
sex unspecified
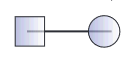
what does this symbol mean?
mating
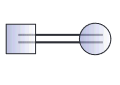
what does this symbol mean?
mating between relatives
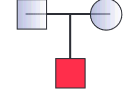
what does this symbol mean?
parents with male child affected
colour blindless results due to defect in
green and red cone
____ % of male are colour blind
8
____ % of female are colour blind
0.4
sickle cell anaemia is an example of
pleiotropy
sickle cell anaemia is caused by substitution of glutamic acid with valine at which position
6th
GAG
glutamic acid
GUG
valine
sickle cell anaemia is caused by the mutation in which chain of RBC
β chain
the inborn error in metabolism inherited as autosomal recessive trait
phenylketonuria
which enzyme converts phenylalanine to tyrosine
phenyl alanine hydroxylase
accumulation of ___ in brain causes mental retardation
phenylpyruvic acid
which disease has the symptoms as : mental retardation, skin pigmentation and reduction of hair
phenylketonuria
autosomal recessive disease in which due to some mutation or deletion results in reduced rate of synthesis of globin chains
thalassemia
anemia is the characteristic of which disease
thalassemia
which type of thalassemia is controlled by two closely related genes of HBA 1 and HBA 2
α-thalassemia
which type of thalassemia is controlled by single gene HBB
β-thalassemia
genes for α-thalassemia is present on____ chromosome of each parent
16
genes for β-thalassemia is present on____ chromosome of each parent
11
quantitative anemia
thalassemia
qualitative anemia
sickle cell anemia
failure of segregation of chromatids during cell division resulting in the gain or loss of chromosomes
aneuploidy
failure of cytokinesis after the telophase stage of cell division result in an increase in a whole set of chromosomes in an organism
polyploidy
trisomy of chromosome 21 was 1st described by
langdon down
short statured, small round head, furrowed tongue, partially opened mouth, flat head, broad palm with characteristic palm crease, physical, psychomotor and mental development is retarded, born with congenital heart disease, many loops on fingers, big wrinkled tongue
down’s syndrome
47, XXY
klinefelter’s syndrome
44+XXY
klinefelter’s syndrome
overall masculine development, gynecomastia, sterile
klinefelter’s syndrome
45,XO
turner’s syndrome
44+XO
turner’s syndrome
rudimentary ovaries, lack of secondary sexual characters and sterile
turner’s syndrome